-
木质结构保温板(structural insulated panel,SIP)是以2片具有承载能力的木质材料为面板,通过施加结构胶黏剂,与硬质泡沫芯板胶合而成的一种3层结构的复合板材,具有质量轻、强度高、节能环保、保温隔声与施工安装便捷等特点,可用于前沿性建筑和轻质商业建筑[1-3]。国外对SIP的研究和应用非常广泛,尤其在北美、北欧、日本等国家和地区,该类材料普遍应用于建筑行业,且已经形成了完整的相关产业及配套设施[3-6]。近年来,随着人们环保意识的增强及对木质建筑特点的认识逐渐加深,国内也越来越重视木质结构保温板材料的发展。目前,构成SIP的木质承重面板主要以定向刨花板、胶合板和纤维板等为主[3, 7]。重组竹由竹纤维复合而成,具有良好的力学性能、耐久性及装饰性,是极具吸引力和应用潜力的新型复合材料[8-12]。王雪花等[13-14]选用重组竹作为承重面板制备了结构保温板,对其保温性能和力学性能进行研究,结果表明:重组竹作为结构保温板的覆面材料具有一定的保温隔热性能,但其导热系数较木质定向刨花板大,作为承重面板并未达到某些应用领域的使用要求。究其原因是由于重组竹密度、厚度和竹束走向及应力集中等所造成的。此外,在SIP类似于“三明治”结构中,界面黏结强度及其连接层结构形态是决定其性能的关键因素[15-17]。因此,结构保温板的界面用胶具有至关重要的作用。本研究采用自制粉状环氧树脂作为胶黏剂。相较于传统的聚氨酯胶黏剂,该胶黏剂具有防潮、低收缩率、高模量、高强度、结构牢固等优点,可实现工业生产中无溶剂、零释放及中低温固化等环保目标。因玻纤膜具有高强度、柔软等特性及保温、防湿、防燃等功能,将其与重组竹和泡沫芯板进行复合,制备重组竹/复合结构保温板复合材料,探究胶黏剂的固化特性,测定复合材料的结合强度、抗弯强度及导热系数,分析自制胶黏剂用量、成型时间及热水浸渍对复合结构保温板的结合强度和抗弯强度的影响,为粉状环氧树脂及重组竹在SIP中的应用提供数据和理论基础。
-
重组竹(BS)由安吉辉篁竹业有限公司提供,浸胶量为15%~18%,密度为1.2 g·cm−3;玻纤布(GF)由无锡创发玻纤材料有限公司提供,中碱玻璃纤维纺织而成,规格为100 g·m−2;聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)泡沫由上海越科新材料股份有限公司提供,密度为0.10 g·cm−3。
粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂由国家木质资源综合利用工程技术研究中心自制:由双酚A环氧树脂E-20(环氧值0.20~0.23,中国石化)、六次甲基四胺(HMTA,化学纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司)和2-甲基咪唑(2-MI,化学纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司)按一定比例均匀共混,即得粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂。
-
平板硫化机(中国浙江湖州东方机械有限公司);人造板万能试验机(MWD-10A,中国济南恒瑞金试验机有限公司);热流法导热性能测试仪(HFM436,德国耐驰);综合热分析仪(STA409PC,德国耐驰);扫描电子显微镜(TM3030,日本日立)。
-
板材制备:以BS为承重面板,PET泡沫为芯板,所有层间均分别涂布有适量粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂,将涂布有适量粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的BS、GF和PET泡沫,按照BS—GF—PET泡沫—GF—BS依次叠放,并置于预热完毕的平板硫化机中进行热压固化。热压结束后,缓慢释压脱模后即得试验样品。试验样品尺寸400 mm×400 mm×20 mm,并裁剪为用于结合强度和抗弯强度测试所需样品尺寸。热压温度为130 ℃(具体热压温度选择见结果与分析),表压为2.5 MPa,热压时间5~20 min。
耐水实验:将制得的样品称量,记为m1;分别浸泡于恒温水浴锅中,温度设置为60、80和100 ℃,持续浸泡3 h;取出样品置于60 ℃鼓风烘箱中,隔12 h称量,记为m2;直至m2≤m1,停止干燥。取出样品进行抗弯强度和结合强度测试以及表面形貌观察。
-
粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂样品分别以5、10、15和20 ℃·min−1的升温速率进行动态DSC测量,温度范围40~300 ℃,氮气流速50 mL·min−1,样品质量5~10 mg。
-
结合强度采用万能试验机,按照GB/T 17657−2013《人造板及饰面人造板理化性能试验方法》进行测试,每组试验样品不少于10个,最终结合强度取平均值。样品表面尺寸为50 mm×50 mm。
-
抗弯强度采用万能试验机,按照GB /T 1936. 1−2009《木材抗弯强度试验方法》进行测试,每组试验样品不少于5个,最终抗弯强度取平均值。样品尺寸为300 mm×20 mm×20 mm。测试速度为5 mm·min−1,当断裂百分比达40%时结束。
-
取经过80 ℃热水浸泡前后的样品侧面,表面喷金处理,在扫描电子显微镜上观察表面形貌。
-
导热性能采用热流法进行测定,按照GB/T 10295−2008《绝热材料稳态热阻及有关特性的测定 热流计法》进行测试。分别设置25、40、60、70 ℃等4个不同测试温度。样品尺寸为300 mm×300 mm×20 mm。
-
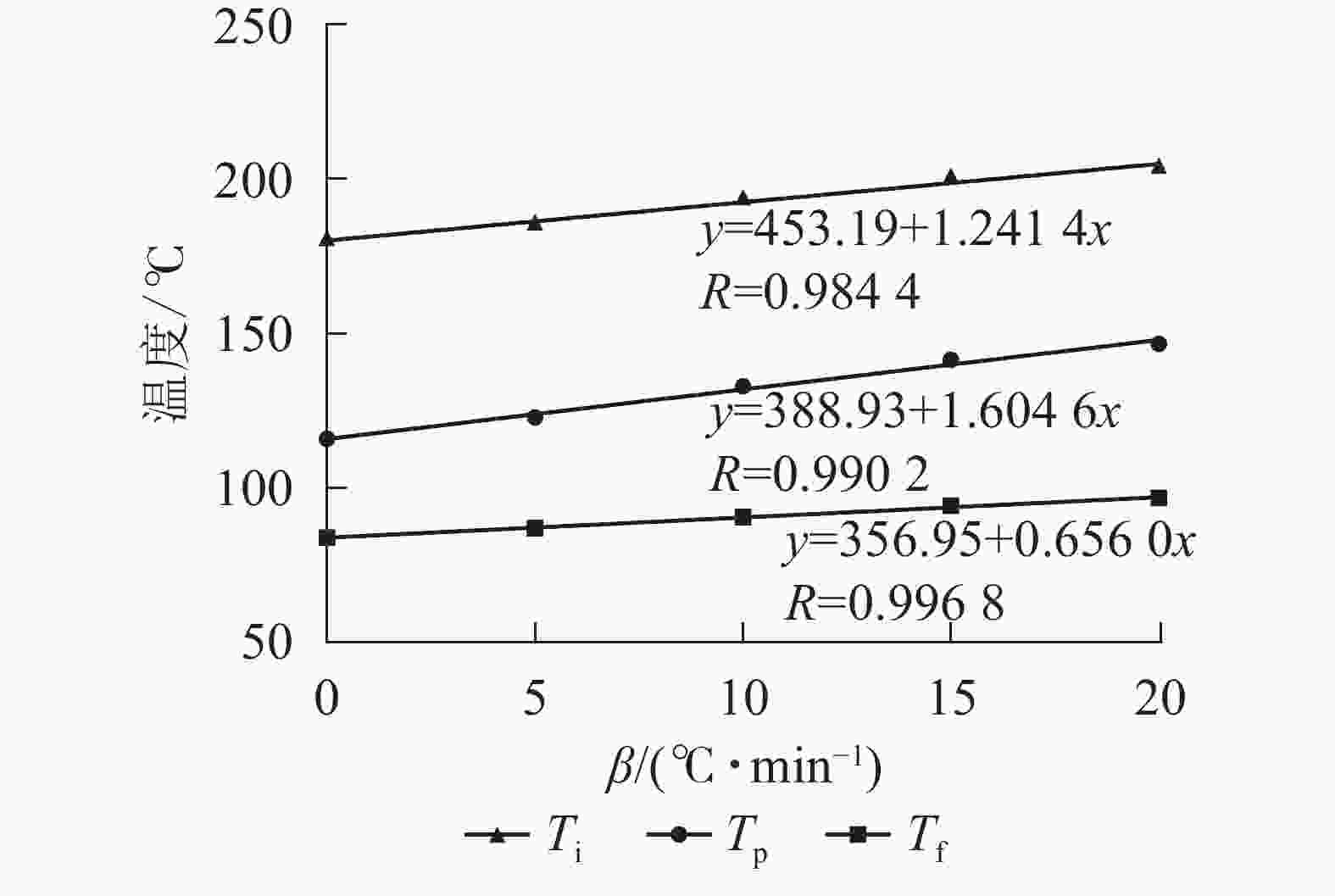
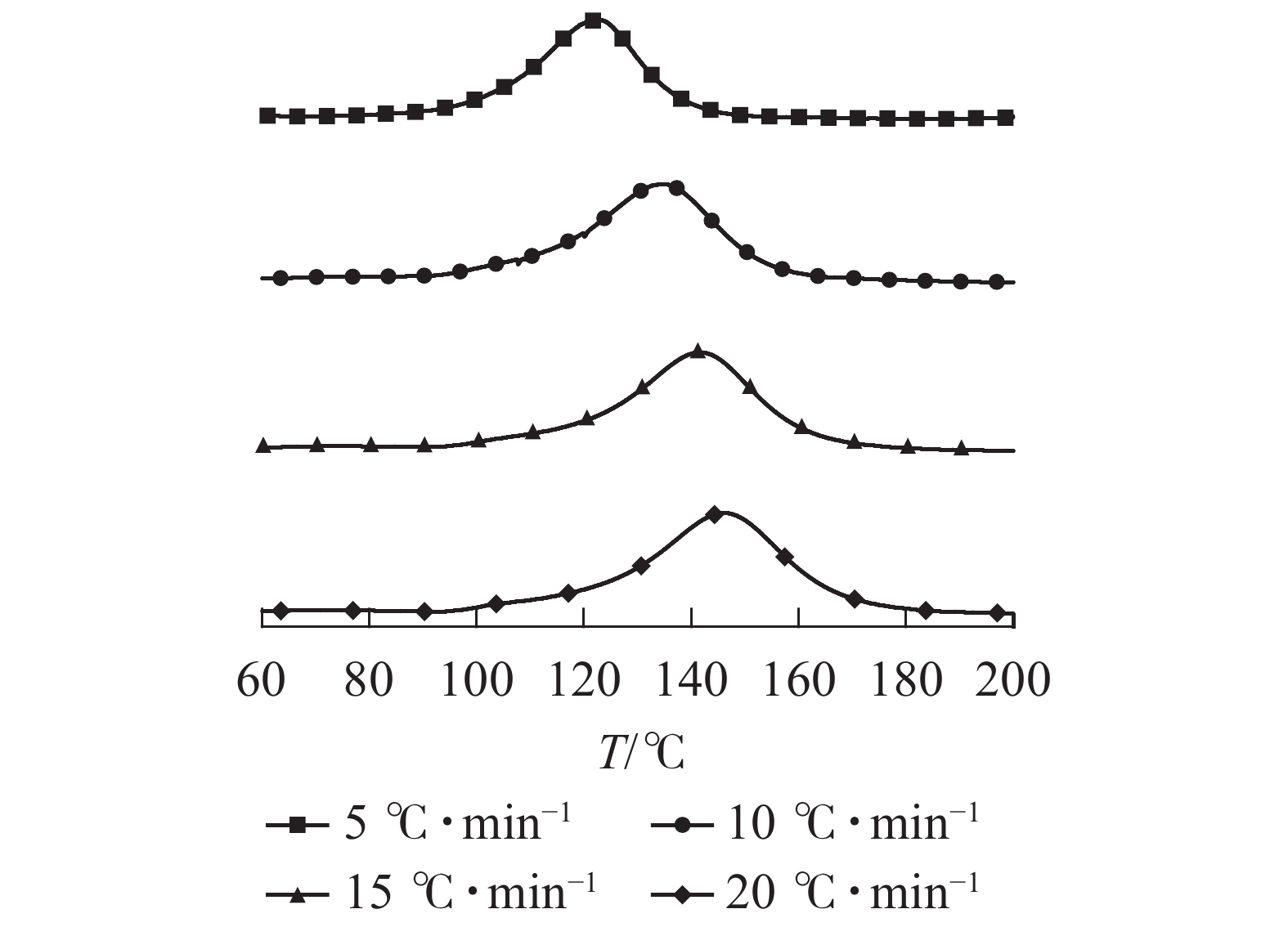
图1给出了不同升温速率(β)对粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂DSC曲线的影响,其固化峰特征参数列于表1。从图1和表1中可以发现:粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂固化反应的特征温度随着升温速率的改变而变化。随着升温速率的提高,粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的初始温度和峰值温度都有所提高,并且具有更宽的固化温度范围,归结于升温速率的提高,单位时间产生的热效应增加,热惯性也随着增大,产生的温度差就越大。因此,粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的特征参数峰始温度(Ti)、峰顶温度(Tp)及峰终温度(Tf)都相应地向高温方向移动。

图 1 粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂在不同升温速率(β)下的DSC曲线图
Figure 1. DSC curves of powdery epoxy resin adhesive at different heating rates (β)
表 1 粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂在不同升温速率下(β)的固化峰特征参数
Table 1. Characteristic parameters of curing peak of powdery epoxy resin adhesive at different heating rates(β)
β/(℃·min−1) Ti /℃ Tp /℃ Tf /℃ 5 86.90 122.65 185.17 10 90.40 132.79 193.27 15 94.10 141.58 200.26 20 96.60 146.53 203.53 说明:Ti为峰始温度;Tp为峰顶温度;Tf为峰终温度 将不同升温速率β与Ti、Tp和Tf分别进行线性拟合,如图2所示。利用外推法,β=0时,可求得理论凝胶温度(Tgel)为83.8 ℃,理论固化温度(Tcuring)为115.8 ℃,理论后处理温度(Ttreat)为180.1 ℃。由此可以确定:该粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的最佳固化条件为:从83.8 ℃开始体系发生固化反应,在115.8 ℃时体系达到充分固化,于180.1 ℃下体系完全固化。鉴于重组竹对热传导的影响[13],并结合以上数据,为了实现复合材料可于中温下制备,本研究中的粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂固化温度选择为130 ℃(略高于可充分固化温度)。这是因为从树脂固化反应特性来看,当实际固化温度高于理论固化温度时,可以有效缩短固化反应时间,从而提高固化速率[18]。此外,由于在固化过程中树脂中心温度远高于固化加工温度,为了避免环氧树脂因温度过高而导致其力学性能受损,因此选择略高于可充分固化温度的130 ℃,以保证复合材料于较短时间能完成固化且具有优秀的力学性能[18-21]。
-
粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的涂胶量对复合材料的结合强度及抗弯强度的影响如图3所示。复合材料的结合强度及抗弯强度随着涂胶量的增加而增强。当涂胶量为80 g·m−2时,复合材料的3层结构出现脱胶开裂,由于涂胶量较少,胶黏剂和BS、GF及PET泡沫无法形成胶合界面或层间结合强度非常小,因此复合材料在加工过程中产生了脱胶开裂的现象,其结合强度和抗弯强度均无法测定,分别以0 MPa表示。从图3中的复合材料结合强度和抗弯性能变化趋势发现,涂胶量由100 g·m−2增加到120 g·m−2时,其结合强度增长速率最快但抗弯强度变化较小。这是因为随着胶黏剂用量的增加,胶黏剂充分地浸润BS、GF及PET泡沫,形成有效的界面结合层,结合强度快速提高。此外,BS和GF表面存在的羟基活性基团可与胶黏剂中的环氧基团发生开环交联反应,从而进一步提高复合材料的结合强度。涂胶量从120 g·m−2增加到150 g·m−2时,过剩的胶黏剂会形成本体环氧树脂胶层,从而使得复合材料的抗弯强度快速增大但结合强度变化不明显。进一步增加涂胶量至200 g·m−2时,复合材料的结合强度和抗弯强度都难以有效提升,可能是由于胶黏剂的用量在复合材料界面结合层中已经达到饱和所致。从综合性能和成本上考虑,该复合材料的最佳涂胶量为150 g·m−2,此时结合强度和抗弯强度分别为0.83和19.8 MPa。
-
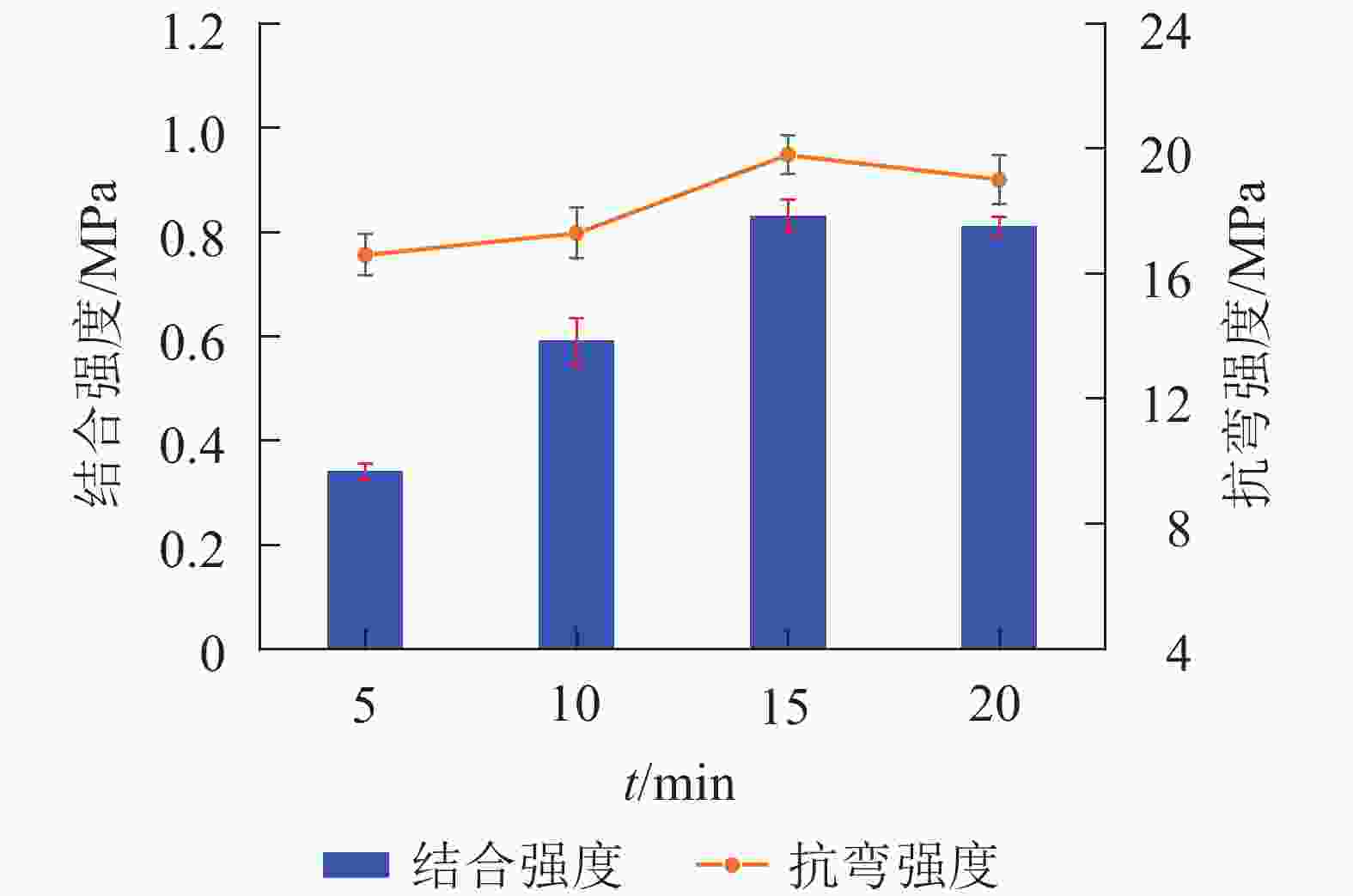
图4给出了不同热压时间对复合材料的结合强度及抗弯强度的影响。从图4中可以看出:复合材料的结合强度与抗弯强度随热压时间增加呈现出先增加后减小的趋势。当热压时间为5 min时,复合材料的结合强度与抗弯强度分别只有0.34和16.6 MPa。延长热压时间(10 min),其结合强度与抗弯强度相较热压时间为5 min的复合材料的结合强度与抗弯强度分别提高了73.5%和4.2%。进一步增加热压时间至15 min,复合材料的结合强度和抗弯强度分别提升至0.83和19.8 MPa,比热压时间为5 min的复合材料的结合强度与抗弯强度分别提高了144.1%和19.3%。这是由于涂布结束后的较短热压时间内,BS、GF和PET泡沫3种材料间的粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂尚未完全反应,适当地延长热压时间,可增加复合材料内的交联程度,从而形成交联网络,使得复合材料的结合强度和抗弯强度也逐渐增大。当进一步增加热压时间到20 min时,其结合强度和抗弯强度反而下降,表明当热压超过一定时间后,在高温下粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂形成的胶层可能受到热氧化而降解。此外,还由于BS和GF的厚度较薄及其导热性能,在高温压制过程中造成复合材料易受热降解破坏,从而导致复合材料的结合强度及抗弯强度减小。因此,本研究粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂用于制备复合材料的最佳热压时间为15 min。
-
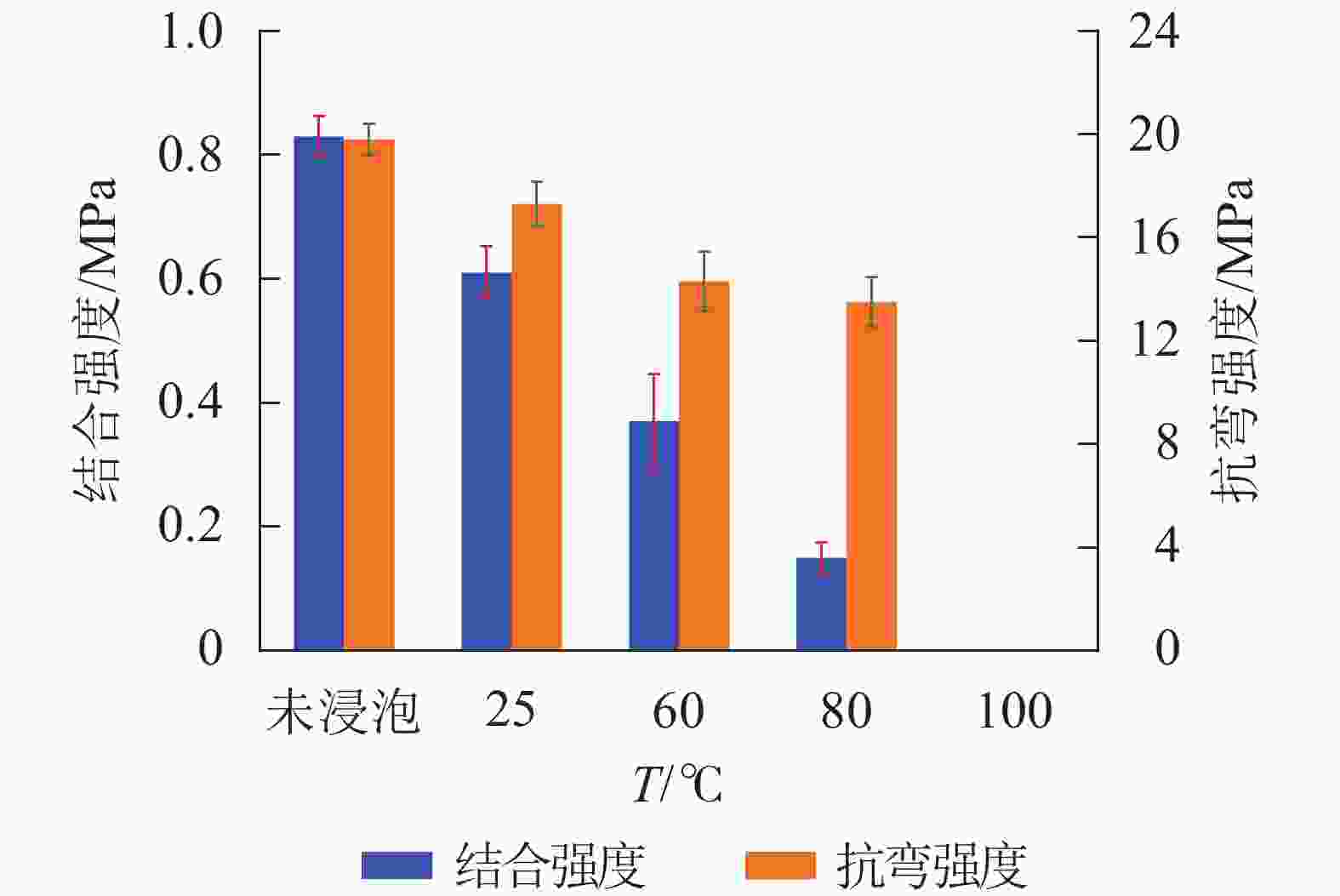
不同温度热水浸泡对复合材料的结合强度及抗弯强度的影响见图5。当复合材料在常温水中(25 ℃)浸泡3 h后,其结合强度和抗弯强度分别为0.61和17.3 MPa,比未浸泡的复合材料的结合强度和抗弯强度分别下降26.5%和12.6%,仍具有良好的机械性能。当热水温度升至80 ℃时,其结合强度和抗弯强度都呈现下降趋势,分别为0.15和13.5 MPa,其中结合强度下降明显。根据JGJ 144−2004《外墙外温工程技术标准》中对外墙外保温系统现场结合强度的最低要求(即干燥状态下结合强度不小于0.1 MPa),该复合材料仍符合标准中的限定值。然而,当浸泡水温升至100 ℃时,复合材料的界面结合层出现开胶/脱胶状况,其结合强度和抗弯强度分别降至0 MPa。以上结果表明:制备的复合结构保温板具备良好的耐热水性,但仍有待进一步提高。
-
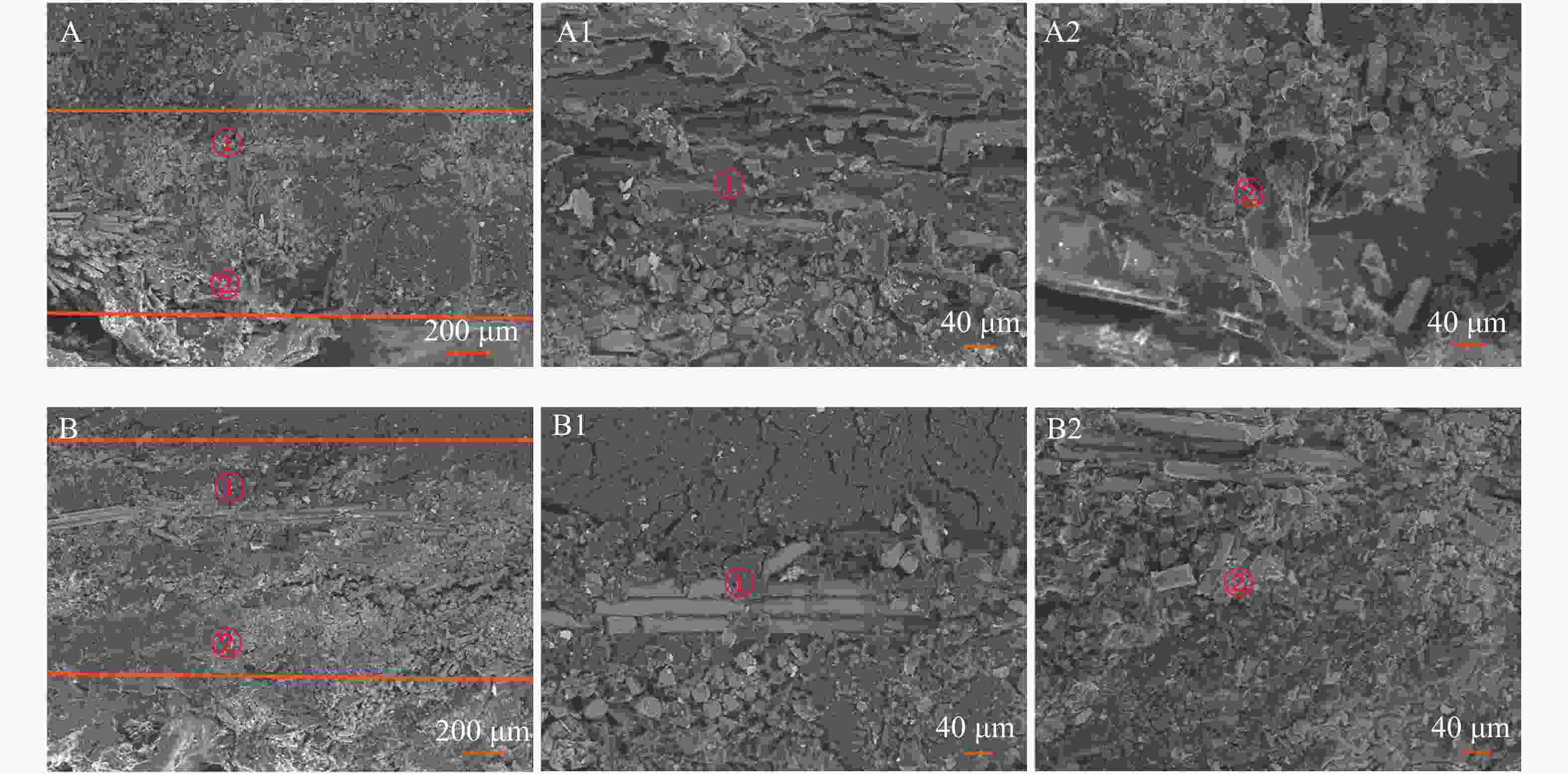
通过扫描电子显微镜对复合材料在80 ℃热水浸泡前后的结合层形貌进行观察,如图6所示。由于复合材料的结构呈“三明治”结构,因此其结合层主要有BS—GF结合层(图6A和图6B中①所示)和GF—PET泡沫结合层(如图6A和图6B中②所示)。从图6中可以观察到未经热水浸泡的复合材料的BS—GF结合层(图6A1)和GF—PET泡沫结合层(图6A2)胶合紧致,没有两相分离现象,表明复合材料层与层间具有良好的结合强度和均一的界面。经过热水浸泡后的复合材料的BS—GF结合层(图6B1)和GF—PET泡沫结合层(图6B2)出现明显的细纹和空隙,这意味着热水侵入复合材料的结合层,出现较明显的相界面,从而使得复合材料的结合强度急剧下降,但并未完全开裂或脱胶。这可能是由于制备的复合结构保温板的结合层未完全形成交联网络,其内部仍存在空隙,导致热水侵入结合层所致。因此,可以考虑改变样品制备过程中的热压压力,促使材料与胶黏剂进行充分的交联反应,避免复合材料的结合层间产生空隙,使复合材料间能够形成均一界面。
-
复合材料的导热系数由热流法测定,从表2可以看出:重组竹、PET泡沫及复合材料的导热系数随着温度的升高而增加,与温度升高引起分子热运动加快有关。在同一温度下,3种材料的导热系数从大到小依次为重组竹、复合材料、PET泡沫,其中复合材料的导热系数与PET泡沫的导热系数相近。在25 ℃时,复合材料的导热系数为0.054 2 W·m−1·K−1,显示出优秀的保温隔热性能。
表 2 复合材料的导热系数测试数据
Table 2. Test data of thermal conductivity of the composites
编号 样品
名称温度/℃ 导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)编号 样品
名称温度/℃ 导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)编号 样品
名称温度/℃ 导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)1 重组竹 25 0.068 6 2 PET泡沫 25 0.051 5 3 复合材料 25 0.054 2 40 0.070 6 40 0.057 0 40 0.059 5 60 0.078 8 60 0.067 8 60 0.069 0 70 0.081 3 70 0.074 1 70 0.074 9 -
采用自制粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂作为界面胶黏剂制备重组竹/玻纤/PET泡沫复合多层结构保温板,研究了粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的基本固化特征及对复合结构保温板的结合强度、抗弯强度及导热系数的影响作用,结果表明:①粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的最佳固化条件为体系从84 ℃开始发生固化反应,在116 ℃时可充分固化,于180 ℃下完全固化,但鉴于重组竹的热传导系数的影响,且为了实现复合材料在中温固化,本研究中的固化温度采用130 ℃。②复合材料的结合强度和抗弯强度随着粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂涂胶量、热压时间的改变而变化,当涂胶量为150 g·m−2,热压时间为15 min时,可获得综合性能最佳的复合材料,其拉伸结合强度、抗弯强度和导热系数分别可达0.83 MPa、19.8 MPa和0.0542 W·m−1·K−1。③复合材料的结合强度和抗弯强度随着热水温度的提高而不断下降,但在80 ℃热水下浸泡3 h后,其结合强度和抗弯强度分别可保持在0.15和13.5 MPa,具有良好的耐热水性,符合JGJ 144−2004《外墙外温工程技术标准》对外墙外保温系统现场结合强度的限定。④热水浸泡前后的复合材料侧面扫描电子显微镜显示浸泡后的复合材料的BS—GF结合层和GF—PET泡沫结合层出现明显的细纹和空隙,是导致复合材料的结合强度和抗弯强度急剧下降的原因。
综合上述,粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的最适固化温度、最优用量及复合材料的最佳热压成型时间显示了粉状环氧树脂作为结构保温板胶黏剂的环保高效、工艺简单、成型快速等优点,有效弥补了传统胶黏剂的制备工艺复杂及成型时间长等缺点,具有极强的工业化生产及实际应用潜力。
Preparation and performance evaluation of bamboo scrimber/glass fiber/PET foam multilayer structural insulated panel
-
摘要:
目的 为了促进木质结构保温板(SIP)的可持续发展,引入具有优良力学性能及装饰效果的可再生重组竹,结合环保型粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂,制备了重组竹/结构保温板复合材料。 方法 通过差示扫描量热法(DSC法)、力学性能测试和导热系数测试研究粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的固化特性及复合材料的结合强度、抗弯强度、导热系数及耐热水性。 结果 ①粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂的最佳固化条件为84 ℃开始发生固化反应,在116 ℃时充分固化,于180 ℃下体系完全固化。②当涂胶量为150 g·m−2,热压时间为15 min时,重组竹/结构保温板复合材料的结合强度和抗弯强度分别可达0.83和19.80 MPa,导热系数为0.054 2 W·m−1·K−1(25 ℃)。在80 ℃热水浸泡3 h后,复合材料的结合强度仍达0.15 MPa。 结论 获得综合性能优异且具有良好耐热水性的重组竹/结构保温板复合材料。图6表2参21 Abstract:Objective The purpose of this study is to introduce renewable bamboo scrimber with excellent mechanical properties and decorative effect, combined with environment-friendly powdery epoxy resin adhesive, to prepare bamboo scrimber/structural insulated panel, so as to promote the sustainable development of woody structural insulated panel(SIP). Method The curing characteristics of powdery epoxy resin adhesive and bonding strength, flexure strength, thermal conductivity as well as hot-water resistance were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), mechanical property test and thermal conductivity tester. Result (1) The optimal curing condition of powdery epoxy resin adhesive was that the curing reaction began at 84 ℃, curing thoroughly at 116 ℃, and curing completely at 180 ℃. (2) When the amount of glue was 150 g·m−2 and the hot pressing time was 15 min, the tensile bonding strength and flexure strength of the composite reached 0.83 MPa and 19.8 MPa respectively, and the thermal conductivity was 0.054 2 W·m−1·K−1 (25 ℃). After being soaked in hot water at 80 ℃ for 3 h, the bonding strength of the composite still reached 0.15 MPa. Conclusion The bamboo scrimber/structural insulated panel composite with excellent comprehensive properties and good hot-water resistance is obtained. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 21 ref.] -
表 1 粉状环氧树脂胶黏剂在不同升温速率下(β)的固化峰特征参数
Table 1. Characteristic parameters of curing peak of powdery epoxy resin adhesive at different heating rates(β)
β/(℃·min−1) Ti /℃ Tp /℃ Tf /℃ 5 86.90 122.65 185.17 10 90.40 132.79 193.27 15 94.10 141.58 200.26 20 96.60 146.53 203.53 说明:Ti为峰始温度;Tp为峰顶温度;Tf为峰终温度 表 2 复合材料的导热系数测试数据
Table 2. Test data of thermal conductivity of the composites
编号 样品
名称温度/℃ 导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)编号 样品
名称温度/℃ 导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)编号 样品
名称温度/℃ 导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)1 重组竹 25 0.068 6 2 PET泡沫 25 0.051 5 3 复合材料 25 0.054 2 40 0.070 6 40 0.057 0 40 0.059 5 60 0.078 8 60 0.067 8 60 0.069 0 70 0.081 3 70 0.074 1 70 0.074 9 -
[1] JING Meng, RAONGJANT W. Fiber reinforced structural insulated panel used as two-way slabs [J]. Mater Sci Forum, 2016, 859: 50 − 55. [2] YANG Jian, LI Zhen, DU Qiang. An experimental study on material and structural properties of structural insulated panels (SIPs) [J]. Appl Mech Mater, 2011, 147: 127 − 131. [3] PANJEHPOUR M, ALI A A A, VOO Y L. Structural insulated panels: past, present, and future [J]. J Eng Proj Prod Manage, 2013, 3(1): 2 − 8. [4] KAWASAKI T, ZHANG Min, WANG Qian, et al. Elastic moduli and stiffness optimization in four-point bending of wood-based sandwich panel for use as structural insulated walls and floors [J]. J Wood Sci, 2006, 52(4): 302 − 310. [5] 查晓雄, 张旭琛. 新型绿色建筑结构绝缘板力学性能的理论研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2011, 41(3): 1 − 5. ZHA Xiaoxiong, ZHANG Xuchen. Theoretical research on mechanical behavior of new green structural insulated panels [J]. Ind Constr, 2011, 41(3): 1 − 5. [6] 刘晓娜, 周海宾. 结构用木质保温板(SIPs)的业现状及发展前景[J]. 木材工业, 2017, 31(2): 14 − 18. LIU Xiaona, ZHOU Haibin. Current status and future development of wood-based structural insulated panels (SIPs) [J]. China Wood Ind, 2017, 31(2): 14 − 18. [7] 严帅, 刘伟庆, 陆伟东, 等. SIP板式结构住宅体系[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2010, 37(8): 35 − 39. YAN Shuai, LIU Weiqing, LU Weidong, et al. Study on SIP slab structure residential system [J]. New Build Mater, 2010, 37(8): 35 − 39. [8] SHARMA B, GATÓO A, BOCK M, et al. Engineered bamboo for structural applications [J]. Constr Build Mater, 2015, 81: 66 − 73. [9] FU Yang, FANG Hai. Study on the properties of the recombinant bamboo by finite element method [J]. Compos Parts B Eng, 2017, 115: 151 − 159. [10] 龚正, 袁少飞, 张建, 等. 重组竹材生产设备现状及发展趋势[J]. 林业机械与木工设备, 2018, 46(9): 4 − 9, 15. GONG Zheng, YUAN Shaofei, ZHANG Jian, et al. Research status and development trend of reconstituted bamboo lumber production equipment [J]. For Mach Woodworking Equip, 2018, 46(9): 4 − 9, 15. [11] 潘金炎, 王立, 张玉强, 等. 基于重组竹的结构用胶合竹材力学性能实验研究[J]. 施工技术, 2018, 47(21): 135 − 139. PAN Jinyan, WANG Li, ZHANG Yuqiang, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of structural glued bamboo based on recombinant bamboo [J]. Constr Technol, 2018, 47(21): 135 − 139. [12] 于文吉. 我国重组竹产业发展现状与机遇[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2019, 17(3): 1 − 4. YU Wenji. Current situation and opportunities for the development of bamboo scrimber industry in China [J]. World Bamboo Ratta, 2019, 17(3): 1 − 4. [13] 王雪花, 费本华, 送莎莎, 等. 覆面材料对SIP保温性能的影响[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2015, 42(5): 67 − 71. WANG Xuehua, FEI Benhua, SONG Shasha, et al. Effect of different facing materials on SIP heat-insulating property [J]. New Build Mater, 2015, 42(5): 67 − 71. [14] 王雪花, 方露, 陈红, 等. 覆面材料对结构保温板力学性能的影响[J]. 林业工程学报, 2017, 2(3): 16 − 21. WANG Xuehua, FANG Lu, CHEN Hong, et al. Mechanical properties of structural insulated panels faced with different materials [J]. J For Eng, 2017, 2(3): 16 − 21. [15] MANDILARAS I, DATSONIOS I A, ZANNIS G, et al. Thermal performance of a building envelope incorporating ETICS with vacuum insulation panels and EPS [J]. Energy Build, 2014, 85: 654 − 665. [16] MIESBAUER O, KUCUKPINAR E, KIESE S, et al. Studies on the barrier performance and adhesion strength of novel barrier films for vacuum insulation panels [J]. Energy Build, 2014, 85: 597 − 603. [17] 米莹娟, 王伟, 张冬梅, 等. 1种新型自粘接预浸料-Nomex蜂窝板面-芯结合强度关键影响因素试验研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(4): 156 − 162. MI Yingjuan, WANG Wei, ZHANG Dongmei, et al. Experimental investigation of key factors on adhesive properties of skin-core for honeycomb sandwich panel with self-adhesive prepreg [J]. Acta Mater Compos Sin, 2013, 30(4): 156 − 162. [18] DONG Hongxing, LI Yonghe, ZHANG Jin, et al. Kinetics simulation and a novel curing procedure to avoid thermal shock during the curing process of epoxy composites [J]. RSC Adv, 2016, 6(70): 65533 − 65540. [19] 何星蔚. 中温固化环氧树脂体系及胶合性能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2018. HE Xingwei. Study on Curing Epoxy Resin System and Adhesive Properties at Medium Temperature[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A&F University, 2018. [20] 吴博. 1种低黏度高玻璃化转变温度的环氧胶的研制[J]. 精细石油化工, 2019, 36(6): 53 − 56. WU Bo. Development of an epoxy adhesive with low viscosity and high glass transition temperature [J]. Spec Petrochem, 2019, 36(6): 53 − 56. [21] 杜姝婧, 龚文化, 许亚洪. RTM用6818高温固化环氧树脂的固化工艺与耐热性研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019, 47(11): 131 − 133. DU Shujing, GONG Wenhua, XU Yahong. Study on curing process and heat resistance of 6818 heat temperature curing epoxy resin system for RTM [J]. New Chem Mater, 2019, 47(11): 131 − 133. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200330






 下载:
下载: