Latest Articles
Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes/issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250268
Abstract:
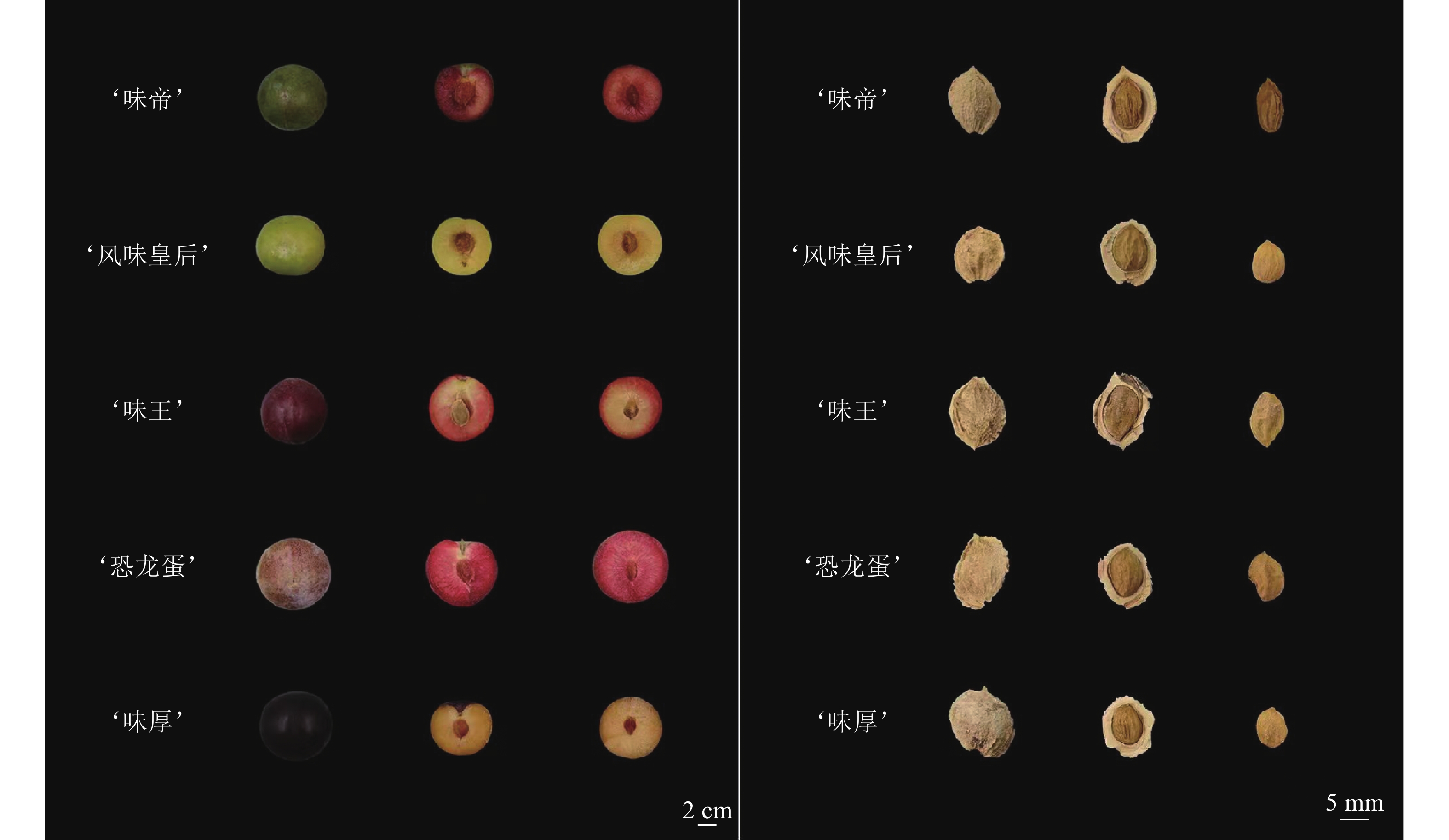
Objective The research aimed to explore the differences of fruit morphological characteristics, fruit appearance, fruit texture and fruit internal quality of five Prunus simonii varieties in Aksu Prefecture, and put forward the excellent Prunus simonii cultivars suitable for Aksu Area. Method In 2024, a field experiment was conducted in a P. simonii orchard in Jiamu Town, Wansu County, Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang. Five 6-year-old cultivars were used to determine and analyze the differences in fruit quality, including fruit appearance, fruit texture, soluble sugar, soluble solids, titratable acid, vitamin C, and sugar-acid components. Result In terms of appearance, the average single fruit weight of ‘Konglongdan’ and ‘Weihou’ is 100−120 g, and the other three cultivars are 50−80 g; the L* value and a* value of ‘Weiwang’ were 68.23 and 16.68, respectively, and the fruit color was bright. In terms of nutrition, ‘Weiwang’ had the highest vitamin C content of 0.967 8 mg·g−1 ; the soluble sugar content of ‘Konglongdan’ was the highest, which was 15.37%, and the titratable acid content of ‘Weidi’ was the highest, which was 1.65%. The soluble solids content of ‘Weidi’ was the highest, which was 20.47%. The flavonoids, total phenols and soluble protein of ‘Konglongdan’ were the highest, which were 2.29, 2.75 and 1.44 mg·g−1, respectively. In terms of sugar and acid components, the sugar component is mainly sorbitol accumulation, and the acid component is mainly citric acid accumulation.The fructose, glucose and sorbitol of ‘Fengweihuanghou’ were significantly higher than those of other cultivars (P<0.05), and the sucrose of ‘Weihou’ was 32.83 mg·g−1, which was significantly higher than that of the other four cultivars (P<0.05). The citric acid and ascorbic acid of ‘Weidi’ were significantly higher than those of the other four cultivars (P<0.05), with the contents of 10.03 and 0.34 mg·g−1, respectively. In the acid category, only ‘Weidi’ contains succinic acid, but ‘Fengweihuanghou’ does not contain fumaric acid. The fruit quality was comprehensively evaluated by principal component analysis, and the scores from high to low were ‘Konglongdan’ ‘Weiwang’ ‘Weihou’ ‘Fengweihuanghou’ and ‘Weidi’. Conclusion The sugar and acid of ‘Weidi’ are balanced, and the taste is relatively soft, but the fruit is relatively small, so the ranking is relatively backward. From the comprehensive point of view of fruit quality: ‘Konglongdan’ not only has large fruit, but also has high and relatively balanced nutrients, which is more suitable for large-scale planting in Aksu area. [Ch, 5 fig. 6 tab. 37 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250431
Abstract:
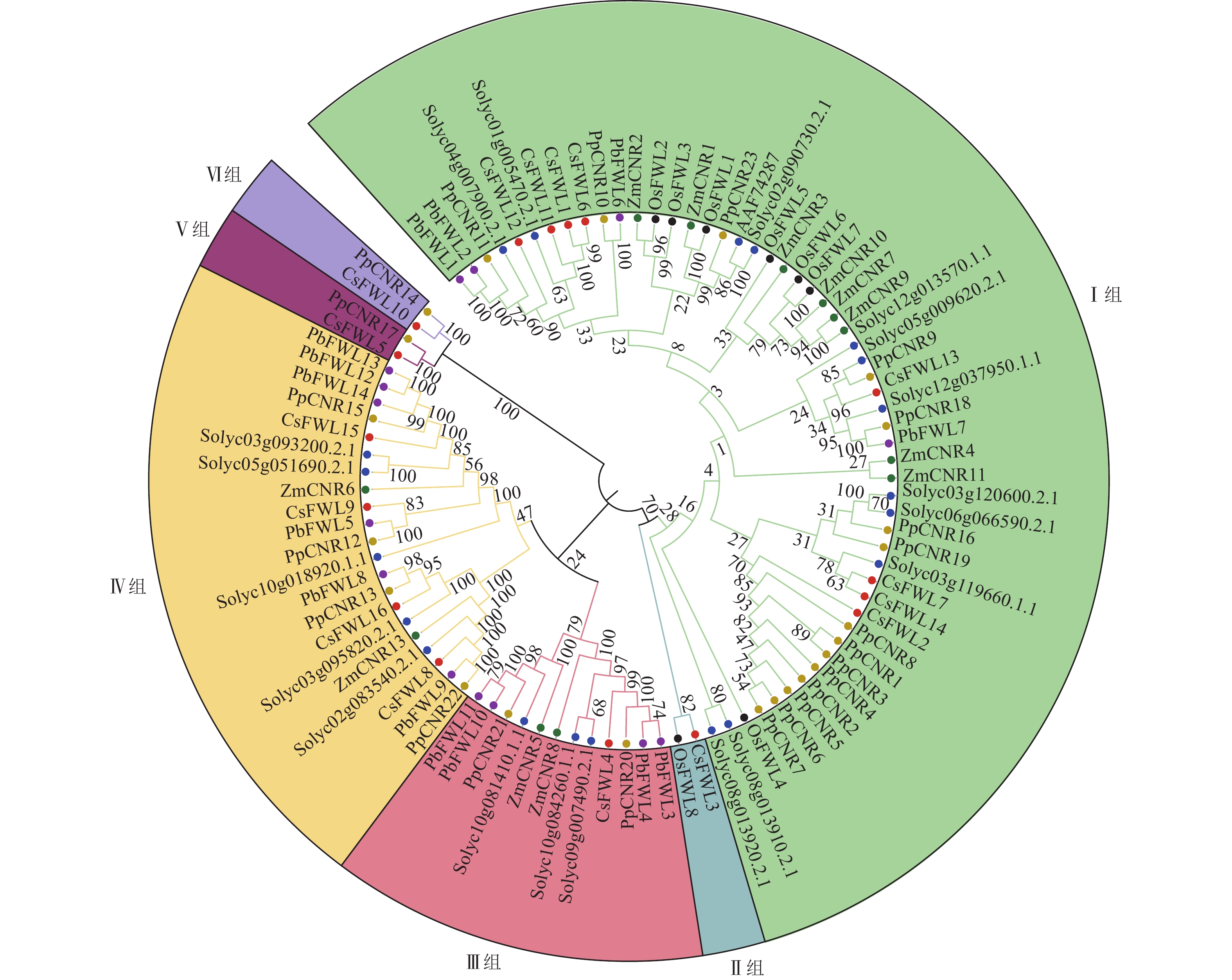
Objective This study aims to identify the members of the FW2.2 family in Citrus sinensis and analyze their structural characteristics and expression patterns during the fruit cell division period, so as to provide a theoretical basis for exploring the function of the FW2.2 gene family in C. sinensis fruit development. Method Based on the whole genome data of C. sinensis, FW2.2 family members were screened and identified. Bioinformatics methods were employed to predict and analyze their gene structure, sequence characteristics, chromosome localization, and cis-acting elements. A phylogenetic tree was constructed with FW2.2 sequences from multiple species. The expression patterns of FW2.2 family members during the fruit cell division period were analyzed by real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) technology. Result A total of 16 FW2.2 genes were identified in C. sinensis, distributed on 6 chromosomes, with a length of 100 to 563 amino acids, containing multiple conserved motifs, and mainly located in the cell membrane. Evolutionary analysis revealed that FW2.2 family members from C. sinensis, Solanum lycopersicum, Pyrus bretschneideri, Prunus persica, Zea mays and Oryza sativa were divided into 6 subgroups. Cis-acting elements analysis showed that the promoters of FW2.2 family genes contained elements related to the hormone, growth and development, and abiotic stress. Gene expression analysis showed that there were differences in the expression trends of FW2.2 family genes during the fruit cell division period. The expression levels of CsFWL5, CsFWL6 and CsFWL12 decreased significantly during the fruit cell division period, and were negatively correlated with the increase in cell layers (P<0.01). Conclusion CsFWLs members exhibit a certain degree of conservation during evolution, and share sequence similarities with FWLs genes in crops such as Pyrus bretschneideri, Prunus persica, and S. lycopersicum. CsFWLs show different gene functions. CsFWL5, CsFWL6 and CsFWL12 may be involved in regulating fruit cell division. [Ch, 6 fig. 3 tab. 33 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250440
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the reasons for dormancy of Clematis dilatata seeds and find effective methods to break dormancy, providing a basis for the protection, development and utilization of this plant. Methods Using seeds of C. dilatata as experimental material, the morphological traits, seed coat permeability, and endogenous inhibitors (using seeds of Brassica rapa var. glabra as the receptor) were observed. Furthermore, treatments with different gibberellin (GA3) concentrations (0, 50, 100, and 200 mg·L−1) were applied, varying durations of cold stratification (0~98 d), and treatments of different temperature (constant and alternating) and photoperiod (alternating light/dark and complete darkness) were combined to screen for the most effective dormancy-breaking method. Result At maturity, seeds of C. dilatata had differentiated but underdeveloped embryos. The seed coat showed good water permeability, posing no barrier to water uptake by the embryo. Aqueous extracts from the seed coat and endosperm had no significant effect on the germination of B. rapa var. glabra seeds. Compared to the constant temperature (25 ℃) or complete darkness, alternatingtemperature (25 ℃ 16 h/15 ℃ 8 h) and a light/dark cycle (light 16 h/dark 8 h) were more conducive to seed germination. Cold stratification significantly reduced the mean time to radicle emergence (21~45 d) compared to the control (75 d). When stratification duration increased, germination rate firstly increased and then decreased, while germination potential firstly increased and then stabilized, and the mean time to radicle emergence decreased progressively until stabilizing. After 70 d of cold stratification, germination rate peaked at (64.33±5.51)%, with a germination potential of (7.33±1.15)% and a mean radicle emergence time of 25 d. Treatment with 50 mg·L−1 GA3 resulted in a high germination rate of (68.33±3.51)%, a germination potential of (8.00±1.00)%, and a mean radicle emergence time of 23 d. However, higher GA3 concentration reduced both germination rate and potential, and prolonged the mean time to radicle emergence. Conclusion Seeds of C. dilatata belong to non-deep simple morphophysiological dormancy. Under alternating temperature and light/dark conditions, treatment with 50 mg·L−1 GA3 or cold stratification for 70 d can effectively seed dormancy. [Ch. 2 fig. 4 tab. 31 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250349
Abstract:
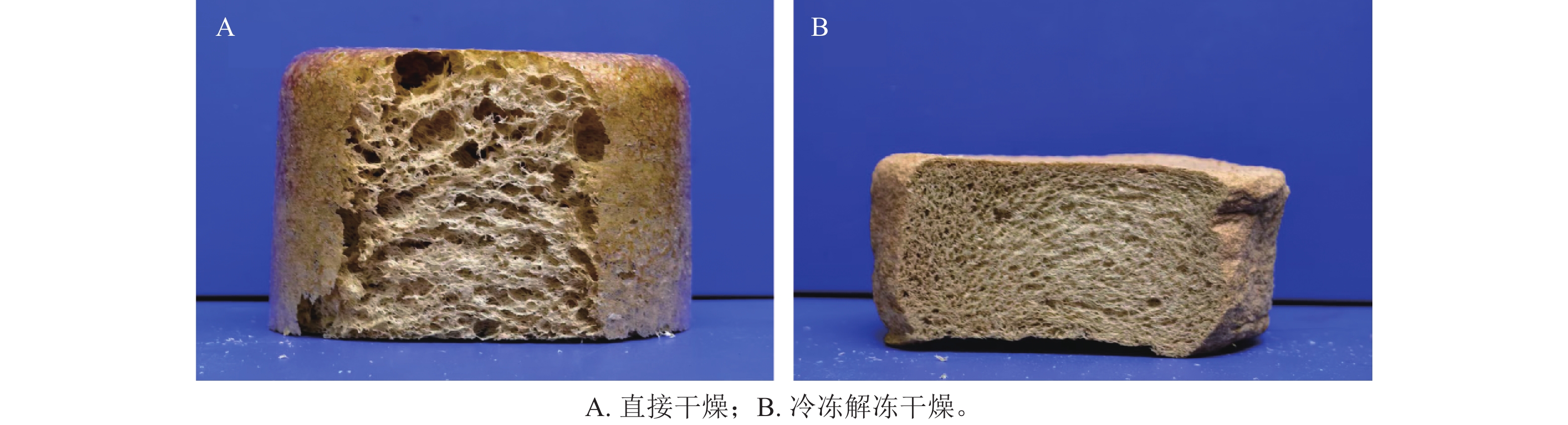
Objective This study aims to develop a cultivable foam made from renewable raw materials for use in soilless cultivation, thereby reducing reliance on conventional molding substrates such as rock wool and polyurethane. Method The soilless culture matrix foam material was prepared by mechanical foaming of wood residue fibers and chitosan gel. The effects of freeze-thaw treatment and Triton X-100 on the macroscopic morphological characteristics and foam volume were investigated. The structure of foam was characterized by microscopic morphology and infrared spectrum, and the effects of of citric acid as a cross-linking agent on the fundamental properties and cultivation performance of foam was evaluated through water retention performance, absorption tests, and cultivation experiments as well. Result The freeze-thaw treatment significantly improved the pore structure of the wood fiber-chitosan foam, with 1 g of triton X-100 (TX-100) as the optimal dosage. The addition of citric acid induced a cross-linked network within the chitosan, which could effectively enhance the pore structure and water retention capacity of the foam. Under the condition of 40 ℃ for 12 hours, the wood fiber-chitosan foam had a water loss rate of only 69.21% and its water absorption capacity reached 68.15%, a significant improvement compared to the foam without citric acid. In the cultivation experiment, the growth performance of Raphanus sativus was second only to that grown in polyurethane foam cultivation substrates. Conclusion The combination of a freeze-thaw process and the use of Triton X-100 can create a uniform pore structure in the foam. The wood fiber-chitosan foam prepared with citric acid as the cross-linking agent can meet the basic requirements for plant growth, demonstrating good application potential in practical cultivation experiments. [Ch, 7 fig. 1 tab. 25 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250398
Abstract:
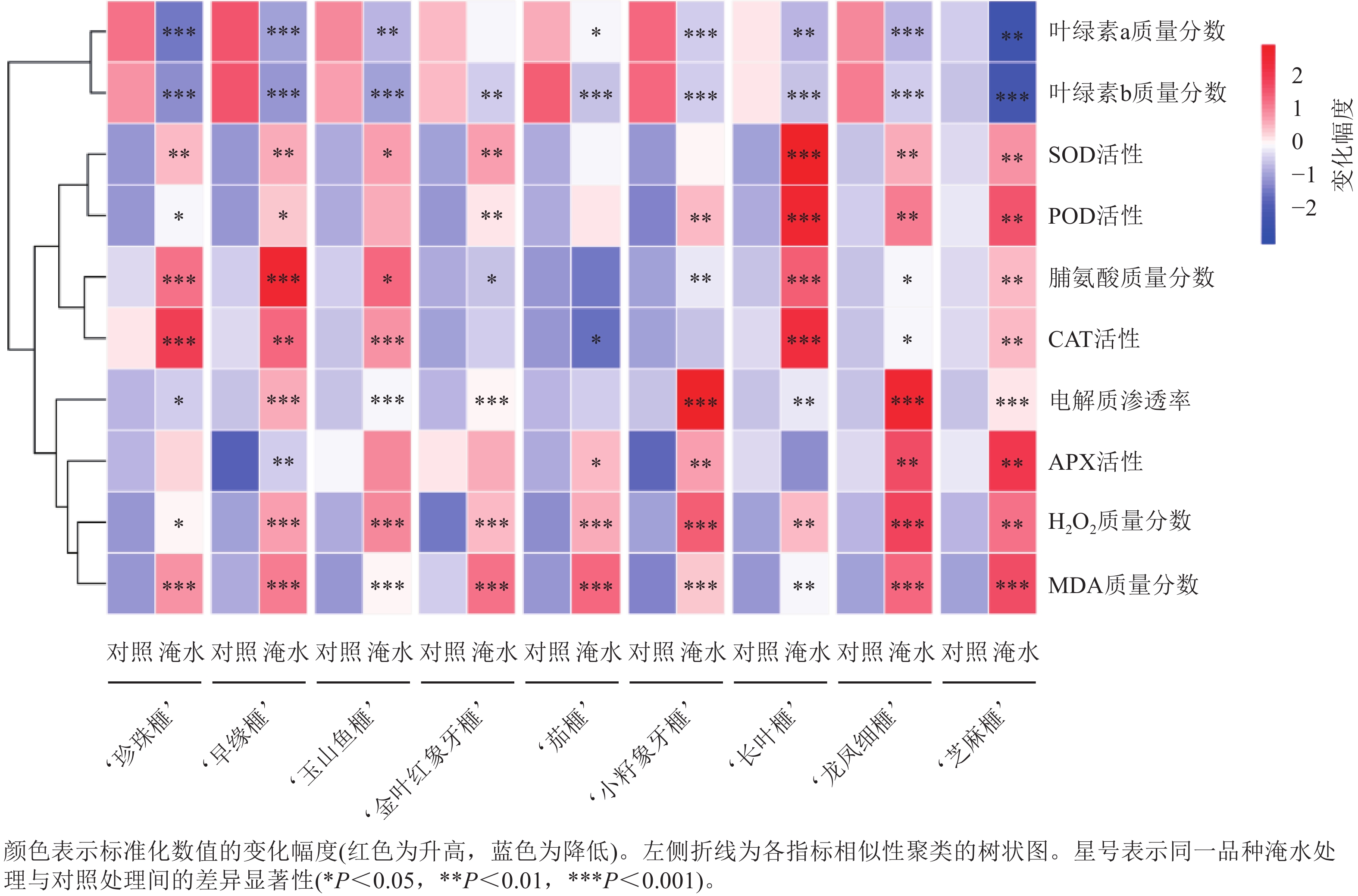
Objective In regions with poor drainage during the rainy season, frequent waterlogging severely constrains the increase in yield and quality of Torreya grandis ‘Merrillii’. This study aims to systematically investigate the physiological response and waterlogging tolerance of rootstocks of different T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ cultivars under waterlogging stress, which not only helps facilitate screening and cultivating waterlogging-tolerant varieties, but also provides a theoretical basis for elucidating the waterlogging-tolerant mechanism of T. grandis ‘Merrillii’. Method Rootstocks of 9 T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ cultivars, namely ‘Zhenzhufei’ ‘Zaoyuanfei’ ‘Yushanyufei’ ‘Jinyehongxiangyafei’ ‘Qiefei’ ‘Changyefei’ ‘Xiaozixiangyafei’ ‘Longfengxifei’ and ‘Zhimafei’ were used as test materials. 2 treatments were set up: normal moisture (control) and waterlogging. The tolerance of each cultivar to waterlogging was comprehensively evaluated by measuring 10 physiological indices in T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ leaves, including chlorophyll a and b contents, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content, malondialdehyde (MDA) content, electrolyte leakage rate, proline (Pro) content, and the activities of ascorbate peroxidase (APX), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and peroxidase (POD). Then, the waterlogging tolerance index of each variety was assessed based on principal component analysis and membership function analysis to comprehensively evaluate waterlogging tolerance capacity of each variety. Result Under waterlogging treatment, the contents of chlorophyll a and b of rootstocks of different cultivars decreased to varying degrees compared to the control. In contrast, the physiological indicators related to oxidative stress, such as H2O2 content, MDA content, electrolyte leakage rate, SOD activity, and POD activity, all increased to varying degrees. Pro content, APX activity, and CAT activity showed an increasing or decreasing trend in different cultivars. Based on principal component analysis and membership function analysis, a comprehensive evaluation of different physiological indicators was conducted to obtain the comprehensive evaluation values of waterlogging tolerance for the 9 cultivars. Conclusion Rootstocks of different T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ cultivars exhibit different changes in osmotic substances and antioxidant protection ability under waterlogging stress. ‘Changyefei’ ‘Jinyehongxiangyafei’ and ‘Yushanyufei’demonstrate high waterlogging resistance, while ‘Xiaozixiangyafei’ ‘Longfengxifei’ and ‘Zaoyuanfei’ show moderate tolerance. ‘Zhenzhufei’ ‘Qiefei’ and ‘Zhimafei’ have the least capacity of waterlogging tolerance. [Ch, 1 fig. 3 tab. 29 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250210
Abstract:
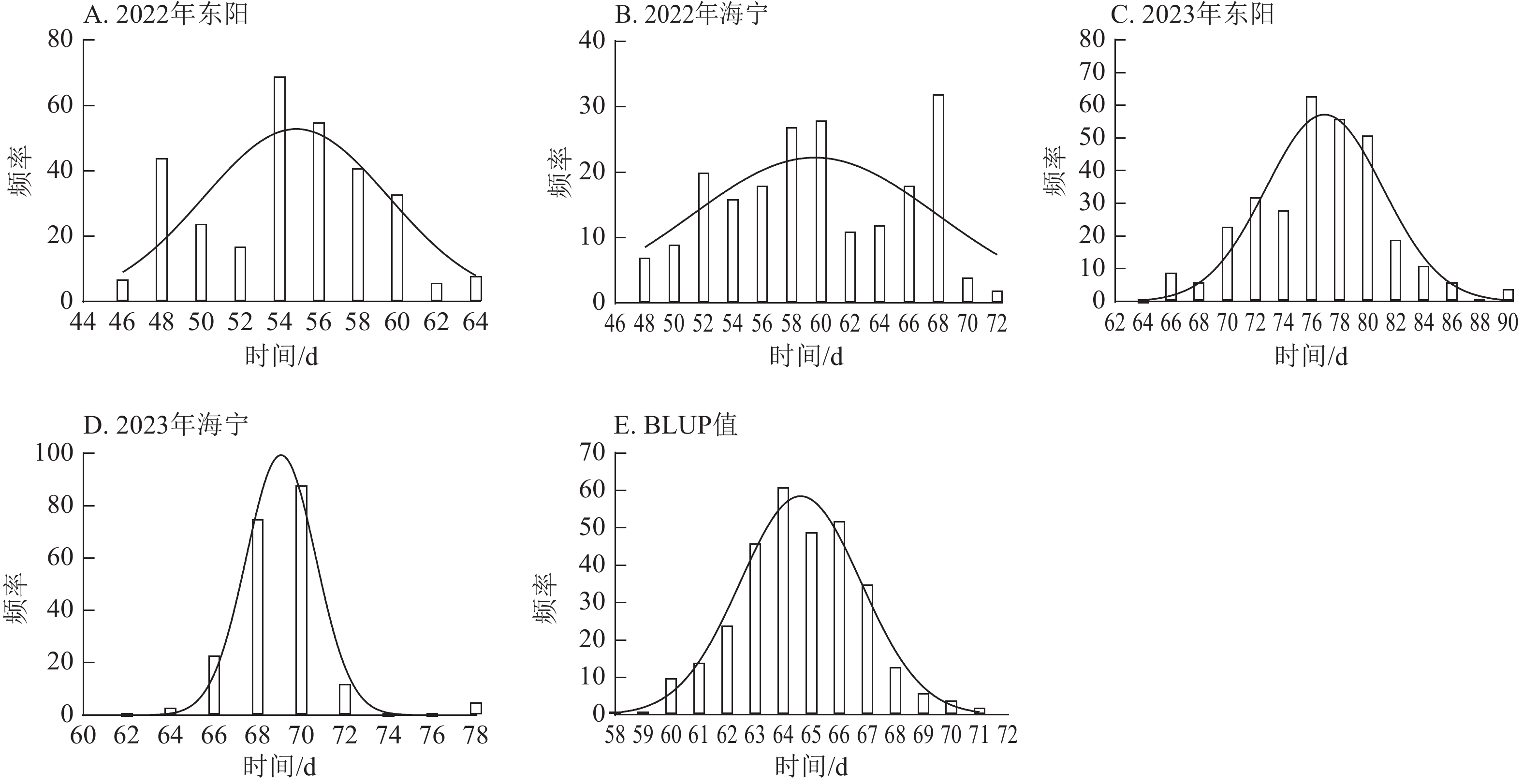
Objective Maize (Zea mays) growth period refers to the complete growth cycle from sowing to maturity, with key representative traits including tasseling stage, anthesis stage, and silking stage. Identifying key genes regulating maize growth period is of great significance for optimizing maize production and promoting industrial quality and efficiency improvement. Method In 2022 and 2023, phenotypic investigations of traits such as tasseling stage, anthesis stage, and silking stage were conducted on 322 maize germplasm resources at 2 locations (Dongyang and Haining, Zhejiang Province). Genome-wide association study (GWAS) was performed on the above traits combined with genotypic resequencing data. Result The frequency distribution of tasseling stage, anthesis stage, and silking stage traits showed a unimodal curve, consistent with a normal distribution. GWAS results revealed: for the tasseling stage, 61, 27, 281, and 57 SNP-associated loci were identified in the 4 experimental sites (Dongyang and Haining in 2022, Dongyang and Haining in 2023) across 322 maize germplasms, explaining phenotypic variation ranging from 7.26% to 10.68% and distributed on all 10 chromosomes. For the anthesis stage, 51, 26, 424, and 58 related loci were identified, explaining phenotypic variation from 7.25% to 11.80% and mainly distributed on chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, and 10. For the silking stage, 47, 277, 212, and 1 169 related loci were identified, explaining phenotypic variation from 7.25% to 41.26% and mainly distributed on chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, and 10. A total of 49, 53, and 24 overlapping SNP loci were detected for tasseling stage, anthesis stage, and silking stage among the 4 experimental sites, respectively. Through comprehensive analysis of SNP locus information, gene annotation, and gene tissue expression profiles, 6 key candidate genes for maize growth period were finally screened out. Conclusion Tasseling stage, anthesis stage, and silking stage traits showed a normal distribution, and a large number of environment-specific and overlapping SNP loci were identified. Ultimately, 6 key candidate genes for growth period were screened out, providing important genetic resources for the genetic improvement of maize growth period and the high-quality development of the industry. [ Ch, 8 fig. 3 tab. 44 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250261
Abstract:
Objective This study aimed to identify the flavonoid components in the leaves of Neosinocalamus affinis and to investigate their inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase and α-amylase, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the deep utilization and development of N. affinis leaf resources. Method Using N. affinis leaves as raw material, purified bamboo leaf flavonoids (PBLF) were obtained by macroporous resin purification. The chemical components of PBLF were identified by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). The inhibitory effects of PBLF on α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities, as well as the hypoglycemic mechanism of PBLF, were investigated through in vitro experiments. Result 18 flavonoid compounds were identified in the N. affinis leaf extract, including glycyrrhizinol, epimedium cyanidin Ⅱ, and baohuoside Ⅰ. Furthermore, the in vitro results demonstrated that PBLF significantly inhibited both α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities. At a concentration of 0.5 mg·mL−1, PBLF inhibited α-amylase by 79.71%±5.02% with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of (0.057±0.005) mg·mL−1, and inhibited α-glucosidase by 74.17%±6.17% with an IC50 of (0.071±0.004) mg·mL−1, and both types of enzyme inhibition showed competitive-noncompetitive mixed inhibition. Conclusion Enzyme inhibition kinetic studies indicated that the flavonoids present in N. affinis leaves likely function as active hypoglycemic components, potentially through a non-competitive inhibition mechanism. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 34 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250225
Abstract:
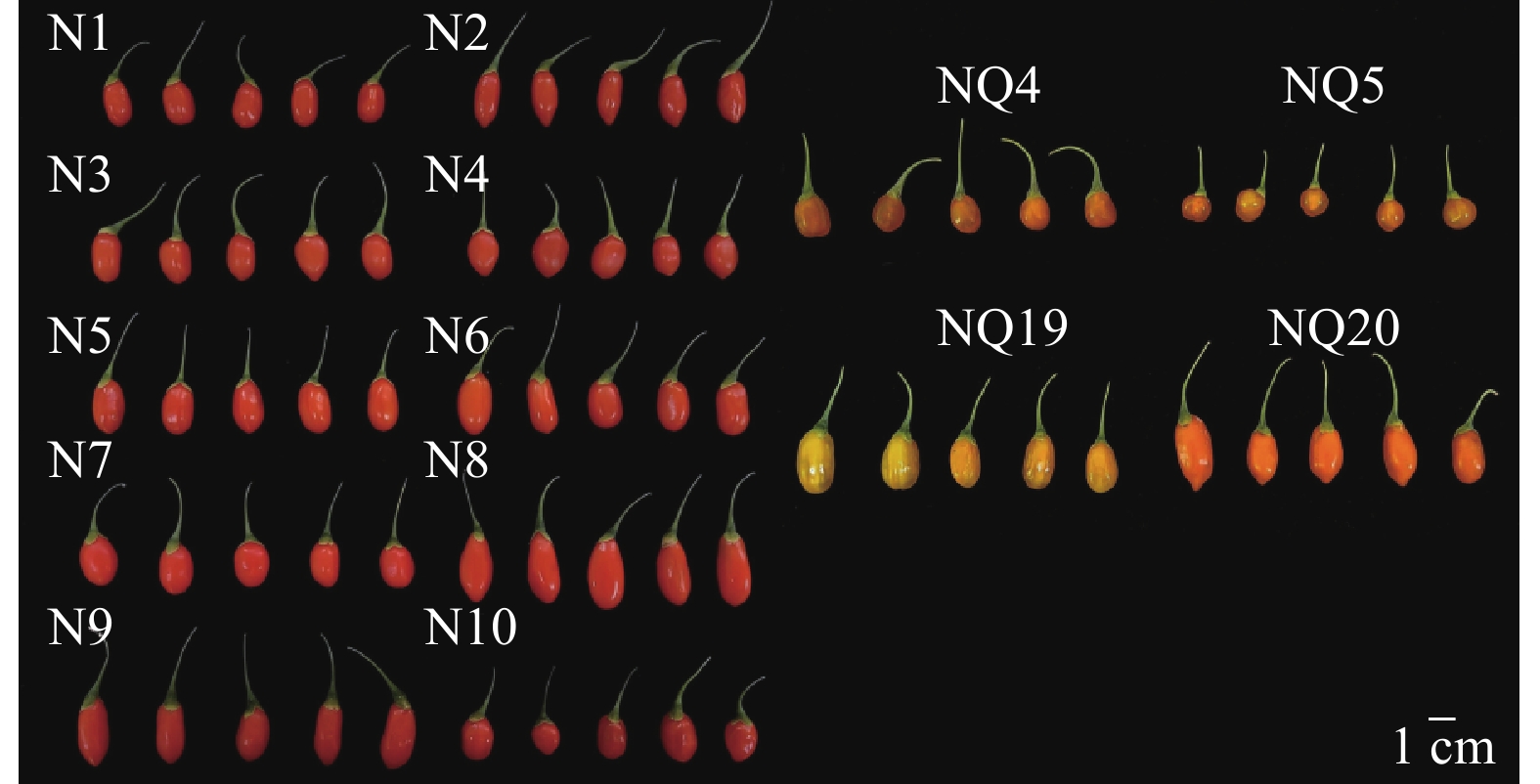
Objective The aim of this study is to determine and analyze the traits and study the variation pattern of seed and fruit traits of different cultivars of Lycium barbarum so as to provide theoretical basis for cultivating good varieties and utilizing germplasm resources. Method 14 L. barbarum cultivars (10 red fruits, 4 yellow fruits) collected from a germplasm repository were selected as research materials. Their seed and fruit traits were measured, followed by correlation analysis, coefficient of variation (CV) analysis, cluster analysis, principal component analysis (PCA), and comprehensive evaluation. Result (1) Significant positive correlation between seed and fruit size and length of fruit stalk of L. barbarum (P<0.05). (2) The CVs of phenotypic traits among cultivars ranged from 0.17% to 59.08%, with an average CV of 19.16%, indicating high phenotypic diversity. Significant differences were observed both within and between varieties (P<0.05). Fruit traits exhibited greater variability (CV=9.69%) compared to seed traits (CV=17.17%). (3) ‘Ningnongqi 20’ was clustered into one class with red fruit L. barbarum under different dimensional clustering, and its variation pattern of seed and fruit traits was more similar to that of red fruit L. barbarum. ‘Ningnongqi 4’ formed an independent cluster (Group Ⅰ) in all analyses, demonstrating unique trait variations. (4) PCA identified 4 principal components with a cumulative contribution rate of 74.478%, capturing most genetic information. Key traits influencing component loadings included adhesiveness, gumminess, chewiness, fruit length/width, fruit shape index, seed length/width, and thousand-seed weight. (5) Comprehensive evaluation ranked ‘Ningnongqi 4’ first, followed by ‘Ningqi 3’ ‘Ningnongqi 20’, and ‘Ningqi 9’. Conclusion The 14 L. barbarum cultivars exhibited substantial phenotypic diversity in seed and fruit traits, providing valuable breeding materials. ‘Ningnongqi 4’ with the highest comprehensive score, showed superior textural properties, its high hardness may facilitate mechanical harvesting, while low elasticity necessitates adjusted processing parameters. [Ch, 3 fig. 7 tab. 40 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250221
Abstract:
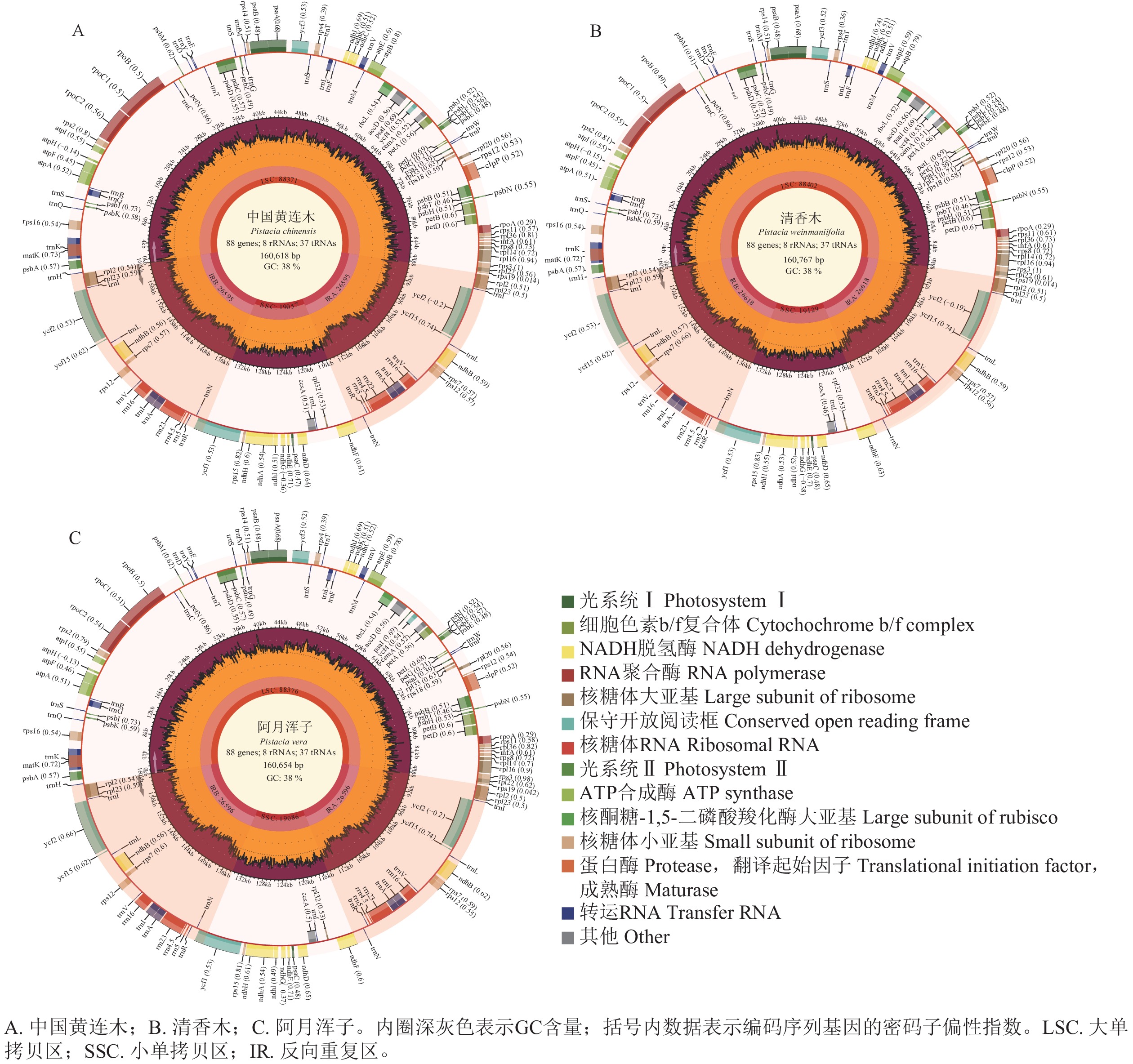
Objective In this study, the chloroplast genomes of 3 Pistacia species were compared to analyze their structural characteristics and genetic evolution. Method 3 publicly available chloroplast genomes of Pistacia species from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) were selected as research materials, and their chloroplast genome structure, repeat sequence, nucleotide polymorphism and genetic relationship were analyzed by relevant bioinformatics methods. Result The chloroplast genomes of the 3 species were tetrad ring structure, and the numbers of protein-coding sequence (CDS), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA) were exactly the same among them; The simple repeat sequences were mainly A (34.35%) or T (39.69%) repeat units in mono-nucleotide, but no hexa-nucleotide. And the number of scattered repeat sequences were mainly palindromic repeats (105) and forward repeats (76), but no reverse repeats; There were different degrees of variation in the conserved non-coding sequences (CNS) of the large single copy (LSC) and small single copy (SSC) of the chloroplast genomes of three species, but there was no significant difference in the contraction or expansion of genes near the tetrad boundary; 5 highly variable sequences ( matK, trnG- UCC~ trnR- UCU, trnT- UGU~ trnL- UAA, petD~ rpoA, rpl22~ rpl2) were identified in the LSC region and the boundary between LSC and inverted repeat b (IRb); Phylogenetic reconstruction based on complete chloroplast genomes demonstrated clear segregation between Pistacia and Rhus, and P. chinensis was closely related to P. weinmaniifolia, while P. vera and P. atlantica could be formed a distinct clade. Conclusion The chloroplast genome structure of the 3 Pistacia species was similar and relatively conservative, and the number of various genes was consistent; The 5 mutant sequences detected could be used as candidate molecular markers for Pistacia species; The genetic relationship between P. chinensis and P. weinmannifolia was similar, while P. vera was relatively distant from former 2 species. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 46 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250375
Abstract:
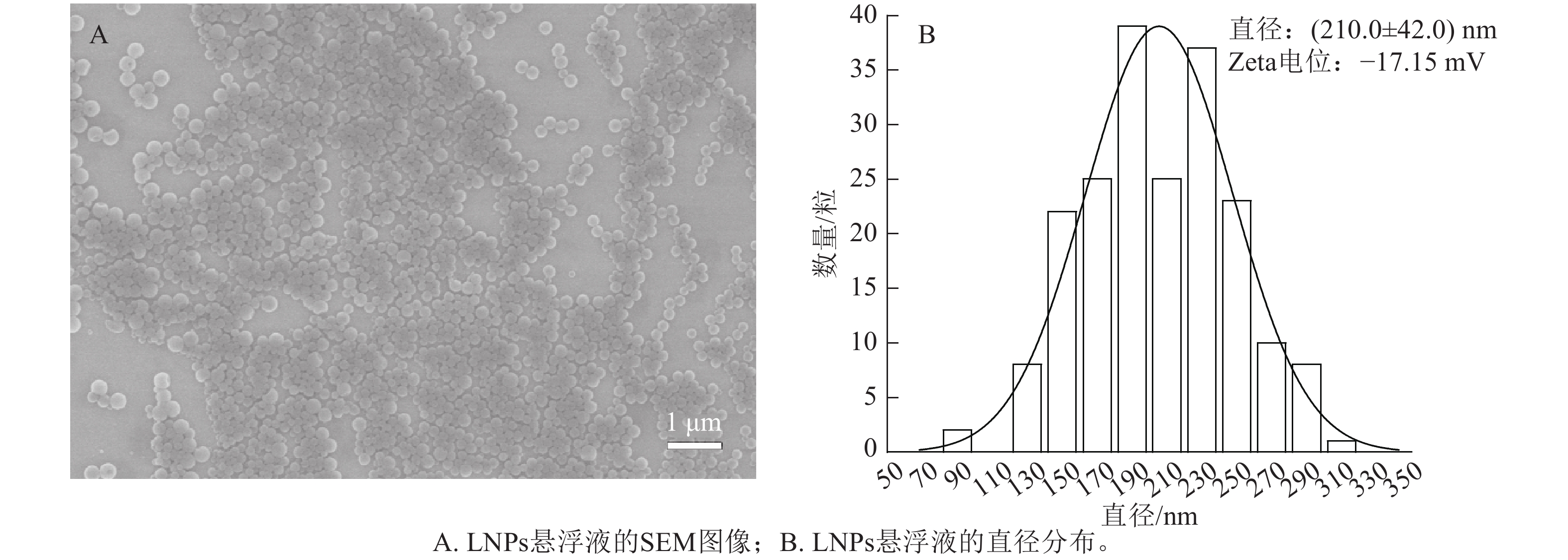
Objective This study aims to prepare a fully biobased composite film with flexible iridescent cellulose nanocrystals (CNC)/phosphorylated cellulose nanofibers (PCNF)/lignin nanoparticles (LNPs), and systematically examine the influence of LNPs mass fraction on the optical properties, morphology, mechanical properties, humidity sensitivity, thermal stability, hydrophobicity, and ultraviolet shielding properties of the composite film. Method Taking CNC as the structural matrix, PCNF as the reinforcing phase, and LNPs as the functional component, a two-step method was employed to prepare a fully biobased, flexible, and iridescent CNC/PCNF/LNPs composite film. Result The structural color and the maximum reflection wavelength (λmax) of the film exhibited a significant redshift with increasing LNPs mass fraction. Hydrophobicity was enhanced, and the water contact angle increased from 39.0° to 76.1°, while humidity sensitivity decreased slightly. Thermal stability improved, with the maximum thermal decomposition temperature rising from 240 ℃ to 261 ℃. Ultraviolet shielding performance was enhanced, and the CNC/P20/L2.0 film (where P20 represented the mass fraction of PCNF relative to CNC as 20.0%, and L2.0 represented the mass fraction of LNPs relative to CNC as 2.0%) achieved UV absorption rates of 95.8% in the ultraviolet region (UV, 200−400 nm) and 99.2% in the mid wave UV region (UVB, 280−320 nm). Conclusion The mass fraction of LNPs can affect the optical properties, morphology, humidity sensitivity, thermal stability, hydrophobicity, and ultraviolet shielding properties of the composite film, but it has little effect on the mechanical properties. [Ch, 7 fig. 26 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250389
Abstract:
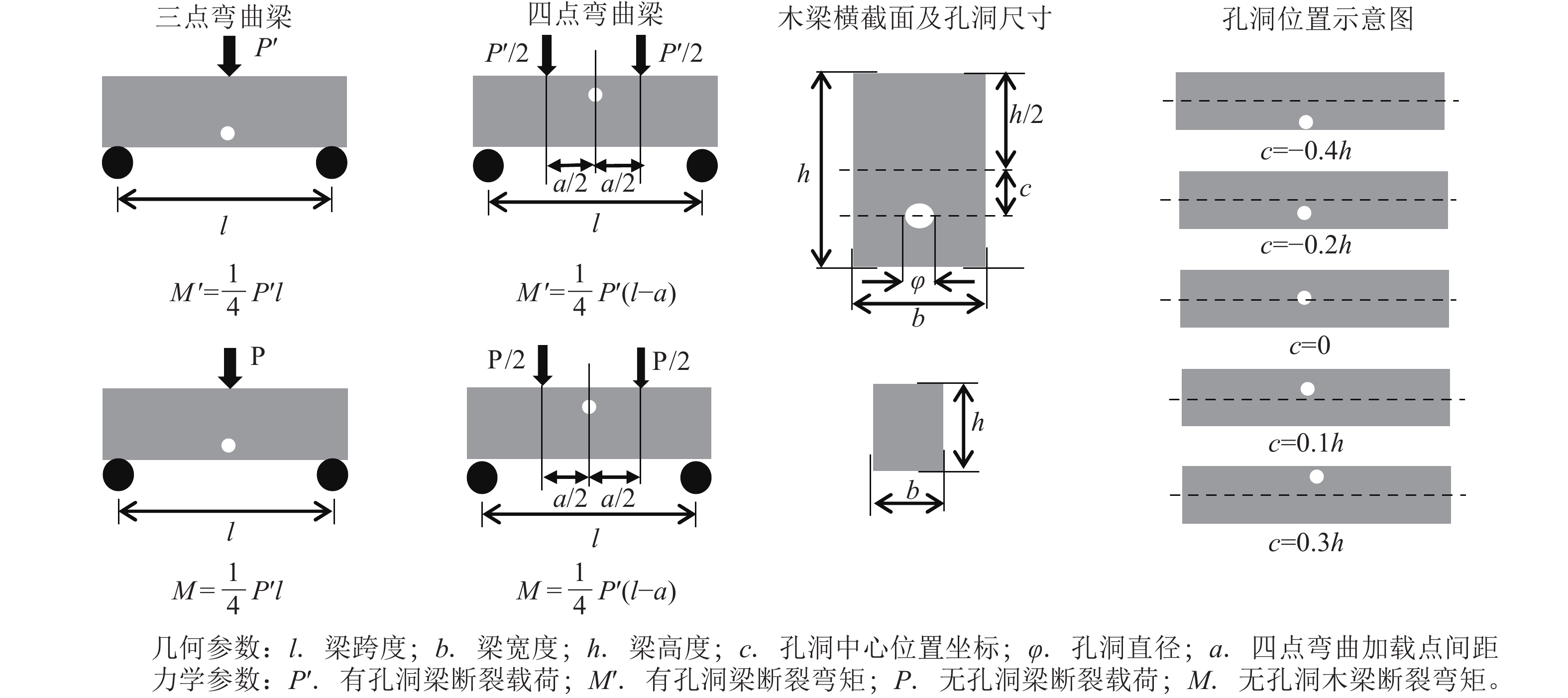
Objective This study aims to examine the influence of circular holes of different positions and sizes on the load-bearing capacity of wooden beams, explore the mechanical mechanism by which wooden beams have a certain tolerance for hole damage, and inspire the design of materials with high hole tolerance or lightweight structures. Method The mechanical concept of hole compatibility was proposed, and the calculation formula for hole compatibility coefficient was provided. By conducting bending and fracture experiments on wooden beams, the fracture bending moment values of wooden beams with holes of different positions and diameters were measured, corresponding relationship curves were drawn, and the hole compatibility coefficient of wooden beams was calculated. By conducting simulation analysis and fracture morphology analysis on representative wooden beams, the mechanism of their hole compatibility mechanical properties was clarified. Result The impact of holes below the neutral layer on the load-bearing capacity of wooden beams was greater than that of holes located above the neutral layer. When the diameter of the hole was less than 1/5 of the beam height, the bearing capacity of the wooden beam did not exceed 10%. Except for wooden beams with extremely high and low densities, the compatibility coefficient of most wooden beams was close to 1.0, which was higher than that of plastic metal aluminum beams and brittle acrylic beams. Finite element analysis showed that the stress distribution below the hole was more uniform than that above the hole, and the fracture morphology analysis revealed that the fracture surface below the hole was smoother. Conclusion When the diameter of the hole is smaller than the critical value, the overall bearing capacity of the wooden beam decreases slightly. When such holes are located in the stretching area of the wooden beam, the bearing capacity of the wood fibers in the lower area of the hole is more evenly exerted, and the wooden beam exhibits a mechanical phenomenon of hole compatibility as a whole. Wooden beams have better hole compatibility mechanical properties than plastic metal aluminum beams and brittle acrylic beams. The mechanical mechanism of hole compatibility can inspire the design of new fiber-reinforced composite materials, lightweight load-bearing structures with holes, and micro porous structural materials. [Ch, 6 fig. 6 tab. 25 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250186
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to construct transgenic homoisoflavones tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) plants based on the homoisoflavones synthase gene ChOMT from alfalfa (Medicago sativa), thereby achieving nutritional fortification of tomatoes. Method ChOMT gene was introduced into tomatoes using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Transgenic identification was carried out through PCR and fluorescence detection. Furthermore, plant-wide targeted metabolomics technology and multivariate statistical analysis methods were employed for precise quantitative analysis of homoisoflavones content. Result Through PCR and fluorescence detection, positive transgenic plants of ChOMT were obtained. Compared with the wild type, the content of homoisoflavonoids significantly increased. Among them, the relative content of (3RS)-5,7-dihydroxy-3-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl)-chroman-4-one (HIF1) in the leaves of transgenic tomatoes was 57019 , which was 260 times higher than the relative content of 220 in the leaves of the wild type. The relative content of 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-chroman-4-one (HIF2) in the fruits of transgenic tomatoes was 15 849 985, which was over 4 000 times higher than the relative content of 3849 in the wild type. Conclusion ChOMT transgenic tomatoes are obtained, which not only provides a theoretical basis for analyzing the catalytic function of ChOMT in plants, but also lays an important foundation of germplasm resources for breeding genetically improved tomato varieties with high homoisoflavonoid content. [Ch, 7 fig. 28 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250331
Abstract:
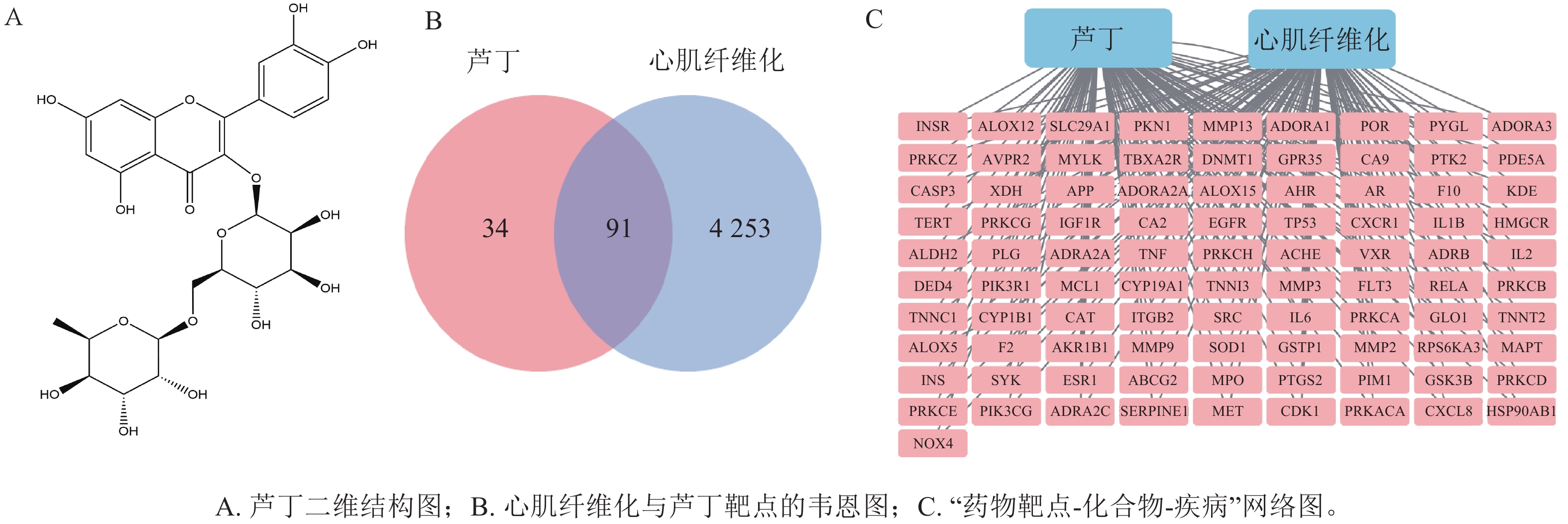
Objective The objective of this study is to explore the mechanism of rutin against myocardial fibrosis (MF) based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and cellular experiments. Method Based on drug and disease databases, disease-associated gene targets related to rutin and MF were identified. A multidimensional “drug-target-disease” interaction network model was constructed using Cytoscape, and the core targets were subjected to Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis using R software. The interaction between rutin and the core target protein was simulated through molecular docking technology. The effect of rutin on the proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) was detected by the CCK-8 method. Result Network pharmacology analysis revealed that rutin acted on 91 MF-related targets, among which IL-6, TNF, TP53, and SRC were the core targets, and they were enriched in signaling pathways such as PI3K-Akt, MAPK, and IL-17. Molecular docking demonstrated that rutin had a good binding activity with the core target protein. Molecular biology experiments showed that rutin could reverse the expression of fibrotic biomarkers in TGF-β1-induced CFs and significantly downregulate the expression of key proteins associated with the MAPK-JNK/ERK signaling pathway (P<0.05). Conclusion Rutin may alleviate TGF-β1-induced fibrosis in CFs by inhibiting the activation of the MAPK-JNK/ERK signaling pathway. [Ch, 7 fig. 2 tab. 31 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250370
Abstract:
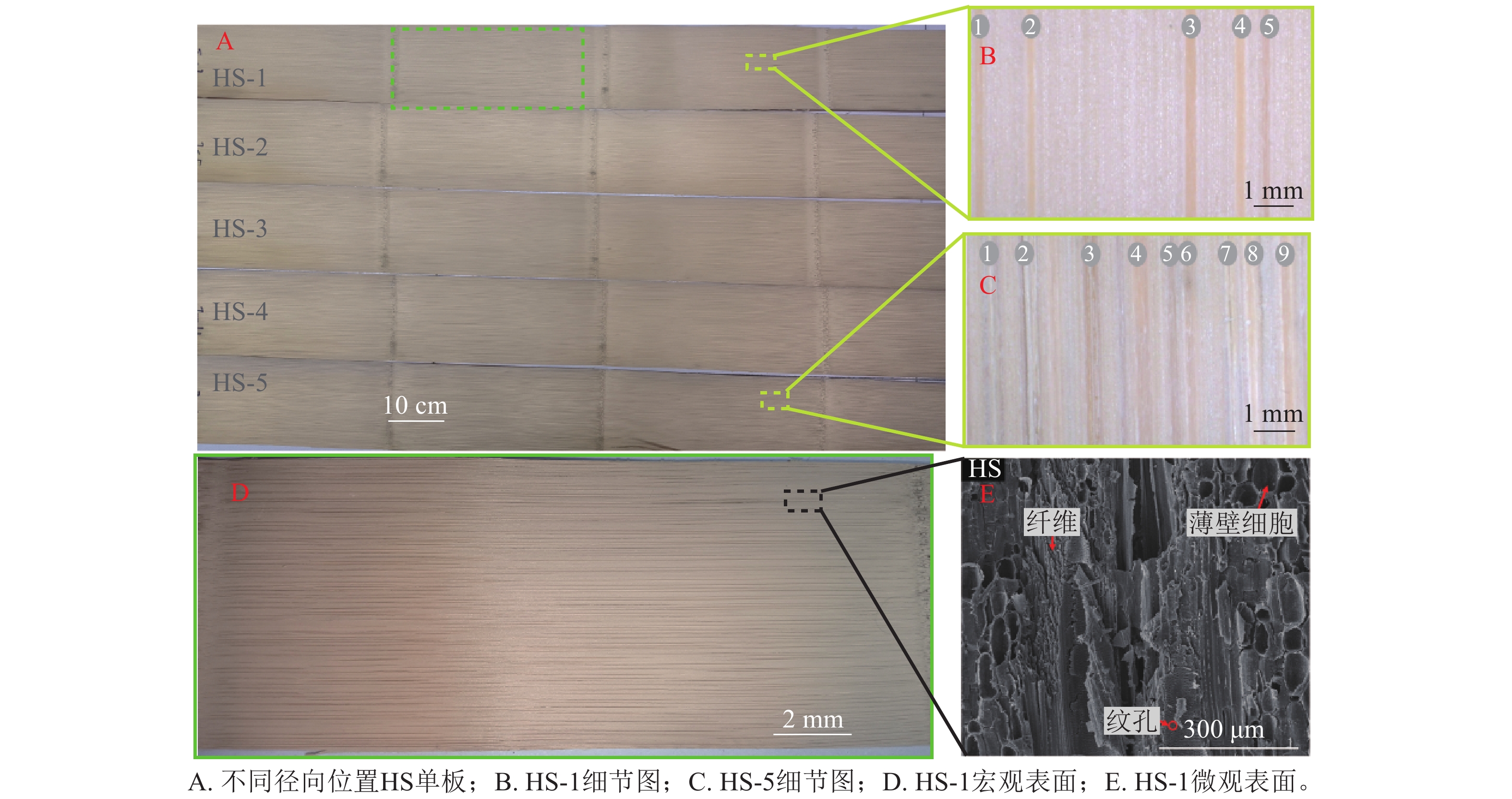
Objective This study aims to investigate the structural and performance differences of sliced bamboo veneers from different radial positions under various treatments, so as to provide fundamental data for achieving “bamboo as a substitute for plastic” and diversified utilization of veneers. Method A comparative study was conducted on the transverse and longitudinal planning methods, as well as water-boiling pretreatment process. Surface quality, flexibility, tensile properties, and chemical composition were taken as evaluation indices to quantify the effects of different processing techniques on the physical and chemical properties of sliced bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) veneers from different radial positions. Result Transverse planing yielded higher surface quality and stability than longitudinal planing. The flexibility gradually decreased from the inner bark to the outer bark of the bamboo. Compared with transverse-planed unboiled veneers at the same gradient positions, the flexibility of transverse-planed boiled veneers and longitudinal-planed veneers decreased by approximately 11.47% and 34.22%, respectively. Conversely, the tensile strength of the sliced veneer increased from the inner bark to the outer bark of the bamboo. At the same gradient position, the transverse-planed boiled and unboiled veneers showed reductions of 11.78% and 21.68%, respectively. Chemical compositions showed no significant variations across radial positions due to gradient-dependent softening effects, while the crystallinity basically showed an upward trend from the inner to the outer layers of the bamboo. Conclusion The mechanical properties of bamboo veneers vary with radial position and planing direction. Directional planing and gradient processing can effectively coordinate mechanical properties of veneers. [Ch, 7 fig. 3 tab. 28 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250346
Abstract:
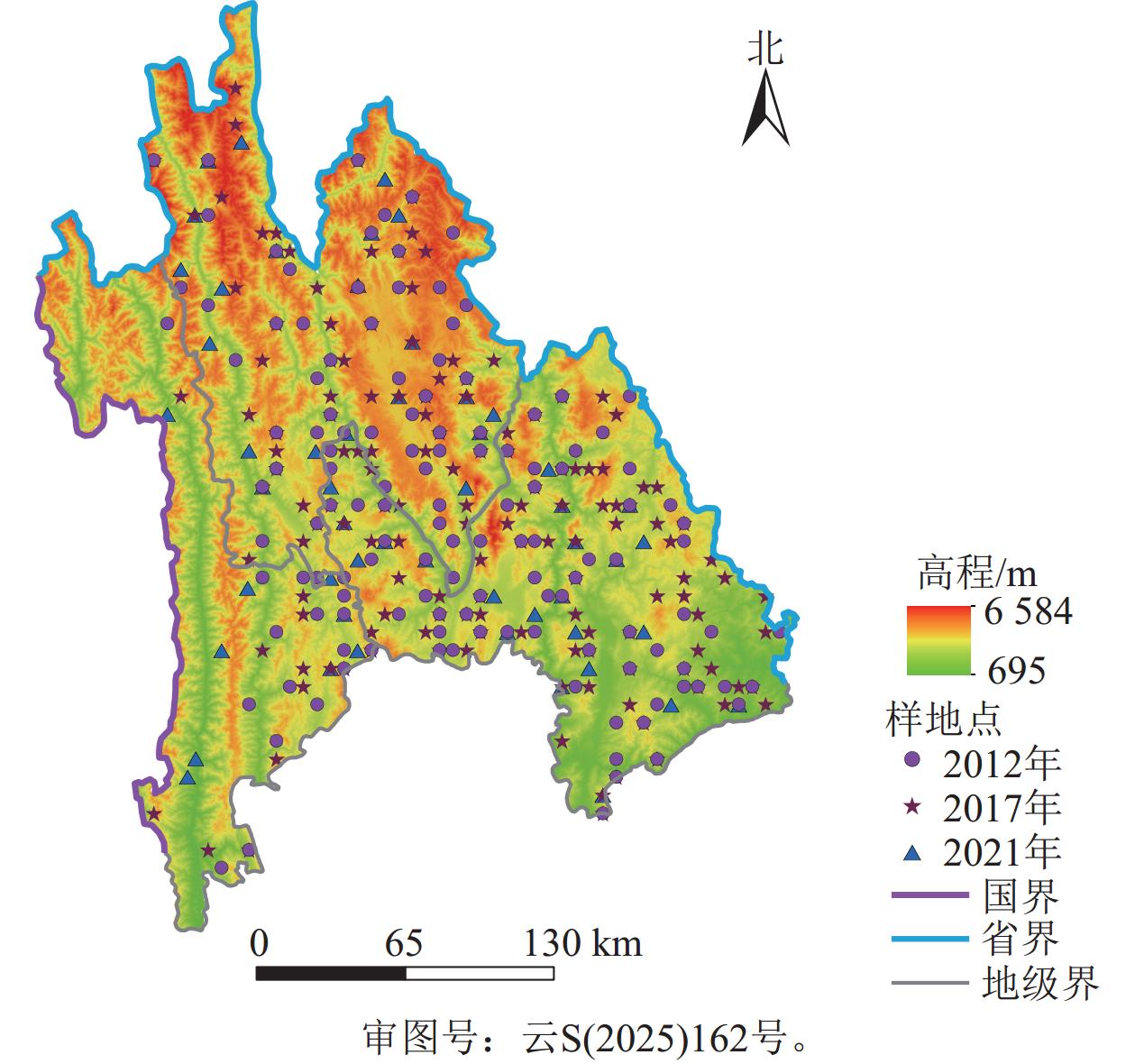
Objective Forest carbon storage plays a vital role in the global climate system and provides an important reference for achieving carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals. Model-based methods are effective for estimating forest carbon storage, while improving prediction accuracy remains a key challenge. Method Using national forest resource inventory data and Landsat 7 and 8 imagery, 5 modeling approaches including geographically and temporally weighted regression (GTWR), random forest (RF), gradient boosting regression tree (GBRT), GTWR-RF, and GTWR-GBRT were applied to estimate forest carbon storage in “Three Parallel Rivers” region from 2012 to 2021, and the optimal model was selected for final estimation. Result (1) GTWR model accounted for both spatial and temporal dimensions, while GBRT model showed clear limitations in explaining spatial heterogeneity. When used individually, all models exhibited limited explanatory power. In contrast, the two-stage hybrid model performed better than the single models, effectively addressing spatial heterogeneity and the nonlinear relationships between carbon storage and environmental variables. (2) GTWR-GBRT model achieved the best fitting performance, with the coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.98, the prediction accuracy of 0.90, and the relative root mean square error (rRMSE) of 5.91, outperforming the other 4 models, indicating that incorporating both spatiotemporal heterogeneity and nonlinearity were essential for accurate forest carbon estimation. (3) Forest carbon storage in the study area exhibited significant positive spatial autocorrelation. Estimates generated by GTWR-GBRT model revealed that forest carbon storage from 2012 to 2021 was unevenly distributed, mainly concentrated in high-altitude regions, showing a general pattern of higher values in the west and lower values in the east, along with some localized high-carbon areas. Conclusion Compared with various single models and other combined models, the GTWR-GBRT hybrid model demonstrates superior fitting and predictive performance, suggesting that integrating spatiotemporal and nonlinear characteristics within a two-stage hybrid framework can yield more accurate estimations of forest carbon storage. [Ch, 3 fig. 6 tab. 30 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250249
Abstract:
Soil inorganic carbon (SIC) is a key component of the soil carbon pool, and its sequestration and loss have profound impacts on the global carbon cycling and climate change. With accelerating urbanization in China, urban ecosystems have become a focal point of ecological research. Urban green spaces, as integral components of urban ecosystems, are closely linked to soil carbon dynamics, climate regulation, and ecosystem services, and their response and feedback to urbanization will inevitably be the focus and priority of study. However, the understanding of SIC cycling in urban green spaces remains limited. This paper examined the potential impacts of human activities such as land management and construction on SIC in urban ecosystems. It systematically overviewed the following aspects: (1) sequestration, loss and influencing factors of SIC in urban green spaces under urbanization; (2) the driving effects of changes in soil physical properties, nitrogen inputs, pH, and salinity on the carbonate dissolution–precipitation balance of SIC in urban green spaces; (3) the impact of soil fauna and microbial communities on SIC formation process. Future research should focus on the driving mechanism of SIC dynamics under urbanization, so as to make up for the research deficiencies in inorganic carbon in urban green spaces and provide theoretical support for improving carbon cycling theory and optimizing ecosystem functions in urban ecosystems. [Ch, 1 tab. 83 ref.]
Soil inorganic carbon (SIC) is a key component of the soil carbon pool, and its sequestration and loss have profound impacts on the global carbon cycling and climate change. With accelerating urbanization in China, urban ecosystems have become a focal point of ecological research. Urban green spaces, as integral components of urban ecosystems, are closely linked to soil carbon dynamics, climate regulation, and ecosystem services, and their response and feedback to urbanization will inevitably be the focus and priority of study. However, the understanding of SIC cycling in urban green spaces remains limited. This paper examined the potential impacts of human activities such as land management and construction on SIC in urban ecosystems. It systematically overviewed the following aspects: (1) sequestration, loss and influencing factors of SIC in urban green spaces under urbanization; (2) the driving effects of changes in soil physical properties, nitrogen inputs, pH, and salinity on the carbonate dissolution–precipitation balance of SIC in urban green spaces; (3) the impact of soil fauna and microbial communities on SIC formation process. Future research should focus on the driving mechanism of SIC dynamics under urbanization, so as to make up for the research deficiencies in inorganic carbon in urban green spaces and provide theoretical support for improving carbon cycling theory and optimizing ecosystem functions in urban ecosystems. [Ch, 1 tab. 83 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250420
Abstract:
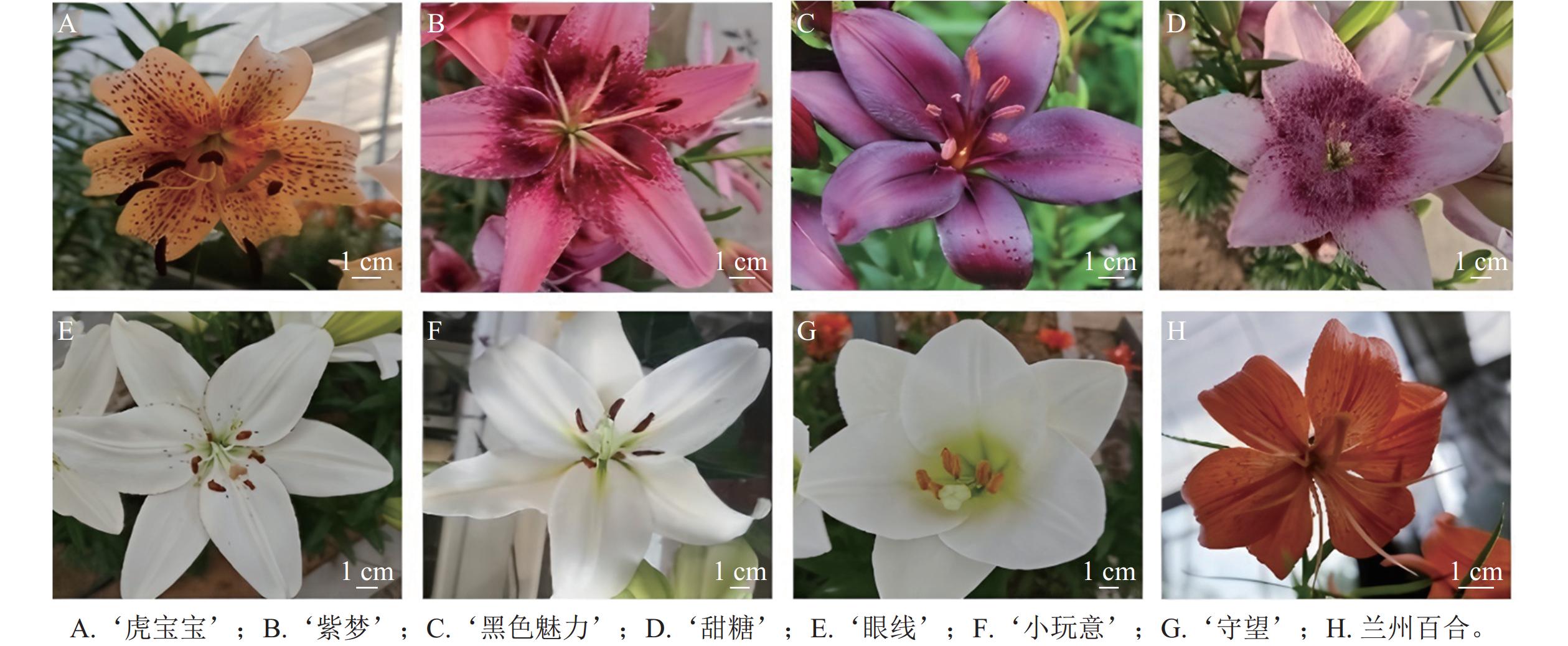
Objective This study aims to investigate hybrid affinity between Lilium davidii var. unicolor and Lilium ornamental cultivars, and to provide germplasm resources and technical support for breeding multi-purpose lilies. Method Pollen viability of all tested lilies was examined. Based on the results, 10 cross combinations were established: using L. davidii var. unicolor as the male parent with ‘Tiger Babies’ ‘Purple Dream’ ‘Black Charm’ ‘Sweet Sugar’ ‘Eye Liner’‘Gizmo’ and ‘Watch Up’ as female parents, and using L. davidii var. unicolor as the female parent with ‘Purple Dream’ ‘Black Charm’ and ‘Watch Up’ as male parents. 3 pollination methods were employed, including direct pollination, cut-style pollination, and stigma application with 1 g·L−1 NAA solution. Cross-compatibility was evaluated based on pollen tube growth and fruit set. The authenticity of hybrid seedlings obtained through embryo culture was assessed using SSR markers. Result (1) Cross-compatibility analysis revealed that ‘Sweet Sugar’ and ‘Black Charm’ exhibited the highest compatibility with L. davidii var. unicolor, followed by ‘Eye Liner’ ‘Tiger Babies’ and ‘Purple Dream’. In contrast, ‘Watch Up’ and ‘Gizmo’ showed low compatibility. (2) Direct pollination was the simplest and most universally applicable method. (3) SSR analysis revealed that all 145 seedlings from the 6 hybrid combinations (‘Sweet Sugar’ × L. davidii var. unicolor, ‘Black Charm’ × L. davidii var. unicolor, ‘Tiger Babies’ × L. davidii var. unicolor, ‘Eye Liner’ × L. davidii var. unicolor, L. davidii var. unicolor × ‘Black Charm’, and L. davidii var. unicolor × ‘Purple Dream’) were authentic hybrids. Conclusion The study revealed distinct cross-compatibility between L. davidii var. unicolor and different lily cultivars, identifying ‘Sweet Sugar’ and ‘Black Charm’ as highly compatible parents. Cut-style pollination is an effective technique for improving fruit set in the cross of ‘Tiger Baby’× L. davidii var. unicolor. SSR marker technology enables early and accurate identification of hybrid seedlings. [Ch, 2 fig. 6 tab. 34 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250455
Abstract:
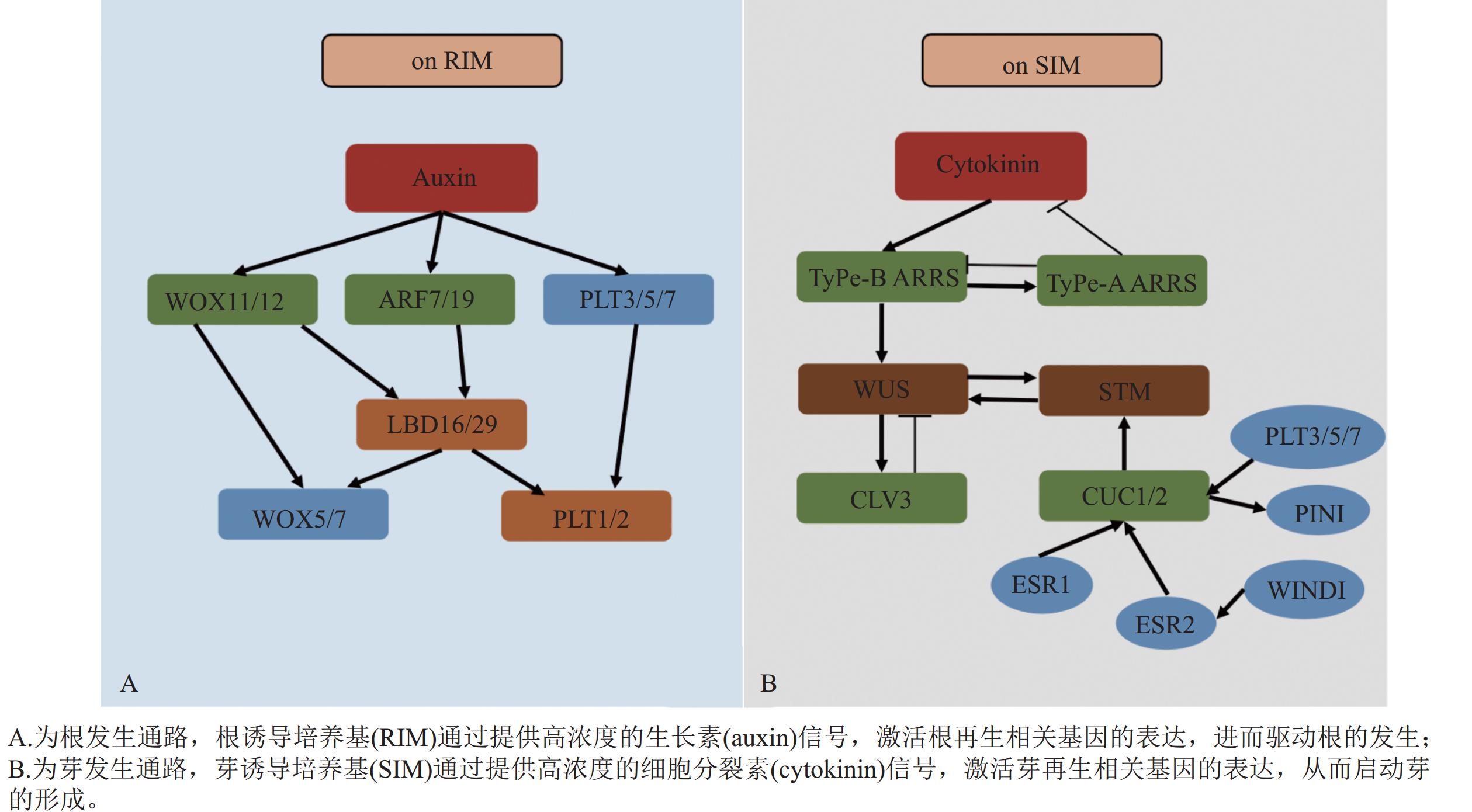
However, the current organogenic regeneration system generally has technical bottlenecks such as rooting difficulties, severe browning and strong genotype dependence in adult materials, which seriously restricts the relevant breeding and breeding process. The key external factors affecting regeneration efficiency, including explant selection, media optimization, and the ratio and treatment timing of plant growth regulators (PGRs) are systematically sorted out. At the molecular mechanism level, the cellular and molecular regulatory mechanisms from callus induction to adventitious root/adventitious bud formation were expounded, and the core mechanisms of auxin signaling (ARF-WOX-LBD pathway) regulating adventitious root genesis and cytokinin signaling (ARR-WUS-CLV3 loop) regulating adventitious bud formation were revealed. In view of the technical bottlenecks such as the difficulty of rooting of adult materials and the serious browning of high-phenolic varieties, a comprehensive countermeasure combining physiological and epigenetic regulation was further proposed. This paper analyzes that the organogenesis of woody plants is jointly regulated by external culture conditions, internal hormone pathways and epigenetic status, and the essence of adult material regeneration disorder is that regeneration-related genes are systematically inhibited at the epigenetic level. In the future, through deepening mechanism analysis and technological innovation, it is expected to systematically break through the regrowth obstacles of woody plants and provide systematic support for precision breeding and gene function research of forest trees. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 82 ref.]
However, the current organogenic regeneration system generally has technical bottlenecks such as rooting difficulties, severe browning and strong genotype dependence in adult materials, which seriously restricts the relevant breeding and breeding process. The key external factors affecting regeneration efficiency, including explant selection, media optimization, and the ratio and treatment timing of plant growth regulators (PGRs) are systematically sorted out. At the molecular mechanism level, the cellular and molecular regulatory mechanisms from callus induction to adventitious root/adventitious bud formation were expounded, and the core mechanisms of auxin signaling (ARF-WOX-LBD pathway) regulating adventitious root genesis and cytokinin signaling (ARR-WUS-CLV3 loop) regulating adventitious bud formation were revealed. In view of the technical bottlenecks such as the difficulty of rooting of adult materials and the serious browning of high-phenolic varieties, a comprehensive countermeasure combining physiological and epigenetic regulation was further proposed. This paper analyzes that the organogenesis of woody plants is jointly regulated by external culture conditions, internal hormone pathways and epigenetic status, and the essence of adult material regeneration disorder is that regeneration-related genes are systematically inhibited at the epigenetic level. In the future, through deepening mechanism analysis and technological innovation, it is expected to systematically break through the regrowth obstacles of woody plants and provide systematic support for precision breeding and gene function research of forest trees. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 82 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250196
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to investigate the species composition and community structure of forest stands on Daishan Island, Zhejiang Province, and provide recommendations for tree species combination models for the restoration of forest communities on islands. Method A quadrat survey was conducted to investigate woody plants with a diameter at breast height (DBH) ≥ 1 cm within the sample plots (100 m×100 m). Species composition, floristic elements, DBH class distribution, species diversity, and tree species combination were analyzed. Result A total of 8 767 woody plant individuals were recorded, belonging to 29 species, 28 genera, and 18 families, with an average tree height of 4.11 m and an average DBH of 4.35 cm. Quercus acutissima, Cinnamomum camphora, and Ficus erecta were the dominant species in the community. At the family level, the flora consisted of 27.78% cosmopolitan, 50.00% tropical, and 22.22% temperate components. At the genus level, 64.29% were tropical, 28.57% temperate, and 7.14% unique to China. The DBH of tree species in the community showed an inverted “J” shape distribution, with 91.80% of plants in the small and relatively small diameter classes. The Shannon-Wiener diversity index, Pielou evenness index, Simpson diversity index, and Margalef richness index were 1.28, 0.38, 0.50, and 3.08, respectively. The community included tree species combinations with good resilience, such as C. camphora-Q. acutissima, Metasequoia glyptostroboides-Q. acutissima, and Q. acutissima-F. erecta. Conclusion The forest community on Daishan Island is dominated by Q. acutissima, C. camphora, F. erecta, Eurya nitida, and Ilex cornuta. The DBH structure displays an inverted “J” shape pattern, and the plant community in this area is dominated by tropical species. The overall distribution of tree species in the community is uneven, resulting in different combinations of tree species. [Ch. 4 fig. 4 tab. 30 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250279
Abstract:
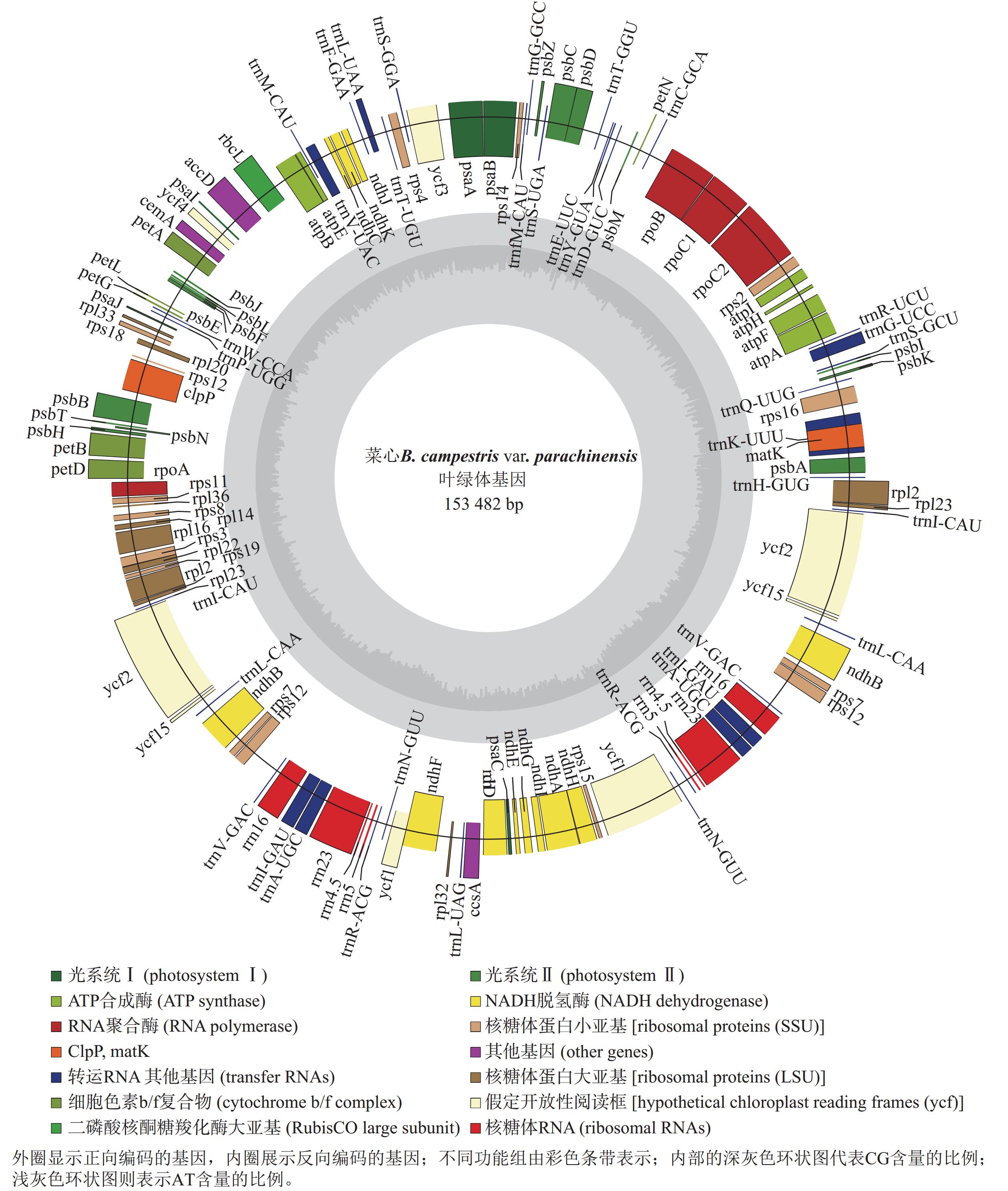
Objective This study aims to assemble, annotate, and analyze the chloroplast genome of flowering Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris var. parachinensis), and to elucidate its phylogenetic relationships with other Brassicaceae crops. Method The complete chloroplast genome of flowering Chinese cabbage was sequenced using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform. Bioinformatics approaches were employed to analyze its genome structure, repetitive sequences, nucleotide diversity, codon usage bias, and phylogenetic relationships by constructing phylogenetic trees with chloroplast genome sequences of other 25 Brassicaceae species. Result The chloroplast genome of flowering Chinese cabbage is 153 482 bp in length with a GC content of 36.36%, exhibiting a typical quadripartite structure. In total, 132 functional genes had been identified and annotated, comprising 86 protein-coding genes, 37 tRNA genes, 8 rRNA genes, and 1 pseudogene. Codon usage bias analysis revealed that leucine (Leu) is the most frequently used amino acid, with 31 codons showing a relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) value greater than 1, predominantly ending with A or U. Repetitive sequence analysis detected 37 dispersed repeats and 315 simple sequence repeats (SSRs), with mononucleotide repeats predominating (72.70% of total SSRs). The nucleotide diversity of small single copy region (SSC) is the highest, while that of inverted repeat region (IR) is the lowest. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that flowering Chinese cabbage exhibits the closest genetic relationship with leafy Chinese cabbage varieties. Conclusion The chloroplast genome of flowering Chinese cabbage exhibits a conserved quadripartite structure and demonstrates close phylogenetic relationships with B. rapa var. chinensis, B. rapa var. purpuraria, and B. rapa subsp. pekinensis. [Ch, 5 fig. 3 tab. 39 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250291
Abstract:
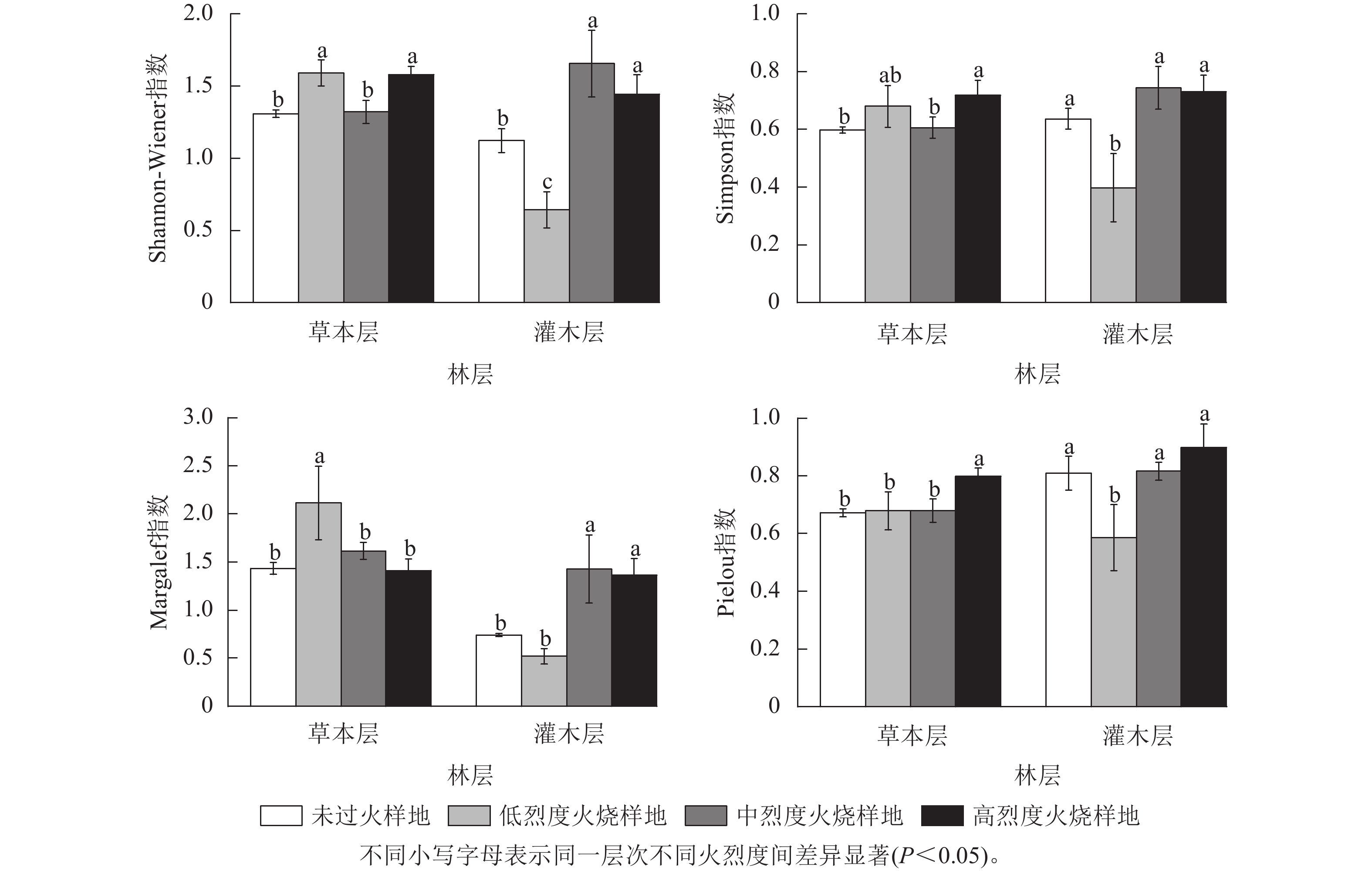
Objective The objective is to investigate the effects of different fire severities on understory vegetation species diversity and soil physicochemical properties, which is of great significance for the restoration and sustainable management of forest ecosystems in burnt areas. Method The study focused on the burnt area 4 years after the fire in Pinus tabuliformis forests in Taiyue Mountain of Shanxi Province. A combination of field investigation and indoor analysis was used to examine the differences and trends in understory vegetation species diversity and soil physicochemical properties in plots with different fire severities (low severity fire, medium severity fire, high severity fire, and no fire), as well as the short-term response of post-fire species diversity to physicochemical properties. Result (1) A total of 50 vascular plant species were recorded, belonging to 20 families and 43 genera. After low-severity fire in the herb layer and medium severity fire in the shrub layer, the number of species was higher than that in unburnt areas. (2) In the shrub layer, the Shannon-Wiener index, Simpson index, and Margalef index ranging from large to small were as follows: medium-severity fire plots, high-severity fire plots, unburnt plots, and low-severity fire plots, while the Pielou index in descending order was high-severity fire plots, medium-severity fire plots, unburnt plots, and low-severity fire plots. In the herb layer, the Shannon-Wiener and Margalef indices significantly increased by 21.38% and 47.55% (P<0.05) in the low-severity fire plots compared to unburnt plots, while the Simpson and Pielou indices significantly increased by 20.00% and 19.40% (P<0.05) in the high-severity fire plots compared to unburnt plots. (3) Different fire severities significantly (P<0.01) affected soil physicochemical properties. Soil moisture content and total porosity decreased with increasing fire severity. Mass fraction of total phosphorus and potassium showed a trend of first decreasing and then increasing with the increase of fire severity, reaching its lowest point in medium-severity fire plots. Soil total porosity, soil organic carbon, total nitrogen and available potassium decreased with deepening of soil layers in different fire severity plots. (4) The redundancy analysis revealed that soil moisture content, capillary porosity, and total potassium mass fraction in the 0−10 cm layer, along with available phosphorus mass fraction, total porosity, and available potassium mass fraction in the 10−20 cm layer, were significant soil factors affecting species diversity in the shrub and herb layers. Conclusion Low severity and medium severity fires promote vegetation regeneration in P. tabuliformis forests, and soil moisture content and available phosphorus are key factors driving post fire species diversity differentiation. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 48 ref.]
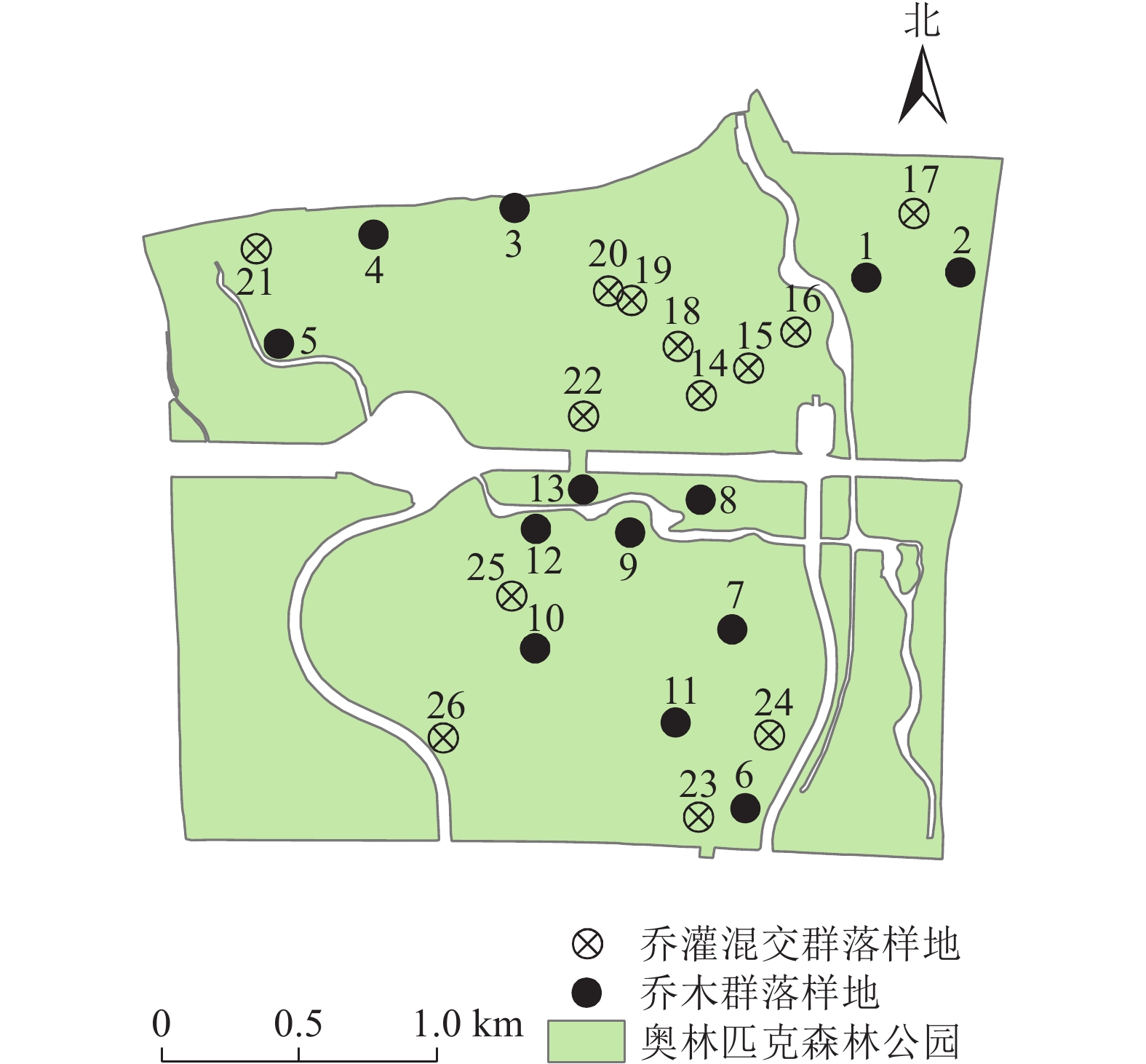
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250206
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to investigate the spatiotemporal dynamics, as well as the driving factors of soil respiration across different vegetation types of urban forests, so as to provide theoretical references for regional carbon estimation. Method Taking Beijing Olympic Forest Park as the research object, a portable soil respiration measurement system was used to measure soil respiration (Rs), soil temperature (Ts), and soil water content (CSW) of 26 sample plots (13 in the arbor community and 13 in the arbor-shrub mixed community) monthly from April to October in 2023. And combined with high-resolution normalized difference vegetation index (INDV), a fitting analysis was conducted on the seasonal and spatial variations of Rs and the influencing factors. Result (1) The seasonal dynamics of Rs and Ts were consistent, showing a unimodal pattern of first increasing and then decreasing. The average Rs in the arbor community (4.83 μmol·m−2·s−1) was higher than that in the arbor-shrub mixed community (4.42 μmol·m−2·s−1). (2) Ts accounted for 90.0% and 73.0% of the seasonal variation in Rs in the arbor and arbor-shrub mixed community, respectively, while CSW explained 28.0% and 37.0%. A dual-factor model incorporating both temperature and moisture could explain 93.0% and 82.0% of the variation, respectively. (3) The spatial coefficient of variation of Rs in the arbor-shrub mixed community was similar to the variation trend of CSW, with a significant positive correlation between the two (R2=0.88, P<0.01). In contrast, there was a highly significant nonlinear relationship between the spatial variation of Rs and Ts (R2=0.65, P<0.01) in the arbor community. (4) The response of Rs to Ts varied in time and space, with an approximately linear increase in time and a nonlinear response in space. Although Rs increased with the increase of CSW in both time and space, the rate of increase varied. Conclusion The response of Rs to environmental factors in urban forests exhibits spatiotemporal variations. Ts is the driving factor of seasonal variations in Rs, while the dominant factors of spatial variation of urban forest Rs vary among different vegetation types. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 38 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250275
Abstract:
Objective The aim is to explore the difference in water conservation function of Robinia pseudoacacia plantations at different growth stages in loess areas of western Shanxi, and provide scientific basis for improving water conservation capacity and management of forest stands. Method Taking R. pseudoacacia plantations of 5 age groups (with forest ages of 15, 23, 27, 34, and 41 years respectively ) in Caijiachuan watershed, Linfen City of Shanxi Province as the research objects, water conservation indicators in vertical layers (canopy, litter, and soil) were measured, including canopy interception rate, litter water-holding capacity, soil physical properties, and water holding characteristics. Comprehensive evaluation of the water conservation function was conducted based on Entropy Weight-Approximate Ideal Solution Ranking (TOPSIS). Result (1) The leaf area index and interception rate of the canopy layer showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing as the age increased, with the highest values observed in middle-aged forests (23 years), and remained stable after maturity. (2) The litter layer in middle-aged forests exhibited the highest accumulation and maximum water holding capacity, while the effective retention capacity was superior in mature stands. (3) Young stands (15 years) had the highest non-capillary and saturated water-holding capacities, while middle-aged stands excelled in capillary water retention. (4) Soil layers contributed the most to water conservation. Water retention capacity first increased and then declined with age, reaching peak in middle-aged stands. Conclusion The water conservation function of the middle-aged R. pseudoacacia plantation is the best. To enhance the water conservation function, inefficient and degraded stands should be selectively harvested and replanted, which is in line with regional project for low efficiency forest transformation and functional improvement. [Ch, 2 fig. 5 tab. 34 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250203
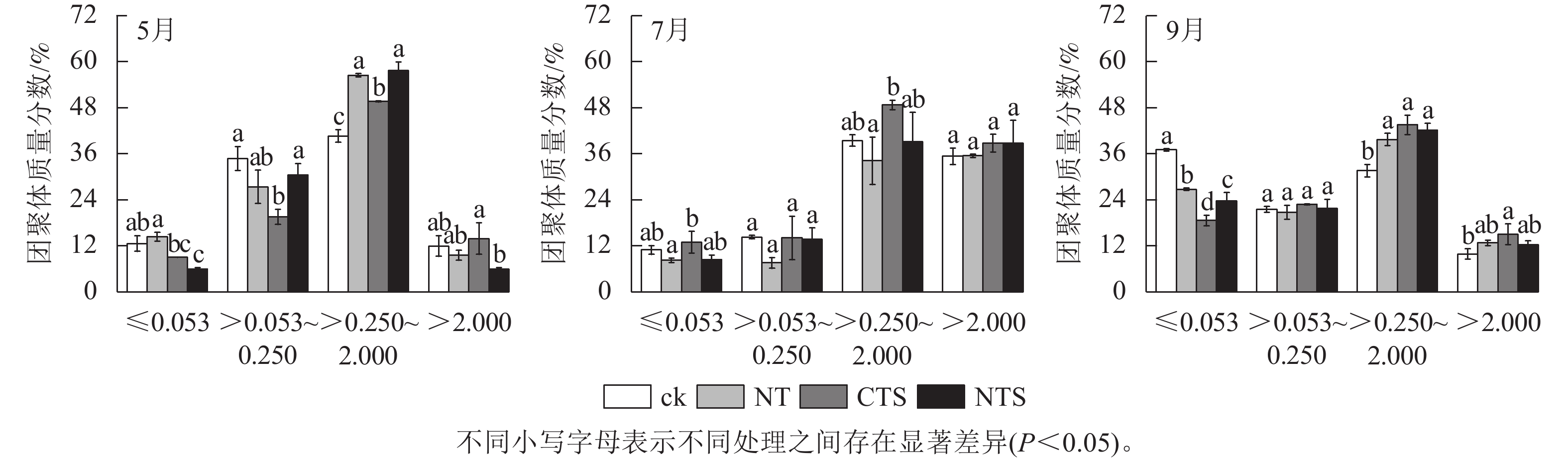
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to investigate the changes in soil physicochemical properties, aggregates and microbial communities in the wine vineyards at the eastern foot of Helan Mountains in Ningxia under conservation tillage measures, and to elucidate the correlation between soil physicochemical properties and microbial communities. Method Taking the wine grape variety Vitis vinifera ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ as the experimental material, natural grass (NT), branch mulching (CTS), and natural grass + branch mulching (NTS) were set up as treatments and clean tillage (ck) was used as the control. The indicators such as soil pH, electrical conductivity (EC), aggregate stability, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, organic matter contents, and relative abundance and diversity of bacteria and fungi were measured and analyzed in the wine vineyards during the flowering period (May), fruit swelling period (July), and fruit ripening period (September). Result (1) Compared with ck, NT, CTS, and NTS treatments significantly increased soil pH and total phosphorus, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, available phosphorus, and organic matter contents at different growth stages of the grapes (P<0.05). In September, the soil organic matter content in NT, CTS, and NTS treatments increased by 34.71%, 93.33%, and 68.73%, respectively. (2) Compared with ck, the stability of soil aggregates under NT, CTS, and NTS treatments was significantly improved (P<0.05). Particularly in September, NTS significantly increased the mean weight diameter (MWD) of aggregates by 26.23%, the mean geometric diameter (MGD) of aggregates by 67.65%, and the percentage of aggregates larger than 0.250 mm (R0.25) by 31.33%, resulting in an improvement in soil structure. (3) NT, CTS, and NTS treatments significantly increased the relative abundance and diversity of bacteria and fungi in the soil (P< 0.05), and altered the microbial community structure. Conclusion NT, CTS, and NTS treatments can significantly improve soil physical-chemical and microbial properties in the ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ vineyard. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 54 ref.]
, Available online doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250213
Abstract:
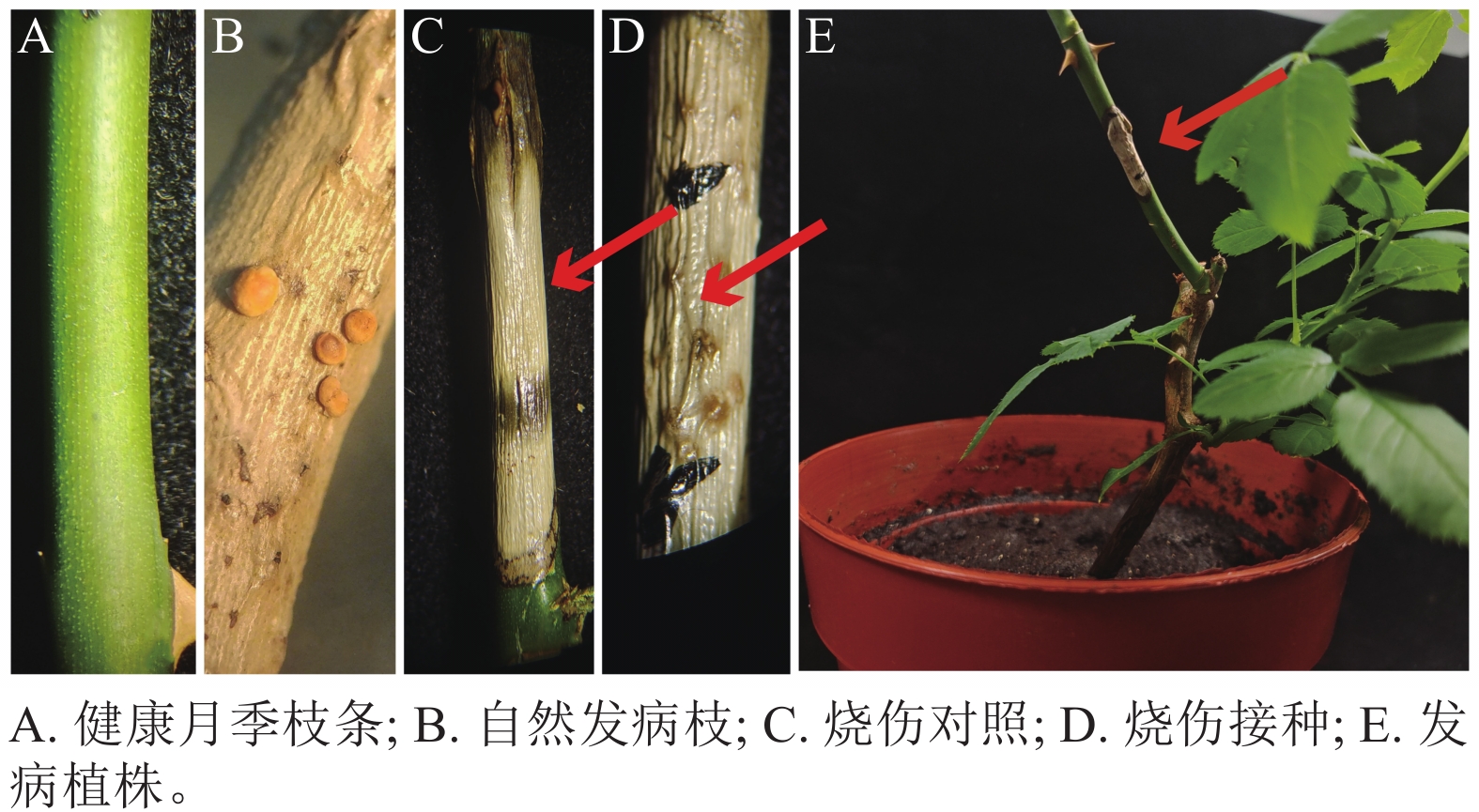
Objective This study aimed to identify the causal pathogen of branch blight in Rosa chinensis, characterize its biological properties, and evaluate effective fungicides to establish a scientific foundation for disease for disease control. Method The pathogen was isolated and purified using tissue isolation. The isolate was characterized morphologically and phylogenetically by multi-locus sequence analysis. Mycelial growth kinetics were assessed under varying carbon/nitrogen sources, pH values, and temperatures using the growth rate method. Five fungicides were evaluated for inhibitory effects by poisoned medium technique. Result The purified strain R1007 induced disease symptoms upon wound inoculation, and the same strain was re-isolated from infected tissues. Morphological characteristics matched Nectria ulmicola, and Blast analysis with phylogenetic analysis confirmed high genetic similarity to the type strain CFCC52117 of N. ulmicola. Optimal growth conditions were maltose (carbon source), yeast extract (nitrogen source), pH 7.17, and 25 ℃. Among tested fungicides, carbendazim showed the strongest inhibition (EC50=0.338 8 mg·L−1). Conclusion The causal agent of R. chinensis branch blight was identified as N. ulmicola. The optimal growth conditions were maltose and yeast extract as carbon and nitrogen sources, pH 7.17, and 25 ℃. Carbendazim shows promise as an effective fungicide for disease control. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 28 ref.]