-
白颈长尾雉Syrmaticus ellioti为中国特有种,国家Ⅰ级重点保护动物和世界受胁物种,主要分布在长江以南,24°~31°N的华东和华南地区[1-2],为地栖性森林鸟类,飞翔与扩散能力较弱,躲避天敌能力较差,对周围环境的依赖性强,因此所面临的威胁日趋严重[3]。其中,生境的丧失与片断化已成为白颈长尾雉最主要胁迫因子[4]。许多学者曾对白颈长尾雉开展了多方面的研究,取得许多成果。其生境利用和选择已进行过一些报道,但这些研究多针对于某一地区进行研究[5-8]。或在受人为干扰影响较大的人工针叶林中进行[7-8],难以全面地反映该雉对生境选择的要求。迄今为止,尚缺乏专门对白颈长尾雉冬季生境选择的相关报道。冬季是一年中觅食最困难的时期,它们不仅不能获得足够的食物供应,随着天气逐渐变凉、变寒、食物极度缺乏和天气寒冷迫使动物表现出对不同生境的选择和利用模式,动物所表现出的各种行为都与其特定的生境条件相适应[9]。因此,生境选择在该时期显得尤为重要,直接影响其存活率[10-11]。适宜的生境是野生动物赖以生存的基本条件[12]。已有研究表明,白颈长尾雉以阔叶林为其最适生境,针阔混交林等为次适生境[5]。官山自然保护区是国内白颈长尾雉最主要集中分布地之一,植被群落结构完整,原生性强,人为干扰很低[13]。为此,我们于2009年11月-2010年2月在官山国家级自然保护区对白颈长尾雉冬季生境进行了研究,为阐述白颈长尾雉不同林型下对生境利用与选择的差异性,同时为了解白颈长尾雉在不同地点的生存状况提供科学依据,以期为白颈长尾雉的保护提供依据。
-
江西官山国家级自然保护区位于江西西北部的宜春市,28°30′~28°40′N,114°19′~114°45′E,地跨宜丰、铜鼓2县,地处九岭山脉西段,区内最低海拔为200 m,最高海拔1 480 m,总面积11 500.5 hm2。该保护区总体上属于中山山地面貌,属中亚热带温暖湿润气候区,四季分明,阳光充足,无霜期长,年均气温为16.2 ℃,年均降水量1 950~2 100 mm。研究区域植被以常绿阔叶林和落叶阔叶林为典型,区内还有发育良好针阔混交林、针叶林、竹林等植被类型,保护区森林覆盖率高达93.8%,地形地貌复杂[13]。
-
采取样线法对白颈长尾雉的活动位点进行调查,参照官山国家级保护区的地形图和林相图,根据保护区的地形、植被、水文及土地利用状况等特征,在研究区内选取不重复样线6条,样线宽为25 m。样线覆盖了白颈长尾雉的所有生境类型。每天调查时间为8:00-10:00,16:00-18:00,至少重复3次·样线-1。在样线上发现白颈长尾雉的实体或羽毛作为其活动点,利用全球卫星定位仪(GPS)定位,以它为中心,设置10 m × 10 m的大样方,在大样方内的中心及四角取5个1 m × 1 m小样方,对样方内的生境特征进行记录。大样方内记录的项目包括海拔、坡度、坡向、乔木盖度、乔木种类、乔木数量、灌木盖度、灌木种数、灌木数量、距水源距离、林型等11个特征参数,小样方内记录的项目为草本盖度、草本种类、草本数量,取其均值作为该因子在10 m × 10 m大样方中的特征。
各生境的因子变量的测定参照文献[14-15],生境变量的测量及划分如下:(1)海拔。用全球卫星定位仪(GPS)直接测定高度。可将海拔划分为≤600 m和>600 m等2个等级。(2)坡度。 DQL-5型罗盘仪记录看到白颈长尾雉实体或痕迹的所在地的坡面倾斜度。将坡度分为2个等级:缓坡≤30°,陡坡>30°。(3)坡向。用DQL-5型罗盘仪将其划分3种类型:阳坡S67.5°E~S22.5°W,半阴半阳坡N22.5°E~S67.5°E和S22.5°W~N67.5°W,阴坡N67.5°W~N22.5°E。(4)乔木盖度。以观察点为中心的10 m × 10 m范围内对乔木盖度测量。可划分为3个等级:>70%为高,40%~70%为中,≤40%为低。(5)乔木种类。在10 m × 10 m范围内记录乔木种类,划分为>3种和≤3 种2个等级。(6)乔木数量。在10 m × 10 m范围内记录乔木数量,划分为>11株和≤11株等2个等级。(7)灌木盖度。在10 m × 10 m范围内对乔木盖度测量,划分为3个等级:>70%为高,30%~70%为中,≤30%为低。(8)灌木种类。跟乔木种类测量和划分标准一样。(9)灌木数量。在10 m × 10 m范围内记录灌木数量,分为>20株和≤20株等2个等级。(10)草本盖度。在10 m × 10 m范围内分别在其中心和四角取1 m × 1 m的小样方。并取其平均值,划分3个等级:>60%为高,20%~60%为中,≤20%为低。(11)草本种类。测量方法和草本盖度相同,划分为>2种和≤2种等2个等级。(12)草本数量。测量方法同上,划分>10株和≤10株等2个等级。(13)水源距离。距白颈长尾雉实体或痕迹最近水源的垂直距离,划分为3个级:>150 m,50~150 m,≤50 m。(14)林型。根据优势乔木的种类,分为阔叶林、针阔混交林、针叶林等3个大类。
对白颈长尾雉冬季生境各种生态因子分析,根据各因子出现频次的百分比(Po)确定白颈长尾雉在冬季对不同生态因子的偏爱。Po=[(各因子出现的次数)/(记录到的活动痕迹总数)]×100%。Po值越大表明白颈长尾雉对这种生态因子越偏爱。
-
采用SPSS for Windows 12.0对有关变量进行统计。对冬季生境特征的有关变量,计算各种生态因子在所调查的样方出现的频次及所占百分比;以聚类分析法对样方进行分类,分析各样方组的重要生态因子差异情况。
-
对34个白颈长尾雉活动痕迹周围的生态因子统计发现(表 1),生境选择主要特征为:海拔≤600 m(91.2%),坡度在0~30°(94.1%)的缓坡范围内,水源距离≤150 m(79.4%),乔木种类>3种(76.5%),乔木数量>11株(70.6%),灌木数量>20株(67.6%),灌木种类>3种(88.2%),草本数量>10株(82.4%),草本种类>2种(76.5%)的生境中活动。在坡向上多选择阳坡(52.9%)或半阴半阳(41.9%),只有2处白颈长尾雉的活动痕迹在阴坡发现,对于林型多选择阔叶林(55.9%)或针阔混交林(35.3%)中活动。初步分析认为:白颈长尾雉在冬季偏爱低海拔、缓坡、乔木盖度和灌木盖度较高、乔木数量和灌木数量以及种类较多、水源距离较近、林型多选择阔叶林或针阔混交林、坡向位于阳坡或半阴半阴坡的生境作为冬季生境。不喜欢高海拔、陡坡、阴坡、乔木盖度和灌木盖度低、乔木数量和灌木数量及种类少、水源距离远、草本数量和种类少的生境。不喜欢在针叶林中活动。
表 1 白颈长尾雉冬季生境各生态因子分布频数
Table 1. Distribution frequency of ecological factors about winter habitat of Syrmαticus ellioti
项目 频数 百分比/% 海拔/m >600 3 8.8 ≤600 31 91.2 坡度/(°) >30 2 5.9 ≤30 32 94.1 坡向/(°) 阳坡 18 52.9 半阴半阳 14 41.2 阴坡 2 5.9 乔木盖度/% >70 9 26.5 40-70 19 55.9 ≤40 6 17.6 灌木数量/株 >20 23 67.6 ≤20 11 32.4 草本种类/种 >2 26 76.5 ≤2 8 23.5 水源距离/m >150 7 20.6 50-150 18 52.9 ≤50 9 26.5 乔木种类/种 >3 26 76.5 ≤3 8 23.5 乔木数量/株 >11 24 70.6 ≤11 10 29.4 灌木盖度/% >70 3 8.8 30-70 17 50 <30 14 41.2 灌木种类/种 >3 30 88.2 ≤3 4 11.8 草本盖度/% >60 3 8.8 20-60 16 47.1 ≤20 15 44.1 草本数量/株 >10 28 82.4 ≤10 6 17.6 林型 阔叶林 19 55.9 针阔混交林 12 35.3 针叶林 3 8.8 -
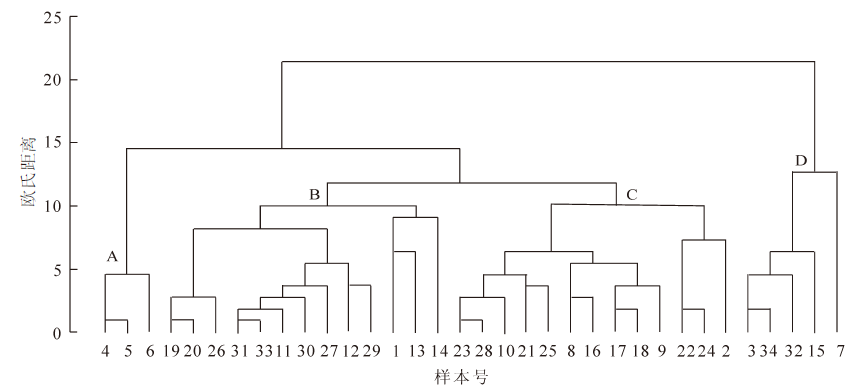
在分析各生态因子分布频数的基础上,用聚类分析法对白颈长尾雉冬季生境样本进行分组,按组分析各个生态因子在白颈长尾雉冬季生境选择中的重要性[16-18],得出白颈长尾雉对冬季生境选择的倾向。图 1显示了34个冬季生境样本对于14个生态因子的聚类结果,在欧氏距离10的水平上将34个样本分为A,B,C,D 等4个类群。
A类共有3个样本,样本号为4,5,6; B类共有13个样本,样本号为19,20,26,31,33,11,30,27,12,29,1,13,14;C类共有13个样本,样本号为23,28,10,21,25,8,16,17,18,9,22,24,2;D类共有5个,样本号为3,32,34,15,7。其中B类和C类共有样本26个,占总样本的76.5%,基本反应了白颈长尾雉对生境选择的类型,它们的共同特征是海拔≤600 m,坡度≤30°,乔木盖度40%~70%,灌木数量>20株,灌木种类>3种,草本数量>10株,水源距离≤150 m,草本盖度>20%。A,D 2类包含的样本数为8个,占总样本数的23.5%,这2组的共同特征是:海拔≤600 m,坡度≤30°,灌木种类>3种,草本数量>10株,水源距离>150 m,草本盖度≤20%。由此看出草本盖度≤20%和水源距离>150 m与B和C 2类明显不同,由此可知白颈长尾雉对生境的选择中避免草本盖度≤20%,水源距离>150 m的生境。在海拔、坡度、灌木种数、草本数量等因子方面与B和C类的共同特征一致,可以作为B和C类的补充。除了B组外,其他各组中,灌木盖度都显示了较高的频次。
聚类结果分析表明:白颈长尾雉冬季生境选择的重要因子是坡度、海拔、乔木盖度、灌木数量、灌木种类、草本数量、水源距离、草本盖度等8个生态因子。与各生态因子分布频数的分析结果基本相似。而在灌木盖度因子上有差异,分组频次分析没有显示为各组共有高频次特征。
-
对所有样本14个生态因子的主成分分析见表 2。由于前5个主成分的特征值均大于1,其累积贡献率达70.9%。表明前5个主成分基本包含了这14个生态因子所具有的信息。因此取前5个主成分进行分析。
由表 2可知:第1主成分的特征值为2.883,贡献率达到22.175%。其中相关系数绝对值较大的为草本种数、草本数量和海拔,其特征值分别为0.647,0.735和0.681,反映了白颈长尾雉对生境食物有很高的要求。
表 2 各生态因子主成分分析结果
Table 2. Principal components of 14 ecological factors for Syrmaticus ellioti selection
变量 主成分 1 2 3 4 5 乔木盖度 0.068 0.252 0.79 0.120 0.046 乔木种类 0.142 0.244 0.03 0.032 0.209 乔木数量 0.541 -0.197 -0.378 0.311 -0.245 灌木盖度 0.012 0.432 0.79 0.062 -0.002 灌木种数 0.519 0.52 0.178 0.808 0.336 灌木数量 0.106 0.403 0.322 0.132 -0.078 草本盖度 0.255 -0.659 0.177 0.509 -0.069 草本种数 0.647 0.049 0.448 0.091 0.156 草本数量 0.735 0.118 -0.026 0.383 -0.116 水源距离 0.093 0.78 -0.153 0.153 0.103 林型 0.176 0.020 -0.211 0.713 -0.136 海拔 0.681 0.159 -0.315 -0.461 0.149 坡度 0.091 -0.022 -0.104 0.520 -0.709 坡向 -0.005 0.058 -0.035 -0.018 0.945 特征值 2.883 2.299 1.78 1.222 1.040 贡献率/% 22.175 17.682 13.692 9.401 7.998 累积贡献率/% 22.175 39.857 53.549 62.950 70.948 在第2个主成分中载荷系数绝对值较大的是草本盖度和水源距离,其特征值分别为-0.659和0.780;第3个主成分载荷系数绝对值较大的是乔木盖度和灌木盖度,其特征值分别都为0.790;第4个主成分载荷系数绝对值较大的是灌木种数和林型,其特征值分别为0.808和0.713;第5主成分载荷系数绝对值较大的是坡度和坡向,其特征值分别为-0.709和0.945。该结果与各生态因子分布频次分析的结果基本一致,在支持聚类分组分析结果的基础上,进一步明确了灌木盖度对生境选择的作用。
-
决定动物的生境选择因素是复杂的,包括要考虑生境本身特性,动物本身特性,食物有效性,捕食和竞争等因素[19]。白颈长尾雉是典型的地栖性森林鸟类,主食木本植物果实(种子)、草本植物的茎叶、苔藓和蕨类等植物性食物,所以与食物和隐蔽程度有关的植被和地形因子成了影响白颈长尾雉生境选择的主要因子。
-
地形因子主要包括坡度、海拔和水源距离等。白颈长尾雉选择的坡度较缓(≤30°),由于较大的坡度不利于白颈长尾雉的活动所致。在坡向方面,大多偏向阳坡,避免阴坡。与其他雉类冬季生境选择的研究报道一致[20-22],在于研究区域的南向和北向之间所存在的差异,朝南的山坡相对比较温暖,并且地面也相对干燥,这对于白颈长尾雉抵御较为寒冷的冬季,以及在落叶层里寻找落果和小型节肢动物等食物比较有利。由表 1可知:冬季大约91.2%的白颈长尾雉在低于600 m的海拔活动,其平均海拔高度为503 m,与徐言朋等[23]对江西省官山白颈长尾雉活动区海拔高度季节变化中冬季海拔平均高度研究相似。这是因为气温在低海拔比在高海拔要高,利于白颈长尾雉抵御冬季寒冷,而且海拔较低的地方食物丰富度也高。但在浙江省开化县水坞山区和浙江省泰顺县乌岩岭的白颈长尾雉海拔高度的研究结果不一,这与所栖息的地区环境差异有关,水坞山区海拔高度较低(200~600 m)[5-6],而浙江省泰顺县乌岩岭的海拔区域虽然较高,但由于低海拔区域干扰较大,高海拔区域干扰相对较小,所以,白颈长尾雉主要栖居在1 000~1 200 m的区域[24]。
同时白颈长尾雉越冬期生境选择中对水源的距离较近(≤150 m)。水源是野生动物生境选择的三大要素之一,直接影响着野生动物对生境的选择[25]。本研究显示:水源距离在第2 成分中载荷量相对较大,在白颈长尾雉冬季生境选择中有着重要的作用。我们在野外的调查发现,白颈长尾雉多在溪流附近的生境中活动,可能与官山自然保护区冬季干旱少雨有关[26],水源距离太远又会增加人为影响的程度。
-
植被主要包括乔木盖度、灌木盖度、草本盖度、草本种类、草本数量等生态因子。草本种类、草本数量为白颈长尾雉提供食物来源。有报道认为:鸡形目鸟类一般喜欢选择食物较为丰富的区域活动[27-29],食物是影响鸟类生境利用的重要因素[30]。主成分表明:草本种类和数量在第1主成分中载荷量相对较大。因此,在冬季白颈长尾雉生境选择中,食物因素是其冬季生境选择最主要的因素,这与石鸡Alectoris chukar研究结果一致[22],隐蔽条件则是影响白颈长尾雉夜栖息地选择的最主要因子[7]。白颈长尾雉冬季生境选择中,灌木层因子的作用大于草本层因子[6];这可能是研究地点的林型几乎为人工杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata林,而研究显示针叶树种不能为白颈长尾雉提供食物,只是在提供隐蔽条件方面起一定作用。因此,作为白颈长尾雉生境的针叶林其植被灌木层发育良好,并且有较多种类的阔叶灌木树种构成灌木层[31]。本研究发现:在冬季,过高盖度的生境对白颈长尾雉是不利的。相反,太低的盖度对隐蔽程度要求较高的白颈长尾雉也是不利的。随着盖度逐渐升高,林下灌草层变得稀疏,且盖度越高,林下小生境的温度就越低[32],白颈长尾雉便会逐渐退出这个生境。因而在冬季,白颈长尾雉多选择乔木盖度适中(40%~70%),灌木盖度适中(30%~70%),草本盖度中等(20%~60%),较多草本种类(>2种)和数量(>10种)的生境。因此,有一定乔木盖度、灌木盖度、草本盖度、草本数量和种类的生境能给白颈长尾雉提供良好的食物来源,并且可以增加其栖息生境的隐蔽度,还可以防止天敌的侵害,有利于行动和躲避天敌。在林型上,主要选择在阔叶林和针阔混交林,偏向于阔叶林,避免针叶林中的活动,一是白颈长尾雉为地栖性鸟类,阔叶林、针阔混交林下生境均比较开阔,适宜其活动。二是阔叶林和针阔混交林隐蔽性高,在冬季食物资源相对短缺,白颈长尾雉要增加活动量来寻求获取食物,丰富的食物来源提供了白颈长尾雉日常所需。这就要求白颈长尾雉对其生境的隐蔽性要高。研究显示:白颈长尾雉冬季主要在食物更为丰富的阔叶林中生活[24]。三是可能与官山国家级自然保护区植被类型有关,植被以常绿阔叶林和落叶阔叶林为典型,针叶林在官山国家级自然保护区主要分布在海拔800~1 100 m。而且面积比例小[13]。白颈长尾雉能对不同的环境因子做出选择,表明它能够识别生境中微环境的变化。
-
为了维持江西省官山国家级自然保护区白颈长尾雉种群的长期稳定和发展,在保护工作中,应针对生境关键因子进行相应管理,加强对生境的保护与科学管理,制定切实可行的保护计划。①首先,应采取措施保护好白颈长尾雉现存的适宜生境,应注意控制好保护区内阔叶林和针阔混交林的生长。②水源是白颈长尾雉冬季生境选择的重要因子之一。官山国家级自然保护区冬季干旱少雨[26],应加强对水源的管理,重点加强中低海拔及阔叶林和针阔混交林周边水源管理。③减少人为干扰。调查发现,冬季农户进山采集野生食用菌和冬笋活动,冬季白颈长尾雉主要在600 m以下活动,农户采集行为干扰了该雉的正常觅食。因此,应加大野生动物保护宣传,增强当地人的保护意识。④应对白颈长尾雉的生境选择特征进行长期研究,以综合分析白颈长尾雉生境选择年际变化,为白颈长尾雉保护提供科学的依据。
Winter habitat selection for elliot's pheasant in Guanshan National Nature Reserve,Jiangxi Province
-
摘要: 2009年11月-2010年2月,采用野外直接观察法和样方法对江西省官山国家级自然保护区白颈长尾雉Syrmaticus ellioti冬季生境进行调查,运用聚类分析和主成分分析法,对白颈长尾雉冬季生境选择因子进行了分析。结果表明:白颈长尾雉越冬期多选择低海拔(≤600 m),缓坡(坡度≤30°),乔木盖度适中(40%~70%),灌木数量偏高(>20株),灌木种类较多(>3种),草本盖度中等(20%~60%),草本种类(>2种)和草本数量较多(>10株),水源距离近(≤150 m)的生境,偏爱阳坡和阔叶林,较少选择草本盖度≤20%和水源距离较远(>150 m)的生境,避开陡坡(>30°)和阴坡的活动。影响白颈长尾雉冬季生境选择的主要因子为草本种数、草本数量和海拔高度;次要因子为草本盖度、水源距离、乔木盖度、灌木盖度、灌木种数、林型、坡度和坡向。
-
关键词:
- 动物学 /
- 白颈长尾雉 /
- 官山国家级自然保护区 /
- 冬季 /
- 生境
Abstract: Syrmaticus ellioti (elliot's pheasant),is endemic to China and regarded as "Vulnerable" in the 2004 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Its population size believed to be declining because of ongoing habitat loss and hunting. From November 2009 to February 2010,direct observation and plot sampling in the field were utilized to survey the winter habitat selection of elliot's pheasant in Guanshan National Nature Reserve of Jiangxi Province. We collected 14 ecological factors from 34 sites used of elliot's pheasants in 6 transects throughout the study area. Cluster analysis and principal component analysis were employed to analyze the data. Results showed that S. ellioti preferred environmental factors of low elevation(≤600 m),shallow slope(≤30°),medium tree coverage(40%-70%),high shrub quantity (>20 trees),greater shrub diversity (>3 species),medium herbage coverage (20%-60%),greater herbage diversity (>3 species),greater herbage quantity (> 10 herbs),and close proximity to water (≤150 m). Sunny slopes and broadleaf forests were their favorite. Habitats with herbage cover of ≤20% and far from water(>150 m) were not suitable. S. ellioti avoided were steep(>30°) or shady slopes. A rotated matrix of the eigenvectors for S. ellioti habitat selection in winter revealed all 14 ecological factors grouped into three main factors and eight secondary factors. The main factors included herbage species,herbage quantity,and elevation;the secondary factors were herbage coverage, distance to water,tree coverage,shrub coverage,shrub species diversity,vegetation type, slope degree,and slope orientation.-
Key words:
- zoology /
- Syrmaticus ellioti /
- Guanshan National Nature Reserve /
- winter /
- habitat
-
表 1 白颈长尾雉冬季生境各生态因子分布频数
Table 1. Distribution frequency of ecological factors about winter habitat of Syrmαticus ellioti
项目 频数 百分比/% 海拔/m >600 3 8.8 ≤600 31 91.2 坡度/(°) >30 2 5.9 ≤30 32 94.1 坡向/(°) 阳坡 18 52.9 半阴半阳 14 41.2 阴坡 2 5.9 乔木盖度/% >70 9 26.5 40-70 19 55.9 ≤40 6 17.6 灌木数量/株 >20 23 67.6 ≤20 11 32.4 草本种类/种 >2 26 76.5 ≤2 8 23.5 水源距离/m >150 7 20.6 50-150 18 52.9 ≤50 9 26.5 乔木种类/种 >3 26 76.5 ≤3 8 23.5 乔木数量/株 >11 24 70.6 ≤11 10 29.4 灌木盖度/% >70 3 8.8 30-70 17 50 <30 14 41.2 灌木种类/种 >3 30 88.2 ≤3 4 11.8 草本盖度/% >60 3 8.8 20-60 16 47.1 ≤20 15 44.1 草本数量/株 >10 28 82.4 ≤10 6 17.6 林型 阔叶林 19 55.9 针阔混交林 12 35.3 针叶林 3 8.8 表 2 各生态因子主成分分析结果
Table 2. Principal components of 14 ecological factors for Syrmaticus ellioti selection
变量 主成分 1 2 3 4 5 乔木盖度 0.068 0.252 0.79 0.120 0.046 乔木种类 0.142 0.244 0.03 0.032 0.209 乔木数量 0.541 -0.197 -0.378 0.311 -0.245 灌木盖度 0.012 0.432 0.79 0.062 -0.002 灌木种数 0.519 0.52 0.178 0.808 0.336 灌木数量 0.106 0.403 0.322 0.132 -0.078 草本盖度 0.255 -0.659 0.177 0.509 -0.069 草本种数 0.647 0.049 0.448 0.091 0.156 草本数量 0.735 0.118 -0.026 0.383 -0.116 水源距离 0.093 0.78 -0.153 0.153 0.103 林型 0.176 0.020 -0.211 0.713 -0.136 海拔 0.681 0.159 -0.315 -0.461 0.149 坡度 0.091 -0.022 -0.104 0.520 -0.709 坡向 -0.005 0.058 -0.035 -0.018 0.945 特征值 2.883 2.299 1.78 1.222 1.040 贡献率/% 22.175 17.682 13.692 9.401 7.998 累积贡献率/% 22.175 39.857 53.549 62.950 70.948 -
[1] BAILLIE J E M,HILTON-TAYLOR C,STUART S N. 2004 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species TM:A Globe Species Assessment[M]. Switzerland:IUCN,2004. [2] 丁平,诸葛阳. 白颈长尾雉[J]. 动物学杂志,1989,24(2):39-42. DING Ping,ZHUGE Yang. Elliot's pheasant[J]. Chin J Zool,1989,24(2):39-42. [3] JOHNSGARD P A. The Pheasant of the World:Biology and Natural History[M]. Washington D C:Smithsonian Institution Press,1999. [4] 丁平,姜仕仁,诸葛阳. 浙江西部白颈长尾雉生境片断化研究[J]. 动物学研究,2000,21(1):65-69. DING Ping,JIANG Shiren,ZHUGE Yang. The study on fragmentation of habitat used by Elliot's pheasant in western Zhejiang[J]. Zool Res,2000,21(1):65-69. [5] 杨月伟,丁平,姜仕仁,等. 针阔混交林内白颈长尾雉生境利用的影响因子研究[J]. 动物学报,1999,45(3):279-286. YANG Yuewei,DING Ping, JIANG Shiren,et al. Factors affecting habitat used by Elliot's pheasant in mixed coniferous and broadleaf forest[J]. Acta Zool Sin,1999,45(3):279-286. [6] 丁平,李智,姜仕仁,等. 白颈长尾雉生境小区利用度影响因子研究[J]. 浙江大学学报:理学版,2002,29(1):103-108. DING Ping,LI Zhi,JIANG Shiren,et al. Studies on the factors affecting patch use degree by Elliot's pheasant[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Nat Sci Ed,2002,29(1):103-108. [7] 丁平,杨月伟,李智,等. 白颈长尾雉的夜宿地选择研究[J]. 浙江大学学报:理学版,2002,29(5):564-568. DING Ping,YANG Yuewei,LI Zhi,et al. Studies on the selection of roosting sites of Elliot's pheasant[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Nat Sci Ed,2002,29(5):564-568. [8] 彭岩波,丁平. 白颈长尾雉春季扩散活动的影响因子[J]. 动物学研究,2005,26(4):373-378. PENG Yanbo,DING Ping. Factors affecting movement of spring dispersal of Elliot's pheasants[J]. Zool Res, 2005,26(4):373-378. [9] 谢东明,路纪琪,吕九全. 太行山猕猴的冬季生境选择[J]. 兽类学报,2009,29(3):252-258. XIE Dongming,LU Jiqi,LÜ Jiuquan. Winter habitat selection of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis) in Taihang Mountains,Jiyuan,China[J]. Acta Theri Sin,2009,29(3):252-258. [10] PERKINS A L,CLARK W R,RILEY T Z,et al. Effects of landscape and weather on winter survival of ring-necked pheasant hens[J]. J Wild life Manage,1997,61:634-644. [11] YOUNG L,ZHENG Guangmei,ZHANG Zhengwang. Winter movements and habitat use by Cabot's tragopans Tragopan caboti in south-eastern China[J]. Ibis,2008,133:121-126. [12] ROSENZWEIG M L. Some theoretical aspects of habitat selection[G]//CODY M L. Habitat Selection in Birds. New York:Academic Press,1985. [13] 刘信中,吴和平. 江西官山自然保护区科学考察与研究[M]. 北京:中国林业出版社,2005. [14] 吴逸群,刘迺发. 甘肃南部蓝马鸡的巢址选择[J]. 生态学杂志,2010,29(7):1393-1397. WU Yuqun,LIU Naifa. Nest site selection of blue-eared pheasant (Crossoptilon auritum) in south Gansu,China[J]. Chin J Ecol,2010,29(7):1393-1397. [15] 周宏力,王磊,李春玉. 红花尔基自然保护区黑琴鸡越冬末期生境选择[J]. 生态学杂志, 2011,30(4):730-733. ZHOU Hongli,WANG Lei,LI Chunyu. Habitat selection of Lyrurus tetrix at its late wintering stage in Honghuaerji Nature Reserve,Inner Mongolia[J]. Chin J Zool,2011,30(4):730-733. [16] 鲁庆彬,胡锦矗. 岷山黑熊生境选择的初步分析[J]. 兽类学报,2003,23(2):98-103. LU Qingbin,HU Jinchu. Preliminary analysis on the habitat selection of black bears in the Minshan Mountains[J]. Acta Theri Sin,2003,23(2):98-103. [17] 李春喜,王志和,王文林. 生物统计学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2000. [18] 张尧庭,方开泰. 多元统计分析引论[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1982. [19] 颜忠诚,陈永林. 动物的生境选择[J]. 生态学杂志,1998,17(2):43-49. YAN Zhongcheng,CHEN Yonglin. Habitat selection of animal[J]. Chin J Ecol,1998,17(2):43-49. [20] 张国钢,郑光美,张正旺,等. 山西芦芽山褐马鸡越冬生境选择的多尺度研究[J]. 生态学报,2005,25(5):952-957. ZHANG Guogang,ZHENG Guangmei,ZHANG Zhengwang,et al. Scale-dependent wintering habitat selection by brown-eared pheasant in Luyashan Nature Reserve of Shanxi,China[J]. Acta Ecol Sin,2005,25(5):952-957. [21] 徐基良,张晓辉,张正旺,等. 白冠长尾雉越冬期生境选择的多尺度分析[J]. 生态学报, 2006,26(7):2061-2067. XU Jiliang,ZHANG Xiaohui, ZHANG Zhengwang,et al. Multi-scale analysis on wintering habital selection of Reeves's pheasant (Syrmaticus reevesii) in Dongzhai National Nature Reserve,Henan Province,China[J]. Acta Ecol Sin,2006,26(7):2061-2067. [22] 周晓禹,王晓明,姜振华. 贺兰山石鸡越冬期生境的选择[J]. 东北林业大学学报,2008, 36(4):32-39. ZHOU Xiaoyu,WANG Xiaoming,JIANG Zhenhua. Wintering habitat selection of a lectoris chukar potanini in Helan mountains[J]. J Northeast For Univ,2008,36(4):32-39. [23] 徐言朋,郑家文,丁平,等. 官山白颈长尾雉活动区域海拔高度的季节变化及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性,2007,15(4):337-342. XU Yanpeng,ZHENG Jiawen,DING Ping,et al. Seasonal change in ranging of Elliot's pheasant and its determining factors in Guanshan National Nature Reserve[J]. Biodiv Sci,2007,15(4):337-342. [24] 石建斌,郑光美. 白颈长尾雉生境的季节变化[J]. 动物学研究,1997,18(3):275-283. SHI Jianbin,ZHENG Guangmei. The seasonal changes of habitats of Elliot's pheasant[J]. Zool Res,1997,18(3):275-283. [25] 冯江,高玮,盛连喜. 动物生态学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2005. [26] 陈俊豪,黄晓凤,鲁长虎,等. 白颈长尾雉与白鹇秋冬季空间生态位比较[J]. 生态学杂志,2009,28(12):2546-2552. CHEN Junhao,HUANG Xiaofeng,LU Changhu,et al. Spatial niches of Syrmaticus ellioti and Lophura nycthemera in antumn and winter[J]. Chin J Ecol,2009,28(12):2546-2552. [27] 李宏群,廉振民,陈存根. 陕西黄龙山自然保护区褐马鸡春季栖息地的选择[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2008,36(4):228-234. LI Hongqun, LIAN Zhenmin,CHEN Cungen. Foraging-sites and day-roosting selection of brown eared pheasant (Crossoptilon mantchuricum) in spring in Huanglong Mountains, Shaanxi Province[J]. J Northwest A & F Univ Nat Sci Ed,2008,36(4):228-234. [28] 刘鹏,顾署生,黄晓凤,等. 官山自然保护区勺鸡冬季栖息地选择[J]. 江西农业大学学报,2011,33(6):1257-1262. LIU Peng,GU Shusheng,HUANG Xiaofeng,et al. Habitat selection of sympatric four pheasants in Guanshan National Nature Reserve[J]. Acta Agric Univ Jiangxi,2011,33(6):1257-1262. [29] 刘鹏,黄晓凤,顾署生,等. 江西官山自然保护区四种雉类的生境选择差异[J]. 动物学研究, 2012,33(2):170-176. LIU Peng,HUANG Xiaofeng,GU Shusheng,et al. Habitat selection of sympatric four pheasants in Guanshan National Nature Reserve[J]. Zool Res,2012,33(2):170-176. [30] 丁平,杨月伟,李智,等. 白颈长尾雉生境的植被特征研究[J]. 浙江大学学报:理学版, 2001,28(5):557-562. DING Ping,YANG Yuewei,LI Zhi,et al. Vegetation characteristics of habitats used by Elliot's pheasant[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Nat Sci Ed,2001,28(5):557-562. [31] ROOT R B. The niche exploitation pattern of the blue-gray gnatcatcher[J]. Ecol Monogr,1967,37(4):317-350. [32] ALTHOFF D P,STORM G L,DEWALLE D R. Daytime habitat selection by cottontails in central Pennsylvania[J]. J Wildlife Manage,1997,61(2):450-451. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.01.014







 下载:
下载: