-
植物挥发油是一类存在于植物体中的有芳香气味、在常温下能挥发、可随水蒸气蒸馏出的油状液体的总称,广泛应用于制药、香料、香精、化妆品及食品等工业[1]。植物挥发油主要含有萜烯、倍半萜烯及其氧化物,另外含有羰基化合物、酯、醇等成分[2],这些成分性质各异,生理活性表现多样。临床试验证明,植物挥发油具有抗炎、抗菌、镇咳、祛痰、平喘、镇疼、杀虫、驱虫等作用[3]。因此,近年来,植物挥发油化学成分分析越来越受到国内外学者的重视。金钱松Pseudolarix amabilis隶属于松科Pinaceae金钱松属Pseudolarix,为中国特有的单种属植物,也是国家二级保护植物。分布于江苏、安徽、浙江、江西、湖南等地。金钱松的根皮和近根皮部分被称为土槿皮,因为性辛,温,有毒,具有止痒、杀虫、治疗癣症等作用,在中国民间作为中药入药已有悠久的历史[4]。目前,国内外对该植物的研究主要集中在生物学和生理学特性[5]、遗传多样性[6]以及化学成分[7-8]等方面。而对其叶片挥发油的化学成分研究尚未见相关报道。本研究采用水蒸气蒸馏法提取金钱松叶片挥发油,利用气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)联用技术分析和鉴定挥发油的化学成分,以期为金钱松的综合开发利用提供科学依据。
HTML
-
从江西省林业科学院内随机选取10株金钱松作为样木,植株生长状态良好,无病虫害,树龄41~42 a,于2012年5月中旬采集样叶,随采随蒸。
-
将采集的金钱松鲜叶片剪碎,浸泡1 h,然后分别在自制水蒸气蒸馏器中加入适量沸水和200 g样品蒸馏2 h,收集挥发油,用无水硫酸钠干燥,得淡黄色油状物(提取率为0.04%)。将10株样木叶片提取的挥发油等量吸取并充分混合后,进行GC-MS检测。
-
金钱松叶片挥发油样品中的化学成分及其含量测定采用气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)技术分析。GC(Perkin Elmer Clarus 680型)工作条件:色谱柱为30 m× 0.25 mm×0.25 μm的Elite-5 MS柱,程序升温:初始温度50 ℃保持2 min,以3 ℃· min-1升至140 ℃,保持2 min,再以15 ℃· min-1升至280 ℃保持10 min。进样口温度280 ℃,载气为He,流速1.0 mL· min-1,进样量0.5 μL,分流比10:1。MS(Perkin Elmer Clarus 600 C)工作条件:EI-MS,EI离子源温度180 ℃,接口温度:260 ℃,扫描范围(m/z):50~600。
-
采用Nist谱库、文献检索和人工解析等联合方法,鉴定、确认各成分,利用峰面积归一法计算出各成分相对百分含量。
1.1. 材料
1.2. 方法
1.2.1. 金钱松叶片挥发油提取
1.2.2. 挥发油成分组成及相对含量的测定
1.2.3. 数据处理及质谱检索
-
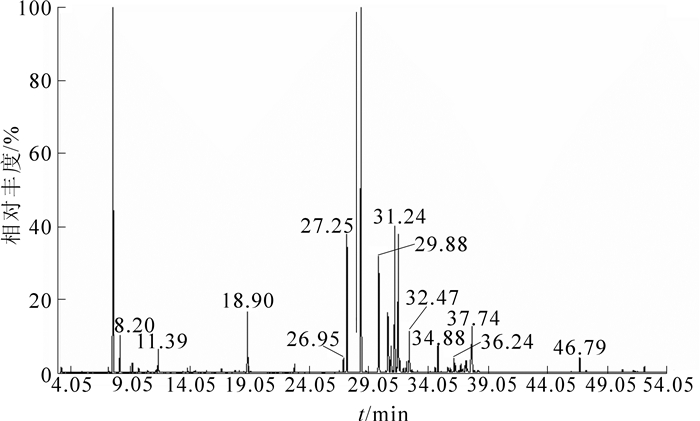
金钱松叶片挥发油经气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)联用分析,从其叶片挥发油中共定量分离出62个组分,经化学工作站数据处理系统和用面积归一化法从其总离子流图(图 1)中计算各组分相对含量,按各峰质谱图经计算机质谱数据库检索,并按各峰质谱裂片图与资料文献核对,确定了其中的49个组分,占总成分的93.35%(表 1)。由表 1可见:金钱松叶片挥发油成分由烃、醇、醛、酯、氧化物等5类化合物组成。在这些成分中,烃类物质有30种,醇类物质有15种,醛类物质有1种,酯类物质有2种,氧化物类物质1种;在挥发油相对含量方面,烃类物质占84.46%,其中(+)-α-蒎烯占31.72%,石竹烯占18.57%;醇类物质占6.76%,醛类物质占0.43%,酯类物质占0.43%,氧化物类物质占1.27%。以烃类化合物相对含量最高,其中在烃类化合物中,又以(+)-α-蒎烯相对含量最高,石竹烯次之。由此可见,金钱松叶片挥发油的主要组分是烃类化合物,(+)-α-蒎烯化合物是单一物质成分最多的。
编号 t/min 化学物 分子式 分子量 相对含量/% 1 3.27 3-甲基-1, 3, 5-戍三醇1, 3, 5-pentanetriol, 3-methyl- C6H14O3 134 0.13 2 7.23 三环萜tricyclene C10H16 136 0.18 3 7.61 (+)-α-薇埽(+)-α-pinene C10H16 136 31.72 4 8.20 莰稀camphene C10H16 136 1.17 5 9.25 对-薄荷-1(7), 3-二烯P-mentha-1 (7), 3-diene C10H16 136 0.32 6 9.78 月桂烯myrcene C10H16 136 0.14 7 10.10 5, 8-二乙基十二院5, 8-diethyldodecane C16H34 226 0.32 8 10.55 顺式-3-己烯醇甲酸酷cis-3-hexenyl formate C7H12O2 128 0.07 9 10.91 顺-β-松油醇cis-β-terpineol C10H18O 154 0.02 10 11.21 邻伞花烃O-cymene C10H14 134 0.09 11 11.39 (-)-梓檬烯(-)-limonene C10H16 136 0.84 12 11.64 桉叶油素cineole C10H18O 154 0.64 13 13.86 萜品油烯terpinolene C10H16 136 0.16 14 14.52 十一烷undecane C11H24 156 0.08 15 15.44 小茴香醇(1R)-(+)-fenchyl alcohol C10H18O 154 0.10 16 15.80 龙脑烯醒campholenic aldehyde C10H16O 152 0.43 17 16.72 5-[1-甲基乙烯基]-2-亚甲基-环己醇cycloHexanol, 2-methylene-5-(1-methylethenyl)- C10H16O 152 0.15 18 17.45 异龙脑isoborneol C10H18O 154 0.67 19 18.22 (-)-4-萜品醇(-)-terpinen-4-ol C10H18O 154 0.59 20 18.60 2-(4-甲基苯基)丙-2-醇2-(4-methylphenyl)propan-2-ol C10H14O 150 0.10 21 18.90 α-萜品醇P-menth-1-en-8-ol C10H18O 154 2.25 22 19.16 1, 8-间孟二烯M-mentha-1, 8diene C10H16 136 0.46 23 22.83 乙酸冰片酷bornyl acetate C12H20O2 196 0.36 24 24.92 石竹烯氧化物caryophyllene oxide C15H24O 220 1.27 25 25.45 (-)-a-荜澄茄油烯(-)-a-Cubebene C15H24 204 0.42 26 26.34 雪松烯Cedrene C15H24 204 0.07 27 26.62 可巴烯Copaene C15H24 204 0.07 28 26.95 法呢烯farnesene C15H24 204 0.60 29 27.25 β-榄香烯β-elemene C15H24 204 5.64 30 28.44 石竹烯caryophyllene C15H24 204 18.57 31 28.85 大牻牛儿烯D germacrene D C15H24 204 0.06 32 30.49 α-愈创木烯α-guaiene C15H24 204 5.28 33 30.65 β-按叶烯β-Eeudesmol C15H24 204 3.36 34 31.24 β-瑟林烯β-selinene C15H24 204 6.16 35 31.69 a-衣兰油烯a-muurolene C15H24 204 5.71 36 32.23 γ-衣兰油烯γ-muurolene C15H24 204 0.47 37 32.47 δ-杜松烯δ-cadinene C15H24 204 1.79 38 32.58 杜松院-1, 3, 5-三烯cadina-1, 3, 5-triene C15H22 202 0.10 39 33.32 1(10), 3, 8-杜松三烯cadala-1(10), 3, 8-trie C15H22 202 0.05 40 34.63 石竹烯醇Caryophyllenyl alcohol C15H26O 222 0.26 41 35.71 异丁子香烯isocaryophillene C15H24 204 0.28 42 36.24 蛇床-6-烯-4-醇selina-6-en-4-ol C15H26O 222 0.54 43 36.36 律草院-1, 6.二烯-3-醇humulane-1, 6-dien-3-ol C15H26O 222 0.25 44 36.64 异喇叭烯isoledene C15H24 204 0.06 45 36.81 桉叶醇eudesmol C15H26O 222 0.35 46 37.18 香樞醇nuciferol C15H26O 222 0.24 47 37.25 τ-杜松醇T au.-cadinol C15H26O 222 0.47 48 38.24 (+)-喇叭烯(+)-ledene C15H24 204 0.16 49 46.79 西柏烯cembrene C20H32 272 0.73 Table 1. Components and their contents for essential oil from the leaves of Pseudolarix amabilis
-
GC-MS联用技术是将色谱技术、质谱技术与计算机技术3种现代化技术紧密结合的产物,是目前分析植物挥发油成分十分有效的方法。该技术可以对化学组成极其复杂的挥发油进行定性、定量分析,不仅能确定化合物的元素组成,还能鉴定化合物的分子结构。经过GC-MS联用技术对金钱松叶片挥发油的测定,发现金钱松叶片挥发油成分中以烃类物质种类最多,达30种;其次是醇类物质,达15种;醛类与氧化物类物质种类数相当,各为1种;酯类物质种类有2种。金钱松叶片挥发油组分中相对含量最高的是(+)-α-蒎烯(31.72%),石竹烯(18.57%)次之。在所鉴定的成分中,许多主成分具有可开发利用价值和前景,例如α-蒎烯以及含有α-蒎烯的植物精油对储藏物害虫衣鱼Lepisma saccharina,斜纹夜蛾Spodoptera litura,大田害虫棉铃虫Helicoverpa armigera,土传病菌尖孢镰刀菌Fusarium oxysporum具有良好的控制作用[9];此外,α-蒎烯有明显镇咳和祛痰功能,并有抗真菌、驱虫、杀虫、除螨的作用[10];石竹烯、β-瑟林烯、α-衣兰油烯、α-愈创木烯、δ-杜松烯、莰烯成分常作为香精香料合成原料[11];β-榄香烯是抗肿瘤有效成分,具有很强杀灭肿瘤细胞及抑制肿瘤生长作用,其乳剂是临床应用与治疗肿瘤的二类新药[12]。金钱松叶片挥发油组分中石竹烯、β-瑟林烯、α-衣兰油烯、α-愈创木烯、δ-杜松烯、莰烯等均可作为香精香料合成原料,应用前景广泛。







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: