-
黄土高原地区水土流失严重,不仅会导致河道淤塞、加剧洪水灾害,还会引起土地退化[1]。晋西黄土残塬沟壑区地理环境特殊,易导致土壤水分匮乏、养分贫瘠[2]。植被恢复是防治水土流失的主要手段。20世纪90年代初,晋西黄土残塬沟壑区开始实施大规模退耕还林还草工程,改变了区域植被格局和下垫面条件[3],也使地表物质迁移、土壤结构、水文状况、土壤肥力等理化性质发生变化,从而影响土壤质量[4]。
土壤质量是指土壤在一定生态系统内净化环境、支持生物生产、促进动植物和人体健康的能力[5]。土壤质量状况与地理位置、自然组成、土壤类型、土壤内部的相互作用和土地利用方式关系密切[6]。土壤质量是农业可持续发展的根本保证,人类通过不同的利用方式干预和调整土壤的生物地球化学循环的方向、变化速率以及地表物质再分配过程,从而使土壤质量发生变化[7]。合理的土地利用方式可改善土壤结构,增强土壤对外界环境变化的抵抗力。不合理的土地利用方式,会导致土壤质量下降,增加土壤侵蚀,降低生物多样性[8]。土地利用变化是影响土壤质量的关键因素,不同土地利用方式对土壤理化性质具有重要影响。杨亚辉等[9]基于黄土高原王东沟小流域9个径流小区的观测实验,针对植被覆盖条件影响土壤理化性质的研究显示:饱和持水量、毛管持水量、土壤有机质表现为草、灌地显著优于纯林和混交林,而土壤容重、饱和导水率各小区间差异不显著,黄土塬区植被恢复应遵循草本与灌木和乔木相结合的方式。刘春利等[10]对六道沟流域不同土地利用方式下土壤水力特性的研究显示:相同土壤吸力(基质势)条件下,土壤水分以农田最大、林地最小;饱和导水率则相反,除土壤水分消耗期的林地和苜蓿Medicago sativa地土壤水分随土层深度增加呈上升趋势外,其他时期各土地利用方式下土壤水分均随土层深度的增加而降低。王凯博等[11]在黄土丘陵区开展的天然和人工植被类型影响土壤理化性质的研究显示:与农田相比,天然灌木林地、天然草地和人工灌木林地土壤有机质、全氮都有明显提高,而人工乔木林地和果园提高不明显。
在黄土高原地区,人们已经围绕土壤质量开展了大量研究。吕春花等[12]在黄土高原子午岭地区通过测定土壤物理、化学、生物学指标,运用主成分分析法对土壤质量综合指数的研究发现:该地区植被自然恢复150 a期间,土壤质量指数随植被恢复年限增加总体呈增加趋势,变化范围为0.2~0.8 。白文娟等[13]对黄土高原地区水蚀风蚀交错带土壤质量进行综合评价发现:研究区土壤质量从高到低依次为刺槐Robinia peudoacacia林地、农地、退耕草地、油松Pinus tabulaeformis林地、沙蒿 Artemisia desertorum地、柠条 Caragana korshinski灌木地、杨树 Populus疏林地。邱莉萍[14]对黄土高原植被恢复生态系统土壤质量变化的研究发现:南小河沟流域不同土地利用方式土壤质量从高到低依次为油松林、刺槐林、荒坡地、草地,纸坊沟流域土壤质量从高到低依次为刺槐+狼牙刺 Sophora vicifolia混交林、狼牙刺林、柠条灌木林、刺槐林;子午岭土壤质量从高到低依次为林地、摆荒未翻耕地、农用地、摆荒翻耕地。佘雕[15]对黄土高原水土保持型灌木林地土壤质量特征及评价的研究显示:3种灌木林地土壤质量从高到低依次为沙棘林地、柠条林地、天然次生林地,土壤质量分级表明沙棘林地为Ⅱ级,土壤质量较高;柠条林地和天然次生林地均为Ⅲ级,土壤质量中等。
残塬是黄土塬的典型地貌类型,剧烈的土壤侵蚀导致塬面破碎化严重。植被恢复是流域生态治理的主要举措,然而,围绕残塬沟壑区植被恢复对土壤质量的影响报道较少。鉴于此,本研究以地处黄土残塬沟壑区的典型流域清水河流域为研究区域,对比流域内4种典型土地利用类型(农地、林地、灌草地、果园)的土壤理化性质,采用多元统计分析筛选土壤质量评价指标,运用主成分分析法以及土壤质量综合指数法,对清水河流域植被恢复过程中不同土地利用类型的土壤质量进行量化评价,以期为评估流域植被恢复的土壤保持效益及开展流域综合治理提供依据。
-
清水河流域地处吕梁山脉大背斜的南端,位于山西省吉县境内(36°02′18″~36°16′23″N,110°36′47″~110°56′00″E),海拔为830~1 820 m,地势东高西低。该流域发源于吉县高天山,向西经曹庄、川庄、城关、东城,在蛤蟆滩注入黄河,全长为59.24 km,水文站设在县城,水文站以上河长为36.4 km,流域面积为436 km²。
流域土壤表层为第四纪风积黄土覆盖,下层为第三纪红土。清水河两岸及一些沟底为二叠纪的红色砂岩。高天山、人祖山及河岸有三叠纪的红色砂岩和砂质岩出露。流域内属黄土残塬沟壑区。流域内土壤主要为褐土,主要植被乔木有辽东栎Quercus liaotungensis、山杨Populus davidiana、白桦Betula platyphylla、侧柏Platycladus orientalis、白皮松Pinus bungeana等。灌木有虎榛子Ostryopsis davidiana、胡枝子Lespedeza bicolon、荆条Vitex chinensis、黄栌Cotinus coggygria、连翘Forsythia suspensa等。草本有铁杆蒿Artemisia sacrorum、羊胡子草Carex rigescens等。人工林主要为刺槐、油松和杨树等。经济林主要有苹果Malus pumila、白梨Pyrus bretschneideri、杏Armeniaca sibirica、山桃Amygdalus davidiana、山核桃Carya cathayensis等。农作物主要是小麦Triticum aestivum和玉米Zea mays等。
-
于2020年生长季(7—9月)在清水河流域内沿着主沟道布设采样点,选择流域内农地、林地、果园和灌草地4种典型的土地利用类型进行取样。农地为玉米地;林地主要为辽东栎-山杨混交林,现树龄已达40 a;果园主要为苹果园。采样时,先去除土体表面的凋落物、动物残体和石砾,接着用环刀分别采集0~20、20~40,40~60、60~80、80~100 cm土层土壤样品,测定土壤容重,并且每层均取1 kg的土壤样品作为分析样,用来测定容重(BD)、有机质(OM)、pH、全氮(TN)、全磷(TP)、速效钾(AK)、机械组成等土壤理化指标。
将野外采集的土样经风干、研磨后,分别过2.00、1.00、0.25和0.15 mm孔径的筛子后装袋保存。容重采用环刀法测定,有机质采用重铬酸钾-外加热法测定[16],速效钾采用中性乙酸铵溶液浸提,火焰光度计法测定,pH采用pH酸度计电位法测定,全氮[17]和全磷[18]用全自动化学分析仪(Smartchem 200)测定,机械组成采用激光粒度仪分析法测定。
-
采用主成分分析筛选影响土壤质量的最小数据集(MDS),对不同土地利用类型土壤质量进行评价。主成分分析将土壤指标的数量减少到有限的一组向量中,并将它们分组为若干关键指标,这些指标代表了特定的土壤功能。主成分分析法通过对数据的筛选,减少参评土壤指标的数量,解决了数据冗余的问题[19]。利用主成分分析可以实现变量的约减和降维,从而将复杂的分析过程简化[20]。首先提取特征值≥1的主成分,然后选择每个主成分中最高因子荷载的20%以内的指标作为高荷载指标,如果该主成分中只有1个高荷载指标,则直接将该指标纳入最小数据集,如果该主成分有多个高荷载指标,那么需要对各个高荷载指标进行相关性分析,挑选出与高荷载指标具有显著相关性的指标[21]。
土壤数据集能够涵盖土壤特性,且每个指标都会对土壤质量的变化作出敏感反应。将最小数据集中的每个土壤指标通过隶属度函数转换为从0~1.00的无量纲分数,通过线性或非线性的得分函数来计算土壤指标的得分[19]。本研究采用的隶属度函数如下:
$$ f\left(x\right)=a/[1+({x/{x}_{0})}^{b}]\mathrm{。} $$ (1) 式(1)中:f(x)为标准化后的标准值,a=1,x为主成分分析筛选出的土壤指标值,x0为筛选出的土壤指标平均值,b为常数,当b取值−2.5时表示该指标对土壤质量产生正效应,当b取值2.5时表示该指标对土壤质量产生负效应。最后采用加权求和指数法计算研究区域的土壤质量,其数学模型如下[21]:
$$ {I}_{{\rm{SQ}}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}{W}_{i}{S}_{i} 。 $$ (2) 式(2)中: ISQ为加权求和土壤质量指数;Wi为第$ i $项指标的隶属度值;Si为第i项指标的权重;n为指标数。土壤质量指数(ISQ) 为0~1。土壤质量指数越大表明土壤质量越好。指标的权重由主成分分析中的公因子方差决定,公因子方差描述了由主成分分析模型所解释的每个土壤指标的方差比例[22]。
-
方差分析、相关性分析和主成分分析采用R3.6.3 (princomp)完成,相关数据用平均值±标准差表示,同一因素不同水平间差异显著性采用最小显著差数法(LSD)进行检验(显著性水平为0.05),采用Origin 2021进行数据处理和制图。
-
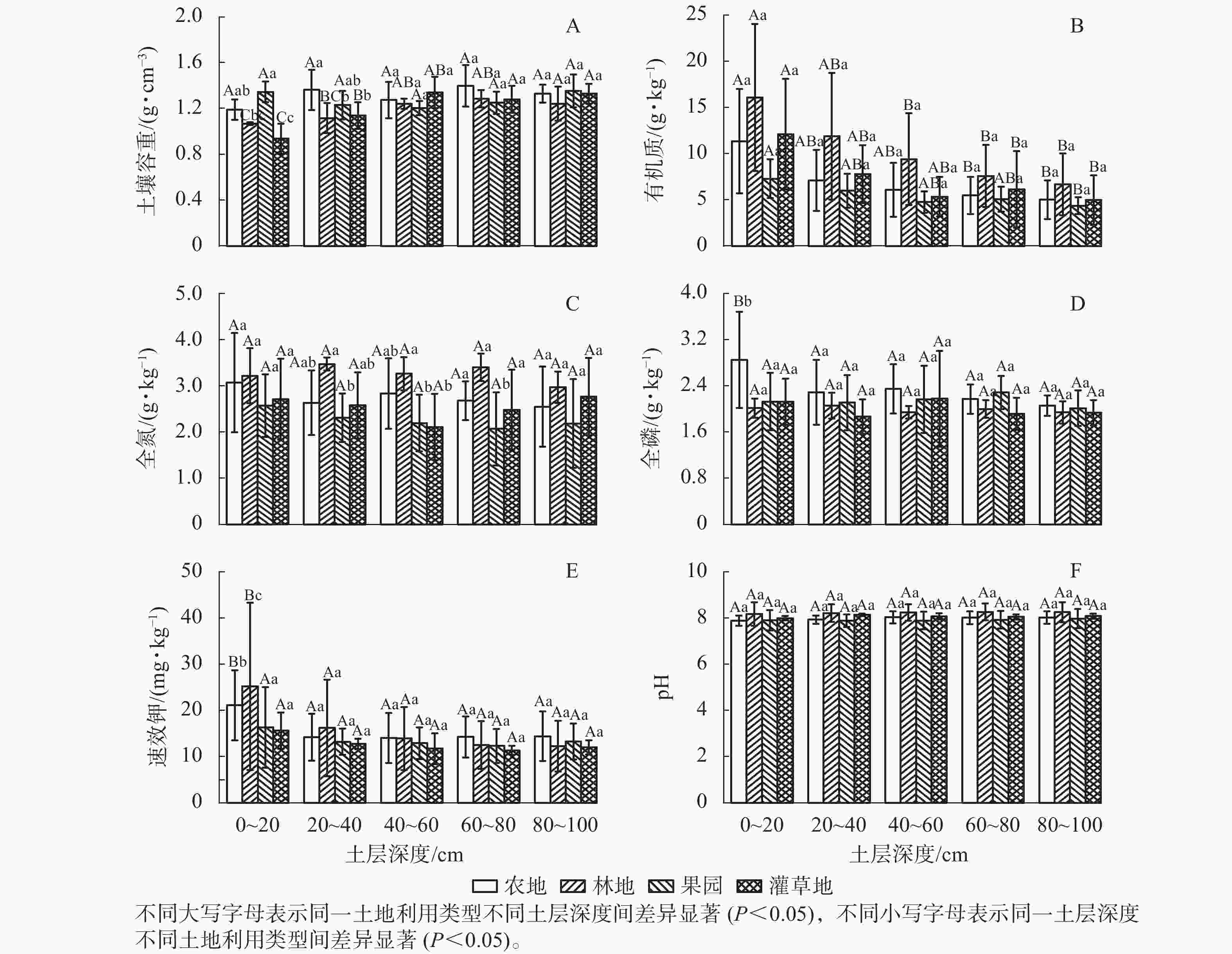
由图1A可知:不同土地利用方式和土层对土壤容重影响显著(P<0.05)。0~20 cm土层中,果园土壤容重最大[(1.34±0.09) g·cm−3],且显著高于灌草地[(0.94±0.13) g·cm−3] (P<0.05),灌草地的土壤容重最小[(0.94±0.13) g·cm−3]。20~40 cm土层中,农地的土壤容重最大[(1.36±0.17) g·cm−3],且显著大于林地[(1.11±0.13) g·cm−3]和灌草地[(1.14±0.12) g ·cm−3] (P<0.05)。其余土层的不同土地利用类型的土壤容重差异并不显著。40~60 cm土层中灌草地土壤容重[(1.34±0.14) g·cm−3]最大,果园土壤容重[(1.20±0.06) g·cm−3]最小。林地土壤容重在不同土壤深度间差异显著。在60~80 cm土层的土壤容重最大[(1.28±0.08) g·cm−3],在0~20 cm土层的土壤容重最小[(1.07±0.01) g·cm−3]。灌草地在40~60 cm土层的土壤容重最大[(1.34±0.14) g·cm−3],在0~20 cm土层的土壤容重最小[(0.94±0.13) g·cm−3]。农地和果园在不同土层的土壤容重差异不显著。
从图1B可看出:在各个土层中,林地的有机质质量分数最高[(10.34±3.38) g·kg−1],依次分别为农地[(7.27±2.61) g·kg−1]、灌草地[(7.01±2.27) g·kg−1]和果园[(5.50±1.01) g·kg−1]。在0~20 cm土层中,林地的有机质质量分数[(16.09±7.96) g·kg−1]最高,果园的有机质质量分数[(7.30±2.11) g·kg−1]最低。在20~40 cm土层中,有机质质量分数从大到小依次为林地[(11.89±6.85) g·kg−1]、灌草地[(7.79±3.12) g·kg−1]、农地[(7.13±3.30) g·kg−1]、果园[(5.99±1.85) g·kg−1]。在40~60 cm土层,有机质质量分数最高的是林地[(9.41±4.15) g·kg−1],最低的是果园[(4.76±1.15) g·kg−1]。总体来看,在同种土地利用类型中,不同土层间有机质质量分数差异显著,随着土层深度的增加,土壤有机质质量分数降低。
从图1C可知:不同土地利用方式对土壤全氮质量分数影响显著(P<0.05),而同一土地利用类型在不同土层的差异不显著。在0~20和80~100 cm土层中,4种土地利用方式的差异不显著,而在20~40和60~80 cm土层中,林地的全氮质量分数显著高于果园(P<0.05),农地和灌草地的全氮质量分数差异不显著。在40~60 cm土层中,林地的全氮质量分数[(3.26±0.36) g·kg−1]显著高于果园[(2.19±0.61) g ·kg−1]和灌草地[(2.11±0.72) g·kg−1]( P<0.05)。总体来看,林地的全氮质量分数最高,为(3.47±0.14) g·kg−1,果园的全氮质量分数最低,为(2.07±0.79) g ·kg−1。
由图1D可以看出:在0~20 cm土层中,农地的全磷质量分数最高[(2.85±0.84) g·kg−1],且显著高于其他3种土地利用类型(P<0.05),而其余土层不同土地利用类型之间差异不显著。在20~40 cm土层中,农地的全磷质量分数[(2.29±0.56) g·kg−1]最高,灌草地的全磷质量分数[(1.87±0.30) g·kg−1]最低。在40~60 cm土层中,农地全磷质量分数最高[(2.35±0.43) g·kg−1],林地全磷质量分数最低[(1.94±0.11) g·kg−1]。在60~80 cm土层中,全磷质量分数从大到小依次为果园[(2.29±0.29) g·kg−1]、农地[(2.17±0.25) g·kg−1]、林地[(2.00±0.15) g·kg−1]、灌草地[(1.92±0.28) g·kg−1]。在80~100 cm土层中,全磷质量分数从大到小依次为农地[(2.06±0.18) g·kg−1]、果园[(2.02±0.31) g·kg−1]、林地[(1.94±0.19) g·kg−1]、灌草地[(1.93±0.22) g·kg−1]。总体来看,在4种土地利用类型中,农地的全磷质量分数最高。
由图1E可知:林地在0~20 cm土层的速效钾质量分数最高,且显著高于其他土层速效钾质量分数(P<0.05);农地在 0~20 cm土层的速效钾质量分数显著高于其他土层(P<0.05),其余土层间的差异不显著。在0~20 cm土层中,速效钾质量分数从大到小依次为林地[(25.22±8.08) mg·kg−1]、农地[(21.12±7.59) mg·kg−1]、果园[(16.35±4.73) mg·kg−1]、灌草地[(15.61±3.90) mg·kg−1]。不同土地利用类型在其余土层间速效钾质量分数的差异不显著。
由图1F可知:不同土地利用方式和土层对土壤pH影响不大,不同土层pH之间的差异不显著。同一土层的4种土地利用类型中,林地的pH最高,为8.27,果园的pH最低,为7.89。
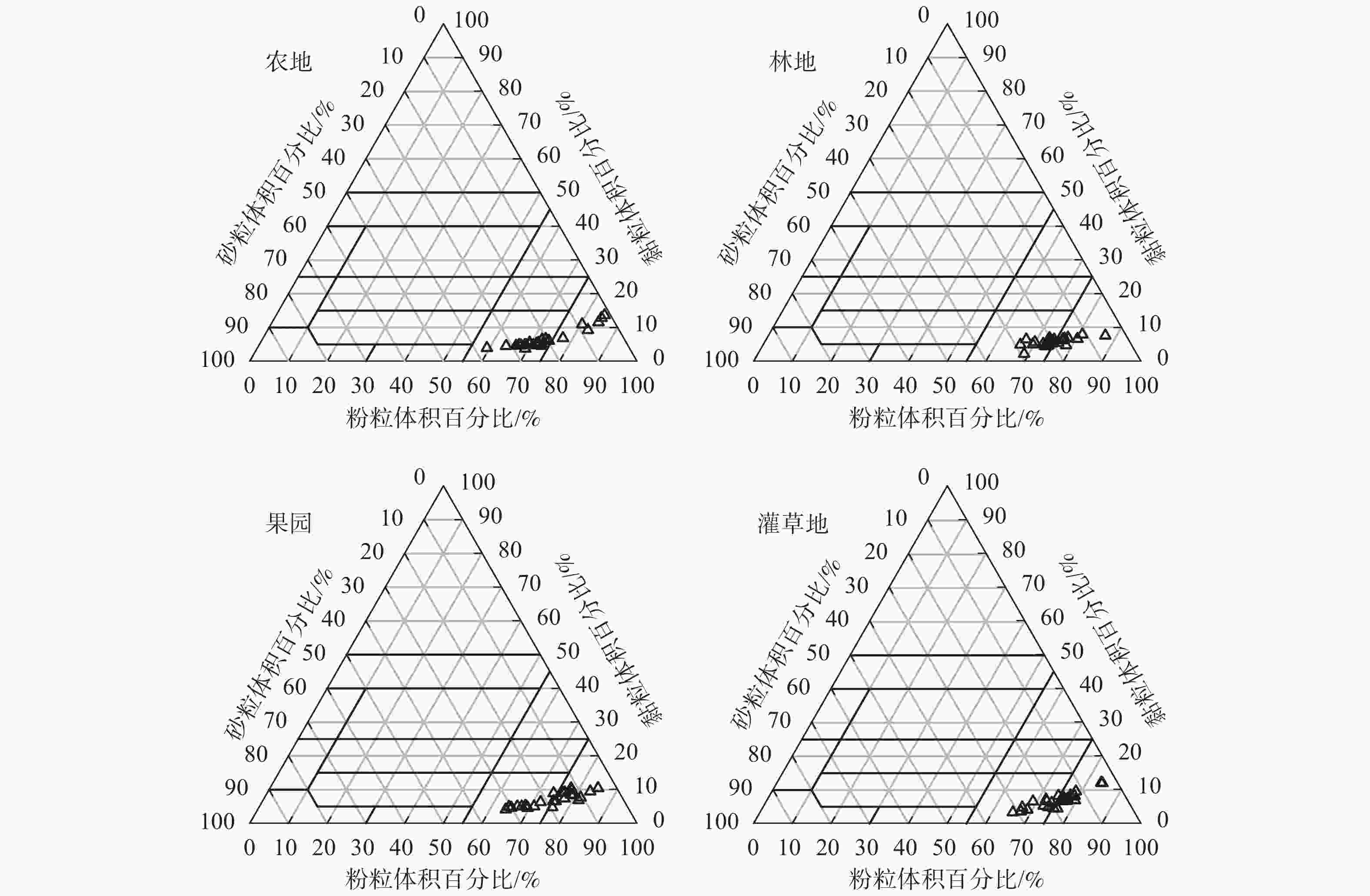
从图2可以看出:4种土地利用类型的砂粒体积百分比占0~35%,黏粒体积百分比占10%~50%,粉粒体积百分比占65%~90%,表明清水河流域的土壤属于粉砂质壤土。
-
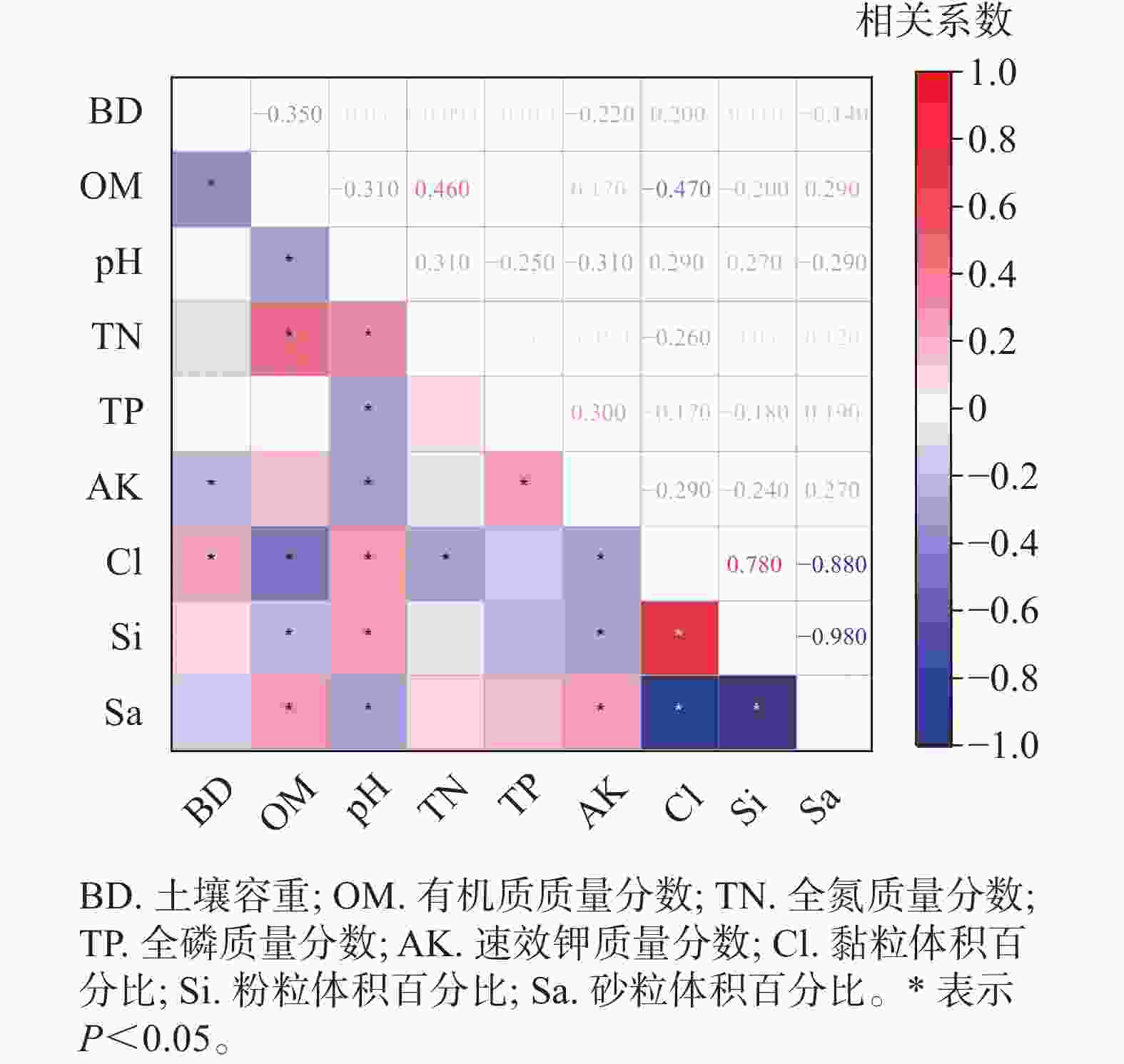
主成分分析结果(表1)表明:前3个主成分的特征值>1.0,解释了总方差的71.42%。在第1主成分中,砂粒体积百分比的加权参数最高,且与高加权参数黏粒体积百分比、粉粒体积百分比具有显著的负相关关系(P<0.05)(图3),因此剔除黏粒和粉粒体积百分比这2个指标,选择砂粒体积百分比作为计算ISQ的指标之一。在第2个主成分中,土壤容重和有机质质量分数是高加权参数,土壤容重和有机质质量分数的相关性不显著,但是有机质质量分数和砂粒体积百分比有显著的正相关关系(P<0.05),因此只将土壤容重纳入计算ISQ的指标之一。而在第3主成分中,只有速效钾质量分数是高加权参数。因此,通过主成分分析确定土壤容重、速效钾质量分数、砂粒体积百分比为计算ISQ的指标。
表 1 土壤指标在各主成分上的旋转因子载荷
Table 1. Rotation factor load of soil index on each principal component
指标 主成分 指标 主成分 1 2 3 1 2 3 土壤容重 0.07 0.51 0.16 黏粒体积百分比 0.49 0.09 −0.10 有机质质量分数 0.07 −0.53 0.16 粉粒体积百分比 0.47 −0.11 −0.21 pH 0.31 −0.27 0.18 砂粒体积百分比 −0.51 0.05 0.19 全氮质量分数 −0.25 −0.34 0.28 特征值 1.85 1.52 1.05 全磷质量分数 −0.30 0.16 −0.36 贡献率 0.38 0.21 0.12 速效钾质量分数 −0.17 0.03 −0.81 累计贡献率 0.38 0.60 0.71 -
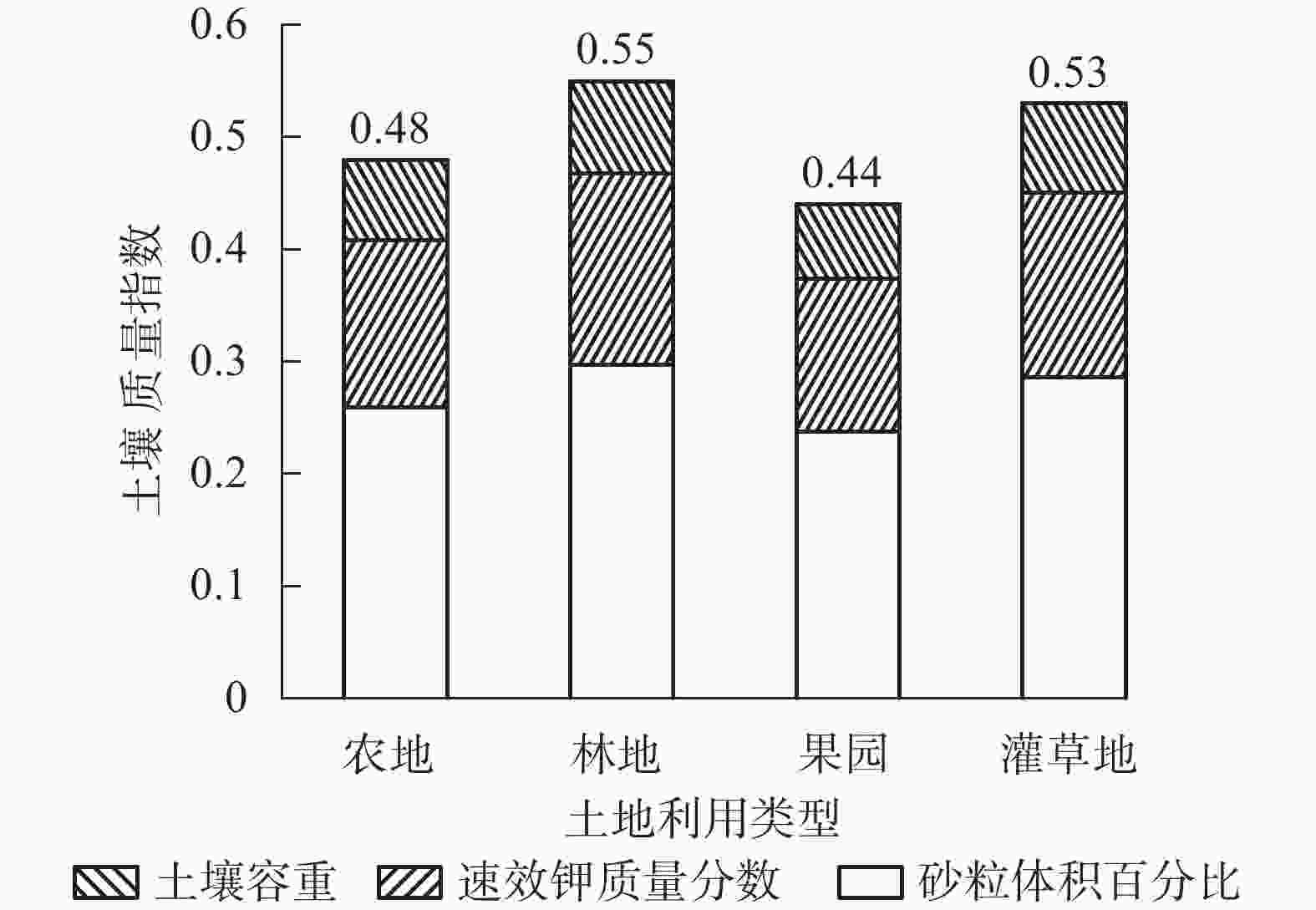
为了更直观地对比各采样点的土壤质量,以0.2为组距将土壤质量指数分为5个等级,分别为低(0<ISQ≤0.2)、较低(0.2<ISQ≤0.4)、中(0.4<ISQ≤0. 6)、较高(0.6<ISQ≤0.8)、高(0.8<ISQ≤1)[23]。清水河流域20个采样点的ISQ为0.4~0.7,有4个采样点的ISQ高于0.6,达到了较高水平(以林地为主),其均值为0.50±0.08,处于中等水平。由图4可知:林地的ISQ在4种土地利用类型中最大(0.55),其次是灌草地(0.53)、农地(0.48),果园最小(0.44)。可以看出,砂粒体积百分比对ISQ的贡献最大,其次为土壤容重和速效钾质量分数。
如使用非线性评分函数将选定的土壤质量指标(砂粒体积百分比、土壤容重、速效钾质量分数)转化为得分,并将经过标准化的指标数值和其加权乘积相加来计算ISQ,则ISQ的计算公式为:ISQ=0.54S1+0.31S2+0.15S3。其中:S1、S2、S3分别为砂粒体积百分比、土壤容重、速效钾质量分数的标准化得分。3个土壤质量指标的标准化方程如表2所示。
表 2 土壤质量指标权重因子和标准化方程
Table 2. Weight factors and standardization equations of soil quality index
指标 权重因子 加权因子 标准化方程 砂粒体积百分比(S1) 0.38 0.54 S1=1/[1+(x/22.42)2.5] 土壤容重(S2) 0.22 0.31 S2=1/[1+(x/1.13)2.5] 速效钾质量分数(S3) 0.11 0.15 S3=1/[1+(x/19.58)−2.5] 说明:x表示主成分分析筛选出的土壤指标值。 对环境因子与土壤理化因子和ISQ进行相关性分析发现:3个环境因子中,只有海拔与ISQ存在显著的相关关系(P<0.05),坡度和坡向与各土壤理化因子的相关性并不显著。对于ISQ和海拔来说,两者呈正相关关系,随着海拔的上升,土壤质量升高。
-
本研究表明:林地对土壤的改良效果最好,土壤质量最高,其次为灌草地、农地,果园的土壤质量最低。当土地利用方式发生变化时,地上部分及土壤中有机物质的数量及分解循环过程发生变化,减少了碳源输入,从而降低土壤养分[24]。地处黄土残塬沟壑区的清水河流域,土地利用方式对土壤养分影响显著。土壤全氮质量分数从大到小依次为林地、农地、灌草地、果园,可能是因为研究区林地大多为针阔混交林,其凋落物层分解较快。流域内的果园属于掠夺式土地利用类型,均由原来的林地或草地开垦种植而来。开垦所导致土壤养分的流失加上人为管理不当,致使果园的全氮质量分数最低,全磷和速效钾质量分数也处于较低的水平。农地的全氮、全磷、速效钾均高于果园和灌草地,这主要是受人为耕作和长期施用氮磷钾等肥料的影响[25]。本研究结果与李庆梅等[26]对黄河三角洲土壤养分的研究结果类似。
土壤有机质是形成土壤结构和肥力的重要因子,直接影响着土壤持水能力、水稳性团聚体以及土壤容重等物理特性[27]。4种土地利用类型中,林地有机质质量分数最高,果园有机质质量分数最低,农地和灌草地的有机质质量分数差异不显著。灌草地植被茂盛,即使被烧或者刈割,仍能保留大量的植物凋落物和死亡植物根系,使得灌草地有机质相对较高[25]。相关性分析表明:有机质和全氮呈显著的正相关,可能是大量氮素参与有机质的合成,从而降低了氮素的矿化效率,并且土壤有机质中含有大量富氮物质[28]。研究中4种土地利用类型的土壤容重存在显著差异,其中果园的土壤容重最大,农地处于居中位置。在0~20 cm土层中,灌草地的土壤容重最小,而在20~40 cm土层中,林地的土壤容重最小。果园在管理期和采摘期,受人为踩踏的影响,导致土壤板结,所以土壤容重较大。对于0~20 cm的表层土壤来说,灌草地拥有大量根系浅而发达的植物,土质疏松,土壤容重最小。
土壤质量指数(ISQ)被广泛用于评估土壤质量,其可靠性和准确性已被国内外学者证明[29]。外国学者提出土壤质量的最小数据集(MDS)概念[30]。有学者对国内外土壤质量评价 MDS 的研究成果进行了汇总[31],其结果几乎涵盖了土壤质量的物理、化学和生物等各个方面的特征,土壤容重、pH、有机质、粉粒体积百分比、砂粒体积百分比、速效磷以及含水量等具有较高的使用频率[21]。本研究所使用的土壤容重、砂粒体积百分比与大多数国内外研究基本一致。除此之外,速效钾质量分数入选了该研究区的MDS。王文武等[32]在大渡河干暖河谷区进行典型植被土壤质量评价时也将速效钾作为MDS评价指标体系之一。
相关性分析发现:在本研究采样的海拔范围(830~1 820 m)内,ISQ与海拔呈显著的正相关关系,即随着海拔的增加, ISQ也随之增加。高海拔地区,人为活动较少,有利于土壤养分的形成与累积,同时,随海拔的升高,气温的降低,降水的增多,生物累积过程强烈,有助于土壤发育[33],所以高海拔地区的ISQ更高。但也有研究显示:当海拔为1 700 m时,ISQ达最大值[34]。
-
研究区林地各土层的有机质、全氮质量分数在4种土地利用类型中均为最高;在0~20 cm土层中,农地的土壤容重和全磷质量分数显著高于其他土地利用类型;在0~20 cm土层中,林地的速效钾质量分数显著高于其他3种土地利用类型;4种土地利用类型间的pH无显著差异;4种土地利用类型的有机质质量分数均随土层的增加而降低,并且和全氮质量分数表现出显著的正相关关系。研究区土壤质量指数评价的最小数据集包括土壤容重、砂粒体积百分比以及速效钾质量分数。4种土地利用类型的ISQ从大到小依次为林地、灌草地、农地、果园。在研究区采样海拔范围内,土壤质量指数随海拔的升高而升高。研究区土壤质量整体状况较好,林地和灌草地土壤质量较高,而农地和果园土壤质量相对较低。由此可见,植被恢复在改善黄土高原小流域生态环境和提高土壤质量中发挥着重要作用。
Soil quality assessment of different land use types in Qingshui River Basin of western Shanxi Province
-
摘要:
目的 探索和评价黄土高原残塬沟壑区清水河流域不同土地利用方式下的土壤质量,并量化其与环境因子的关系。 方法 以该流域4种典型的立地类型(农地、林地、果园、灌草地)为研究对象,基于土壤容重、土壤机械组成、土壤养分(有机质、全氮、全磷、全钾、速效钾)质量分数等9种土壤理化性质指标,采用主成分分析和相关性建立最小数据集(MDS),并根据加权求和指数法计算不同土地利用类型的土壤质量。 结果 ①清水河流域内林地各土层的有机质、全氮质量分数在4种立地类型中均为最高;在0~20 cm土层,农地的容重和全磷质量分数显著高于其他立地类型(P<0.05);在0~20 cm土层,林地的速效钾质量分数显著高于其他3种土地利用类型(P<0.05);各土地利用类型间的pH无显著差异;有机质质量分数均随土壤深度的增加逐渐降低,且与全氮表现出显著正相关关系(P<0.05)。②土壤质量指数评价的最小数据集包括土壤容重、砂粒体积百分比以及速效钾质量分数。4种土地利用类型间的土壤质量从高到低依次为林地、灌草地、农地、果园,土壤质量指数随海拔的升高而升高。 结论 清水河流域土壤质量整体状况较好,林地和灌草地土壤质量较高,而农地和果园土壤质量相对较低。图4表2参34 Abstract:Objective This study aims to explore and evaluate the soil quality under different land use types in Qingshui River Basin in gully regions of the Loess Plateau, and quantify its relationship with environmental factors. Method Taking 4 typical site types (agricultural land, forest land, orchard, and irrigated grassland) in the basin as the study site, and based on 9 soil physical and chemical property indicators including soil bulk density, soil mechanical composition, soil nutrient content (organic matter, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, total potassium, and available potassium), principal component analysis and correlation were used to establish a minimum data set (MDS), and the soil quality of different land use types was calculated according to the weighted summation index method. Result (1) The contents of organic matter and total nitrogen of each soil layer in the forest land were the highest among the 4 site types. In 0−20 cm soil layer, the bulk density and total phosphorus content of agricultural land were significantly higher than those of other land types (P<0.05). In 0−20 cm soil layer, the available potassium content in forest land was significantly higher than that in other 3 land use types (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in pH among different land use types. The content of organic matter decreased gradually with the increase of soil depth and showed a significant positive correlation with total nitrogen (P<0.05). (2) MDS for soil quality index evaluation included bulk density, sand percentage and available potassium content. The soil quality of the 4 land use types from high to low was forest land, irrigated grassland, agricultural land, and orchard. The soil quality index increased with the increase of altitude. Conclusion The overall soil quality of Qingshui River Basin is good, and the soil quality of forest land and irrigated grassland is high, while the soil quality of agricultural land and orchard is relatively low. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 34 ref.] -
表 1 土壤指标在各主成分上的旋转因子载荷
Table 1. Rotation factor load of soil index on each principal component
指标 主成分 指标 主成分 1 2 3 1 2 3 土壤容重 0.07 0.51 0.16 黏粒体积百分比 0.49 0.09 −0.10 有机质质量分数 0.07 −0.53 0.16 粉粒体积百分比 0.47 −0.11 −0.21 pH 0.31 −0.27 0.18 砂粒体积百分比 −0.51 0.05 0.19 全氮质量分数 −0.25 −0.34 0.28 特征值 1.85 1.52 1.05 全磷质量分数 −0.30 0.16 −0.36 贡献率 0.38 0.21 0.12 速效钾质量分数 −0.17 0.03 −0.81 累计贡献率 0.38 0.60 0.71 表 2 土壤质量指标权重因子和标准化方程
Table 2. Weight factors and standardization equations of soil quality index
指标 权重因子 加权因子 标准化方程 砂粒体积百分比(S1) 0.38 0.54 S1=1/[1+(x/22.42)2.5] 土壤容重(S2) 0.22 0.31 S2=1/[1+(x/1.13)2.5] 速效钾质量分数(S3) 0.11 0.15 S3=1/[1+(x/19.58)−2.5] 说明:x表示主成分分析筛选出的土壤指标值。 -
[1] 彭文英, 张科利, 陈瑶, 等. 黄土坡耕地退耕还林后土壤性质变化研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2005, 20(2): 272 − 278. PENG Wenying, ZHANG Keli, CHEN Yao, et al. Research on soil quality change after returning farmland to forest on the loess sloping croplands [J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2005, 20(2): 272 − 278. [2] 田宁宁, 张建军, 李玉婷, 等. 晋西黄土区退耕还林地涵养水源和保育土壤功能评价[J]. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(5): 124 − 129. TIAN Ningning, ZHANG Jianjun, LI Yuting, et al. Functional assessment of soil and water conservation under conversion of cropland to forest in Loess Plateau of Western Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(5): 124 − 129. [3] WEI Xi, BI Huaxing, LIANG Wenjun, et al. Relationship between soil characteristics and stand structure of Robinia pseudoacacia L. and Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. mixed plantations in the Caijiachuan Watershed: an application of structural equation modeling[J/OL]. Forests, 2018, 9(3): 124[2022-06-20]. doi:10.3390/f9030124. [4] 张晓霞, 杨宗儒, 查同刚, 等. 晋西黄土区退耕还林22年后林地土壤物理性质的变化[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(2): 416 − 424. ZHANG Xiaoxia, YANG Zongru, ZHA Tonggang, et al. Changes in the physical properties of soil in forestlands after 22 years under the influence of the conversion of cropland into farmland project in loess region, Western Shanxi Province [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(2): 416 − 424. [5] 王璇, 安娟. 沂蒙山区不同土地利用方式对土壤质量的影响[J]. 鲁东大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 36(2): 168 − 175. WANG Xuan, AN Juan. Effects of different land use patterns on soil quality in Yimeng mountain area [J]. Journal of Ludong University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 36(2): 168 − 175. [6] 刘占锋, 傅伯杰, 刘国华, 等. 土壤质量与土壤质量指标及其评价[J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(3): 901 − 913. LIU Zhanfeng, FU Bojie, LIU Guohua, et al. Soil quality: concept, indicators and its assessment [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(3): 901 − 913. [7] 胡江玲, 张高, 赵枫, 等. 新疆精河流域不同土地利用方式对土壤质量的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2010, 17(4): 92 − 95, 99. HU Jiangling, ZHANG Gao, ZHAO Feng, et al. Effects of land use on soil quality in Jinghe Basin of Xinjiang [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 17(4): 92 − 95, 99. [8] 王莉, 张强, 牛西午, 等. 黄土高原丘陵区不同土地利用方式对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2007, 15(4): 53 − 56. WANG Li, ZHANG Qiang, NIU Xiwu, et al. Effects of different land-uses on soil physical and chemical properties in the Loess Plateau of Shanxi Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2007, 15(4): 53 − 56. [9] 杨亚辉, 赵文慧, 木热提江·阿不拉, 等. 不同植被对土壤理化性质影响——以王东沟小流域为例[J]. 水土保持通报, 2016, 36(1): 249 − 252. YANG Yahui, ZHAO Wenhui, Abla Mureat, et al. Impacts of vegetation cover on soil physic-chemical properties: a case study in Wangdonggou Watershed [J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 36(1): 249 − 252. [10] 刘春利, 邵明安. 黄土高原六道沟流域不同土地利用方式下土壤水力特性及其对土壤水分的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(11): 2400 − 2407. LIU Chunli, SHAO Ming’an. Soil hydraulic properties and their influences on soil water content under different land uses in Liudaogou watershed of Loess Plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(11): 2400 − 2407. [11] 王凯博, 时伟宇, 上官周平. 黄土丘陵区天然和人工植被类型对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(15): 80 − 86. WANG Kaibo, SHI Weiyu, SHANGGUAN Zhouping. Effects of natural and artificial vegetation types on soil properties in Loess Hilly region [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(15): 80 − 86. [12] 吕春花, 郑粉莉. 黄土高原子午岭地区植被恢复过程中的土壤质量评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2009, 7(3): 12 − 18, 29. LÜ Chunhua, ZHENG Fenli. Evaluation of soil quality during vegetation restoration in the Ziwuling Area of Loess Plateau [J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 7(3): 12 − 18, 29. [13] 白文娟, 郑粉莉, 董莉丽, 等. 黄土高原地区水蚀风蚀交错带土壤质量综合评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2010, 8(3): 28 − 37. BAI Wenjuan, ZHENG Fenli, DONG Lili, et al. Integrated assessment on soil quality in the water-wind erosion region of the Loess Plateau area [J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 8(3): 28 − 37. [14] 邱莉萍. 黄土高原植被恢复生态系统土壤质量变化及调控措施[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2007. QIU Liping. Change of Soil Quality and Its Regulation in Re-vgetation Ecosystem of the Loess Plateau[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2007. [15] 佘雕. 黄土高原水土保持型灌木林地土壤质量特征及评价[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2010. SHE Diao. The Characteristics and Assessment on Soil Quality of Shrub Lands in Loess Plateau[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2010. [16] 李晓萍, 梁哲军, 杨志国, 等. 土壤有机质测定方法的改进与探索[J]. 现代农业科技, 2021(20): 155 − 157. LI Xiaoping, LIANG Zhejun, YANG Zhiguo, et al. Improvement and exploration of soil organic matter determination method [J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021(20): 155 − 157. [17] 汪欣, 向兆, 李策, 等. 全自动凯氏定氮仪测定土壤全氮含量方法的优化探索[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 51(3): 438 − 440, 446. WANG Xin, XIANG Zhao, LI Ce, et al. Optimization of the method for determination of total nitrogen in soil by automatic Kjeldahl Apparatus [J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 51(3): 438 − 440, 446. [18] 向晓黎, 马小宁, 魏向利, 等. 土壤全磷测定方法要点分析[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2015, 5(5): 30 − 31. XIANG Xiaoli, MA Xiaoning, WEI Xiangli, et al. Analysis of essentials for the determination of soil total phosphorus [J]. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 2015, 5(5): 30 − 31. [19] 刘鑫, 王一博, 吕明侠, 等. 基于主成分分析的青藏高原多年冻土区高寒草地土壤质量评价[J]. 冰川冻土, 2018, 40(3): 469 − 479. LIU Xin, WANG Yibo, LÜ Mingxia, et al. Soil quality assessment of alpine grassland in permafrost regions of Tibetan Plateau based on principal component analysis [J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2018, 40(3): 469 − 479. [20] GUO Linlin, SUN Zhigang, OUYANG Zhu, et al. A comparison of soil quality evaluation methods for fluvisol along the lower Yellow River [J]. Catena, 2017, 152: 135 − 143. [21] 李鹏飞, 张兴昌, 郝明德, 等. 基于最小数据集的黄土高原矿区复垦土壤质量评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(16): 265 − 273. LI Pengfei, ZHANG Xingchang, HAO Mingde, et al. Soil quality evaluation for reclamation of mining area on Loess Plateau based on minimum data set [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(16): 265 − 273. [22] 金慧芳, 史东梅, 陈正发, 等. 基于聚类及PCA分析的红壤坡耕地耕层土壤质量评价指标[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(7): 155 − 164. JIN Huifang, SHI Dongmei, CHEN Zhengfa, et al. Evaluation indicators of cultivated layer soil quality for red soil slope farmland based on cluster and PCA analysis [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(7): 155 − 164. [23] 胡玉福, 彭佳佳, 邓良基, 等. 围栏种植红柳对川西北高寒沙地土壤颗粒组成和矿质养分的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2015, 46(1): 54 − 61. HU Yufu, PENG Jiajia, DENG Liangji, et al. Influences of fencing and planting branchy tamarisk on soil particles composition and mineral nutrients in desertization land in northwestern Sichuan Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2015, 46(1): 54 − 61. [24] 侯春兰, 杨瑞, 杨宝勇, 等. 贵州威宁草海不同土地利用类型土壤理化性质研究[J]. 林业资源管理, 2020(5): 138 − 143. HOU Chunlan, YANG Rui, YANG Baoyong, et al. Study on physiochemical properties of soil of different land use types in Caohai, Weining of Guizhou Province [J]. Forest Resources Management, 2020(5): 138 − 143. [25] 徐海军, 姚琴, 王晓飞, 等. 大庆不同土地利用下土壤理化性质及肥力变化[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(35): 55 − 63. XU Haijun, YAO Qin, WANG Xiaofei, et al. Soil physical and chemical properties and fertility under different land use patterns in Daqing [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(35): 55 − 63. [26] 李庆梅, 侯龙鱼, 刘艳, 等. 黄河三角洲盐碱地不同利用方式土壤理化性质[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(6): 1132 − 1136. LI Qingmei, HOU Longyu, LIU Yan, et al. Properties of saline-alkaline soil under different land use types in Yellow River Delta [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2009, 17(6): 1132 − 1136. [27] 刘梦云, 安韶山, 常庆瑞. 不同土地利用方式下土壤化学性质特征研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 33(1): 39 − 42. LIU Mengyun, AN Shaoshan, CHANG Qingrui. Features of soil chemical property under different land use [J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 33(1): 39 − 42. [28] 杨丹丽, 喻阳华, 钟欣平, 等. 干热河谷石漠化区不同土地利用类型的土壤质量评价[J]. 西南农业学报, 2018, 31(6): 1234 − 1240. YANG Danli, YU Yanghua, ZHONG Xinping, et al. Soil quality assessment of different land use patterns in dry-hot valley rocky desertification region [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 31(6): 1234 − 1240. [29] KARLEN D L, DITZLER C A, ANDREWS S S, et al. Soil quality: why and how? [J]. Geoderma, 2003, 114(3/4): 145 − 156. [30] ANDREWS S S, CARROLL C R. Designing a soil quality assessment tool for sustainable agroecosystem management [J]. Ecological Applications, 2001, 11(6): 1573 − 1585. [31] 陈正发, 史东梅, 金慧芳, 等. 基于土壤管理评估框架的云南坡耕地耕层土壤质量评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(3): 256 − 267. CHEN Zhengfa, SHI Dongmei, JIN Huifang, et al. Quality evaluation of cultivated-layer soil quality on sloping farmland in Yunnan based on soil management assessment framework (SMAF) [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(3): 256 − 267. [32] 王文武, 朱万泽, 李霞, 等. 基于最小数据集的大渡河干暖河谷典型植被土壤质量评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2021, 19(6): 54 − 59. WANG Wenwu, ZHU Wanze, LI Xia, et al. Soil quality assessment of typical vegetation in dry and warm valley of Dadu River based on minimum data set [J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 19(6): 54 − 59. [33] 贺燕. 祁连山区中西部土壤质量及侵蚀特征研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020. HE Yan. Study on Soil Quality and Soil Erosion Characteristics in Middle-Western Qilian Mountains[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2020. [34] ZHANG Hengshuo, YU Yang, ZHA Tonggang, et al. Assessing previous land-vegetation productivity relationships on mountainous areas hosting coming Winter Olympics Games in 2022[J/OL]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 788: 147870[2022-06-13]. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147870. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220498






 下载:
下载: