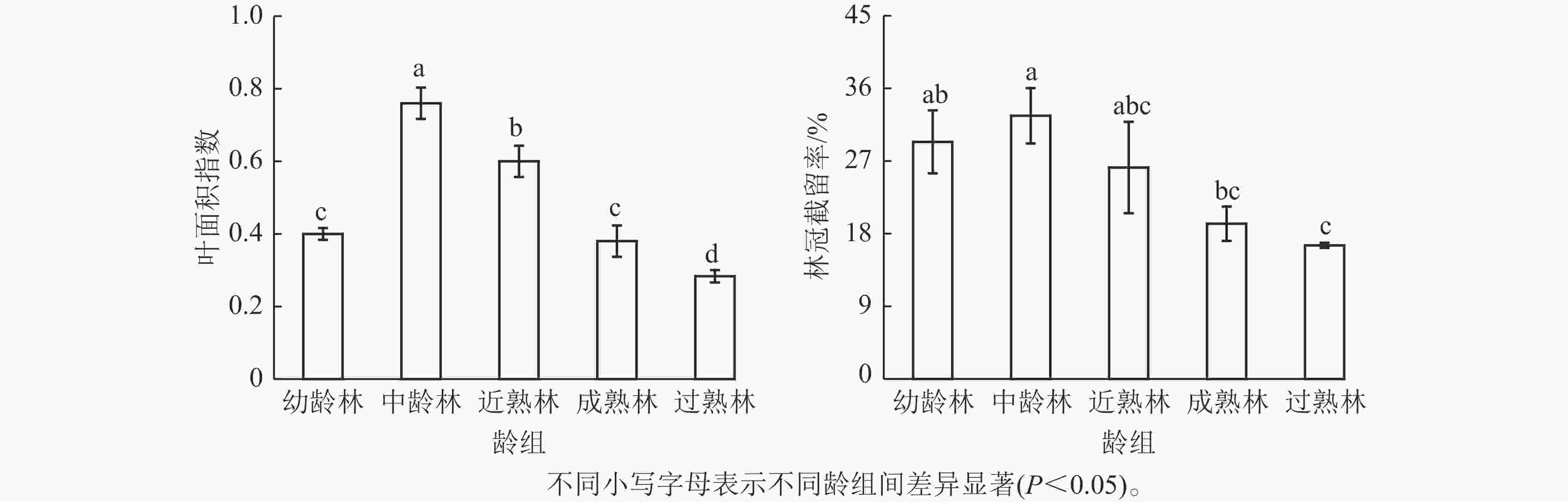
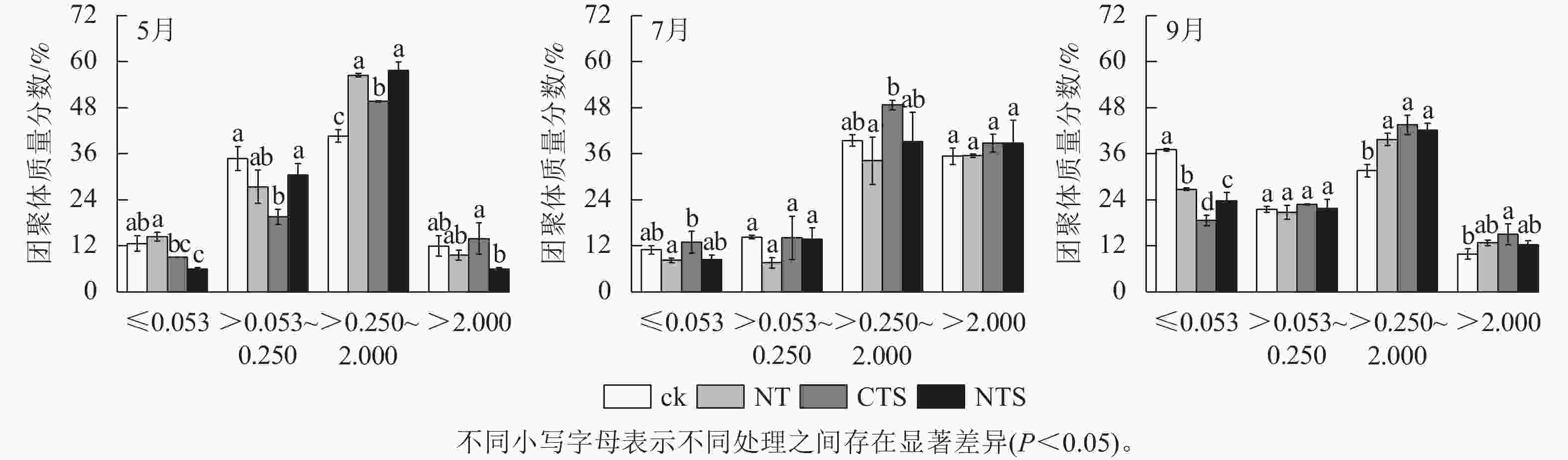
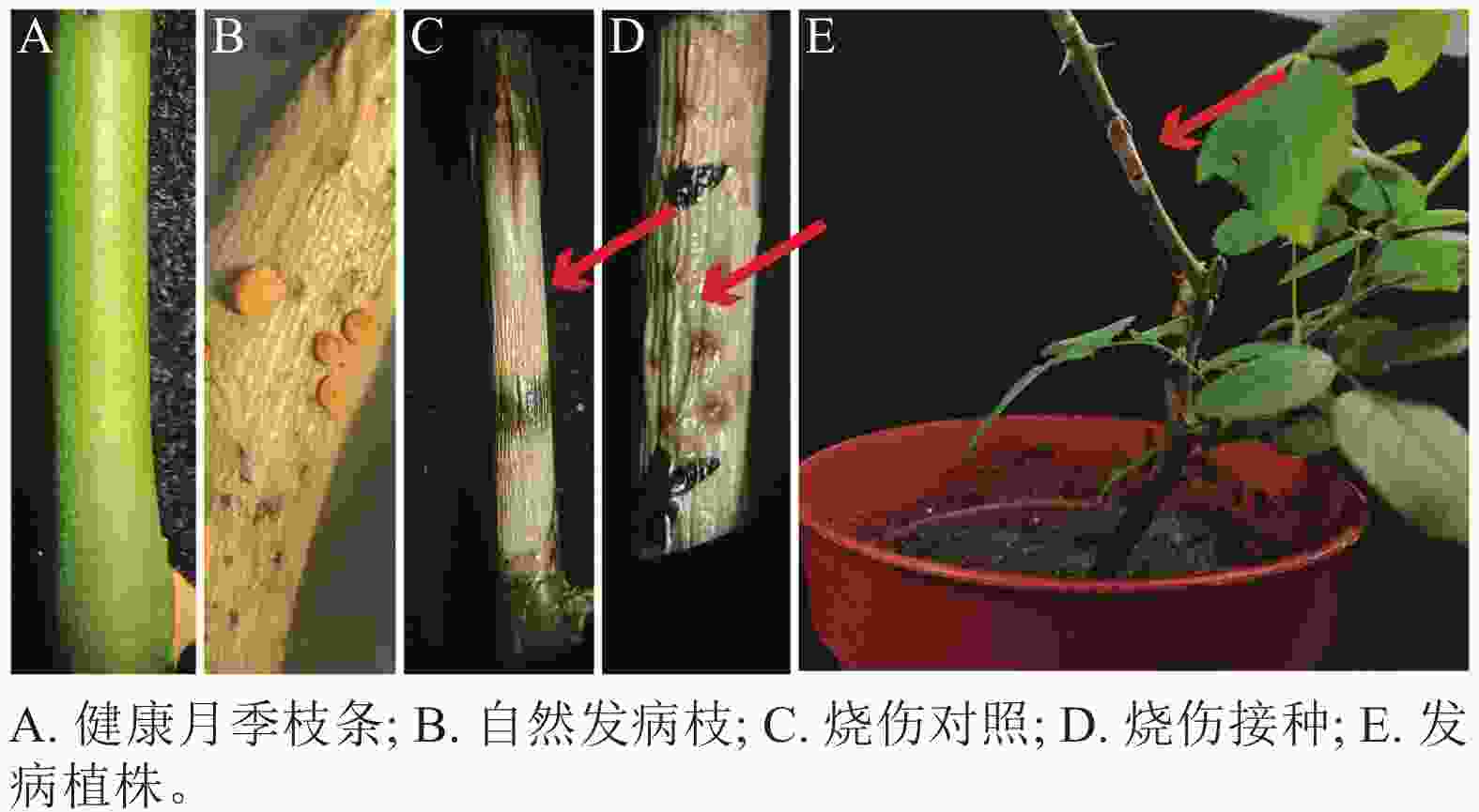
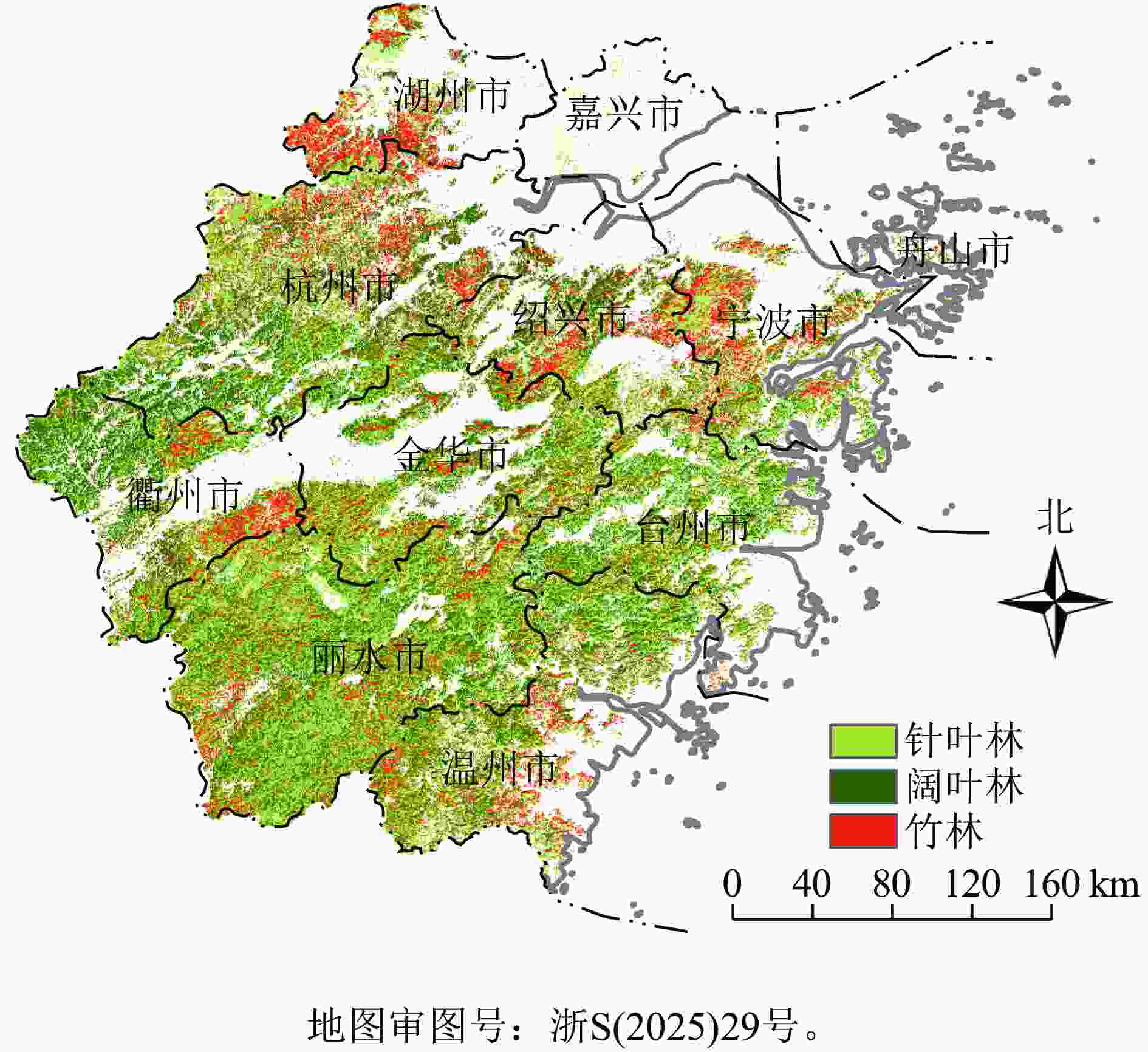
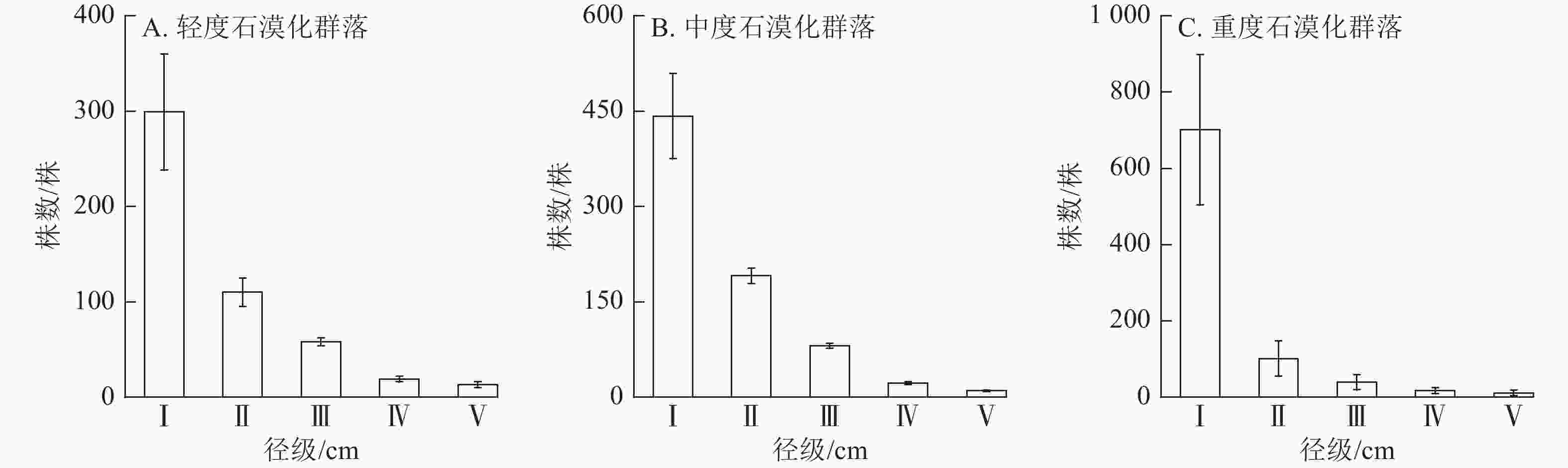
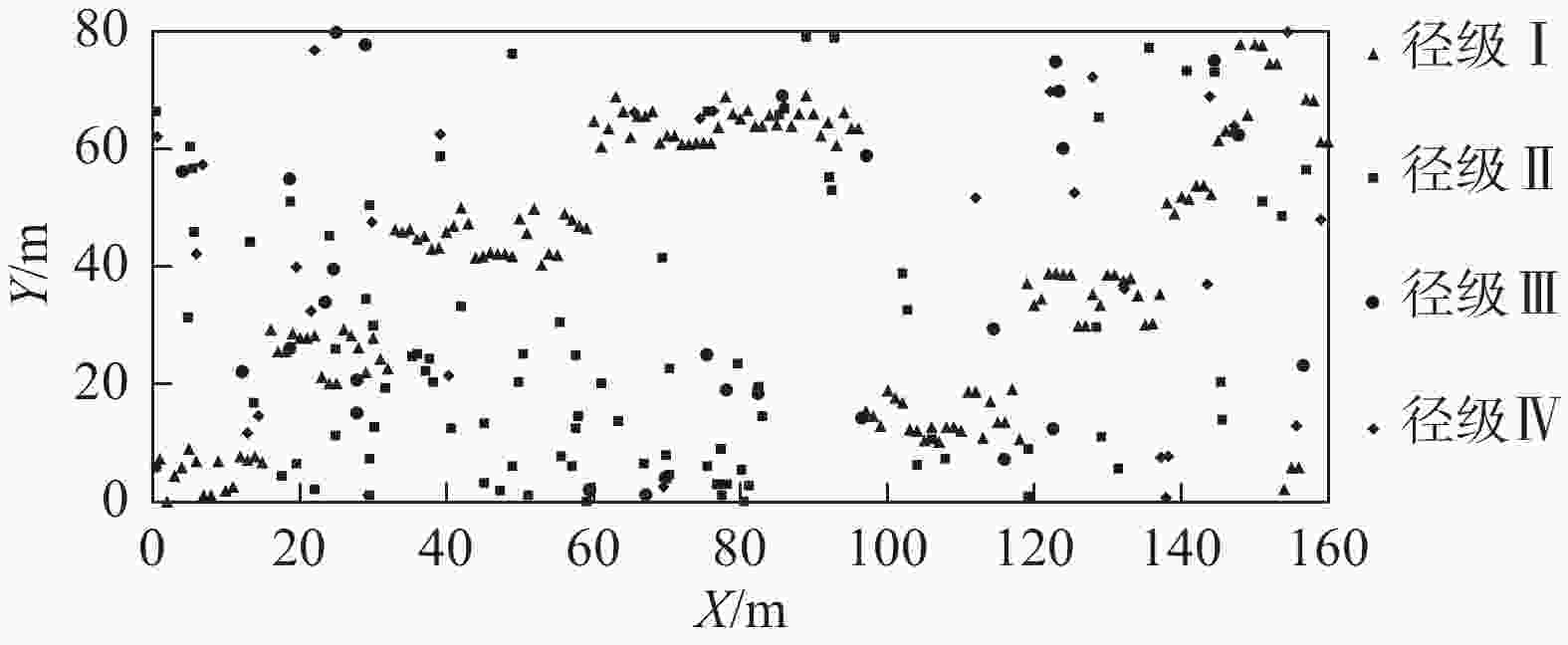
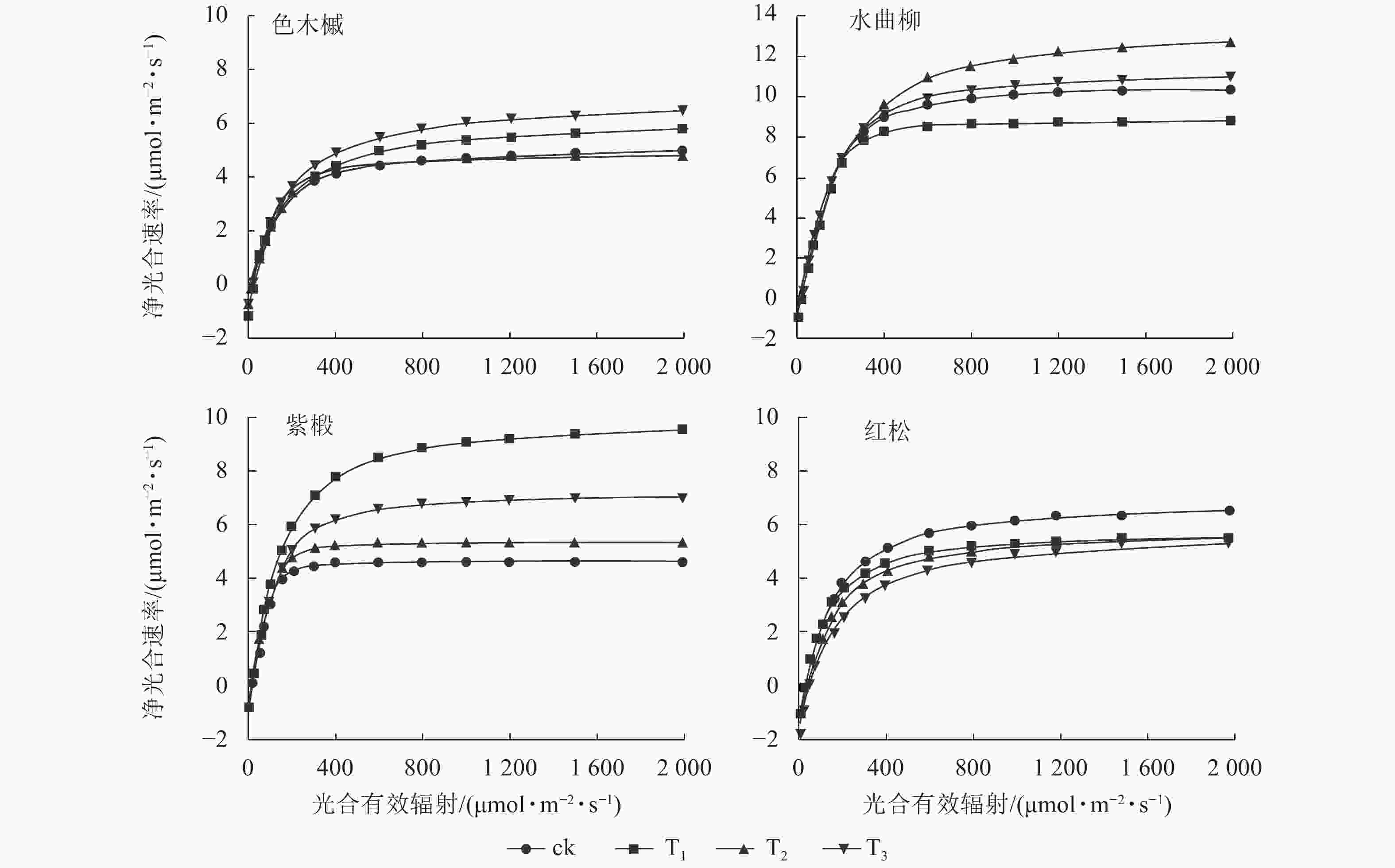
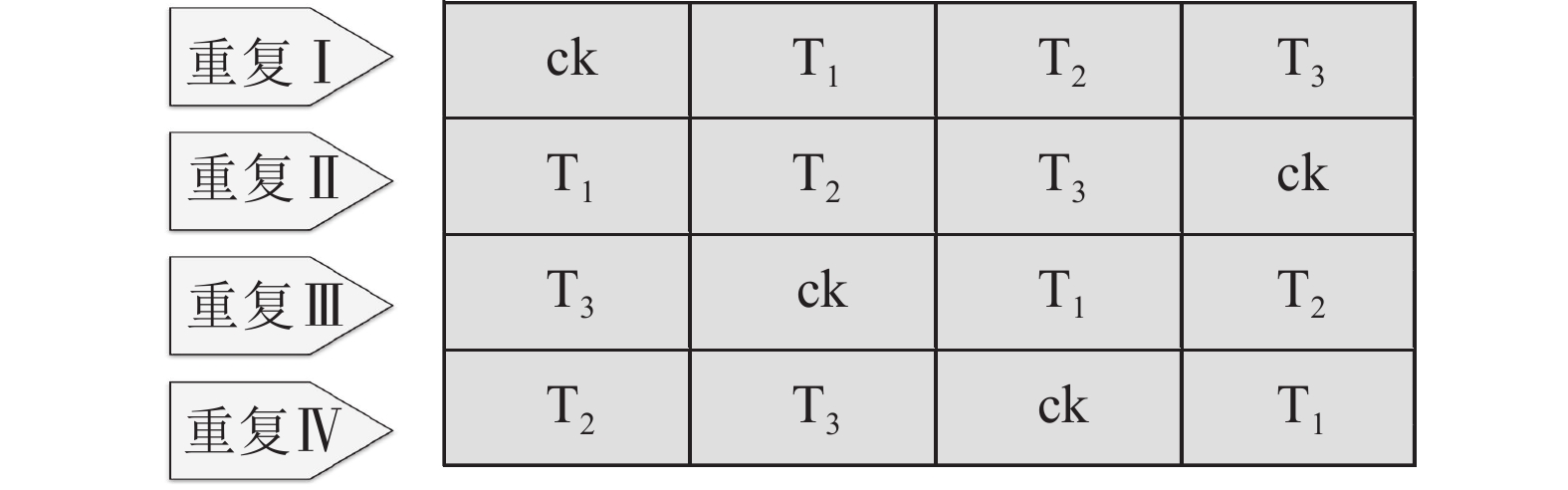
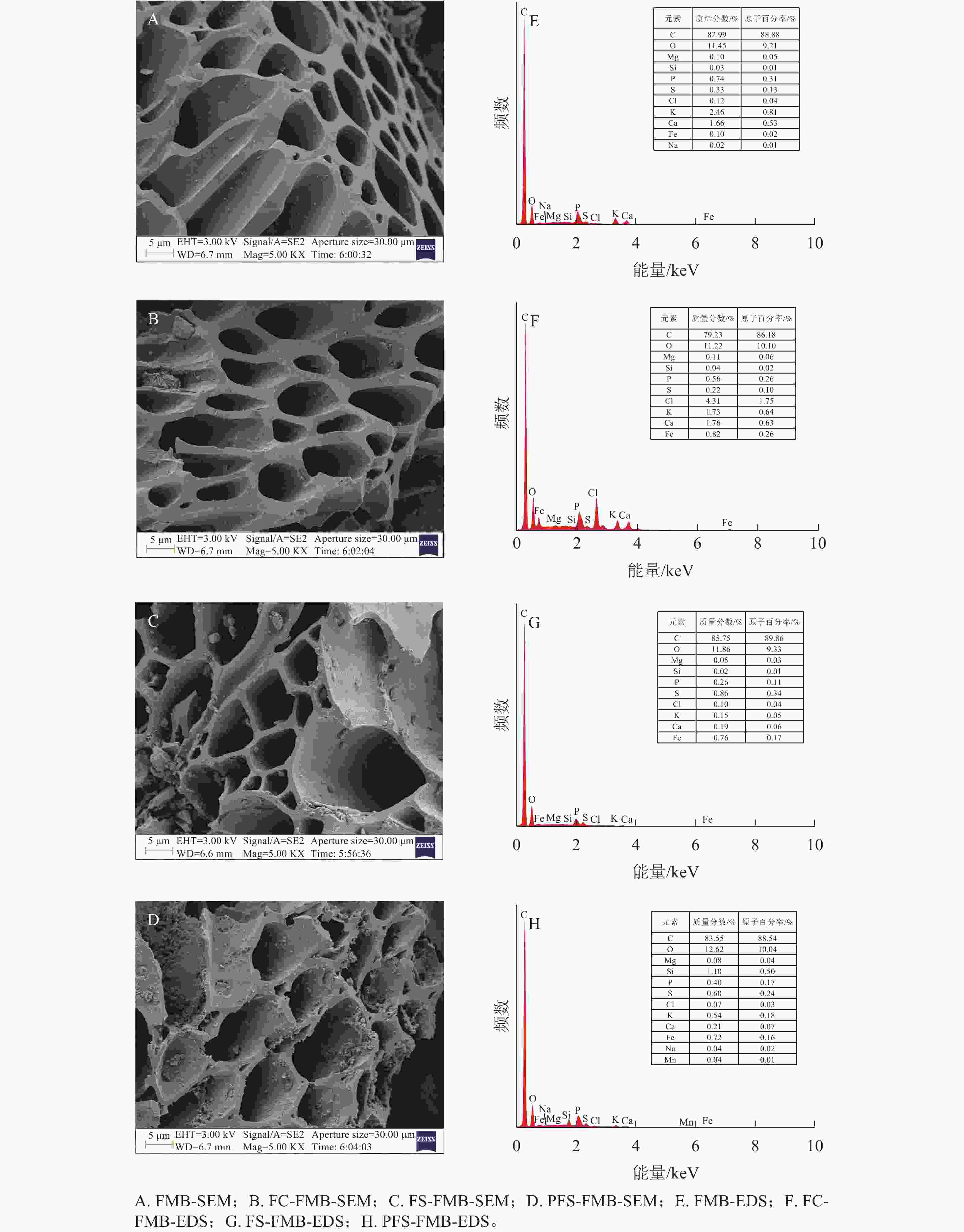
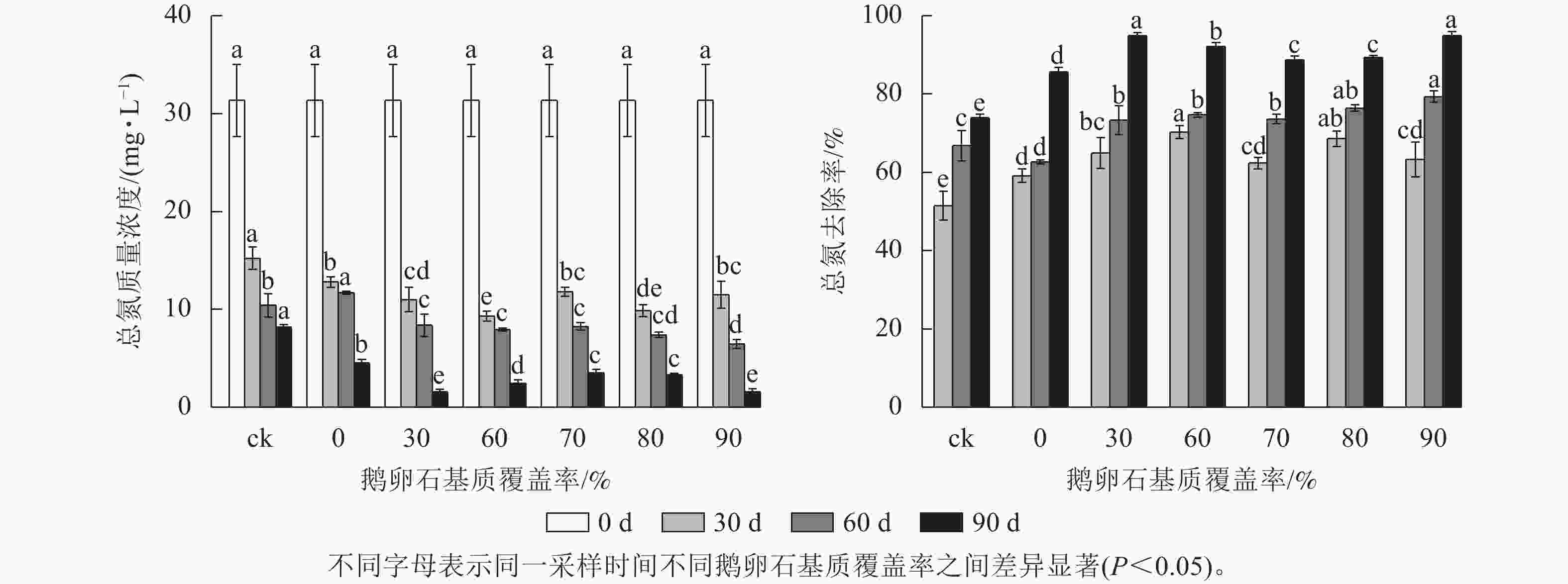
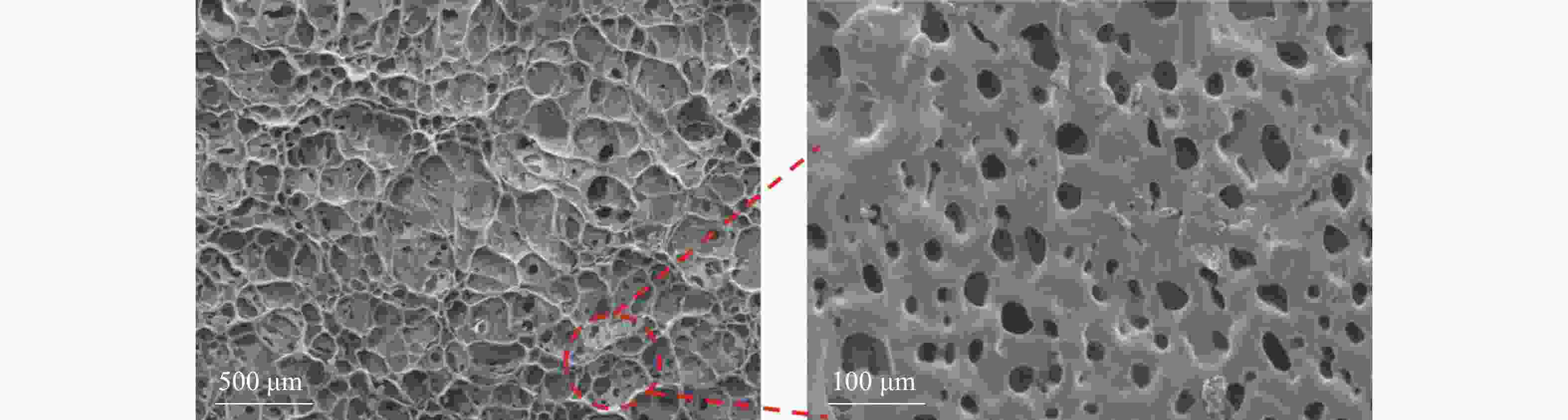
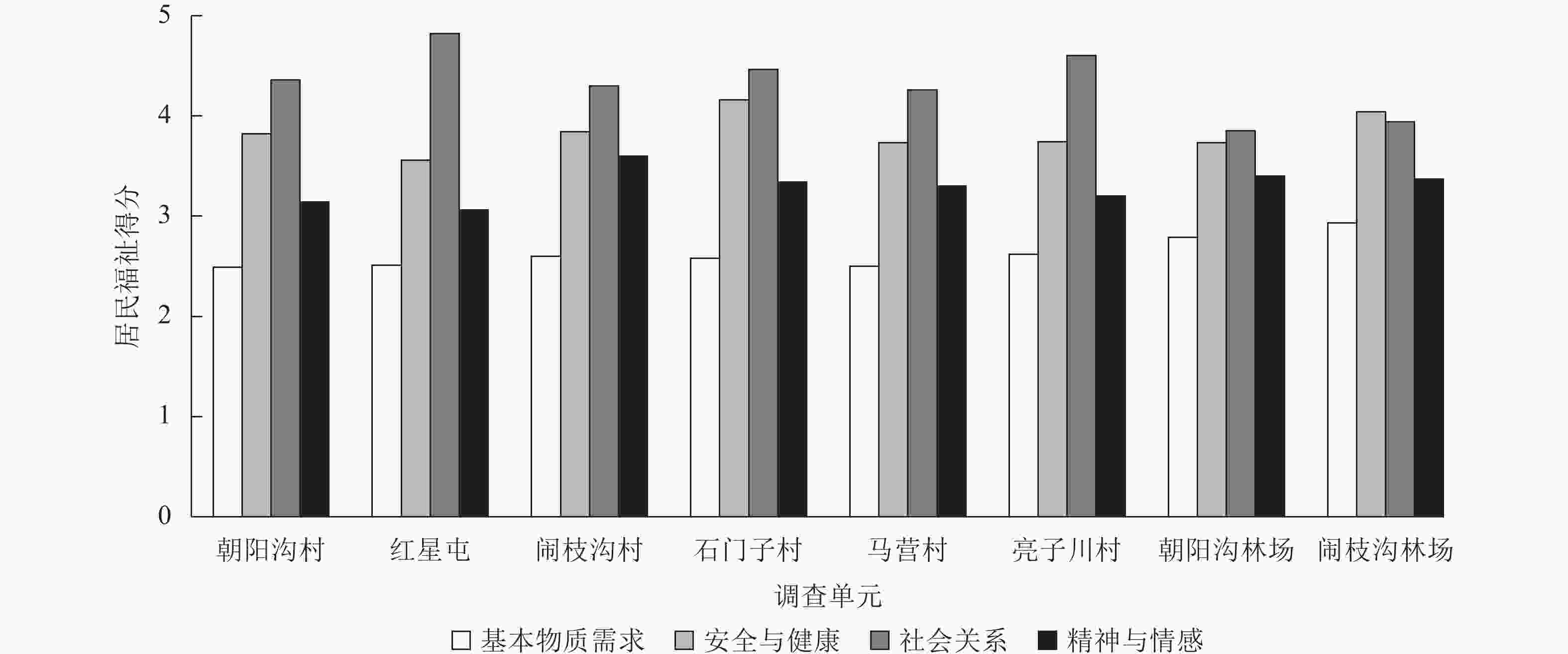
Soil inorganic carbon (SIC) is a key component of the soil carbon pool, and its sequestration and loss have profound impacts on the global carbon cycling and climate change. With accelerating urbanization in China, urban ecosystems have become a focal point of ecological research. Urban green spaces, as integral components of urban ecosystems, are closely linked to soil carbon dynamics, climate regulation, and ecosystem services, and their response and feedback to urbanization will inevitably be the focus and priority of study. However, the understanding of SIC cycling in urban green spaces remains limited. This paper examined the potential impacts of human activities such as land management and construction on SIC in urban ecosystems. It systematically overviewed the following aspects: (1) sequestration, loss and influencing factors of SIC in urban green spaces under urbanization; (2) the driving effects of changes in soil physical properties, nitrogen inputs, pH, and salinity on the carbonate dissolution–precipitation balance of SIC in urban green spaces; (3) the impact of soil fauna and microbial communities on SIC formation process. Future research should focus on the driving mechanism of SIC dynamics under urbanization, so as to make up for the research deficiencies in inorganic carbon in urban green spaces and provide theoretical support for improving carbon cycling theory and optimizing ecosystem functions in urban ecosystems. [Ch, 1 tab. 83 ref.]
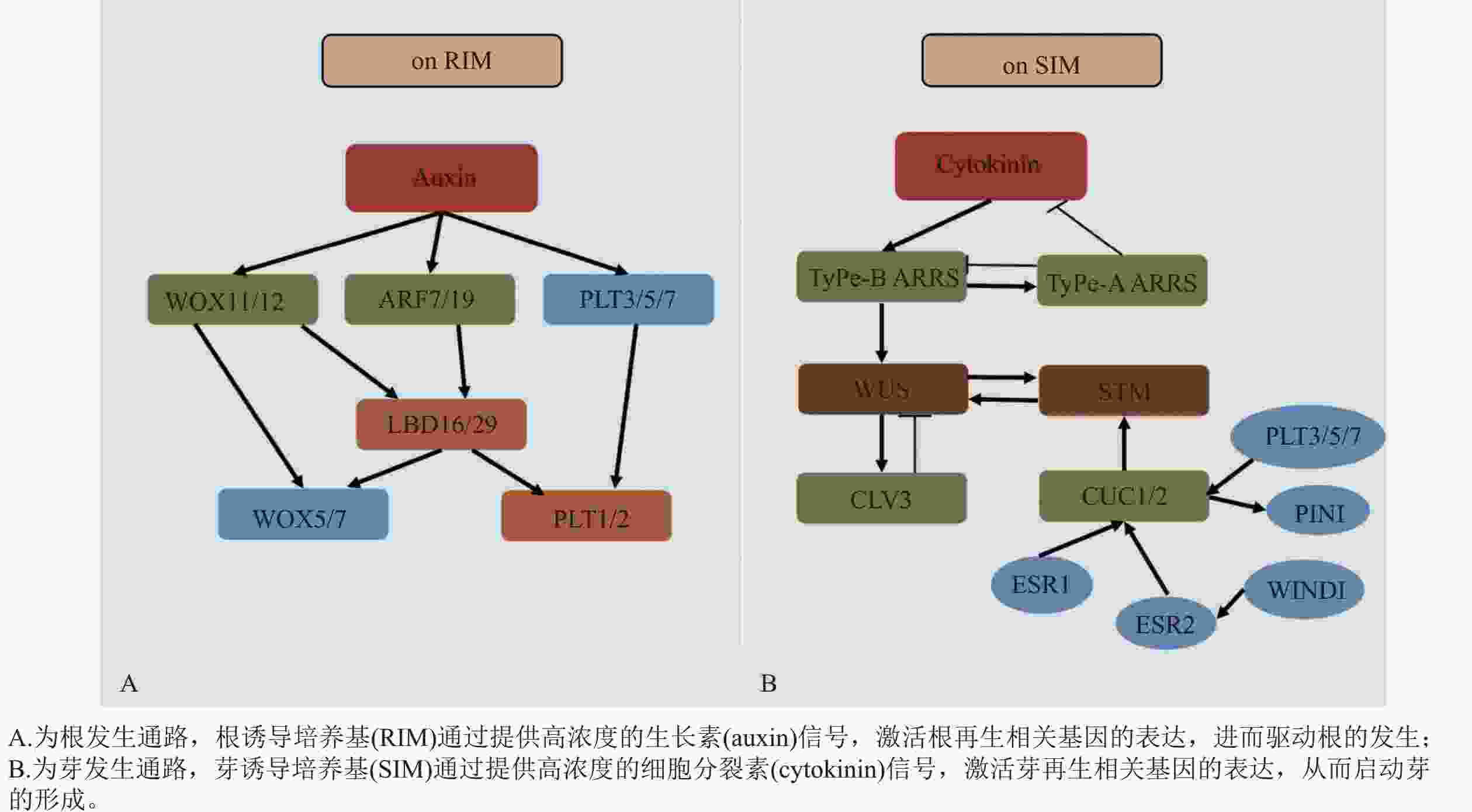
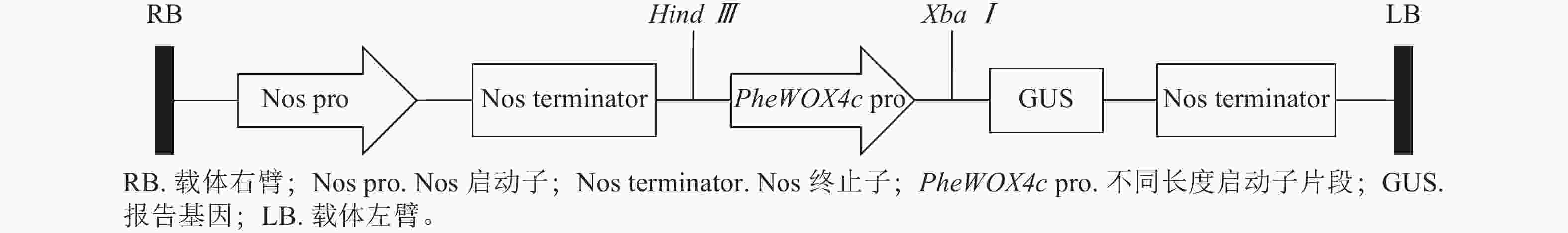
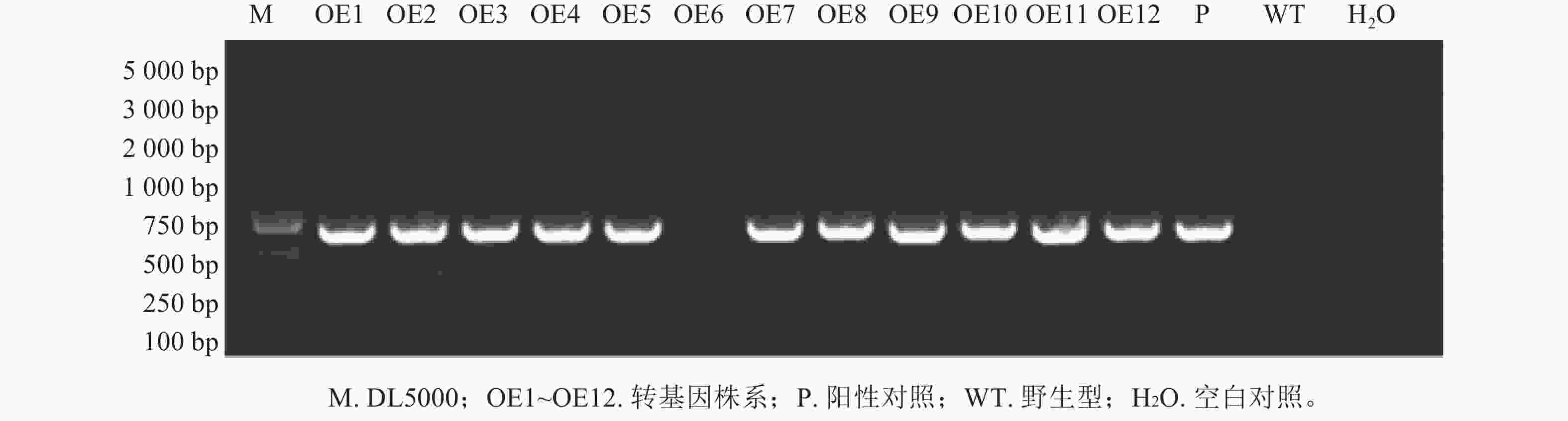
However, the current organogenic regeneration system generally has technical bottlenecks such as rooting difficulties, severe browning and strong genotype dependence in adult materials, which seriously restricts the relevant breeding and breeding process. The key external factors affecting regeneration efficiency, including explant selection, media optimization, and the ratio and treatment timing of plant growth regulators (PGRs) are systematically sorted out. At the molecular mechanism level, the cellular and molecular regulatory mechanisms from callus induction to adventitious root/adventitious bud formation were expounded, and the core mechanisms of auxin signaling (ARF-WOX-LBD pathway) regulating adventitious root genesis and cytokinin signaling (ARR-WUS-CLV3 loop) regulating adventitious bud formation were revealed. In view of the technical bottlenecks such as the difficulty of rooting of adult materials and the serious browning of high-phenolic varieties, a comprehensive countermeasure combining physiological and epigenetic regulation was further proposed. This paper analyzes that the organogenesis of woody plants is jointly regulated by external culture conditions, internal hormone pathways and epigenetic status, and the essence of adult material regeneration disorder is that regeneration-related genes are systematically inhibited at the epigenetic level. In the future, through deepening mechanism analysis and technological innovation, it is expected to systematically break through the regrowth obstacles of woody plants and provide systematic support for precision breeding and gene function research of forest trees. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 82 ref.]
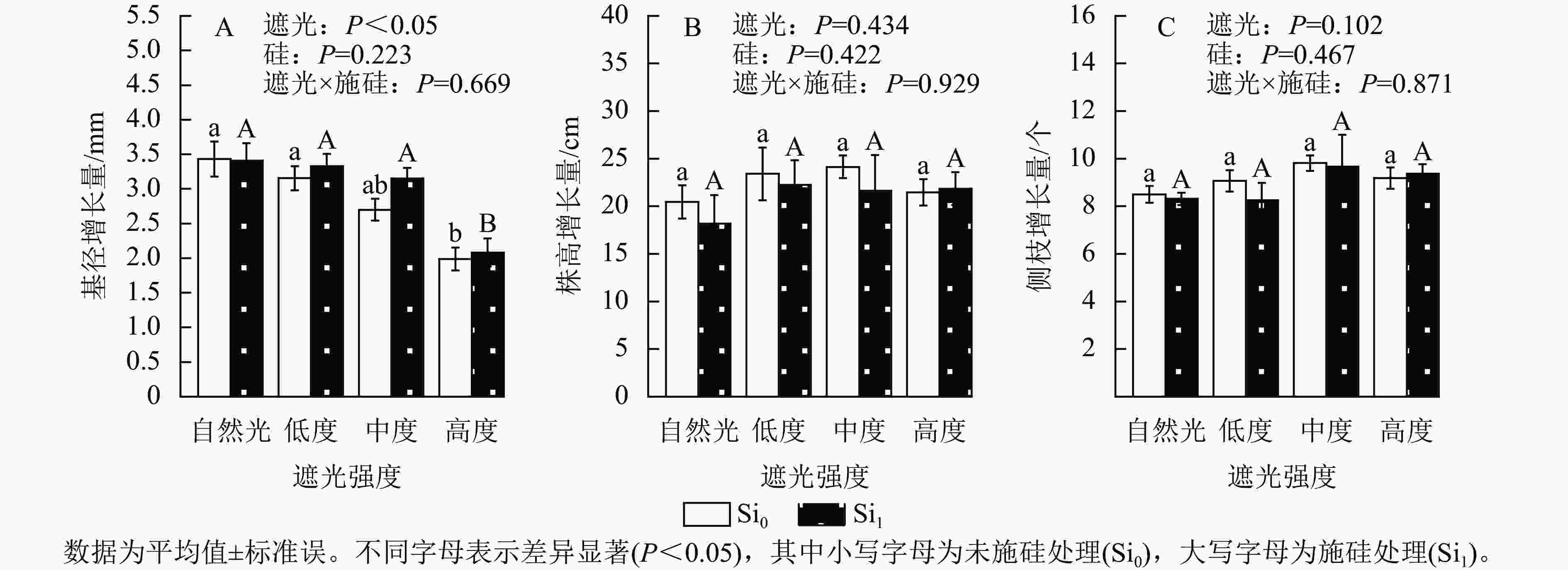
Plant belowground foraging traits are crucial for plant nutrient acquisition and environmental adaptation. Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) availability, as key driving factors, have a profound impact on plant belowground nutrient acquisition strategies. First, it introduces the classification of plant belowground foraging traits. This include absorptive root traits (morphology, architecture, and proliferation), mycorrhizal traits (mycorrhizal fungal colonization rate and hyphal density), and exudation traits (root carbon exudation rate and root enzyme activity). Subsequently, it illustrates the effects of N and P addition on these foraging traits. Regarding absorptively root traits, studies have shown that the effects of N and P addition vary depending on tree species and nutrient conditions. Plants optimize resource acquisition by altering their morphology, architecture, and proliferation characteristics. For mycorrhizal traits, mycorrhizal fungi regulate belowground resource acquisition through differentiated strategies (For example, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi rely on hyphal extension for inorganic nutrient uptake, while ectomycorrhizal fungi secrete enzymes to decompose organic matter), however, N and P addition generally suppress mycorrhizal colonization rates. As for exudation traits, root acid phosphatase and nitrate reductase, which are key indicators reflecting plant P and N acquisition and metabolism, were significantly regulated by N and P addition. Next, it also explores the coordination mechanisms among belowground foraging traits. This includes synergies and trade-offs among traits, as well as cost-benefit optimization in resource allocation. Finally, addressing current research gaps, future research directions are proposed, focusing on N-P interactions, the synergistic response mechanisms among root secretory traits, absorptive roots, and mycorrhizal traits, in situ observations of mature plants in the field, and foraging strategies of different mycorrhizal types of tree species. These directions aim to deepen our understanding of plant belowground nutrient acquisition strategies and their adaptation mechanisms to environmental changes, providing a scientific basis for the management of forest ecosystems. [Ch, 2 tab. 95 ref.]
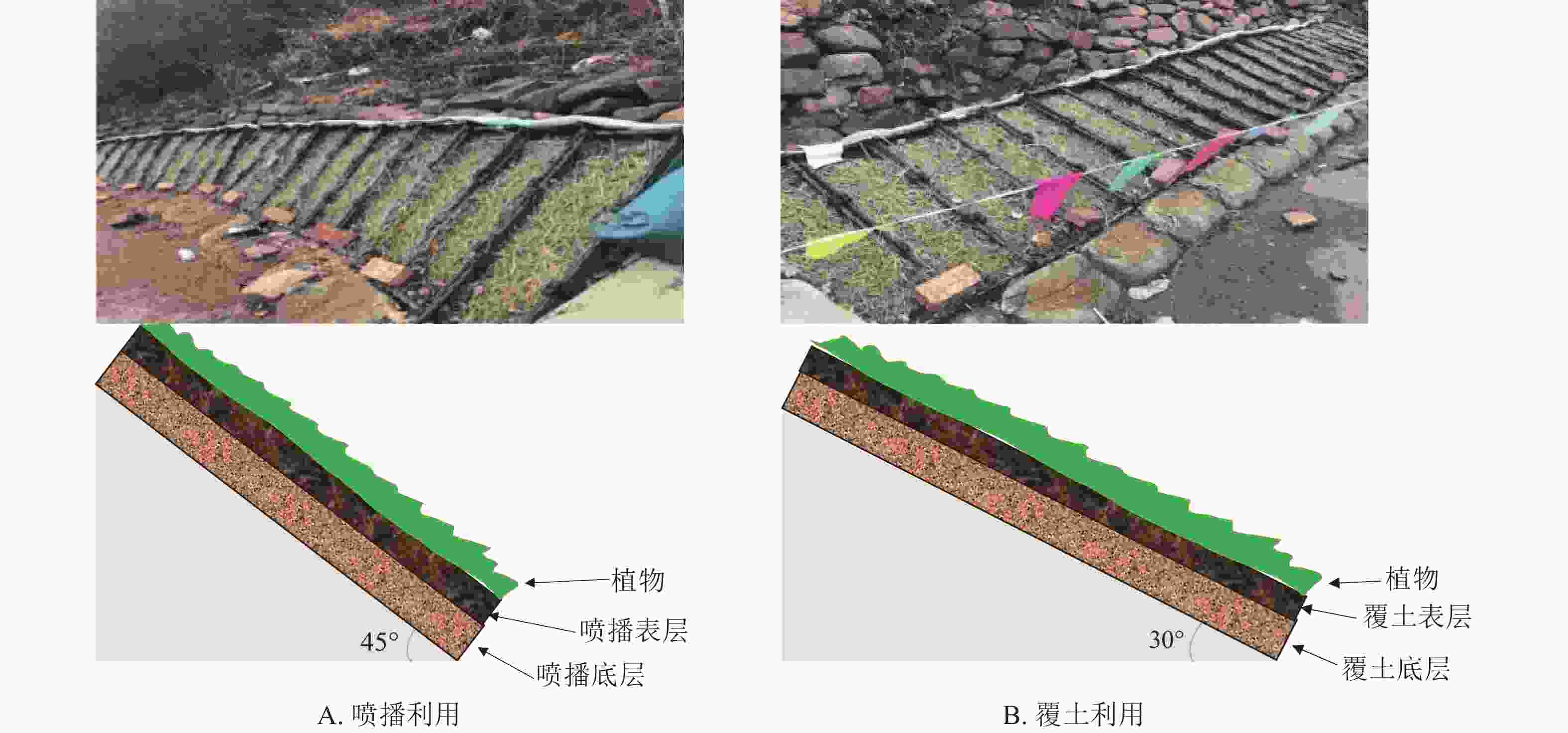
The slope where forest fire occurs is typically covered with the ash layer of the fire, which is a critical factor altering post-fire hydrological and erosional processes on hill slopes. Due to the multiple opposing effects of forest fire ash coverage on slope hydrological and erosional processes, the superimposed effects may lead to highly variable and context-dependent results. By reviewing relevant research literature, the impact mechanism and role of forest fire ash on slope hydrological and erosional processes are summarized. The fire ash layer covers the soil surface, forming a dual system of fire ash and soil. The “ash blanket” effect or sealing effect of forest fire ash can increase or decrease slope permeability and water holding capacity. The erodibility or crust formation sealing can either reduce or increase the slope’s resistance to erosion. The erosion and migration of forest fire ash layer on the slope may form fire ash patches or mud, which reduces or increases the surface runoff erosion capacity. Fire ash particles and their aqueous solutions infiltrating into soil can alter soil physicochemical properties through multiple pathways: potentially diminishing infiltration capacity via pore clogging, enhancing erosion resistance through promoting formation of soil aggregates, and exerting long-term impacts by either facilitating or inhibiting ecological recovery via fertilization effects or biological toxicity. Identification of dominant impact mechanism of forest fire ash on slope hydrological and erosional processes under specific wildfire, precipitation, and soil conditions is crucial to improving the simulation ability of post fire hydrological erosion and the accuracy of risk prediction. [Ch, 73 ref.]
Bimonthly, Start in 1984
Supervisor:Department of Education of Zhejiang Province
Sponsor:Zhejiang A&F University
Editor-in-Chief:WU Jiasheng
Editor:Editorial Department of Journal of Zhejiang A&F University
Tel:0571-63732749
E-mail:zlxb@zafu.edu.cn
-
1
Carbon-fixing oriented management patterns of Phyllostachys pubescens and their benefits
WANG Xi-feng, SHEN Yue-qin, WANG Feng, ZHENG Xu-li, HU Zhong-ming -
2
Continuum removal based hyperspectral characteristic analysis of leaves of different tree species
DING Li-xia, WANG Zhi-hui, GE Hong-li -
3
Research progress on agronomic characteristics of Miscanthus
ZHAN Wei-jun, REN Jun-xia, JIN Song-heng, HUANG You-jun, PAN Yin-hui, ZHENG Bing-song -
4
Efficacy of three insecticides against Phenacoccus kaxinus and Eucryptorrhynchus brandti
CHU Jiamiao, ZHONG Tailin, HUANG Shanshan -
5
Application and prospect of organic biocides in timber preservation
SUN Fang-li, BAO Bin-fu, CHEN An-liang, ZHOU Yue-ying, YU Hong-wei, DU Chun-gui