-
以热塑性树脂,如高密度聚乙烯(high density polyethylene,HDPE),聚丙烯(polypropylene,PP)等作为木材胶黏剂,利用热压-冷压串联的平压工艺制备木质原料/热塑性树脂复合材料,不仅能从根源上解决游离甲醛释放的问题,而且能为热塑性树脂的回收利用提供一条新的路径[1-3]。目前,热塑性树脂已与异氰酸酯基胶黏剂、大豆基胶黏剂等共同成为环保型木材胶黏剂的重要发展方向[4-6]。热塑性树脂在一定温度下熔融后,能与多孔性的木材单板形成胶钉结合,赋予复合材料一定的强度[7],但表面自由能低、结晶度高、与木质原料相容性差,是HDPE和PP等热塑性树脂作为胶黏剂的最大缺陷,导致复合材料的耐沸水和耐高温破坏能力较弱,应用范围受限[8-9]。通过减少木质原料表面的羟基数量,或促进木质原料与热塑性树脂发生化学交联,是提高界面相容性的根本方法[10-14]。笔者前期研究发现[15]:以乙烯基三甲氧基硅烷(A-171)和引发剂过氧化二异丙苯(DCP)为改性剂制备的硅烷化杨木单板,能够与HDPE薄膜形成优良的胶接,复合材料的胶合强度、耐水性能和耐高温能力显著增强。与传统的脲醛树脂(UF)等热固性胶黏剂不同,热塑性树脂胶黏剂具有受热软化、冷却固化的特性,其对木材的胶合是其在木材表面熔融软化、流展、渗透和冷却固化的过程。因此,对于特定的热塑性树脂胶黏剂,必须确定适当的热压温度,使胶黏剂既能在木材表面充分的流展、渗透,且不会出现因黏度过低而发生过度渗透导致胶层过薄等现象,同时能够促进硅烷化木材单板与HDPE薄膜达到充分胶合状态。本研究分析了不同的热压温度对硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料性能的影响。
HTML
-
单板:107杨Populus× euramericana,幅面为300 mm × 300 mm × 1.60 mm,含水率为6%~8%;高密度聚乙烯(HDPE)薄膜,厚度为0.06 mm,密度为0.92 g·cm-3;硅烷偶联剂,乙烯基三甲氧基硅烷(A-171),购买于广东中杰化工有限公司;过氧化二异丙苯(DCP),纯度99%,百灵威科技。
-
配制质量分数为95.0%,pH 3.00~3.50的乙醇溶液,一边搅拌一边加入硅烷A-171(杨木单板质量的2.0%)和引发剂DCP(HDPE薄膜质量的0.1%),使溶液质量分数达到4.0%,水解1 h。用配好的溶液对杨木单板进行喷淋处理,室温晾置24 h后转入烘箱中,在120 ℃的条件下处理2 h。
在不同热压温度(140,150,160,170 ℃)下,将上述硅烷化杨木单板与HDPE薄膜进行复合,制备5层结构复合材料,每2层单板之间使用1层HDPE薄膜。其中:热压时间为1 min·mm-1,热压压力1.00 MPa,冷压压力1.00 MPa,冷压时间5 min。其中,试验条件重复3次·组-1。
-
按照GB/T 17657-2013《人造板及饰面人造板理化性能试验方法》测定硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料的胶合强度(Ⅰ类),静曲强度(MOR),弹性模量(MOE),吸水率(WA),吸水厚度膨胀率(TS)。
-
利用DMA(Q2980,TA)的3点弯曲模式测定硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜在25~200 ℃范围内的储能模量(E′)和损耗角正切(tanδ)变化。其中,升温速率为3 ℃·min-1,振幅为0.03 mm,频率为1 HZ,试样尺寸为60 mm(长)×12 mm(宽)×3 mm(厚)。
-
对硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料的胶合端面进行喷金处理,利用扫描电子显微镜SEM(Hitachi S-4800)观察硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜的胶接界面结构。
1.1. 材料
1.2. 硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料的制备
1.3. 性能测试
1.3.1. 物理力学性能
1.3.2. 动态热力学性能(DMA)
1.3.3. 胶合界面分析(SEM)
-
热压温度对硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料胶合强度和抗弯性能的影响分别如图 1A 图 1B所示。由图 1A可知:复合材料的胶合强度在一定范围内随着热压温度的升高而增加,当热压温度从140 ℃增加至160 ℃时,胶合强度从1.27 MPa逐渐增加至1.89 MPa。这是由于热压温度直接影响HDPE大分子的黏度变化,140 ℃时HDPE的黏度相对较高,不利于其在硅烷化杨木单板表面充分流展,因此,进入单板多孔性结构中HDPE含量少,形成的胶钉数量减少。同时,较低的温度下HDPE大分子的链段运动受到限制,抑制了引发剂DCP对HDPE的诱导反应,削弱了HDPE薄膜与硅烷化杨木单板的化学反应。当热压温度升高至160 ℃时,HDPE的黏度降低,流动性能改善,一方面使得机械结合作用力增强,另一方面HDPE自由基与硅烷改性单板之间的化学反应得到增强。但如果继续增加热压温度,HDPE的黏度会进一步降低,更多的HDPE大分子进入单板内部,使得保留在胶层上的HDPE大分子及其自由基数量减少,胶合界面处的化学作用力减弱,胶合强度开始降低。
热压温度对抗弯性能的影响与胶合强度类似:当热压温度从140 ℃增加至160 ℃时,MOR和MOE值分别从63.90 MPa和5 970.00 MPa增加到72.20 MPa和6 710.00 MPa。当热压温度增加至170 ℃时,胶合板的MOR和MOE值分别下降至67.40 MPa和6 621.00 MPa(图 1B)。抗弯性能的变化趋势仍然与HDPE大分子在单板中的浸透程度及其与杨木单板之间化学作用力的强弱相关。
-
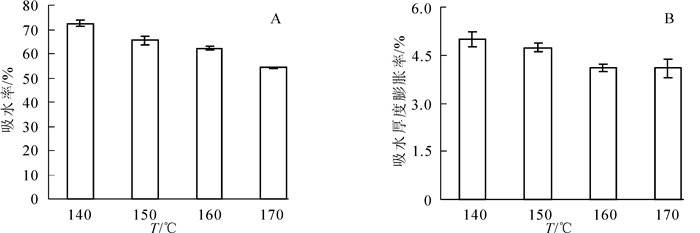
HDPE薄膜是一种憎水性的材料,本身不吸收水分,具有比UF树脂胶黏剂更加优异的耐水性能,但是木材单板/HDPE薄膜的界面相容性差,导致复合材料的整体耐水性能较低[3]。因此,本研究还测定了热压温度对硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料吸水率(WA)和吸水厚度膨胀率(TS)的影响(图 2)。
由图 2A和图 2B可知:硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料的耐水性能随着热压温度的升高逐渐增强。当热压温度为170 ℃时,复合材料的吸水性最低,浸泡24 h后WA和TS值分别为54.22%和4.09%。这是因为:热压温度越高,一方面HDPE大分子自由基与硅烷化杨木单板在胶合界面处的化学反应活性越强,形成紧密的胶接界面结构,可以有效地阻碍水分的进入;另一方面更多熔融的HDPE大分子进入杨木单板内部,憎水性的HDPE包覆亲水性的木材组分,可以降低水分子进入的速度。同时,较高的热压温度有利于杨木单板表面吸水性较强的羟基数量的进一步减少,类似于一个短时的高温处理过程,同样有助于复合材料耐水性能的改善。
-
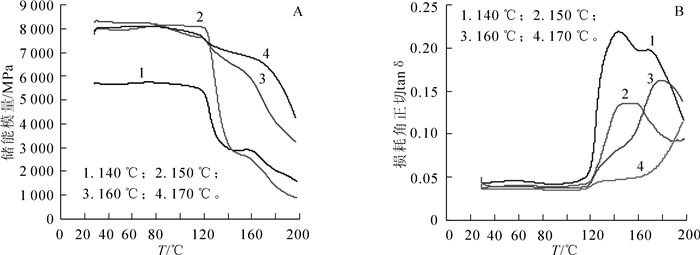
图 3A和图 3B分别是3点弯曲模式下测定的热压温度对硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜储能模量(E′)和损耗角正切(tanδ)的影响。随着热压温度的升高,复合材料的耐高温破坏能力增强,即在相同的环境温度下储能模量(E′)保留率增大(图 3A)。当热压温度从140 ℃增加至170 ℃时,复合材料在130 ℃时的E′值由3 524.00 MPa增加到7 240.00 MPa,E′值的保留率由62.31%提高到92.01%。当热压温度为170 ℃时,储能模量在环境温度为200 ℃的条件下保留率仍然有53.87%,约为热压温度为140 ℃时保留率的2倍。
热压温度的提高同样有利于增加复合材料胶接界面层的刚性,主要体现在tanδmax的减小(图 3B)。当热压温度由140 ℃增加到170 ℃时,tanδmax的值由0.22降至0.11,到达tanδmax的温度点从144 ℃延后至200 ℃,此时,对应的储能模量值分别为2 897.00 MPa和4 239.00 MPa。这说明适当的热压温度有助于HDPE大分子活性自由基与硅烷化杨木单板达到充分胶合,显著提高胶接界面层的耐高温破坏能力。
-
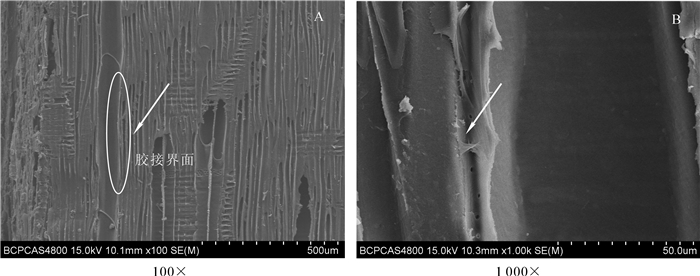
热压温度对硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料的胶接界面结构影响较大(图 4和图 5)。在较低的热压温度下(140~150 ℃),HDPE大分子链段运动不活跃,与硅烷化杨木单板间的机械结合力和化学作用力较弱。因此,胶接界面处会存在较大的间隙(图 4B)。胶合界面处存在的间隙直接影响了硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料物理力学性能和热稳定性,这与前面的分析是一致的。当热压温度提高到160 ℃时,在硅烷偶联剂A-171和引发剂DCP的共同作用下,硅烷化木材单板与HDPE大分子自由基发生了有效的化学反应,形成了紧密的胶接界面结构,在两相结合处几乎观察不到间隙的存在(图 5B),复合材料的各项性能都显著改善。
2.1. 热压温度对复合材料力学性能的影响
2.2. 热压温度对复合材料耐水性能的影响
2.3. 热压温度对复合材料热稳定性的影响
2.4. 硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜的胶合界面形貌
-
适宜的热压温度是硅烷化木材单板与HDPE大分子自由基发生有效化学反应的必要条件,能够促进良好胶接界面结构的形成,进而改善复合材料的各项物理力学性能。热压温度为160 ℃时复合材料的综合性能最佳。
当热压温度从140 ℃增加到160 ℃时,硅烷化杨木单板/HDPE薄膜复合材料的胶合强度、抗弯性能、耐水性能和耐高温破坏能力都显著增强。但继续增加热压温度,会降低胶接界面层上的HDPE大分子及其自由基数量减少,减弱胶合界面处的化学作用力,导致胶合强度和抗弯性能降低。
利用荧光显微镜等手段,进一步分析不同热压温度下HDPE大分子在硅烷化木材单板中的渗透路径和渗透性能,阐明热压温度对复合材料性能的影响机理,将是日后研究的重点。















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: