-
杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata是中国南方最重要速生树种之一,具有较强的萌芽能力[1-2]。随着现代林业的发展,无性林业成为当今社会林业发展的一个主要方向。随着近十几年来的杉木苗木繁育技术的研究,杉木无性繁殖取得了较大的突破,无性系造林面积越来越大。组培和扦插是杉木无性繁育的2个主要途径。由于杉木组培工厂化育苗过程中还普遍存在增殖系数低、生根率低等问题,扦插繁殖是杉木无性繁育的最主要途径。杉木采穗圃是提供穗条的最主要场所,为促进杉木的萌蘖能力,提高穗条的产量,去顶、压弯及基部损伤处理是常用的几种措施。目前,对母树的弯干、截干、浅栽、施肥等方面进行了研究[3-4]。机械损伤后,植物产生一系列次生代谢产物,如酚类、黄酮类、萜类、生物碱等,它们集中在伤口及其附近,参与伤口愈合反应,抵抗昆虫或病原体的入侵[5]。抗氧化酶在催化这一途径中起着非常重要的作用,对植物生长发育、紫外线辐射防治、抗虫害和植物支持系统的形成具有重要的意义和价值,其活性可作为衡量植物抗逆性强弱的指标[6]。酚类物质在植物抗生物胁迫机制中起着重要作用。机械损伤也被认为是诱导植物防御的重要手段之一[7]。虽然近年来对机械损伤影响植物防御酶的影响研究较多,但是关于机械损伤和不同埋土深度处理对杉木无性系萌蘖抗氧化酶活性的机制研究却鲜少报道。本研究以萌蘖能力较强的杉木无性系洋020扦插苗为研究对象,通过室内盆栽试验,分析机械损伤和不同埋土深度对无性系萌蘖能力及不同器官抗氧化酶活性的影响,为揭示杉木萌蘖机制以及杉木人工林的高效培育奠定理论依据。
-
材料为福建省洋口国有林场提供的1年生杉木洋020扦插苗。挑选生长健壮、长势一致、无病虫害的苗木,平均苗高30 cm,地径为5 mm。盆栽土壤为山地黄心土,有机质49.00 g·kg−1,全氮1.09 g·kg−1,水解氮1.32 mg·kg−1,速效磷2.30 mg·kg−1,速效钾151.30 mg·kg−1。
-
试验在福建农林大学国家林业草原杉木工程技术研究中心田间实验室内进行。2019年3月中旬将杉木无性系洋020扦插苗种植于花盆(21 cm×26 cm×27 cm)中,3株·盆−1。培养基为黄心土。采用随机区组试验,6个处理,处理1为去顶埋土深度0 cm (TP1),处理2为去顶埋土深度3 cm (TP2),处理3为去顶埋土深度6 cm (TP3),处理4为未去顶埋土深度0 cm (ck1),处理5为未去顶埋土深度3 cm (ck2),处理6为未去顶埋土深度6 cm (ck3);去顶处理为苗木培养7 d后剪去顶稍1 cm;每个处理40盆,共240盆。盆栽后定期调查不同处理杉木基部的萌芽数。培养期间定期给苗木浇自来水,保持土壤含水率在65%左右;定期除草。2019年6月30日(萌蘖初期)、7月31日(萌蘖中期)、8月31日(萌蘖后期)取已萌芽的洋020扦插苗的枝叶、基部皮及根尖样品,每个处理采集9株,每3株混成1个待测样,每个部位待测样3个重复。不同部位样品取样后迅速放入液氮中,置于−80 ℃超低温冰箱中保存待测。
-
2019 年4月30日、5月31日、6月30日、7月31日、8月31日分别调查不同处理幼苗的萌蘖数。
-
参照李合生的方法[8]取叶片、基部皮及根尖0.2 g,加入0.05 mol·L−1 pH 7.8磷酸缓冲液228.75 mL,母液B(NaH2PO4)21.25 mL,用蒸馏水稀释至1 000 mL。在冰浴中用研钵研磨成匀浆,稀释至4 mL刻度离心管,在4 ℃下以10 000 r·min−1的速度冷冻离心20 min,并将上清液置于4 ℃冰箱中冷藏。超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性测定参照丁红等[9]方法,以抑制氮蓝四唑(NBT)光还原的50%为1个酶活性单位。过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性参照SHALATA等[10]的方法测定。
-
数据用Excel 2010和SPSS 22.0软件进行整理和相关性分析。
-
表1结果显示:随着培养时间的延长,杉木萌蘖均呈上升趋势,随着埋土深度的增加,杉木萌蘖能力呈逐渐下降的趋势,在相同埋土深度条件下,去顶处理比未去顶处理杉木萌蘖能力更强。萌蘖后期(8月),埋土深度0、3、6 cm去顶处理苗的萌蘖数与同一埋土深度未去顶处理相比分别提高15.11%、6.73%及3.49%;去顶处理苗埋土深度6 cm处理的萌蘖数分别比埋土深度3及0 cm处理降低5.67%及34.29%,未去顶处理苗埋土深度6 cm处理的萌蘖数分别比埋土深度3及0 cm处理降低4.21%及25.87%。
表 1 机械损伤和不同埋土深度处理下杉木无性系萌蘖差异
Table 1. Difference of tillering of Chinese fir clones treated by mechanical damage and different soil depth
处理 萌蘖/株 2019-06-30 2019-07-31 2019-08-31 TP1 0.65 ± 0.08 ab 2.90 ± 0.20 bc 3.50 ± 0.50 ac TP2 0.54 ± 0.06 bc 2.40 ± 0.18 a 3.10 ± 0.30 b TP3 0.43 ± 0.03 a 2.13 ± 0.16 b 2.54 ± 0.30 a ck1 1.50 ± 0.02 b 2.89 ± 0.40 a 3.35 ± 0.42 b ck2 1.20 ± 0.11 a 2.20 ± 0.30 b 3.00 ± 0.40 a ck3 0.80 ± 0.06 a 2.10 ± 0.20 b 2.20 ± 0.30 a 说明:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05) -
由图1看出:在萌蘖后期,杉木幼苗基部皮SOD活性除TP2较低外,其余处理均显著高于前期和中期。ck1、ck2、ck3、TP1、TP3的杉木幼苗枝叶萌蘖后期SOD活性相比于前期分别提高36.08%、45.76%、63.65%、31.56%、57.27%,相比于中期分别提高了41.99%、25.77%、49.59%、49.00%、21.23%。杉木幼苗枝叶SOD活性普遍以TP1较低,在萌蘖前期、中期和后期分别为300.99、343.08、354.89×16.67 nkat·g−1。在后期,ck3、ck2和TP3的杉木幼苗枝叶SOD活性相比于前期和中期显著上升,其中相比于前期分别提升了40.57%、54.06%和76.00%,相比于中期分别提升了18.28%、46.95%和45.86%。而杉木幼苗不同机械损伤和不同埋土深度间处理下的杉木幼苗根尖SOD活性则不具有明显规律。
-
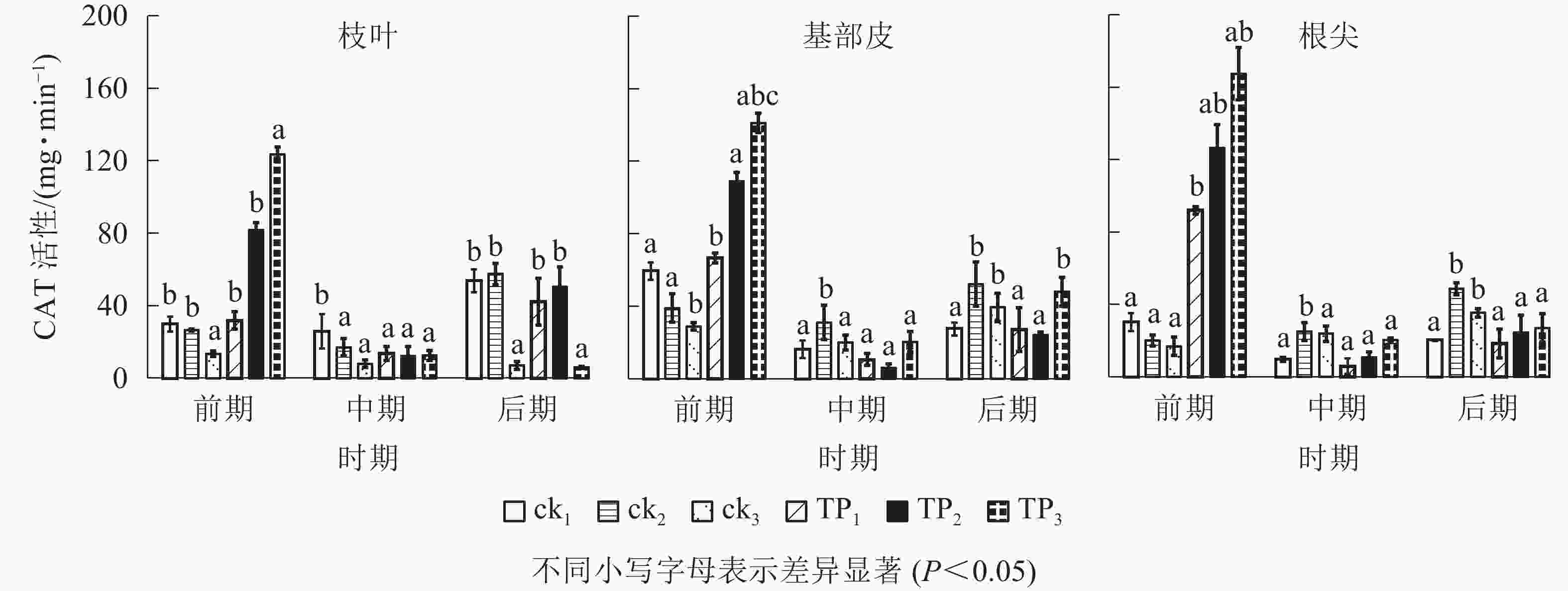
由图2可以看出:在萌蘖前期,杉木幼苗枝叶、基部皮和根尖CAT活性,从高到低排序均为TP3、TP2、TP1,ck1、ck2和ck3。TP3处理杉木枝叶CAT活性相比于TP2、TP1、ck3、ck2和ck1分别高出了459.29%、1 004.03%、366.34%、81.98%和20.30%,基部皮分别高出了419.75%、241.20%、204.15%、86.01%和43.44%;根尖分别高出了1 123.06%、933.10%、125.46%、63.93%和23.83%。在中期和后期,杉木幼苗枝叶、基部皮和根尖CAT活性均迅速下降,在中期,TP3、TP2、TP1、ck3、ck2和ck1的杉木叶片CAT活性相比于前期分别下降了36.35%、41.02%、57.08%、85.01%、89.90%和90.82%,杉木基部皮CAT活性相比于前期分别下降了20.56%、66.32%、84.29%、94.55%、85.56%和95.33%,杉木根尖CAT活性相比于前期分别下降了−47.49%、−18.77%、88.11%、92.36%、87.91%、4.52%。杉木幼苗枝叶CAT活性在中期ck2和ck1较高,在后期TP2、TP1、ck2和ck1较高。在中期和后期,杉木幼苗基部皮和根尖CAT活性规律较为统一,且总体处于较低水平。基部皮CAT活性在中、后期从高到低排序为ck2、TP3、ck3、ck1、TP1、TP2,根尖CAT活性在中、后期从高到低排序为ck2、ck3、TP3、TP2、ck1、TP1。
-
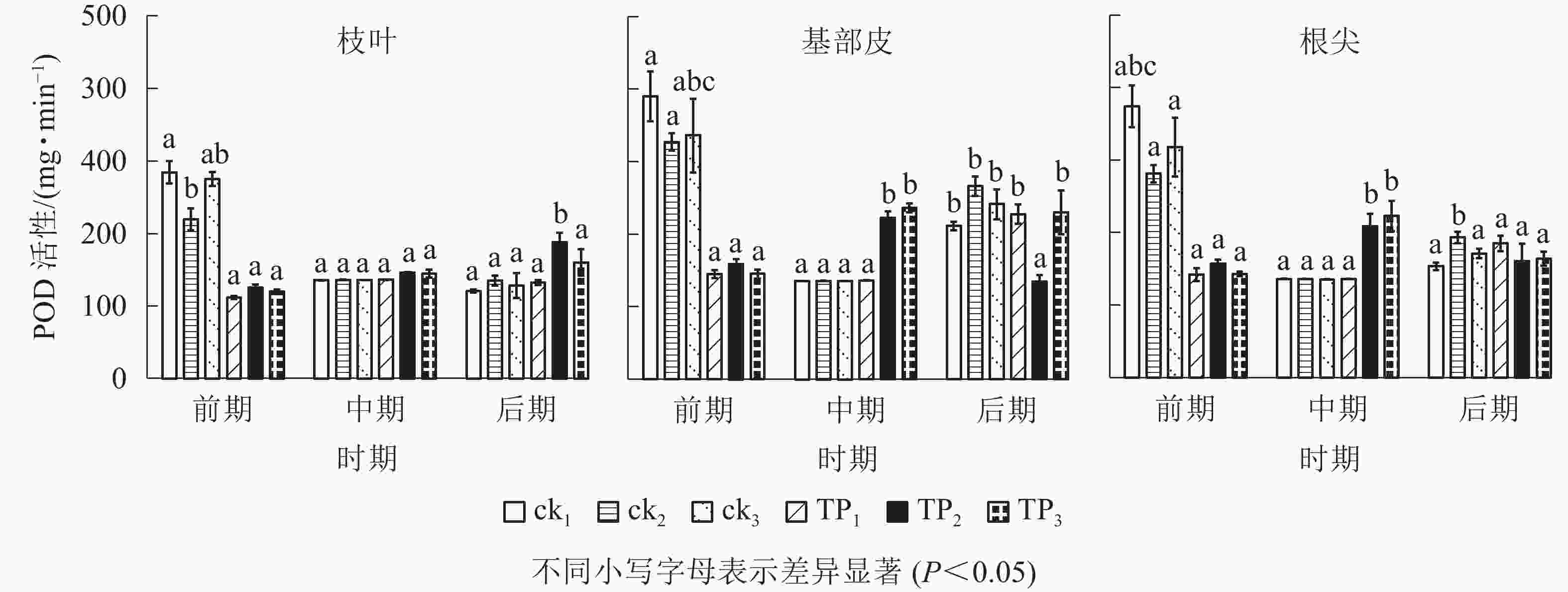
由图3可以看出:在萌蘖前期,未去顶的杉木枝叶、基部皮和根尖POD活性高于中期和后期。杉木枝叶POD活性前期ck1、ck2和ck3比中期分别提高了109.85%、61.63%和102.35%,比后期分别提高了135.99%、62.85%和115.02%;杉木基部皮POD活性前期ck1、ck2和ck3比中期分别提高了147.98%、141.16%和187.70%,比后期分别提高了59.14%、22.82%和61.56%;杉木根尖POD活性前期ck1、ck2和ck3比中期分别提高了174.74%、107.14%和134.69%,比后期分别提高了143.91%、45.47%和85.89%。在萌蘖前期,未去顶的杉木苗枝叶、基部皮和根尖POD活性普遍较高,POD活性从高到低依次为ck1、ck3、ck2。在中期,杉木幼苗基部皮和根尖POD活性以TP2、TP3较高。
-
由多因素方差分析(表2)可知:不同时期、不同机械损伤和不同部位之间SOD和POD活性具有极显著差异(P<0.01),且3种因素之间具有极显著的交互作用(P<0.01)。不同时间、不同机械损伤、不同埋土深度和不同部位之间CAT活性具有极显著差异(P<0.01),4种因素之间具有极显著的交互作用(P<0.01)。
表 2 杉木幼苗SOD、CAT和POD活性方差分析
Table 2. Variance analysis of SOD, CAT and POD enzyme activities in Chinese fir seedlings
因素 SOD活性 CAT活性 POD活性 均方 F 均方 F 均方 F 时期 82 807.915 35.981** 97 192.403 734.535** 34 187.296 54.764** 机械损伤 44 879.393 19.501** 19 211.774 145.194** 43 239.496 69.264** 埋土深度 6 918.106 3.006 2 910.454 21.996** 2 831.071 4.535* 器官部位 114 489.454 49.747** 2 658.569 20.092** 54 248.127 86.899** 时期×机械损伤 5 232.712 2.274 31 600.742 238.824** 92 412.000 148.032** 时期×埋土深度 25 120.655 10.915** 3 616.950 27.335** 2 911.318 4.664** 时期×器官部位 41 964.818 18.234** 2 074.813 15.680** 4 762.197 7.628** 机械损伤×埋土深度 5 197.325 2.258 2 605.106 19.688* 2 015.723 3.229* 机械损伤×器官部位 4 442.049 1.930 978.874 7.398** 1 977.118 3.167* 埋土深度×器官部位 1 881.679 0.818 1 063.093 8.034** 1 069.296 1.713 时期×机械损伤×埋土深度 1 147.752 0.499 2 396.590 18.112** 7 094.747 11.365** 时期×机械损伤×器官部位 23 470.572 10.198** 761.769 5.757** 3 770.859 6.040** 时期×埋土深度×器官部位 7 876.366 3.422** 402.710 3.043** 1 433.927 2.297** 机械损伤×埋土深度×器官部位 9 597.720 4.170** 331.124 2.502* 1 302.148 2.086 时期×机械损伤×埋土深度×器官部位 10 678.306 4.640** 179.372 1.356 2 428.758 3.891** 说明:*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;**表示在0.01水平(双侧)上极显著相关 -
由表3可见:萌蘖数与机械损伤呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);萌蘖数与萌蘖时期呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),SOD活性与萌蘖时期呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);SOD活性与萌蘖数呈显著正相关(P<0.05),CAT活性与机械损伤呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);CAT活性与萌蘖时期、萌蘖数和SOD活性呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),POD活性与萌蘖时期、萌蘖数呈显著正相关(P<0.05);POD活性与SOD活性呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),POD与CAT活性呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。
表 3 机械损伤和不同埋土深度处理杉木无性系萌蘖酶活性相关性
Table 3. Correlation between mechanical damage and tillering enzyme activity of Chinese fir clones under different soil depth treatments
项目 机械损伤 萌蘖时期 萌蘖数 SOD活性 CAT活性 POD活性 机械损伤 1.000 萌蘖时期 0.000 1.000 萌蘖数 −0.613** 0.540** 1.000 SOD活性 0.017 0.445** 0.125* 1.000 CAT活性 0.293** −0.670** −0.614** −0.387** 1.000 POD活性 0.109 0.239* 0.082* 0.290** −0.269* 1.000 说明:*表示显著相关(P<0.05),**表示极显著相关(P<0.01) -
本研究表明:随着培养时间的延长,杉木萌蘖均呈上升趋势;随着埋土深度的增加,杉木萌蘖能力逐渐呈下降的趋势。在萌蘖后期,TP1、TP2和TP3的萌蘖数与同一埋土深度ck1、ck2和ck3相比分别提高15.11%、6.73%及3.49%。说明适度的机械损伤对杉木萌蘖影响较大,利于无性系的繁殖。植物通过自然选择和人工选择,逐渐形成相应的防御机制,有助于损伤部位的愈合,并诱发全株反应,防止进一步损伤的发生。可以根据植物对机械损伤的特殊反应强化植物的抗虫抗病能力,减少施药对人类健康以及生态环境的损害,也可以探索防御反应的发生机制,以期遏制植株的“过度反应”,减少生产上的经济损失[11−12]。
生物转化是利用细胞、器官或酶等生物体系进行催化的反应。由于生物转化的多样性涉及到许多酶,SOD活性过高,会影响某些正常的氧化代谢过程[13]。由于SOD具有亲核性和还原性,一定微环境下,具有很强的氧化损伤作用[14]。低CAT活性的植株对过氧化氢(H2O2)胁迫更加敏感,CAT作为植物体内重要活性氧清除酶,可与质膜透性一起表征植物受逆境伤害的程度,两者在胁迫发生后一段时间内的变化态势,可反映植物自身修复过程中的一些信息[15-16]。POD在回收过程中具有双重功能。一方面,POD可以在逆境或衰老的早期表达以去除H2O2,是活性氧保护酶系统的成员之一;另一方面,POD也可以在逆境或衰老的后期表达以参与活性氧的产生和叶绿素的降解,引起膜脂过氧化,这是植物衰老的产物,可以作为衰老的指标。本研究表明:去顶后埋土3 cm和去顶后埋土6 cm处理下的杉木幼苗叶片SOD活性相比于萌蘖前期和后期明显上升,不同部位中CAT活性总体呈下降趋势,叶、基部皮和根尖中POD活性呈增长趋势。李惠梅等[17]研究了增强UV-B辐射对麻花龙胆Gentiana straminea抗氧化酶系统的影响。结果表明:UV-B处理后,麻花龙胆叶片中SOD和POD活性在处理初期升高,但随着处理时间的延长,SOD和POD活性降低,CAT活性显著降低。这与本研究结果有一致和不同之处。生物代谢中酶活性的变化反映了环境物理化学变化,可以为环境变化提供早期预测。因此,越来越多的学者关注逆境下植物体内酶的变化,试图利用酶的变化来判断植物对环境的响应[18]。不同植物对逆境的应激方式不尽相同,适应逆境的机制十分复杂。
-
随着埋土深度的增加,不同埋土深度杉木无性系苗萌蘖能力均呈降低的趋势,同一埋土深度下机械损伤处理无性系苗萌蘖力高于未机械损伤。随着埋土深度的增加,杉木幼苗枝叶SOD活性呈上升趋势,CAT活性呈下降趋势;埋土6 cm处理有利于枝叶及根尖POD的积累;杉木幼苗不同器官植物抗氧化酶活性的差异应与杉木对机械损伤和埋土深度处理的生理应答机制有关。本研究结果在一定程度上反映机械损伤和不同埋土深度处理后杉木无性系萌蘖SOD、CAT和POD活性的变化规律,但在杉木萌蘖过程中抗氧化酶活性之间如何维持平衡,以及如何协同作用调控杉木萌蘖等的机制尚不清楚,这有待于今后进一步深入研究。
Effects of mechanical damage and deep soil treatment on sprouting and antioxidant enzyme activities of Cunninghamia lanceolata
-
摘要:
目的 研究分析机械损伤处理下杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata无性系萌蘖能力与抗氧化酶活性的相关关系,从酶活性代谢生理角度阐述杉木萌蘖机制,为解决杉木无性系萌蘖问题提供理论依据。 方法 以杉木无性系洋020的1年生扦插苗为材料,通过盆栽试验,设置去顶和未去顶处理,0、3、6 cm埋土深度处理,在萌蘖初期、中期、后期分别取样,观测无性系萌蘖状况,通过酶活吸光度方法测定杉木无性系萌蘖过程中枝叶、基部韧皮部、根尖等不同器官超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和过氧化物酶(POD)活性差异,并进行相关性分析。 结果 随着埋土深度的增加,去顶和未去顶不同埋土深度杉木无性系苗萌蘖能力均呈降低的趋势,且不同埋土深度处理会影响植物的抗氧化酶的活性。随着埋土深度的增加,杉木幼苗枝叶SOD活性呈上升趋势,CAT活性呈下降趋势;埋土6 cm处理有利于增强枝叶及根尖POD的活性。 结论 机械损伤和不同埋土深度对杉木无性萌蘖有一定的影响;同一埋土深度,去顶处理杉木无性系的萌蘖能力高于未去顶处理。不同器官植物抗氧化酶活性是影响杉木无性系机械损伤和不同埋土深度处理萌蘖的主要影响因子之一。图3表3参18 Abstract:Objective With an analysis conducted of the relationship between the sprouting ability of Cunninghamia lanceolata (Chinese fir) clones and the activity of antioxidant enzymes under the treatment of mechanical injure as well as an elaboration on the sprouting mechanism of C. lanceolata from the metabolic physiology of enzyme activity, this study is aimed to provide theoretical basis for solving the sprouting problem of C. lanceolata clones. Method Using the 1-year-old cuttings of Chinese fir Clone Yang 020 as experimental materials, with pot experiment and treatments of topping removal and no topping set at depths of 0, 3 and 6 centimeters, the enzyme activity absorbance test was carried out to measure and analyze the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD) in different organs, such as branches and leaves, basal phloem and root tip. Result (1) With the increase of soil depth, the tillering capacity of seedlings of Chinese fir clones with and without mechanical damage at different soil depths decreased, and treatments of different soil depths could affect the activity of antioxidant enzymes. (2) With the increase of soil depth, SOD activity of branches and leaves of Chinses fir seedlings increased, while CAT activity decreased. (3) The soil depth of 6 centimeters was conducive to pod accumulation of branches and leaves and root tips. Conclusion In conclusion, the mechanical damage and treatments of different soil depths had impact on the clonal tillering of Chinese fir. Of the same soil depth, the tillering of Chinese fir with the removal of topping is higher than the one without the removal. Also, the antioxidant enzyme activity of different organs plants was one of the main factors that affect the mechanical damage of C. lanceolata clones and the tillering of treatments of different soil depths. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 18 ref.] -
Key words:
- Cunninghamia lanceolata /
- mechanical damage /
- sprouting /
- antioxidant enzyme
-
表 1 机械损伤和不同埋土深度处理下杉木无性系萌蘖差异
Table 1. Difference of tillering of Chinese fir clones treated by mechanical damage and different soil depth
处理 萌蘖/株 2019-06-30 2019-07-31 2019-08-31 TP1 0.65 ± 0.08 ab 2.90 ± 0.20 bc 3.50 ± 0.50 ac TP2 0.54 ± 0.06 bc 2.40 ± 0.18 a 3.10 ± 0.30 b TP3 0.43 ± 0.03 a 2.13 ± 0.16 b 2.54 ± 0.30 a ck1 1.50 ± 0.02 b 2.89 ± 0.40 a 3.35 ± 0.42 b ck2 1.20 ± 0.11 a 2.20 ± 0.30 b 3.00 ± 0.40 a ck3 0.80 ± 0.06 a 2.10 ± 0.20 b 2.20 ± 0.30 a 说明:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05) 表 2 杉木幼苗SOD、CAT和POD活性方差分析
Table 2. Variance analysis of SOD, CAT and POD enzyme activities in Chinese fir seedlings
因素 SOD活性 CAT活性 POD活性 均方 F 均方 F 均方 F 时期 82 807.915 35.981** 97 192.403 734.535** 34 187.296 54.764** 机械损伤 44 879.393 19.501** 19 211.774 145.194** 43 239.496 69.264** 埋土深度 6 918.106 3.006 2 910.454 21.996** 2 831.071 4.535* 器官部位 114 489.454 49.747** 2 658.569 20.092** 54 248.127 86.899** 时期×机械损伤 5 232.712 2.274 31 600.742 238.824** 92 412.000 148.032** 时期×埋土深度 25 120.655 10.915** 3 616.950 27.335** 2 911.318 4.664** 时期×器官部位 41 964.818 18.234** 2 074.813 15.680** 4 762.197 7.628** 机械损伤×埋土深度 5 197.325 2.258 2 605.106 19.688* 2 015.723 3.229* 机械损伤×器官部位 4 442.049 1.930 978.874 7.398** 1 977.118 3.167* 埋土深度×器官部位 1 881.679 0.818 1 063.093 8.034** 1 069.296 1.713 时期×机械损伤×埋土深度 1 147.752 0.499 2 396.590 18.112** 7 094.747 11.365** 时期×机械损伤×器官部位 23 470.572 10.198** 761.769 5.757** 3 770.859 6.040** 时期×埋土深度×器官部位 7 876.366 3.422** 402.710 3.043** 1 433.927 2.297** 机械损伤×埋土深度×器官部位 9 597.720 4.170** 331.124 2.502* 1 302.148 2.086 时期×机械损伤×埋土深度×器官部位 10 678.306 4.640** 179.372 1.356 2 428.758 3.891** 说明:*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;**表示在0.01水平(双侧)上极显著相关 表 3 机械损伤和不同埋土深度处理杉木无性系萌蘖酶活性相关性
Table 3. Correlation between mechanical damage and tillering enzyme activity of Chinese fir clones under different soil depth treatments
项目 机械损伤 萌蘖时期 萌蘖数 SOD活性 CAT活性 POD活性 机械损伤 1.000 萌蘖时期 0.000 1.000 萌蘖数 −0.613** 0.540** 1.000 SOD活性 0.017 0.445** 0.125* 1.000 CAT活性 0.293** −0.670** −0.614** −0.387** 1.000 POD活性 0.109 0.239* 0.082* 0.290** −0.269* 1.000 说明:*表示显著相关(P<0.05),**表示极显著相关(P<0.01) -
[1] 薛瑶芹, 张文辉, 马莉薇, 等. 不同生境下栓皮栎伐桩萌苗的生长特征及在种群更新中的作用[J]. 林业科学, 2012, 48(7): 23 − 29. XUE Yaoqin, ZHANG Wenhui, MA Liwei, et al. The growth features of Quercus variabilis stump sprouts and its contribution to population regeneration in different habitats [J]. Sci Silv Sin, 2012, 48(7): 23 − 29. [2] 俞新妥. 中国杉木研究[J]. 福建林学院学报, 1988, 8(3): 203 − 220. YU Xintuo. Study on Chinese fir [J]. J Fujian For Univ, 1988, 8(3): 203 − 220. [3] 潘洁琳, 李晨燕, 王讷敏, 等. 杉木采穗圃管理技术研究[J]. 亚热带农业研究, 2017, 13(3): 211 − 215. PAN Jielin, LI Chenyan, WANG Namin, et al. Study on the management technology of Chinese fir cutting nursery [J]. Subtrop Agric Res, 2017, 13(3): 211 − 215. [4] 张敏, 蓝芳菊. 杉木优良无性系采穗圃营建与扦插育苗技术评价[J]. 现代农业科技, 2014(3): 183 − 186. ZHANG Min, LAN Fangju. Evaluation on the construction of scion collecting nursery and cutting seedling raising technology of fine Chinese fir clones [J]. Mod Agric Sci Technol, 2014(3): 183 − 186. [5] BOHLMANN J, CROCK J, JETTER R, et al. Terpenoid-based defenses in conifers: cDNA cloning, characterization, and functional expression of wound-inducible (E)-a- bisabolene synthase from grand fir (Abies grandis) [J]. Proc Nat Acad Sci, 1998, 95(12): 6756 − 6761. [6] 高雪. 植物苯丙氨酸解氨酶研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技, 2009(1): 30 − 33. GAO Xue. Research progress of plant phenylalanine ammonia lyase [J]. Mod Agric Sci Technol, 2009(1): 30 − 33. [7] 方海涛, 段立清. 机械损伤诱导林木抗虫性研究进展[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2011, 26(6): 91 − 94. FANG Haitao, DUAN Liqing. Research progress on insect resistance of trees induced by mechanical damage [J]. J Northwest For Univ, 2011, 26(6): 91 − 94. [8] 李合生. 现代植物生理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002: 415 − 419. [9] 丁红, 张智猛, 戴良香, 等. 水分胁迫和氮肥对花生根系形态发育及叶片生理活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(2): 450 − 456. DING Hong, ZHANG Zhimeng, DAI Liangxiang, et al. Effects of water stress and nitrogen fertilization on peanut root morphological development and leaf physiological activities [J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2015, 26(2): 450 − 456. [10] SHALATA A, MITTOVA V, VOLOKITA M, et al. Response of the cultivated tomato and its wild salt-tolerant relative Lycopersicon pennellii to salt-dependent oxidative stress antioxidative system [J]. Physiol Plant, 2001, 112(1): 487 − 494. [11] WANG Yibo, FENG Huyuan, QU Ying, et al. The relationship between reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide in ultraviolet-B-induced ethylene production in leaves of maize seedlings [J]. Environ Exp Bot, 2005, 57(1): 141 − 147. [12] 丁国华, 程淑婉, 叶镜中. 杉木不同季节采伐伐桩萌芽的内源激素动态[J]. 福建林学院学报, 1996, 16(2): 109 − 113. DING Guohua, CHENG Shuwan, YE Jingzhong. The dynamics of endogenous hormones in the germination of Chinese fir stumps in different seasons [J]. J Fujian For Univ, 1996, 16(2): 109 − 113. [13] 郑荣梁. 自由基医学与农学基础[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2001: 217 − 230. [14] 孙存普, 张建中, 段绍瑾. 自由基生物学导论[M]. 合肥: 中国科技大学出版社, 1999: 280. [15] 白令君, 王建英, 崔乃杰, 等. 抗坏血酸与铁离子反应的ESR及UV-VIS研究[J]. 生物化学与生物物理学报, 1997, 29(6): 527 − 532. BAI Lingjun, WANG Jianying, CUI Naijie, et al. ESR and UV-vis studies on the reaction of ascorbic acid with iron ion [J]. J Biochem Biophysics, 1997, 29(6): 527 − 532. [16] 梁婵娟, 徐青, 陶文沂, 等. 油菜光合作用及CAT对UV-B与AR胁迫的响应(Ⅰ)[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2004, 23(4): 642 − 645. LIANG Chanjuan, XU Qing, TAO Wenyi, et al. Response of defense enzyme and photosynthesis in rape seedling under combined stress of elevated ultraviolet-B radiation and acid rain (Ⅰ) [J]. J Agric Environ Sci, 2004, 23(4): 642 − 645. [17] 李惠梅, 师生波. 增强UV-B辐射对麻花艽叶片的抗氧化酶的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2005, 25(3): 519 − 524. LI Huimei, SHI Shengbo. Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on antioxidant enzymes of Gentiana straminea leaves [J]. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 2005, 25(3): 519 − 524. [18] 唐光辉, 田鹏鹏, 陈安良, 等. 2种农药树干注射对垂柳叶内PPO和POD活性及同工酶谱的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 35(4): 145 − 149. TANG Guanghui, TIAN Pengpeng, CHEN Anliang, et al. Effects of trunk injection of two pesticides on PPO and POD activities and isozyme patterns in leaves of weeping willow [J]. J Northwest A&F Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2007, 35(4): 145 − 149. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200323







 下载:
下载: