-
联合国环境规划署《2013年全球汞评估报告》指出:中国是全球汞(Hg)的主要排放国,总排放量为全球的1/3,亚洲的3/4。表明在中国开展汞的生物地球化学研究对人体健康和生态安全具有重要意义[1]。湖泊水库等水体中的汞主要来自河流输入和大气沉降,甲基汞(MeHg)则来源于水体汞的甲基化或沉积物中MeHg的释放[2],通过生物富集作用和食物链传递的生物放大作用,最终在人体内积累,对人类安全危害极大。丁之勇等[3]发现:中国31个湖泊沉积物中汞的平均质量分数为0.076 mg·kg−1;多个湖泊沉积物中汞的地累积指数达到中度或重度污染,潜在生态风险指数和平均污染程度仅次于镉(Cd)。张杰等[4]发现:太湖流域河流表层沉积物中汞的平均质量分数为0.109 mg·kg−1,超过背景值的采样点占47.87%,潜在生态风险评价处于中等或以上。近年来中国湖泊富营养化较为普遍,藻华时有发生,对湖泊水生生态系统造成极大威胁。溶解性有机质(DOM)是水生生态系统中水体天然有机质的主要成分(占97.1%)[5],通常指能通过0.10~0.70 μm滤膜,包含不同结构、分子量的碳基有机化合物,包括单糖、氨基酸等小分子化合物和蛋白质、腐殖质等大分子化合物。随着藻类暴发性增长,大量初级生产力进入[6],水体中DOM成分随之发生变化。如河流河口的硅藻Bacillariophyta藻华可显著增加DOM中碳水化合物的相对含量[7],类蛋白质荧光组分的峰强变化规律与各浮游藻类密度呈显著相关(r>0.80)[8]。一般认为,藻类正常生长的分泌物和降解的死亡藻体[9]都会造成沉积物中有机质的异常积累,从而改变水质参数,影响化合物形态的转化。DOM的—CH3、—CH2、—OH、—COOH、—C=O、—NH2等多种活性官能团可作为天然的载体与配体,与汞离子(Hg2+)发生氧化还原、络合、螯合、沉淀等一系列反应,从而影响水环境中汞元素的赋存形态、迁移性、溶解性以及最终归趋[10]。此外,DOM还会改变沉积物的氧化还原电位(Eh)和pH[11]、微生物种群等[12]环境因子,间接影响汞的形态转化。目前关于DOM影响汞甲基化的观点仍存在着较大分歧。有学者认为:DOM所含的还原态硫官能团能对汞产生络合作用,抑制其生物甲基化过程;也有研究者发现:较小的有机质会促进Hg的生物甲基化[13],DOM可以直接或在金属离子催化作用下参与非生物甲基化过程[14]。有鉴于水体中DOM来源的复杂性及其化学结构与性质的差异性,在总量水平上研究其对汞的影响难以形成定论。因此,有必要从更微观的角度阐明DOM对汞形态转化影响的作用机制。根据极性和电荷特性,DOM可分为6个成分,即疏水性的碱性、酸性和中性DOM以及亲水性的碱性、酸性和中性DOM[15]。水体富营养化和藻华使得藻体腐解过程产生的有机物成为水环境中DOM的重要来源。本研究通过室内模拟实验,对不同腐解阶段的藻类DOM进行逐步分离,取得6个亲水和疏水性亚组分,系统研究这些亚组分对汞甲基化的影响,以期丰富淡水环境中汞的生物地球化学理论,为汞污染的控制和降低汞污染健康风险提供科学依据。
-
供试藻体采自浙江省杭州市临安区某小型淡水湖泊。选取富营养化严重的湖水区域,用捞网收集水中浮藻,做好标记后放置在收纳箱内带回实验室。去除已腐烂的水藻及其他杂物后用水清洗干净,并用去离子水淋洗3次,冷冻干燥后备用。
冷冻干燥的第0、5、10、20、30、60天各取浮藻样品充分研磨,超纯水浸提法提取DOM[2]。浸提条件为20 mL超纯水与2.0 g浮藻样品混合,黑暗、恒温(25 ℃)下振荡24 h后高速离心;取0.45 μm玻璃纤维滤膜过滤离心后的上清液作为DOM样品,结晶,4 ℃保存备用。
-
取DOM结晶,与溴化钾(KBr)固体混合后制成压片。使用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(IR Prstige-21,日本岛津)测定不同腐解时期DOM的红外光谱。为减少干扰,在分析每个样品前先测定光谱背景值,通过环境空气、二氧化碳(CO2)和水(H2O)矫正光谱。调节扫描波数精度为0.01 cm−1,波数为400~4 000 cm−1。
-
用蠕动泵将DOM样品的原液通过填满树脂的树脂柱,调节四氟丙烯活塞控制液体流动速率。为了防止树脂层中出现气泡,用可拆卸的玻璃砂芯片固定树脂。
-
用体积分数95%的甲醇过Amberlite XAD 4和Amberlite XAD 8树脂柱,赶走柱中气泡,用蒸馏水淋洗至流出液的溶解性有机碳(DOC)质量浓度接近于0。用60 ℃的热水反复清洗阴离子交换树脂和阳离子交换树脂,直到阴离子交换树脂的浸洗水不再褐色、阳离子交换树脂的浸洗水几乎无泡沫;水洗后的阴、阳离子交换树脂用质量分数3%~5%的氢氧化钠(NaOH)和盐酸(HCl)溶液二次清洗,以碱-酸-碱的进液次序过阴离子交换树脂柱,以酸-碱-酸的次序过阳离子交换树脂柱。上述处理步骤完成后,将树脂放置于密封罐中备用[2]。
-
DOM分离参照LEENHEER等[16]和CHEFETZ等[17]方法。根据DOM在不同类型树脂上吸附能力的差异,将其分为疏水碱性(HOB)、疏水中性(HON)、疏水酸性(HOA)、亲水碱性(HIB)、亲水中性(HIN)、亲水酸性(HIA)6种有机组分[18]。其中HOB通过0.10 和0.01 mol·L−1 盐酸溶液反洗XAD-8树脂后获得,HOA由0.10 mol·L−1 氢氧化钠溶液反洗XAD-8树脂后获得,HON通过空气干燥XAD-8树脂并用甲醇索式提取后获得;HIB由0.10 mol·L−1氨水(NH3·H2O)反洗BIO-RAD AG-MP-50离子交换树脂后获得,HIA由3.00 mol·L−1氨水反洗DUOLITE A-7离子交换树脂后获得,HIN用纯水淋洗DUOLITE A-7离子交换树脂后获得。得到的洗脱液置于40 ℃下旋转蒸发,再经过脱盐、冷冻干燥后获得固体样品得固体样品[18]。
-
配制6个质量浓度梯度(100.00、200.00、400.00、800.00、1 600.00、3 200.00 ng·L−1)的氯化汞(HgCl2)溶液,测定未腐解藻体DOM各组分在不同氧气条件(好氧、厌氧)下对汞甲基化的影响。
将装有6种DOM亚组分样品的离心管分组,整齐地放入厌氧袋中,加入配套的厌氧产气包,快速挤出原有空气后密封,室温下放置24 h。
反应皿中加入60 mL经氮吹去氧的超纯水,分别加入DOM各组分,调节总有机碳(TOC)至10 mg·L−1,pH为7,静置1 d后,加入不同质量浓度HgCl2溶液。采用蒋红梅等[19]方法(蒸馏-乙基化结合气相色谱-冷原子荧光,CVAFS法)在BROOKS RAND测汞仪上测定甲基汞质量浓度(最低检出限为0.009 ng·L−1)。
-
配制1 000.00 ng·L−1的Hg2+溶液,分别加入第0、5、10、20、30、60天DOM各亚组分,参照蒋红梅等[19]方法测定甲基汞质量浓度。
-
数据处理和图表制作采用Origin 8.5及Omnic 8.2软件。MeHg测量按10%的平行操作,测定标样和空白样并做标准曲线。分析重复组数据时控制相对标准偏差低于12%。
-
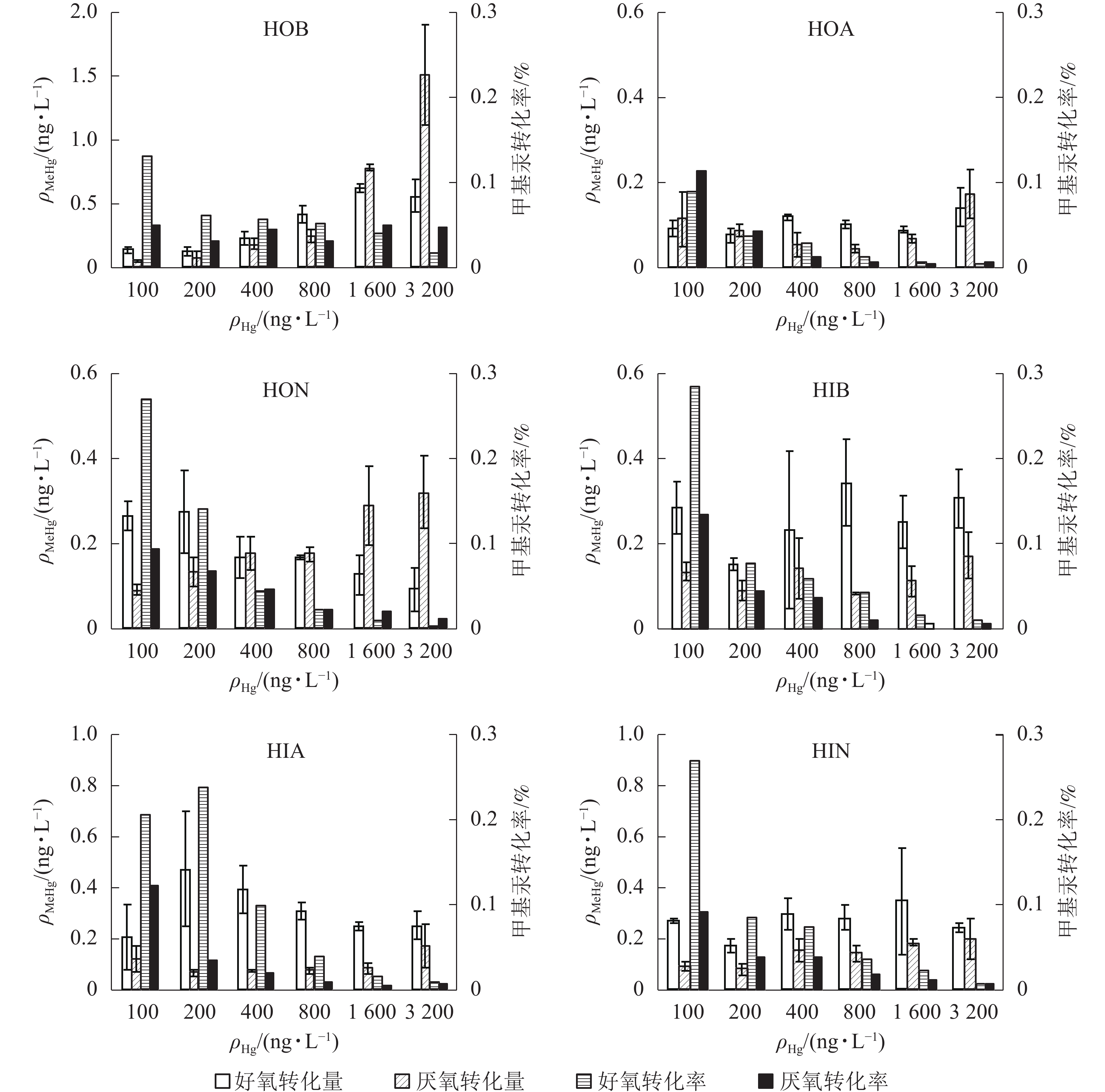
碱性疏水性有机物(HOB)对汞甲基化贡献最高,其次为HON和HIA,其他成分的贡献量都较小,且没有显著差异。3种疏水性有机亚组分的汞甲基化作用由强到弱依次为HOB、HON、HOA。由图1可知:不同氧气条件下,MeHg生成量均随Hg2+质量浓度增加而增加,提示HOB具有明显促进汞甲基化的能力。Hg2+低于1 600 ng·L−1时,好氧条件下MeHg转化量随Hg2+质量浓度的增加而增加,转化率则降低(由13.0%降至1.7%);厌氧条件下MeHg的转化量一直呈上升趋势,转化率则较为平稳;相比之下,厌氧条件更有利于MeHg的生成。HOA与HON一定程度上也能促进MeHg生成,但总体效果不如HOB。两者均在Hg2+质量浓度最大时达最大转化量,但MeHg转化率均随Hg2+质量浓度增加而下降。Hg2+质量浓度为3 200 ng·L−1时,3种组分的MeHg转化量厌氧条件均高于好氧条件。
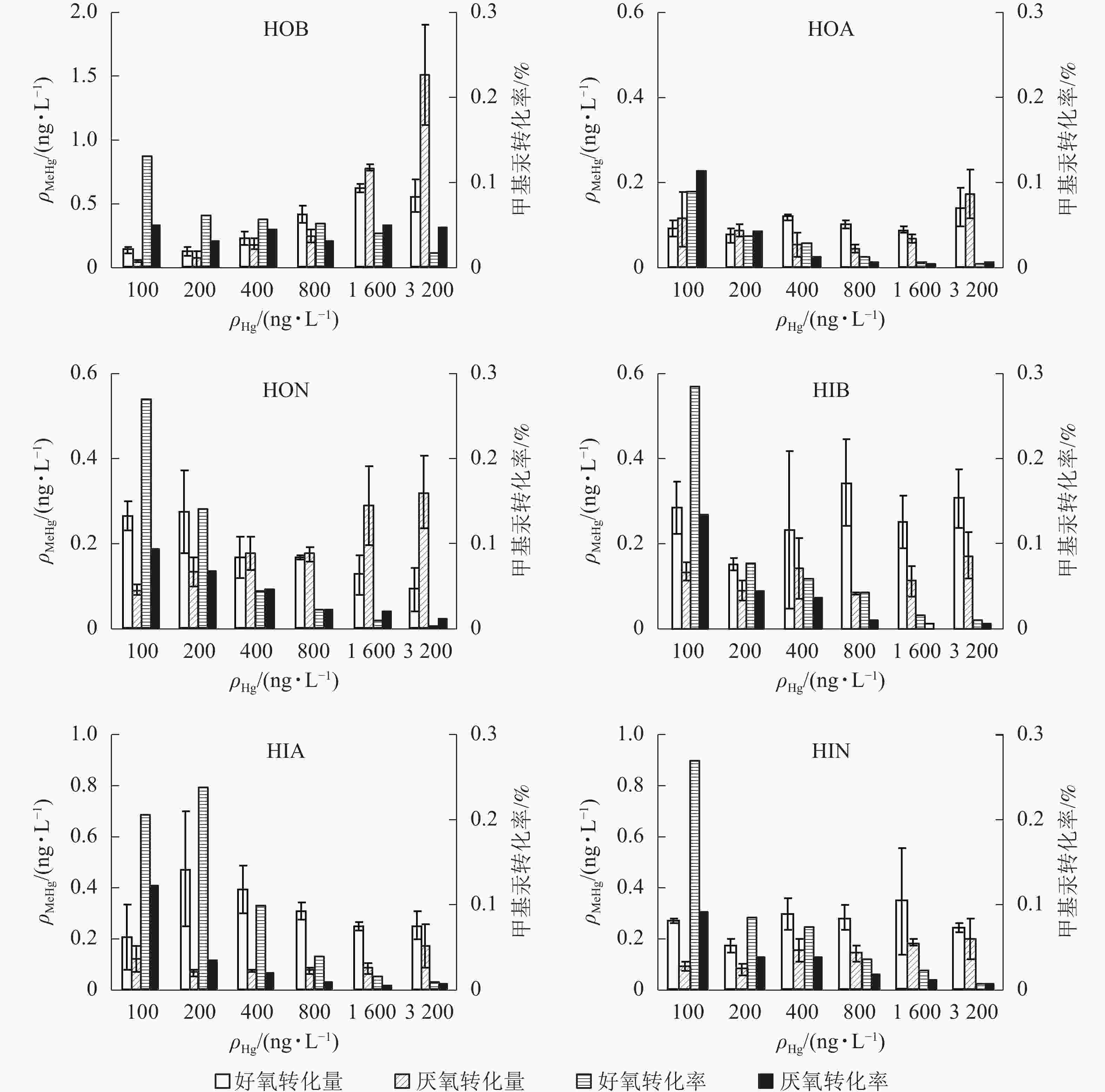
图 1 不同Hg2+质量浓度下DOM各亚组分对汞甲基化的影响
Figure 1. Effect of DOM subcomponents on the production of MeHg at different initial Hg2+ concentrations
3种亲水性有机亚组分中,HIB能略微促进Hg2+的甲基化;厌氧条件下甲基汞生成量较少(最大值0.17 ng·L−1);不同氧气条件下转化率均随Hg2+质量浓度增加而降低,好氧时最高值为29.0%,厌氧时最高值为13.0%。HIA在好氧条件下的MeHg转化量表现为先上升后下降(最大值为0.40 ng·L−1),厌氧条件下的转化量很小(最大值0.15 ng·L−1),转化率随Hg2+质量浓度的升高而降低。HIN对汞形态转化亦有一定的促进作用。好氧、厌氧条件下MeHg转化量随浓度变化的规律性不强,厌氧转化量更低;2种条件下转化率均大致随Hg2+浓度的升高而降低,但厌氧条件下最高转化率仅为好氧时的一半。
以上结果表明:藻体DOM总体上可促进水体中Hg2+的甲基化反应。分离出的6个亚组分中,3个疏水性有机物对甲基汞产生的影响要强于3个亲水性有机物,以HOB的促进作用最为明显。DOM影响重金属在水体中形态变化过程的根本原因是其可以与重金属离子形成络合物,从而影响后者形态、生物有效性和毒性。有机分子的结构组成可以影响DOM对金属的亲合力。GUGGENBERGER等[20]发现:亲水性酸性物质对金属离子有较强的络合能力,是疏水性酸性物质的2~8倍,与本研究中亲水性DOM更易与溶液中的Hg2+结合、降低水体汞甲基化的结论一致。生物配体模型[21]认为:亲水性DOM与自由金属离子络合后使得自由离子平衡浓度下降,进而降低金属离子在有DOM存在时的有效性,与本研究结论也较为一致。研究发现:随着Hg2+质量浓度升高,甲基汞转化率逐渐降低,表明在较高的Hg2+质量浓度条件下,参与甲基化反应DOM的甲基供体数量不足,与LIANG等[22]结论一致。
自然环境下,汞的甲基化特别是生物甲基化主要发生在厌氧条件下。本研究发现,不同亚组分在好氧/厌氧条件下对甲基汞产生的影响不同。对于HOB来说,厌氧条件更利于汞的甲基化反应,厌氧条件下甲基汞产生量高于好氧条件,而其他成分在好氧、厌氧条件下的甲基汞产生量则无太大变化。
-
对不同腐解时长下的藻体DOM作红外光谱(图2)分析可知:未腐解的DOM各官能团种类最为丰富,随腐解时间的延长,基团簇度呈逐渐减少趋势;腐解第60天时,1 364 cm−1处的叔丁基[—C(CH3)]、2 900 cm−1处的饱和C—H键(—CH3)的伸缩和亚甲基(—CH2—)的反对称伸缩、3 400 cm−1处游离态和缔合态的羟基(O—H伸缩振动)的峰已很不明显。总体来看,腐解0~10 d的DOM官能团变化较小,较稳定。对比1 060 cm−1处的波动,可以看出不同腐解时长下C—O键的簇数明显下降。综上所述,不同腐解时长下,DOM官能团的数量和种类均发生变化,并影响各亚组分对汞的甲基化作用。
-
HOB、HOA和HON为DOM的3个疏水性有机组分。由图3可知:不同腐解时间产生的HOB,汞甲基化能力不尽相同。腐解初期(0~10 d)甲基化能力呈下降趋势,第10天MeHg转化量仅为0.20 ng·L−1,10~20 d转化量大幅增加,增幅达61.9%,之后小幅波动,第60天时达最高值(0.71 ng·L−1)。腐解初期(0~10 d)HOA对汞的甲基化基本没有影响,但随腐解时间增长,HOA的汞甲基化能力逐渐加强。相比之下,HON促进汞甲基化能力总体较大;腐解初期略低,但最小值(第10天)也达到了1.20 ng·L−1,此后转化量大幅增加,第60天达到最大转化量(1.55 ng·L−1)。

图 3 不同腐解时间DOM亚组分对MeHg生成量的影响
Figure 3. Variation of MeHg concentrations of DOM subcomponents at different decomposition intervals
相比而言,3个亲水性组分的汞甲基化能力略低。其中,HIB的甲基汞转化量最小,HIA和HIN随着腐解时间的增加,汞甲基化能力先增加后降低,在第60天时达到了最低,与疏水性有机组分的结果正好相反。
以上研究结果表明,随着腐解的进行,亲水性组分的促进汞甲基化能力表现为先升高再降低乃至消失;疏水性组分则表现为先降低再逐渐升高。3种疏水性亚组分对汞甲基化的影响效应均在60 d时达到极值。随着藻类腐解进程,藻体逐渐释放出大量DOM。冯胜等[23]发现:狐尾藻Myriophyllum verticillatum腐烂过程中释放出大量类蛋白物质,DOM荧光组分和荧光峰呈先逐渐增强后逐渐降低趋势;表明在腐解过程中,DOM先增加后减少。藻类DOM以类色氨酸成分为主,可以很快被微生物利用并降解转变为类腐殖质物质[24]。本研究中,疏水性亚组分的汞甲基化能力高于亲水性亚组分,由此推测:水体DOM的疏水性亚组分是汞甲基化的主导原因,即DOM对汞甲基化的影响主要为疏水性亚组分对汞甲基化的影响。SWIETLIK等[18]研究:HON富含碳氢化合物、多碳(>5)脂肪族醇、酯、酮和芳香结构,具有比其他亚组分更加丰富的官能团(如羟基、羰基和羧基等),因此作为甲基化电子供体更为有效,促进汞甲基化能力也更强。
-
DOM的6种亚组分中,疏水性亚组分的汞甲基化能力高于亲水性亚组分,其中以HOB为最,原因在于亲水性亚组分易与游离态的Hg2+发生络合,降低后者生物有效性;疏水性亚组分因表面官能团更为丰富,不易与Hg2+络合,更有利于Hg2+甲基化。随着游离Hg2+的增加,甲基供体数量逐渐减少,甲基汞转化率逐渐降低。
富营养化藻类的DOM主要包含羟基、甲基、亚甲基、芳环C=C等官能团,随腐解时间延长,这些基团的簇度逐渐减少,使得不同腐解时期DOM各组分对汞的形态转化呈现较大差异。
藻体腐解过程中,DOM的疏水性有机组分汞甲基化能力高于亲水性有机组分;不同腐解时长下释放的相同亚组分,其汞甲基化效应亦有所差异。
Influence of algal derived dissolved organic matter on mercury methylation in water
-
摘要:
目的 探究藻源溶解性有机质(DOM)各亚组分在不同腐解时间、不同汞(Hg2+)质量浓度下对水体中汞甲基化的影响。 方法 应用树脂串联技术分离藻体DOM的6种亚组分,利用室内培养方式进行Hg2+的甲基化试验。 结果 藻类DOM主要由羟基、烃基和芳环C=C等官能团组成;未经腐解的DOM各亚组分中,疏水性有机组分对汞甲基化的影响高于亲水性有机组分;随腐解时间延长,DOM官能团逐渐减少,疏水性有机组分对汞甲基化的影响表现为先降低后升高;亲水性有机组分抑制汞甲基化。 结论 DOM相对含量的升高抑制了汞的甲基化,DOM降解后,释放出来的Hg2+被微生物重新利用,甲基化程度加剧。图3参24 -
关键词:
- 汞 /
- 溶解性有机质(DOM) /
- 甲基化 /
- 有机质亚组分 /
- 藻类
Abstract:Objective To determine the effects of subcomponents of algae dissolved organic matter (DOM) on mercury methylation at different decomposition intervals and different Hg2+ concentrations. Method Six subcomponents of the DOM derived from the algae through a tandem connection of resin, and then conducted simulation experiments separately. Result Algae DOM was mainly composed of hydroxyl group, alkyl group and C=C of aromatic hydrocarbon, etc. Different subcomponents of DOM before decomposition, the influence of hydrophobic component on mercury methylation was significantly stronger than that of hydrophilic component. With the progress of algal decomposition, the relative content of functional groups was gradually decreasing while the influence of hydrophobic components on Hg methylation first weakened and then enhanced during the decomposition process and hydrophilic component can inhibit Hg methylation. Conclusion The increase in relative content of DOM results in the inhibition of Hg methylation. After the decomposition of DOM, the Hg2+ released got methylated by bacteria again, which helped promote the degree of methylation. [Ch, 3 fig. 24 ref.] -
Key words:
- mercury /
- dissolved organic matter /
- methylation /
- DOM subcomponents /
- algae
-
-
[1] 王德铭. 水环境汞污染及其毒理反应系统的研究进展[J]. 水科学进展, 1997, 8(4): 60 − 65. WANG Deming. Advances of studies on mercury pollution in aquatic environment and its toxicological response system [J]. Adv Water Sci, 1997, 8(4): 60 − 65. [2] 杨淇茹. 渔排养殖区溶解性有机质对汞形态变化影响研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2019. YANG Qiru. Effect of Dissolved Organic Matter on the Change of Mercury Form in Fish Culture Area[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A&F University, 2019. [3] 丁之勇, 蒲佳, 吉力力·阿不都外力. 中国主要湖泊表层沉积物重金属污染特征与评价分析[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(6): 136 − 141, 102. DING Zhiyong, PU Jia, Jilili Abuduwaili. Heavy metal contamination characteristics and its assessment in surface sediments of major lakes in China [J]. Environ Eng, 2017, 35(6): 136 − 141, 102. [4] 张杰, 郭西亚, 曾野, 等. 太湖流域河流沉积物重金属分布及污染评估[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(5): 2202 − 2210. ZHANG Jie, GUO Xiya, ZENG Ye, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in river sediments from Lake Taihu basin [J]. Environ Sci, 2019, 40(5): 2202 − 2210. [5] 何伟, 白泽琳, 李一龙, 等. 溶解性有机质特性分析与来源解析的研究进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(2): 359 − 372. HE Wei, BAI Zelin, LI Yilong, et al. Advances in the characteristics analysis and source identification of the dissolved organic matter [J]. Acta Sci Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(2): 359 − 372. [6] 纪振, 尹业新, 单爱琴, 等. 浅论微生物技术控藻[J]. 资源开发与市场, 2007, 23(2): 138 − 140, 104. JI Zhen, YIN Yexin, SHAN Aiqin, et al. Shallow talk on the control of algae with using microbial techniques [J]. Resour Dev Market, 2007, 23(2): 138 − 140, 104. [7] 贾国元, 曾提, 贾国东. 淡水环境中可溶有机质研究进展[J]. 绿色科技, 2013(3): 151 − 154. JIA Guoyuan, ZENG Ti, JIA Guodong. Research progress on freshwater dissolved organic matter [J]. J Green Sci Technol, 2013(3): 151 − 154. [8] 樊磊磊, 黎司, 虞丹尼, 等. 三峡水库回水末端浮游藻类分布特征及其与DOM荧光特性的相关性研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(8): 2198 − 2202. FAN Leilei, LI Si, YU Danni, et al. Planktonic algae’s distribution and correlation with dissolved organic matters’ fluorescence in the end of the Three Gorges Reservoir’s back water zone [J]. Spectrosc Spectral Anal, 2015, 35(8): 2198 − 2202. [9] 冯伟莹, 朱元荣, 吴丰昌, 等. 太湖水体溶解性有机质荧光特征及其来源解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(2): 475 − 482. FENG Weiying, ZHU Yuanrong, WU Fengchang, et al. The fluorescent characteristics and sources of dissolved organic matter in water of Tai Lake, China [J]. Acta Sci Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(2): 475 − 482. [10] 张玉涛, 程劲松, 李琳, 等. 溶解性有机质对水体汞还原反应影响机制研究进展[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 37(1): 101 − 104. ZHANG Yutao, CHENG Jinsong, LI Lin, et al. Progress in research on influences of dissolved organic matter on mercury reduction in water [J]. J China Three Gorges Univ Nat Sci, 2015, 37(1): 101 − 104. [11] SCHARTUP A T, BALCOM P H, MASON R P. Sediment-porewater partitioning, total sulfur, and methylmercury production in Estuaries [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2014, 48(2): 954 − 960. [12] PARKS J M, JOHS A, PODAR M, et al. The genetic basis for bacterial mercury methylation [J]. Science, 2013, 339(6125): 1332 − 1335. [13] 冯新斌, 仇广乐, 付学吾, 等. 环境汞污染[J]. 化学进展, 2009, 21(2/3): 436 − 457. FENG Xinbin, QIU Guangle, FU Xuewu, et al. Mercury pollution in the environment [J]. Progr Chem, 2009, 21(2/3): 436 − 457. [14] 阴永光, 李雁宾, 马旭, 等. 天然有机质介导的汞生物地球化学循环: 结合作用与分子转化[J]. 化学进展, 2013, 25(12): 2169 − 2177. YIN Yongguang, LI Yanbin, MA Xu, et al. Role of natural organic matter in the biogeochemical cycle of mercury: binding and molecular transformation [J]. Progr Chem, 2013, 25(12): 2169 − 2177. [15] HUANG Yujuan, CHENG Miaomiao, LI Wenhong, et al. Simultaneous extraction of four classes of antibiotics in soil, manure and sewage sludge and analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with the isotope-labelled internal standard method [J]. Anal Methods, 2013, 5(15): 3721. [16] LEENHEER J A, HUFFMAN E W D. Classification of organic solutes in water by using macroreticular resin [J]. J Res US Geol Surv, 1976, 4(6): 737 − 751. [17] CHEFETZ B, HADAR Y, CHEN Yona. Dissolved organic carbon fractions formed during composting of municipal solid waste: properties and significance [J]. Clean Soil Air Water, 1998, 26(3): 172 − 179. [18] SWIETLIK J, DABROWSKA A, RACZYK-STANISLAWIAK U, et al. Reactivity of natural organic matter fractions with chlorine dioxide and ozone [J]. Water Res, 2004, 38(3): 547 − 558. [19] 蒋红梅, 冯新斌, 梁琏, 等. 蒸馏-乙基化GC-CVAFS法测定天然水体中的甲基汞[J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(5): 568 − 571. JIANG Hongmei, FENG Xinbin, LIANG Lian, et al. Determination of methyl mercury in waters by distillation-GC-CVAFS technique [J]. China Environ Sci, 2004, 24(5): 568 − 571. [20] GUGGENBERGER G, GLASER B, ZECH W. Heavy metal binding by hydrophobic and hydrophilic dissolved organic fractions in a spodosol A and B horizon [J]. Water Air Soil Pollut, 1994, 72: 111 − 127. [21] 王春艳, 陈浩, 安立会, 等. BLM预测水中重金属生物有效性研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2011, 34(8): 75 − 80. WANG Chunyan, CHEN Hao, AN Lihui, et al. An updated review on biotic ligand model in predicting metal bioavailability in surface waters [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2011, 34(8): 75 − 80. [22] LIANG Peng, SHAO Dingding, WU Shengchun, et al. The influence of mariculture on mercury distribution in sediments and fish around Hong Kong and adjacent mainland China waters [J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 82(7): 1038 − 1043. [23] 冯胜, 袁斌. 狐尾藻腐烂过程中DOM的三维荧光光谱特征[J]. 常州大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 30(4): 46 − 52. FENG Sheng, YUAN Bin. Fluorescence spectra characteristics of DOM during the decay process of Myriophyllum [J]. J Changzhou Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2018, 30(4): 46 − 52. [24] 姚昕, 张运林, 朱广伟, 等. 湖泊草、藻来源溶解性有机质及其微生物降解的差异[J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(3): 688 − 694. YAO Xin, ZHANG Yunlin, ZHU Guangwei, et al. Different degradation mechanism of dissolved organic matter derived from phytoplankton and macrophytes in Lake Taihu, China [J]. Acta Sci Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(3): 688 − 694. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200146






 下载:
下载: