-
毛竹Phyllostachys edulis物理力学性能优异,原竹可代替建筑物中的钢承载结构[1],但竹壁厚度较小,不利于直接利用,将原竹进行碾压、机械疏解制成横向不断裂纵向松散的竹束,后对竹束进行胶合压制可得一定尺寸规格的材料——重组竹,重组竹的出现在一定程度上解决了竹材尺寸限制所带来的应用障碍。但由于重组竹压制过程压力较高,导致其密度较高,这在一定程度上限制了它的应用。对竹材进行浸泡处理,一方面可以使竹材软化,便于压制胶合;另一方面也可起到润胀的作用,这两者对重组竹的压制都有积极作用。对竹材的软化[2-3],可采用氢氧化钠水溶液、氨水、尿素水溶液、或直接水煮,都可取得较好的效果,但对竹材润胀化学试剂的选择,依然是一个待解决的问题。润胀是所有弹性材料都具有的特性,但由于材料与溶剂的不同,润胀效果往往具有较大差异。KEYLWERTH[4]用水浸泡木材后观察其润胀效果,发现温度的升高、抽提物的减少均有助于促进木材在水中的润胀,并首次提出了木材润胀激活能的概念;MANTANIS等[5]研究了木材在有机水溶液中的润胀效果,结果表明有机水溶液的pH值、摩尔质量与木材体积增大率的对数呈负相关;NAYER等[6]也验证了润胀激活能的高低、木材润胀效果的大小与氢键有着密不可分的关系。木材和竹材[7-9]同属木质纤维素材料,两者在化学成分、显微结构上相近,对木材的润胀研究可以为竹材提供借鉴。润胀的原因是纤维素和半纤维素分子中的羟基与水分子产生极性吸引,水分子进入纤维素的无定形区,使纤维素分子链之间距离增大,引起纤维变形[10]。研究竹材的润胀,介质的选择是关键。WEN等[11]利用碱性水溶液分离竹材中的碱溶性半纤维素,发现水溶液pH值是消除半纤维素与木质素间连接的关键因素,碱性水溶液是半纤维素与木质素分离的理想水溶液;KULA等[12]发现氯化锌具有良好的吸附作用,在纳米结构[13-16]中能够得到有效的分散,这意味着氯化锌水溶液对竹材的润胀效果较好。鉴于此,本研究使用碱性水溶液(碳酸钠、氢氧化钠)、弱酸性水溶液(氯化锌)以及去离子水分别对毛竹进行润胀,研究竹材在不同介质中的润胀效果,以期为竹材改性技术开发提供更多的理论支撑。
HTML
-
毛竹采自安徽省六安市金寨县,3年生,在胸高1.5 m处取长度为10 cm的圆环,去青皮和髓环后,制成尺寸为1 cm × 1 cm × 1 cm的试样,气干后,测量体积,封存待用。实验所用氯化锌、硝酸、氢氧化钠和无水碳酸钠均为分析纯。
-
分别配置1.0与0.5 mol·L-1的氢氧化钠水溶液与碳酸钠水溶液各250 mL,充分震荡,待水溶液变澄清且降至室温后将毛竹试样放入,3块·组-1;浸入去离子水作为对照。观察瓶中试样变化,记录竹块外观与水溶液颜色,1周后采集数据。
-
试样首先放入硝酸水溶液(0,100,150 g·L-1)中,水浴80 ℃处理20 min,取出后用去离子水漂洗至中性;之后分别置于100与500 g·L-1的氯化锌水溶液中。持续观察试样的变化,做好记录。
-
润胀效果以试样尺寸及体积增大率来表征,毛竹试样尺寸变化分为轴向、弦向、径向,以试样浸泡前后尺寸的变化求得变化率,体积增大率以浸泡前后试样的体积变化来表示,即体积增大率=(浸泡后的尺寸-浸泡前的尺寸)/浸泡前的尺寸。尺寸数据由螺旋测微器测量。浸泡后的试样通过电脑切片机(YD-335,益迪医疗设备有限公司,金华)切片,切片厚度为20 μm;使用透反射偏光显微镜(PLM,60XC,汇科仪器设备有限公司,天津)观察;另一部分试样在纯水中浸泡,饱和后切片标定特定的维管束及其附近的薄壁细胞,然后试样移入水溶液中,润胀完成后,找到标定的特定维管束及其附近薄壁细胞,计算浸泡纯水中与水溶液中之间,纤维鞘及薄壁细胞相同区域面积的变化。
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 实验方法
1.2.1. 氢氧化钠水溶液及碳酸钠水溶液对毛竹的润胀
1.2.2. 氯化锌水溶液对毛竹的润胀
1.2.3. 试样宏观及微观结构变化
-
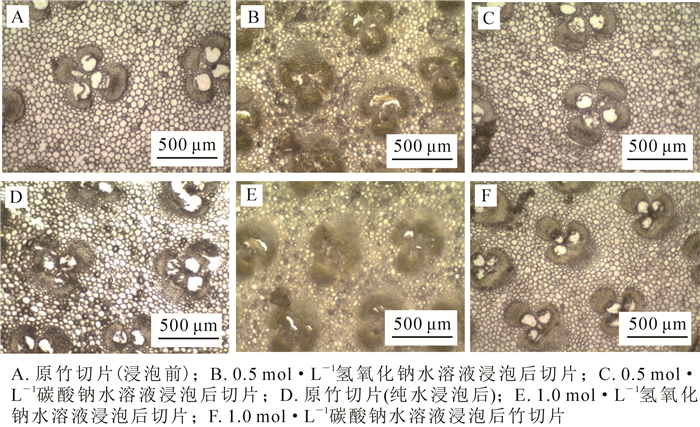
试样在氢氧化钠与碳酸钠2种碱性水溶液中的宏观润胀差异较大。氢氧化钠为强碱,浸泡毛竹试样时,水溶液颜色加深,试样边缘逐渐透明,外部维管束周围出现絮状物;碳酸钠为弱碱水溶液,浸泡毛竹试样时,维管束颜色变深,水溶液颜色加深程度小于氢氧化钠。从试样外观来看,氢氧化钠与碳酸钠水溶液对毛竹都具有明显润胀效果。由图 1可知:随着碳酸钠物质的量浓度的上升,毛竹弦向、径向、体积都呈明显的增大趋势;而在氢氧化钠水溶液中,试样尺寸先变大,再减小,当氢氧化钠为0.5 mol·L-1时达最大值。对比毛竹试样在轴向、径向、弦向的尺寸变化发现,无论是在氢氧化钠水溶液还是在碳酸钠水溶液中,毛竹试样的径向尺寸变化最大,轴向尺寸变化率最小。毛竹是由纤维素作为骨架物质,木质素和半纤维素作为填充物质组成的复合结构,浸泡在氢氧化钠水溶液中时,水溶液中的氢氧根离子能够与木质素中的酚羟基发生反应,促使被破坏的木质素流出细胞壁,流出的木质素与抽提物在氢氧化钠水溶液中会产生絮凝反应而在维管束周围生成絮状物[17];另一方面,木质素流出也使纤维素与半纤维素向外扩张的限制被减弱,细胞壁被润胀的程度增大。相对于低浓度氢氧化钠水溶液,高浓度水溶液中含有较多的氢氧根离子,絮凝反应过多,所产生的絮状物堵塞毛竹的孔隙而影响水溶液的渗透,限制了竹材的润胀[13]。碳酸钠水溶液呈弱碱性,低浓度的碳酸钠水溶液中氢氧根离子较低,纤维素与半纤维素在弱碱性条件下的反应较为温和,在润胀的同时,絮凝反应也相对高浓度较弱,因此具有较好的润胀效果。
-
图 2为碱性水溶液与去离子水浸泡下毛竹试样的切面构造。浸泡前,原竹切片(图 2A)维管束明显,导管孔清晰、规整,纤维排列整齐,薄壁细胞细胞壁较薄(厚度为1.002 μm),整体呈灰色;浸泡后原竹切片(图 2D)与浸泡前(图 2A)无明显差别。氢氧化钠水溶液浸泡对毛竹试样内部微观构造的影响较大(图 2B和图 2E),薄壁细胞细胞壁增厚(厚度为1.605 μm),纤维呈现堆叠褶皱,维管束边缘变模糊,导管孔径减小明显,整体呈现浅黄色,浓度越高,这种变化越明显,说明氢氧化钠水溶液浸泡对细胞壁的结构破坏较大。陈红[9]与张双燕[18]研究认为:氢氧化钠对纤维中的半纤维素有较强的降解作用,被降解半纤维素后的纤维拉伸强度与模量都呈不同程度的下降,因此推测毛竹试样被氢氧化钠润胀后,力学性能受到了影响。而作为弱碱性的碳酸钠水溶液对毛竹试样(图 2C和图 2F)微观结构的影响则并不明显。
-
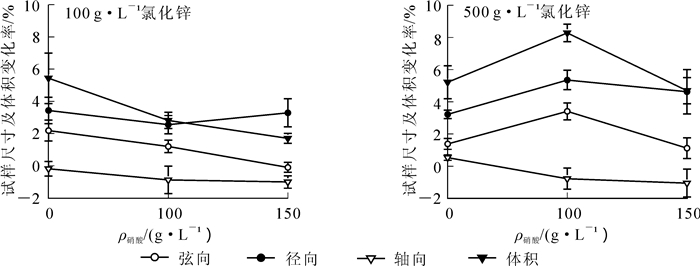
氯化锌水溶液为弱酸性,因其水溶液密度较大,硝酸预处理可以使试样较易浸没在水溶液中。毛竹试样在氯化锌水溶液中浸泡时,表面也会产生絮状物,但薄壁细胞与维管束分界线变得明显,水溶液颜色无明显变化,但经硝酸预处理后,水溶液颜色随浸泡日期的延长逐渐变深,高浓度硝酸预处理后此现象更明显。由图 3可知:氯化锌水溶液对毛竹试样具有一定的润胀效果,无预处理情况下,低浓度与高浓度氯化锌水溶液对毛竹试样的润胀效果相近,弦向与径向尺寸变化较大,轴向尺寸变化很小,与去离子水对毛竹试样的润胀效果相近;100 g·L-1硝酸水溶液预处理使得高浓度氯化锌水溶液对于毛竹材的润胀有显著提升,而低浓度氯化锌水溶液的润胀效果变差;150 g·L-1硝酸水溶液预处理使得氯化锌水溶液的润胀效果有明显的抑制作用。主要原因是:氯化锌水溶液与毛竹试样表面接触时,试样表面的羟基、酚羟基、羰基等极易与锌离子络合[19]生成不溶的絮状物,堵塞试样表面的孔隙,限制了水溶液离子的进入,只有小分子的水可缓慢渗透;水溶液无色也表明细胞内木质素以及抽提物并未溶出。100 g·L-1硝酸水溶液的预处理使得试样细胞壁内层遭到破坏,浸泡时有较多的黄色物质溶出,表明木质素与抽提物溶出较多,虽然纤维素与半纤维素润胀限制被解除,因细胞壁内壁木质素含量较高,力学损失较多,细胞壁内壁应力减小,这导致润胀过程向细胞腔内发展,宏观表现为体积变化不明显[13];高浓度的氯化锌水溶液由于锌离子浓度较高,絮凝效果更加明显。150 g·L-1硝酸水溶液预处理,对细胞壁内层的破坏更明显,对应组分试样的润胀效果下降,细胞溶出物过多,润胀效果不佳。
-
由图 4可以看出:100 g·L-1氯化锌水溶液浸泡后,试样薄壁细胞的细胞壁增厚较为明显,厚度为1.589 μm,维管束内导管孔径减小,整体颜色加深(图 4A);500 g·L-1氯化锌水溶液浸泡后,毛竹试样(图 4D)情况类似于图 4A,细胞壁厚增加更明显。100 g·L-1硝酸水溶液预处理下,毛竹试样在500 g·L-1氯化锌水溶液中薄壁细胞的细胞壁增厚,厚度为1.316 μm,维管束变黑明显,纤维排布密集(图 4E);而在100 g·L-1氯化锌水溶液中,毛竹试样薄壁细胞的细胞壁增厚更明显,厚度为1.724 μm,维管束结构也更清晰,整体呈现黄色,氯化锌水溶液浓度越高,水溶液颜色越深(图 4B)。150 g·L-1硝酸预处理下,毛竹试样在500 g·L-1氯化锌水溶液中薄壁细胞的细胞壁增厚幅度减小,厚度为1.081 μm,维管束易破碎(图 4F);而在100 g·L-1氯化锌水溶液中,毛竹试样薄壁细胞的细胞壁变化不明显,厚度为1.095 μm,维管束结构很清晰(图 4C)。
-
在介质对竹材润胀的过程中,发生变化的主要是细胞壁物质,毛竹内纤维和薄壁细胞结构及细胞壁密度差异很大,并且处理方式会对细胞壁的结构产生影响。基于此,对毛竹的维管束及薄壁细胞分别划定区域,计算处理前(浸泡于纯水中)和处理后(浸泡于水溶液后)特定区域的面积变化,探究促使毛竹体积润胀的主要物质。图 5为划定区域内纤维和薄壁细胞在润胀前后面积的变化,可知润胀前后,纤维与薄壁细胞分布形状基本维持不变。
由图 6可知:不同介质对毛竹润胀后,划定区域的纤维与薄壁细胞的面积变化差别较大。1.0 mol·L-1碳酸钠水溶液润胀效果最明显,纤维区域和薄壁细胞区域的面积增大率分别为14.55%和1.37%。0.5 mol·L-1氢氧化钠水溶液的润胀效果次之,划定区域的面积增大率分别为13.41%和0.65%。500 g·L-1氯化锌水溶液浸泡(100 g·L-1硝酸水溶液预处理)润胀效果较差,划定区域的面积增大率分别为5.40%和0.53%。参考图 1和图 3可知:1.0 mol·L-1碳酸钠水溶液与0.5 mol·L-1氢氧化钠水溶液浸泡后的竹材试样体积增大率分别为10.60%与9.69%,500 g·L-1氯化锌水溶液浸泡(100 g·L-1硝酸水溶液预处理)后的竹材试样体积增大率为7.98%,与纤维区域与薄壁细胞区域面积变化率相比,差异较大。

Figure 6. Increasing rate of distribution area of fiber and parenchyma cell before and after swelling
对比纤维区域和薄壁细胞区域的面积变化,纤维的分布面积增幅较大,薄壁细胞分布面积变化较小,其中碳酸钠水溶液浸泡后薄壁细胞的分布面积增大要略高于氢氧化钠水溶液与氯化锌水溶液。综上所述,润胀后纤维鞘分布面积的变化较大,而薄壁细胞分布面积变化相对较小,毛竹润胀后体积变化的主要原因是纤维区域面积的变化。主要是因为在润胀的过程中,浸泡的水溶液进入细胞壁内部,破坏内部氢键[5],与细胞壁发生一系列复杂的物理化学反应,充实细胞壁,以此达到润胀的目的。由于纤维细胞壁较厚,基本密度较大,导致其在润胀过程中润胀率较大,宏观表现为纤维鞘分布面积的增大。
2.1. 碱性水溶液对毛竹的润胀效果
2.1.1. 试样尺寸及体积变化
2.1.2. 试样解剖特征变化
2.2. 酸性水溶液对毛竹材的润胀效果
2.2.1. 试样尺寸及体积变化
2.2.2. 试样解剖特征变化
2.3. 水溶液润胀对纤维鞘和薄壁细胞的影响
-
氢氧化钠水溶液与碳酸钠水溶液对毛竹试样都具有良好的润胀效果,1.0 mol·L-1碳酸钠水溶液对毛竹试样的润胀效果最佳,且对毛竹微观结构的影响较小,相反,氢氧化钠水溶液会破坏毛竹微观结构。硝酸水溶液预处理毛竹试样可增强氯化锌水溶液对毛竹试样的润胀效果,氯化锌水溶液对毛竹试样的润胀效果较为明显,对微观结构的影响也较小。水溶液润胀前后纤维区域和薄壁细胞区域面积变化明显,其中纤维区域面积的变化较大,毛竹试样润胀后体积变化的主要原因是纤维区域面积的变化。















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: