-
由于经济快速发展和环境基础设施建设滞后,中国水体污染较为严重[1-2]。利用水生植物及其根系负载生物膜的吸收、吸附和降解作用,并通过收获植物移除水中污染物,是一种简单易行、成本低廉且极具景观效应的技术,在污染水体治理中得到了广泛应用[3-4]。然而,实践表明,该技术运维过程中需定期对水生植物进行修剪、收割,否则植物残体腐烂后,植物体内吸收的物质将重新释放进入水体,造成二次污染[5-6]。近年来,由于植物养护不到位,许多河道出现生态修复效果不稳定,水质反弹等现象。近几年生态环境状况公报表明,中国大部分水体主要污染物为氮磷营养物质,主要污染源为生活污水[7]。污染水体实为营养过剩的场所,在水域上种植生物量大、营养吸收能力强的经济作物,一方面降低水中氮磷等营养物质的浓度,另一方面也能产生可观的经济效益,刺激植物的养护工作,保障植物治理效果的长效稳定。根茎类淀粉在世界淀粉产量中占有重要的比例。由于淀粉植物资源丰富、价廉、生物可降解,各国一直十分重视淀粉植物资源的开发、利用和研究[8-9]。美人蕉Canna indica、黄菖蒲Iris pseudacorus和水芋Calla palustris为污染水体修复中常见的挺水植物,生物量大、具块茎。目前,关于此类植物块茎的资源化开发和利用鲜见报道。本研究以这3种挺水植物为研究对象,考察其对污染水体中氮、磷营养物质的净化能力,分析植物块茎淀粉产量,探讨块茎资源化利用的可行性和潜在风险,以期为块茎类水生植物的应用和资源化利用提供基础数据,也为污染水体治理提供一种新的思路。
-
块茎类水生植物美人蕉、黄菖蒲和水芋均取自浙江温州河道,采用自来水清洗去除泥土后,自来水预培养2周待用。
霍格兰营养液:硫酸镁493 mg·L−1,铁盐2.5 mL,微量元素5 mL。其中铁盐:七水硫酸亚铁2.78 g,乙二胺四乙酸二钠3.73 g,溶于500 mL去离子水。微量元素:碘化钾0.830 mg,硼酸6.200 mg,硫酸锰22.300 mg,硫酸锌8.600 mg,钼酸钠0.250 mg,硫酸铜0.025 0 mg,氯化钴0.025 0 mg,溶于1 L去离子水。
-
试验装置采用上部内径30.5 cm、下部内径25.5 cm、高32 cm、容积17 L的塑料桶。选择生长良好,高度基本一致的3种植物(高20 cm),称取鲜质量后移栽于直径20 cm、厚5 cm的泡沫板上。采用磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)、氯化铵(NH4Cl)和质量分数为1% Hoagland营养液配制试验用水,体积为14 L,初始氨氮(NH4+-N)、总磷(TP)质量浓度分别为7.37~7.53和0.41~0.45 mg·L−1。每种植物3个重复,并设不种植物的空白对照。试验开始后,隔4 d添加少量蒸馏水至刻度线,补充蒸发水量。试验在温州大学简易温室进行,温度为21~31 ℃,周期为20 d。
隔4 d采集水样,当天测定氨氮(NH4+-N)、硝态氮(NO3−-N)、总氮(TN)和总磷(TP)质量分数。试验结束,取出植物,蒸馏水清洗后称鲜质量,将植株根、茎、叶、块茎分开,放入烘箱,105 ℃杀青0.5 h,75 ℃烘干至恒量,称取植物干质量,测定植物各部组织中磷、氮质量分数。
-
选择生长良好,高度基本一致的3种植物(高20 cm)各3株,分别放入塑料桶(大小与1.2.1中的相同),以污染水体中常见的重金属Cu2+、Zn2+、Cr3+、Pb2+为研究对象,与质量分数1% Hoagland营养液{上述配方中添加硝酸钙[Ca(NO3)2·4H2O] 945 mg·L−1,硝酸钾(KNO3) 506 mg·L−1,硝酸氨(NH4NO3) 80 mg·L−1,磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4) 136 mg·L−1}配制重金属污染水体,体积为14 L,Cu2+、Zn2+、Cr3+、Pb2+初始质量浓度分别为2.01~2.08、2.56~2.87、0.22~0.26、0.24~0.26 mg·L−1。周期为20 d,每种植物设置3个重复,以不加重金属处理为对照。
-
将块茎切块后放入搅碎机,搅至泥状,置于烧杯。加水搅拌混匀,用纱布过滤,加水洗涤3次。滤液于阴凉处静置24 h,倾去3/4左右上层液体,余下部分放入离心机,2 000 r·min−1离心10 min,倾去上层液体,沉淀物置于烘箱中,30 ℃烘干至恒量,冷却至室温,称量。
-
水中总磷和氨氮质量浓度参照《水和废水监测分析方法》(第4版)[10],总氮质量浓度采用TOC/TN分析仪测定,重金属质量浓度通过火焰原子吸收光谱仪测定。植物组织中氮质量分数通过浓硫酸(H2SO4)-混合催化剂法消解后,用全自动凯氏定氮仪测定;磷质量分数采用浓H2SO4-H2O2法消解后,通过钒钼黄比色法测定[11]。块茎中淀粉质量分数采用酒石酸铜滴定法分析,淀粉中重金属质量浓度采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪ICP-OES测定。
-
数据采用SPSS 17.0软件处理,数据比较采用单因素方差分析(Turkey HSD),Origin 8.0绘图。
-
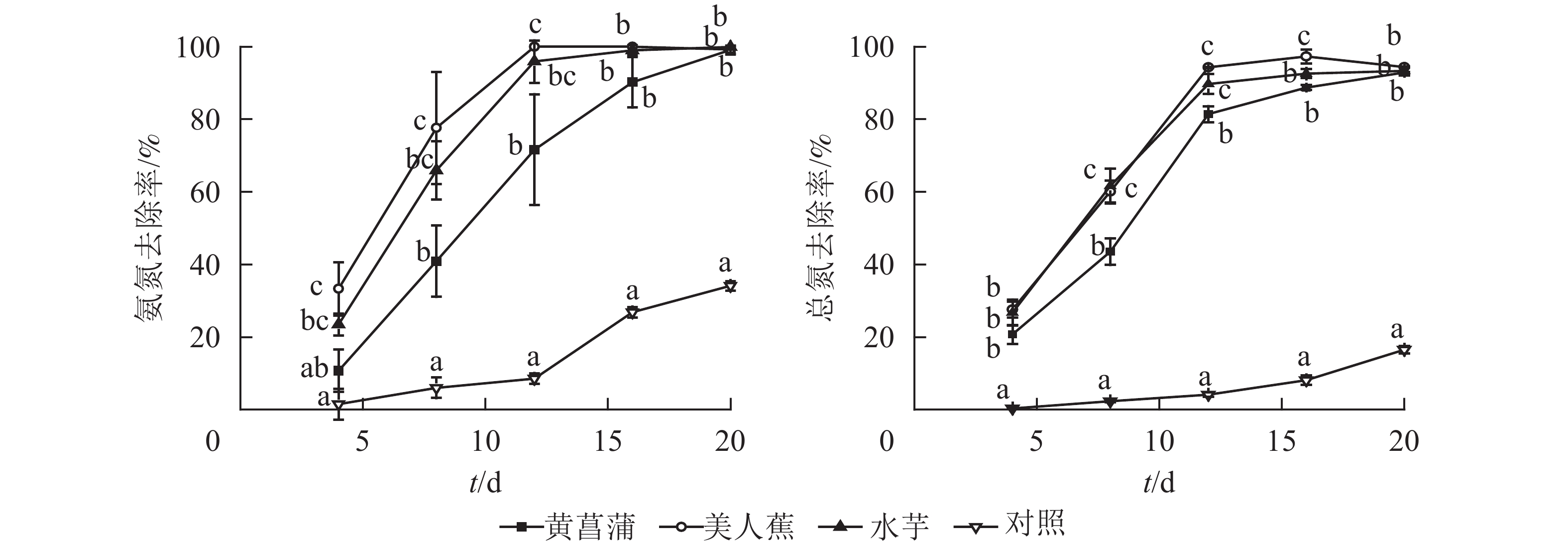
从图1可见:3种植物对氮均具有良好的净化能力。试验期间,植物处理组氨氮和总氮去除率均显著高于对照(P<0.05),且前期差异更为显著。美人蕉和水芋组氨氮去除率以12 d为节点,分为快速增长和趋于平缓2个阶段。处理12 d,美人蕉和水芋组氨氮去除率分别达100%和95.9%。处理期间,黄菖蒲组氨氮去除率随时间增加而增大,未出现明显的节点。对照组氨氮去除率变化与美人蕉及水芋组相反,处理12 d内,氨氮去除率增加缓慢,后去除率增加显著。20 d时,植物处理氨氮质量浓度由7.37~7.53 mg·L−1降至0.01~0.07 mg·L−1,满足GB 3838−2002《地表水环境质量标准》之Ⅲ类水标准限值要求,去除率达99.1%~99.9%,对照组氨氮去除率为34.1%。
3种植物对总氮的去除率变化趋势基本一致,均可分为快速增加和缓慢增加2个阶段。试验结束时,植物处理组总氮降至0.61~0.91 mg·L−1,去除率达91.7%~94.5%。对照组总氮去除率随时间呈上升趋势,20 d时,总氮降至9.45 mg·L−1,去除率为16.5%。3种植物对氮的净化能力无显著差异。
研究表明:水中氮的去除途径为植物同化吸收、根系吸附、氨挥发及硝化反硝化[12]。当pH<8.5时,氨挥发作用较小[13]。从图1可见:3种植物处理组氨氮去除率均大于总氮。分析认为可能存在微生物作用,一部分氨氮经微生物的作用转化为硝态氮。但3种植物根系表面生物膜量较少,水中硝态氮质量浓度较低(硝态氮质量浓度<0.05 mg·L−1),故氮的去除主要为植物的吸收作用,这与其他研究结果一致[14-15]。静止水体易滋生藻类。后期对照水面出现少量藻类,藻类的吸收作用可能为对照氨氮和总氮去除的主要原因。
-
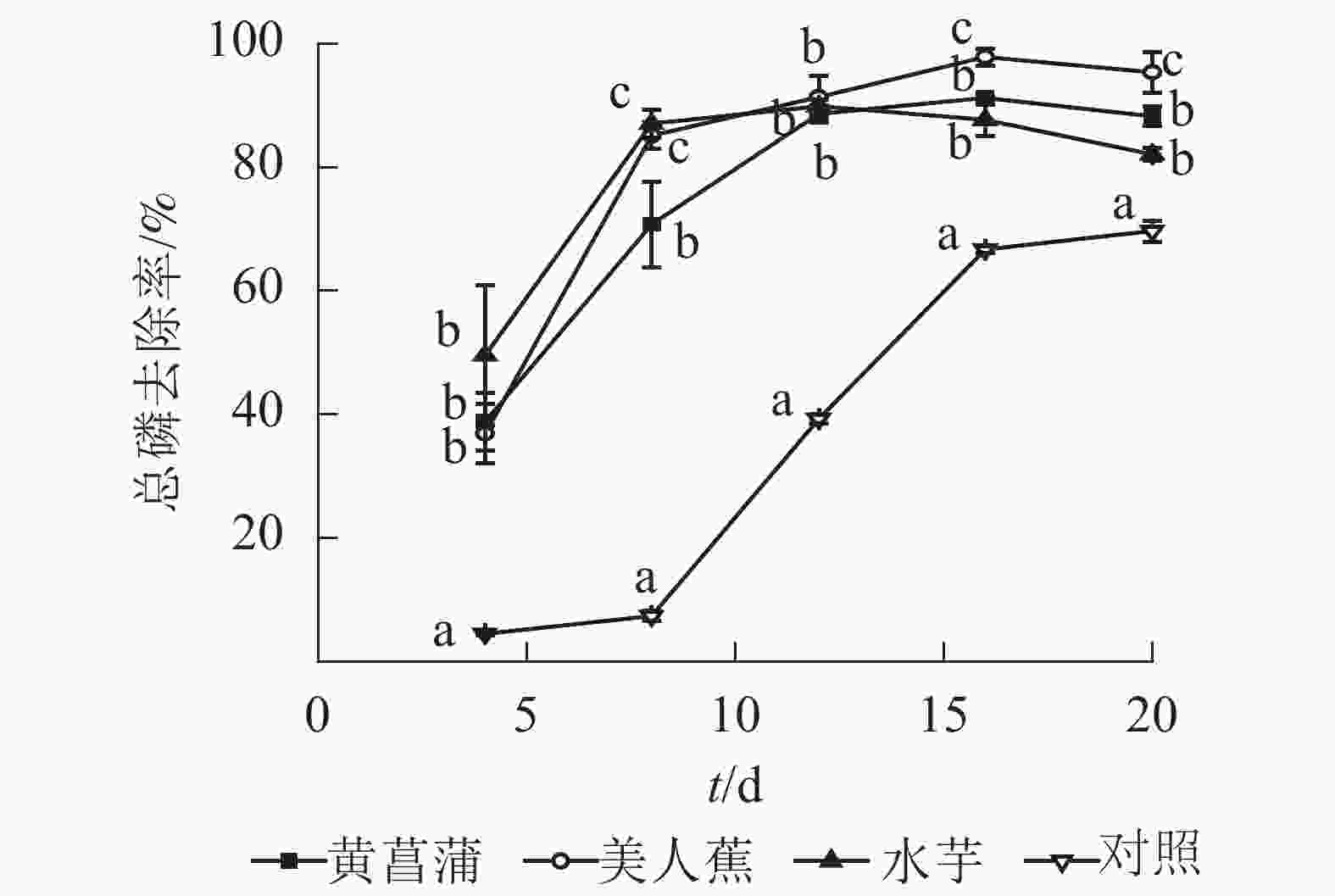
植物处理促进水中磷的去除。处理4 d,美人蕉、黄菖蒲和水芋处理组总磷去除率分别为36.9%、38.8%和49.6%,较对照高32.4%、34.3%和45.1%(图2)。与氮变化相似,植物处理总磷去除率也呈现2个阶段:快速增加和缓慢变化。试验结束时,植物处理总磷质量浓度降至0.025~0.031 mg·L−1,满足GB 3838−2002《地表水环境质量标准》之Ⅱ类水标准限值要求,去除率为90.2%~94.0%。3种植物总磷去除率从大到小依次为美人蕉、黄菖蒲、水芋。试验8 d后,对照处理总磷去除率快速升高,20 d时,总磷质量浓度降至0.14 mg·L−1,去除率为68.9%。对照组总磷去除率较高有2个原因,一是藻类吸收,二是水中部分磷酸根离子与Hoagland营养液中Mg2+、Fe2+、Mn2+、Zn2+等金属离子形成沉淀。
-
3种植物生长良好,没有出现叶片枯黄、腐烂等现象,植物生物量有不同程度的增加。20 d时,黄菖蒲、美人蕉和水芋平均生物量分别由136.0、138.1、140.0 g增至168.9、242.2、176.8 g,增幅分别为24.2%、75.3%和26.3%。可见,3种植物中,美人蕉的生物量增量最高,黄菖蒲和水芋则没有显著差异。吴建强等[16]和洪瑜等[17]采用浮床植物吸收水体氮磷时,也发现美人蕉的生物量增量远大于黄菖蒲。
-
20 d时,植物组织中氮、磷质量分数如图3所示。黄菖蒲无法分离茎和块茎,故而无茎数据。从图3可见,不同植物,氮磷的组织分布差异显著(P<0.05),同一植物,氮和磷在组织中的分布也不相同。美人蕉组,根、茎、叶、块茎中氮和磷质量分数均无显著差异,各组织中氮、磷质量分数分别为14.58~20.19和3.04~3.54 mg·kg−1。黄菖蒲块茎中氮质量分数较高,为30.30 mg·kg−1,分别比根、叶高15.2%和30.6%;磷则根中较高,叶和块茎中无显著差异。水芋中氮主要在叶中积累,氮质量分数达39.4 mg·kg−1,高于其他组织62.1%~79.9%;茎、叶和块茎中磷质量分数无显著差异,但均显著(P<0.05)高于根组织。对比3种植物块茎,黄菖蒲中氮质量分数显著(P<0.05)高于其他2种植物;黄菖蒲与水芋的磷质量分数无显著差异,但均高于美人蕉。
-
黄菖蒲、美人蕉和水芋块茎中,提取淀粉量分别为61.3、14.1和64.0 g·kg−1。考虑到试验周期较短,块茎产量较低。在温州某河道内划定3个相邻的100 m2水域,分别种植黄菖蒲、美人蕉和水芋,8个月后收获植株,取块茎,得到3种植物的块茎产量分别为23.3、8.5和4.1 kg。因而,黄菖蒲、美人蕉和水芋块茎中可回收的淀粉量分别为14.3、1.2、2.6 kg·m−2。由此可见,种植黄菖蒲可得到相对较高的淀粉产量。
-
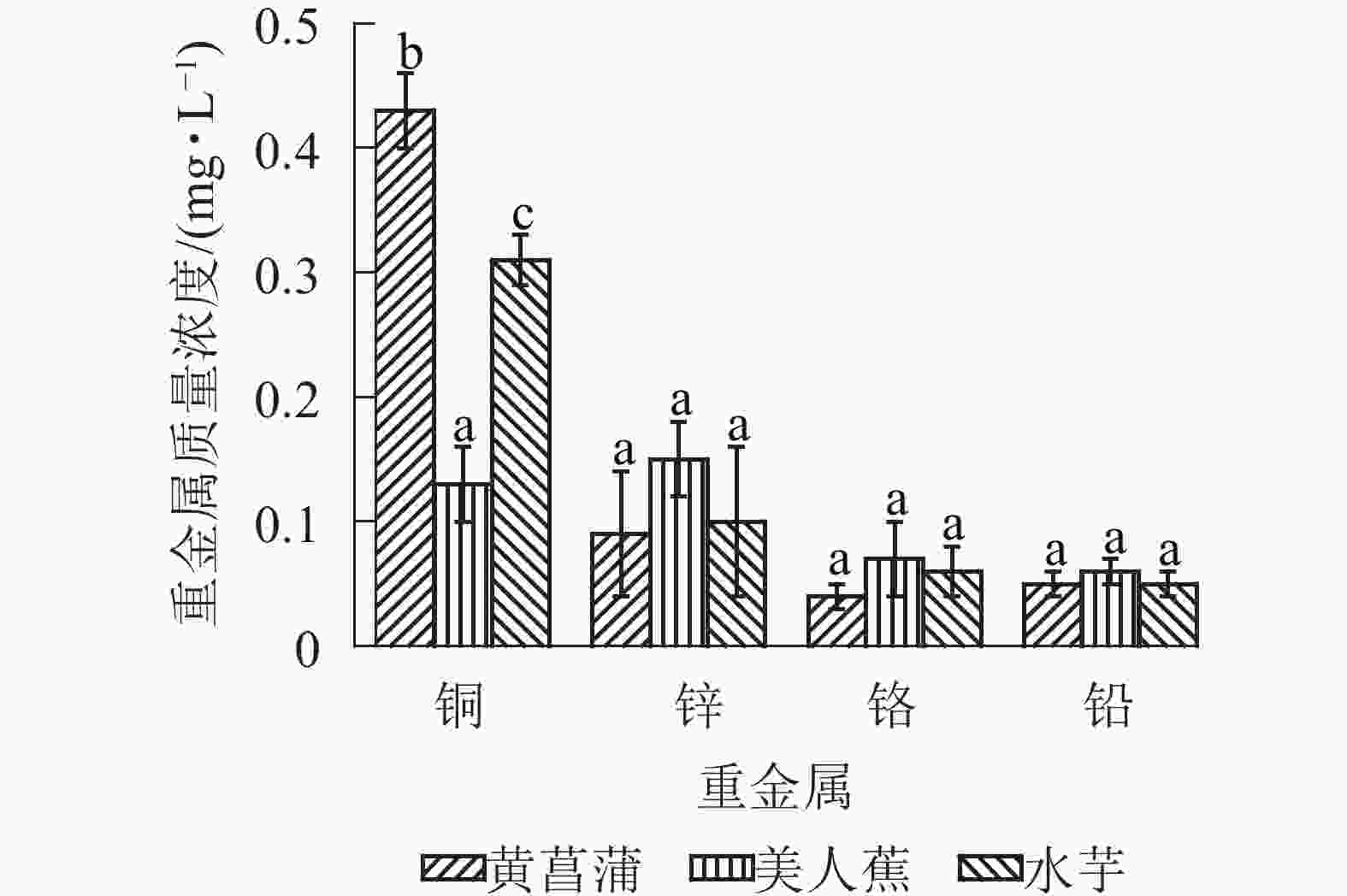
3种植物对重金属具有良好的净化能力。20 d时,植物处理组Cu2+、Zn2+、Cr3+和Pb2+质量浓度分别降至0.13~0.43、0.09~0.15、0.04~0.07和0.05~0.06 mg·L−1(图4),优于GB 3838−2002《地表水环境质量标准》之Ⅴ类水标准。3种植物对4种重金属的净化能力各异,黄菖蒲处理组4种重金属的去除率从大到小依次为Zn2+(96.8%)、Cr3+(83.8%)、Cu2+(79.1%)、Pb2+(77.5%);美人蕉组依次为Zn2+(94.3%)、Cu2+(93.7%)、Pb2+(74.9%)、Cr3+(69.7%);水芋组则依次为Zn2+(96.2%)、Cu2+(84.7%)、Pb2+(80.5%)、Cr3+(74.4%)。20 d时,黄菖蒲块茎淀粉中铜、锌、铬和铅平均质量分数分别为10.30、46.7、12.03和1.74 mg·kg−1,美人蕉块茎淀粉中4种重金属质量分数依次为12.68、44.67、8.15和1.32 mg·kg−1,水芋块茎淀粉中4种重金属质量分数则依次为19.28、66.91、9.63和3.97 mg·kg−1。这与水中重金属的去除率数据一致。由此可见,植物块茎中具有较高的重金属富集量。因此,污染水体中共存重金属时,不建议对植物块茎进行资源化利用。
-
黄菖蒲、美人蕉、水芋3种块茎类挺水植物对水中氮磷具有良好的净化能力。氨氮、总磷初始质量浓度分别为7.37~7.53、0.41~0.45 mg·L−1时,试验20 d时,植物处理组氨氮、总氮、总磷质量浓度分别降至0~0.10、0.61~0.91、0.025~0.031 mg·L−1。满足GB 3838−2002《地表水环境质量标准》之Ⅲ类水标准限值要求。3种植物生长良好,未出现叶片枯黄、腐烂等现象。20 d时,黄菖蒲、美人蕉和水芋生物量(平均值)分别增加24.2%、7.3%和26.3%,块茎组织中氮质量分数分别为30.30、24.26,14.73 mg·kg−1,磷质量分数分别为4.14、3.04和4.74 mg·kg−1。黄菖蒲、美人蕉和水芋块茎中淀粉提取量分别为61.3、14.1和64.0 g·kg−1。河道100 m2植物种植区,8个月后,黄菖蒲、美人蕉和水芋块茎可回收淀粉量分别为14.3、1.2、2.6 kg·m−2。
3种植物对水中Cu2+、Zn2+、Cr3+、Pb2+具有良好的净化效果。黄菖蒲处理组4种重金属的去除率从大到小依次为Zn2+(96.8%)、Cr3+(83.8%、Cu2+(79.1%)、Pb2+(77.5%);美人蕉组依次为Zn2+(94.3%)、Cu2+(93.7%)、Pb2+(74.9%)、Cr3+(69.7%);水芋组则依次为Zn2+(96.2%)、Cu2+(84.7%)、Pb2+(80.5%)、Cr3+(74.4%)。黄菖蒲块茎淀粉中铜、锌、铬和铅质量分数分别为10.30、46.7、12.03和1.74 mg·kg−1,美人蕉依次为12.68、44.67、8.15和1.32 mg·kg−1,水芋则为19.28、66.91、9.63和3.97 mg·kg−1。污染水体中共存重金属时,不建议对植物块茎进行资源化利用。
Water purification efficiency and resource utilization of three tuberous emergent aquatic plants
-
摘要:
目的 研究常见块茎类水生植物对污染水体营养物质的净化能力及植物块茎淀粉产量,探明淀粉资源化利用的可行性及潜在风险。 方法 通过水培试验,对比黄菖蒲Iris pseudacorus、美人蕉Canna indica、水芋Calla palustris对污染水体的净化性能,以不种植物处理作空白对照,每组设3个重复。考察水中氨氮、总氮和总磷的去除效率,分析氮磷在植物根、茎、叶和块茎中的积累及分配,测定植物块茎中淀粉质量分数及重金属铜(Cu)、锌(Zn)、铬(Cr)和铅(Pb)的富集量。 结果 水中氨氮和总磷初始质量浓度为7.37~7.53、0.41~0.45 mg·L−1时,试验20 d,植物处理组氨氮、总氮和总磷质量浓度分别降至0.01~0.07、0.61~0.91和0.025~0.031 mg·L−1,满足GB 3838−2002《地表水环境质量标准》之Ⅲ类水标准限值要求。黄菖蒲、美人蕉和水芋块茎淀粉提取量分别为61.3、14.1和64.0 g·kg−1。100 m2植物种植试验区,黄菖蒲、美人蕉和水芋区分别回收淀粉量14.3、1.2、2.6 kg。植物块茎可富集重金属,当水中Cu2+、Zn2+、Cr3+和Pb2+初始质量浓度为2.01~2.08、2.56~2.87、0.22~0.26、0.24~0.26 mg·L−1时,黄菖蒲块茎淀粉中铜、锌、铬和铅质量分数分别为10.30、46.7、12.03和1.74 mg·kg−1,美人蕉依次为12.68、44.67、8.15和1.32 mg·kg−1,水芋则为19.28、66.91、9.63和3.97 mg·kg−1。 结论 3种块茎类水生植物对氮磷等营养物质具有较强的净化能力,可回收较为可观的淀粉量,但若污染水体中共存重金属时,不建议对植物块茎进行资源化利用。图4参17 Abstract:Objective This study aims to investigate the purification capacity for nutrients in polluted water and the yield of tuber starch of three common tuberous aquatic plants, and estimate the feasibility and potential risk of starch resource utilization. Method Purification efficiency of Iris pseudacorus, Canna indica and Calla palustris for polluted water body was compared using hydroponic experiment, and three replicates were set for each group. No plant treatment was used as control group. Removal efficiency of ammonium nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus in water was investigated. The contents of nitrogen and phosphorus in plant roots, stems, leaves and tubers were analyzed. The content of starch and heavy metals including Cu, Zn, Cr and Pb in plant tubers were measured. Result When initial concentrations of ammonium nitrogen and total phosphorus were 7.37−7.53 and 0.41−0.45 mg·L−1, concentrations of ammonium nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus in plant treatment groups decreased to 0.01−0.07, 0.61−0.91, and 0.025−0.031 mg·L−1 respectively after 20 days of treatment, which met the Class Ⅲ standard for surface water environmental quality (GB 3838−2002). The starch extracted from tubers of I. pseudacorus, C. indica and C. palustris was 61.3, 14.1 and 64.0 g·kg−1, respectively. Starch yields of these plant species were 14.3, 1.2 and 2.6 kg·m−2 respectively in the 100 m2 trial plot. The tuber could accumulate heavy metals. As initial concentrations of Cu2+, Zn2+, Cr3+ and Pb2+ in water were 2.01−2.08, 2.56−2.87, 0.22−0.26, and 0.24−0.26 mg·L−1, the contents of Cu, Zn, Cr and Pb in tuber starch of I. pseudacorus were 10.30, 46.7, 12.03, and 1.74 mg·kg−1, respectively and those of C. indica were 12.68, 44.67, 8.15 and 1.32 mg·kg−1, respectively, while those of C. palustris were 19.28, 66.91, 9.63 and 3.97 mg·kg−1, respectively. Conclusion The three tuberous aquatic plants can effectively purify nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, and recover a considerable amount of starch. However if heavy metals coexist in the polluted water, plant tubers are not recommended for resource utilization. [Ch, 4 fig. 17 ref.] -
Key words:
- tuberous plant /
- starch /
- heavy metal /
- nitrogen /
- phosphorus /
- polluted water /
- purification efficiency
-
-
[1] SHAO Yuanyuan, PEI Haiyan, HU Wenrong, et al. Bioaugmentation in lab scale constructed wetland microcosms for treating polluted river water and domestic wastewater in northern China [J]. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation, 2014, 95: 151 − 159. [2] 郭炜超, 王趁义, 李琳琳, 等. 潜水式生态介质箱对黑臭水体的修复效果[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(8): 2837 − 2844. GUO Weichao, WANG Chenyi, LI Linlin, et al. The role of submerged group ecological media box in repairing black and odorous water body [J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2019, 30(8): 2837 − 2844. [3] LI Hong, ZHAO Heping, HAO Hulin, et al. Enhanced of nutrient removal from eutrophic water by a plant-microorganisms combined system [J]. Environ Eng Sci, 2011, 28(8): 543 − 554. [4] SRICOTH T, MEEINKUIRT W, PICHTEL J, et al. Synergistic phytoremediation of wastewater by two aquatic plants (Typha angustifolia and Eichhornia crassipes) and potential as biomass fuel [J]. Environ Sci Poll Res, 2017, 25: 5344 − 5358. [5] YU Cencen, SHI Chenfei, JI Ming, et al. Taste and odor compounds associated with aquatic plants in Taihu Lake: distribution and producing potential [J]. Environ Sci Poll Res, 2019, 26(33): 34510 − 34520. [6] CESCHIN S, SGAMBATO V, ELLWOOD N T W, et al. Phytoremediation performance of Lemna communities in a constructed wetland system for wastewater treatment [J]. Environ Exp Bot, 2019, 162(6): 67 − 71. [7] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 2018年中国生态环境状况公报[R]. 北京: 生态环境部, 2019. [8] HOOVER R. Composition, molecular structure, and physicochemical properties of tuber and root starch: a review [J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2001, 45(3): 253 − 267. [9] 杨丽英, 隋启君, 李军, 等. 云南省块根块茎淀粉植物资源开发现状及其发展[J]. 云南农业大学学报, 2005, 20(6): 871 − 874. YANG Liying, SUI Qijun, LI Jun, et al. The utilization situation and development of root and tuber starch resources in Yunnan Province [J]. J Yunnan Agric Univ, 2005, 20(6): 871 − 874. [10] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [11] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. [12] 金树权, 周金波, 朱晓丽, 等. 10种水生植物的氮磷吸收和水质净化能力比较研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(8): 1571 − 1575. JIN Shuquan, ZHOU Jinbo, ZHU Xiaoli, et al. Comparison of nitrogen and phosphorus uptake and water purification ability of ten aquatic macrophytes [J]. J Agro-Environ Sci, 2010, 29(8): 1571 − 1575. [13] 谢东升, 朱文逸, 陈劲鹏, 等. 5种华南地区水生植物对城市生活污水的净化效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(8): 1903 − 1908. XIE Dongshen, ZHU Wenyi, CHEN Jinpeng, et al. Effects of five aquatic plants in south China on purification of municipal wastewater [J]. Chin J Environ Eng, 2019, 13(8): 1903 − 1908. [14] XIAO Jibo, CHU Shuyi, TIAN Guangming, et al. An eco-tank system containing microbes and different aquatic plant species for the bioremediation of N, N-dimethylformamide polluted river waters [J]. J Hazardous Mater, 2016, 320: 564 − 570. [15] XIAO Jibo, WANG Huiming, CHU Shuyi, et al. Dynamic remediation test of polluted river water by eco-tank system [J]. Environ Technol, 2013, 34(1/4): 553 − 558. [16] 吴建强, 王敏, 吴健, 等. 4种浮床植物吸收水体氮磷能力试验研究[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(4): 995 − 999. WU Jianqiang, WANG Min, WU Jian, et al. Study on the nitrogen and phosphorus uptake ability of four plants cultivated on floating-bed [J]. Environ Sci, 2011, 32(4): 995 − 999. [17] 洪瑜, 王英, 王芳, 等. 5种浮床植物对宁夏引黄灌区稻田退水中氮磷的去除效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(11): 2637 − 2645. HONG Yu, WANG Ying, WANG Fang, et al. Removal effect of nitrogen and phosphorus in the return flow of rice paddy in Ningxia Yellow River irrigation region by five plants cultivated on floating-bed [J]. Chin J Environ Eng, 2019, 13(11): 2637 − 2645. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200124






 下载:
下载: