-
汞是一种危害和毒性极强的重金属元素,自20世纪50年代日本水俣病事件以来,汞污染事件就被全球所重视。汞在自然界环境中的存在有多种形态,不同形态之间特征有较明显的差异,且不同形态之间可以进行转化。自然水体中把汞形态分为活性汞(RHg)、溶解性气态汞(DGM)、甲基汞(MeHg)和二甲基汞等[1]。DGM是水体中汞的一种主要形态,虽然其毒性不是最强,但影响也不容小觑。DGM的主要存在形式是零价态汞,在水中的质量浓度一般低于0.2 ng·L−1[2]。区别于其他重金属,汞在常温下可以以气态形式挥发,因此零价态汞在全球汞的循环中占有重要的作用。水体及陆地表面的零价汞可以挥发进入到大气中,且在大气中停留时间较长,从而进行长距离迁移,最终通过干沉降或湿沉降进入水生环境和陆地环境。在人为活动较少的南极、北极以及中国青藏高原地区,也都监测到较高浓度的汞[1]。这说明汞的污染是全球性的,而零价态汞的生成又异常重要。抗生素滥用已经成为中国环境主要问题之一。土霉素(OTC)是四环素家族的一员,也是兽医和水产养殖中使用的广谱抗生素之一。由于抗生素耐药性在微生物中的传播,引起了越来越多的关注。它被广泛地用作养殖鱼的饲料添加剂和家畜的生长刺激物质,也可用于植物细菌性疾病的预防性治疗。在欧洲,超过2 500 t四环素类作为兽药治疗,其中以土霉素应用最广泛[3]。中国在2003年时土霉素产量已经达10 000 t,占世界总产量的65%[4]。然而,它很难在动物体内被代谢,这导致土霉素会随粪便或尿液排出体外。由于其水溶性和耐降解性,土霉素已在土壤环境、沿海环境甚至饮用水中被广泛检测到。在水体、底泥以及污泥硝化过程中,重金属会和抗生素发生络合反应,或促进或抑制抗生素的降解。同时,金属与抗生素之间的络合对金属的价态也会产生一定影响。由于汞的特殊性,抗生素与汞之间的络合反应有可能会对汞形态变化产生影响。但是,目前关于抗生素与汞的络合反应还鲜有报道。鉴于此,本研究采用实验室模拟水生环境,配制汞和抗生素的混合反应溶液,研究不同环境因子对抗生素与汞络合条件下DGM产生的影响,以期为解决抗生素与汞复合污染提供理论依据。
-
用氯化汞(HgCl2)粉末(250 g,贵州省铜仁化学试剂厂)配制1 μmol·L−1的HgCl2溶液,同时用四环素类抗生素中的土霉素(25 g,上海源叶生物科技有限公司)配制1 μmol·L−1的OTC溶液。
-
取40 mL HgCl2溶液和40 mL OTC溶液,等体积混合加入到100 mL离心管中,处理共分3组,pH分别为3(pH 3)、7(pH 7)和11(pH 11)。
-
取40 mL HgCl2溶液和40 mL OTC溶液,等体积混合加入到100 mL离心管中,遮光条件为用锡箔纸彻底包住混合后的100 mL离心管,再将其放入箱子内进行避光;光照条件为1个5 W的LED灯持续垂直照射。同时准备1组40 mL HgCl2溶液和40 mL超纯水混合的对照组。处理共分4组,分别为超纯水与汞溶液混合后的遮光条件(水-遮光)、超纯水与汞溶液混合后的光照条件(水-光照)、土霉素与汞溶液混合后的遮光条件(土霉素-遮光)以及土霉素与汞溶液混合后的光照条件(土霉素-光照)。
-
取40 mL HgCl2溶液和40 mL OTC溶液,等体积混合加入到100 mL离心管中,海水条件为称取175 g海盐溶解于5 000 mL超纯水中制成海水,并用超纯水作为淡水对照。同时准备40 mL HgCl2溶液分别与40 mL超纯水和40 mL海水混合,作为淡水和海水对照组。处理共分4组,分别为超纯水与汞溶液混合后的海水条件(水-海水)、超纯水与汞溶液混合后的淡水条件(水-淡水)、土霉素与汞溶液混合后的海水条件(土霉素-海水)以及土霉素与汞溶液混合后的淡水条件(土霉素-淡水)。
-
取40 mL HgCl2溶液和40 mL OTC溶液,等体积混合加入到100 mL离心管中,好氧条件为实验室室内需氧条件;厌氧条件为在1个密封性好的盒子中放入样品,放入厌氧产气袋,用以吸收氧气释放二氧化碳,并放入1个厌氧指示剂,最后用保鲜膜和胶带密封盒子,以创造1个密封的厌氧环境。同时准备1组40 mL HgCl2溶液和40 mL超纯水混合的对照组。处理共分4组,分别为超纯水与汞溶液混合后的厌氧条件(水-厌氧)、超纯水与汞溶液混合后的好氧条件(水-好氧)、土霉素与汞溶液混合后的厌氧条件(土霉素-厌氧)以及土霉素与汞溶液混合后的好氧条件(土霉素-好氧)。
-
溶液在不同因子影响下分别反应,经过1、4、8和16 d取样品10 mL加入到15 mL离心管中,并加样品体积分数0.4%的盐酸(HCl)后放入0 ℃冰箱保存待测。
-
将样品稀释40倍,称39 g超纯水于50 mL离心管中,再从冰箱内取出样品,取1 mL加入。从稀释40倍后的溶液中取1 mL到25 mL比色管中,用超纯水定容至25 mL。测总汞时加入125 μL氯化溴(BrCl)溶液,摇匀,常温下放置24 h后待测。测DGM时无需添加其他试剂,取1 mL已定容至25 mL的溶液加入到鼓泡瓶中,用高纯氮气(N2)以350 mL·min−1鼓吹21 min富集至金砂管上,再用热解析冷原子荧光光谱仪测定,所用仪器为Brooks Rand(美国)测汞仪。测土霉素时,取冰箱内样品1 mL加入到2 mL进样瓶中,加入25 μL体积分数0.1%甲酸溶液后用HPLC液相色谱仪测定,所用仪器为Thermo Fisher Scientific UltiMate 3000 HPLC液相色谱仪。取样工具、测样比色管和鼓泡瓶等,都按汞元素分析的质量控制要求进行清洗净化[5]。总汞、DGM和土霉素浓度均采用平均值±标准差表示。
-
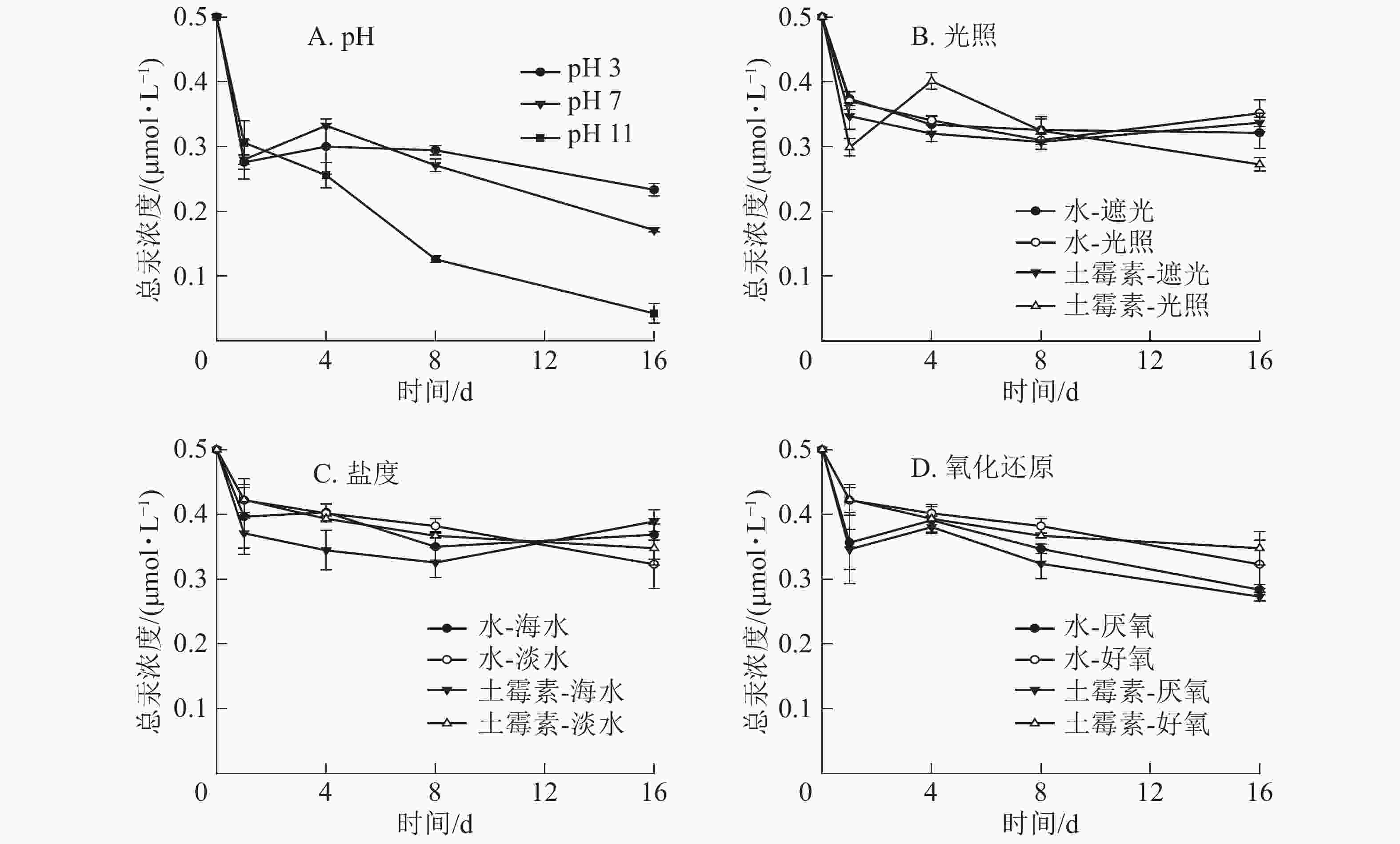
从图1可以看出:反应初始条件溶液总汞浓度为0.5 μmol·L−1,随着反应的进行,总汞浓度逐渐降低。在碱性条件下总汞浓度降低最为明显,主要由于碱性条件下,生成了氢氧化汞会造成水体中总汞浓度降低。而另外3个处理的总汞浓度略微降低,主要由于常温下,汞可以以气态形式挥发。试验过程中,所有反应容器均为密闭条件,但样品采集等过程难以避免溶液暴露等,造成水体总汞浓度略微降低。
-
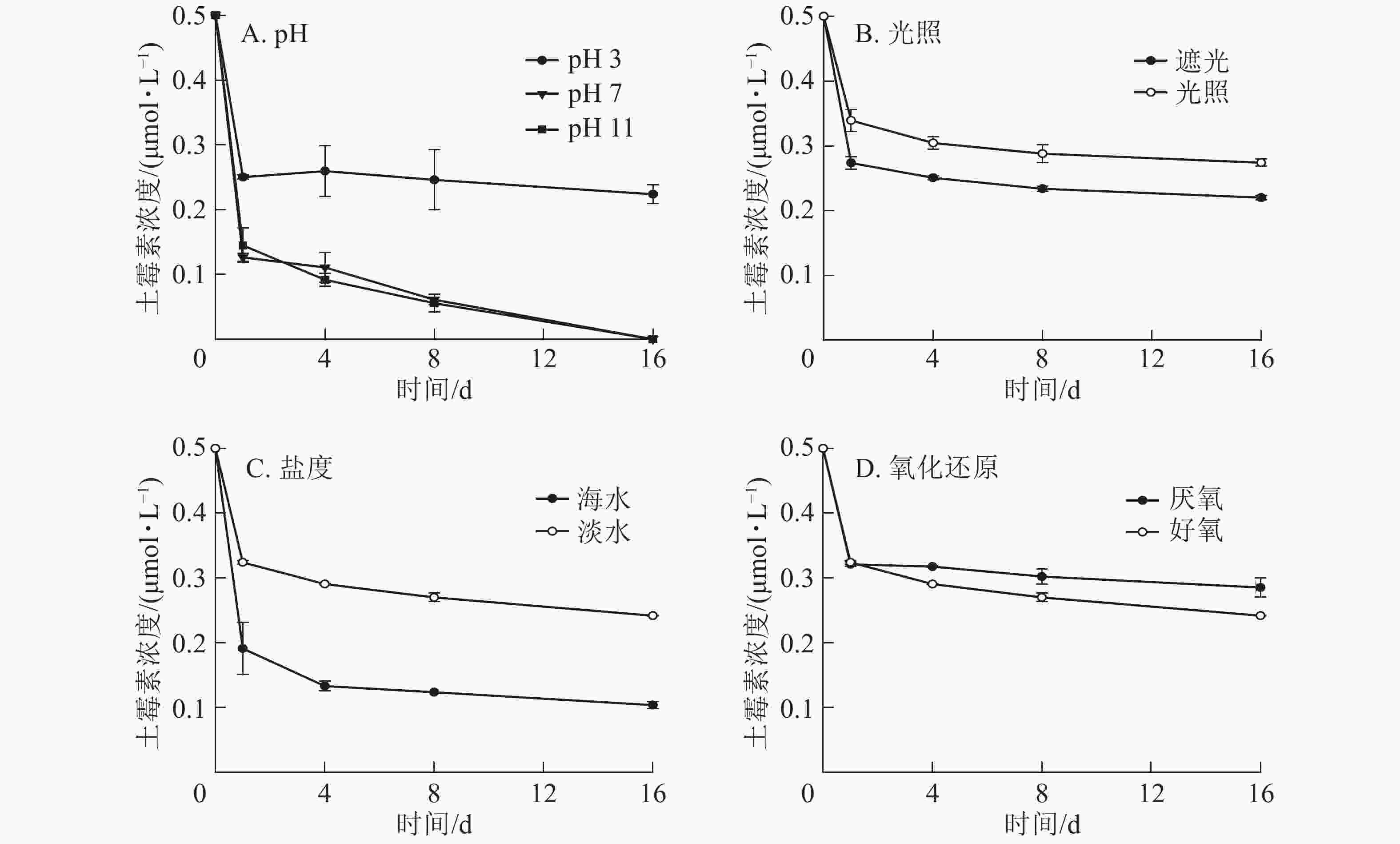
从图2A可以看出:在不同的pH条件下,DGM随时间的增加呈先升高后降低的趋势,酸性和中性条件下DGM浓度基本保持一致,但是碱性条件下浓度逐渐降低。第16天时,在pH为3的条件下,DGM浓度比第1天升高0.036~0.076 μmol·L−1,而pH为7和11的条件下,DGM浓度比第1天分别降低0.004~0.024 和0.059~0.062 μmol·L−1。
-
图2B显示:在光照与遮光处理下,前8 d的DGM浓度变化一致,呈先上升后降低的趋势。8 d后,遮光处理下汞和土霉素的混合溶液中DGM逐渐减少,而光照处理下DGM逐渐上升。光照处理下产生的DGM比遮光条件下的高,尤其在最后第16天时更明显。此外,在第16天时,光照处理下,添加了土霉素处理的溶液中,DGM浓度明显高于无土霉素组,说明添加土霉素在光照处理下有利于DGM的生成。
-
由图2C可知:在海水处理下,汞和土霉素的混合溶液中DGM整体呈不变趋势,浓度很低,最高为0.059 μmol·L−1,最低为0.010 μmol·L−1。而在淡水处理下,汞和土霉素的混合溶液中DGM先明显增加至最高点(0.408 μmol·L−1),然后再逐渐减少。
-
图2D显示:在好氧条件下,汞和土霉素的混合溶液中DGM先明显增加,然后再逐渐减少;而在厌氧条件下,汞和土霉素的混合溶液中DGM呈先上升后逐渐降低,最后再迅速上升的趋势。好氧条件下DGM前8 d高于厌氧条件,9 d后低于厌氧条件。
-
图3显示:不同的pH下土霉素降解速率有较明显的差异。在酸性条件下,土霉素浓度基本保持不变,而在中性和碱性条件下,土霉素浓度逐渐降低。不同光照下土霉素浓度逐渐降低,遮光下土霉素降解更多。在不同盐度下,海水中土霉素浓度低于淡水。同样,好氧条件下也有利于土霉素的分解。
-
DGM主要是由单质汞组成,它在水中形成途径很多,有甲基化作用[6],水中沉积物里细菌的还原作用[6-7],水中有机物(富里酸和腐植酸等)的还原作用[8],水体中的光致还原作用[9-14]。这些都会把水中的二价汞转换为气态零价汞。冯新斌等[15]研究指出:光致还原作用对水体中DGM的产生起了主导作用。
-
对于同一种土霉素和汞混合溶液,DGM浓度随pH的增加而减少,而在碱性较强时,DGM浓度很低。AHN等[16]发现:pH越低,DGM的浓度越高。这主要是因为所有的二价汞离子与有机配体或无机配体结合,在低pH条件下,水体中带负电荷的配体较少,与二价汞离子的络合性较差,使其更容易通过非生物或生物过程而被光还原成零价态汞,DGM的浓度也就随之增大[17-18]。而在碱性条件下,二价汞离子容易与氢氧根离子反应生成氢氧化汞,导致溶液中的二价汞离子无法被还原成零价态汞,故而DGM的浓度很低。
-
光致还原是DGM产生的一个重要过程。张金香[19]发现相同条件下,光诱导产生的DGM是黑暗条件的2.4~9.0倍。何天容等[20]研究季节变化对于红枫湖的DGM影响时,也表明光对于零价汞的形成起了至关重要的作用,强光有利于零价汞的形成。光照能使水体中的二价汞离子被还原成零价汞,促进了DGM的形成和释放。光照还原反应是一个持续的长久反应,以至于从第1天到第16天,DGM浓度总体处于上升趋势,且总体都比黑暗条件下高。
-
盐度也会影响汞在海水中的络合作用。海水中由于富含氯离子,而二价汞离子又容易与氯离子反应生成较稳定的氯化汞,导致能被还原成零价汞的二价汞离子显著减少,所以DGM的产生量也是显著降低。同时,在海水中汞还可能以三氯化汞和四氯化汞的形式存在。MARUMOTO等[21]研究也表明:沿海地区总汞浓度与盐度呈显著负相关。
-
在有氧气存在的情况下,溶液中光还原反应和光氧化反应都会发生。由于光致还原作用是主反应,所以反应一开始溶液中二价汞离子都被迅速还原成零价汞离子,因此气态汞先显著升高,之后由于氧气的存在,被逐渐氧化,导致气态汞降低。而在厌氧条件下,随着厌氧细菌的活性逐渐增强使气态汞逐渐上升。有研究表明:光还原和光氧化过程之间的平衡已被确定为DGM浓度的重要决定因素[12]。厌氧条件可能是DGM产生的一个重要因素。POULAIN等[22]研究所示:DGM浓度与沉积物-水的氧气水平呈负相关。
-
土霉素属于有机物质的一种,在水中能和汞形成有机络合态汞,为汞的光还原反应提供基质。一方面它释放出的二价态汞离子能成为光还原反应的反应物,使其转变为零价态汞,同时,有机物和汞的络合物释放的有机分子也能为光致还原反应提供所需的电子使其促进DGM的产生[23]。LIANG等[24]在探究抗生素对海洋沉积物中汞甲基化中的作用时发现,将土霉素加入到海洋沉积物中,一段时间后沉积物中甲基汞的浓度会有所增加。
土霉素与汞发生络合的条件主要有2个:一个是抗生素的官能团,另一个则是汞的金属特性。研究表明:官能团与金属离子易发生反应形成复合污染[25]。从官能团来讲,抗生素分子的官能团中有大量的羧基、羟基、氨基等基团和电子供体,都可以和金属发生络合反应,为反应提供电子[26]。同时,抗生素分子中含氮、氧等富电子基团种类和数量越多,与金属离子的络合能力越强[27],而土霉素分子中含有很多羟基、羰基和氨基,因此容易与汞发生络合。从金属特性来讲,汞的电负性很强,为2.0,电负性越强则金属离子吸引电子的能力也越强,也就越容易络合。土霉素含有丰富的电子,汞有很强的吸电子能力,因此它们之间极易发生络合。LIANG等[24]认为土霉素在和二价汞离子(Hg2+)反应后形成OTC-Hg2+有机络合化合物,由于二价汞离子的高电负性,产生了电子的迁移,土霉素与汞的络合导致电子从土霉素向汞离子转移,汞离子得电子后变为零价汞,因此气态汞的浓度会增大。所以从图2B和图2D可以看出:在光照和厌氧条件下,添加土霉素溶液中的DGM浓度显著高于没有添加土霉素溶液中的DGM。
-
对于土霉素和汞溶液混合体,DGM浓度随pH的增加而减少,在碱性较强时,DGM浓度很低,其原因可能是二价汞离子在碱性条件下容易与氢氧根离子反应生成氢氧化汞,导致溶液中的二价汞离子无法被还原成零价汞。光照还原反应是一个持续的长久反应,从第1天到第16天,DGM的浓度总体处于上升趋势,且总体浓度都比黑暗条件高。与淡水中的DGM相比,海水中的DGM浓度很低,可能是由于大量氯离子存在的影响。在实验开始时,DGM浓度在厌氧条件下比好氧条件下低,在第10天之后大于好氧条件。土霉素的添加促进了DGM的生成。
Effects of different factors on dissolved gaseous mercury in the complexation reaction of antibiotics with mercury
-
摘要:
目的 研究不同环境因子下土霉素(OTC)与汞(Hg)络合后溶解性气态汞(DGM)的变化特征,可了解抗生素与汞的复合污染问题。 方法 利用实验室模拟实验,以OTC(1 μmol·L−1)和氯化汞(HgCl2 1 μmol·L−1)溶液为材料,以pH、光照、盐度和氧化还原为不同影响条件,探究反应后DGM的变化特征。 结果 不同环境因子对水体DGM的影响起主要作用,DGM随pH的增加呈减少趋势,酸性条件下的DGM显著高于碱性条件。光照条件下DGM略高于黑暗条件。淡水条件中的DGM显著高于海水条件。厌氧条件下的DGM在试验初期低于好氧条件,在第10天之后高于好氧条件。 结论 OTC与汞会发生络合反应,且络合反应有利于DGM的形成。不同环境因子也会影响两者络合后产生的DGM。OTC与Hg络合后反应生成的DGM要高于对照组,但OTC的影响程度低于本身环境因子的影响。图3参27 Abstract:Objective To better understand the combined pollution of antibiotics and mercury, an investigation is conducted of the influence of different environmental factors on the dissolved gases mercury (DGM) formed in the liquid phase after the complexion reaction of oxytetracycline (OTC) with mercury. Method With OTC solution (1 μmol·L−1) and mercury chloride (HgCl2 1 μmol·L−1) selected as materials, simulation experiments were conducted in the laboratory with pH, light, salinity, and redox employed as the environmental factors to explore the changing characteristics of DGM concentration after the reaction. Result Environmental factors have significant impact on the formation of DGM. There is a significant decrease in DGM concentration with the increase of pH. The DGM concentration in the condition of light irradiation was slightly higher than that in the dark condition. The DGM concentration in sea water was significantly higher than that in freshwater. The DGM concentration in anaerobic condition was slightly lower than that in aerobic condition but the situation was reversed after ten days. Conclusion The complexation reaction of OTC with mercury occurs and is beneficial to the formation of DGM which is subject to the impact of different environmental factors. The DGM formed by the reaction of OTC and Hg is higher than that in the control group. However, the influence of OTC on the formation of DGM is not as strong as the environmental factors. [Ch, 3 fig. 27 ref.] -
Key words:
- environmental chemistry /
- dissolved gases mercury(DGM) /
- antibiotic /
- pH /
- light /
- salinity /
- redox
-
-
[1] 冯新斌, 仇广乐, 付学吾, 等. 环境汞污染[J]. 化学进展, 2009, 21(2/3): 436 − 457. FENG Xinbin, QIU Guangle, FU Xuewu, et al. Environmental mercury pollution [J]. Prog Chem, 2009, 21(2/3): 436 − 457. [2] HE Tianrong, FENG Xinbin, GUO Yanna, et al. The impact of eutrophication on the biogeochemical cycling of mercury species in a reservoir: a case study from Hongfeng Reservoir, Guizhou, China [J]. Environ Pollut, 2008, 154(1): 56 − 67. [3] SARMAH A K, MEYER M T, BOXALL A B A. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment [J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 65(5): 725 − 759. [4] RICHARDSON B J, LAM P K S, MARTIN M. Emerging chemicals of concern: pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Asia, with particular reference to Southern China [J]. Mar Pollut Bull, 2005, 50(9): 913 − 920. [5] 闫海鱼, 冯新斌, 商立海, 等. 天然水体中痕量汞的形态分析方法研究[J]. 分析测试学报, 2003, 22(5): 10 − 13. YAN Haiyu, FENG Xinbin, SHANG Lihai, et al. Study on speciation analysis method of trace mercury in natural water [J]. J Anal Test, 2003, 22(5): 10 − 13. [6] FITZGERALD W F, MASON R P, VANDAL G M, et al. Air-water cycling of mercury in lakes[C]//WATRAS C J, HUCKABEE J W. Mercury Pollution-Integration and Synthesis. Michigan: Lewis Publisher, 1994: 203 − 220. [7] MASON R P, MOREL F M M, HEMOND H F. The role of microorganisms in elemental mercury formation in natural waters [J]. Water Air Soil Pollut, 1995, 80(1): 775 − 787. [8] ALLARD B, ARSENIE I. Abiotic reduction of mercury by humic substances in aquatic system-an important process for mercury cycle [J]. Water Air Soil Pollut, 1991, 56: 457 − 464. [9] AMYOT M, GILL G A, MOREL F M M. Production and loss of dissolved gaseous mercury in coastal seawater [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1997, 31(12): 3606 − 3611. [10] AMYOT M, LEAN D, MIERLE G. Photochemical formation of volatile mercury in high Artic lakes [J]. Environ Toxicol Chem, 1997, 16(10): 2054 − 2063. [11] AMYOT M, MIERLE G M, LEAN D, et al. Effect of solar radiation on the formation of dissolved gaseous mercury in temperate lakes [J]. Geochem Cosmochim Acta, 1997, 61(5): 975 − 987. [12] AMYOT M, MCQUEEN D G, MIERLE G, et al. Sunlight-induced formation of dissolved gaseous mercury in lake waters [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1994, 28(13): 2366 − 2371. [13] COSTA M, LISS P S. Photoreduction of mercury in sea water and its possible implication for Hg0 air-sea fluxes [J]. Mar Chem, 1999, 68(1/2): 87 − 95. [14] NRIAGU J O. Mechanistic steps in the photoreduction of mercury in natural waters [J]. Sci Total Environ, 1994, 154(1): 1 − 8. [15] 冯新斌, JONAS S, KATARINA G, 等. 夏季自然水体与大气界面间气态总汞的交换通量[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2002, 32(7): 609 − 616. FENG Xinbin, JONAS S, KATARINA G, et al. Exchange flux of gaseous total mercury between natural water bodies and atmospheric interfaces in summer [J]. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci, 2002, 32(7): 609 − 616. [16] AHN M C, KIM B, HOLSEN T M, et al. Factors influencing concentrations of dissolved gaseous mercury (DGM) and total mercury (TM) in an artificial reservoir [J]. Environ Pollut, 2010, 158(2): 347 − 355. [17] AIKEN G, HAITZER M, RYAN J N, et al. Interactions between dissolved organic matter and mercury in the Florida Everglades [J]. J de Physique, 2003, 107: 29 − 32. [18] KELLY C A, RUDD J W M, HOLOKA M H. Effect of pH on mercury uptake by an aquatic bacterium: implications for Hg cycling [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2003, 37(13): 2941 − 2946. [19] 张金香. 湖水中溶解气态汞的光诱导形成[J]. 国外环境科学技术, 1996(2): 16 − 22. ZHANG Jinxiang. Light induced formation of dissolved gaseous mercury in lake water [J]. Foreign Environ Sci Technol, 1996(2): 16 − 22. [20] 何天容, 冯新斌, 郭艳娜, 等. 红枫湖水体中活性汞和溶解气态汞的分布特征及其控制因素[J]. 环境科学研究, 2008, 21(2): 14 − 17. HE Tianrong, FENG Xinbin, GUO Yanna, et al. Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of active mercury and dissolved gaseous mercury in Hongfeng Lake water [J]. Environ Sci Res, 2008, 21(2): 14 − 17. [21] MARUMOTO K, IMAI S. Determination of dissolved gaseous mercury in seawater of Minamata Bay and estimation for mercury exchange across air-sea interface [J]. Mar Chem, 2015, 168: 9 − 17. [22] POULAIN A, AMYOT M, FINDLAY D, et al. Biological and photochemical production of dissolved gaseous mercury in a boreal lake [J]. Limnol Oceanogr, 2004, 49(6): 2265 − 2275. [23] 崔雪晴. 光照对近岸海水溶解性气态汞产生的影响研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014. CUI Xueqing. Effect of Light on the Production of Soluble Gaseous Mercury in Coastal Seawater[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. [24] LIANG Peng, WU Shengchun, ZHANG Chan, et al. The role of antibiotics in mercury methylation in marine sediments [J]. J Hazard Mater, 2018, 360: 1 − 5. [25] 钱钱, 杨兴, 郭明, 等. 生物质炭对土壤吸附Zn2+-DEP复合污染溶液中Zn2+的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(6): 1051 − 1061. QIAN Qian, YANG Xing, GUO Ming, et al. Adsorption of Zn2+ from a Zn2+-DEP (diethyl phthalate)composite solution using biochars in soil [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2019, 36(6): 1051 − 1061. [26] 傅海霞, 刘怡, 董志英, 等. 抗生素与重金属复合污染的生态毒理效应研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(4): 60 − 63, 104. FU Haixia, LIU Yi, DONG Zhiying, et al. Progress in research on ecological toxicity of combined pollution of antibiotics and heavy metals [J]. Environ Eng, 2016, 34(4): 60 − 63, 104. [27] 黄翔峰, 熊永娇, 彭开铭, 等. 金属离子络合对抗生素去除特性的影响研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(1): 133 − 140. HUANG Xiangfeng, XIONG Yongjiao, PENG Kaiming, et al. Advances in studies on the effects of metal ion complexation on antibiotic removal characteristics [J]. Environ Chem, 2016, 35(1): 133 − 140. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190568






 下载:
下载: