-
营养盐是水生生态系统中生物生长所必需的重要营养元素和化学物质,也是生态系统食物链的基础[1]。氮、磷作为水体环境中主要营养盐,被认为是影响水生态环境富营养化程度的关键性因子[2]。过量的氮、磷输入导致农村沟渠水体富营养化程度日益加重,加快藻类的生长和异常繁殖,进而破坏沟渠水体生态系统及其功能[3]。沟渠中氮、磷等营养盐在底泥和上覆水间存在着一定的动态平衡。当沟渠生态系统环境发生变化时,底泥会通过扩散、对流、底泥再悬浮等作用向上覆水体释放氮磷污染物,造成“二次污染”[4]。大量研究表明:营养盐在底泥-上覆水间的动态迁移转化主要受溶解氧[5]、pH[6]、温度[7]、氧化还原电位[8]、盐度[9]、扰动和微生物[10]等因素影响,其中以pH的影响最为显著。张茜[11]对溶解氧、pH、温度的正交实验发现:影响水库沉积物中总磷、总氮释放量的环境因子中,显著性从大到小依次为pH、温度、溶解氧;JENSEN等[12]发现:丹麦大部分湖泊中,强碱促进溶解性活性磷的释放;李家兵等[13]研究表明:偏酸性条件会抑制河口湿地沉积物中氮的硝化和反硝化活性,但不直接影响氮的矿化作用。目前学者多关注于河流、湖泊、城市内河、河口湿地和水库中的底泥研究,对山地农村沟渠底泥-水界面氮磷营养盐的迁移释放报道较少。云贵高原山地农村沟渠地形条件特殊,流域边界明显,是下游河流、湖泊富营养化治理的重点区域;沟渠污水来源差异大,主要包括厨余垃圾、畜禽粪便浸出水和生活污水等,沟中氮磷营养盐沉降和累积明显[14],同时由于水深较浅、流动性差、分布密度大和流域来水量少,农村沟渠水环境污染日益严重[15-16]。本研究以云贵高原滇池流域典型高原山地农村沟渠底泥为对象,采用室内模拟静态培养实验法探析不同pH条件下沟渠底泥-水界面氮磷营养盐动态迁移释放特征,为进一步提高农村生态环境质量,保护高原湖泊、河流和建设美丽乡村提供科学依据。
-
研究区昆明市官渡区小康郎小村(25°06′~25°07′ N,102°53′~102°54′ E )位于滇池东北岸,属于滇池流域宝象河子流域。于2019年夏季对研究区沟渠进行现场采样。利用彼得森采泥器采集表层(0~15 cm)底泥样品20 kg,风干,捡出杂物,研磨后过100目不锈钢筛,分别采用酸溶-钼锑抗比色法和凯氏定氮法测定底泥总磷(TP)和总氮(TN)质量分数。采用四步连续提取法测定钙结合态磷(Ca-P)、铁铝结合态磷(Fe/Al-P),采用重铬酸钾法测定有机质(OM)。利用水质采样器(BC-9600)采集底层原位水15 L,24 h内测定上覆水中TN、TP、溶解性总磷(DTP)、铵态氮(
${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $ -N)质量浓度,具体参照文献[17]方法进行。营养盐基本理化指标如表1所示。利用哈希HQ30D便携式多参数水质分析仪测定上覆水、底泥溶解氧(DO)、氧化还原电位(ORP)、pH等理化指标。表 1 沟渠营养盐基本理化指标
Table 1. Basic physical and chemical indexes of nutrients in ditch
指标 底泥 上覆水 TN/(mg·kg−1) TP/(mg·kg−1) ${{\rm{NH}}_4^{+} }$-N/(mg·L−1) DTP/(mg·L−1) TP/(mg·L−1) TN/(mg·L−1) 最大值 5 618.12 1 854.21 81.64 0.19 0.23 113.12 最小值 4 875.08 1 548.23 56.34 0.11 0.19 69.12 平均值 5 016.60 1 760.22 72.29 0.15 0.20 97.22 -
农村沟渠pH通常为6.5~8.5[4],但也有局部农村地区沟渠pH大于10.5[4, 15-16]。设置灭菌和未灭菌2个处理,4个pH梯度[酸性(pH 5.5),中性(pH 7.5),弱碱性(pH 9.5),强碱性(pH 11.5)],重复3次。以2 L有机玻璃容器作为静态模拟释放反应器,其中灭菌组为棕色瓶,上覆水高温灭菌处理(121 ℃,30 min),底泥三氯甲烷灭菌处理(1 L底泥与500 mL三氯甲烷均匀混合,浸泡24 h后过滤)[8],橡胶塞塞紧瓶口并用凡士林密封,避光放置。以1 mol·L−1氢氧化钠和1 mol·L−1盐酸调节上覆水pH,处理持续30 d;隔5 d测定上覆水物理指标(pH、DO、Eh),分别采集底泥和水样,测定氮磷含量。每次采样后补充等量的沟渠原位水至玻璃容器原始刻度处,以pH 7.5作为各组对照。
-
根据上覆水体总氮和溶解性总磷质量浓度随时间的变化,可计算出沉积物的营养盐氮磷释放通量。其计算公式为[18-19]:
$$r = {{\left[ {V \left( {C_n - C_0} \right) + \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {V_i \left( {C_{i - 1} - C_{\rm{a}}} \right)} } \right]}\Big/{A t}}\text{。}$$ 其中r为释放通量(mg·m−2·d−1);V为上覆水体积(L),Cn为第n次取样水中营养盐质量浓度(mg·L−1),C0为上覆水初始营养盐质量浓度(mg·L−1),Vi为每次采集水样的体积(L),Ca为添加沟渠原水中营养盐质量浓度(mg·L−1),Ci−1为第i−1次采样时水中营养盐的质量浓度(mg·L−1),A为沉积物表面积(m2),t为释放时间(d)。
采用Excel预处理数据,Origin 2019制图,Canoco 5.0进行冗余分析,用SPSS 21.0进行统计分析。
-
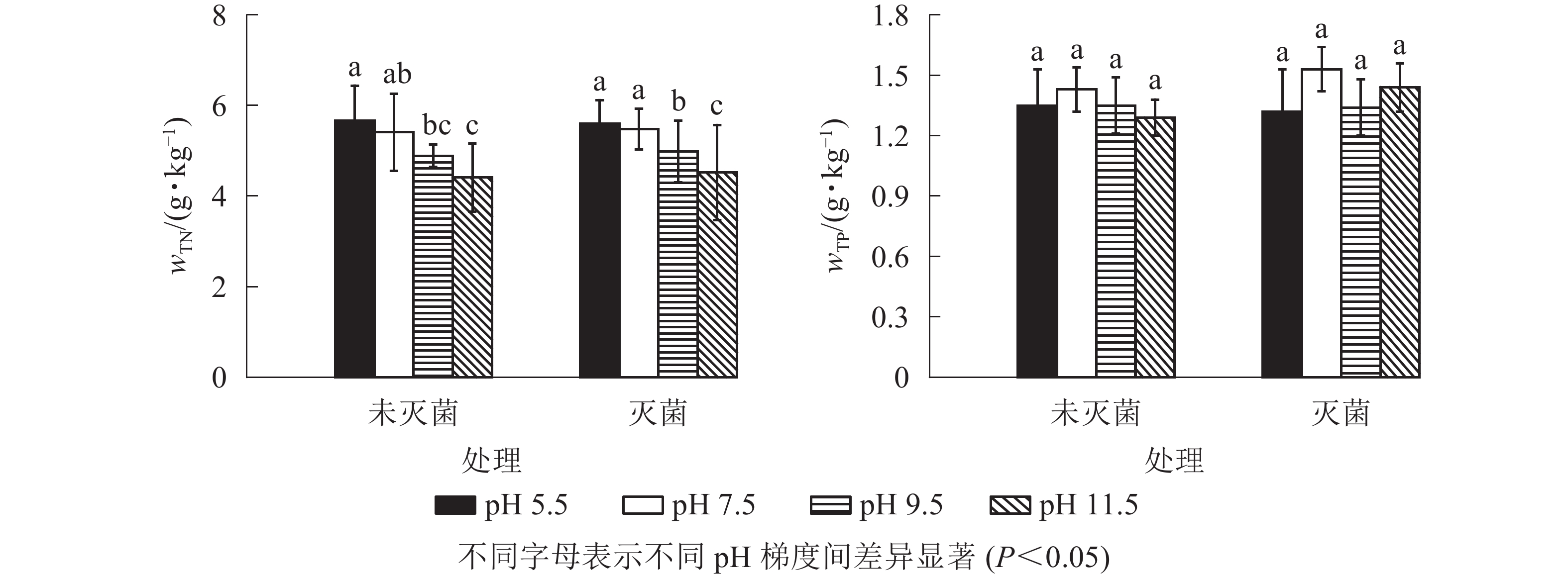
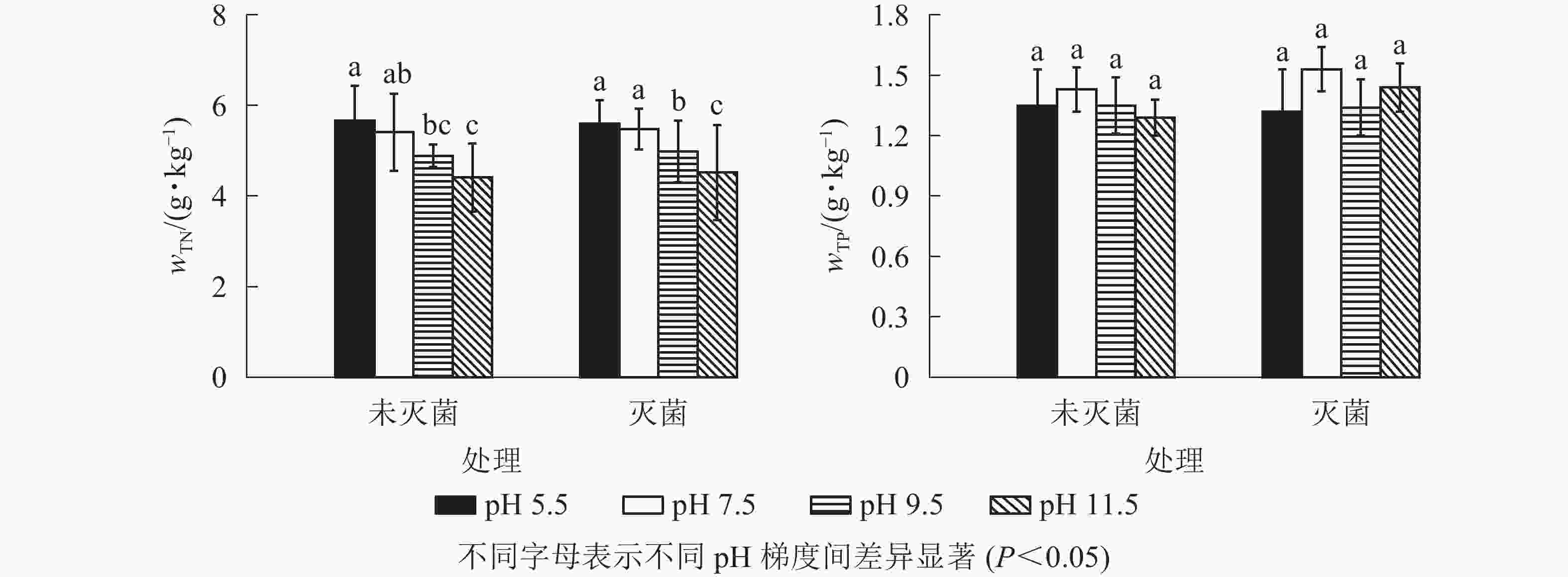
如图1所示:随着pH升高,未灭菌与灭菌处理的底泥TN质量分数均不断下降,酸性(pH 5.5)条件下TN质量分数显著高于弱碱性(pH 9.5)和强碱性(pH 11.5)(P<0.05),但和对照差异不显著(P>0.05)。底泥中TP质量分数未灭菌与灭菌处理均以对照最高,分别为1.43和1.53 g·kg−1;随着pH升高,未灭菌底泥中TP质量分数持续下降,灭菌处理组在pH 11.5时又小幅上升,但不同pH条件间无显著差异(P>0.05)。
-
随培养时间延长,不同pH条件下上覆水中TN质量浓度表现出不同的变化特征,平均质量浓度从大到小依次为pH 11.5、pH 5.5、pH 9.5、pH 7.5。从图2可以看出:培养0~10 d,未灭菌处理下pH 7.5和pH 9.5条件下TN质量浓度均呈下降趋势,10~20 d呈不同程度的上升,20 d后平缓下降,30 d时达到最小值。随培养时间延长,pH 11.5条件下TN质量浓度不断下降,25 d时达到最小值(101.29 mg·L−1),此后小幅上升。pH 5.5条件下TN质量浓度不断上升,25 d时出现最大值(103.66 mg·L−1),此后小幅下降。培养0~10 d,灭菌组pH 5.5和pH 9.5条件下TN质量浓度呈上升趋势,10 d后保持稳定。pH 7.5条件下,TN质量浓度在0~10 d呈下降趋势,此后趋于稳定。而pH 11.5条件下TN质量浓度随时间推移起伏较大,在20 d后逐渐下降并趋于平缓。
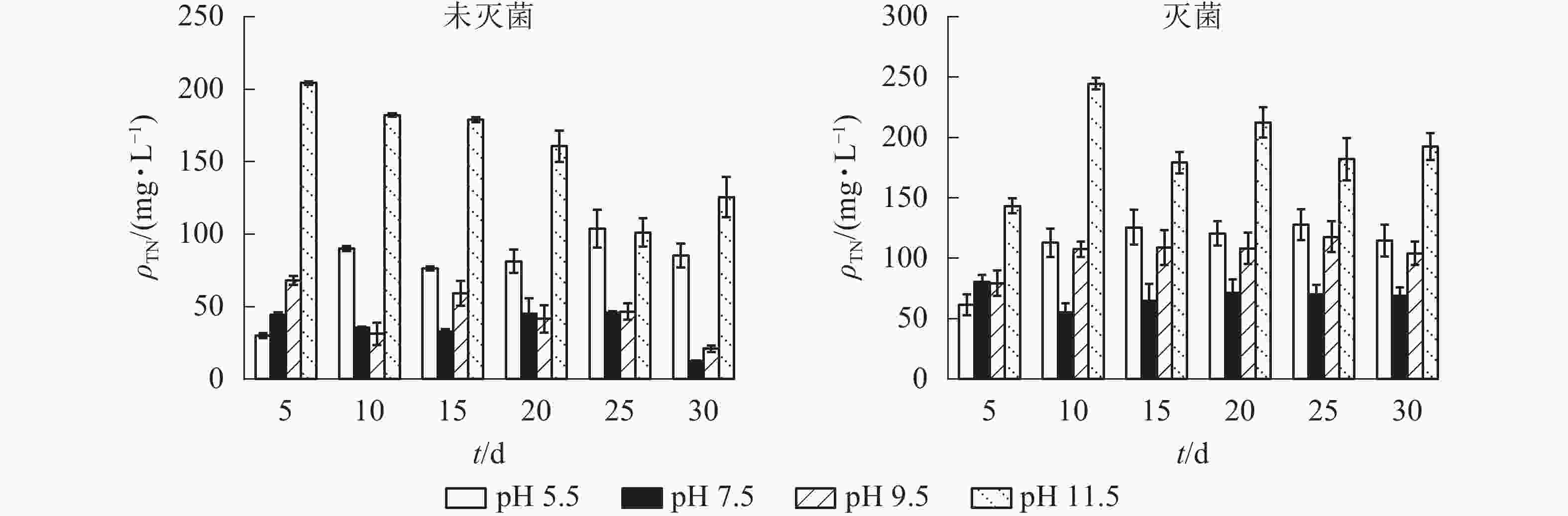
图 2 不同pH条件下上覆水中总氮变化特征
Figure 2. Variation characteristics of total nitrogen in overlying water under different pH conditions
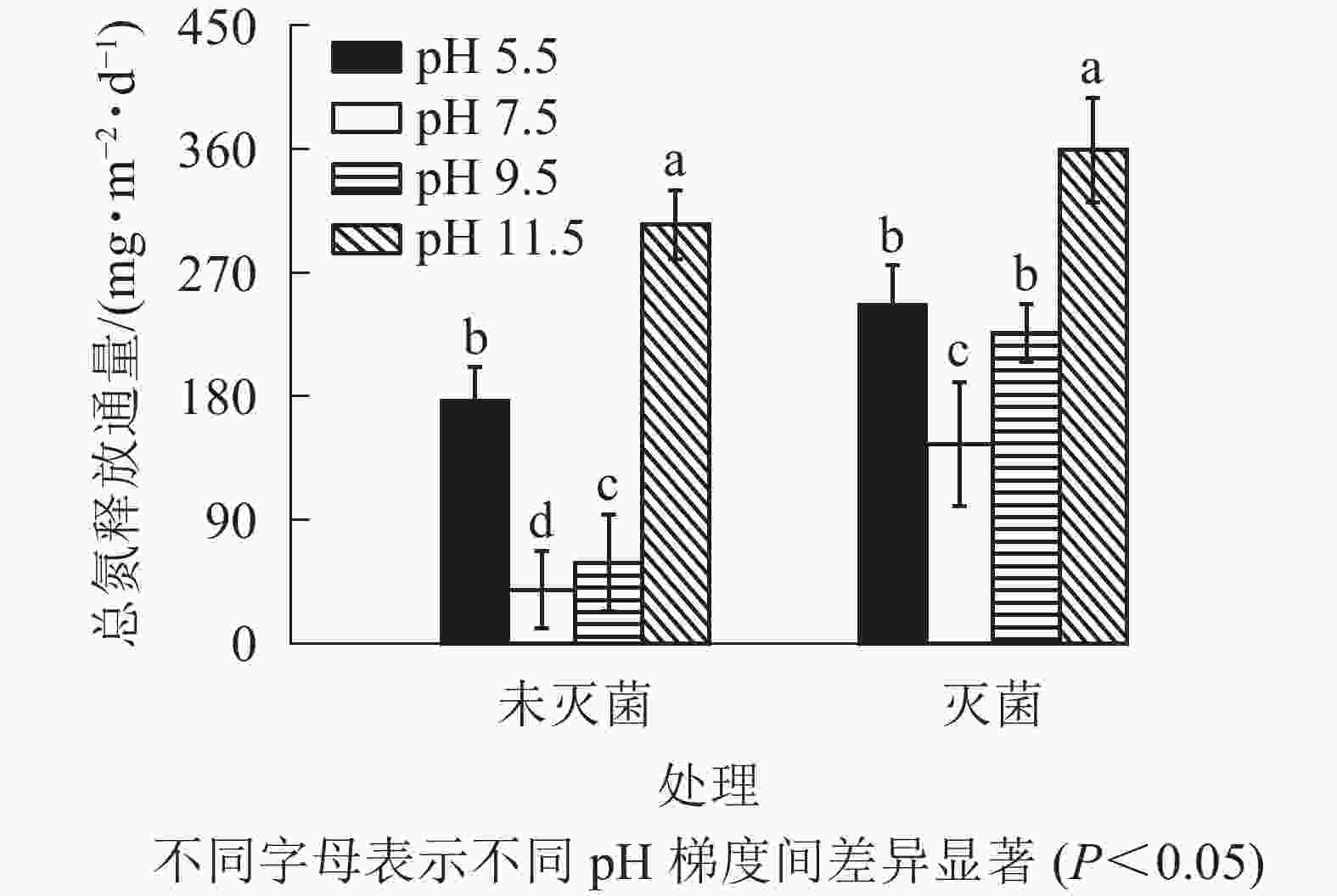
由图3可知:未灭菌组和灭菌组TN释放通量分别为39.18~305.09和145.36~359.50 mg·m−2·d−1,均在对照处理下达到最小值;随着pH升高,TN释放通量均呈先减小后增加的趋势。未灭菌处理组强碱性(pH 11.5)和酸性(pH 5.5)条件下TN释放通量分别是对照的8和4倍,不同pH条件间差异显著(P<0.05);灭菌处理组强碱性、弱碱性和酸性条件下TN释放通量均显著高于对照(P<0.05),但pH 5.5和pH 9.5条件间差异不显著(P>0.05)。
-
由图4可知:未灭菌和灭菌处理组不同pH下上覆水DTP平均质量浓度从大到小依次为pH 11.5、pH 9.5、pH 7.5、pH 5.5。pH 5.5和pH 7.5的DTP质量浓度整个培养期均较低,趋势相对稳定。 pH 9.5和pH 11.5条件下,0~15 d,DTP质量浓度相对稳定,之后不同程度上升,表明碱性条件下磷素在底泥-上覆水界面扩散趋势明显。未灭菌组pH 9.5和pH 11.5的DTP质量浓度在第30 天时最大,分别为9.96、25.98 mg·L−1,灭菌组pH 9.5和pH 11.5的DTP质量浓度在第25 天时最大,分别为13.74和19.61 mg·L−1,之后相对下降。
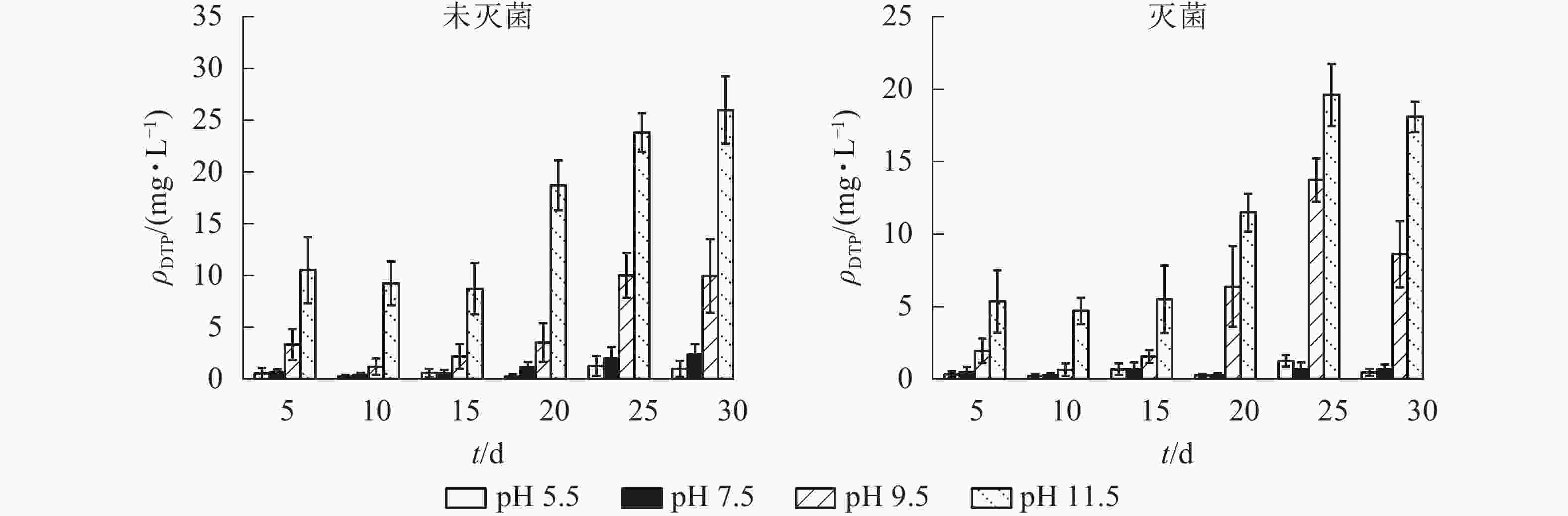
图 4 不同pH条件下上覆水中溶解性总磷变化
Figure 4. Characteristics of total dissolved phosphorus in overlying water under different pH conditions
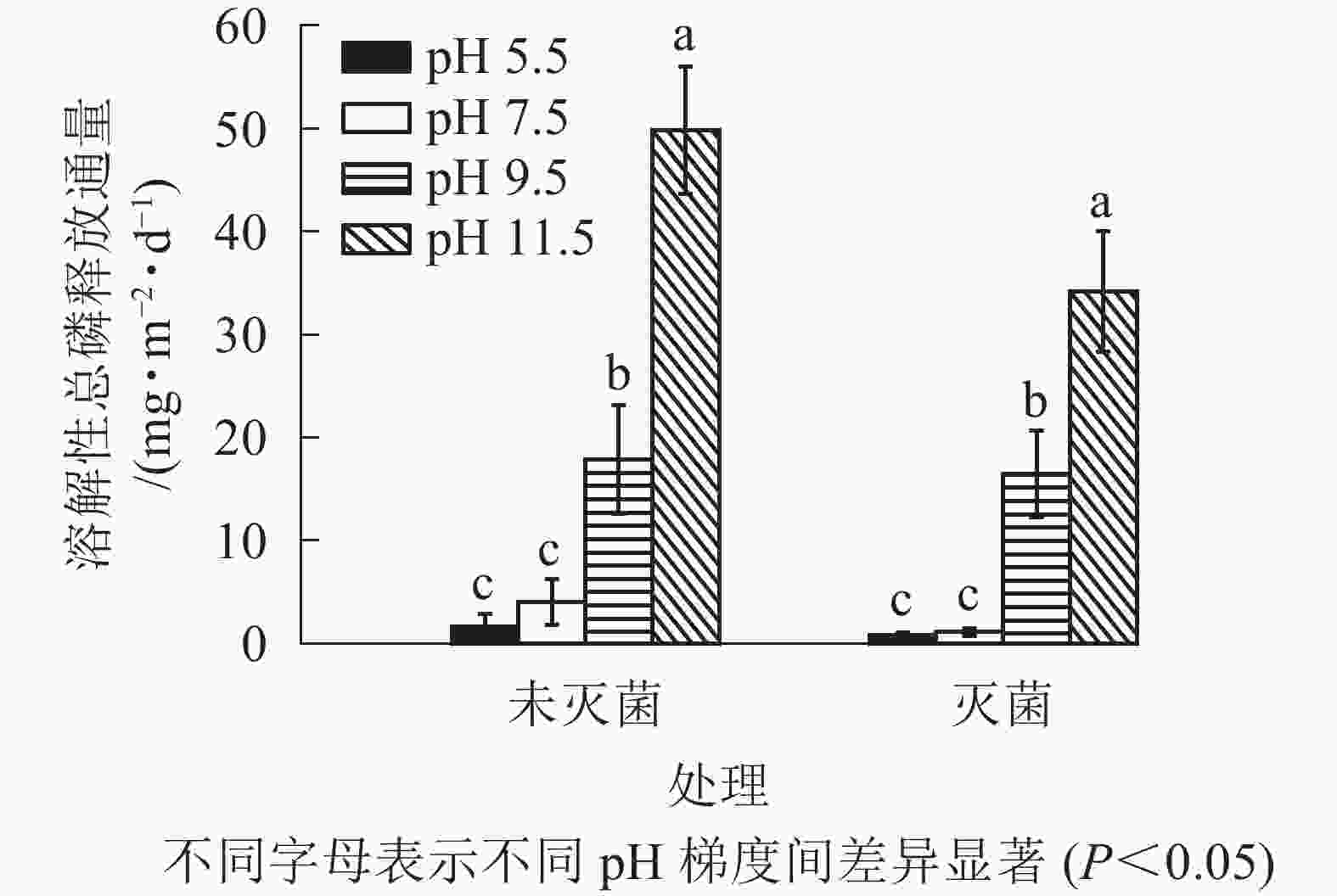
未灭菌和灭菌处理,底泥-上覆水界面DTP释放通量随pH升高而增加,不同pH条件间存在显著差异(P<0.05);碱性条件下DTP释放通量显著高于对照,而酸性条件和对照间差异不显著(P>0.05)(图5)。未灭菌处理组DTP释放通量为1.67~49.85 mg·m−2·d−1,其中强碱性(pH 11.5)和弱碱性(pH 9.5)的DTP释放通量分别是对照的12和4倍;灭菌处理组DTP释放通量为0.84~34.21 mg·m−2·d−1,强碱性和弱碱性的DTP释放通量分别是对照的30和15倍。相比之下,未灭菌处理组DTP释放通量要高于灭菌处理组;表明沟渠底泥是溶解性总磷(DTP)的“源”,磷元素由底泥界面不断扩散进入上覆水中。
-
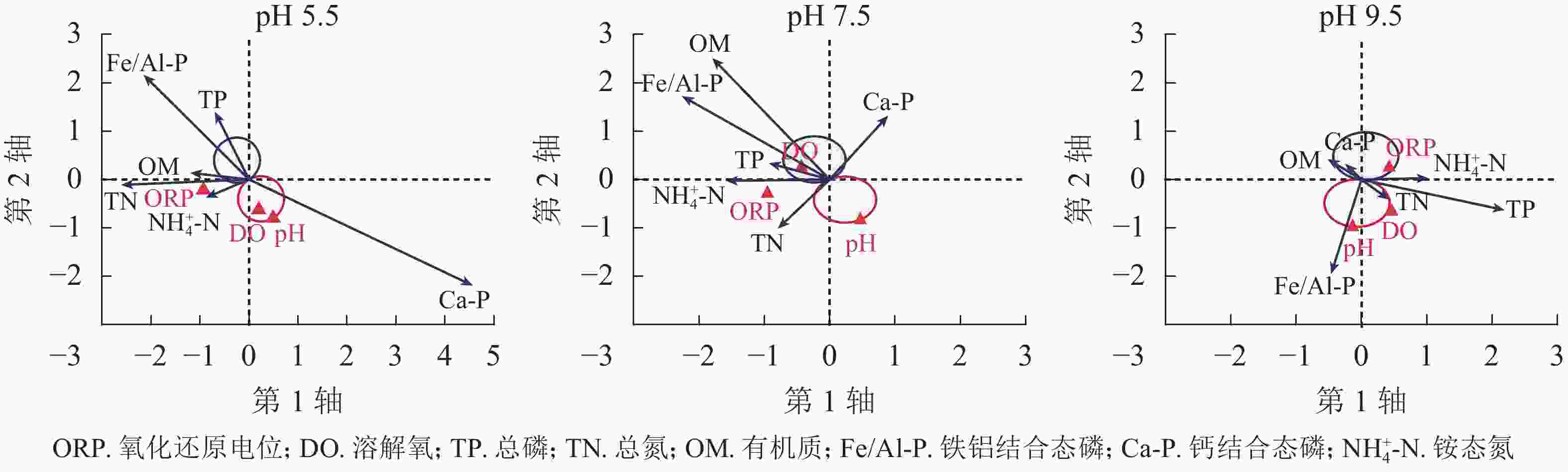
由图6可知:pH 5.5条件下,钙结合态磷(Ca-P)穿过红线圈,而总磷(TP)、铁铝结合态磷(Fe/Al-P)、有机质(OM)、总氮(TN)和铵态氮(
${\rm{NH}}^{+}_{4}\text{-}{\rm{N}}$ )均穿过蓝线圈,表明酸性条件与Ca-P呈正相关。pH 7.5条件下,TN穿过红线圈,而其他指标(OM、Ca-P、TP、Fe/Al-P和${\rm{NH}}^{+}_{4}\text{-}{\rm{N}} $ )均穿过蓝线圈,表明中性(pH 7.5)条件与TN呈正相关,而与其他指标均为负相关。pH≥9.5时,TN、TP、Fe/Al-P穿过红线圈,OM、Ca-P和${\rm{NH}}^{+}_{4}\text{-}{\rm{N}} $ 穿过蓝线圈,表明碱性条件与TN、TP和Fe/Al-P正相关,与OM、Ca-P、$ {\rm{NH}}^{+}_{4}\text{-}{\rm{N}} $ 负相关。Ca-P是一种惰性磷,仅酸性条件能促进Ca-P释放,碱性条件则促进Fe/Al-P、TN、TP释放。中性条件对底泥中氮磷释放影响较小。 -
整个研究周期内,上覆水总氮平均质量浓度和释放通量从大到小依次为pH 11.5、pH 5.5、pH 9.5、pH 7.5;表明强碱和酸性条件有利于TN的释放,而中性条件TN释放相对较弱。沟渠中氮由底泥向上覆水界面迁移释放,其释放规律随时间的推移表现出不同的差异。原因可能是:随着废水的不断排入,沟渠上覆水酸碱度波动较大;酸性条件下,底泥中胶体吸附的铵根(
$ {\rm{NH}}^{+}_{4} $ )与氢离子(H+)发生离子交换,pH越小,H+越多,离子交换作用就越强烈;H+和$ {\rm{NH}}^{+}_{4} $ 竞争吸附位置,氯离子(Cl−)则与硝酸根($ {\rm{NO}}^{-}_{3} $ )竞争吸附位置[20],促进底泥氮的释放,上覆水中总氮质量浓度升高。而碱性条件下,上覆水中存在大量的氢氧根(OH−),pH越大,则OH−越多,与底泥胶体中$ {\rm{NH}}^{+}_{4} $ 结合发生化学反应也越剧烈;底泥中$ {\rm{NH}}^{+}_{4} $ 以气态形式(NH3,氨气)逸出[21],使上覆水中铵态氮质量浓度降低,造成两相间浓度差变大,进而促进底泥中TN向上覆水体释放。卢俊平等[22]对水库和湖泊中底泥进行室内模拟释放研究发现:酸性和碱性条件均有利于底泥中总氮的释放,而中性条件下底泥中总氮的释放强度最弱,与本研究结果基本一致。此外,底泥TN质量分数随pH升高而下降,强碱性条件下底泥中TN质量分数相对最小,也说明了强碱性条件下底泥中氮营养盐最容易从底泥向上覆水界面迁移释放。曾巾等[23]、PAUER等[24]研究发现:底泥表面和水体中存在比较强烈的硝化反应。本研究发现:实验初期,pH 5.5条件下上覆水TN质量浓度不断上升,10 d后相对稳定,表明系统初期底泥-上覆水界面存在较强的硝化作用,原因在于好氧环境和高氧化还原电位条件加快底泥表面的硝化细菌活性[10]。相比之下未灭菌处理组上覆水TN质量浓度上升更为剧烈,说明在好氧环境下,酸性条件有利于底泥中的氮素转化。强碱(pH 11.5)条件下上覆水TN质量浓度随着时间推移变化起伏较大,这是由于底泥和上覆水间的含氮营养盐存在一定的质量浓度差;实验初期营养盐中氮由底泥迅速向上覆水释放,随时间延长营养盐中氮素逐渐消耗,要使氮素营养盐进一步释放,则需要底泥中含氮有机质矿化;而每次采样后加入的原位水稀释速率大于含氮有机质的矿化速率,使得底泥中总氮的释放量不断减少。相比之下,未灭菌处理组微生物细菌总数相对较多,微生物活性强,可分解底泥中一些难溶形态的氮[25];而培养时间延长,体系中微生物活性逐渐减弱,因而总氮质量浓度不断下降。有研究表明[26]:pH为7~11时,底泥中的反硝化细菌活性随pH升高而增大,加上水溶液中OH−较多,底泥中无机氮被快速转化为有机氮释放到上覆水中,是强碱条件下总氮释放通量和上覆水质量浓度要高于其他3个pH梯度的原因。与裴佳瑶等[20]研究结果一致。由此看来,农村沟渠上覆水pH对沟渠底泥中氮释放迁移具有一定的影响,实时监测和有效调控沟渠上覆水酸碱度是农村生态环境治理的关键。
-
上覆水溶解性总磷平均质量浓度和释放通量从大到小依次为pH 11.5、pH 9.5、pH 7.5、pH 5.5,磷元素从底泥向上覆水界面释放,反应初期相对稳定,随着培养时间延长,释放速率相对增加。不同处理下DTP释放通量和上覆水质量浓度均随pH升高而增大,且碱性(pH≥9.5)条件显著高于中性(pH 7.5)和酸性(pH 5.5)条件。这是由于排入物主要为厨余垃圾、农业灌溉废水和畜禽养殖废水,沟渠水深较浅、流域来水量少、分布密度大、流动性差,随时间延长,上覆水酸碱度变化较大。碱性条件下,磷释放以离子交换为主;高pH条件下水溶液中存在的大量OH−与底泥中的铁铝结合磷酸根离子竞争吸附位置[27],铝离子(Al3+)、铁离子(Fe3+)与OH−结合生成稳定的氢氧化物,而磷元素在离子交换作用下被重新释放到上覆水中[28]。当pH为7.5时,水溶液中的磷以磷酸二氢根(
$ {\rm{H}}_{2}{\rm{PO}}^{-}_{4} $ )和磷酸氢根($ {\rm{HPO}}^{2-}_{4} $ )的形式存在,容易与底泥中溶解的腐殖质、Fe3+等金属元素结合而被吸附绑定在底泥表面[29];随着系统中磷释放-吸附的不断发生,中性条件下上覆水中磷释放量不断降低。而酸性条件下,底泥中磷释放主要以溶解为主;低pH时,大量H+影响底泥矿物表面基团质子化,可吸附上覆水中一部分磷[30];同时,在偏酸性条件下,底泥中的Fe3+、Al3+与上覆水中磷相互作用,形成难溶性磷酸盐,抑制水溶液中活性磷酸酶的水解作用[31],导致上覆水中磷质量浓度进一步降低。农村沟渠底泥中存在的大量微生物细菌是影响底泥磷污染物释放的另一原因。左乐等[32]研究发现:微生物可加速沉积物中有机磷向无机磷转化,提高磷的生物可利用效率。本研究中,碱性(pH≥9.5)条件下反应前期(0~15 d)溶解性总磷质量浓度相对稳定,15 d后不同程度上升。一方面可能是底泥中解有机磷细菌的作用,随pH升高,这种菌会将底泥中不易被植物吸收的磷转化为可被吸收利用的可溶性磷[33]。另一方面微生物代谢过程中会产生一种促进有机磷转化的胞外酶[34],导致磷脂、核酸等有机磷的P−N、P−O和P−S键断裂,矿化出溶解性磷酸盐,释放到上覆水中[35]。随着pH升高,微生物细菌活性不断增强,氧气消耗量变大,底泥中氧化还原电位下降[36],底泥中Fe3+被还原为亚铁离子(Fe2+),导致溶解性磷酸盐不断释放到上覆水中。本研究中发现:未灭菌处理组底泥中微生物细菌较多,活性较大,分解难溶性磷能力较强;灭菌处理杀死了一部分底泥中的微生物细菌,伴随时间推移,剩余微生物[36]的活性降低,是灭菌处理组DTP释放通量和上覆水质量浓度均低于未灭菌处理组的原因。
山地农村沟渠是氮磷营养盐释放风险较高区域,上覆水酸碱度的变化直接影响底泥氮磷营养盐的迁移释放。加强对山地农村沟渠水环境pH的实时监控,定期清淤,保障沟渠通畅,从而降低营养盐释放风险。此外,需加强对沟渠上游及周边农村的排污管控,切断沟渠外源污染,从根本上控制农村沟渠水环境污染问题。
-
山地农村沟渠底泥中氮磷元素由底泥向上覆水界面迁移释放,随着pH升高,底泥中总氮质量分数减少。总氮释放通量在强碱性(pH 11.5)和酸性(pH 5.5)条件下最高,说明偏酸性和强碱性条件更利于底泥中氮的释放。底泥中总磷质量分数随着pH升高呈先增加后减小趋势,上覆水溶解性总磷质量浓度和释放通量未灭菌处理组始终高于灭菌处理组。碱性(pH≥9.5)条件更有利于底泥中磷的释放,中性(pH 7.5)条件磷释放量最小。不同pH条件下底泥灭菌处理会降低微生物活性,阻碍底泥中磷的释放。冗余分析表明:酸性(pH 5.5)条件能促进Ca-P释放,碱性(pH≥9.5)条件能促进总氮、总磷和Fe/Al-P释放,而中性(pH 7.5)条件对底泥中氮磷释放影响最小。
Effects of pH on the dynamic migration of nutrient salts in the sediment of ditches in mountain rural areas
-
摘要:
目的 酸碱度是影响沟渠底泥营养盐迁移释放的关键性因子。探究不同pH条件下山地农村沟渠底泥营养盐释放迁移的动态变化,为农村生态环境治理提供理论依据。 方法 采集滇池流域典型山地农村沟渠底泥,通过室内模拟实验测定未灭菌与灭菌处理下不同pH (5.5、7.5、9.5、11.5)条件的底泥、上覆水中营养盐含量,估算底泥-水界面营养盐释放通量。 结果 底泥中总氮质量分数随着pH升高而减少,未灭菌组强碱性(pH 11.5)和酸性(pH 5.5)条件下总氮释放通量分别是对照(pH 7.5)的8和4倍,灭菌组均为对照的2倍。上覆水中溶解性总磷质量浓度和释放通量随pH升高而增加,未灭菌组强碱性(pH 11.5)和弱碱性(pH 9.5)条件下溶解性总磷释放通量分别是对照的12和4倍,灭菌组分别是对照的30和15倍;未灭菌组溶解性总磷释放通量高于灭菌组。冗余分析表明:酸性条件促进底泥中钙结合态磷(Ca-P)的释放,碱性(pH≥9.5)条件促进总氮、总磷和铁铝结合态磷(Fe/Al-P)的释放,中性(pH 7.5)条件对底泥中氮/磷释放影响较小。 结论 碱性(pH≥9.5)和酸性显著促进山地农村沟渠底泥中氮磷营养盐释放,中性条件下释放量最小。底泥灭菌处理降低了不同pH下的微生物活性,阻碍山地农村沟渠底泥中氮磷向上覆水体迁移释放。图6表1参36 Abstract:Objective As pH is a key factor affecting the migration and release of nutrients in the ditch sediment, this study, with an investigation of the dynamic changes of nutrient release and migration in the bottom mud of mountainous rural ditches under different pH conditions, is aimed to provide a theoretical basis for rural ecological environment management. Method With the bottom mud of typical mountainous rural ditches in the Dianchi Lake Basin collected, indoor simulation experiments were conducted to determine the nutrient salt content of the bottom mud and the overlying water under different pH (pH 5.5, 7.5, 9.5, 11.5) conditions under non-sterilized and sterilized treatments after which the nutrient release flux at the sediment-water interface was estimated. Result The mass fraction of total nitrogen (TN) in the bottom sludge decreased with the increase of pH. The total nitrogen release flux under the strong alkaline (pH 11.5) and acidic (pH 5.5) conditions of the non-sterilized group was 8 and 4 times of the control (pH 7.5), and its release flux in the sterilization group was 2 times of that in the control. The mass concentration and release flux of soluble total phosphorus (DTP) in the overlying water increased with the increase of pH. The release of DTP under the conditions of strong alkaline (pH 11.5) and weak alkaline (pH 9.5) in the non-sterilized group was 12 and 4 times of that in the control, respectively, and its release flux in the sterilized group was 30 and 15 times of that in the control while the non-sterilized group had higher DTP release flux than the sterilized group. RDA shows that acidic conditions promote the release of calcium-bound phosphorus (Ca-P) in sediments, and alkaline (pH≥9.5) conditions promote the release of total nitrogen, total phosphorus and iron-aluminum-bound phosphorus (Fe/Al-P). Neutral (pH 7.5) conditions have little effect on the release of nitrogen or phosphorus in the sediments. Conclusion Alkalinity (pH≥9.5) and acidity significantly promote the release of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in the bottom mud of mountain rural ditches, and the release amount is the smallest under neutral conditions. Also, the sterilization of the bottom sludge reduces the microbial activity at different pH levels, and prevents the migration and release of nitrogen and phosphorus in the bottom sludge of mountain and rural ditches to the overlying water. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 36 ref.] -
Key words:
- pH /
- mountain rural ditches /
- sediment /
- nutrients /
- dynamic migration
-
表 1 沟渠营养盐基本理化指标
Table 1. Basic physical and chemical indexes of nutrients in ditch
指标 底泥 上覆水 TN/(mg·kg−1) TP/(mg·kg−1) ${{\rm{NH}}_4^{+} }$-N/(mg·L−1) DTP/(mg·L−1) TP/(mg·L−1) TN/(mg·L−1) 最大值 5 618.12 1 854.21 81.64 0.19 0.23 113.12 最小值 4 875.08 1 548.23 56.34 0.11 0.19 69.12 平均值 5 016.60 1 760.22 72.29 0.15 0.20 97.22 -
[1] 李庚辰, 刘足根, 张敏, 等. 升温对超富营养型浅水湖泊沉积物营养盐动态迁移的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(12): 4016 − 4025. LI Gengchen, LIU Zugen, ZHANG Min, et al. A preliminary study of effects of warming on the nutrients dynamic in sediment of hypereutrophic shallow lake [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2015, 35(12): 4016 − 4025. [2] 王志齐, 刘新星, 姚志宏, 等. 丹江口水库氮磷内源释放对比[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(11): 4953 − 4961. WANG Zhiqi, LIU Xinxing, YAO Zhihong, et al. Endogenous release of nitrogen and phosphorus in the Danjiangkou Reservoir [J]. Environ Sci, 2019, 40(11): 4953 − 4961. [3] 袁海英, 梁启斌, 侯磊, 等. 洱海入湖河口湿地沉积物氨氮释放潜力研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2020, 36(6): 762 − 769. YUAN Haiying, LIANG Qibin, HOU Lei, et al. Research on the release potential of ammonia in the estuarine wetland sediments of Erhai Lake [J]. J Ecol Rural Environ, 2020, 36(6): 762 − 769. [4] 梅涵一, 刘云根, 郑寒, 等. 云南分散畜禽养殖密集型农村污水特征及污染风险评价[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(7): 46 − 51. MEI Hanyi, LIU Yungen, ZHENG Han, et al. Characteristics of sewage pollution and environment risk assessment of dispersion livestock intensive village in Yunnan [J]. Environ Eng, 2016, 34(7): 46 − 51. [5] KAISER D, UNGER D, QIU Guanglong, et al. Natural and human influences on nutrient transport through a small subtropical Chinese estuary [J]. Sci Total Environ, 2013, 450/451: 92 − 107. [6] 雷晓玲, 韩亚鑫, 冉兵, 等. 环境因子对三峡库区底泥污染物释放的影响研究[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(1): 47 − 64. LEI Xiaoling, HAN Yaxin, RAN Bing, et al. Impact of environmental factors on contaminants release from the sediment of Three Gorges Reservoir Area [J]. Environ Eng, 2016, 34(1): 47 − 64. [7] LIANG Zhen, LIU Zhimei, ZHEN Shuming, et al. Phosphorus speciation and effects of environmental factors on release of phosphorus from sediments obtained from Taihu Lake, Tien Lake, and East Lake [J]. Toxicol Environ Chem, 2015, 97(3/4): 335 − 348. [8] 黄廷林, 周瑞媛, 夏超, 等. 氧化还原电位及微生物对水库底泥释磷的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(6): 930 − 936. HUANG Tinglin, ZHOU Ruiyuan, XIA Chao, et al. Effects of oxidation-reduction potential and microorganism on the release of phosphorus from sediments [J]. Environ Chem, 2014, 33(6): 930 − 936. [9] LI Rufeng, FENG Chenghong, WANG Dongxin, et al. Role of salinity in the multiphase redistribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediment suspension [J]. Environ Earth Sci, 2016, 75: 116. [10] 张文斌, 董昭皆, 徐书童, 等. 微生物和藻类分解对荣成天鹅湖沉积物氮磷释放的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(4): 561 − 567. ZHANG Wenbin, DONG Zhaojie, XU Shutong, et al. Effects of microorganism and algal decomposition on nitrogen and phosphorus release from the sediments in Rongcheng Swan Lake [J]. Marine Environ Sci, 2019, 38(4): 561 − 567. [11] 张茜. 漳泽水库沉积物和上覆水污染特征及氮磷释放规律研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2019. ZHANG Qian. Study on Pollution Characteristics and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Release of Sediments and Overlying Water in Zhangze Reservoir [D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2019. [12] JENSEN H S, ANDERSEN F Ø. Importance of temperature, nitrate, and pH for phosphate release from aerobic sediments of four shallow, eutrophic lakes [J]. Limnol Oceanogr, 1992, 37(3): 577 − 589. [13] 李家兵, 张党玉, 吴春山, 等. pH对闽江河口湿地沉积物氮素转化关键过程的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(1): 272 − 278. LI Jiabing, ZHANG Dangyu, WU Chunshan, et al. Effects of pH on the key nitrogen transformation processes of the wetland sediment in the Min River estuary [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2017, 31(1): 272 − 278. [14] 冀峰, 王国祥, 韩睿明, 等. 太湖流域农村黑臭河流沉积物中磷形态的垂向分布特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(1): 55 − 63. JI Feng, WANG Guoxiang, HAN Ruiming, et al. Vertical distribution characteristics of phosphorus fractions in the sediments of a rural malodorous black river in Taihu Lake area [J]. Acta Sci Circum, 2016, 36(1): 55 − 63. [15] 梅涵一, 刘云根, 郑寒, 等. 普者黑流域畜禽养殖型农村沟渠底泥磷形态分布特征及风险评价[J]. 土壤通报, 2017, 48(1): 195 − 201. MEI Hanyi, LIU Yungen, ZHENG Han, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of phosphorus speciation in livestock rural ditch sediments of Puzhehei Basin [J]. Chin J Soil Sci, 2017, 48(1): 195 − 201. [16] 梅涵一, 王妍, 刘云根, 等. 云南不同类型农村沟渠底泥中氮赋存形态分布[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(10): 2060 − 2070. MEI Hanyi, WANG Yan, LIU Yungen, et al. Distribution of nitrogen speciation in ditch sediments from different rural types in Yunnan [J]. Environ Chem, 2016, 35(10): 2060 − 2070. [17] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002: 239 − 284. [18] 张红, 陈敬安, 王敬富, 等. 贵州红枫湖底泥磷释放的模拟实验研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2015, 43(2): 243 − 251. ZHANG Hong, CHEN Jing’an, WANG Jingfu, et al. A simulation study on the release of phosphorus from sediments in Lake Hongfeng, Guizhou Province, China [J]. Earth Environ, 2015, 43(2): 243 − 251. [19] 王敬富, 陈敬安, 罗婧, 等. 红枫湖沉积物内源氮磷释放通量估算方法的对比研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2018, 46(1): 1 − 6. WANG Jingfu, CHEN Jing’an, LUO Jing, et al. Comparative study on quantitative estimations of phosphorus release flux from sediments of Lake Hongfeng, Guizhou Province, China [J]. Earth Environ, 2018, 46(1): 1 − 6. [20] 裴佳瑶, 冯民权. 环境因子对雁鸣湖沉积物氮磷释放的影响[J]. 环境工程学, 2020, 14(12): 3447 − 3459. PEI Jiayao, FENG Minquan. Effects of environmental factors on the release of nitrogen and phosphorus from the sediment othe Yanming Lake, China [J]. Chin J Environ Eng, 2020, 14(12): 3447 − 3459. [21] 孙英, 何江, 吕昌伟, 等. 岱海表层沉积物中影响氨氮释放的模拟研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(7): 1464 − 1468. SUN Ying, HE Jiang, LÜ Changwei, et al. The simulation research of ammonium nitrogen release from the surface sediments of the Daihai Lake [J]. J Agro-Environ Sci, 2009, 28(7): 1464 − 1468. [22] 卢俊平, 贾永芹, 张晓晶, 等. 上覆水环境变化对底泥释氮强度影响模拟研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2018, 34(10): 924 − 929. LU Junping, JIA Yongqin, ZHANG Xiaojing, et al. Simulation study on influence of change of overlying water environment on nitrogen release intensity of sediment [J]. J Ecol Rural Environ, 2018, 34(10): 924 − 929. [23] 曾巾, 杨柳燕, 肖琳, 等. 湖泊物地球化学循环及微生物的作用[J]. 湖泊科学, 2007, 19(4): 382 − 389. ZENG Jin, YANG Liuyang, XIAO Lin, et al. Biogeochemical cycling of nitrogen in lakes and the role of microorganisms in conversion of nitrogen compounds [J]. J Lake Sci, 2007, 19(4): 382 − 389. [24] PAUER J J, AUER M T. Nitrification in the water column and sediment of a hypereutrophic lake and adjoining river system [J]. Water Res, 2000, 34(4): 1247 − 1254. [25] 魏烈群, 徐书童, 王效昌, 等. 微生物和硬毛藻对天鹅湖不同湖区沉积物氮磷释放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(3): 580 − 588. WEI Liequn, XU Shutong, WANG Xiaochang, et al. Effects of microbial activity on nitrogen and phosphorus release from sediments in different lakes of Swan Lake [J]. Ecol Environ Sci, 2020, 29(3): 580 − 588. [26] 代政, 祁艳丽, 唐永杰, 等. 上覆水环境因子对滨海水库沉积物氮磷释放的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2016, 29(12): 1766 − 1772. DAI Zheng, QI Yanli, TANG Yongjie, et al. Effects of environmental factors of overlying water on the release of nitrogen and phosphorus from sediment of coastal reservoir [J]. Res Environ Sci, 2016, 29(12): 1766 − 1772. [27] 王新建, 王松波, 耿红. 东湖、汤逊湖和梁子湖沉积物磷形态及pH对磷释放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(5): 810 − 814. WANG Xinjian, WANG Songbo, GENG Hong. Phosphorus fractions and the influence of pH on the release of phosphorus from sediments in the Donghu Lake, Tangxun Lake and Liangzi Lake [J]. Ecol Environ, 2013, 22(5): 810 − 814. [28] WANG Kang, LIN Zhongbing, ZHANG Renduo. Impact of phosphate mining and separation of mined materials on the hydrology and water environment of the Huangbai River basin, China [J]. Sci Total Environ, 2016, 543: 347 − 356. [29] TEMPORETTI P, BEAMUD G, NICHELA D, et al. The effect of pH on phosphorus sorbed from sediments in a river with a natural pH gradient [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 228: 287 − 299. [30] 郭志勇, 李晓晨, 王超, 等. pH值对玄武湖沉积物中磷的释放及形态分布的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(3): 873 − 877. GUO Zhiyong, LI Xiaochen, WANG Chao, et al. Influence of pH value on the release and the chemical fractious of phosphorus in sediments of Xuanwu Lake [J]. J Agro-Environ Sci, 2007, 26(3): 873 − 877. [31] 张义, 刘子森, 张垚磊, 等. 环境因子对杭州西湖沉积物各形态磷释放的影响[J]. 水生生物学报, 2017, 41(6): 1354 − 1361. ZHANG Yi, LIU Zisen, ZHANG Yaolei, et al. Effects of varying environmental conditions on release of sediment phosphorus in West Lake, Hangzhou, China [J]. Acta Hydrobiol Sin, 2017, 41(6): 1354 − 1361. [32] 左乐, 吕昌伟, 何江, 等. 微生物对冰封期湖泊沉积物中有机磷降解释放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(12): 4501 − 4508. ZUO Le, LÜ Changwei, HE Jiang, et al. Impacts of microorganisms on degradation and release characteristics of organic phosphorus in lake sediments during freezing season [J]. Environ Sci, 2015, 36(12): 4501 − 4508. [33] 李楠, 单保庆, 张洪, 等. 沉积物中有机磷在pH和温度影响下的矿化机制[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(4): 1008 − 1014. LI Nan, SHAN Baoqing, ZHANG Hong, et al. Organic phosphorus mineralization in the sediments under the impact of pH and temperature [J]. Environ Sci, 2011, 32(4): 1008 − 1014. [34] ZBOIŃSKA E, MALISZEWSKA I, LEJCEAK B, et al. Degradation of organophosphonates by Penicillium citrinum [J]. Lett Appl Microbiol, 1992, 15(6): 269 − 272. [35] 鲍林林, 李叙勇. 河流沉积物磷的吸附释放特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(2): 350 − 356. BAO Linlin, LI Xuyong. Release and absorption characteristics of phosphorus in river sediment and their influential factors [J]. Ecol Environ Sci, 2017, 26(2): 350 − 356. [36] 周进, 林光辉, 蔡中华. 微生物在藻际环境中的物质循环作用[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(8): 2708 − 2716. ZHOU Jin, LIN Guanghui, CAI Zhonghua. Roles of microbes in matter cycles in phycosphere niche [J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2016, 27(8): 2708 − 2716. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200709






 下载:
下载: