-
中国岩溶(喀斯特)区面积巨大(90.7 万km2),约占国土总面积的9.45% [1-3];岩溶区人地矛盾突出、植被破坏严重、基岩裸露度高、土地生产力下降甚至丧失[4]。岩溶生态系统脆弱,石漠化成为岩溶区限制社会经济发展的重大生态环境问题[5-7]。植被恢复是石漠化综合治理的关键[8],是生态系统功能恢复与重建的基础[9-10]。深入研究石漠化区自然植被的恢复过程,认识植被群落结构、动态变化,对科学指导石漠化治理中人工促进植被恢复具有重要的作用。相比于其他地区,岩溶区植被群落生态学研究较为薄弱。目前,学者们仅对部分岩溶区植被群落结构、生物多样性进行了初步研究[11-14],且多集中在云南、贵州、广西3省;岩溶区分布广,面积大,异质性非常高,现有研究难以支撑全国不同岩溶区植被恢复。南水北调是世界上规模最大的跨流域调水工程,河南省淅川县是其中线工程渠首所在地、核心水源区和主要淹没区,从地理位置看,淅川县位于岩溶集中分布连片区的北端[15-16],石漠化区域总面积348.82 km2[17]。脆弱的生态环境严重威胁着南水北调中线工程持续发展。然而,该岩溶区天然森林群落特征尚无研究报道,限制了地方林业生态建设中物种与结构模式配置等关键技术的研发。对此,本研究以淅川县岩溶区6个不同恢复年限的天然次生林为对象,研究其物种组成、群落结构及生物多样性特征,拟揭示渠首石漠化区植被恢复过程,为科学制定该区植被恢复策略与确定合适的植被恢复物种和结构配置模式及数量指标提供理论与数据基础,以支撑该区石漠化综合治理。
HTML
-
淅川县(32°55′~33°23′N,110°58′~111°53′E)位于河南省南阳市西南边陲,豫、鄂、陕三省交界的黄金地带,因淅水纵贯境内形成冲击平川而得名,是南水北调中线工程核心水源地和渠首工程所在地,其境内的丹江口水库为亚洲最大的人工淡水湖。淅川县为北亚热带向暖温带过度的季风性气候,四季分明,年平均气温为15.8 ℃,无霜期约228 d。境内雨量充沛,年降水量为391.3~1 423.7 mm,多年平均降水量为804.3 mm,6−10月为雨季,约占全年降水量的65%。辖区岩溶面积占比较大,主要分布在丹江库区的周边12个乡镇,以金河镇、西簧乡、荆紫关镇为主要代表,样地植被是以栓皮栎Quercus variabilis为建群种的次生林。
-
2018年7−9月,选取淅川县金河镇、荆紫关镇及西簧乡,以“空间代替时间”的方法选取20、28、35、40、53、70 a 共6个不同恢复年限天然次生林样地(皆为全部采伐后自然恢复)。各恢复年限样地设置3个20 m×30 m乔木样方,对其中胸径≥2 cm且树高≥2 m的木本植物进行每木检尺,记录物种名、胸径、树高和南北冠幅,胸径<2 cm或树高<2 m的计算为灌木。在乔木样方四角以及中心布设5个2 m×2 m的灌木样方和5个1 m×1 m的草本样方,分别记录样方中胸径<2 cm或树高<2 m的木本植物和草本植物的种类、株丛数、平均高度及盖度。本次共调查乔木样方18个,总调查面积10 800 m2。样地基本情况见表1。
样地 地点 恢复年份(时长) 平均胸径/cm 平均树高/m 坡度/(°) 海拔/m 平均土壤厚度/cm 土壤类型 样方数量/个 P1 西簧桃花村 1998(20 a) 9.09 8.8 32 461 16 黑色,石灰土 3 P2 金河渭营村 1990(28 a) 10.63 11.3 25 322 23 黑色,石灰土 3 P3 金河小江沟村 1983(35 a) 10.94 11.8 21 290 27 黑色,石灰土 3 P4 金河渭营村 1978(40 a) 11.49 12.0 24 278 22 黑色,石灰土 3 P5 金河江沟村 1965(53 a) 10.99 11.3 23 243 23 黑色,石灰土 3 P6 荆紫关林场 1948(70 a) 13.33 14.4 29 550 18 黑色,石灰土 3 Table 1. Sample information
-
选择密度(株·hm−2)、平均冠幅(m)、盖度(%)、平均胸径(cm)、平均高度(m)等指标度量群落结构,其中盖度为所有树木树冠的椭圆形面积和与占地面积的比值[18]。分别用树高、径阶来研究林分的垂直结构和径级结构[11]。
物种多样性以重要值作为多样性指数测定依据[18]。丰富度指数R=样地内物种的总数(S);Shannon-Wiener指数
$H = - \mathop \sum \limits_{i= 1}^S {P_i}\ln{P_i}$ 。Simpson指数$D= 1 - \mathop \sum \limits_{i = 1}^S P_i^2$ 。Pielou均匀度指数J =$ \left( { - \mathop \sum \limits_{i = 1}^S {P_i}\ln{P_i}} \right)/\ln S$ 。其中:S为样地内物种总数,Pi为样地内i种的重要值。群落相似性采用Jaccard相似性系数计算[19-20]:q=w/(a+b−w)。其中:q表示群落的相似性系数;w表示2个植物群落中的共同物种数;a和b分别表示群落A、B的物种总数。根据Jaccard相似性原理,当q为0~0.25时为极不相似,0.25~0.50时为中等不相似,0.50~0.75时为中等相似,0.75~1.00时为极相似[21-22]。
-
数据采用Excel 2016和SPSS 18.0软件进行统计分析与处理。
2.1. 样地设置及调查
2.2. 群落组成、多样性指数和群落相似性计算方法
2.3. 数据处理
-
由表2可知:研究区不同恢复年限的样地(P1~P6)中共有植物13科13属13种、14科14属14种、13科17属17种、18科23属24种、23科27属27种、22科28属31种。根据中国植被生活型分类方法,发现研究区植物中常绿针叶乔木和落叶针叶乔木出现概率极低,除P3和P6样地常绿阔叶乔木最多外,其余样地均以落叶阔叶乔木占优势地位,占比高于66.7%。所有样地的灌木全部为落叶阔叶灌木。草本多为多年生,只在P4和P6样地出现1年生草本;藤本多为落叶藤本,仅在P5样地出现1种常绿藤本。所有样地乔木层树种的占比依次为53.8%、35.7%、58.8%、33.3%、48.1%和45.2%;灌木层物种占比依次为23.1%、42.9%、29.4%、20.8%、29.6%和25.8%;草本层物种占比依次为15.4%、14.3%、11.8%、37.5%、18.5%和19.4%。不同恢复年限样地中藤本植物出现的频率均较低,其中P4和P5样地出现了3种,P6出现2种,其余为1种或0种。不同样地植物科的数量和种的数量基本一致,提示单科单属单种的概率极大。
样地 科 属 种 针叶乔木/种 阔叶乔木/种 落叶阔
叶灌木草本/种 藤本/种 常绿 落叶 常绿 落叶 1年生 多年生 常绿 落叶 P1 13 13 13 0 1 0 6 3 1 1 0 1 P2 14 14 14 1 0 1 4 5 1 1 0 1 P3 13 17 17 0 0 2 8 5 0 2 0 0 P4 18 23 24 1 0 1 6 5 3 5 0 3 P5 23 27 27 1 0 1 11 6 1 4 1 2 P6 22 28 31 1 0 2 11 6 3 6 0 2 总计 40 58 63 1 1 3 23 10 3 13 1 8 Table 2. Vegetation families, genera, species and life forms of different restoration years in karst area of Xichuan County
-
根据Jaccard相似性系数公式计算淅川县岩溶区不同恢复年限样地相似性。如表3所示:样地间的相似性系数为0.137~0.225,位于0~0.25区间,属于极不相似水平。P1与P6间相似性最小(0.137),P2与P5相似性最大(0.225),P6与其他样地的相似系数均小于其他恢复时间之间的相似系数。同时,随着恢复年限的增加,相似系数整体出现下降的趋势。
样地 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P1 1 P2 0.181 1 P3 0.167 0.205 1 P4 0.139 0.191 0.162 1 P5 0.189 0.225 0.209 0.177 1 P6 0.137 0.167 0.143 0.167 0.159 1 Table 3. Vegetation community similarity coefficient of different restoration years in karst area of Xichuan County
-
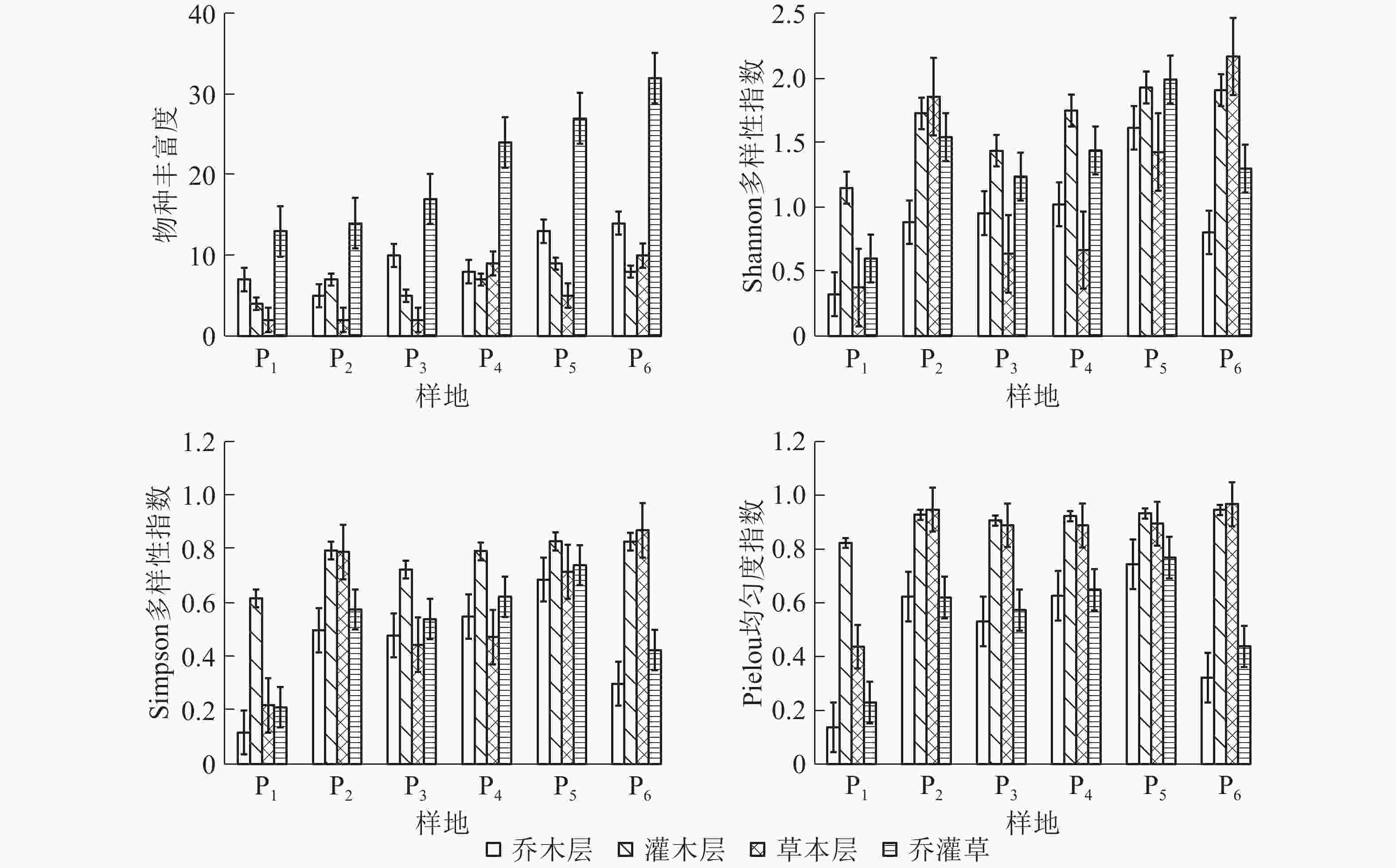
Shannon多样性指数反映了个体出现的不确定程度,Simpson多样性指数反映了生境中物种多样性的综合优势度[23]。由表4可以看出:不同样地各个层Shannon多样性指数不同。P5样地的群落、乔木层、灌木层Shannon多样性指数最大,分别为1.989、1.615和1.927,P1样地最低,分别为0.377、0.325和1.149。P6样地草本层Shannon多样性指数最大,为2.168,P1样地最小,为0.377。不同样地各个层Simpson多样性指数不同。P5样地的乔木层、灌木层和群落最大,分别为0.686、0.829、0.740,P1样地最小,分别为0.118、0.617、0.212。P6样地草本层Simpson多样性指数最大,为0.870,P1样地最小,为0.219。Pielou均匀度指数在乔木层中随着恢复时间增加而增加,以P5样地中最大,为0.744,而在P6(恢复70 a)样地中出现了下降;灌木层和草本层Pielou均匀度随着恢复年限的增加总体呈增加趋势,P1最低,为0.823和0.438,P6(恢复70 a)最大,为0.946和0.967。
样地 Shannon多样性指数(H) Simpson多样性指数(D) Pielou均匀度指数(J) 乔木层 灌木层 草本层 群落 乔木层 灌木层 草本层 群落 乔木层 灌木层 草本层 群落 P1 0.325 1.149 0.377 0.602 0.118 0.617 0.219 0.212 0.138 0.823 0.438 0.230 P2 0.883 1.726 1.856 1.542 0.498 0.795 0.789 0.576 0.624 0.928 0.947 0.621 P3 0.953 1.437 0.637 1.236 0.479 0.724 0.444 0.540 0.532 0.906 0.889 0.574 P4 1.022 1.748 0.666 1.44 0.549 0.792 0.473 0.623 0.627 0.923 0.888 0.650 P5 1.615 1.927 1.427 1.989 0.686 0.829 0.716 0.740 0.744 0.933 0.895 0.769 P6 0.804 1.906 2.168 1.299 0.299 0.828 0.870 0.425 0.322 0.946 0.967 0.439 Table 4. Species diversity in karst areas of xichuan county
由图1可以看出:各个层的物种丰富度(R)、Shannon多样性指数(H)、Simpson多样性指数(D)和Pelou均匀度指数(J)随着恢复年限增加没有明显的规律,具有一定的波动性,但总体趋势为缓慢上升。
-
对淅川县岩溶区不同恢复年限森林样地群落结构进行多重比较发现(表5):6个样地群落密度没有显著性差异;P1与P6样地的胸径、树高差异显著(P<0.05),其余样地间差异不显著;P6样地平均冠幅显著高于其他5个样地,而这5个样地间无显著差异;P6样地盖度显著高于P1、P2,其余样地间无显著性差异。群落结构5个指标(胸径、树高、冠幅、盖度、密度)变异系数存在差异,胸径变异较大的是P5和P6 (变异系数分别为51.6%和54.8%),其余样地的变异系数均低于50%;树高变异较大的是P5,密度变异系数最大的是P6;不同恢复年限样地的冠幅、盖度较稳定,变异系数为5.4%~41.0%。
样地 胸径 树高 冠幅 盖度 密度 平均值/cm 变异度/% 平均值/m 变异度/% 平均值/m 变异度% 平均值/% 变异度/% 平均值/(株·m−2) 变异度/% P1 9.09±0.25 a 38.2 8.78±0.20 a 41.8 3.79±0.08 a 38.6 2.49±0.60 a 41.0 0.194±0.003 a 3.0 P2 10.63±0.21 ab 38.2 11.30±0.22 ab 37.7 4.16±0.07 a 31.9 3.02±0.24 a 13.7 0.207±0.032 a 3.0 P3 10.94±0.27 ab 42.6 11.84±0.31 ab 45.5 4.42±0.09 a 34.9 2.87±0.29 ab 17.2 0.171±0.016 a 16.4 P4 11.49±0.25 ab 37.5 11.97±0.27 ab 38.6 3.88±0.08 a 36.2 2.08±0.18 ab 14.6 0.162±0.006 a 6.8 P5 10.99±0.30 ab 51.6 11.28±0.31 ab 52.3 3.93±0.08 a 38.7 2.78±0.09 ab 5.4 0.204±0.024 a 20.6 P6 13.33±0.41 b 54.8 14.39±0.27 b 38.6 5.11±0.10 b 34.0 4.00±0.84 b 36.1 0.181±0.060 a 60.0 说明:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05) Table 5. Community structure of different restoration time samples in karst area of Xichuan County
-
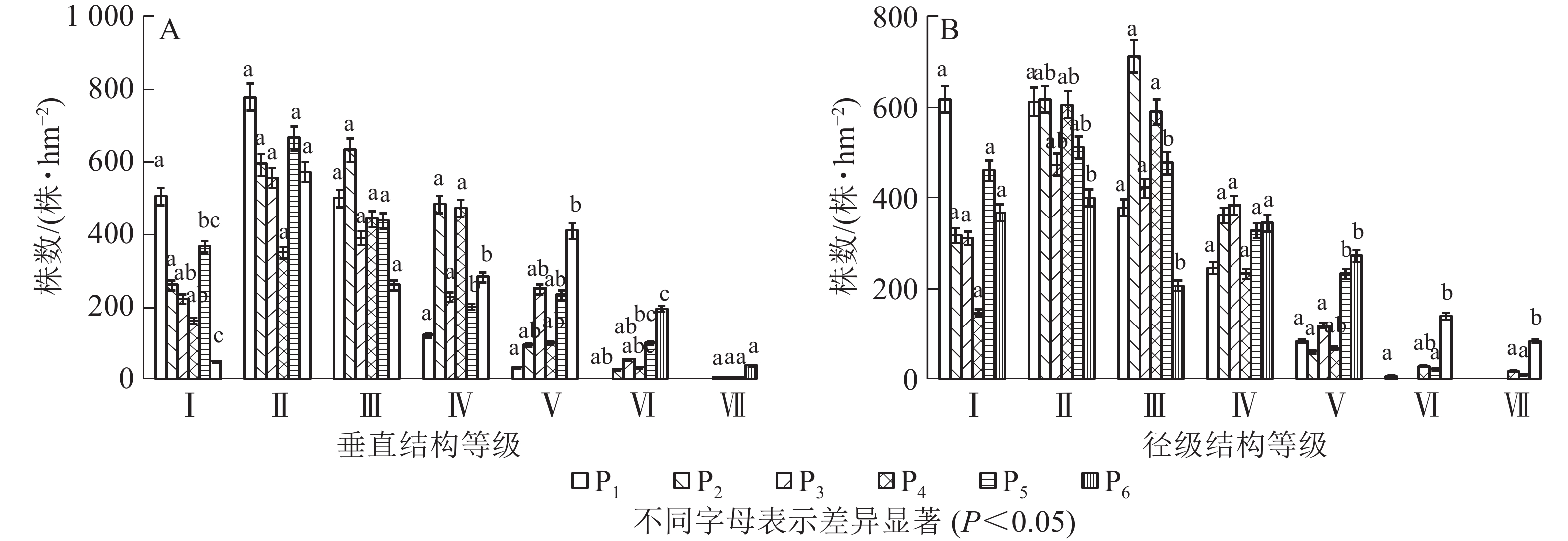
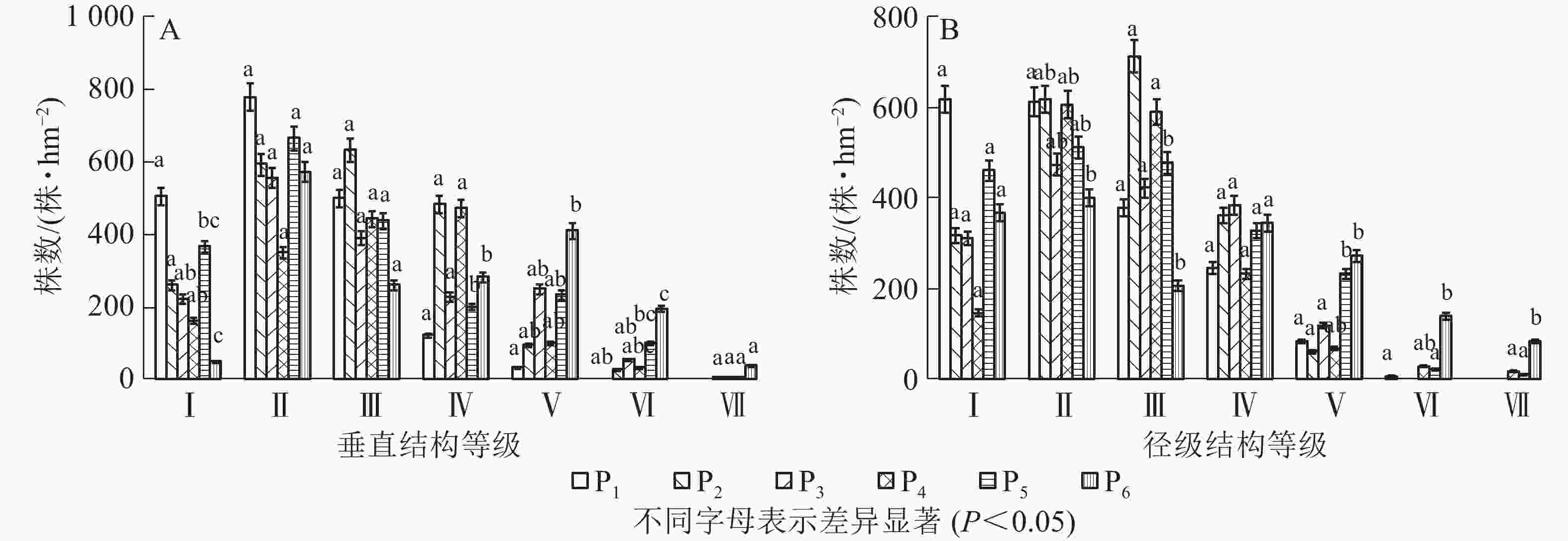
样地中灌木和草本对群落的结构特征影响不明显,所以只研究不同恢复年限样地乔木层垂直结构和径级结构。本研究将乔木的树高(m)分为7个等级:2~6 m 为Ⅰ级,6~10 m为Ⅱ级,10~14 m为Ⅲ级,14~18 m为Ⅳ级,18~22 m为Ⅴ,22~26 m为Ⅵ级,高于26 m为Ⅶ级。如图2A可知:P1样地乔木垂直结构只有Ⅴ级,P2样地有Ⅵ级,P3~P6有Ⅶ级;即恢复初期树高主要集中在前3级,随着恢复年限增加,树高在每一径级趋于均匀,当恢复年限达到70 a时,第Ⅰ级和第Ⅶ级树高的株数较少。调查发现:不同样地中树高大于18 m的密度分别为33、122、312、139、339和644株·hm−2。本研究将乔木的胸径(cm)分为7个等级:2~6 cm为Ⅰ级,6~10 cm 为Ⅱ级,10~14 cm 为Ⅲ级,14~18 cm为Ⅳ级,18~22 cm为Ⅴ级,22~26 cm 为Ⅵ级,大于26 cm为Ⅶ级。如图2B所示:P1样地乔木径级结构有Ⅵ级,P2和P3样地有Ⅴ级,P4~P6有Ⅶ级;P1样地中Ⅰ级径阶株数最多,P2样地中Ⅱ级、Ⅲ级径阶株数最多,P3样地中Ⅳ级径阶株数最多,Ⅴ级、Ⅵ级、Ⅶ级径阶中株数最多的是P6样地。调查发现:不同样地中胸径大于18 cm的密度分别为89、61、117、111、267和494株·hm−2。
3.1. 物种组成
3.2. 群落相似性系数
3.3. 物种多样性
3.4. 群落结构
3.4.1. 群落结构特征
3.4.2. 乔木层垂直结构和径级结构特征
-
本研究调查了18个天然次生林样地,总面积10 800 m2,共发现维管束植物63种,隶属40科58属。淅川县地处北亚热带向暖温带过度区域,多年年均降水量仅为804 mm,显著低于中国西南亚热带岩溶区。不同于西南亚热带地区的常绿落叶阔叶混交林,淅川县岩溶区天然次生林形成以栓皮栎占绝对优势的落叶阔叶林,其物种组成相对较为简单,丰富度较低,科、属、物种数均少于桂西南岩溶区(46科81属85种)[24]、贵州普定县岩溶区(89科218属365种)[11]和湘南岩溶区(63科131属173种)[25]。与淅川县周边非岩溶区相比发现:淅川县岩溶区维管束植物显著低于伏牛山自然保护区和秦岭地区,这可能与岩溶区土壤持水能力低有关,喀斯特岩溶区土壤瘠薄,保水能力差、渗透作用强烈,特殊的二元水文系统致使植物即使在雨季也可能受到干旱的威胁[26]。
岩溶区植被恢复的主要驱动力是植物多样性[27-28]。物种多样性是植被群落结构特征的属性之一[29],可表征生物群落结构的复杂性,是影响生态系统功能和服务发挥作用的关键因素之一,同时物种多样性是岩溶区植被恢复的重要特征之一[30-31],一般认为随着恢复时间的增加物种多样性指数和均匀度指数缓慢增加。本研究发现:不同恢复时间样地中物种多样性并不是线性上升,均出现先上升后下降的变化,但整体趋势为缓慢上升。随着恢复时间增加,群落物种多样性呈上升趋势,但出现单科单属单种的概率极大,这是因为随着恢复时间增加,群落覆盖度增加,为植物生长提供了适宜的环境。草本层Shannon多样性指数出现先上升后下降再上升的趋势;乔木层、灌木层和群落变化趋势一致。有研究认为Shannon多样性指数一般为1.5~3.5[32]。本研究中Shannon多样性指数整体偏低,乔木层、灌木层和群落Shannon多样性指数在恢复20 a最低(0.325、1.149、0.602),恢复53 a最高(1.615、1.927、1.989),说明恢复时间达53 a时,群落结构最好。Simpson多样性指数在恢复53 a的样地中最大,恢复20 a样地中最低;推测原因是岩溶区独特的水热条件和高度的景观异质性,土壤浅薄且不连续,基岩裸露率高,植物大多生长在岩石缝和岩石上,既要有石生性、耐旱性和喜钙性,又要有强壮而发达的根系。HILLEBRAND等[33]认为随着物种均匀度的提升,群落稳定性也将提高。本研究发现:随着恢复时间增加,Pielou均匀度指数呈上升趋势,群落稳定性提升。
河南省淅川县岩溶区随着恢复年限的增加群落形成了以栓皮栎为建群种的植被类型,群落科、属、种数随着恢复时间的增加而增加,物种组成分布趋于均匀状态,优势木重要值呈下降趋势。Jaccard相似性原理分析发现:不同恢复年限的群落样地间相似系数为0.137~0.225,为极为不相似。植物群落相似性指数的大小是植物群落之间异质性的量化,同时是植物群落生境条件异质性的体现[34]。虽然样地的建群种同为栓皮栎,但群落之间为极为不相似,说明不同恢复年限样地的共有植物较少,植物组成差异较大。这可能与岩溶区植物群落生境异质性较大有关,后续研究需要进一步增加大样地数量。本研究中乔木层的树高大都为6~14 m,胸径主要为6~14 cm,随着恢复年限的增加,乔木层的树高和胸径增加不明显。这主要是跟调查样地的土壤厚度有关,本次调查的样地土壤厚度仅为16~27 cm,土壤瘠薄,植物生长缓慢,且在后期所需的养分较多,浅薄的土层不能提供生长所需的养分。随着恢复年限的增加可以对其进行人工管理,采用修枝、间伐等措施促进林木生长。













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: