-
随着乡村振兴战略的提出,在乡村产业发展的驱动下,乡村景观环境建设成为乡村振兴的核心内容。但乡村景观环境建设仍停留在建筑、道路等物质环境层面,乡村景观的地方性和特色性不明显。究其原因,一是规划人员缺乏对乡村景观地域性特征的认识,盲目模仿城市景观或套用其他乡村的景观营造模式[1];二是对乡村景观资源的优劣认识不足,没能科学地分析乡村景观资源,从而导致资源利用效率低[2]。因此,亟需识别乡村独有的景观特征并明确其景观价值,确定合适的景观营造模式。
景观特征是指某个区域内使景观与众不同并创造出一种特定场地感受的因素,景观特征评估作为理解和表达景观特征的一种工具已经被很多国家运用于国家、地方尺度的景观特征评估[3-6]。在国内主要应用于各种规模尺度的城镇、乡村、风景区和自然保护地层面[7-11]的景观特征评估。景观特征评估包括2个阶段:一是“特征化”阶段,即景观特征识别,目的是对景观特征进行识别、绘制、分类和描述;二是“做出判断”阶段,即景观特征识别结果的应用,目的是根据景观差异形成景观政策分区和发展目标,确保随着时间的变化和发展不会破坏特定景观的特征。景观特征评估强调的是景观的差异和多样性,坚持价值统一原则,认为每处景观都是独一无二的,而要确定景观的“好坏”,有针对性地提出改善景观的对策,则应结合景观评价等其他方法对景观特征进行价值评估。在村域尺度进行的景观评价主要是从乡村生态学[12]、景观美学[13-14]等单方面进行评价,或者从乡村景观质量[15-16]、景观功能[17]等角度进行综合评价[18-19],但很少将景观特征识别和景观综合评价结合起来研究乡村景观的营造模式。为此,本研究选择浙江省杭州市瓶窑镇为案例,以景观特征识别的结果为依据构建景观综合评价模型,进行乡村景观的特征研究,提出有针对性的乡村景观营造模式,为乡村景观规划提供理论支持。
-
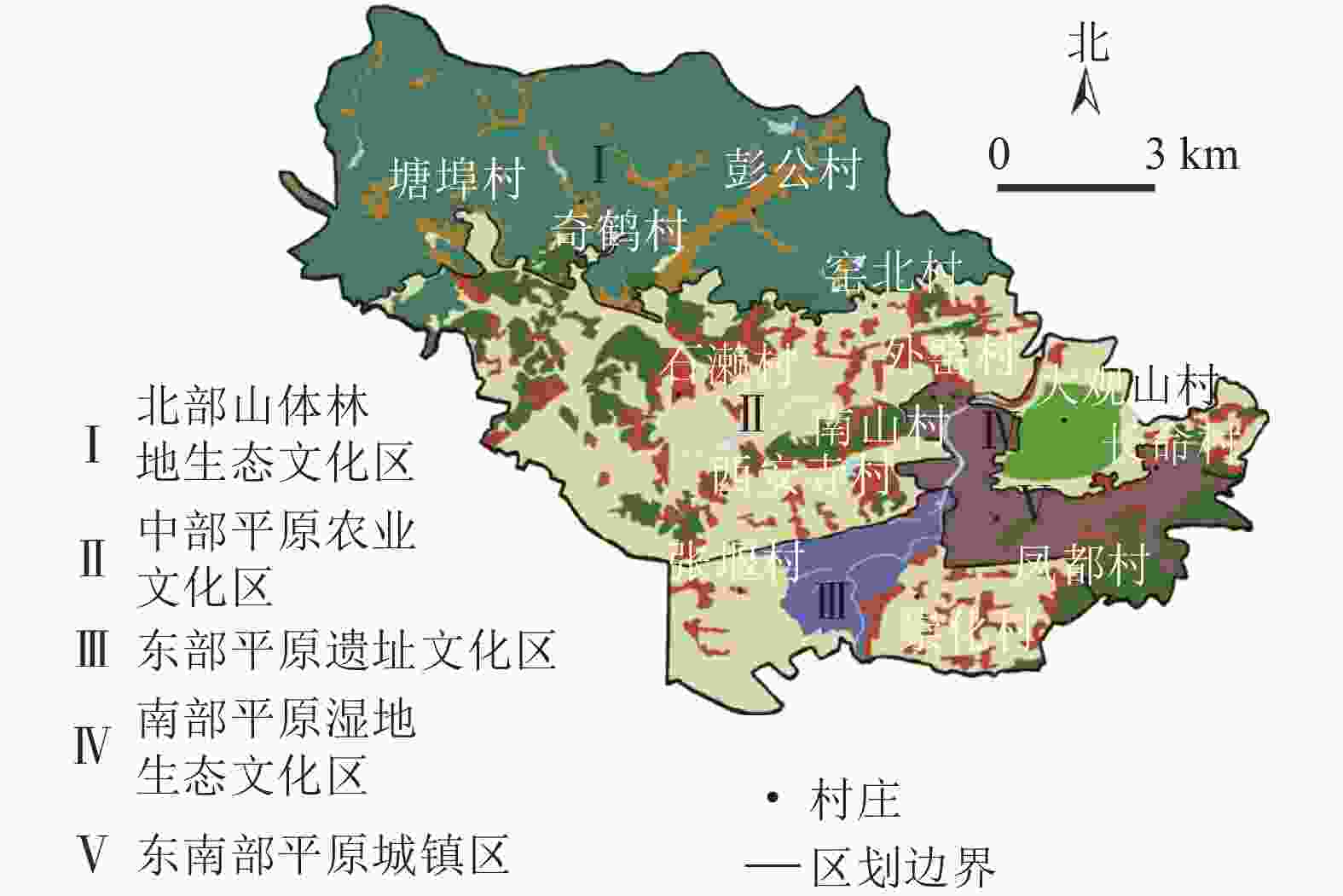
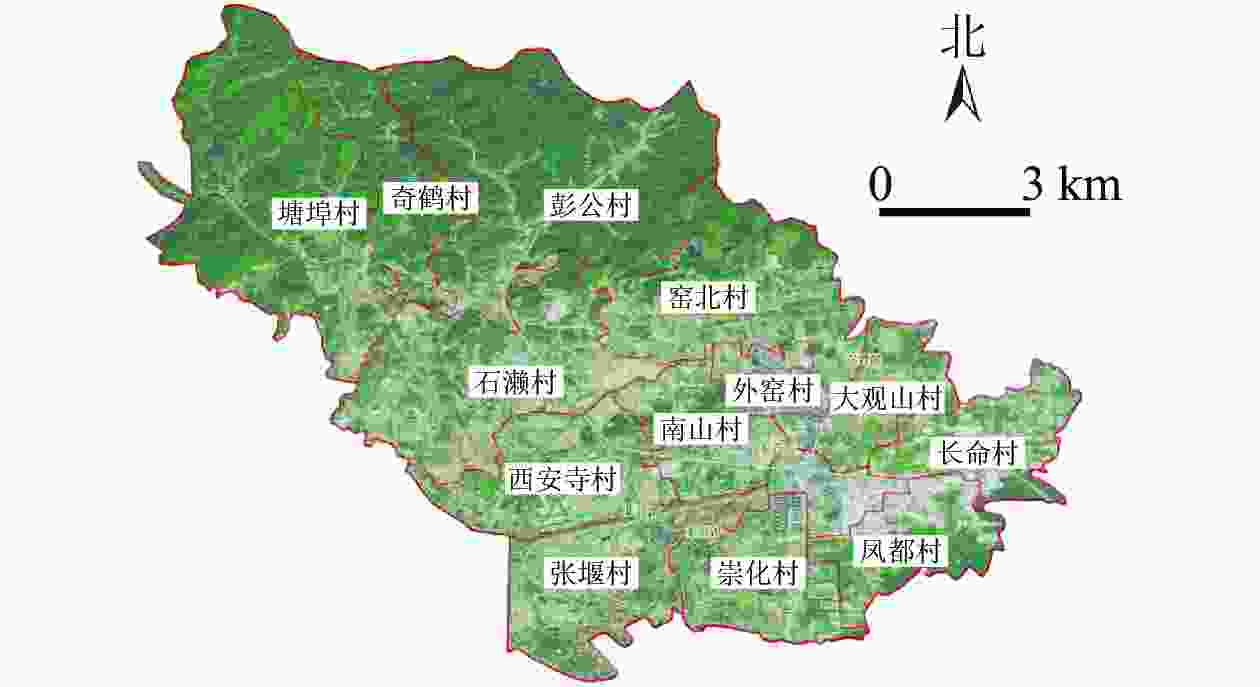
瓶窑镇位于杭州市北郊,距杭州市中心25 km,下辖13个建制村(外窑村、南山村、张堰村、长命村、西安寺村、石濑村、塘埠村、凤都村、大观山村、崇化村、窑北村、彭公村、奇鹤村)和6个社区(图1),总人口5.78万人,总面积128.81 km2。瓶窑境内,人文资源中以良渚文化及其遗址最为突出,苕溪文化、老街文化、南山文化、民俗文化等多元文化是对良渚文化内涵的丰富和延展,除了有以物质形态为主的“有形”文化遗产,还有非物质文化遗产,如余杭纸伞、风筝制作技艺等。瓶窑镇处于天目山系的末端,宏观构造特征大体可分为西部山地丘陵区和东部平原区,境内地势由北向南倾斜,以东苕溪为界,西部为山地丘陵河谷,东部为水网平原。镇境西北属天目山东麓山脉之余脉。因苕溪而成的河谷平原分布在南、中、北3条苕溪谷口至东苕溪一带,低河漫滩,地势起伏,自然资源丰富。在良渚遗址申遗成功和全域旅游发展的背景下,旅游资源的快速开发使瓶窑镇的乡村景观发展面临极大的机遇和挑战。
-
景观特征识别所需资料包括文字资料和图片资料。文字资料包括相关的研究文献、该地区的规划报告、历史文化信息等。图片资料包括瓶窑镇村庄行政边界、城乡用地现状图(浙江省城乡规划设计研究院);4.12 m分辨率天地影像图、8.24 m分辨率数据高程模型(DEM)和2020年30 m分辨率地表覆盖图(来源于91位图助手);人文景观矢量图为笔者自绘,通过文字资料和实际调研获取景观点的地理位置和景观资源等级,在谷歌地球中根据获取的地理位置进行坐标校对后绘制景观点,最后将其导入ArcGIS,根据景观点的影响程度即景观资源等级给景观点赋予权重值,构建瓶窑镇人文景观信息数据库。
-
通过地理信息系统(GIS)中的重分类、聚类分析、核密度分析等空间分析工具,对图片和文字资料进行处理分析,得到景观特征区域的初步分类图。具体步骤如下:①要素筛选。总结乡村景观分类的相关研究[20-22],参考乡村地区的景观特征识别案例,根据瓶窑镇的现状筛选出具有代表性的景观特征要素,包括自然和人文2种类型,其中自然景观特征包括2类景观要素10个要素因子,人文景观特征包括3大景观要素12个要素因子(表1)。
表 1 瓶窑镇景观特征要素分类
Table 1. Classification of landscape characteristic elements in Pingyao Town
自然景观要素 要素因子 面积/km2 占比/% 人文景观要素 要素因子 地形起伏 平原(0~30) 68.12 52.88 遗址遗迹 人类活动遗址、废弃生产地废城、聚落遗迹 台地(30~70) 20.92 16.25 丘陵(70~200) 39.60 30.74 山地(200~500) 0.17 0.13 地表覆盖类型 耕地 55.27 42.91 人文旅游地 康体游乐休闲度假地、宗教与祭祀活动场所、文 化活动场所、军事观光地 森林 51.22 39.76 草地 4.12 3.20 湿地 1.89 1.47 景观建筑设施 单体活动场馆、景观建筑与附属型建筑、传统与 乡土建筑、归葬地、交通建筑 水体 2.17 1.68 人造地表 14.14 10.98 说明:地形起伏要素因子括号内数据为海拔(m) ②要素特征区域划分。重分类与聚类分析:通过ArcGIS10.2软件按照分类标准对自然景观信息数据库中的数据进行重分类,得到每种自然景观要素的空间图示表达,然后使用地图代数法,在ArcGIS中输入地形起伏度和地表覆盖类型2个因子进行聚类叠加分析[10],得到聚类稳定的乡村自然景观特征类型,对特征类型进行命名,得到自然景观特征客观分类图。
将人文景观资源点作为源点,对筛选出的每种人文景观要素进行核密度分析,源点的核密度越高,核密度分析的颜色越深,表示事件发生的概率越高[23]。将人文景观要素核密度分析图影响范围的轮廓作为划分人文景观特征区域的边界参考。利用ArcGIS将各要素的核密度图进行加权总和。在划分人文景观特征区域时优先考虑区域内的关键文化特征,将同样或比较相似的文化景观相连成片,同时弱化并整合离散和异质的区域,得到乡村人文景观特征初步分类图。
-
场地调研的目的是对自然和人文景观特征初步分类图进行完善和修正,同时对资料中描述不全面的土地利用情况、自然景观、人文景观、景观感知等方面的信息进行补充。调研记录主要包括土地现状利用和景观覆盖情况,景观特征区域的特色和特征描述,景观价值和质量评价。
-
将调整和修正后的乡村自然景观特征空间分类和人文景观特征空间分类进行空间整合,得到最终的景观特征分区图,根据每个区域的景观特征对划分好的景观特征区域进行命名,根据调研时记录的景观信息对每个景观特征区域的地形地势、水体特征、植被特征、农产业特征、聚落特征和人文特征进行描述。
-
景观综合评价分为2个步骤:一是评价指标和权重的确定。在选取评价指标时,以研究区的景观特征识别结果和乡村的关键特征作为选取指标的依据,参考“结构-功能-价值”对指标进行分类[24]。选择风景园林、城乡规划、旅游规划等不同领域的15位专家筛选指标,构建指标体系。因素层和指标层的指标权重通过德尔菲法[15]及层次分析法来确定,依据评价指标体系构建两两判断矩阵,邀请15位专家采用“1~9标度法”对判断矩阵进行打分,整理专家填写的判断矩阵,求解每个矩阵的最大特征值,λmax以及其对应的特征向量ω,对求出的特征向量进行归一化得到权重值,并对矩阵进行一致性检验。二是景观评价结果的计算和分析。釆用多目标线性加权函数法求各指标的评价分值:
${C=\displaystyle \sum _{i=1}^{m}({W}_{i}{D}_{i})}$ ,$ B=\displaystyle \sum_{j=1}^{n}({W}_{j}{C}_{j}) $ 。其中:C为要素指标得分,m为功能指标的个数,Wi为第i个功能指标的权重,Di为第i个功能指标的得分;B为项目指标得分,n为要素指标的个数,Wj为第j个要素指标的权重,Cj为第j个要素指标的得分。定量指标数据来源于相关文献资料,结合指标的具体定义给定指标的上下限值作为定量指标的评分区间,再将指标的实际调查值参考评分区间进行赋分,进而得到定量指标的分值;定性指标由专家打分获得评分值。 -
通过景观特征识别,将各自然景观要素叠加后得到17种自然风景特征单元,聚类分析后划分为6种乡村自然景观特征类型,经人工修正和调整,最终得到细化的乡村自然景观特征分类(图2)。可见瓶窑镇主要呈现为村镇聚落特征类型(包括不同类型和区域的村镇)和自然地理特征类型(包括山林、河湖、湿地、田园等)两大类;村镇特征类型在瓶窑镇全域范围内均有分布;北—中—南呈现出不同的自然地理特征类型,北部以山林景观为主,中部以田园景观为主,南部则以湿地景观为主。
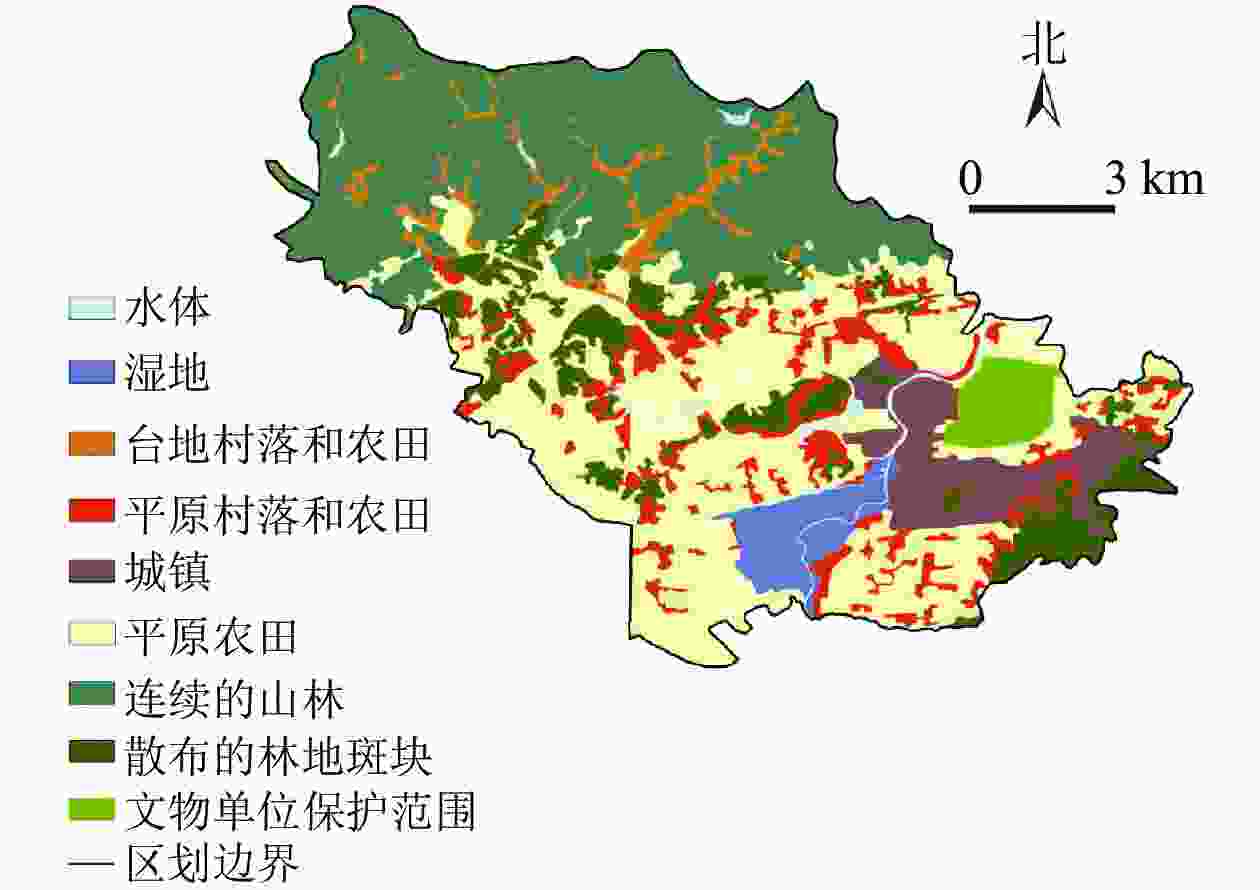
图 2 瓶窑镇乡村自然景观特征分类示意图
Figure 2. Classification map of rural natural landscape features in Pingyao Town
通过对人文景观要素中的遗址遗迹、人文旅游地、景观建筑设施共3种景观进行核密度分析,再将各要素的核密度图进行加权总和,每个要素的权重值默认为1,最终得到人文景观特征空间分析图(图3)。图3表明:瓶窑镇人文底蕴丰厚,文化和建筑设施遗存较多,几乎遍布整个研究区域,瓶窑镇人文景观呈现以良渚文化为内核、多元文化融合的特征。
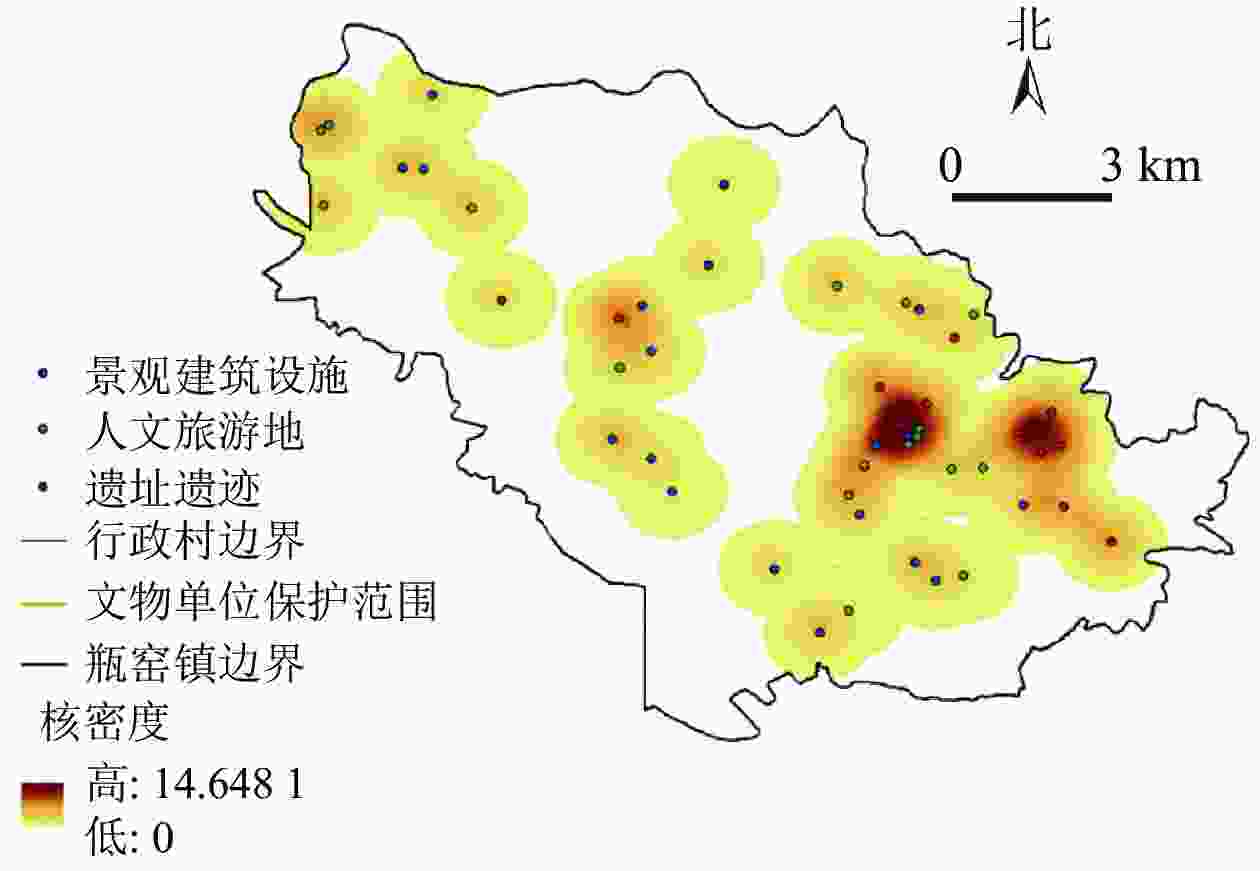
图 3 瓶窑镇人文景观特征空间分析示意图
Figure 3. Spatial analysis map of human landscape characteristics in Pingyao Town
将瓶窑镇乡村自然景观特征分类图和人文景观特征分类图进行叠加,绘制瓶窑镇乡村景观特征图(图4)。瓶窑镇乡村景观可分为北部山体林地生态文化区、中部平原农业文化区、东部平原遗址文化区、南部平原湿地生态文化区4个乡村景观特征区域和1个东南部平原城镇区(不在分析范围)。其中北部山体林地生态文化区地形以山地丘陵为主,有少部分平地;水体以水库和自然溪流为主,水面景观开阔,水质清澈;植被覆盖率高于80%,自然植被以毛竹Phyllostachys edulis居多;农田面积很少,产业以林场以及竹制品加工业为主;聚落沿道路和河流顺应地形呈狭长带状分布;文化资源包括古寺、古道、古戏台、古村落和非物质文化遗产(余杭纸伞制作技艺、风筝制作技艺、笋干制作技艺)。中部平原农业文化区地形以平地为主,有少部分的丘陵;水体以水塘和沟渠为主,水塘较小且形状破碎,水体景观性较差;植被分布在散落的林地斑块区以及村庄内的公共空间;农田是主要的农业土地利用类型,农田分布集中且边界规整,农家多种稻、养蚕;聚落组团或呈格网状分布,聚落周边多为乔木林地和农田;区域内包括南山文化、窑业文化和民俗文化(如石濑花灯、石濑花灯舞)等人文景观资源。东部平原遗址文化区地形以平地为主,边界处地势略高;水体以溪流为主,有少量规则的鱼塘,水质一般;植被覆盖率较低,集中在溪流边坡地带以及人工林地区;耕地多为人工规划种植区,以果蔬大棚种植为主、人工种植林及水稻作为辅;聚落整体呈组团分布,林地斑块和果蔬园地围绕聚落分布;良渚文化及其遗址是该区域内最为突出的人文景观资源。南部平原湿地生态文化区地形以平地和洼地为主,湿地旁有较高的堤坝;水网密布且形式丰富,沟渠和坑塘与农田镶嵌呈格网状规则分布;植被覆盖率高,以自然、湿生植物为主,人工生态林为辅;农业主要以水田、经济果蔬为主,农田和水网之间有大量的鱼塘发展渔业;聚落散落分布在农耕用地之中,房前屋后仅靠水塘和农田;在人文特征方面,以水网、湿地草荡、田园景观为基地,融合苕溪文化、窑山文化、老街文化、禅修文化等文化资源,形成稻作、渔业、水利等风俗。
-
自然景观特征以自然和半自然景观为主,包括生产性景观和生态性景观,如农田耕地、森林、草地、湿地等,人文景观在空间上则表现为以生活景观为中心,两者镶嵌构成“社会—经济—环境”复合生态系统。评价模型的项目层从“生活—生产—生态”共3个层面分为乡村生活性景观、生产性景观和生态性景观三大指标,因素层的指标以瓶窑镇乡村景观构成要素为依据,指标层的指标则以瓶窑镇乡村景观特征和要素指标的主要功能为依据,以此建立景观特征与评价指标的联系。邀请15位相关专业的专家对指标进行分析筛选,最终确定了4个层次3个项目层指标8个因素层指标22个功能指标(表2)。
表 2 乡村景观综合评价体系的指标与权重
Table 2. Indicators and weights of the comprehensive evaluation system of rural landscape
目标层 项目层 权重 因素层 权重 归一化权重 指标层 权重 归一化权重 乡村景观综合评价A 生活性景观B1 1/3 道路景观C1 0.387 4 0.129 1 道路通达性D1 0.833 3 0.107 6 道路的景观性和舒适度D2 0.166 7 0.021 5 人文景观C2 0.443 4 0.147 8 历史遗址丰富度D3 0.227 0 0.033 6 历史遗址知名度D4 0.423 6 0.062 6 非物质文化遗产辨识度D5 0.227 0 0.033 6 人文活动丰富度D6 0.122 4 0.018 1 聚落景观C3 0.169 2 0.056 4 景观建筑设施多样性D7 0.553 6 0.031 2 聚落空间有序性D8 0.099 0 0.005 6 民居建筑统一性D9 0.232 2 0.013 1 聚落整体美观性D10 0.115 2 0.006 5 生产性景观B2 1/3 农业生产景观C4 0.500 0 0.166 7 农业用地面积D11 0.344 5 0.057 4 农业耕作景观特色度D12 0.108 5 0.018 1 地方农产品丰富度D13 0.546 9 0.091 2 农业休闲景观C5 0.500 0 0.166 7 休闲农业景观吸引力D14 0.833 3 0.138 9 农业景观整体性D15 0.166 7 0.027 8 生态性景观B3 1/3 地文景观C6 0.217 6 0.072 5 地形地貌丰富度D16 0.800 0 0.058 0 地形地貌美感度D17 0.200 0 0.014 5 水域景观C7 0.691 0 0.230 3 水域景观多样性D18 0.558 4 0.128 6 水体亲水性D19 0.122 0 0.028 1 水体观赏性D20 0.319 6 0.073 6 植物景观C8 0.091 4 0.030 5 植被覆盖率D21 0.857 1 0.026 1 乡村植物多样性D22 0.142 9 0.004 4 -
构建综合评价体系的目的在于通过生活性景观、生产性景观和生态性景观指标的得分排序,结合评价区域的关键特征和各指标得分情况,选择适合乡村的景观营造模式,因此项目层的指标应是等权重的,即生活性景观、生产性景观、生态性景观3项指标权重均为1/3[25]。依据评价指标体系构建C1~C3、C4~C5、C6~C8、D1~D2、D3~D6、D7~D10、D11~D13、D14~D15、D16~D17、D18~D20、D21~D22等11个两两判断矩阵,对特征向量进行归一化得到权重值(表2)。11个判断矩阵的一致性比率分别为0.017 6、0.000 0、0.051 6、0.000 0、0.003 9、0.050 4、0.051 6、0.000 0、0.000 0、0.017 6、0.000 0,均小于0.1,通过了一致性性检验,权重分配合理。
-
由表3可见:4个乡村景观特征区的项目层指标得分从高到低排序分别为北部山体林地生态文化区(生态性景观>生活性景观>生产性景观)、中部平原农业文化区(生产性景观>生活性景观>生态性景观)、东部平原遗址文化区(生活性景观>生产性景观>生态性景观)、南部平原湿地生态文化区(生态性景观>生产性景观>生活性景观)。
表 3 乡村景观特征区综合评价结果
Table 3. Comprehensive evaluation results of rural landscape
项目层 因素层 北部山体林地生态文化区 中部平原农业文化区 东部平原遗址文化区 南部平原湿地生态文化区 得分 总分 得分 总分 得分 总分 得分 总分 生活性景观
B1道路景观C1 0.738 0 2.097 6 0.981 2 2.141 5 1.071 6 2.767 9 0.925 2 1.906 6 人文景观C2 0.972 6 0.830 6 1.291 3 0.623 4 聚落景观C3 0.387 0 0.329 7 0.405 0 0.358 0 生产性景观
B2农业生产景观C4 0.657 7 1.471 7 1.409 1 2.803 8 0.835 3 1.885 5 1.092 0 1.861 7 农业休闲景观C5 0.814 0 1.394 7 1.050 2 0.769 7 生态性景观
B3地文景观C6 0.533 6 2.337 0 0.232 0 1.359 0 0.365 4 1.680 9 0.471 3 2.689 8 水体景观C7 1.533 3 0.974 5 1.163 0 1.996 2 植物景观C8 0.270 1 0.152 5 0.152 5 0.222 3 由4个乡村景观特征区的因素层指标的评价分值(表3)可见:北部山体林地生态文化区和南部平原湿地生态文化区最突出的特征是自然生态景观,北部山体林地生态文化区距离城镇较远而拥有丰富的自然景观和生物资源以及较低的人口密度,由此体现出优越的自然生态环境,南部平原湿地生态文化区拥有磨盘滩湿地等绝佳的生态资源,使得该村有宜人的生态居住环境;中部平原农业文化区最突出的特征是农业景观,该区为典型的江南平原农业景观类型,区域内较高的农业用地面积及其景观特色度为休闲农业的发展奠定了良好的基础;东部平原遗址文化区最突出的特征是人文景观,因为该区拥有以良渚遗址为核心的优越的文
化资源。 -
景观特征识别作为一种获取研究区域景观特点的工具,能为各种类型的乡村景观规划设计提供准确的信息参考,避免在规划设计的过程中破坏乡村原有的景观风貌。基于本研究结果,针对瓶窑镇提出4种兼顾景观特征和景观价值的典型乡村景观营造模式:①自然纯朴、强化本土价值的山地聚落景观营造模式。北部山体林地生态文化区的景观营造模式应该以保护乡村自然生态环境为前提,充分挖掘人文景观资源,强化本土价值的塑造、自然纯朴的回归,疏解工业发展与自然生态的矛盾,通过发展绿色环保产业维持乡村经济可持续力,如利用良好的生态环境和深厚的人文资源开发餐饮、民俗、民宿等旅游产品,打造山地康养度假地、户外运动休闲基地等吸引游客观光体验。
②创新田园、结合娱乐体验的平原农业景观营造模式。充分考虑中西部平原农业文化区的景观特征和资源条件,立足于典型江南平原乡村景观、生态农业和文化积淀,打造休闲与观光相协调、农业与创新相结合、文化产业相促进的田园休闲景观发展模式。一方面,强化休闲农业资源点,植入文创产业和艺术产业元素,使其成为极具吸引力的游憩娱乐节点;另一方面注重水域、林地与农田景观的结合,增强平原农田景观特征区域景观形态多样性;最后,可以利用农业和自然资源条件,建立农业生态园、农艺园、农学教育基地等来实现生态田园创新发展。
③文物保护、突出文化主题的历史遗址景观营造模式。对于中东部平原遗址文化区的景观营造模式建议是在保护文物遗址的同时,不缩小现有稻田、水库、水渠、潭堰等水体的面积,同时采取封山育林、水源涵养等措施维护遗址区周边的生态环境,维持生物多样性和植被覆盖率;另外,整合遗产、乡村等资源和元素,集遗址再现、文化科普、田园休闲等功能,打造历史文化主题突出的乡村景观。
④多元循环、紧密遵循生态的平原湿地景观营造模式。为保护南部平原湿地生态文化区的水域湿地等生物资源和生态环境,应防止农业生产破坏自然用地的完整性和多样性,建议采用还原生态用地,引导绿色生态产业发展的景观模式,如建设湿地公园,以生态为本底、亲水为吸引,在打造湿地的生态观光和休闲功能的同时能够有效的保护自然景观资源,促进景观特征系统内部的循环可持续发展。另外,通过建立生态资源的价值补贴机制,逐渐缩减建设用地,并分阶段使低效耕地退出生态影响区,使得乡村生态资源的多元价值实现,形成长效利用的景观营造模式。
Rural landscape construction model based on the recognition and evaluation of landscape features
-
摘要:
目的 探索符合乡村个性特征的景观营造模式,提出优化乡村景观风貌的规划方法。 方法 以杭州市瓶窑镇为例,从乡村景观特征识别和景观综合评价的角度出发,基于瓶窑镇的空间数据和调研信息,通过ArcGIS对景观特征要素进行空间图示表达,划分景观特征区域,并构建与景观特征相联系的景观功能评价模型,对乡村景观特征区域进行评价。 结果 ①瓶窑镇形成北部山体林地生态文化区、中部平原农业文化区、东部平原遗址文化区、南部平原湿地生态文化区4个乡村景观特征区域;②4个乡村景观特征区的项目层指标得分从高到底排序分别是:北部山体林地生态文化区(生态性景观>生活性景观>生产性景观)、中部平原农业文化区(生产性景观>生活性景观>生态性景观)、东部平原遗址文化区(生活性景观>生产性景观>生态性景观)、南部平原湿地生态文化区(生态性景观>生产性景观>生活性景观)。 结论 景观特征识别能为乡村景观规划提供准确信息,鉴于此,本研究为杭州市瓶窑镇提出了4种兼顾景观特征和景观价值的典型乡村景观营造模型:瓶窑镇山地聚落景观营造模式、平原农业景观营造模式、历史遗址景观营造模式和平原湿地景观营造模式,可为乡村景观建设提供了科学依据。图4表3参25 Abstract:Objective With an investigation of the characteristics of the the rural landscape, the study is aimed to research its construction model and propose a planning method for optimization. Method First, taking Pingyao Town of Hangzhou as an example, with the conduct of rural landscape character identification and comprehensive landscape evaluation and the collection of spatial data and survey information, spatial pictorial representation was carried out of the landscape features whereas the areas were divided using ArcGIS. Then a landscape function evaluation model related to landscape character was constructed to assess the rural landscape featured areas. Result (1) Pingyao Town enjoys four rural landscape featured areas, namely, the northern mountain forest ecological and cultural area, the central plain agricultural and cultural area, the eastern plain cultural area and the southern plain wetland ecological and cultural area; (2) Of the four rural landscape featured areas, the northern mountain forest ecological and cultural area (ecological landscape>living landscape>productive landscape) scored the highest, followed by the central plain agricultural and cultural area (productive landscape>living landscape>ecological landscape), the eastern plain area of historical sites (living landscape>productive landscape>ecological landscape) and the southern plain wetland ecological and cultural area (ecological landscape>productive landscape>living landscape). Conclusion In accordance with the regional and historical features of Pingyao Town in Hangzhou, four landscape construction models have been proposed: the mountain settlement landscape model, the plain agricultural landscape model, the historical site landscape model and the plain wetland landscape model, which provides a scientific basis for other and further rural landscape construction. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 25 ref.] -
表 1 瓶窑镇景观特征要素分类
Table 1. Classification of landscape characteristic elements in Pingyao Town
自然景观要素 要素因子 面积/km2 占比/% 人文景观要素 要素因子 地形起伏 平原(0~30) 68.12 52.88 遗址遗迹 人类活动遗址、废弃生产地废城、聚落遗迹 台地(30~70) 20.92 16.25 丘陵(70~200) 39.60 30.74 山地(200~500) 0.17 0.13 地表覆盖类型 耕地 55.27 42.91 人文旅游地 康体游乐休闲度假地、宗教与祭祀活动场所、文 化活动场所、军事观光地 森林 51.22 39.76 草地 4.12 3.20 湿地 1.89 1.47 景观建筑设施 单体活动场馆、景观建筑与附属型建筑、传统与 乡土建筑、归葬地、交通建筑 水体 2.17 1.68 人造地表 14.14 10.98 说明:地形起伏要素因子括号内数据为海拔(m) 表 2 乡村景观综合评价体系的指标与权重
Table 2. Indicators and weights of the comprehensive evaluation system of rural landscape
目标层 项目层 权重 因素层 权重 归一化权重 指标层 权重 归一化权重 乡村景观综合评价A 生活性景观B1 1/3 道路景观C1 0.387 4 0.129 1 道路通达性D1 0.833 3 0.107 6 道路的景观性和舒适度D2 0.166 7 0.021 5 人文景观C2 0.443 4 0.147 8 历史遗址丰富度D3 0.227 0 0.033 6 历史遗址知名度D4 0.423 6 0.062 6 非物质文化遗产辨识度D5 0.227 0 0.033 6 人文活动丰富度D6 0.122 4 0.018 1 聚落景观C3 0.169 2 0.056 4 景观建筑设施多样性D7 0.553 6 0.031 2 聚落空间有序性D8 0.099 0 0.005 6 民居建筑统一性D9 0.232 2 0.013 1 聚落整体美观性D10 0.115 2 0.006 5 生产性景观B2 1/3 农业生产景观C4 0.500 0 0.166 7 农业用地面积D11 0.344 5 0.057 4 农业耕作景观特色度D12 0.108 5 0.018 1 地方农产品丰富度D13 0.546 9 0.091 2 农业休闲景观C5 0.500 0 0.166 7 休闲农业景观吸引力D14 0.833 3 0.138 9 农业景观整体性D15 0.166 7 0.027 8 生态性景观B3 1/3 地文景观C6 0.217 6 0.072 5 地形地貌丰富度D16 0.800 0 0.058 0 地形地貌美感度D17 0.200 0 0.014 5 水域景观C7 0.691 0 0.230 3 水域景观多样性D18 0.558 4 0.128 6 水体亲水性D19 0.122 0 0.028 1 水体观赏性D20 0.319 6 0.073 6 植物景观C8 0.091 4 0.030 5 植被覆盖率D21 0.857 1 0.026 1 乡村植物多样性D22 0.142 9 0.004 4 表 3 乡村景观特征区综合评价结果
Table 3. Comprehensive evaluation results of rural landscape
项目层 因素层 北部山体林地生态文化区 中部平原农业文化区 东部平原遗址文化区 南部平原湿地生态文化区 得分 总分 得分 总分 得分 总分 得分 总分 生活性景观
B1道路景观C1 0.738 0 2.097 6 0.981 2 2.141 5 1.071 6 2.767 9 0.925 2 1.906 6 人文景观C2 0.972 6 0.830 6 1.291 3 0.623 4 聚落景观C3 0.387 0 0.329 7 0.405 0 0.358 0 生产性景观
B2农业生产景观C4 0.657 7 1.471 7 1.409 1 2.803 8 0.835 3 1.885 5 1.092 0 1.861 7 农业休闲景观C5 0.814 0 1.394 7 1.050 2 0.769 7 生态性景观
B3地文景观C6 0.533 6 2.337 0 0.232 0 1.359 0 0.365 4 1.680 9 0.471 3 2.689 8 水体景观C7 1.533 3 0.974 5 1.163 0 1.996 2 植物景观C8 0.270 1 0.152 5 0.152 5 0.222 3 -
[1] 张茜, 李朋瑶, 宇振荣. 基于景观特征评价的乡村生态系统服务提升规划和设计——以长沙市乔口镇为例[J]. 中国园林, 2015, 31(12): 26 − 31. ZHANG Qian, LI Pengyao, YU Zhenrong. Rural ecosystem service enhancement planning and design based on landscape character assessment: a case study of Qiaokou Town, Changsha City [J]. Chin Landscape Archit, 2015, 31(12): 26 − 31. [2] 王建文. 基于AVC的乡村景观综合评价——以福建长汀张地村为例[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版), 2016, 13(27): 23 − 27, 4. WANG Jianwen. Comprehensive evaluation of rural landscape based on AVC: a case study of Zhangdi Village, Changting, Fujian [J]. J Yangtze Univ Self Sci Ed, 2016, 13(27): 23 − 27, 4. [3] TUDOR C. An Approach to Landscape Character Assessment[M]. London: Natural England, 2014. [4] DIACONO M. Landscape Character Assessment-Present Practice and the Future[D]. Oxford: Oxford Brookes University, 1997. [5] BRABYN L. Classifying landscape character [J]. Landscape Res, 2009, 34(3): 299 − 321. [6] WASCHR D M. European Landscape Character Areas-Typologies, Cartography and Indicators for the Assessment of Sustainable Landscapes[M].Wageningen: Landscape Europe, 2005 [7] 刘文平, 宇振荣. 北京市海淀区景观特征类型识别及评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(5): 1338 − 1344. LIU Wenping, YU Zhenrong. Identification and assessment of landscape character of Haidian District, Beijing [J]. Chin J Ecol, 2016, 35(5): 1338 − 1344. [8] 马毅, 赵天宇. 基于数据库分析的东北村镇景观特征与发展模式研究[J]. 建筑学报, 2017(增刊): 128 − 133. MA Yi, ZHAO Tianyu. Research on landscape characteristics and development models of villages and towns in Northeast China based on database analysis [J]. J Archit, 2017(suppl): 128 − 133. [9] 张茜, 刘文平, 宇振荣. 乡村景观特征评价方法——以长沙市乔口镇为例[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(5): 1537 − 1547. ZHANG Qian, LIU Wenping, YU Zhenrong. Evaluation method of rural landscape features: taking Qiaokou Town, Changsha City as an example [J]. J Appl Ecol, 2015, 26(5): 1537 − 1547. [10] 赵烨, 高翅. 名山风景区风景特质理论体系及其实践——以武当山为例[J]. 中国园林, 2019, 35(10): 107 − 112. ZHAO Ye, GAO Chi. The theoretical system and practice of scenic characteristics of famous mountain scenic spots: taking Wudang Mountain as an example [J]. Chin Landscape Archit, 2019, 35(10): 107 − 112. [11] 孙乔昀, 张玉钧. 自然区域景观特征识别及其价值评估——以青海湖流域为例[J]. 中国园林, 2020, 36(9): 76 − 81. SUN Qiaoyun, ZHANG Yujun. Natural area landscape feature recognition and its value evaluation: taking Qinghai Lake Basin as an example [J]. Chin Landscape Archit, 2020, 36(9): 76 − 81. [12] 肖禾, 李良涛, 张茜, 等. 小尺度乡村景观生态评价及重构研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(12): 1554 − 1564. XIAO He, LI Liangtao, ZHANG Qian, et al. Research on ecological evaluation and reconstruction of small-scale rural landscape [J]. Chin J Eco-Agric, 2013, 21(12): 1554 − 1564. [13] GOODEY B. Methods of Environmental Impact Assessment[M]. London: Oxford Brooks University UCL Press, 1995: 78 − 95. [14] 孙漪南, 赵芯, 王宇泓, 等. 基于VR全景图技术的乡村景观视觉评价偏好研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(12): 104 − 112. SUN Yinan, ZHAO Xin, WANG Yuhong, et al. Research on the preference of rural landscape visual evaluation based on VR panoramic image technology [J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2016, 38(12): 104 − 112. [15] 李宇奇, 罗奕爽, 黎燕琼, 等. 基于AHP法的乡村景观质量评价体系构建——以川西林盘为例[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2018, 33(2): 263 − 268. LI Yuqi, LUO Yishuang, LI Yanqiong. Construction of rural landscape quality evaluation system based on AHP method: taking Linpan in west Sichuan as an example [J]. J Northwest For Univ, 2018, 33(2): 263 − 268. [16] ARRIAZA M. Assessing the visual quality of rural landscapes [J]. Landscape Urban Planning, 2004, 69(1): 115 − 125. [17] 谢花林. 乡村景观功能评价[J]. 生态学报, 2004, 24(9): 1988 − 1993. XIE Hualin. Evaluation of rural landscape function [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2004, 24(9): 1988 − 1993. [18] GULINCK H. A framework for comparative landscape analysis and evaluation based on land cover data, with an application in the Madrid region [J]. Landscape Urban Plann, 2001, 55(6): 257 − 270. [19] 蔡洁, 李世平, 董霁红, 等. 文登市乡村景观评价[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2015, 36(2): 70 − 77. CAI Jie, LI Shiping, DONG Jihong, et al. Evaluation of rural landscape in Wendeng City [J]. China Agric Resour Reg, 2015, 36(2): 70 − 77. [20] 王仰麟. 景观生态分类的理论方法[J]. 应用生态学报, 1996, 7(增刊): 121 − 126. WANG Yanglin. A theoretical methodology of landscape eco-classification [J]. J Appl Ecol, 1996, 7(suppl): 121 − 126. [21] MONICA G T. Landscape ecology: the effect of pattern on process [J]. Ann Rev Ecol Syst, 1989, 20: 171 − 197. [22] 肖禾. 不同尺度乡村生态景观评价与规划方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014. XIAO He. Evaluation and Planning Methods Research of Rural Ecological Landscape on Different Scales [D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014. [23] 蔡雪娇, 吴志峰, 程炯. 基于核密度估算的路网格局与景观破碎化分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(1): 158 − 164. CAI Xuejiao, WU Zhifeng, CHENG Jiong. Analysis of road network pattern and landscape fragmentation based on kernel density estimation [J]. Chin J Ecol, 2012, 31(1): 158 − 164. [24] SCHNEIDER A K. Agricultural impacts on landscapes: developing iindicators for policy analysis: proceedings from NIJOS/OECD Expert Meeting on agricultural landscape indicators in Oslo, Norway October 7 − 9, 2002 [J/OL]. Cont Women S Writing, 2003[2021-09-10]. doi: 10.1093/cww/vps028. [25] 郭彦丹. 基于景观功能评价的乡村发展模式研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2015. GUO Yandan. Research on Rural Development Model based on Landscape Function Evaluation [D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2015. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210644






 下载:
下载: