-
夏蜡梅Sinocalycanthus chinensis是1963年发表的新种[1],1964年又被提升为新属[2]。该种是中国特有的第三纪古老孑遗植物,目前仅在浙江、安徽两省有少量分布,数量稀少,在分子上有保守的叶绿体基因组,在分类地位上与美国蜡梅属Calycanthus又有着很深的渊源,对阐明东亚—北美植物区系历史的发展和联系很有意义[3]。近年来,大量研究人员对它的种群分布、生理生化以及园林、药用价值等方面作了深入研究[4-9],但对种群结构和群落种间联结的研究未见报道。天台县境内的夏蜡梅则是1959年阙良寿在大雷山首次发现(阙良寿28677,浙江省自然博物院植物标本馆)。天台大雷山是夏蜡梅的第四纪冰期的避难所之一(另一个是临安大明山),与临安不共享一个单倍型(h3),且多样性较低,表明天台县夏蜡梅的种群是比较孤立的,是一个重要的种群分化中心[3]。本研究尝试通过调查天台县大雷山的夏蜡梅种群结构和群落学特征,研究群落组成树种之间的相关性,反映该种群数量动态,揭示群落的结构和功能,评价该种群与生境间的适合度,并预测群落的发展动态,为境内夏蜡梅种群的保护和发展提供科学依据[10-12]。
-
在天台县夏蜡梅分布区域内,选取有代表性的区域进行样地调查。样地面积为20 m×20 m,均匀分成16个5 m×5 m的样方调查乔木层,后在每个样方的右下角划出2 m×2 m的小样方调查灌木层和草本层。乔木层(胸径≥1 cm)进行每木调查,记录种名、高度、胸径、冠幅等;灌木层和草本层记录种名、高度、株数及盖度,并调查样地内的所有层间植物,同时记录样地环境资料(表1)。测量样地内全部夏蜡梅的树高、胸径、冠幅、年龄、分枝数。
表 1 大雷山夏蜡梅群落样地调查特征
Table 1. Survey characteristics of S. chinensis community plot in Dalei Mountain
样地编号 植被类型 地理坐标 海拔/m 坡向 坡度/(°) 坡位 群落郁闭度 人为干扰 Q1 化香树林 28°59′05.24″N,120°49′12.37″E 808 西坡 17 上坡 0.7 间接 Q2 山胡椒林 28°59′02.56″N,120°49′10.87″E 814 西北坡 28 上坡 0.6 间接 Q3 灯台树林 28°58′53.17″N,120°49′01.14″E 824 东坡 30 下坡 0.6 小 Q4 杉木林 28°58′55.71″N,120°49′01.34″E 827 西南坡 5 谷底 0.5 直接 Q5 毛竹林 28°59′18.20″N,120°48′43.84″E 736 西北 22 下坡 0.8 直接 说明:化香树Platycarya strobilacea,山胡椒Lindera glauca,灯台树Bothrocaryum controversum,杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata,毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis -
乔木层重要值(VI)=(相对密度+相对显著度+相对频度)/3×100%。灌木层、草本层种的重要值(VI)=(相对密度+相对盖度+相对频度)/3×100%。
-
Shannon-Wiener指数:H′=
$ -\sum\limits_{i=1}^{S}{p}_{i}\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}{p}_{i} $ ;Pielou指数(均匀度指数):E=H′/lnS;Simpson指数(多样性指数):P=1−$ \sum\limits_{i=1}^{S}{{p}_{i}}^{2} $ ;Gleason指数(物种丰富度指数):D′=n/lnA。其中:S为种i所在样地的物种总数目,pi为种i的重要值(VI),n为群落中的总物种数,A为样地面积。 -
根据夏蜡梅1个生长季内只形成1次生长高峰,且9月中旬之后就不再生长的特性[18],本研究采用数节法计算夏蜡梅的种群结构。
-
总体关系检验RV=ST2/δT2=(1/N)
$\sum\limits_{j=1}^N(T_j-1)^2 /\sum\limits_{i=1}^{S}{{{P}_{i}(1-P}_{i})}^{} $ ,t=(T1+T2+$\cdots $ +TN)/N,Pi=ni/N。则:W=RVN。其中:N为总样方数,S为物种总数;Tj为样方j内出现的物种数,ni为种i出现的样方数;ST2为总数方差,δT2为总体样本方差。基于物种在样地中出现与不出现数据的方差比率来检验多物种间的总体关联性。如果RV=1,即种间无关联;RV>1,则种间为净的正关联; RV<1,种间为净的负关联。采用统计量W来检验RV偏离1的显著程度。若种间无关联,则W落入χ2分布界限内的概率为90%,χ20.92, N<W<χ20.05, N,否则种间总体相关。共同出现百分率:PC=a/(a+b+c)。PC的值域为[0,1],PC越接近于1,表明2个物种间正联结越紧密;若PC为0,表明该种对间无关联。联结系数:CA=2(ad−bc)/[(a+b)(b+d)+(a+c)(c+d)]。CA用来说明种间联结程度,其值域为[−1,1]。CA为0,说明2个物种间完全独立;CA越接近于1,说明2个物种间正联结越强;CA越接近于−1,说明2个物种间负连接越强。PC和CA计算公式中:a为种A和种B同时出现的样方数,b为只有种A出现的样方数,c为只有种B出现的样方数,d为种A和种B都不出现的样方数。
Pearson积矩相关系数和Spearman相关系数是反映2个物种种间协变线性关系的重要指标,可用来定量分析2个物种间的线性关系,其计算参照文献[21]。
-
根据重要值计算结果,参照《中国植被》的群落命名原则[23],夏蜡梅分布区的植被类型有落叶阔叶林(Q1化香树林、Q2山胡椒林、Q3灯台树林),针叶林(Q4杉木林),竹林(Q5毛竹林)3个类型。乔木层优势种是化香树、山胡椒、灯台树、杉木、毛竹;灌木层优势种是中国绣球Hydrangea chinensis、夏蜡梅、悬铃木叶苎麻 Boehmeria tricuspis;草本层优势种是金星蕨Parathelypteris glanduligera、辽宁堇菜Viola rossii、透茎冷水花Pilea pumila、虎杖Reynoutria japonica(相关重要值详见表2)。这与金则新等[9]调查时认为夏蜡梅主要分布在针阔混交林的结论略有不同,可能是夏蜡梅适应性广,适宜生境中植被类型多样导致。
表 2 大雷山夏蜡梅群落各层重要值前5的物种及重要值一览表
Table 2. List of species and importance values of the top 5 important values of each layer of S. chinensis community in Dalei Mountain
植物 层次 重要值/% Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 灯台树Bothrocaryum controversum 乔木层 10.71 11.16 短柄枹Quercus serrata var. brevipetiolata 乔木层 9.62 化香树Platycarya strobilacea 乔木层 12.86 7.99 黄山松Pinus taiwanensis 乔木层 2.28 黄檀Dalbergia hupeana 乔木层 9.28 柳杉Cryptomeria japonica var. sinensis 乔木层 29.11 毛竹Phyllostachys edulis 乔木层 67.08 榕叶冬青Ilex ficoidea 乔木层 1.47 山胡椒Lindera glauca 乔木层 5.98 13.95 山樱花Cerasus serrulata 乔木层 7.41 杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata 乔木层 32.23 1.39 水马桑Weigela japonica var. sinica 乔木层 9.12 微毛柃Eurya hebeclados 乔木层 5.52 细枝柃Eurya loquaiana 乔木层 6.40 夏蜡梅Sinocalycanthus chinensis 乔木层 6.07 10.07 6.48 16.06 小叶白辛树Pterostyrax corymbosus 乔木层 10.58 窄基红褐柃Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata 乔木层 2.32 浙闽樱桃Cerasus schneideriana 乔木层 7.94 臭辣树Evodia fargesii 灌木层 12.60 红果山胡椒Lindera erythrocarpa 灌木层 5.77 红脉钓樟Lindera rubronervia 灌木层 3.28 黄檀Dalbergia hupeana 灌木层 9.08 木荷Schima superba 灌木层 11.57 蓬蘽Rubus hirsutus 灌木层 14.81 山胡椒Lindera glauca 灌木层 7.47 4.00 山橿Lindera reflexa 灌木层 10.10 6.82 8.49 6.34 7.80 山莓Rubus corchorifolius 灌木层 7.67 太平莓Rubus pacificus 灌木层 5.84 细枝柃Eurya loquaiana 灌木层 4.97 夏蜡梅Sinocalycanthus chinensis 灌木层 13.42 22.21 30.79 50.65 悬铃木叶苎麻 Boehmeria tricuspis 灌木层 27.91 宜昌荚蒾Viburnum erosum 灌木层 3.65 中国绣球Hydrangea chinensis 灌木层 25.76 4.07 3.31 巴东过路黄Lysimachia patungensis 草本层 5.06 穿孔薹草Carex foraminata 草本层 8.11 丛枝蓼Polygonum posumbu 草本层 9.76 褐果薹草Carex brunnea 草本层 6.26 10.40 4.23 虎杖Reynoutria japonica 草本层 29.18 金星蕨Parathelypteris glanduligera 草本层 39.33 6.18 京鹤鳞毛蕨Dryopteris kinkiensis 草本层 5.91 犁头草Viola japonica 草本层 7.13 辽宁堇菜Viola rossii 草本层 30.43 13.94 芒尖薹草Carex doniana 草本层 5.33 南山堇菜Viola chaerophylloides 草本层 9.53 求米草Oplismenus undulatifolius 草本层 10.35 8.22 柔枝莠竹Microstegium vimineum 草本层 13.92 三脉紫菀Aster ageratoides 草本层 6.10 透茎冷水花Pilea pumila 草本层 18.34 长梗黄精Polygonatum filipes 草本层 8.87 长江蹄盖蕨Athyrium iseanum 草本层 9.76 长柱头薹草Carex teinogyna 草本层 9.60 紫花堇菜Viola grypoceras 草本层 6.47 7.94 从重要值看,在乔木层,夏蜡梅处在伴生种位置,而在灌木层夏蜡梅常处在优势种或常见种位置,尤其是在毛竹林下,夏蜡梅重要值为50.65%,达到最高。
-
通过上述3个多样性指数来分析样地物种多样性。计算(表3~5)表明:乔木层物种多样性指数从大到小依次为阔叶林、针叶林、毛竹林,除均匀度指数外,其余指数阔叶林约是毛竹林的2倍,差异明显,说明阔叶林物种丰富、多样性明显、均匀度高。灌木层物种丰富度指数从大到小依次为阔叶林、毛竹林、针叶林,物种多样性和均匀度指数为阔叶林≈针叶林>毛竹林,说明灌木层阔叶林物种多样性指数最高,毛竹林物种丰富度较高,但均匀度低。草本层物种多样性指数除均匀度指数外,均为针叶林>阔叶林≈毛竹林,说明针叶林物种丰富度高,但均匀度低。
表 3 夏蜡梅群落5个样地乔木层物种多样性指数
Table 3. Species diversity index of trees in 5 plots of S. chinensis community
样地号 优势种 VI/% S P H′ E D′ Q1 化香树 12.86 39 0.94 1.36 0.37 6.51 Q2 山胡椒 13.95 36 0.94 1.35 0.38 6.01 Q3 灯台树 11.16 43 0.94 1.39 0.37 7.18 Q4 杉木 32.23 25 0.80 0.93 0.29 4.17 Q5 毛竹 67.08 19 0.52 0.58 0.20 3.17 平均值 27.45 32 0.83 1.12 0.32 5.41 表 4 夏蜡梅群落5个样地灌木层物种多样性指数
Table 4. Species diversity index of shrubs in 5 plots of S. chinensis community
样地号 优势种 VI/% S P H′ E D′ Q1 中国绣球 25.76 34 0.89 1.22 0.34 8.18 Q2 夏蜡梅 22.21 40 0.91 1.27 0.34 9.62 Q3 夏蜡梅 30.79 36 0.87 1.18 0.33 8.66 Q4 悬铃木叶苎麻 27.91 24 0.88 1.12 0.35 5.77 Q5 夏蜡梅 50.65 33 0.73 0.98 0.28 7.93 平均值 31.46 33 0.86 1.15 0.33 8.03 表 5 夏蜡梅群落5个样地草本层物种多样性指数
Table 5. Species diversity index of herbs in 5 plots of S. schinensis community
样地号 优势种 VI/% S P H′ E D′ Q1 金星蕨 39.33 26 0.82 1.04 0.32 6.25 Q2 辽宁堇菜 30.43 22 0.88 1.14 0.37 5.29 Q3 辽宁堇菜 13.94 25 0.92 1.21 0.38 6.01 Q4 透茎冷水花 18.34 45 0.92 1.29 0.34 10.82 Q5 虎杖 29.18 25 0.88 1.16 0.36 6.01 平均值 26.24 29 0.88 1.17 0.35 6.88 夏蜡梅在群落内的优势度与均匀度指数呈负相关,表明夏蜡梅的种间竞争较弱,是一种集群分布的物种。
-
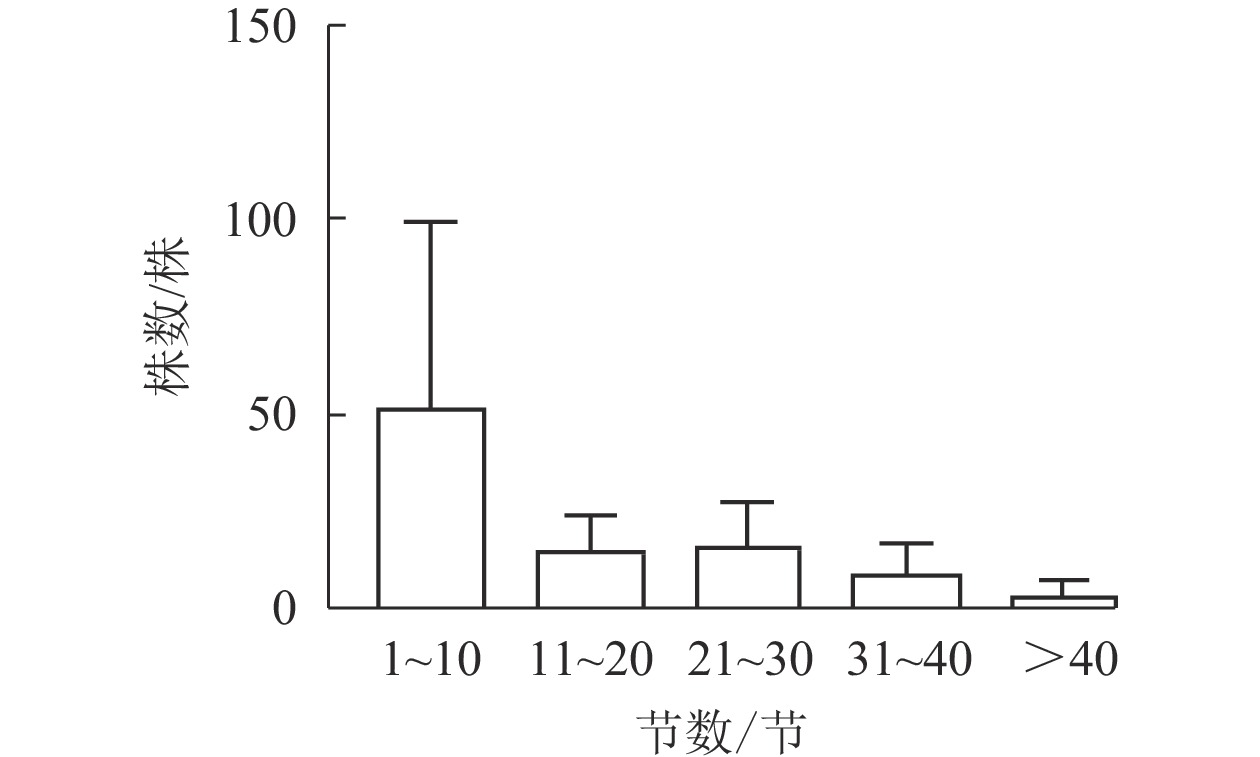
图1显示:5个样地中共有夏蜡梅453株,个体中节数最少的为1节,最多的为46节,平均16节,株数最多为1节,共177株,占39.07%。按10节为1级,共分5个级别,编制种群结构图,可见第Ⅰ级(1~10节)的个体比率最高,占56.51%,整体呈增长型中的“金字塔”型,Ⅰ级个体比较丰富,这与金则新等[9]的结论一致。说明天台大雷山的生境适宜夏蜡梅种群的生长与更新,同时也说明数节法在分析夏蜡梅的种群内部结构是可行的。
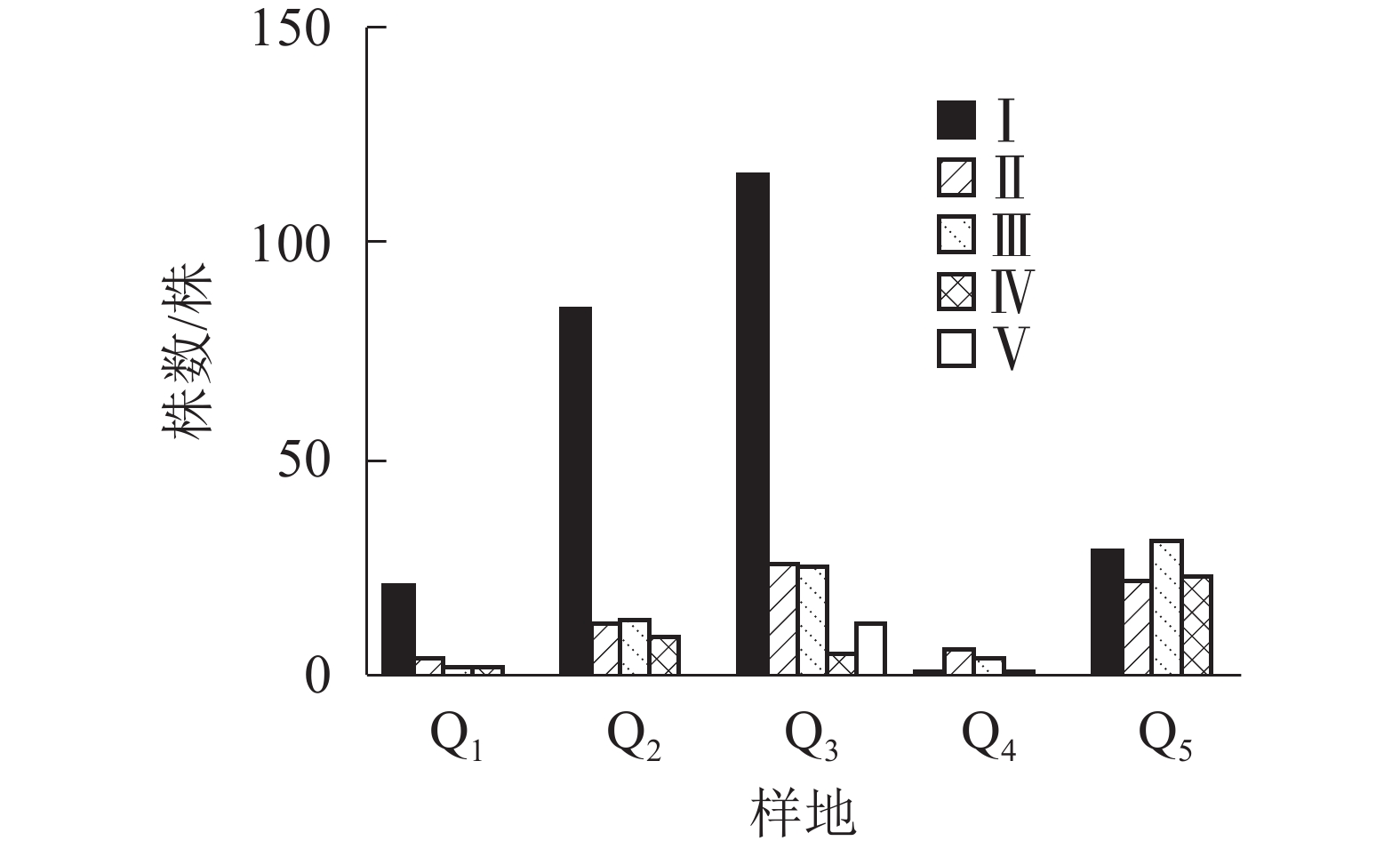
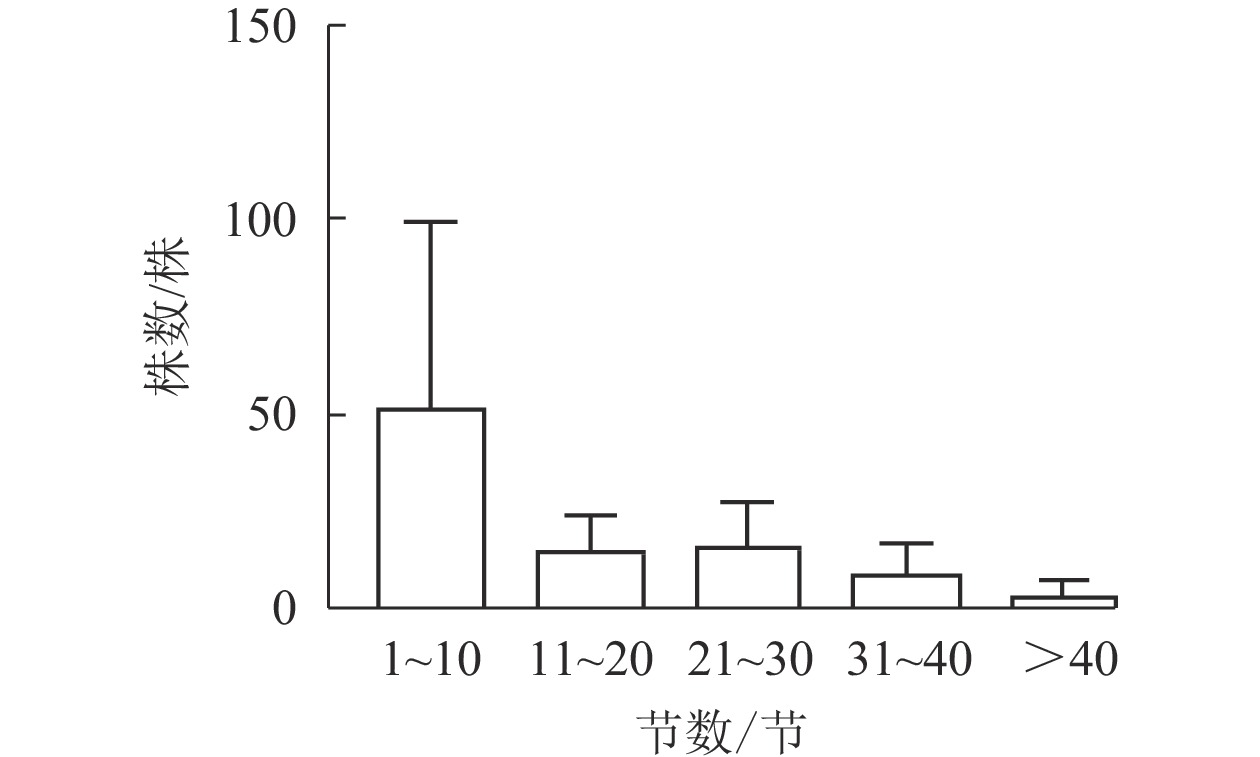
由图2显示:不同的样地中,Q1、Q2、Q3都是Ⅰ级个体较多,种群结构呈“金字塔”型,属增长型;在Q4中,Ⅰ级个体极少,种群结构呈“壶”型,属衰退型;Q5中,种群结构呈“钟”型,属稳定型。
-
根据夏蜡梅群落中乔木层和灌木层重要值大于5%的物种分别在5个样地中出现(1)和不出现(0)矩阵,计算出方差比率RV和统计量W。
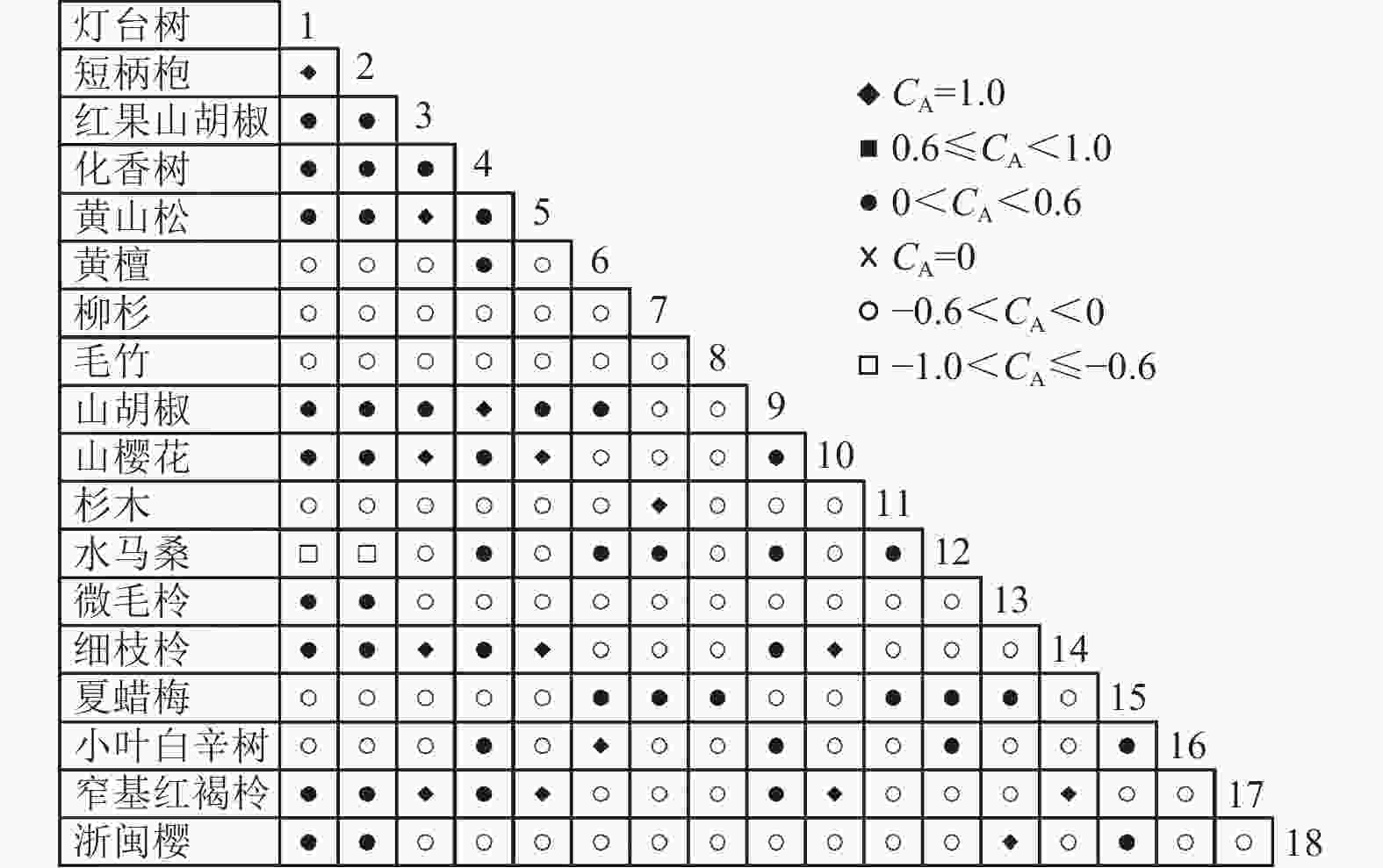
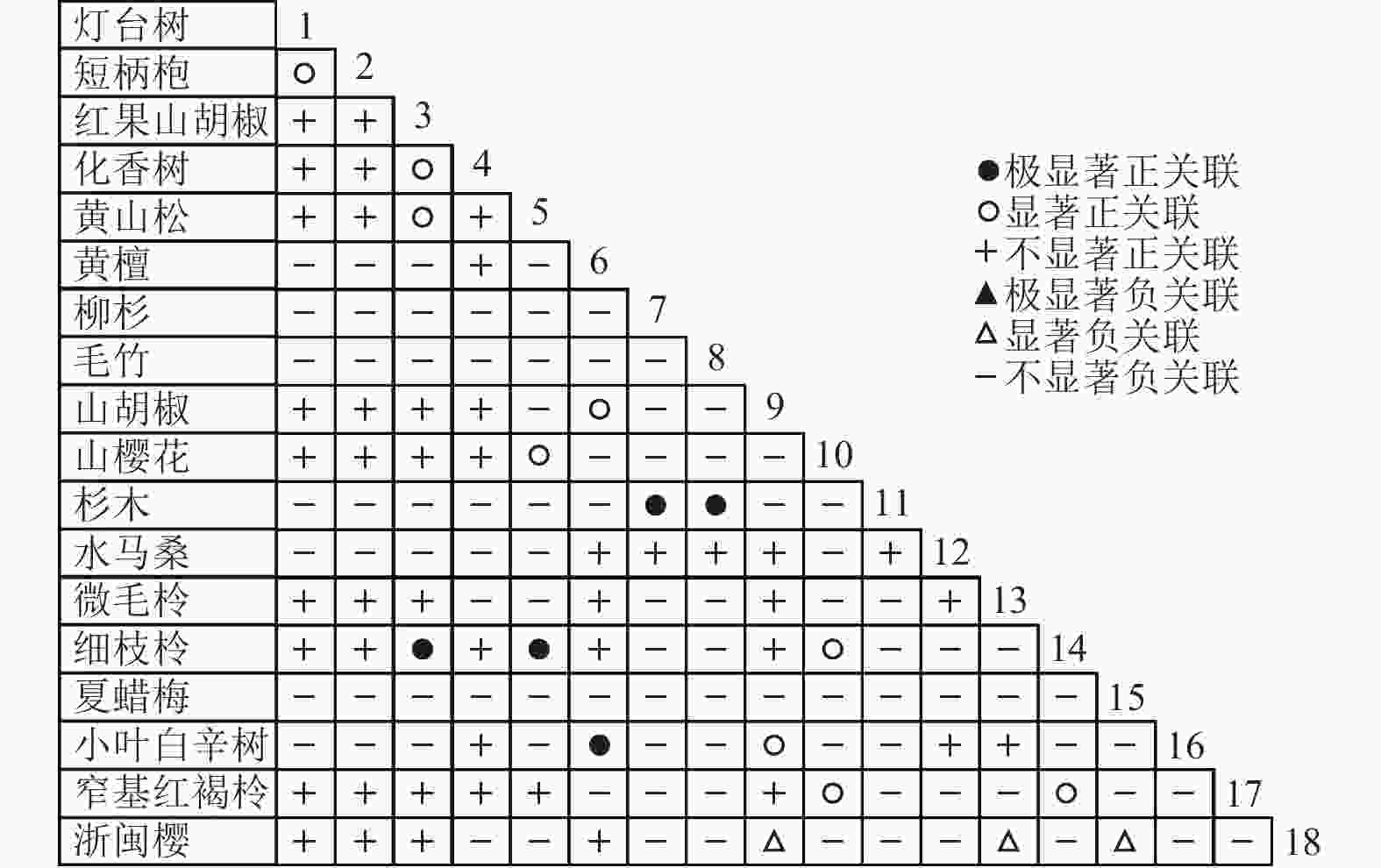
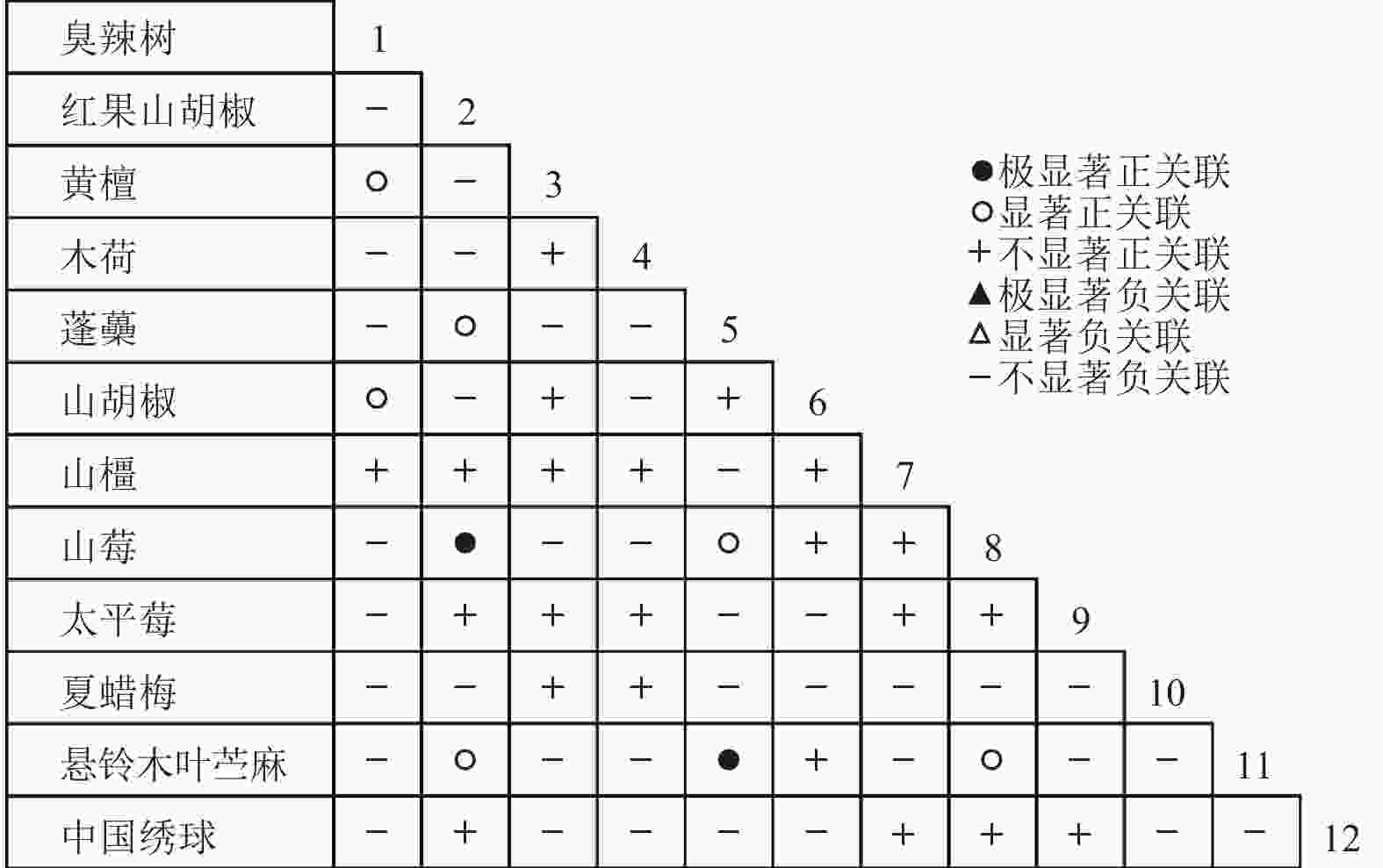
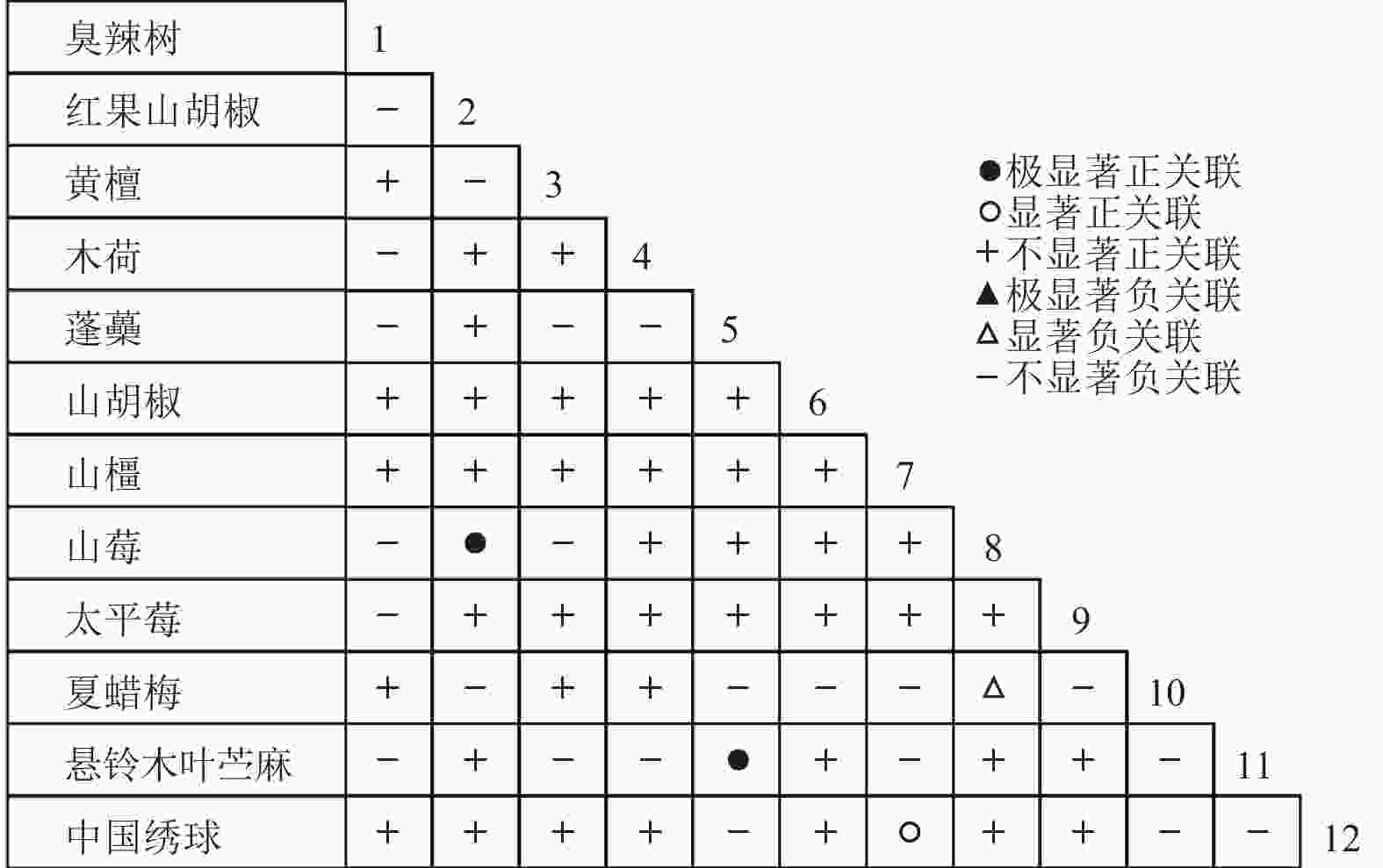
乔木层中共选取了18个物种,RV=1.634>1,表明种间呈净的正关联;灌木层中共选取了12个物种,RV=1.250>1,表明种间呈净的正关联。由于N=5,乔木层和灌木层的统计量W分别为8.171和6.250。查表得:χ20.50,5=4.351,χ20.10,5=9.236,乔木层和灌木层的W值均落入χ20.50,5和χ20.10,5之间,即RV偏离1不显著。因此,乔木层18个物种和灌木层12个物种均在整体上表现出不显著的净的正关联。
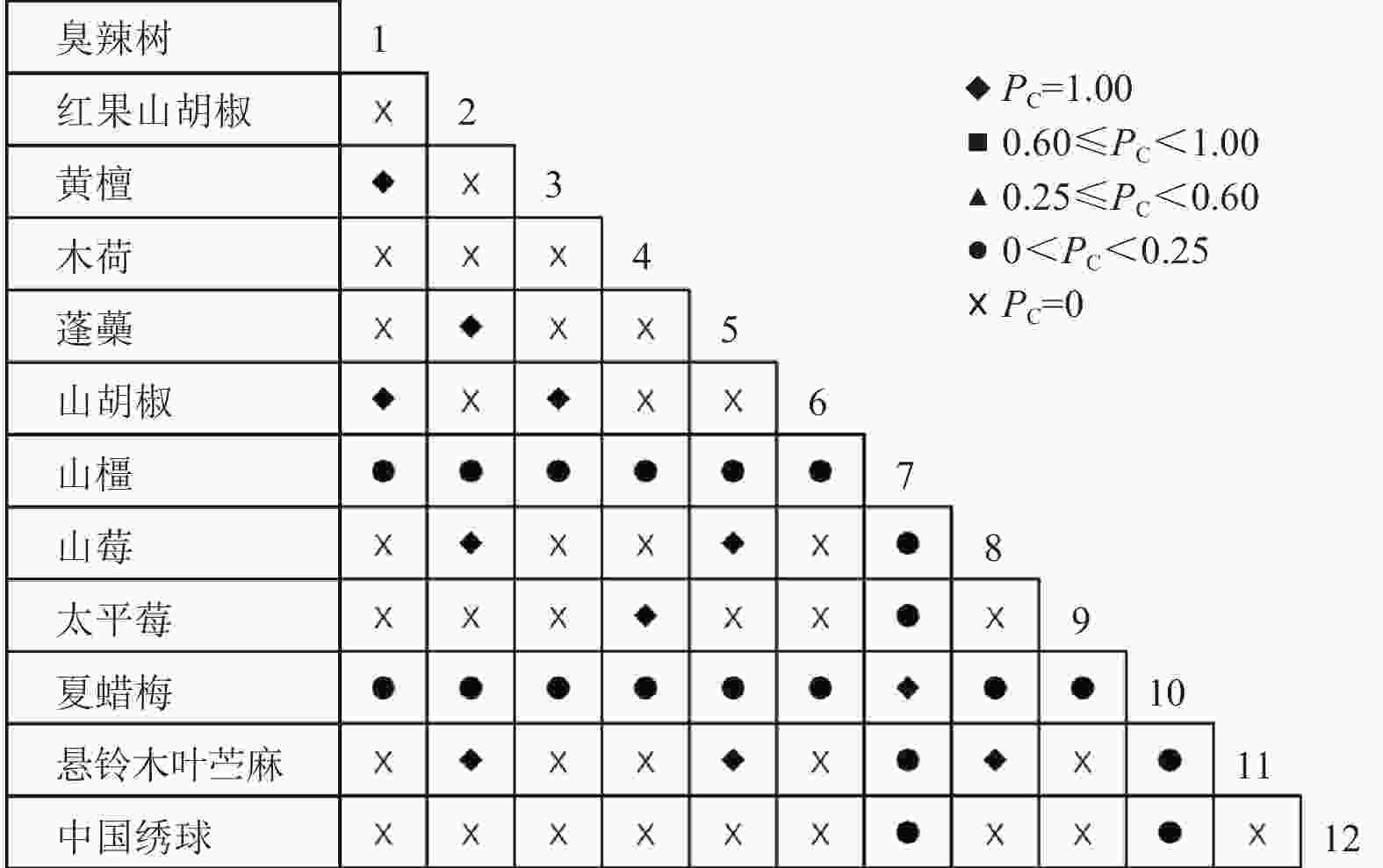
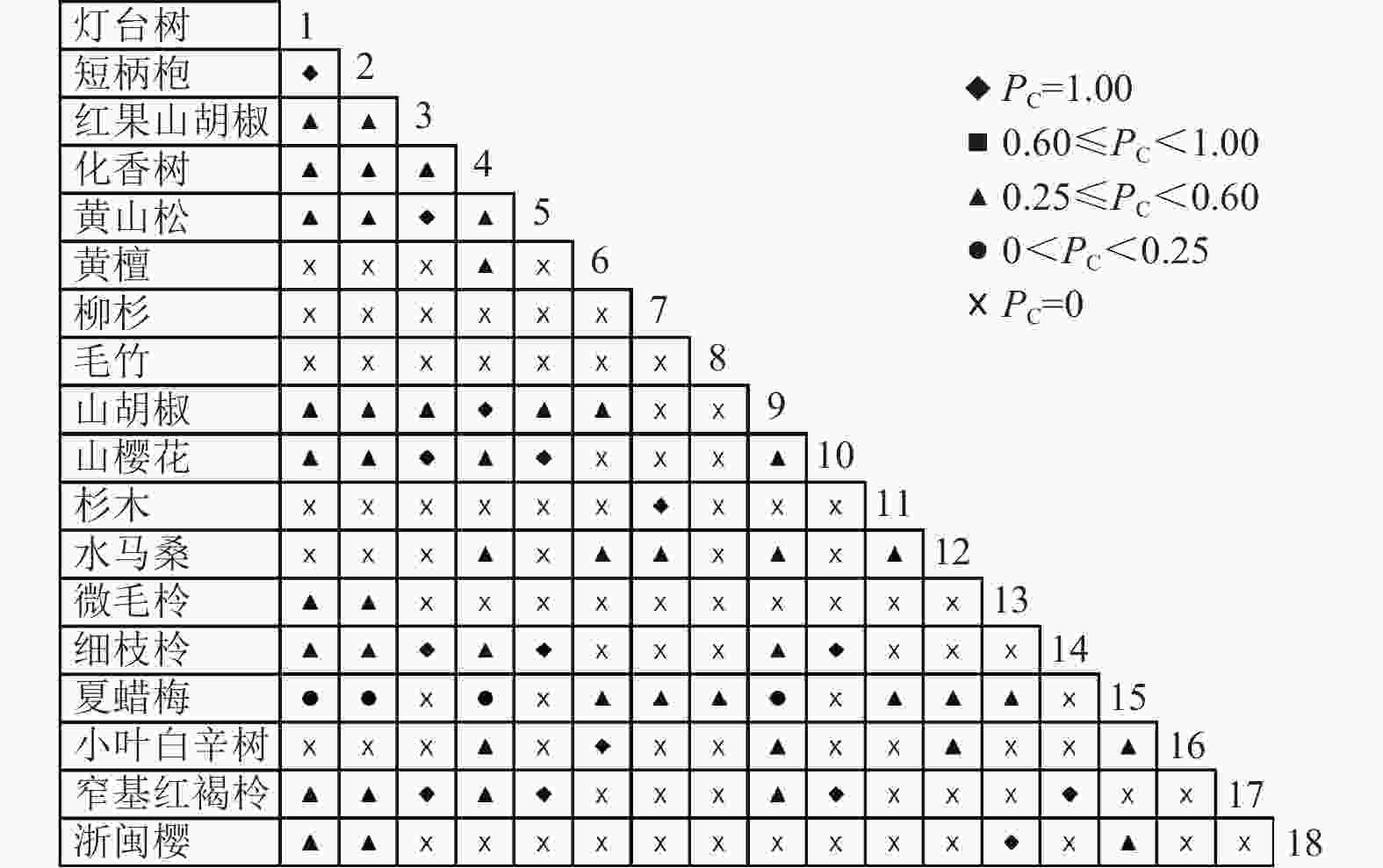
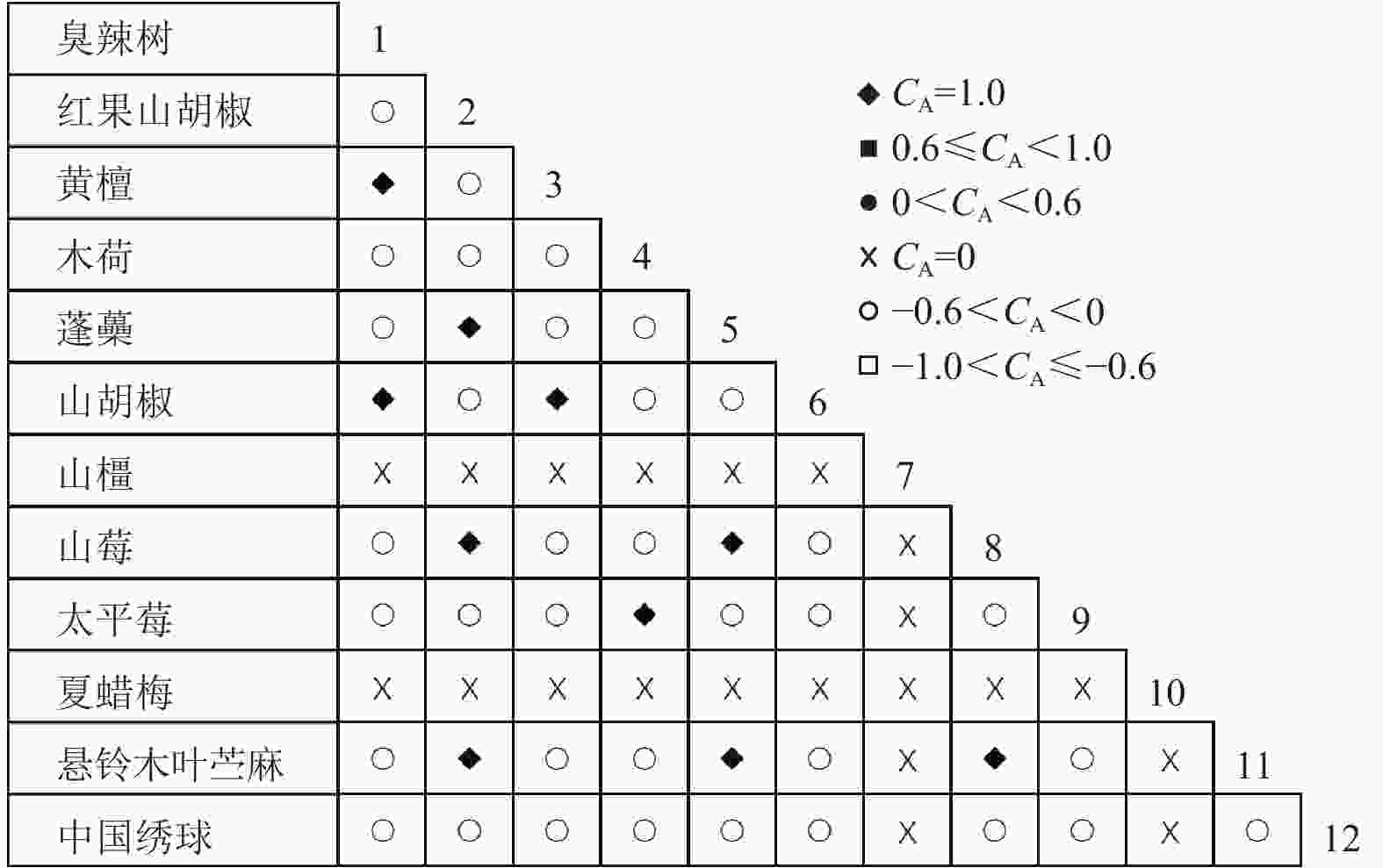
通过共同出现百分率检测、Pearson相关系数检验、Spearman秩相关系数检验等方法分析种间联结和种间相关性,结果(图3~10)显示:乔木层和灌木层中夏蜡梅与大部分物种间均无关联,仅在乔木层中,夏蜡梅与红果山胡椒呈极显著负相关,与化香树和浙闽樱桃呈显著负相关;在灌木层中夏蜡梅与山莓呈显著负相关,与山橿间的联结性较强。
-
本研究表明:夏蜡梅所处的群落类型多样,有落叶阔叶林、针叶林、毛竹林,乔木层优势种有化香树、山胡椒、灯台树、杉木、毛竹;灌木层优势种有中国绣球、夏蜡梅、悬铃木叶苎麻;草本层优势种有金星蕨、辽宁堇菜、透茎冷水花等。夏蜡梅种群主要集中分布在落叶阔叶林和毛竹林中。生物多样性指数最高的是灯台树林,最低的是毛竹林;均匀度指数最高的是杉木林,最低的是毛竹林。
-
夏蜡梅的种群结构是增长型中的“金字塔”型,幼林个体丰富,与早期“天台县夏蜡梅产地由于植被破坏严重,夏蜡梅都呈散生状”的描述相比[6],种群得到了很好的保护。
除柳杉疏林外,落叶林、毛竹林下的夏蜡梅种群数量都比较多,特别是毛竹林下种群数量达到最高。这可能是夏蜡梅是喜荫植物,午间强光、高温会导致其叶肉细胞活性降低,进而引起光合能力的下降,直至幼苗、幼树死亡[24]。落叶林、毛竹林的林冠能为其遮光,减弱强烈的光照,降低土壤表明温度,减少土壤水分蒸发,从而促进幼苗的萌发和存活。这也为今后野外保护、繁育夏蜡梅提供了很好的指示。
-
3种检验结果表现出一致性,正负关联比均大于1,说明各树种联系紧密,群落的结构和功能趋于完善。夏蜡梅与大部分树种无相关关系,说明夏蜡梅在群落中可能处于一个相对独立的地位。群落中与夏蜡梅呈负相关关系的主要是红果山胡椒、山莓、浙闽樱桃、化香树等树种,说明这些种与夏蜡梅有竞争关系。建议在后期夏蜡梅野外保育过程中,对与夏蜡梅有竞争关系的物种,采取适当人为择伐、抚育,营造良好的生长环境。
-
人为干扰对夏蜡梅种群的影响不尽相同。在柳杉林等人工经营林,由于砍伐强度大,露出大量林窗,生境遭到破坏,夏蜡梅种群结构趋于衰退;在毛竹林中,虽然人工干预强烈,但对夏蜡梅的生境破坏不强,使得种群结构趋于稳定;在化香树林、山胡椒林等落叶阔叶林中,是先有人为干扰,后干扰逐渐减弱,群落进入自然演替,夏蜡梅种群则开始恢复,表现出种群增长的模型。
-
浙江农林大学赵宏波审阅全文并提出修改意见;浙江省森林资源监测中心钟建平,浙江中医药大学林王敏、董荧荧、金晓青、王志栋等参加野外调查;杭州师范大学陈伟杰帮助内业计算。在此一并致谢!
Community characteristics of Sinocalycanthus chinensis in Dalei Mountains of Tiantai County
-
摘要:
目的 探索浙江省天台县大雷山野生夏蜡梅Sinocalycanthus chinensis群落的物种组成、种群结构和种间联结,补充大雷山野生夏蜡梅资源分布情况。 方法 在实地踏查的基础上,结合以往研究资料,选取天台县大雷山夏蜡梅的典型群落,建立5个20 m×20 m样地,进行群落学调查。 结果 ①夏蜡梅所处的群落类型多样,主要有落叶阔叶林、针叶林和竹林,分层明显,乔木层优势种有化香树Platycarya strobilacea、山胡椒Lindera glauca、灯台树Bothrocaryum controversum、杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata、毛竹Phyllostachys edulis;灌木层优势种有中国绣球Hydrangea chinensis、夏蜡梅、悬铃木叶苎麻 Boehmeria tricuspis;草本层优势种有金星蕨Parathelypteris glanduligera、辽宁堇菜Viola rossii、透茎冷水花Pilea pumila。②夏蜡梅的种群结构为“金字塔”型,第Ⅰ级个体比率最高,占56.51%,说明种群正处在增长阶段。③对夏蜡梅群落内的乔木层和灌木层物种对进行种间关联与相关性分析显示,正负关联比均大于1,说明夏蜡梅与大部分树种无相关关系。 结论 大雷山野生夏蜡梅群落中各树种联系紧密,群落的结构和功能趋于完善,但夏蜡梅在群落中可能处于相对独立的地位。鉴于夏蜡梅与红果山胡椒Lindera erythrocarpa、山莓Rubus corchorifolius、浙闽樱桃Cerasus schneideriana、化香树等树种呈负相关关系,具有竞争关系,建议在后期夏蜡梅野外保育过程中,采取适当人为择伐和抚育措施,营造良好的生长环境。图10表5参24 Abstract:Objective This study aims to explore the species composition, population structure and interspecific association of wild Sinocalycanthus chinensis community, and to supplement the distribution of wild S. chinensis resources in Tiantai County, Zhejiang Province. Method On the basis of field survey and previous research data, five 20 m × 20 m sample plots of S. chinensis were established for community investigation. Result (1) The community types of S. chinensis were diverse, mainly including deciduous broad-leaved forest, coniferous forest and bamboo forest, with obvious stratification. The dominant species of tree layer were Platycarya strobilacea, Lindera glauca, Botrocarpyum contoversum, Cunninghamia lanceolata, and Phyllostachys edulis. The dominant species of shrub layer were Hydrangea chinensis, S. chinensis, and Boehmeria tricuspis. The dominant species of herb layer were Parathylyperis glandulgera, Viola rossii, and Pilea pumila. (2)The population structure of S. chinensis was “Pyramid” type, with the highest proportion of individuals in gradeⅠ, accounting for 56.51%, indicating that the population was in the growth stage. (3) The analysis of interspecific association and correlation of species pairs in tree layer and shrub layer showed that the positive and negative correlation ratios were both greater than 1, and there was no correlation between S. chinensis and most tree species. Conclusion The species of S. chinensis community are closely related, and the structure and function of the community tend to be perfect, but S. chinensis may be relatively independent in the community. In view of its negative correlation and competitive relationship with Lindera erythrocarpa, Rubus corchorifolius, Cerasus schneideriana, Platycarya strobilacea and other tree species, it is suggested that in the later stage of S. chinensis field conservation, appropriate artificial selective cutting and tending measures should be taken to create a good growth environment. [Ch, 10 fig. 5 tab. 24 ref.] -
表 1 大雷山夏蜡梅群落样地调查特征
Table 1. Survey characteristics of S. chinensis community plot in Dalei Mountain
样地编号 植被类型 地理坐标 海拔/m 坡向 坡度/(°) 坡位 群落郁闭度 人为干扰 Q1 化香树林 28°59′05.24″N,120°49′12.37″E 808 西坡 17 上坡 0.7 间接 Q2 山胡椒林 28°59′02.56″N,120°49′10.87″E 814 西北坡 28 上坡 0.6 间接 Q3 灯台树林 28°58′53.17″N,120°49′01.14″E 824 东坡 30 下坡 0.6 小 Q4 杉木林 28°58′55.71″N,120°49′01.34″E 827 西南坡 5 谷底 0.5 直接 Q5 毛竹林 28°59′18.20″N,120°48′43.84″E 736 西北 22 下坡 0.8 直接 说明:化香树Platycarya strobilacea,山胡椒Lindera glauca,灯台树Bothrocaryum controversum,杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata,毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis 表 2 大雷山夏蜡梅群落各层重要值前5的物种及重要值一览表
Table 2. List of species and importance values of the top 5 important values of each layer of S. chinensis community in Dalei Mountain
植物 层次 重要值/% Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 灯台树Bothrocaryum controversum 乔木层 10.71 11.16 短柄枹Quercus serrata var. brevipetiolata 乔木层 9.62 化香树Platycarya strobilacea 乔木层 12.86 7.99 黄山松Pinus taiwanensis 乔木层 2.28 黄檀Dalbergia hupeana 乔木层 9.28 柳杉Cryptomeria japonica var. sinensis 乔木层 29.11 毛竹Phyllostachys edulis 乔木层 67.08 榕叶冬青Ilex ficoidea 乔木层 1.47 山胡椒Lindera glauca 乔木层 5.98 13.95 山樱花Cerasus serrulata 乔木层 7.41 杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata 乔木层 32.23 1.39 水马桑Weigela japonica var. sinica 乔木层 9.12 微毛柃Eurya hebeclados 乔木层 5.52 细枝柃Eurya loquaiana 乔木层 6.40 夏蜡梅Sinocalycanthus chinensis 乔木层 6.07 10.07 6.48 16.06 小叶白辛树Pterostyrax corymbosus 乔木层 10.58 窄基红褐柃Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata 乔木层 2.32 浙闽樱桃Cerasus schneideriana 乔木层 7.94 臭辣树Evodia fargesii 灌木层 12.60 红果山胡椒Lindera erythrocarpa 灌木层 5.77 红脉钓樟Lindera rubronervia 灌木层 3.28 黄檀Dalbergia hupeana 灌木层 9.08 木荷Schima superba 灌木层 11.57 蓬蘽Rubus hirsutus 灌木层 14.81 山胡椒Lindera glauca 灌木层 7.47 4.00 山橿Lindera reflexa 灌木层 10.10 6.82 8.49 6.34 7.80 山莓Rubus corchorifolius 灌木层 7.67 太平莓Rubus pacificus 灌木层 5.84 细枝柃Eurya loquaiana 灌木层 4.97 夏蜡梅Sinocalycanthus chinensis 灌木层 13.42 22.21 30.79 50.65 悬铃木叶苎麻 Boehmeria tricuspis 灌木层 27.91 宜昌荚蒾Viburnum erosum 灌木层 3.65 中国绣球Hydrangea chinensis 灌木层 25.76 4.07 3.31 巴东过路黄Lysimachia patungensis 草本层 5.06 穿孔薹草Carex foraminata 草本层 8.11 丛枝蓼Polygonum posumbu 草本层 9.76 褐果薹草Carex brunnea 草本层 6.26 10.40 4.23 虎杖Reynoutria japonica 草本层 29.18 金星蕨Parathelypteris glanduligera 草本层 39.33 6.18 京鹤鳞毛蕨Dryopteris kinkiensis 草本层 5.91 犁头草Viola japonica 草本层 7.13 辽宁堇菜Viola rossii 草本层 30.43 13.94 芒尖薹草Carex doniana 草本层 5.33 南山堇菜Viola chaerophylloides 草本层 9.53 求米草Oplismenus undulatifolius 草本层 10.35 8.22 柔枝莠竹Microstegium vimineum 草本层 13.92 三脉紫菀Aster ageratoides 草本层 6.10 透茎冷水花Pilea pumila 草本层 18.34 长梗黄精Polygonatum filipes 草本层 8.87 长江蹄盖蕨Athyrium iseanum 草本层 9.76 长柱头薹草Carex teinogyna 草本层 9.60 紫花堇菜Viola grypoceras 草本层 6.47 7.94 表 3 夏蜡梅群落5个样地乔木层物种多样性指数
Table 3. Species diversity index of trees in 5 plots of S. chinensis community
样地号 优势种 VI/% S P H′ E D′ Q1 化香树 12.86 39 0.94 1.36 0.37 6.51 Q2 山胡椒 13.95 36 0.94 1.35 0.38 6.01 Q3 灯台树 11.16 43 0.94 1.39 0.37 7.18 Q4 杉木 32.23 25 0.80 0.93 0.29 4.17 Q5 毛竹 67.08 19 0.52 0.58 0.20 3.17 平均值 27.45 32 0.83 1.12 0.32 5.41 表 4 夏蜡梅群落5个样地灌木层物种多样性指数
Table 4. Species diversity index of shrubs in 5 plots of S. chinensis community
样地号 优势种 VI/% S P H′ E D′ Q1 中国绣球 25.76 34 0.89 1.22 0.34 8.18 Q2 夏蜡梅 22.21 40 0.91 1.27 0.34 9.62 Q3 夏蜡梅 30.79 36 0.87 1.18 0.33 8.66 Q4 悬铃木叶苎麻 27.91 24 0.88 1.12 0.35 5.77 Q5 夏蜡梅 50.65 33 0.73 0.98 0.28 7.93 平均值 31.46 33 0.86 1.15 0.33 8.03 表 5 夏蜡梅群落5个样地草本层物种多样性指数
Table 5. Species diversity index of herbs in 5 plots of S. schinensis community
样地号 优势种 VI/% S P H′ E D′ Q1 金星蕨 39.33 26 0.82 1.04 0.32 6.25 Q2 辽宁堇菜 30.43 22 0.88 1.14 0.37 5.29 Q3 辽宁堇菜 13.94 25 0.92 1.21 0.38 6.01 Q4 透茎冷水花 18.34 45 0.92 1.29 0.34 10.82 Q5 虎杖 29.18 25 0.88 1.16 0.36 6.01 平均值 26.24 29 0.88 1.17 0.35 6.88 -
[1] 郑万钧, 章绍尧, 洪涛, 等. 中国经济树木新种及学名订正[J]. 林业科学, 1963, 8(1): 1 − 14. CHENG Wanchun, CHANG Shaoyao, HONG Tao, et al. Species novae et nomines emendata arborum utilium Chinae [J]. Sci Silv Sin, 1963, 8(1): 1 − 14. [2] 郑万钧, 章绍尧. 蜡梅科的新属: 夏蜡梅属[J]. 植物分类学报, 1964, 9(2): 135 − 138. CHENG Wanchun, CHANG Shaoyao. Genus novum Calycanthacearum Chinae orientalis [J]. J Syst Evol, 1964, 9(2): 135 − 138. [3] 谈探. 濒危植物夏蜡梅种群遗传多样性与分子系统地理学研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2008. TAN Tan. Genetic Diversity and Molecular Phylogeography of Sinocalycanthus chinensis, an Endangered Plant Endemic to China[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2008. [4] 刘华红, 周莉花, 黄耀辉, 等. 群落演替对夏蜡梅种群分布和数量的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(3): 620 − 628. LIU Huahong, ZHOU Lihua, HUANG Yaohui, et al. Effects of community succession on population distribution and size of Sinocalycanthus chinensis (Cheng et S. Y. Chang) Cheng et S. Y. Chang [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2016, 36(3): 620 − 628. [5] 李林初. 夏蜡梅属起源的探讨[J]. 西北植物学报, 1988, 8(2): 67 − 72. LI Linchu. Critical note on the origin of Calycanthus L. [J]. Acta Bot Boreali-Occident Sin, 1988, 8(2): 67 − 72. [6] 徐耀良, 张若蕙, 周骋. 夏蜡梅的群落学研究[J]. 浙江林学院学报, 1997, 14(4): 355 − 362. XU Yaoliang, ZHANG Ruohui, ZHOU Cheng. Study on communities of Calycanthus chinensis [J]. J Zhejiang For Coll, 1997, 14(4): 355 − 362. [7] 金则新, 李钧敏, 朱小燕. 夏蜡梅总黄酮、总绿原酸含量及其环境因子相关性分析[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 2007, 34(4): 459 − 464. JIN Zexin, LI Junmin, ZHU Xiaoyan. Content of total flavonoids and total chlorogenic acid in the endangered plant Sinocalycanthus chinensis and their correlations with the environmental factors [J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci Ed, 2007, 34(4): 459 − 464. [8] 刘丽丽, 金则新, 李建辉. 浙江大雷山夏蜡梅群落植物物种多样性及其与土壤因子相关性[J]. 植物研究, 2010, 30(1): 57 − 64. LIU Lili, JIN Zexin, LI Jianhui. Plant species diversity inSinocalycanthus chinensis community and its correlation with soil factors in Dalei Mountain of Zhejiang Province [J]. Bull Bot Res, 2010, 30(1): 57 − 64. [9] 金则新, 李钧敏, 柯世省, 等. 夏蜡梅保护生物学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 1 − 353. [10] MANUEL C, MOLLES J. Ecology, Concept and Applications[M]. 2nd. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, 2002: 186 − 254. [11] CRAWLEY M J. Plant Ecology[M]. London: Bllackwell Scientific Publications, 1986: 97 − 185. [12] 董瑞瑞, 唐战胜, 陈建华, 等. 珍稀濒危植物紫茎群落树种的种间联结性[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2018, 46(5): 127 − 129, 153. DONG Ruirui, TANG Zhansheng, CHEN Jianhua, et al. Interspecific correlations among tree species in the Stewartia sinensis community in Qianjiangyuan National Park, Zhejiang Province [J]. J Anhui Agric Sci, 2018, 46(5): 127 − 129, 153. [13] 洪仲棉. 天台山森林植被及其利用和保护[J]. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 1988, 12(3): 232 − 236. HONG Zhongmian. The rational utilize and protect of forest vegetation in Tian-Tai Mountain [J]. Acta Phytoecol Geobot Sin, 1988, 12(3): 232 − 236. [14] 张彩绯. 天台45年气候变化规律初探[J]. 浙江气象, 2007, 28(2): 12 − 15. ZHANG Caifei. A preliminary study on the climate change of Tiantai in the past 45 years [J]. J Zhejiang Meteorol, 2007, 28(2): 12 − 15. [15] 胡正华, 于明坚, 丁炳扬, 等. 古田山国家级自然保护区常绿阔叶林类型及其群落物种多样性研究[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2003, 9(4): 341 − 345. HU Zhenghua, YU Mingjian, DING Bingyang, et al. Types of evergreen broad-leaved forests and their species diversity in Gutian Mountain National Nature Reserve [J]. Chin J Appl Environ Biol, 2003, 9(4): 341 − 345. [16] 马克平, 黄建辉, 于顺利, 等. 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究(Ⅱ)丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性指数[J]. 生态学报, 1995, 15(3): 268 − 277. MA Keping, HUANG Jianhui, YU Shunli, et al. Plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China (Ⅱ) species richness, evenness and species diversities [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 1995, 15(3): 268 − 277. [17] 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 等. 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(6): 533 − 548. FANG Jingyun, WANG Xiangping, SHEN Zehao, et al. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory [J]. Biodiversity Sci, 2009, 17(6): 533 − 548. [18] 张若蕙, 刘洪谔, 沈锡康, 等. 8种蜡梅的繁殖[J]. 浙江林业科技, 1994, 14(1): 1 − 7. ZHANG Ruohui, LIU Honge, SHEN Xikang, et al. Propagation of eight species of Calycanthaceae [J]. J Zhejiang For Sci Technol, 1994, 14(1): 1 − 7. [19] SCHLUTER D. A variance test for detecting species associations, with some example application [J]. Ecology, 1984, 65(3): 998 − 1005. [20] 王伯荪, 彭少麟. 南亚热带常绿阔叶林种间联结测定技术研究(Ⅰ)种间联结测试的探讨与修正[J]. 植物生态学报, 1985, 9(4): 274 − 285. WANG Bosun, PENG Shaolin. Studies on the measuring techniques of interspecific association of lower-subtropical evergreen-broadleaved forests (Ⅰ) The exploration and the revision on the measuring formulas of interspecific association [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 1985, 9(4): 274 − 285. [21] 陈珍慧. 珍稀特有植物华顶杜鹃的种群特征和保护遗传学研究[D]. 杭州: 杭州师范大学, 2016: 23 − 24. CHEN Zhenhui. Studies on Population Characteristics and Protective Genetics of Rhododendron huadingense, A Rare Species Endemic to China[D]. Hangzhou: Hangzhou Normal University, 2016: 23 − 24. [22] 周先叶, 王伯荪, 李鸣光, 等. 广东黑石顶自然保护区森林次生演替过程中群落的种间联结性分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2000, 24(3): 332 − 339. ZHOU Xianye, WANG Bosun, LI Mingguang, et al. An analysis of interspecific associations in secondary succession forest communities in Heishiding Natural Reserve, Guangdong Province [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2000, 24(3): 332 − 339. [23] 吴征镒. 中国植被[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1995: 143 − 430. [24] 马金娥, 金则新, 张文标. 濒危植物夏蜡梅及其伴生植物的光合日进程[J]. 植物研究, 2007, 27(6): 708 − 714. MA Jin’e, JIN Zexin, ZHANG Wenbiao. The diurnal changes of photosynthesis in the endangered plant Sinocalycanthus chinensis and its accompanying plants [J]. Bull Bot Res, 2007, 27(6): 708 − 714. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200349






 下载:
下载: