2019 Vol. 36, No. 1
column
2019, 36(1): 1-6.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.001
Abstract:
The dream of agricultural power is the strong support of the Chinese dream. China's higher agricultural education stands at an important historical node and is in a new period of historical opportunity. It needs us to think about how to bulid a higher agricultural education which is satisfactory to the people. This requires us to further emancipate our mind and change the previous education concepts that focus on serving the industrial economy, cultivating professional and technical personnel. We also need to deepen the reform of education and explore the way to realize the comprehensive development of Agricultural Students and the value of life through four fundamental changes.
The dream of agricultural power is the strong support of the Chinese dream. China's higher agricultural education stands at an important historical node and is in a new period of historical opportunity. It needs us to think about how to bulid a higher agricultural education which is satisfactory to the people. This requires us to further emancipate our mind and change the previous education concepts that focus on serving the industrial economy, cultivating professional and technical personnel. We also need to deepen the reform of education and explore the way to realize the comprehensive development of Agricultural Students and the value of life through four fundamental changes.
2019, 36(1): 7-13.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.002
Abstract:
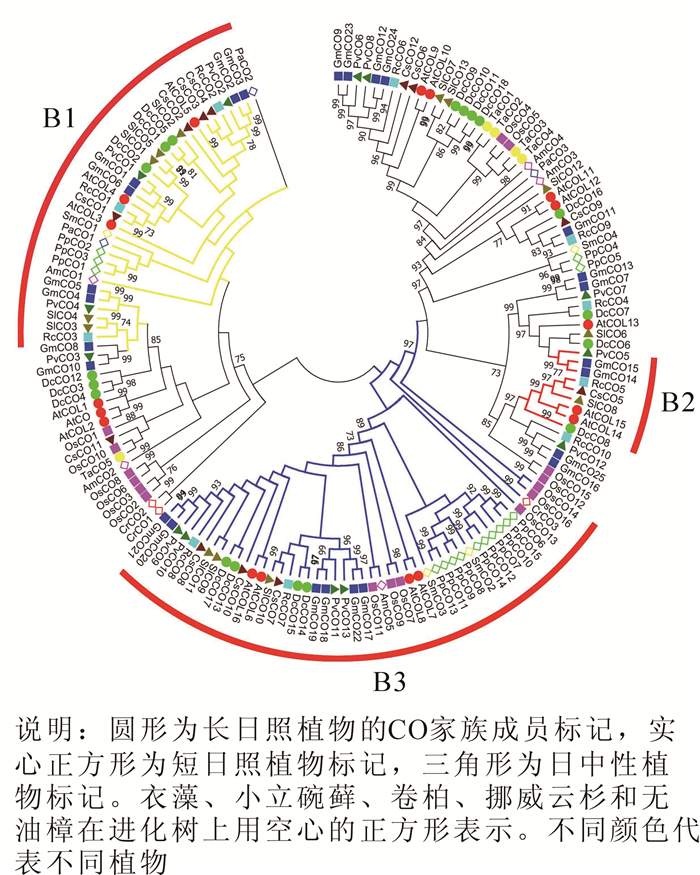
CONSTANS(CO), an essential element for monitoring the duration of a day and an important gene responding to photoperiod regulation, can transform light and biological clock signals into flowering signals, as well as activate the expression of downstream genes (FT), which induces plant flowering. However, their evolutionary history and patterns have not been examined systematically. In this study, a total of 14 species, whose whole-genomes have been sequenced, were selected. Then, via the analyses of bioinformatics, the CO family was studied in regards to exon-intron structure, gene duplication, and differential expression. Results showed 159 members in the CO family. For each plant species, the CO family existed in the form of multiple copies. Almost every copy contained 2 to 4 exons indicating diversity in the evolution process. The synteny analysis showed that expansion of duplicate genes in the CO family was related to genome duplication. In addition, the gene differential expression analysis showed that CO members were expressed in roots, flag leaves, flowers, and seeds of rice (Oryza sativa). Especially, OsCO3 was up-regulated in the process of floral development; whereas, the expression of OsCO7 was down-regulated. This suggested that members of the CO gene family played different roles in rice.
CONSTANS(CO), an essential element for monitoring the duration of a day and an important gene responding to photoperiod regulation, can transform light and biological clock signals into flowering signals, as well as activate the expression of downstream genes (FT), which induces plant flowering. However, their evolutionary history and patterns have not been examined systematically. In this study, a total of 14 species, whose whole-genomes have been sequenced, were selected. Then, via the analyses of bioinformatics, the CO family was studied in regards to exon-intron structure, gene duplication, and differential expression. Results showed 159 members in the CO family. For each plant species, the CO family existed in the form of multiple copies. Almost every copy contained 2 to 4 exons indicating diversity in the evolution process. The synteny analysis showed that expansion of duplicate genes in the CO family was related to genome duplication. In addition, the gene differential expression analysis showed that CO members were expressed in roots, flag leaves, flowers, and seeds of rice (Oryza sativa). Especially, OsCO3 was up-regulated in the process of floral development; whereas, the expression of OsCO7 was down-regulated. This suggested that members of the CO gene family played different roles in rice.
2019, 36(1): 14-20.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.003
Abstract:
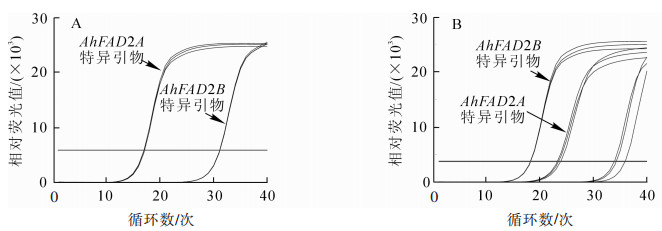
The fatty acid desaturase 2 (FAD2) in peanut (Arachis hypogaea), a crucial enzyme for controlling the ratio of oleic acid to linoleic acid (O/L) in the seed, with presently two FAD2-encoding genes (AhFAD2A and AhFAD2B) has unknown spatial and temporal expression patterns. To determine the expression patterns of AhFAD2A and AhFAD2B in seven different tissues (root, stem, leaf, flower, and seeds at 20, 40, and 60 d after pollination) of two distinct cultivars, 'Shanhua 15' with an O/L of approximately 1.0 and a high-oleate peanut mutant, were analyzed. In doing so, real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed using different pairs of specific primers, suitable for distinguishing AhFAD2A from AhFAD2B, which were designed based on the difference in the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) sequences of these two genes. Results showed that AhFAD2A and AhFAD2B were expressed in all the tissues tested. Among the three developmental stages of the peanut pods for the two cultivars, the highest expression of AhFAD2A and AhFAD2B occurred 40 d after pollination. In addition, the expression of AhFAD2B was shown to be much higher than that of AhFAD2A in the pods of 'Shanhua 15' than the high-oleate peanut mutant. Thus, the AhFAD2B may play a more important regulatory role in the conversion of oleic acid to linoleic acid in peanut seed compared to AhFAD2A, and possibly the expression level of the FAD2 genes at the 40 d stage may exert a large effect on the final ratio of O/L in peanut seed oil.
The fatty acid desaturase 2 (FAD2) in peanut (Arachis hypogaea), a crucial enzyme for controlling the ratio of oleic acid to linoleic acid (O/L) in the seed, with presently two FAD2-encoding genes (AhFAD2A and AhFAD2B) has unknown spatial and temporal expression patterns. To determine the expression patterns of AhFAD2A and AhFAD2B in seven different tissues (root, stem, leaf, flower, and seeds at 20, 40, and 60 d after pollination) of two distinct cultivars, 'Shanhua 15' with an O/L of approximately 1.0 and a high-oleate peanut mutant, were analyzed. In doing so, real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed using different pairs of specific primers, suitable for distinguishing AhFAD2A from AhFAD2B, which were designed based on the difference in the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) sequences of these two genes. Results showed that AhFAD2A and AhFAD2B were expressed in all the tissues tested. Among the three developmental stages of the peanut pods for the two cultivars, the highest expression of AhFAD2A and AhFAD2B occurred 40 d after pollination. In addition, the expression of AhFAD2B was shown to be much higher than that of AhFAD2A in the pods of 'Shanhua 15' than the high-oleate peanut mutant. Thus, the AhFAD2B may play a more important regulatory role in the conversion of oleic acid to linoleic acid in peanut seed compared to AhFAD2A, and possibly the expression level of the FAD2 genes at the 40 d stage may exert a large effect on the final ratio of O/L in peanut seed oil.
2019, 36(1): 21-30.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.004
Abstract:
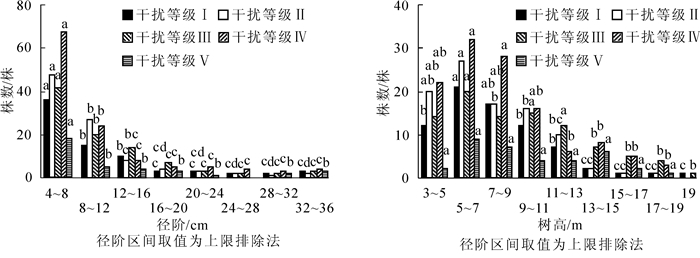
To provide scientific evidence for vegetative recovery and biodiversity protection of evergreen broadleaved secondary forests, changes in stand structure and tree species diversity across a disturbance gradient of evergreen broadleaved secondary forests in Jiangle Forest Farm, Fujian Province were studied. The representative locations with similar site condition were selected through the field surveys, then a total of 25(0.04-0.12 hm2) permanent sample plots were set using typical sampling methods for evergreen broadleaf secondary forests. Five disturbance gradients (Ⅰ-Ⅴ with Ⅴ having the most disturbance) were assigned based on the relative value of major disturbance indicators. Then using ANOVA and LSD multiple comparision to analyze changes in stand structure and species diversity along a disturbance gradient. Results showed that for the five disturbance gradients, individual tree diameter conformed to an inverse J-shape curve. The individual number of Ⅴ disturbance gradient was significantly lower than other disturbance gradients (P=0.022) indicating the lowest capacity of natural regeneration and productivity. The individual tree heights of Ⅰ-Ⅳ disturbance gradients conformed to a normal curve; whereas, the Ⅴ disturbance gradient conformed to a bimodal curve indicating the lower stability in the forests vertical structure. With an increasing disturbance gradient, uniform angle indexes(P=0.045) increased, but neighborhood comparison indexes(P=0.039) and mingling indexes(P=0.017) decreased. The alpha diversity measures declined(P < 0.05) along the disturbance gradient as dominance increased(P=0.000). In addition, the similarity in species composition between each pair of disturbed forests was generally low (Jaccard's similarity index < 47%). With an increase in disturbance gradient, average DBH, average tree height, and alpha diversity measures decreased(P < 0.05), but the dominance index increased(P=0.000). Overall, as the disturbance gradient increased in the evergreen broadleaf secondary forests, the diversity index and stability of the forest structure decreased, which was not conducive to vegetative recovery and species diversity.
To provide scientific evidence for vegetative recovery and biodiversity protection of evergreen broadleaved secondary forests, changes in stand structure and tree species diversity across a disturbance gradient of evergreen broadleaved secondary forests in Jiangle Forest Farm, Fujian Province were studied. The representative locations with similar site condition were selected through the field surveys, then a total of 25(0.04-0.12 hm2) permanent sample plots were set using typical sampling methods for evergreen broadleaf secondary forests. Five disturbance gradients (Ⅰ-Ⅴ with Ⅴ having the most disturbance) were assigned based on the relative value of major disturbance indicators. Then using ANOVA and LSD multiple comparision to analyze changes in stand structure and species diversity along a disturbance gradient. Results showed that for the five disturbance gradients, individual tree diameter conformed to an inverse J-shape curve. The individual number of Ⅴ disturbance gradient was significantly lower than other disturbance gradients (P=0.022) indicating the lowest capacity of natural regeneration and productivity. The individual tree heights of Ⅰ-Ⅳ disturbance gradients conformed to a normal curve; whereas, the Ⅴ disturbance gradient conformed to a bimodal curve indicating the lower stability in the forests vertical structure. With an increasing disturbance gradient, uniform angle indexes(P=0.045) increased, but neighborhood comparison indexes(P=0.039) and mingling indexes(P=0.017) decreased. The alpha diversity measures declined(P < 0.05) along the disturbance gradient as dominance increased(P=0.000). In addition, the similarity in species composition between each pair of disturbed forests was generally low (Jaccard's similarity index < 47%). With an increase in disturbance gradient, average DBH, average tree height, and alpha diversity measures decreased(P < 0.05), but the dominance index increased(P=0.000). Overall, as the disturbance gradient increased in the evergreen broadleaf secondary forests, the diversity index and stability of the forest structure decreased, which was not conducive to vegetative recovery and species diversity.
2019, 36(1): 31-37.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.005
Abstract:
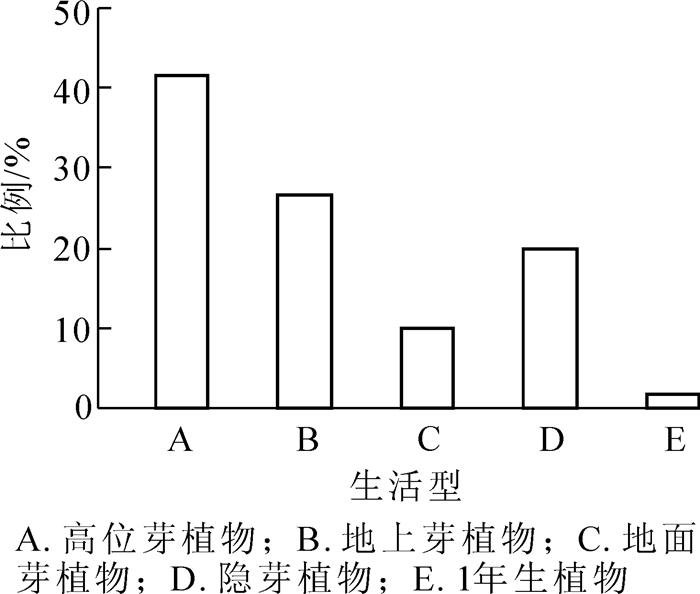
Ostrya multinervis is an endangered species to China. To understand the O. multinervis plant community's structural characteristics and species diversity so as to protect this rare and endangered plant. A survey of the community structure and species diversity of O. multinervis was conducted through quadrat sampling at Shiyang Forest Farm, Wencheng County, Zhejiang Province. Using permanent plots and the technique of examining every individual, all trees in quadrats established in the community to quantify the community structural characteristics were identified and measured. Analysis included the Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes. Results showed 40 families, 52 genera, and 60 species of vascular plants with eight species of pteridophyte belonging to seven genera in six families, one species of gymnosperms belonging to one genus in one family, and 51 species of angiosperms belonging to 44 genera in 33 families. The vertical structure was composed of three layers:tree layer, shrub layer, and herb layer, in which O. multinervis was the dominant species in the tree layer, Illicium lanceolatum was the dominant species in the shrub layer, and Diplopterygium glaucum was the dominant species in the herb layer. Overall, phanerophytes accounted for the greatest number (41.7%). Species richness for the shrub layer was the largest of the three communities with the Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes larger than herb and tree layers(P < 0.05). Tree height distribution in the tree layer for whole trees was relatively uniform, the diameter order was an inverse J type species distribution, and tree height and diameter structure showed near normal distributions for O. multinervis. In summary, O. multinervis communities had a high species diversity and community stability, but were endangered by a lack of young individuals which could be overcome with closure of hillsides to facilitate afforestation, strengthening of research on highly efficient breeding technologies for O. multinervis, and implementation of artificial rearing measures to ensure a normal development of the population.
Ostrya multinervis is an endangered species to China. To understand the O. multinervis plant community's structural characteristics and species diversity so as to protect this rare and endangered plant. A survey of the community structure and species diversity of O. multinervis was conducted through quadrat sampling at Shiyang Forest Farm, Wencheng County, Zhejiang Province. Using permanent plots and the technique of examining every individual, all trees in quadrats established in the community to quantify the community structural characteristics were identified and measured. Analysis included the Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes. Results showed 40 families, 52 genera, and 60 species of vascular plants with eight species of pteridophyte belonging to seven genera in six families, one species of gymnosperms belonging to one genus in one family, and 51 species of angiosperms belonging to 44 genera in 33 families. The vertical structure was composed of three layers:tree layer, shrub layer, and herb layer, in which O. multinervis was the dominant species in the tree layer, Illicium lanceolatum was the dominant species in the shrub layer, and Diplopterygium glaucum was the dominant species in the herb layer. Overall, phanerophytes accounted for the greatest number (41.7%). Species richness for the shrub layer was the largest of the three communities with the Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes larger than herb and tree layers(P < 0.05). Tree height distribution in the tree layer for whole trees was relatively uniform, the diameter order was an inverse J type species distribution, and tree height and diameter structure showed near normal distributions for O. multinervis. In summary, O. multinervis communities had a high species diversity and community stability, but were endangered by a lack of young individuals which could be overcome with closure of hillsides to facilitate afforestation, strengthening of research on highly efficient breeding technologies for O. multinervis, and implementation of artificial rearing measures to ensure a normal development of the population.
2019, 36(1): 38-46.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.006
Abstract:
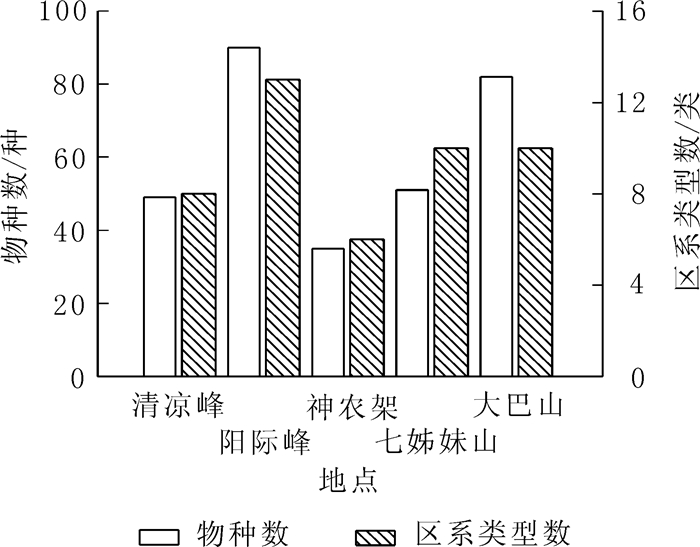
This research collected 210 liverworts specimens in the Qizimei Mountain National Nature Reserve. A total of 51 species belonging to 33 genera in 26 families, were identified and recorded in the research site, among which 15 species were new records for Hubei Province. The family Haplomitriaceae and two genera Metacalypogeia and Haplomitrium were also new for Hubei. The floristic elements of liverworts in the research site were complex, belonging to 10 different distribution elements. North temperate and Eastern Asian were two main elements. Comparison with other nature reserves in species similarity showed a highest similarity between the Qizimei and Qingliangfeng, a lowest value with Shiwandashan natural reserve. The geographical proximity resulted in a high similarity of floristic elements. Regional climate environment could affect plant species and floristic features. The study provided basic information of species diversity, floristic study, and protection of bryophytes for the Qizimei Mountain National Nature Reserve and Hubei Province.
This research collected 210 liverworts specimens in the Qizimei Mountain National Nature Reserve. A total of 51 species belonging to 33 genera in 26 families, were identified and recorded in the research site, among which 15 species were new records for Hubei Province. The family Haplomitriaceae and two genera Metacalypogeia and Haplomitrium were also new for Hubei. The floristic elements of liverworts in the research site were complex, belonging to 10 different distribution elements. North temperate and Eastern Asian were two main elements. Comparison with other nature reserves in species similarity showed a highest similarity between the Qizimei and Qingliangfeng, a lowest value with Shiwandashan natural reserve. The geographical proximity resulted in a high similarity of floristic elements. Regional climate environment could affect plant species and floristic features. The study provided basic information of species diversity, floristic study, and protection of bryophytes for the Qizimei Mountain National Nature Reserve and Hubei Province.
2019, 36(1): 47-53.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.007
Abstract:
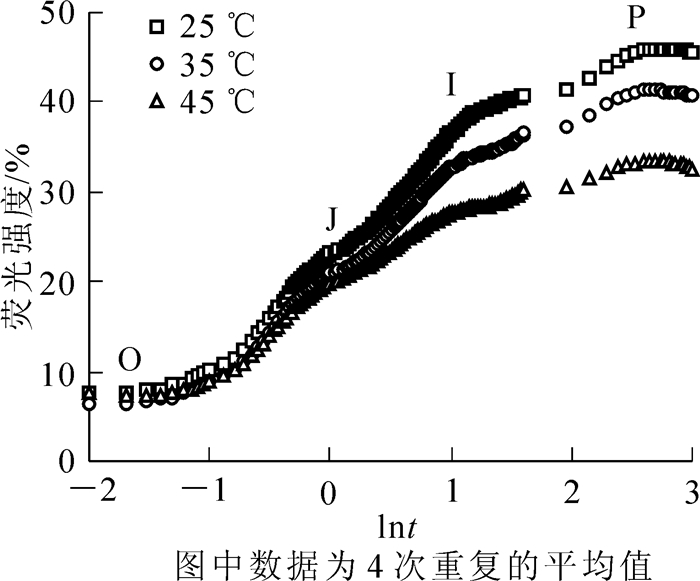
Photosynthesis is the most sensitive physiological process for environmental variation. To uncover any detriment of high temperature from photosynthesis on Cinnamomum camphora, the effects of high temperature stress on chlorophyll fluorescence transients, gas exchange rate, and water use efficiency in the plants treated with high temperature at 25℃ (the control), 35℃ and 45℃, respectively, were studied, and one-way analyses of variance was performed to analyze the effects of high temperature. Results showed that fluorescence intensity from O to P point in chlorophyll fluorescence transients in C. camphora declined as temperature increased. Fluorescence transient parameters significantly decreased by 21.7% (P < 0.01) in absorption flux per reaction center, 17.6% (P < 0.01) in trapped energy flux per reaction center, 38.8% (P < 0.01) in electron transport flux per reaction center, 60.2% (P < 0.01) in performance index based on absorption, and 26.9% (P < 0.01) in driving force based on absorption at 45℃. Compared to the control, dissipated energy flux per reaction center significantly increased by 13.5% (P < 0.05) and 78.4% (P < 0.01), respectively, under high temperature at 35 and 45℃. In addition, the photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, transpiration rate, and water use efficiency declined at 35 and 45℃. The maximum photosynthetic rate significantly reduced by 16.0% (P < 0.05) and 44.6% (P < 0.01), respectively, at 35 and 45℃. Therefore, high temperature stress reduced C. camphora photosystem Ⅱ efficiency by reducing light energy absorption, quantum yield, and electron transportation as well as by increasing the absorbed light energy dissipated as heat, which resulted in an assimilatory power reduction and photosynthetic rate decline.
Photosynthesis is the most sensitive physiological process for environmental variation. To uncover any detriment of high temperature from photosynthesis on Cinnamomum camphora, the effects of high temperature stress on chlorophyll fluorescence transients, gas exchange rate, and water use efficiency in the plants treated with high temperature at 25℃ (the control), 35℃ and 45℃, respectively, were studied, and one-way analyses of variance was performed to analyze the effects of high temperature. Results showed that fluorescence intensity from O to P point in chlorophyll fluorescence transients in C. camphora declined as temperature increased. Fluorescence transient parameters significantly decreased by 21.7% (P < 0.01) in absorption flux per reaction center, 17.6% (P < 0.01) in trapped energy flux per reaction center, 38.8% (P < 0.01) in electron transport flux per reaction center, 60.2% (P < 0.01) in performance index based on absorption, and 26.9% (P < 0.01) in driving force based on absorption at 45℃. Compared to the control, dissipated energy flux per reaction center significantly increased by 13.5% (P < 0.05) and 78.4% (P < 0.01), respectively, under high temperature at 35 and 45℃. In addition, the photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, transpiration rate, and water use efficiency declined at 35 and 45℃. The maximum photosynthetic rate significantly reduced by 16.0% (P < 0.05) and 44.6% (P < 0.01), respectively, at 35 and 45℃. Therefore, high temperature stress reduced C. camphora photosystem Ⅱ efficiency by reducing light energy absorption, quantum yield, and electron transportation as well as by increasing the absorbed light energy dissipated as heat, which resulted in an assimilatory power reduction and photosynthetic rate decline.
2019, 36(1): 54-61.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.008
Abstract:
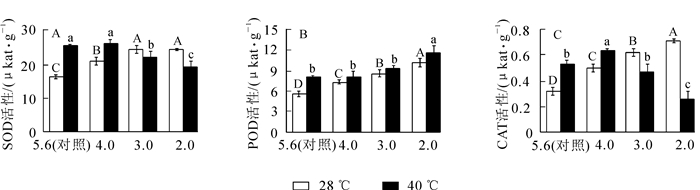
To reveal the physiological and biochemical mechanisms of Osmanthus fragrans, regarding the resistance to acid rain and heat stress, this study used the leaves of O. fragrans (cultivar 'Hangzhou Huang') as the material. Plants grown in pots treated with simulated acid rain stress[pH 5.6(ck), 4.0, 3.0, and 2.0] and heat stress (40℃) treatments were analyzed. Photosynthetic pigment content, active oxygen (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA) content, antioxidant enzyme activity, and non-structural carbon changes in composition and content were measured. Results showed that (1) generally, the contents of chlorophyll a (Chl a), total chlorophyll(Chl t), and the ratio of Chl a/b ratio decreased after acid rain and heat as individual stresses. After the co-stresses of acid rain and heat, there is significant decreases (P < 0.05) of Chl a (27.7%), Chl t (23.8%), and the Chl a/b (19.5%) compared to the control of pH 2.0. (2) ROS and MDA increased significantly (P < 0.05) after acid rain or heat as individual stress. After co-stresses, the content of O2·- and MDA increased significantly (P < 0.05) as pH decreased, and increased 158.3% (O2·-) and 142.0% (MDA) compared to the control of pH 2.0. The content of H2O2 significantly increased (P < 0.05) and reached a maximum of 180.0% compared to the control of pH 3.0. (3) Superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT) activities increased significantly (P < 0.05) with individual acid rain or heat stresses, and the three enzymes cooperated to resist stress damage. After co-stresses, the SOD and CAT activities firstly increased and then decreased; whereas, POD still maintained a high activity and increased 107.3% compared to the control of pH 2.0. (4) After acid rain stress, the contents of glucose and fructose were relatively stable, but sucrose and starch decreased significantly (P < 0.05). Non-structural carbon contents decreased significantly after heat stress (P < 0.05). After co-stresses, non-structural carbon content decreased even further:among them, fructose, sucrose, and starch content decreased 38.1% -41.6% (P < 0.05); and glucose content decreased 22.4% compared to the control of pH 2.0(P < 0.05). The results indicate that O. fragrans 'Hangzhou Huang' could reduce the damages of acid rain and heat stresses by regulating activities of protective enzymes and non-structural carbon metabolism.
To reveal the physiological and biochemical mechanisms of Osmanthus fragrans, regarding the resistance to acid rain and heat stress, this study used the leaves of O. fragrans (cultivar 'Hangzhou Huang') as the material. Plants grown in pots treated with simulated acid rain stress[pH 5.6(ck), 4.0, 3.0, and 2.0] and heat stress (40℃) treatments were analyzed. Photosynthetic pigment content, active oxygen (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA) content, antioxidant enzyme activity, and non-structural carbon changes in composition and content were measured. Results showed that (1) generally, the contents of chlorophyll a (Chl a), total chlorophyll(Chl t), and the ratio of Chl a/b ratio decreased after acid rain and heat as individual stresses. After the co-stresses of acid rain and heat, there is significant decreases (P < 0.05) of Chl a (27.7%), Chl t (23.8%), and the Chl a/b (19.5%) compared to the control of pH 2.0. (2) ROS and MDA increased significantly (P < 0.05) after acid rain or heat as individual stress. After co-stresses, the content of O2·- and MDA increased significantly (P < 0.05) as pH decreased, and increased 158.3% (O2·-) and 142.0% (MDA) compared to the control of pH 2.0. The content of H2O2 significantly increased (P < 0.05) and reached a maximum of 180.0% compared to the control of pH 3.0. (3) Superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT) activities increased significantly (P < 0.05) with individual acid rain or heat stresses, and the three enzymes cooperated to resist stress damage. After co-stresses, the SOD and CAT activities firstly increased and then decreased; whereas, POD still maintained a high activity and increased 107.3% compared to the control of pH 2.0. (4) After acid rain stress, the contents of glucose and fructose were relatively stable, but sucrose and starch decreased significantly (P < 0.05). Non-structural carbon contents decreased significantly after heat stress (P < 0.05). After co-stresses, non-structural carbon content decreased even further:among them, fructose, sucrose, and starch content decreased 38.1% -41.6% (P < 0.05); and glucose content decreased 22.4% compared to the control of pH 2.0(P < 0.05). The results indicate that O. fragrans 'Hangzhou Huang' could reduce the damages of acid rain and heat stresses by regulating activities of protective enzymes and non-structural carbon metabolism.
2019, 36(1): 62-69.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.009
Abstract:
From January 2012 to December 2012, we monitored the temperature and humidity of Quercus acutissima forest in Nanjing Tongshan Forest Farm. The nudation was used as the control group to study the changes of temperature and humidity inside and outside the Q. acutissima forest, for analyzing its cooling and humidification effect. Results show that:The diurnal variation curve of temperature inside and outside the forest showed changes of a "parabolic curve" while the diurnal variation curve of humidity showed a U-shape.During the growing season of Q. acutissima forest, the monthly variation range of temperature and humidity inside the forest was less than that outside the forest. The cooling effect of the Q. acutissima forest from May-August is the most significant. In a year, the cumulative temperature inside the Q. acutissima forest had a drop of 13 661.4℃ than that outside the forest. The temperature difference between that inside and outside the forest in four season is as follows:summer > spring > winter > autumn. The annual RH inside the forest increased by 417.7% compared with that outside the forest. The RH difference between that inside and outside the forest in four seasons is as follows:summer > spring > autumn > winter. The internal(y) and external(x) temperature showed outstanding linear regression equation:y=0.886 6x + 1.207 6, R2=0.972 3, as well as the humidity inside (y) and outside (x) the forest. That is:y=0.961 8x + 0.042 3, R2=0.978 0. The annual average temperature and humidity inside the forest were not significantly changed compared with that outside the forest. The humidity inside the forest changed significantly during the summer compared with that outside the forest. Exceptionally, for different periods in a day, the temperature and humidity inside the forest changed the most significantly and also showed the most significant colling effect, at 12:00-14:00 periods compared with that outside the forest.
From January 2012 to December 2012, we monitored the temperature and humidity of Quercus acutissima forest in Nanjing Tongshan Forest Farm. The nudation was used as the control group to study the changes of temperature and humidity inside and outside the Q. acutissima forest, for analyzing its cooling and humidification effect. Results show that:The diurnal variation curve of temperature inside and outside the forest showed changes of a "parabolic curve" while the diurnal variation curve of humidity showed a U-shape.During the growing season of Q. acutissima forest, the monthly variation range of temperature and humidity inside the forest was less than that outside the forest. The cooling effect of the Q. acutissima forest from May-August is the most significant. In a year, the cumulative temperature inside the Q. acutissima forest had a drop of 13 661.4℃ than that outside the forest. The temperature difference between that inside and outside the forest in four season is as follows:summer > spring > winter > autumn. The annual RH inside the forest increased by 417.7% compared with that outside the forest. The RH difference between that inside and outside the forest in four seasons is as follows:summer > spring > autumn > winter. The internal(y) and external(x) temperature showed outstanding linear regression equation:y=0.886 6x + 1.207 6, R2=0.972 3, as well as the humidity inside (y) and outside (x) the forest. That is:y=0.961 8x + 0.042 3, R2=0.978 0. The annual average temperature and humidity inside the forest were not significantly changed compared with that outside the forest. The humidity inside the forest changed significantly during the summer compared with that outside the forest. Exceptionally, for different periods in a day, the temperature and humidity inside the forest changed the most significantly and also showed the most significant colling effect, at 12:00-14:00 periods compared with that outside the forest.
2019, 36(1): 70-79.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.010
Abstract:
To quickly and accurately measure the car on sink in forest carbon sequestration projects and to monitor carbon storage changes in forest vegetation of Guangdong Province, Cinnamomum camphora trees were selected as the object to establish a carbon storage model. Based on the 8th continuous forest inventory data for C. camphora distribution in Guangdong Province in 2012, all 90 sample trees were classified in 10 diameter classes according to 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 20, 26, 32, and 38 cm. The weighted mean and total carbon storage were calculated for individual trees of C. camphora including components of stem wood, bark, leaves, branches, and roots among different diameter levels by using the analysis of variance (ANOVA) method. Results showed that:(1) The average carbon rate of C. camphora in Guangdong was 0.509 6. There were no significant differences among stems, leaves, branches, and roots (P>0.05) for the average carbon content in DBH levels, but the carbon content of bark was significantly lower than other components (P < 0.05). (2) Carbon content increased with age in period of mature and near-mature forests, but declined in period of over-mature forests. (3) The carbon content of the artificial forest was higher than the natural forest and increased with increasing latitude, but decreased with the increasing of altitude. (4) The proportion of carbon storage in each component was stem > branch > root > bark > leaf. (5) With an increase in DBH, the ratio of stem carbon storage increased first and then decreased, the proportion of bark carbon reserves was stable at an early age but decreased in later stages, the proportion of leaves and roots changed little, and the carbon storage of branches was stable first and increased in a later period at a significant level of 0.05. (6) The optimal carbon storage(Ct) model of C. camphora and R2 for age (A) was Ct=0.019 4A2.652 0, R2=0.602 9; for DBH was Ct=0.011 8D2.937 6, R2=0.943 2; and for D2H was Ct=0.001 6(D2H)1.268 6, R2=0.910 5. Through cross validation, the model fitting effect was significant (P < 0.01). The fitting carbon storage model of C. camphora with D and D2H was better than the age vatiable. In the model application, the model with D and D2H should be selected to estimate the carbon storage. When the diameter (D) and D2H were not easy to be measured but the age was easy to know, the age could be used to estimate the carbon storage.
To quickly and accurately measure the car on sink in forest carbon sequestration projects and to monitor carbon storage changes in forest vegetation of Guangdong Province, Cinnamomum camphora trees were selected as the object to establish a carbon storage model. Based on the 8th continuous forest inventory data for C. camphora distribution in Guangdong Province in 2012, all 90 sample trees were classified in 10 diameter classes according to 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 20, 26, 32, and 38 cm. The weighted mean and total carbon storage were calculated for individual trees of C. camphora including components of stem wood, bark, leaves, branches, and roots among different diameter levels by using the analysis of variance (ANOVA) method. Results showed that:(1) The average carbon rate of C. camphora in Guangdong was 0.509 6. There were no significant differences among stems, leaves, branches, and roots (P>0.05) for the average carbon content in DBH levels, but the carbon content of bark was significantly lower than other components (P < 0.05). (2) Carbon content increased with age in period of mature and near-mature forests, but declined in period of over-mature forests. (3) The carbon content of the artificial forest was higher than the natural forest and increased with increasing latitude, but decreased with the increasing of altitude. (4) The proportion of carbon storage in each component was stem > branch > root > bark > leaf. (5) With an increase in DBH, the ratio of stem carbon storage increased first and then decreased, the proportion of bark carbon reserves was stable at an early age but decreased in later stages, the proportion of leaves and roots changed little, and the carbon storage of branches was stable first and increased in a later period at a significant level of 0.05. (6) The optimal carbon storage(Ct) model of C. camphora and R2 for age (A) was Ct=0.019 4A2.652 0, R2=0.602 9; for DBH was Ct=0.011 8D2.937 6, R2=0.943 2; and for D2H was Ct=0.001 6(D2H)1.268 6, R2=0.910 5. Through cross validation, the model fitting effect was significant (P < 0.01). The fitting carbon storage model of C. camphora with D and D2H was better than the age vatiable. In the model application, the model with D and D2H should be selected to estimate the carbon storage. When the diameter (D) and D2H were not easy to be measured but the age was easy to know, the age could be used to estimate the carbon storage.
2019, 36(1): 80-87.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.011
Abstract:
To determine species composition and soil nutrients in different lava platforms as well as the relationship between plant diversity and soil nutrients, volcanic lava platforms of different ages in Wudalianchi were used as research samples using a spatial sequence approach instead of a temporal sequence and correlation analysis. Richness, Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes were also used. Results showed that as the age of the volcanoes increased, the number of genera and species of plants was lowest in new volcanic lava platforms and was highest in old volcanic lava platforms. Richness, Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes of tree and shrub were highest in volcanic lava platforms erupted at 170 000 years than others (P < 0.05), howere, Richness, Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes of herb layers were highest in volcanic lava platforms erupted at 280 000 years than others (P < 0.05), which all initially increased and then decreased in support of the "intermediate disturbance hypothesis" in the forest ecosystem. Total P, total K, available N, and pH in the soil was highest in new volcanic lava platforms(290 years) than others (P < 0.05), which initially decreased and then increased. However, soil organic carbon, total N, ammonium N, nitrate N, and available P was highest in volcanic lava platforms erupted at 400 000-500 000 years than others(P < 0.05), which initially increased and then decreased. Moreover, richness, Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes of different layers were positively correlated with pH, total N, and total K in the soil(P < 0.05).
To determine species composition and soil nutrients in different lava platforms as well as the relationship between plant diversity and soil nutrients, volcanic lava platforms of different ages in Wudalianchi were used as research samples using a spatial sequence approach instead of a temporal sequence and correlation analysis. Richness, Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes were also used. Results showed that as the age of the volcanoes increased, the number of genera and species of plants was lowest in new volcanic lava platforms and was highest in old volcanic lava platforms. Richness, Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes of tree and shrub were highest in volcanic lava platforms erupted at 170 000 years than others (P < 0.05), howere, Richness, Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes of herb layers were highest in volcanic lava platforms erupted at 280 000 years than others (P < 0.05), which all initially increased and then decreased in support of the "intermediate disturbance hypothesis" in the forest ecosystem. Total P, total K, available N, and pH in the soil was highest in new volcanic lava platforms(290 years) than others (P < 0.05), which initially decreased and then increased. However, soil organic carbon, total N, ammonium N, nitrate N, and available P was highest in volcanic lava platforms erupted at 400 000-500 000 years than others(P < 0.05), which initially increased and then decreased. Moreover, richness, Shannon-Wiener, Simpson, and Pielou indexes of different layers were positively correlated with pH, total N, and total K in the soil(P < 0.05).
2019, 36(1): 88-95.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.012
Abstract:
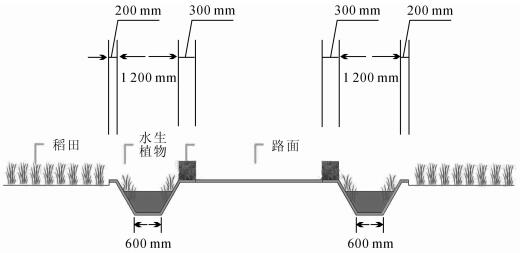
Due to heavy fertilizer application and improper management in the process of agricultural production, large amounts of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in farmlands have been lost and have affected surrounding water bodies. To study the effect of aquatic plants on the absorption of N and P in farmland drainage ditches, Oenanthe javanica, Acorus tatarinowii, and Vallisneria spinulosa were planted in ecological ditches. In June 2015, the change of N and P content with the water flow in the ditch were estimated through field investigation and laboratory bioassay. Results showed that plants in ditches had a total nitrogen (TN) removal rate of 56.18% -74.58%, an ammonium (NH4+) nitrogen removal rate of 36.23% -59.33%, a nitrate (NO3-) nitrogen removal rate of 34.35% -66.88%, and a total phosphorus (TP) removal rate of 44.38% -76.35%. From the point of view of the monitoring sites, the concentration of N and P in ditches decreased overall with a prolonged water flow path. Also, with an increase in time, the concentration of N and P in different sampling sites showed a strong downward movement. Thus, this study could be a guide for ecological restoration projects in lakes or other water bodies with aquatic plants.
Due to heavy fertilizer application and improper management in the process of agricultural production, large amounts of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in farmlands have been lost and have affected surrounding water bodies. To study the effect of aquatic plants on the absorption of N and P in farmland drainage ditches, Oenanthe javanica, Acorus tatarinowii, and Vallisneria spinulosa were planted in ecological ditches. In June 2015, the change of N and P content with the water flow in the ditch were estimated through field investigation and laboratory bioassay. Results showed that plants in ditches had a total nitrogen (TN) removal rate of 56.18% -74.58%, an ammonium (NH4+) nitrogen removal rate of 36.23% -59.33%, a nitrate (NO3-) nitrogen removal rate of 34.35% -66.88%, and a total phosphorus (TP) removal rate of 44.38% -76.35%. From the point of view of the monitoring sites, the concentration of N and P in ditches decreased overall with a prolonged water flow path. Also, with an increase in time, the concentration of N and P in different sampling sites showed a strong downward movement. Thus, this study could be a guide for ecological restoration projects in lakes or other water bodies with aquatic plants.
2019, 36(1): 96-106.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.013
Abstract:
As a new soil conditioner, biochar not only maintains soil fertility, improves soil degradation, and resolves pollution problems, also enhances crop growth and production efficiency. To promote a low-carbon economy for the world with biochar development, the Songnen Plain black soil area was selected as the research object. A total of ten treatments were set with three biochar application levels (C5-5 t·hm-2, C10-10 t·hm-2, and C15-15 t·hm-2); three different application schemes (F1-applied in autumn, F2-half applied in spring and half in autumn. and F3-applied in spring) for each application level; and one control group (BL-no biochar applied), and each test was processed in parallel. Combined with crop growth period, and regular artificial sampling. On this basis, the characteristics of the plant root system, nitrogen (N) spatial distribution, root respiration, and N-use efficiency for different treatment conditions were compared and analyzed. A correlation function of biochar amount and N-use efficiency versus the harvest index was constructed, and then the relationship between the biochar control mode and crop production efficiency was expounded. Results of the study showed that compared to the BL treatment, root length of plants with biochar treatments increased for C5F1(1 009.10 cm), for C10F1(1 640.05 cm), and for C15F1(1 270.24 cm) as did F2 and F3 for the three biochar application treatments and the results passed the significance test of P < 0.05. The control effect of biological carbon effectively inhibited the ineffective loss of soil N, and the N fixation effect of the soil reached the best level with the C10F1 treatment. Biochar's water retention and fertility enhanced the respiration rate of the plant roots; an increase in the biochar application rate first increased and then decreased the respiration rate(P < 0.05). Regulation of biochar additions promoted the accumulation of crop yield with an increase in the biochar application rate and adjustment of the application scheme; the C10F1 treatment had the best yield, N-use efficiency, and harvest index(P < 0.05). In addition, there was a quadratic function relationship between the biochar application rate and crop yield, N-use efficiency(P < 0.05), and other indicators meaning that there was an optimal threshold between biochar supply and plant productivity. Through the above studies, it can be seen that appropriate amount of biochar, with appropriate addition period, can effectively increase the growth and metabolism of crop lines, thereby increasing the yield and production efficiency of crops. Thus, this study provided theoretical guidance for seeking a reasonable and efficient management model with biochar, and showed that appropriately increasing the amount of biochar could effectively promote plant root metabolism.
As a new soil conditioner, biochar not only maintains soil fertility, improves soil degradation, and resolves pollution problems, also enhances crop growth and production efficiency. To promote a low-carbon economy for the world with biochar development, the Songnen Plain black soil area was selected as the research object. A total of ten treatments were set with three biochar application levels (C5-5 t·hm-2, C10-10 t·hm-2, and C15-15 t·hm-2); three different application schemes (F1-applied in autumn, F2-half applied in spring and half in autumn. and F3-applied in spring) for each application level; and one control group (BL-no biochar applied), and each test was processed in parallel. Combined with crop growth period, and regular artificial sampling. On this basis, the characteristics of the plant root system, nitrogen (N) spatial distribution, root respiration, and N-use efficiency for different treatment conditions were compared and analyzed. A correlation function of biochar amount and N-use efficiency versus the harvest index was constructed, and then the relationship between the biochar control mode and crop production efficiency was expounded. Results of the study showed that compared to the BL treatment, root length of plants with biochar treatments increased for C5F1(1 009.10 cm), for C10F1(1 640.05 cm), and for C15F1(1 270.24 cm) as did F2 and F3 for the three biochar application treatments and the results passed the significance test of P < 0.05. The control effect of biological carbon effectively inhibited the ineffective loss of soil N, and the N fixation effect of the soil reached the best level with the C10F1 treatment. Biochar's water retention and fertility enhanced the respiration rate of the plant roots; an increase in the biochar application rate first increased and then decreased the respiration rate(P < 0.05). Regulation of biochar additions promoted the accumulation of crop yield with an increase in the biochar application rate and adjustment of the application scheme; the C10F1 treatment had the best yield, N-use efficiency, and harvest index(P < 0.05). In addition, there was a quadratic function relationship between the biochar application rate and crop yield, N-use efficiency(P < 0.05), and other indicators meaning that there was an optimal threshold between biochar supply and plant productivity. Through the above studies, it can be seen that appropriate amount of biochar, with appropriate addition period, can effectively increase the growth and metabolism of crop lines, thereby increasing the yield and production efficiency of crops. Thus, this study provided theoretical guidance for seeking a reasonable and efficient management model with biochar, and showed that appropriately increasing the amount of biochar could effectively promote plant root metabolism.
2019, 36(1): 107-117.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.014
Abstract:
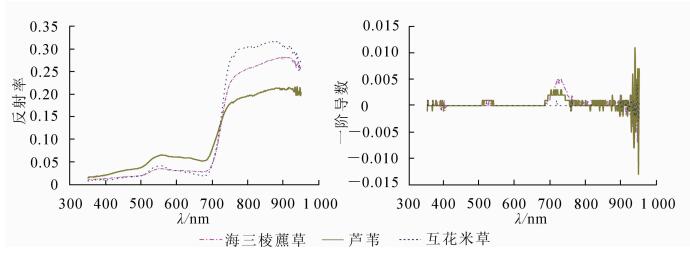
To consider different vegetation types, coverage, soil types, soil moisture, and gradient elevation of a tidal flat so as to determine the effect of the tide, three typical saltmarsh vegetation types in the Yangtze Estuary were chosen as research objects. Vegetation transects and samples(1 m×1 m) were selected for the above factors, and the growth environment of the saltmarsh was simulated. An ASD Fieldspec HandHeld 2 was used to measure the spectrum of the saltmarsh vegetation canopy; then the spectral reflectance and the first derivative (350-950 nm) were calculated, and correlations between coverage/soil/tidal level and spectral reflectance were analyzed. Results showed that vegetation coverage and the underlying surface greatly affected spectral reflectance of the saltmarsh. For the same soil conditions, spectral reflectance of different saltmarsh vegetation coverages in the visible light band was negatively correlated (r≈-1.00) with coverage and in the near infrared positively correlated (r≈0.99). For both low coverages and high coverages, spectral reflectance of different soil types in the visible light band was positively correlated (r≈0.97) but in the near infrared was less correlated. The saltmarsh and tidal level were significantly correlated (r≈0.97). Also spectral reflectance of the saltmarsh at high tide was higher than at low tide, and the reflectance increased as the tide rose. When the tide level rose to a certain height, spectral reflectance of the saltmarsh was lower than without a tide, and this generally decreased as the tide level fell. The effect of vetegation coverage, underlying(soil types and soil moisture) should not be ignored when monitoring saltmarsh vegetation.
To consider different vegetation types, coverage, soil types, soil moisture, and gradient elevation of a tidal flat so as to determine the effect of the tide, three typical saltmarsh vegetation types in the Yangtze Estuary were chosen as research objects. Vegetation transects and samples(1 m×1 m) were selected for the above factors, and the growth environment of the saltmarsh was simulated. An ASD Fieldspec HandHeld 2 was used to measure the spectrum of the saltmarsh vegetation canopy; then the spectral reflectance and the first derivative (350-950 nm) were calculated, and correlations between coverage/soil/tidal level and spectral reflectance were analyzed. Results showed that vegetation coverage and the underlying surface greatly affected spectral reflectance of the saltmarsh. For the same soil conditions, spectral reflectance of different saltmarsh vegetation coverages in the visible light band was negatively correlated (r≈-1.00) with coverage and in the near infrared positively correlated (r≈0.99). For both low coverages and high coverages, spectral reflectance of different soil types in the visible light band was positively correlated (r≈0.97) but in the near infrared was less correlated. The saltmarsh and tidal level were significantly correlated (r≈0.97). Also spectral reflectance of the saltmarsh at high tide was higher than at low tide, and the reflectance increased as the tide rose. When the tide level rose to a certain height, spectral reflectance of the saltmarsh was lower than without a tide, and this generally decreased as the tide level fell. The effect of vetegation coverage, underlying(soil types and soil moisture) should not be ignored when monitoring saltmarsh vegetation.
2019, 36(1): 118-129.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.015
Abstract:
Wetland ecosystems have important ecological functions such as storing flooding waters, protecting shorelines, adjusting climate, and providing habitats for fish and wildlife. Evaluation on service value of wetlands ecosystems is a hot research topic in ecology. Hangzhou Bay, as a typical coastal wetland in China, was selected as a case for this research. In order to scientifically evaluate the value and change characteristics of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland ecosystem services, a wetland ecosystem assessment system was constructed. The ecosystem services were divided into four main categories, namely, provision, regulating, supporting and cultural services. The above four categories were further subdivided into 12 subcategories. Based on the remote sensing data and social statistics data, combined with ecological and economic methods, ecosystem services were analyzed. The results showed that the total value of ecosystem services for Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland in 2000, 2005, 2010 and 2015 was 413.01×108, 261.25×108, 259.52×108, and 224.30×108 RMB respectively, showing a decreasing trend. The main service category of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland was the regulating service, the value of which accounting for more than 60.00 per cent of the total ecosystem service value. The main functions of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland were climate regulation, water purification and soil conservation, the values of which accounting for more than 80 per cent of the total ecosystem service value. Over-reclamation and urban construction reduced wetland area, resulting in the decreasing ecosystem values. This study quantitatively evaluated the service value of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland between 2000 and 2015. It is suggested that the study should be taken as a guide to strengthen the ecological protection of the existing resources of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland.
Wetland ecosystems have important ecological functions such as storing flooding waters, protecting shorelines, adjusting climate, and providing habitats for fish and wildlife. Evaluation on service value of wetlands ecosystems is a hot research topic in ecology. Hangzhou Bay, as a typical coastal wetland in China, was selected as a case for this research. In order to scientifically evaluate the value and change characteristics of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland ecosystem services, a wetland ecosystem assessment system was constructed. The ecosystem services were divided into four main categories, namely, provision, regulating, supporting and cultural services. The above four categories were further subdivided into 12 subcategories. Based on the remote sensing data and social statistics data, combined with ecological and economic methods, ecosystem services were analyzed. The results showed that the total value of ecosystem services for Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland in 2000, 2005, 2010 and 2015 was 413.01×108, 261.25×108, 259.52×108, and 224.30×108 RMB respectively, showing a decreasing trend. The main service category of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland was the regulating service, the value of which accounting for more than 60.00 per cent of the total ecosystem service value. The main functions of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland were climate regulation, water purification and soil conservation, the values of which accounting for more than 80 per cent of the total ecosystem service value. Over-reclamation and urban construction reduced wetland area, resulting in the decreasing ecosystem values. This study quantitatively evaluated the service value of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland between 2000 and 2015. It is suggested that the study should be taken as a guide to strengthen the ecological protection of the existing resources of Hangzhou Bay coastal wetland.
2019, 36(1): 130-137.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.016
Abstract:
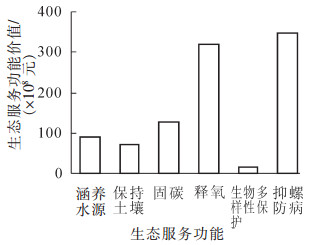
To assess the ecosystem services value of forests for snail control and schistosomiasis prevention in the Yangtze River Basin, The Benefit Of Forestry Schistosomiasis Prevention Ecological Project, referenced as Specifications for Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Services in China (LY/T 1721-2008), was evaluated scientifically by market value method and shadow engineering method selecting water conservation, soil conservation, carbon sequestration, oxygen released, biodiversity conservation, snail control and schistosomiasis prevention to value ecosystem services. Results showed that ecosystem service ecological benefit of forests for snail control and schistosomiasis prevention in the Yangtze River Basin was great from 2006-2013 with water conservation totaling 16.16×108 tons, soil conservation 1.46×108 tons, carbon sequestration 0.10×108 tons, oxygen released 0.29×108 tons, snail area decreasing 24.35×107 square meters, and the number of schistosomiasis patients decreasing by 613.1 thousand. This was a saving of about 967.20×108 Yuan in all. Snail control and schistosomiasis prevention had the greatest value accounting for 35.87%, oxygen release accounted for 33.06%, carbon sequestration accounted for 13.02%, water conservation accounted for 9.17%, soil conservation accounted for 7.31%, and biodiversity conservation had the least value, accounting for 1.57%. The ecosystem services value for different provinces was Hunan > Hubei > Jiangxi > Anhui > Jiangsu > Sichuan > Yunnan. Of the seven provinces, snail control and schistosomiasis prevention of Anhui Province was greatest accounting for 18.17%. The other five function values were largest in Hunan Province. The study found that the comprehensive ecosystem service of snail prevention and control, oxygen release, carbon sequestration, water conservation, and soil conservation accounted for 98.43% of the ecosystem service value. The government of Hunan Province attached great importance to the prevention and treatment of schistosomiasis and undertook suppressing snail work the most. In hilly regions of Yunnan Province, Oncomelania Snail has a variety of environment, and its vitality is strong and its reproduction is fast, the difficulty of the prevention and control of schistosomiasis is relatively large, and the benefit of the snail suppression is not significant. This study provided a scientific basis for understanding the ecological role of snail prevention and control.
To assess the ecosystem services value of forests for snail control and schistosomiasis prevention in the Yangtze River Basin, The Benefit Of Forestry Schistosomiasis Prevention Ecological Project, referenced as Specifications for Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Services in China (LY/T 1721-2008), was evaluated scientifically by market value method and shadow engineering method selecting water conservation, soil conservation, carbon sequestration, oxygen released, biodiversity conservation, snail control and schistosomiasis prevention to value ecosystem services. Results showed that ecosystem service ecological benefit of forests for snail control and schistosomiasis prevention in the Yangtze River Basin was great from 2006-2013 with water conservation totaling 16.16×108 tons, soil conservation 1.46×108 tons, carbon sequestration 0.10×108 tons, oxygen released 0.29×108 tons, snail area decreasing 24.35×107 square meters, and the number of schistosomiasis patients decreasing by 613.1 thousand. This was a saving of about 967.20×108 Yuan in all. Snail control and schistosomiasis prevention had the greatest value accounting for 35.87%, oxygen release accounted for 33.06%, carbon sequestration accounted for 13.02%, water conservation accounted for 9.17%, soil conservation accounted for 7.31%, and biodiversity conservation had the least value, accounting for 1.57%. The ecosystem services value for different provinces was Hunan > Hubei > Jiangxi > Anhui > Jiangsu > Sichuan > Yunnan. Of the seven provinces, snail control and schistosomiasis prevention of Anhui Province was greatest accounting for 18.17%. The other five function values were largest in Hunan Province. The study found that the comprehensive ecosystem service of snail prevention and control, oxygen release, carbon sequestration, water conservation, and soil conservation accounted for 98.43% of the ecosystem service value. The government of Hunan Province attached great importance to the prevention and treatment of schistosomiasis and undertook suppressing snail work the most. In hilly regions of Yunnan Province, Oncomelania Snail has a variety of environment, and its vitality is strong and its reproduction is fast, the difficulty of the prevention and control of schistosomiasis is relatively large, and the benefit of the snail suppression is not significant. This study provided a scientific basis for understanding the ecological role of snail prevention and control.
2019, 36(1): 138-147.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.017
Abstract:
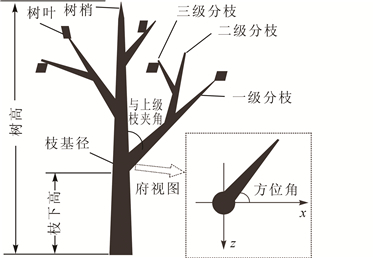
To discuss the theory and methodology of geometrical modeling for a tree and research on interactive modeling and 3D visualization technology, a three-step realization process was established. Results of model development were as follows:Firstly, the geometric structure of real branches was analyzed to construct a generation method for the branch model, and a hexagonal prism was proposed to represent the trunk or branch. The curved shape was realized by using segment elements through continuous deflection and connection. Secondly, based on the generation method for a branch, the whole tree was constructed by a fractal iterative method. To improve the degree of simulation, interference factors were added to make the final stem model not too regular. Finally, the OpenGL graphics technology and Visual C++ were chosen as visualization and development tools. Thus, the modeling system of 3D trees supporting interaction was constructed by a mathematical description of the tree model, a rendering of the scene and a extracting of the feature parameters.
To discuss the theory and methodology of geometrical modeling for a tree and research on interactive modeling and 3D visualization technology, a three-step realization process was established. Results of model development were as follows:Firstly, the geometric structure of real branches was analyzed to construct a generation method for the branch model, and a hexagonal prism was proposed to represent the trunk or branch. The curved shape was realized by using segment elements through continuous deflection and connection. Secondly, based on the generation method for a branch, the whole tree was constructed by a fractal iterative method. To improve the degree of simulation, interference factors were added to make the final stem model not too regular. Finally, the OpenGL graphics technology and Visual C++ were chosen as visualization and development tools. Thus, the modeling system of 3D trees supporting interaction was constructed by a mathematical description of the tree model, a rendering of the scene and a extracting of the feature parameters.
2019, 36(1): 148-153.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.018
Abstract:
Since no reports on the structure and sound formation of Hydrophilidae have been found in Chinese, Hydrochara affinis was used as an example to study the fine structure of Hydrophilidae stridulatory organs. Many specimens were collected from the state forest farm of Northeast Forestry University, and observations were made with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Results showed that both males and females had stridulatory organs. The stridulatory organ size was (15.86±7.60) mm long and (162.10±81.70) μm wide for females but (14.28±7.20) mm long and (142.00±43.50) μm wide for males. The mechanisms of pronunciation for this kind of stridulatory organ were the same as in the model of the underwing radius vein-elytra. Thus, the pronunciation used may be for communication among different individuals of H. affinis.
Since no reports on the structure and sound formation of Hydrophilidae have been found in Chinese, Hydrochara affinis was used as an example to study the fine structure of Hydrophilidae stridulatory organs. Many specimens were collected from the state forest farm of Northeast Forestry University, and observations were made with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Results showed that both males and females had stridulatory organs. The stridulatory organ size was (15.86±7.60) mm long and (162.10±81.70) μm wide for females but (14.28±7.20) mm long and (142.00±43.50) μm wide for males. The mechanisms of pronunciation for this kind of stridulatory organ were the same as in the model of the underwing radius vein-elytra. Thus, the pronunciation used may be for communication among different individuals of H. affinis.
2019, 36(1): 154-161.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.019
Abstract:
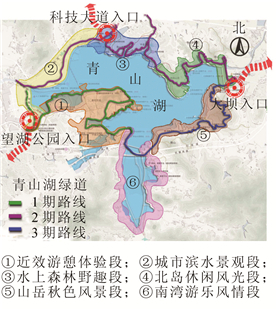
In order to study the characteristics and satisfaction of the use of country greenway, this study took Qingshan Lake Greenway in Lin'an as a research object. Based on the SPSS software platform, it conducted statistical survey, chi-square test, correlation analysis as well as factor analysis, the demographic characteristics, behaviors and experience satisfaction of the population were quantitatively analyzed and evaluated by using interviews and questionnaire survey of greenway users. The research results showed that:(1) Qingshan lake Greenway's users were basically from its neighboring area and Lin'an District; (2) Nearly half of the respondents used the Greenway in rather fixed frequency and most frequent users of the Greenway were neighboring residents; (3) There were many types of recreational activities on the Greenway, and most respondents used the Greenway for walking leisure; (4) The frequency of different leisure spaces in summer was different, people had higher utilization rate of the sequoia forest on the Greenway; (5) Word-of-mouth was the primary way to get information about the greenway; (6) Respondents had the highest satisfaction with the quality of the Greenway landscape, determinants of the overall satisfaction level of the respondents including accessibility, landscape quality, safety protection and service facilities (bicycle rental, public toilet). Based on the above research results, suggestions were put forward to optimize the design of Qingshan Lake Greenway and the construction of country greenway in China.
In order to study the characteristics and satisfaction of the use of country greenway, this study took Qingshan Lake Greenway in Lin'an as a research object. Based on the SPSS software platform, it conducted statistical survey, chi-square test, correlation analysis as well as factor analysis, the demographic characteristics, behaviors and experience satisfaction of the population were quantitatively analyzed and evaluated by using interviews and questionnaire survey of greenway users. The research results showed that:(1) Qingshan lake Greenway's users were basically from its neighboring area and Lin'an District; (2) Nearly half of the respondents used the Greenway in rather fixed frequency and most frequent users of the Greenway were neighboring residents; (3) There were many types of recreational activities on the Greenway, and most respondents used the Greenway for walking leisure; (4) The frequency of different leisure spaces in summer was different, people had higher utilization rate of the sequoia forest on the Greenway; (5) Word-of-mouth was the primary way to get information about the greenway; (6) Respondents had the highest satisfaction with the quality of the Greenway landscape, determinants of the overall satisfaction level of the respondents including accessibility, landscape quality, safety protection and service facilities (bicycle rental, public toilet). Based on the above research results, suggestions were put forward to optimize the design of Qingshan Lake Greenway and the construction of country greenway in China.
2019, 36(1): 162-169.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.020
Abstract:
To determine the feasibility of using visible/near infrared spectroscopy to identify wood samples drilled using an increment borer, and to provide a method of wood identification in the wild, 14 wood species typically found in Northeast China were sampled and drilled with an increment borer through 1.3 m breast-height of the trees from south to north, the samples are about 300 mm in length and 5 mm in diameter. Analysis included use of derivative, logarithmic, and smooth processing to process the wood spectrum and used a distance method to build the identification model. Results showed that without smoothing, the accuracy rate of the first derivative (96.79%) was much better than the second derivative (78.57%) and the third derivative (75.00%). With derivative and smoothing, the accuracy rate of the second derivative + smoothing (98.21%) and the third derivative + smoothing (98.21%) were better than the first derivative + smoothing (97.50%). Accuracy rate of the prediction model was not improved with just smoothing, and the derivative pretreatment improved accuracy. Also, with optimum parameters, there were no major differences between S-G derivative smoothing (98.42%) and the Norris derivative filter (98.57%). Thus, this study provided a new method and idea for rapid identification of wood species.
To determine the feasibility of using visible/near infrared spectroscopy to identify wood samples drilled using an increment borer, and to provide a method of wood identification in the wild, 14 wood species typically found in Northeast China were sampled and drilled with an increment borer through 1.3 m breast-height of the trees from south to north, the samples are about 300 mm in length and 5 mm in diameter. Analysis included use of derivative, logarithmic, and smooth processing to process the wood spectrum and used a distance method to build the identification model. Results showed that without smoothing, the accuracy rate of the first derivative (96.79%) was much better than the second derivative (78.57%) and the third derivative (75.00%). With derivative and smoothing, the accuracy rate of the second derivative + smoothing (98.21%) and the third derivative + smoothing (98.21%) were better than the first derivative + smoothing (97.50%). Accuracy rate of the prediction model was not improved with just smoothing, and the derivative pretreatment improved accuracy. Also, with optimum parameters, there were no major differences between S-G derivative smoothing (98.42%) and the Norris derivative filter (98.57%). Thus, this study provided a new method and idea for rapid identification of wood species.
2019, 36(1): 170-176.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.021
Abstract:
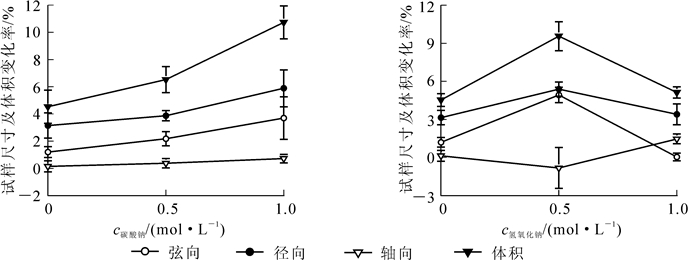
To determine the degree of swelling for bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) in different aqueous solutions, bamboo samples were soaked in different concentrations of Na2CO3, NaOH, ZnCl2 (combined with HNO3 hydrothermal treatment), and deionized water. Changes in macro-and micro-structure were observed with the volume and area expansion rates used as evaluation indexes for the degree of swelling. Results indicated that NaOH and Na2CO3 both showed a good effect on the swelling of bamboo, meanwhile, the swelling effect of bamboo was proportional to concentration of Na2CO3, but inversely proportional to concentration of NaOH. Among the treatments, optimal volume increase rate were found with 0.5 mol·L-1 NaOH (9.69%) and with 1.0 mol·L-1 Na2CO3 (10.57%). Unsatisfactory swelling effect for swelling occurred when ZnCl2 was used alone, but pretreatment with a low concentration of HNO3 solution (500 g·L-1 ZnCl2 with 100 g·L-1 HNO3) improved swelling effect. Meanwhile, area of the bamboo in transverse sections before and after swelling showed that the area of fiber sheath distribution increased, but the area for parenchyma cell distribution after swelling was increased relatively small. Thus, changes in volume of bamboo after swelling was mainly due to changes in the fiber sheath distribution area.
To determine the degree of swelling for bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) in different aqueous solutions, bamboo samples were soaked in different concentrations of Na2CO3, NaOH, ZnCl2 (combined with HNO3 hydrothermal treatment), and deionized water. Changes in macro-and micro-structure were observed with the volume and area expansion rates used as evaluation indexes for the degree of swelling. Results indicated that NaOH and Na2CO3 both showed a good effect on the swelling of bamboo, meanwhile, the swelling effect of bamboo was proportional to concentration of Na2CO3, but inversely proportional to concentration of NaOH. Among the treatments, optimal volume increase rate were found with 0.5 mol·L-1 NaOH (9.69%) and with 1.0 mol·L-1 Na2CO3 (10.57%). Unsatisfactory swelling effect for swelling occurred when ZnCl2 was used alone, but pretreatment with a low concentration of HNO3 solution (500 g·L-1 ZnCl2 with 100 g·L-1 HNO3) improved swelling effect. Meanwhile, area of the bamboo in transverse sections before and after swelling showed that the area of fiber sheath distribution increased, but the area for parenchyma cell distribution after swelling was increased relatively small. Thus, changes in volume of bamboo after swelling was mainly due to changes in the fiber sheath distribution area.
2019, 36(1): 177-182.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.022
Abstract:
Heat treated wood is widely used in indoor and outdoor construction, decoration, and furniture because of its favorable dimensional stability, excellent corrosion resistance, and approximate padauk color. However, with many deficiencies in the existing heat treatment process of wood, such as excessive loss of mechanical strength and timber color being too heavy, this study was conducted to provide a reference during actual production for the feasibility and practical effect of low thermo-vacuum treatments with lower temperatures. Changes in physical and mechanical properties of three kinds of wood-okoume, basswood, and andoung, using the same thermo-vacuum treatment conditions were tested. The three woods were placed in a vacuum carbonization tank at 160℃ and 0 MPa conditions for 3 h. Then the timber was sawn according to experimental requirements with wood density, color deviation, toughness, bending strength, modulus of elasticity in static bending, static hardness, shrinkage, and swelling rate being measured. Results showed that dimensional stability of heat-treated andoung was greatly improved with its volume shrinkage coefficient decreasing 16.00%. Moreover, andoung had an increase in flexural strength and hardness, with increased bending strength (18.00%), hardness of its radial section (19.00%), tangential section (33.00%), and end surface (50.00%). Also, its impact toughness loss was less (24.00%). Overall, low thermo-vacuum treatment could improve dimensional stability of wood as it avoided loss of physical and mechanical properties of the timber.
Heat treated wood is widely used in indoor and outdoor construction, decoration, and furniture because of its favorable dimensional stability, excellent corrosion resistance, and approximate padauk color. However, with many deficiencies in the existing heat treatment process of wood, such as excessive loss of mechanical strength and timber color being too heavy, this study was conducted to provide a reference during actual production for the feasibility and practical effect of low thermo-vacuum treatments with lower temperatures. Changes in physical and mechanical properties of three kinds of wood-okoume, basswood, and andoung, using the same thermo-vacuum treatment conditions were tested. The three woods were placed in a vacuum carbonization tank at 160℃ and 0 MPa conditions for 3 h. Then the timber was sawn according to experimental requirements with wood density, color deviation, toughness, bending strength, modulus of elasticity in static bending, static hardness, shrinkage, and swelling rate being measured. Results showed that dimensional stability of heat-treated andoung was greatly improved with its volume shrinkage coefficient decreasing 16.00%. Moreover, andoung had an increase in flexural strength and hardness, with increased bending strength (18.00%), hardness of its radial section (19.00%), tangential section (33.00%), and end surface (50.00%). Also, its impact toughness loss was less (24.00%). Overall, low thermo-vacuum treatment could improve dimensional stability of wood as it avoided loss of physical and mechanical properties of the timber.
2019, 36(1): 183-192.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.023
Abstract:
Bamboo forest growth is based on the rhizome-root system which plays a significant role in energy flow and material cycle of bamboo forest ecosystem. However, recent researches were more concentrated on the above ground part of bamboo. The influence of underground rhizome-root system on carbon cycle and productivity is still at an exploratory stage, which embodied in the research is limited to the basic research on the growth and distribution of rizome-root system, but lack of research about relevant mechanism and ecological functions, such as carbon sink. Besides, the outworn methods is also the reason why it is hard to take on intensive research. Based on this, this paper reviewed the domestic and foreign researches about rhizome-root system from the structural features, effect of different management measures on practical production. and main observation methods. The paper concluded with an analysis of the remaining problems in research of bamboo rhizome-root system, which will provide reference for a comprehensive study about the structure of rhizome-root system and its effect on bamboo forest ecosystem.
Bamboo forest growth is based on the rhizome-root system which plays a significant role in energy flow and material cycle of bamboo forest ecosystem. However, recent researches were more concentrated on the above ground part of bamboo. The influence of underground rhizome-root system on carbon cycle and productivity is still at an exploratory stage, which embodied in the research is limited to the basic research on the growth and distribution of rizome-root system, but lack of research about relevant mechanism and ecological functions, such as carbon sink. Besides, the outworn methods is also the reason why it is hard to take on intensive research. Based on this, this paper reviewed the domestic and foreign researches about rhizome-root system from the structural features, effect of different management measures on practical production. and main observation methods. The paper concluded with an analysis of the remaining problems in research of bamboo rhizome-root system, which will provide reference for a comprehensive study about the structure of rhizome-root system and its effect on bamboo forest ecosystem.
2019, 36(1): 193-199.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.024
Abstract:
To study volatile components from fresh leaves, fresh twigs, and fresh flowers of Michelia martinii at the same time, volatile oils were extracted by water-steam distillation from the fresh leaves, fresh twigs, and fresh flowers and then detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Results of GC-MS showed that the volatile oils contents from different organizations of M. martinii at the same time had ingredients of 21 kinds from fresh leaves, of 31 kinds from fresh twigs, and of 25 kinds from fresh flowers (peak values below 0.49 were neglected). Among the three fresh organizations of M. martinii, the common components were four kinds of ingredients, such as.gamma.-Elemene, gamma.-Muurolen, Eudesma-4(14), 11-diene, and Cyclohexane, 2, 4-diisopropenyl-1-methyl-. Four kinds of components were common to fresh leaves and fresh flowers, 13 kinds of components were common to fresh flowers and fresh twigs, and 12 kinds of components were common to fresh leaves and fresh twigs. The volatile oils of flowers were rich in terpenes and alcohols with terpenes dominated by monoterpenes up to 36.38%; content of the alcohol compounds was higher than terpenes with content as high as 54.77%. Terpene compounds had.gamma.-Cadinene, Caryophyllene oxide, .alpha.-Selinene, Spathulen, Diepicedrene-1-oxide, (+) -Ledene, -Aristolene, Eudesma-4(14), 11-diene, and DGermacrene D. While the alcohols had Eudesm-4(14) -en-11-, 2-(4, 8-Dimethyl-3, 7-cyclodecadien-1-yl) -2-p, Epiglobulol, .gamma.-Eudesmol, .tau.-Cadinol, Guaiol, and.delta.-Cadinol. In conclusion M. martinii could provide new application ideas on material selection of extracted essential oils, utilization of volatile components, and landscape community construction for health care.
To study volatile components from fresh leaves, fresh twigs, and fresh flowers of Michelia martinii at the same time, volatile oils were extracted by water-steam distillation from the fresh leaves, fresh twigs, and fresh flowers and then detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Results of GC-MS showed that the volatile oils contents from different organizations of M. martinii at the same time had ingredients of 21 kinds from fresh leaves, of 31 kinds from fresh twigs, and of 25 kinds from fresh flowers (peak values below 0.49 were neglected). Among the three fresh organizations of M. martinii, the common components were four kinds of ingredients, such as.gamma.-Elemene, gamma.-Muurolen, Eudesma-4(14), 11-diene, and Cyclohexane, 2, 4-diisopropenyl-1-methyl-. Four kinds of components were common to fresh leaves and fresh flowers, 13 kinds of components were common to fresh flowers and fresh twigs, and 12 kinds of components were common to fresh leaves and fresh twigs. The volatile oils of flowers were rich in terpenes and alcohols with terpenes dominated by monoterpenes up to 36.38%; content of the alcohol compounds was higher than terpenes with content as high as 54.77%. Terpene compounds had.gamma.-Cadinene, Caryophyllene oxide, .alpha.-Selinene, Spathulen, Diepicedrene-1-oxide, (+) -Ledene, -Aristolene, Eudesma-4(14), 11-diene, and DGermacrene D. While the alcohols had Eudesm-4(14) -en-11-, 2-(4, 8-Dimethyl-3, 7-cyclodecadien-1-yl) -2-p, Epiglobulol, .gamma.-Eudesmol, .tau.-Cadinol, Guaiol, and.delta.-Cadinol. In conclusion M. martinii could provide new application ideas on material selection of extracted essential oils, utilization of volatile components, and landscape community construction for health care.
2019, 36(1): 200-205.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.025
Abstract:
The flower of Dendrobium officinalei has important development value for its rich active ingredients. The harvest time and the harvest parts are the key factors that influence the quality of D. officinale flower products. The contents of polysaccharides, total flavonoids and total phenols of dried materials at different flowering stages (bud stage, slightly flowering stage, and flourishing flowering stage) and different parts (perianth, gynostemium, and ovary of flower at flourishing flowering stage) were measured by the methods called phenol-sulfuric acid method, NaNO2-Al(NO3)3-NaOH method and Folin-Cioealteau method, and the optimum harvest time and the best harvest parts of D. officinale flower were determined. Results showed that (1) For the different flowering stages, the polysaccharides content in the flourishing flowering stage (61.5 mg·g-1) differed significantly from those in the slightly flowering stage (55.3 mg·g-1) and the bud stage (45.6 mg·g-1) (P < 0.05). The content of total flavonoids in the slightly flowering stage (17.4 mg·g-1) was significantly lower than the bud stage (19.9 mg·g-1) and the flourishing flowering stage (19.2 mg·g-1) (P < 0.05). The content of total phenols in the flourishing flowering stage (22.2 mg·g-1) was significantly higher than the slightly flowering stage (19.6 mg·g-1) and the bud stage (18.5 mg·g-1) (P < 0.05). (2) On the whole, detection of active components in different floral structures at the flourishing flowering stage showed that the contents of polysaccharides (64.5 mg·g-1), total flavonoids (24.2 mg·g-1) and total phenols (26.5 mg·g-1) of perianth were significantly higher than those of gynostemium and ovary, respectively (P < 0.05). Consequently, in terms of contents of active components of the D. officinale flower, the flourishing flowering stage was considered as the best harvest time and the perianth was the most valuable part.
The flower of Dendrobium officinalei has important development value for its rich active ingredients. The harvest time and the harvest parts are the key factors that influence the quality of D. officinale flower products. The contents of polysaccharides, total flavonoids and total phenols of dried materials at different flowering stages (bud stage, slightly flowering stage, and flourishing flowering stage) and different parts (perianth, gynostemium, and ovary of flower at flourishing flowering stage) were measured by the methods called phenol-sulfuric acid method, NaNO2-Al(NO3)3-NaOH method and Folin-Cioealteau method, and the optimum harvest time and the best harvest parts of D. officinale flower were determined. Results showed that (1) For the different flowering stages, the polysaccharides content in the flourishing flowering stage (61.5 mg·g-1) differed significantly from those in the slightly flowering stage (55.3 mg·g-1) and the bud stage (45.6 mg·g-1) (P < 0.05). The content of total flavonoids in the slightly flowering stage (17.4 mg·g-1) was significantly lower than the bud stage (19.9 mg·g-1) and the flourishing flowering stage (19.2 mg·g-1) (P < 0.05). The content of total phenols in the flourishing flowering stage (22.2 mg·g-1) was significantly higher than the slightly flowering stage (19.6 mg·g-1) and the bud stage (18.5 mg·g-1) (P < 0.05). (2) On the whole, detection of active components in different floral structures at the flourishing flowering stage showed that the contents of polysaccharides (64.5 mg·g-1), total flavonoids (24.2 mg·g-1) and total phenols (26.5 mg·g-1) of perianth were significantly higher than those of gynostemium and ovary, respectively (P < 0.05). Consequently, in terms of contents of active components of the D. officinale flower, the flourishing flowering stage was considered as the best harvest time and the perianth was the most valuable part.
2019, 36(1): 206-210.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.01.026
Abstract:
Marumba dyras species which belongs to Sphingidae family, Marumba genera is a vital leaf pest. The potential risk level of the pest in Jiangmen City, Guangdong Province was analyzed and assessed according to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) pest risk analysis methods, in terms of its distribution, spreading possibility, potential damaging degree, the importance of host plants and risk management difficulty. The results showed that the comprehensive risk "R" value of M. dyras in Jiangmen City, Guangdong Province was 0.96, indicating that M. dyras was a low risk forestry fauna.
Marumba dyras species which belongs to Sphingidae family, Marumba genera is a vital leaf pest. The potential risk level of the pest in Jiangmen City, Guangdong Province was analyzed and assessed according to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) pest risk analysis methods, in terms of its distribution, spreading possibility, potential damaging degree, the importance of host plants and risk management difficulty. The results showed that the comprehensive risk "R" value of M. dyras in Jiangmen City, Guangdong Province was 0.96, indicating that M. dyras was a low risk forestry fauna.