-
百合是百合科Liliaceae百合属Lilium所有种的统称[1]。中国是世界百合的起源中心[2],原产约55种32个变种[3]。卷丹Lilium lancifolium具有很高的观赏、食用和药用价值[4],且适应性强,是为数不多的广布种之一[5-6],在中国各地均有分布,东北地区及中部秦巴山区是野生卷丹的集中分布区。陕西南部地区,包括汉中、安康、商洛三地市的全部辖区及宝鸡太白县、西安周至县的南部山区,地处中国南北气候的分界线,北靠秦岭,南倚巴山[7],汉江自西向东穿流而过。该区域分布着丰富的野生百合种质资源,但是,对于该地区的野生百合资源前人只进行了初步的调查及形态学研究[8-9],仍然缺乏系统的认识和了解。形态多样性主要研究种群在其分布区内各种环境下的表型变异[10],是遗传多样性与环境多样性的综合体现[11],根据表现型差异反映基因型差异是形态学标记检测遗传多样性的关键[12]。通过有效的采样、合理的数学统计方法,采用遗传上较稳定的、不易受环境影响的数量性状,可以揭示种群变异大小及遗传规律[13-14]。本研究在全面调查陕南卷丹种质资源分布基础上,首次对卷丹10个野生种群形态性状的变异进行了研究,旨在揭示卷丹野生资源表型性状的分化和差异,为进一步开展卷丹遗传多样性研究及种质资源保护利用提供理论依据。
-
于2011年6-8月卷丹花期,采取走访、样地调查和线路调查相结合的方法[15],对陕南地区卷丹野生种群进行实地调查,随机选择间隔距离在5 km以上的10个野生种群,分别位于:太白县黄柏塬乡(P1),周至县双庙子乡(P2),洋县溢水镇(P3),岚皋县城关镇(P4),留坝县张良庙乡(P5),城固县石槽河乡(P6),西乡县司上乡(P7),柞水县下梁乡(P8),宁强县舒家坝乡(P9),汉台区天台山乡(P10)。各种群的相对位置和地理生态因子状况见表 1。
表 1 卷丹10个野生种群的地理和生态因子
Table 1. Geographical and ecological factors of 10 wild populations of Lilium lancifolium
种群 北纬 东经 海拔/m 年平均温度/℃ 年降水量/mm 坡向 坡向 P1 33°49′00″ 107°31′46″ 1 283 7.7 800 阴坡 阴坡 P2 33°49′37″ 108°16′50″ 1 455 13.2 800 阳坡 阳坡 P3 33°16′02″ 107°20′50″ 822 14.2 844 阴坡 阴坡 P4 32°17′59″ 108°53′24″ 906 15.1 1 000 阳坡 阳坡 P5 33°40′39″ 106°52′13″ 1 181 11.5 886 阴坡 阴坡 P6 32°32′49″ 107°18′16″ 759 14.2 844 阴坡 阴坡 P7 32°24′41″ 108°27′41″ 919 14.4 1 150 阳坡 阳坡 P8 33°39′56″ 109°08′39″ 895 12.40 742 阴坡 阴坡 P9 32°55′11″ 106°11′01″ 846 13.0 1 178 阳坡 阳坡 P10 33°15′09″ 107°02′24″ 1 141 14.5 855 阳坡 阳坡 -
本研究主要选取开花植株茎、叶、花的16个数量性状为指标[15-16],对卷丹不同野生种群的表型性状进行变异分析。具体性状如下:茎粗指茎秆基部5 cm处的直径;茎秆高度指由地表至花梗基部垂直于地面的植株长度;鳞茎纵径/横径指鳞茎基部到鳞茎顶端的距离与鳞茎最大横切面直径的比值;叶片数指植株成长过程中茎秆上长出所有叶片的数量;选1/6茎高处的叶片作为下部叶进行测量,下部叶宽/长指下部叶面最宽处长度与叶基部到叶尖长度的比值;选1/2茎高处的叶片作为中部叶进行测量,中部叶宽/长指中部叶面最宽处长度与叶基部到叶尖长度的比值;选5/6茎高处的叶片作为上部叶进行测量,上部叶宽/长指上部叶面最宽处长度与叶基部到叶尖长度的比值;苞片宽/长指花序最下部苞片最宽处长度与苞片基部到尖部长度的比值;花部性状均选取花序最下部的第1朵花测量;着花量指每个花序上着生的全部花朵数;花瓣(内)宽/长指内层花瓣的最宽处的长度与内层花瓣连接花梗处到花瓣顶点间的距离的比值;花瓣(外)宽/长指外层花瓣最宽处的长度与外层花瓣连接花梗处到花瓣顶点间的距离的比值;花丝长指花丝连接花梗点和与花药连接点间的长度;花柱长指花柱连接子房点到柱头的长度;柱头宽指柱头横切面最宽处的直径;子房宽/长指子房横切面直径与子房基部连接花梗点到上部连接花柱点间长度的比值;花梗长指连接第1朵花基部与茎杆的花梗长度。
-
以盛花期为标准,对10个卷丹种群均随机选择30株植株,植株间隔在5 m以上,海拔高度至少相差5 m,以避免采样亲缘关系较近,随机测定6朵花·组-1,重复5次。长度测量均使用电子游标卡尺测量,精度为0.01 mm。
-
利用SPSS 19.0和EXCEL 2003对试验数据进行方差分析、相关性分析与聚类分析[16]。
-
本研究中卷丹的10个调查地点主要分布在32°17′~33°49′N,106°11′~109°08′E,海拔高度为759~1 455 m的河边或灌木丛中,呈片状分布。卷丹在周至县双庙子乡的分布海拔最高,在城固县石槽河乡的分布海拔最低。它们大都生长在空气湿润、无阳光直射的灌木丛或河边的草丛。调查中还发现:卷丹的繁衍能力很强,在野生种群中,有很多卷丹的幼苗生长。卷丹伴生植物主要有紫穗槐Amorpha fruticosa,杠柳Periploca sepium,萱草Hemerocallis flava,野艾蒿Artemisia lavandulifolia等。
-
通过对陕南地区分布的10个卷丹野生种群的植物形态学性状系统观察和测定,其形态多样性表现丰富,数量性状在种群内和种群间均存在显著或极显著的差异。
-
由表 2和表 3可知:卷丹16个数量性状的均值比较中,除花丝长和花柱长为较稳定的性状外,其余14个数量性状在10个种群间均存在着明显的差异。在种群间,太白黄柏塬乡种群的外瓣宽长比和子房的宽长比最大,周至县双庙子乡种群的茎粗、茎秆高度、着花量和花梗长最大,岚皋县城关镇种群的鳞茎纵横径比、下部叶宽长比和内瓣宽长比最大,城固县石槽河乡种群的中上部叶宽长比和苞片宽长比最大,西乡县司上乡种群的花柱最长,宁强县舒家坝乡种群的花丝最长,汉台区天台山乡的叶片数和柱头宽最大。
表 2 卷丹10个野生种群营养器官数量性状的均值
Table 2. Mean of qualitative traits in vegetative organ of 10 wild populations of Lilium lancifolium
种群 茎粗/mm 茎秆高度/cm 鳞茎纵径/横径比 叶片数 下部叶宽/长比 中部叶宽/长比 上部叶宽/长比 苞片宽/长比 P1 7.9 d 131.1 bc 0.94 bc 74.2 d 0.11 bc 0.10 bcd 0.28 ab 0.55 ab P2 14.5 a 183.7 a 0.90 c 120.0 bc 0.10 c 0.09 cd 0.17 cd 0.33 f P3 11.9 abc 159.2 ab 0.83 c 112.4 bc 0.12 abc 0.12 abc 0.23 bc 0.49 bc P4 11.9 abc 120.8 c 1.31 a 91.0 cd 0.14 a 0.10 bcd 0.22 bc 0.42 de P5 10.3 bcd 158.4 ab 1.01 bc 133.6 b 0.11 bc 0.08 d 0.23 bc 0.39 ef P6 9.8 cd 145.8 bc 0.86 c 104.4 bcd 0.12 ab 0.13 a 0.30 a 0.60 a P7 11.7 abc 154.2 b 0.99 bc 135.4 b 0.12 abc 0.10 bcd 0.23 bc 0.55 ab P8 14.5 a 136.8 bc 1.15 ab 121.4 bc 0.10 c 0.10 bcd 0.17 cd 0.45 cd P9 11.3 abcd 146.3 bc 0.87 c 120.4 bc 0.11 bc 0.12 ab 0.24 ab 0.52 bc P10 13.5 ab 153.5 b 1.00 bc 222.0 a 0.11 bc 0.09 cd 0.16 d 0.51 bc 平均值 11.7 149 0.98 123.5 0.11 0.10 0.22 0.48 表 3 卷丹10个野生种群生殖器官数量性状的均值
Table 3. Means of qualitative traits in generative organ of 10 wild populations of Lilium lancifolium
种群 着花量 花瓣(内)宽/长 花瓣(外)宽/长 花丝长/mm 花柱长/mm 柱头宽/mm 子房宽/长比 花梗长/mm P1 3.6 b 0.28 ab 0.21 a 73.9 de 66.7 abc 3.4 ab 0.25 a 67.0 de P2 14.0 a 0.24 d 0.20 ab 72.3 e 65.7 bc 3.3 bc 0.24 a 106.6 a P3 5.6 b 0.26 bcd 0.19 bc 77.2 bc 68.5 ab 3.0 cd 0.22 b 81.9 bc P4 4.4 b 0.29 a 0.20 ab 76.0 cd 67.5 abc 3.2 bc 0.20 c 71.4 cde P5 6.8 b 0.27 bc 0.19 bc 76.6 c 69.3 a 3.2 bc 0.22 bc 77.3 bcd P6 3.6 b 0.27 bc 0.18 c 78.1 abc 67.0 abc 2.8 d 0.24 a 87.0 b P7 6.2 b 0.26 cd 0.18 c 79.1 ab 69.5 a 3.1 bcd 0.23 ab 63.4 e P8 3.0 b 0.28 ab 0.19 bc 75.9 cd 65.2 cd 3.0 cd 0.22 c 70.9 cde P9 5.0 b 0.26 bcd 0.19 bc 79.6 a 69.0 a 3.1 bcd 0.25 a 76.7 bcd P10 10.8 a 0.27 bc 0.21 a 77.0 bc 62.7 d 3.6 a 0.23 ab 86.0 b 平均值 6.3 0.27 0.19 76.6 67.1 3.2 0.23 78.8 -
变异系数(CV)可以反映表型性状在种群内和种群间的变异,揭示其变异格局。变异系数越大,则性状值离散程度越大[11]。从表 4可知:卷丹各性状变异不同,在16个数量性状中,变异度从大到小依次为着花量、叶片数、茎粗、上部叶片宽长比、鳞茎纵横径比、中部叶片宽长比、茎秆高度、花梗长、下部叶宽长比、苞片宽长比、外瓣宽长比、子房宽长比、柱头宽、内瓣宽长比、花柱长和花丝长。变异系数越小,表明该性状越稳定,常作为植物分类时重要的指标性状;从16个供测指标中发现,生殖性状的变异系数较营养性状小,这与传统分类时把生殖性状作为主要分类依据相一致。卷丹的16个数量性状在种群内和种群间均存在变异,即不同种群的环境异质性导致了种群形态性状变异的差异。从表 4中还可以看出:各种群形态变异从大到小依次为种群P6(CV=17.18%),种群P4(CV=16.16%),种群P3(CV=14.54%),种群P1(CV=12.98%),种群P7(CV=12.87%),种群P2(CV=12.31%),种群P5(CV=10.96%),种群P9(CV=9.61%),种群P8(CV=7.66%),种群P10(CV=7.52%)。对于多数性状,城固县石槽河乡种群变异幅度并非最大,如花梗长,柞水县下梁乡种群的变异幅度为最大,而鳞茎纵横径比,留坝县张良庙乡的变异却最大。
表 4 卷丹10个野生种群营养器官和生殖器官数量性状的变异系数
Table 4. Coefficient of variation of quantitative traits in vegetative and generative organ of 10 Lilium lancifolium wild populations
种群 变异系数/% 茎粗 茎秆高度 鳞茎纵/横比 叶片数 下部叶宽/长比 中部叶宽/长比 上部叶宽/长比 苞片宽/长比 着花量 花瓣(内)宽/长比 花瓣(外)宽/长比 花丝长 花柱长 柱头宽 子房宽/长比 花梗长 平均值 P1 16.93 16.56 13.13 25.65 11.86 8.32 12.4 9.85 50.46 5.62 5.77 2.76 2.16 7.14 4.41 14.60 12.98 P2 19.20 13.16 6.39 21.87 6.21 12.48 23.94 15.28 44.03 1.98 6.51 2.19 1.49 7.11 4.32 10.76 12.31 P3 24.58 19.55 15.07 34.69 20.82 8.97 12.01 9.32 43.01 3.81 6.66 2.08 6.42 7.10 6.00 12.48 14.54 P4 28.35 18.62 23.14 29.90 8.83 15.07 20.72 5.42 69.31 6.14 2.03 1.77 4.11 10.90 5.35 8.84 16.16 P5 18.92 11.75 23.46 17.87 12.02 21.03 6.35 5.35 16.11 6.36 10.04 2.10 2.91 2.81 10.67 7.64 10.96 P6 40.48 20.65 17.69 23.09 3.60 30.11 33.15 14.98 50.46 7.74 8.59 2.91 3.74 7.78 3.93 5.94 17.18 P7 20.29 11.46 11.97 22.00 18.31 19.15 28.94 5.71 31.02 4.42 7.51 2.39 1.93 4.04 4.38 12.39 12.87 P8 14.80 1.50 16.40 3.93 3.42 7.64 15.20 5.01 0.00 4.13 6.06 1.18 4.15 9.95 8.26 20.92 7.66 P9 20.83 9.95 2.06 23.70 12.29 6.74 14.00 11.64 31.62 2.67 2.77 0.75 0.22 1.66 3.36 9.45 9.61 P10 5.39 3.17 9.98 14.28 9.40 7.77 21.03 6.95 17.81 3.96 3.17 2.59 1.52 5.77 3.24 4.34 7.52 -
茎粗、茎秆高度、叶片数、着花量、外瓣宽长比、柱头宽、子房宽长比、花梗长等8个性状与海拔高度成正相关,其余8个性状与海拔高度成负相关;并且着花量(r=0.684,P<0.05,n=10),外瓣宽长比(r=0.651,P<0.05,n=10)和柱头宽(r=0.729,P<0.05,n=10)与海拔高度有显著正相关性,中部叶宽长比(r=-0.743,P<0.05,n=10)和花丝长(r=-0.795,P<0.01,n=10)与海拔高度有显著负相关性(表 5)。
表 5 卷丹营养性状、生殖性状与主要生态因子的相关性分析
Table 5. Correlation analysis between quantitative traits belonging to vegetative and generative organs and main ecological factors of Lilium lancifolium
生态因子 茎粗 茎秆高度 鳞茎纵/横比 叶片数 下部叶宽/长比 中部叶宽/长比 上部叶宽/长比 苞片宽/长比 着花量 花瓣(内)宽/长比 花瓣(外)宽/长比 花丝长 花柱长 柱头宽 子房宽/长比 花梗长 海拔高度 0.084 0.443 -0.058 0.117 -0.500 -0.743** -0.343 -0.551* 0.684* -0.318 0.651* -0.795** -0.344 0.729* 0.265 0.411 坡向 0.430 0.165 0.200 0.382 0.180 -0.202 -0.434 -0.191 0.534 -0.302 0.196 0.109 -0.113 0.419 0.000 0.169 生境 0.659 0.733 ** -0.203 0.718** -0.464 -0.434 -0.707* -0.295 0.752** -0.681* 0.000 0.024 -0.209 0.361 0.087 0.334 说明:*和**分别表示在5%水平和1%水平上差异显著。 -
中上部叶宽长比、苞片宽长比、内瓣宽长比、花柱长等5个性状与坡向成负相关,其余11个性状与坡向成正相关;但坡向与卷丹数量性状并无显著相关性(表 5)。
-
鳞茎纵横径比、叶宽长比、苞片宽长比、内瓣宽长比、花柱长等7个性状与生境成负相关,其余9个性状与生境成正相关;并且茎秆高度(r=0.733,P<0.01,n=10),叶片数(r=0.718,P<0.01,n=10)和着花量(r=0.752,P<0.01,n=10)与生境有显著正相关性,上部叶宽长比(r=-0.707,P<0.05,n=10)和内瓣宽长比(r=-0.681,P<0.05,n=10)与生境有显著负相关性(表 5)。
-
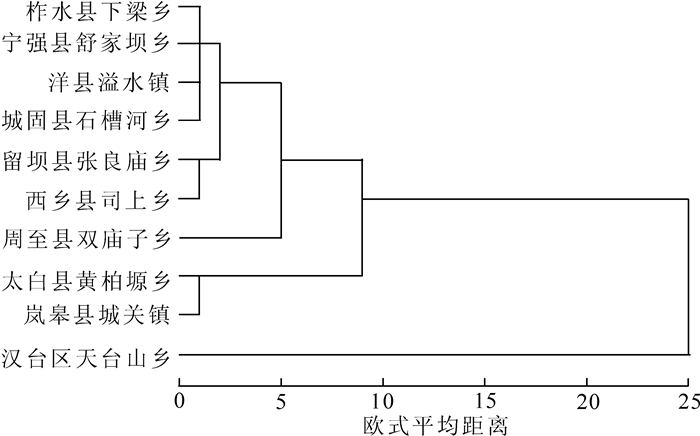
为研究卷丹种群间的相似性及亲缘关系,根据其形态特征的16个数量性状,对10个卷丹野生种群用SPSS 19.0进行聚类分析。结果(图 1)显示:10个卷丹野生种群在阈值为10.0处明显分为2大类,汉台区天台山乡种群单独聚为一类,其余种群聚为一类。此外,性状的表型特征并没有依地理距离而聚类,说明卷丹种群间表型性状变异存在不连续性。
-
不同植物的遗传变异不同,本研究中陕南卷丹10个种群16个数量性状变异系数变幅为2.07%~35.38%,平均为13.26%,低于云南含笑Michelia yunnanensis[17]的23.81%,蒙古栎Quercus mongolica[14]的24.89%,岷江百合Lilium regale[15]的30.46%,高于皂荚Gleditsia sinensis[18]的11.20%。与上述几种物种相比,卷丹变异系数处于中等偏低水平, 这可能与卷丹的无性繁殖方式有关。本研究中卷丹茎的3个性状平均变异系数(15.85%)>叶的5个性状平均变异系数(14.77%)>花的8个性状平均变异系数(9.18%),说明卷丹花与茎、叶性状相比遗传稳定性最高,茎、叶性状变异较大,环境因素对茎、叶的影响大;这与蒙古栎[14]、五角枫Acer mono[19]等表型研究中得到的生殖器官变异较营养器官变异小的结论一致,进一步阐明了花的性状在植物分类中的重要地位。卷丹种群间变异较大,生境的异质性是造成卷丹种群间分化的主要原因[20]。研究中卷丹同一种群内不同个体间也存在着较大变异,而卷丹属是为数不多只进行无性繁殖的百合种,这反映着基因突变等重要信息,因此加强对卷丹无性系繁殖的研究将对卷丹育种和生产具有重大意义。
-
环境因素的多样性是影响植物变异的重要因子之一,分布区的环境条件越复杂,则种群的表型变异越大[18]。供试的10个野生种群,地理跨度较大,海拔、坡向及生境都有很大的差异,而且其分布呈间断的不连续性,使得卷丹的表型数量性状变异较大,进而导致不同野生种群卷丹没有完全依地理距离而聚类,这与岷江百合Lilium relale[15]研究结果一致,说明卷丹种群间表型性状的变异不连续。本研究发现:随着海拔升高,卷丹叶片宽长比显著减小,着花量和柱头宽度显著增大,营养生长减慢,生殖生长加速,这与姬志峰等[19]提到的叶面积随海拔升高有减小趋势的观点是相同的;随着卷丹远离森林,接近水源,卷丹植株高度、叶片数和着花量显著提升,营养生长旺盛。这是对温度、水分和光照条件的一种适应[18],对后续野生卷丹的引种栽培有指导意义。
-
由于卷丹分布区跨度大、生长环境条件多样,经过长期的地理隔离、自然选择与人工选择,使其产生了丰富的表型变异,其中也必然蕴藏着一定的遗传变异[17]。了解物种的遗传背景是对物种采取正确保护措施的基础[13],因此,应尽可能地保护较多的种群。在进行卷丹种质资源的就地保护的同时,还应通过采集尽可能多的珠芽,利用组织培养技术扩繁异地保存。形态是基因转录、翻译和表达的结果[15-16],因此,对卷丹种质资源系统地进行生物化学及分子生物学方面的研究成为目前亟待研究的重点方向。
Diversity in wild populations of Lilium lancifolium native to southern Shaanxi Province
-
摘要: 为揭示陕南地区卷丹Lilium lancifolium野生种群的表型变异程度和规律, 以该区10个有代表性的卷丹野生种群, 每个种群30个个体为试材, 对其茎、叶、花的茎粗、叶片数、着花量等16个数量性状指标进行方差分析、相关性分析及聚类分析, 探讨种群间及种群内表型多样性的变异特点。结果表明:①卷丹数量性状在种群间和种群内均存在一定程度的变异, 不同性状的平均变异系数为2.07%(花丝长)~35.38%(着花量), 种群间的平均变异系数为7.52%(汉台区天台山乡种群)~17.18%(城固县石槽河乡种群)。②相关性分析表明, 着花量(r=0.684, P < 0.05, n=10), 外瓣宽长比(r=0.651, P < 0.05, n=10), 柱头宽(r=0.729, P < 0.05, n=10)与海拔高度有显著正相关性, 中部叶宽长比(r=-0.743, P < 0.05, n=10), 花丝长(r=-0.795, P < 0.01, n=10)与海拔高度有显著负相关性; 且茎秆高度(r=0.733, P < 0.01, n=10), 叶片数(r=0.718, P < 0.01, n=10), 着花量(r=0.752, P < 0.01, n=10)与生境有显著正相关性, 上部叶宽长比(r=-0.707, P < 0.05, n=10), 内瓣宽长比(r=-0.681, P < 0.05, n=10)与生境有显著负相关性; ③Q聚类分析显示, 陕南地区10个卷丹野生种群可以初步分为2组, 汉台区天台山乡种群单独为一组。Abstract: To reveal the phenotypic variation of wild Lilium lancifolium and to determine variation in characteristics of phenotypic diversity within and among populations, three stem characters, five leaf characters and eight flower characters in 30 plants from each of 10 populations in L. lancifolium native to southern Shaanxi Province were chosen as materials based on field investigations and analysis of the natural population. Analysis of variance, correlation analysis, and cluster analysis were carried out for 16 quantitative traits, such as stem diameter, blade number, flower number and so on. Results indicated (1) the average variation coefficient varied from 2.1% (length of filament) to 35.4% (number of flowers), and the average coefficient of variation among populations ranged between 7.5% (populations native to Tiantaishan Town in Hantai County) and 17.2% (populations native to Shicaohe Town in Chenggu County). (2) The correlation analysis showed that altitude was significantly and positively correlated to quantitative traits of flower number (r=0.684, P < 0.05, n=10), width-length ratio of outside petals (r=0.651, P < 0.05, n=10) and width of stigmas (r=0.729, P < 0.05, n=10), and was significantly and negatively correlated to width-length ratio of middle leaves (r=-0.743, P < 0.05, n=10) and filament length(r=-0.795, P < 0.01, n=10). Habitat was significantly and positively correlated to quantitative traits of stem height (r=0.733, P < 0.01, n=10), blade number (r=0.718, P < 0.01, n=10) and flower number (r=0.752, P < 0.01, n=10), and was significantly and negatively correlated to width-length ratio of top leaves (r=-0.707, P < 0.05, n=10) and width-length ratio of inside petals (r=-0.681, P < 0.05, n=10). (3) The cluster analysis showed that the 10 wild populations could be divided into two groups with the population native to Tiantaishan Town in Hantai County forming one cluster. These findings offer basic data for further studies on genetic breeding and conservation biology of this species.
-
Key words:
- botany /
- Lilium lancifolium /
- population /
- phenotypic variation
-
表 1 卷丹10个野生种群的地理和生态因子
Table 1. Geographical and ecological factors of 10 wild populations of Lilium lancifolium
种群 北纬 东经 海拔/m 年平均温度/℃ 年降水量/mm 坡向 坡向 P1 33°49′00″ 107°31′46″ 1 283 7.7 800 阴坡 阴坡 P2 33°49′37″ 108°16′50″ 1 455 13.2 800 阳坡 阳坡 P3 33°16′02″ 107°20′50″ 822 14.2 844 阴坡 阴坡 P4 32°17′59″ 108°53′24″ 906 15.1 1 000 阳坡 阳坡 P5 33°40′39″ 106°52′13″ 1 181 11.5 886 阴坡 阴坡 P6 32°32′49″ 107°18′16″ 759 14.2 844 阴坡 阴坡 P7 32°24′41″ 108°27′41″ 919 14.4 1 150 阳坡 阳坡 P8 33°39′56″ 109°08′39″ 895 12.40 742 阴坡 阴坡 P9 32°55′11″ 106°11′01″ 846 13.0 1 178 阳坡 阳坡 P10 33°15′09″ 107°02′24″ 1 141 14.5 855 阳坡 阳坡 表 2 卷丹10个野生种群营养器官数量性状的均值
Table 2. Mean of qualitative traits in vegetative organ of 10 wild populations of Lilium lancifolium
种群 茎粗/mm 茎秆高度/cm 鳞茎纵径/横径比 叶片数 下部叶宽/长比 中部叶宽/长比 上部叶宽/长比 苞片宽/长比 P1 7.9 d 131.1 bc 0.94 bc 74.2 d 0.11 bc 0.10 bcd 0.28 ab 0.55 ab P2 14.5 a 183.7 a 0.90 c 120.0 bc 0.10 c 0.09 cd 0.17 cd 0.33 f P3 11.9 abc 159.2 ab 0.83 c 112.4 bc 0.12 abc 0.12 abc 0.23 bc 0.49 bc P4 11.9 abc 120.8 c 1.31 a 91.0 cd 0.14 a 0.10 bcd 0.22 bc 0.42 de P5 10.3 bcd 158.4 ab 1.01 bc 133.6 b 0.11 bc 0.08 d 0.23 bc 0.39 ef P6 9.8 cd 145.8 bc 0.86 c 104.4 bcd 0.12 ab 0.13 a 0.30 a 0.60 a P7 11.7 abc 154.2 b 0.99 bc 135.4 b 0.12 abc 0.10 bcd 0.23 bc 0.55 ab P8 14.5 a 136.8 bc 1.15 ab 121.4 bc 0.10 c 0.10 bcd 0.17 cd 0.45 cd P9 11.3 abcd 146.3 bc 0.87 c 120.4 bc 0.11 bc 0.12 ab 0.24 ab 0.52 bc P10 13.5 ab 153.5 b 1.00 bc 222.0 a 0.11 bc 0.09 cd 0.16 d 0.51 bc 平均值 11.7 149 0.98 123.5 0.11 0.10 0.22 0.48 表 3 卷丹10个野生种群生殖器官数量性状的均值
Table 3. Means of qualitative traits in generative organ of 10 wild populations of Lilium lancifolium
种群 着花量 花瓣(内)宽/长 花瓣(外)宽/长 花丝长/mm 花柱长/mm 柱头宽/mm 子房宽/长比 花梗长/mm P1 3.6 b 0.28 ab 0.21 a 73.9 de 66.7 abc 3.4 ab 0.25 a 67.0 de P2 14.0 a 0.24 d 0.20 ab 72.3 e 65.7 bc 3.3 bc 0.24 a 106.6 a P3 5.6 b 0.26 bcd 0.19 bc 77.2 bc 68.5 ab 3.0 cd 0.22 b 81.9 bc P4 4.4 b 0.29 a 0.20 ab 76.0 cd 67.5 abc 3.2 bc 0.20 c 71.4 cde P5 6.8 b 0.27 bc 0.19 bc 76.6 c 69.3 a 3.2 bc 0.22 bc 77.3 bcd P6 3.6 b 0.27 bc 0.18 c 78.1 abc 67.0 abc 2.8 d 0.24 a 87.0 b P7 6.2 b 0.26 cd 0.18 c 79.1 ab 69.5 a 3.1 bcd 0.23 ab 63.4 e P8 3.0 b 0.28 ab 0.19 bc 75.9 cd 65.2 cd 3.0 cd 0.22 c 70.9 cde P9 5.0 b 0.26 bcd 0.19 bc 79.6 a 69.0 a 3.1 bcd 0.25 a 76.7 bcd P10 10.8 a 0.27 bc 0.21 a 77.0 bc 62.7 d 3.6 a 0.23 ab 86.0 b 平均值 6.3 0.27 0.19 76.6 67.1 3.2 0.23 78.8 表 4 卷丹10个野生种群营养器官和生殖器官数量性状的变异系数
Table 4. Coefficient of variation of quantitative traits in vegetative and generative organ of 10 Lilium lancifolium wild populations
种群 变异系数/% 茎粗 茎秆高度 鳞茎纵/横比 叶片数 下部叶宽/长比 中部叶宽/长比 上部叶宽/长比 苞片宽/长比 着花量 花瓣(内)宽/长比 花瓣(外)宽/长比 花丝长 花柱长 柱头宽 子房宽/长比 花梗长 平均值 P1 16.93 16.56 13.13 25.65 11.86 8.32 12.4 9.85 50.46 5.62 5.77 2.76 2.16 7.14 4.41 14.60 12.98 P2 19.20 13.16 6.39 21.87 6.21 12.48 23.94 15.28 44.03 1.98 6.51 2.19 1.49 7.11 4.32 10.76 12.31 P3 24.58 19.55 15.07 34.69 20.82 8.97 12.01 9.32 43.01 3.81 6.66 2.08 6.42 7.10 6.00 12.48 14.54 P4 28.35 18.62 23.14 29.90 8.83 15.07 20.72 5.42 69.31 6.14 2.03 1.77 4.11 10.90 5.35 8.84 16.16 P5 18.92 11.75 23.46 17.87 12.02 21.03 6.35 5.35 16.11 6.36 10.04 2.10 2.91 2.81 10.67 7.64 10.96 P6 40.48 20.65 17.69 23.09 3.60 30.11 33.15 14.98 50.46 7.74 8.59 2.91 3.74 7.78 3.93 5.94 17.18 P7 20.29 11.46 11.97 22.00 18.31 19.15 28.94 5.71 31.02 4.42 7.51 2.39 1.93 4.04 4.38 12.39 12.87 P8 14.80 1.50 16.40 3.93 3.42 7.64 15.20 5.01 0.00 4.13 6.06 1.18 4.15 9.95 8.26 20.92 7.66 P9 20.83 9.95 2.06 23.70 12.29 6.74 14.00 11.64 31.62 2.67 2.77 0.75 0.22 1.66 3.36 9.45 9.61 P10 5.39 3.17 9.98 14.28 9.40 7.77 21.03 6.95 17.81 3.96 3.17 2.59 1.52 5.77 3.24 4.34 7.52 表 5 卷丹营养性状、生殖性状与主要生态因子的相关性分析
Table 5. Correlation analysis between quantitative traits belonging to vegetative and generative organs and main ecological factors of Lilium lancifolium
生态因子 茎粗 茎秆高度 鳞茎纵/横比 叶片数 下部叶宽/长比 中部叶宽/长比 上部叶宽/长比 苞片宽/长比 着花量 花瓣(内)宽/长比 花瓣(外)宽/长比 花丝长 花柱长 柱头宽 子房宽/长比 花梗长 海拔高度 0.084 0.443 -0.058 0.117 -0.500 -0.743** -0.343 -0.551* 0.684* -0.318 0.651* -0.795** -0.344 0.729* 0.265 0.411 坡向 0.430 0.165 0.200 0.382 0.180 -0.202 -0.434 -0.191 0.534 -0.302 0.196 0.109 -0.113 0.419 0.000 0.169 生境 0.659 0.733 ** -0.203 0.718** -0.464 -0.434 -0.707* -0.295 0.752** -0.681* 0.000 0.024 -0.209 0.361 0.087 0.334 说明:*和**分别表示在5%水平和1%水平上差异显著。 -
[1] 龙雅宜, 张金政, 张兰年.百合:球根花卉之王[M].北京:金盾出版社, 1999:1-6. [2] 张云, 原雅玲, 刘青林.百合的品种改良与生物技术研究进展[J].北京林业大学学报, 2001, 23(6):56-59. ZHANG Yun, YUAN Yaling, LIU Qinglin. Proceedings on cultivar improvement and biotechnology in Lilium[J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2001, 23(6):56-59. [3] RONG Liping, LEI Jiajun, WANG Chong. Collection and evaluation of the genus Lilium resources in Northeast China[J]. Genet Resour Crop Evol, 2010, 58(1):115-123. [4] 王润丰, 牛立新, 张延龙, 等.野生卷丹百合黄酮类化合物抗氧化能力的研究[J].西北农业学报, 2011, 20(11):152-155. WANG Runfeng, NIU Lixin, ZHANG Yanlong, et al. Antioxidant ability of flavonoids from wild Lilium lancifolium[J]. Acta Agric Boreal-Occident Sin, 2011, 20(11):152-155. [5] 中国科学院西北植物研究所.秦岭植物志[M].北京:科学出版社, 1976. [6] 陈心启, 许介眉, 梁松筠, 等.中国植物志:第14卷[M].北京:科学出版社, 1980. [7] 任志远, 李晶.陕南秦巴山区植被生态功能的价值测评[J].地理学报, 2003, 58(4):503-511. REN Zhiyuan, LI Jing. The valuation of ecological services from the vegetation ecosystems in the Qinling-Daba Mountains[J]. Acta Geogr Sin, 2003, 58(4):503-511. [8] 赵祥云, 陈新露, 王玉栋, 等.秦巴山区野生百合种质资源研究初报[J].西北农业大学学报, 1990(16):80-84. ZHAO Xiangyun, CHEN Xinlu, WANG Yudong, et al. Preliminary studies on wild resources of genus Lilium L. in Qin-Ba Mountain Areas[J]. Acta Univ Agric Boreal-Occident, 1990(16):80-84. [9] 向地英, 张延龙, 牛立新.秦巴山区及毗邻地区野生百合的形态多样性研究[J].武汉植物学研究, 2005, 23(4):385-388. XIANG Diying, ZHANG Yanlong, NIU Lixin. Study on morphological diversity of wild lily from Qinba Mountain and its adjacent area[J]. J Wuhan Bot Res, 2005, 23(4):385-388. [10] 魏宗贤, 宋满珍, 牛艳丽, 等.庐山地区野生藤本植物区系与生活型[J].浙江农林大学学报, 2013, 30(4):505-510. WEI Zongxian, SONG Manzhen, NIU Yanli, et al. Flora and life-form of wild vine resources in the Lushan Mountain[J]. J Zhejiang A & F Univ, 2013, 30(4):505-510. [11] 丁艳来, 赵团结, 盖钧镒.中国野生大豆的遗传多样性和生态特异性分析[J].生物多样性, 2008, 16(2):133-142. DING Yanlai, ZHAO Tuanjie, GAI Junyi. Genetic diversity and ecological differentiation of Chinese annual wild soybean (Glycine soja)[J]. Biodiversity Sci, 2008, 16(2):133-142. [12] PODGOMIK M, VUK I, VRHOVNIK I, et al. A survey and morphological evaluation of fig (Ficus carica L.) genetic resources from Slovenia[J]. Sci Hortic, 2010, 125(3):380-389. [13] 谢云, 李纪元, 潘文英.浙江红山茶野生种质资源现状及保护对策[J].浙江农林大学学报, 2011, 28(6):973-981. XIE Yun, LI Jiyuan, PAN Wenying. Status and conservation strategies for germplasm resources of wild Camellia chekiangoleosa[J]. J Zhejiang A & F Univ, 2011, 28(6):973-981. [14] 李文英, 顾万春.蒙古栎天然群体表型多样性研究[J].林业科学, 2005, 41(1):49-56. LI Wenying, GU Wanchun. Study on phenotypic diversity of natural population in Quercus mongolica[J]. Sci Silv Sin, 2005, 41(1):49-56. [15] 张彩霞, 明军, 刘春, 等.岷江百合天然群体的表型多样性[J].园艺学报, 2008, 35(8):1183-1188. ZHANG Caixia, MING Jun, LIU Chun, et al. Phenotypic variation of natural populations in Lilium relale Wilson[J]. Acta Hortic Sin, 2008, 35(8):1183-1188. [16] 刘冬云, 刘燕.山丹不同居群花器官的形态多样性研究[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2012, 13(6):997-1004. LIU Dongyun, LIU Yan. Floral diversity of the different populations of Lilium pumilum DC[J]. J Plant Gen Resour, 2012, 13(6):997-1004. [17] 宋杰, 李世峰, 刘丽娜, 等.云南含笑天然居群的表型多样性分析[J].西北植物学报, 2013, 33(2):0272-0279. SONG Jie, LI Shifeng, LIU Li'na, et al. Phenotypic diversity of natural populations of Michelia yunnanensis[J]. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 2013, 33(2):0272-0279. [18] 李伟, 林富荣, 郑勇奇, 等.皂荚南方天然群体种实表型多样性[J].植物生态学报, 2013, 37(1):61-69. LI Wei, LIN Furong, ZHENG Yongqi, et al. Phenotypic diversity of pods and seeds in natural populations of Gleditsia sinensis in southern China[J]. J Plant Ecol, 2013, 37(1):61-69. [19] 姬志峰, 高亚卉, 李乐, 等.山西霍山五角枫不同海拔种群的表型多样性研究[J].园艺学报, 2012, 39(11):2217-2228. JI Zhifeng, GAO Yahui, LI Le, et al. Phenotypic diversity of populations of Acer mono in Huoshan Mountain of Shanxi at different altitude[J]. Acta Hortic Sin, 2012, 39(11):2217-2228. [20] RANA M S, SAMANT S S. Population biology of Lilium polyphyllum D. Don ex Royle:a critically endangered medicinal plant in a protected area of Northwestern Himalaya[J]. J Nat Conserv, 2011, 19(3):137-142. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.06.009







 下载:
下载: