-
氮是中国水体主要污染物,可引起水体富营养化并使其发黑变臭。中国在“十二五”期间把氨氮纳入污染物总量控制指标体系,对氨氮进行重点控制。生物法是目前最常用的废水脱氮方法,通过硝化作用将氨氮转化为硝态氮,然后通过反硝化作用将硝态氮还原成为氮气,以此达到脱氮的目的。然而这种脱氮技术在应用过程中存在碳源不足、脱氮时间长、耗能大、处理高浓度含氮废水时效果不理想等问题,其应用和发展也因此受到很大限制;开发处理效果好、应用前景广的新型脱氮技术一直是研究的热点[1-2]。限制自养硝化反硝化(OLAND)工艺是比利时Gent大学微生物生态实验室开发的一种新型的生物脱氮工艺[3],相对于传统生物脱氮具有能耗低、反应时间短、污泥产量少、不需投加碳源、脱氮效率高等优点[4]。笔者基于OLAND工艺原理,分析了系统中活性微生物的种类、分布及特性,讨论了脱氮过程的主要影响因素及厌氧氨氧化过程的强化措施,并指出了该工艺需要进一步研究的方向和重点,以期为该工艺的深入研究和推广应用提供参考。
HTML
-
OLAND是限氧亚硝化与厌氧氨氧化相耦合的生物脱氮工艺,在亚硝态氮向硝态氮的转化中通过控制溶解氧含量,使反应因缺少足够的氧气作电子受体而受到阻碍,从而使氨氧化反应主要产生亚硝态氮;随后厌氧氨氧化菌(anammox)在厌氧条件下以亚硝态氮作电子受体将氨氮氧化成氮气[5]。反应方程式为[6]硝化:1.300 NH4++1.950 O2 = 1.300 NO2-+ 2.600 H++1.300 H2O;厌氧氨氧化:NH4++1.300 NO2- = 0.200 NO3-+1.050 N2+2.000 H2O;总反应:NH4++0.850 O2 = 0.090 NO3-+0.455 N2+1.140 H++1.430 H2O。
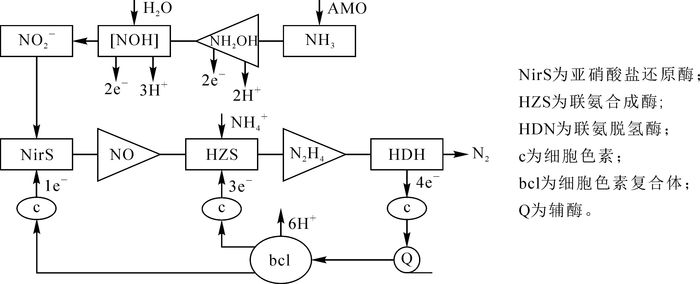
目前,OLAND工艺的代谢途径尚不明确。大量实验数据表明其脱氮过程主要分为以下几步:短程硝化阶段,氨(NH3)在氨单加氧酶(AMO)的作用下被氧化成羟胺(NH2OH),后者在羟氨氧化还原酶(HAO)的作用下生成硝酰基(NOH),并进一步被氧化为亚硝态氮,其中所需氧来源于水分子[7-9]。厌氧氨氧化阶段,亚硝态氮在亚硝酸盐还原酶(NirS)的作用下被还原为一氧化氮,与氨氮一起在联氨合成酶(HZS)的催化下缩合生成联氨(N2H4),并最终在联氨脱氢酶(HDH)的作用下转化为氮气[10]。其可能的代谢途径如图 1所示。
-
OLAND系统中主要含有氨氧化菌(AOB)和厌氧氨氧化菌(AnAOB)2种微生物。其中AOB主要生活在有氧区,其菌属以亚硝化单胞菌属Nitrosomonas和亚硝化螺菌属Nitrosospira为主[11]。张丹等[12]利用亚硝化单胞菌属和亚硝化螺菌特异探针NSM156,NSV443和荧光标记原位杂交技术(fluorescence in situ hybridization,简称FISH)对OLAND稳定运行阶段的氨氧化菌进行了分析,发现亚硝化单胞菌属数量在AOB中占72.5%左右,而亚硝化螺菌并未被检测到,说明在OLAND稳定运行过程中氨氧化菌主要为硝化单胞菌属。
缺氧区和厌氧区主要分布菜花型的生物聚集体,CHEN等[13]推测这些生物聚集体可能以AnAOB为主。目前已知的AnAOB共有5个属,分别为Scalindua,Kuenenia,Anammoxoglobus,Jettenia以及Brocadia[14]。纯化细胞的16S rRNA系统发育分析显示,AnAOB存在于浮霉状菌目Planctomycetales谱系中,呈球形或者卵形,大小一般为0.8~1.0 μm,颜色一般呈红色,性状黏稠,含有较多的胞外聚合物,其结构如图 2所示[15];此外,AnAOB至少需要1010 ~ 1011个·L-1细胞密度才能较好地显现厌氧氨氧化活性[16-17]。WINKLER等[18-19]利用FISH技术研究了厌氧颗粒污泥反应器内细菌的空间分布,并且与亚硝化/厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥(AGS)和移动床生物膜反应器(MBBR)微生物群落进行了比较,发现AnAOB的优势菌属为Brocadia,同时发现MBBR生物膜上还存在少量的Anammoxoglobus。
-
OLAND工艺的核心技术是在限氧亚硝化阶段通过严格控制溶解氧水平,将50%物质的量的氨氮转化为亚硝态氮,从而实现硝化阶段氨氮/亚硝态氮=1:(1.2±0.2)的稳定出水比例,为厌氧氨氧化阶段提供理想的进水,提高整个工艺的脱氮效率[20]。有研究发现[21]:AOB的氧饱和常数为0.2~0.4 mg·L-1,亚硝酸氧化菌(NOB)的氧饱和常数为1.2~1.5 mg·L-1,因而,低质量浓度的溶解氧是实现亚硝态氮积累的先决条件。董远湘等[22]研究溶解氧对生物膜反应器硝化性能的影响发现,溶解氧质量浓度为0.5~1.0 mg·L-1时,氨氧化阶段出水比例为氨氮/亚硝态氮=1:(1.2±0.2);当溶解氧在0.5 mg·L-1以下时,氨氮质量浓度急剧升高;而溶解氧低于0.2 mg·L-1时可能导致系统严重损坏。高质量浓度溶解氧使AnAOB活性受到抑制。研究表明:当溶解氧质量浓度为0.064 mg·L-1时,AnAOB的活性受到可逆性的抑制,而当溶解氧质量浓度达0.576 mg·L-1时则不可逆[23]。STEOUS等[24]通过间歇式曝气方式也发现,氧体积分数大于0.5%空气饱和度(以空气中氧体积分数为100%)时,AnAOB的活性完全消失,而冲入氩气排除反应器内的氧气后,AnAOB的活性得以恢复。由此可见,氨氧化阶段和厌氧氨氧化阶段对溶解氧的响应互相矛盾,如何满足这2个阶段对溶解氧的要求,需对工艺做进一步的优化。
-
OLAND反应器内的底物主要为氨氮和亚硝态氮。高质量浓度氨氮对微生物细胞有毒害作用,其毒害效果由游离氨(FA)引起。VADIVELU等[25]研究表明:AOB活性在FA质量浓度为10.0~150.0 mg·L-1时受到抑制,NOB活性在FA质量浓度为0.1~1.0 mg·L-1时即受到抑制[25-26],因此可通过调高系统中FA质量浓度来抑制NOB活性,从而控制硝态氮的形成,达到积累亚硝态氮的目的。但FA质量浓度过高也会抑制AnAOB活性,WAKI等[27]发现13.0~90.0 mg·L-1的FA对AnAOB有毒害作用。因此,FA的质量浓度须控制在适宜范围。KUMAR等[28]研究认为:20.0~30.0 mg·L-1的FA利于亚硝态氮的积累及厌氧氨氧化的稳定进行。
亚硝酸盐作为一种生物抑制剂,对厌氧氨氧化过程有明显的抑制作用[29-30]。STROUS等[31]研究发现:温度在20~43 ℃,pH值在pH 6.7~8.3,亚硝态氮质量浓度高于100.0 mg·L-1时,AnAOB活性受到抑制,但这种抑制是可逆的,通过添加微量的羟胺和肼就可恢复。EGLI等[23]实验表明:亚硝态氮质量浓度由60.0 mg·L-1升至75.0 mg·L-1,AnAOB活性下降约28%;亚硝态氮质量浓度高于70.0 mg·L-1,AnAOB失去竞争优势;亚硝态氮质量浓度达185.0 mg·L-1时,AnAOB完全失去活性。因此,氨氮和亚硝酸盐的影响是相互的,需综合考虑这2种底物对脱氮过程的抑制作用。
-
pH值对脱氮过程的影响主要源于其对AOB和NOB活性的影响。研究表明:AOB适宜pH值为pH 7.0~8.5,NOB为pH 6.0~7.5,可见弱碱性条件有利于亚硝态氮的累积。原因可能是碱性条件下亚硝态还原酶的活性受到抑制,而硝态氮还原酶活性基本不受影响[32-33]。弱碱性条件也利于厌氧氨氧化的稳定进行。EGLI等[23]研究发现:当系统氢离子浓度指数为pH 8.0时,厌氧氨氧化的反应速率达到最大;郑平等[29]研究表明,当系统中氢离子浓度指数为pH 6.0~7.5时,厌氧氨氧化速率随pH值升高逐渐增加,但当pH值继续升至pH 9.5,厌氧氨氧化速率则不断下降,由此认为:最适pH值为pH 7.5左右。陈曦等[34]也得到了类似结论。
OLAND工艺脱氮主要通过AOB和AnAOB实现,这2种菌都存在适宜其生长繁殖的温度范围。研究发现,温度高于20.0 ℃时AOB的最大生长速率大于NOB,而温度超过40.0 ℃时,AOB体内酶就会遭到破坏。AnAOB是中温菌,适宜的生长温度为32.0~34.0 ℃[24],DAVEREY等[35]研究表明:当温度在25.0~33.5 ℃时,厌氧氨氧化活性(SAA)随温度升高而增大。在实际生产应用中废水温度多为常温,甚至低于常温,因此,许多研究者对低温条件下实现高效厌氧氨氧化技术进行了探索。少数实验在低温条件下成功启动了厌氧氨氧化反应器,但启动时间较长,氮去除速率相对较低[36-37]。CLIPPELEIR等[38]通过提高溶解氧质量浓度,在15.0 ℃低温条件下,脱氮速率达到了0.5 g·L-1·d-1(与29.0 ℃相当),但相关反应机制并未报道。因此,可将温度控制在25.0~34.0 ℃,以保证AOB和AnAOB的正常代谢。
DAVEREY等[39]采用多元回归对实验数据进行分析,发现SAA与pH和温度(T)的关系可用二阶多项式方程表示:
YSAA=-0.183 775+0.001 389T+0.042 741pH-0.000 023T2-0.002 906pH2+0.000 12·T·pH。
JAROSZYSKI等[40]研究发现FA质量浓度也受pH值和温度的影响,表达式为: ρFA=(ρ总氮×10pH)/(e[6 344/(293+T)] +10pH)。
由此可见:通过pH值和温度的相互协作可以提高SAA,调节FA质量浓度,提升系统的脱氮效率。目前,各因子之间的交互影响研究较少。如何合理协调pH值、温度、溶解氧、FA等因素可能是进一步提高OLAND脱氮效率的研究方向。
3.1. 溶解氧质量浓度对脱氮过程的影响
3.2. 底物质量浓度对脱氮过程的影响
3.3. pH值及温度对脱氮过程的影响
-
AnAOB的生长非常缓慢,对环境条件较为敏感,一定程度上制约了厌氧氨氧化效率,从而限制了OLAND工艺的脱氮效率。目前,OLAND工艺的强化研究重点在于提高反应器中AnAOB的生物量和生物活性,提高厌氧氨氧化脱氮效率,从而提升厌氧氨氧化效率。
-
竹炭不仅具有较高的比表面积,而且还含有羟基、羧基以及呈碱性的芳香族等,这些特性为微生物提供了有利的生长环境[41]。CHEN等[42]在厌氧污泥启动试验中发现,竹炭有利于AnAOB聚集;就厌氧氨氧化反应启动时间而言,添加体积分数约10%的竹炭比添加相同量的多面空心塑料球要短12 d。因此认为,可通过添加适量的竹炭或竹炭制品作为微生物载体用以聚集AnAOB,以达到快速启动厌氧氨氧化过程的目的。然目前对于相关的机理问题还不甚明了,需进一步深入探索研究。
适量的二氧化锰(MnO2)能够提高AnAOB体内酶的活性,从而提高厌氧氨氧化效率。QIAO等[43]通过添加二氧化锰使酶活性提高了78.2%,反应器总氮去除负荷从0.465 kg·m-3·d-1升至0.921 kg·m-3·d-1。AnAOB体内富含血红素,而铁离子是参与血红素合成的重要元素,因此可通过添加铁离子促进AnAOB的生长。张蕾等[44]研究表明:当二价铁浓度从0.050 mmol·L-1增至0.065 mmol·L-1时,氨氮和亚硝酸氮去除率分别增加200.0%和150.0%;三价铁浓度从0.050 mmol·L-1升至0.065 mmol·L-1,氨氮和亚硝酸氮去除率分别增加128.0%和65.8%。彭厦等[45]发现当进水二价铁浓度为0.080 mmol·L-1时,氨氮和亚硝酸氮的去除率达95.0%。这些研究表明:添加适当浓度的MnO2和铁离子有利于提高系统的脱氮效率。
-
菌种流加技术也是强化厌氧氨氧化反应的有效途径,不仅补充了所需微生物的数量,而且还引入了微生物生长所必不可少的生长因子,使微生物的活性得到进一步的激发。采用菌种流加技术可有效缩短厌氧氨氧化的启动时间。唐崇俭等[46]向上流式滤器中添加高效厌氧氨氧化污泥(比污泥活性为1.68 g·g-1·d-1),反应器立即呈现厌氧氨氧化功能。此外,菌种流加也可有效缓解基质自抑制作用,克服有机物和毒物所致的负面影响。唐崇俭等[46]在研究流加菌种对含氮有机废水和制药废水厌氧氨氧化处理效果的影响时发现流加菌种后,有机含氮废水(有机物质量浓度为500 mg·L-1)氨氮去除率由不足20%升至70%~80%;制药废水处理水力停留时间由16.00 h缩短为1.11 h,氨氮去除率由20%升至80%。TANG等[47]通过连续添加生物催化剂(富含高效厌氧氨氧化菌的污泥)强化富铵废水中氮的去除时发现,当连续添加0.5 g·d-1时,脱氮效果得到显著的改进。
-
STROUS等[31]研究表明:联氨(N2H4)是厌氧氨氧化过程的中间产物,厌氧氨氧化反应能以联氨(N2H4)为电子供体、NO2-为电子受体进行脱氮反应;适量的联氨(N2H4)可快速解决高质量浓度NO2-对AnAOB的抑制作用。蔡庆等[48]在序批式活性污泥法(SBR)反应器中接种全自养脱氮污泥启动厌氧氨氧化过程时发现,当联氨(N2H4)质量浓度低于4.51 mg·L-1时,总氮去除速率随联氨(N2H4)质量浓度增加而增大,联氨(N2H4)质量浓度为4.51 mg·L-1时,总氮去除速率达最大,为不添加联氨(N2H4)时的1.45倍;然而继续提升联氨(N2H4)质量浓度时,总氮去除速率呈下降趋势,当联氨(N2H4)质量浓度为21.87 mg·L-1时总氮的去除速率仅为4.51 mg·L-1时的73.1%;硝态氮的产生速率随联氨(N2H4)质量浓度增加显著降低,当联氨(N2H4)质量浓度为21.87 mg·L-1时,几乎检测不到硝态氮。Andrews抑制模型拟合结果表明N2H4的半饱和常数为0.68 mg·L-1,抑制常数为26.96 mg·L-1。
-
一定强度的外加磁场或电场可迅速提升AnAOB的降解速率[49]。LIU等[50]研究发现:外加磁场强度为75 mT(实验区间16.8~95.0 mT)时,AnAOB的活性达到最大,与不外加磁场相比提高了50%;连续稳定厌氧氨氧化实验表明:外加磁场(磁场强度为60 mT)后,启动时间缩短1/4,最大脱氮速率提高30%。ZHANG等[51]采用铁电极强化厌氧氨氧化过程,当电压小于0.6 V时,AnAOB的脱氮能力为1.21 kg·m-3·d-1,与空白组相比提高了24%。ZHAN等[52]研究了微生物电解电池优化厌氧氨氧化反应,发现当外加电场电压为0.2 V时,总氮去除率为70.3%,电压为0.4 V时,总氮去除率升至92.6%,但继续提高电压强度总氮去除率呈下降趋势。
4.1. 添加物的强化
4.2. 菌种流加的强化
4.3. N2H4的强化
4.4. 电磁场的强化
-
OLAND工艺通过控制溶解氧质量浓度,将50%物质的量的氨氮转化为亚硝态氮,并以亚硝态氮为电子受体将氨氮氧化成氮气,具有能耗低、反应时间短、污泥产量少、不需外加碳源、脱氮效率高等优点,在含氮废水处理方面具有潜在的应用前景。然而环境因子对OLAND工艺脱氮效率的影响非常复杂,各因子间的交互作用,厌氧氨氧化菌生长缓慢,对环境条件敏感,启动较慢等问题限制了OLAND工艺的在实际工程中的应用推广。今后,OLAND工艺研究可以从以下几方面加以深入和突破。① 多因子的交互作用及机制研究,优化实现高脱氮效率工艺条件。② 因子影响的机制探索。将各因子对脱氮效率影响的宏观表现与微观机制有机结合,有效控制因子条件。③ 强化措施及机制研究。将厌氧氨氧化过程强化措施应用于OLAND工艺,分析强化方法的可行性,探明强化作用机制,进一步提高脱氮效率。











 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
