-
转座子(transposable elements,TEs)被定义为能够在生物体基因组中移动的DNA序列,能在同一染色体的不同位点或者不同染色体之间转移[1]。由于起源和进化路径的差异,TEs包含不同的家族。FINNEGAN[2]首次根据TEs的转座中间体和转座机制将转座子分为Ⅰ类RNA转座子(retrotransposons)和Ⅱ类DNA转座子(DNA transposons)。Ⅰ类通过RNA介导的复制-粘贴过程迅速增殖,RNA转座子进一步分为:长末端重复序列反转录转座子(long terminal repeat,LTR,也称为内源性逆转录病毒)、非LTR反转录转座子(non-LTR)、PLEs(penelope-like elements)、DIRS(dictyostelium intermediate repeat sequence)[3]。Ⅱ类使用剪切-粘贴机制增加拷贝数[4-5],包括末端反向重复序列(terminal inverted repeat,TIR)、微型反向重复序列转座子(miniature inverted repeat transposable elements,MITEs)和Helitrons[2]。自然选择和遗传漂变导致TEs在不同物种中类别的比例和含量都不相同,在同一物种的个体之间也存在差异[6]。研究表明:人类基因组大约一半为TEs[7],其中RNA反转座子约42%[8],LTR反转座子约8%[9];在小鼠Mus musculus和人类的基因组中,长散在核元件(long interspersed nuclear elements-1,LINE-1)大约20%[10];小麦Triticum aestivum和小麦白粉病真菌Blumeria graminis基因组中,90%的序列是TEs[11];水稻Oryza sativa转座子的20%~40%中,Ⅱ类DNA转座子含量甚至高于Ⅰ类RNA转座子4倍以上[12],其中LTR约14%,而non-LTR反转座子却只有1%[13]。在玉米Zea mays基因组中,TEs含量高达85%,其中LTR反转座子和其他TEs家族含量分别为70%和15%[14-15]。通常,TEs对宿主有很多积极的影响。例如,TEs的插入控制着包括牵牛花Ipomoea purpurea在内的所有花色变化[16],贡献了可供选择的性状。反转录转座子的正常转座不仅可以产生果肉呈红色的血橙Citrus sinensis[17],还控制着葡萄Vitis vinifera[18]和番茄Solanum lycopersicum[19]等果实的颜色和形状,也参与着番茄茎尖分生组织的形成[20],还影响着哺乳动物骨骼的发育[21]。并且,可以利用TEs的激活诱导疾病的发生,从而明确疾病的机理,寻找出治疗的药物与方法。然而,由于TEs的负面影响而被称为“垃圾DNA”。例如,LINE-1是人类基因组中唯一的自主转座元件,它的表达成为许多恶性肿瘤的标志[22],并且导致包括精神分裂症在内的众多精神疾病[23],人类的120多种遗传疾病都是由于LINE-1的插入而引起的[24],其拷贝数的增加会导致腺瘤性息肉病基因(APC)肿瘤抑制基因突变从而引发人类直肠癌(colorectal cancer,CRC)[25]。ZmNAC111
基因是维持玉米幼苗耐旱性的关键基因,MITE转座子的插入会下调ZmNAC111的表达,从而引起玉米幼苗的干旱敏感性增强[26]。在小鼠生殖系中,TEs增加拷贝数会导致其不育[27],并有调控具有双向命运细胞的潜能[28]。TEs插入基因组中不仅破坏基因的功能,而且对邻近基因的表达有极性影响[29],对着丝粒稳定性同样具有重要的作用。由此可见,TEs转座破坏了宿主基因组的稳定,也搅动了宿主的基因表达调控网络,因此,TEs活性通常受到宿主多种表观遗传修饰机制的调控,例如,DNA甲基化、抑制性组蛋白修饰、小RNA途径和染色质途径。DNA甲基化是高等真核生物中广泛存在的保持TEs沉默的表观遗传修饰方式,包括从头甲基化、维持甲基化和脱甲基3个水平[30]。哺乳动物基因组中主要为CG二核苷酸序列环境的胞嘧啶甲基化,由DNA甲基转移酶1(DNA methyltransferase 1,DNMT1)和DNA甲基转移酶3(DNA methyltransferase 3,DNMT3)维持,植物中还具有CHG和CHH(H表示A、T或C)胞嘧啶环境的甲基化[31],则是由与DNMT3相似的域重排甲基转移酶1(domains rearranged methyltransferase 1,DRM1)和域重排甲基转移酶2(domains rearranged methyltransferase 2,DRM2)催化[32]。本研究论述了TEs沉默与DNA甲基化的关系,重点总结了以DNA甲基化为主的转座子沉默机制最新研究进展,归纳了环境因素通过DNA去甲基化调控转座子跳跃的机理。 -
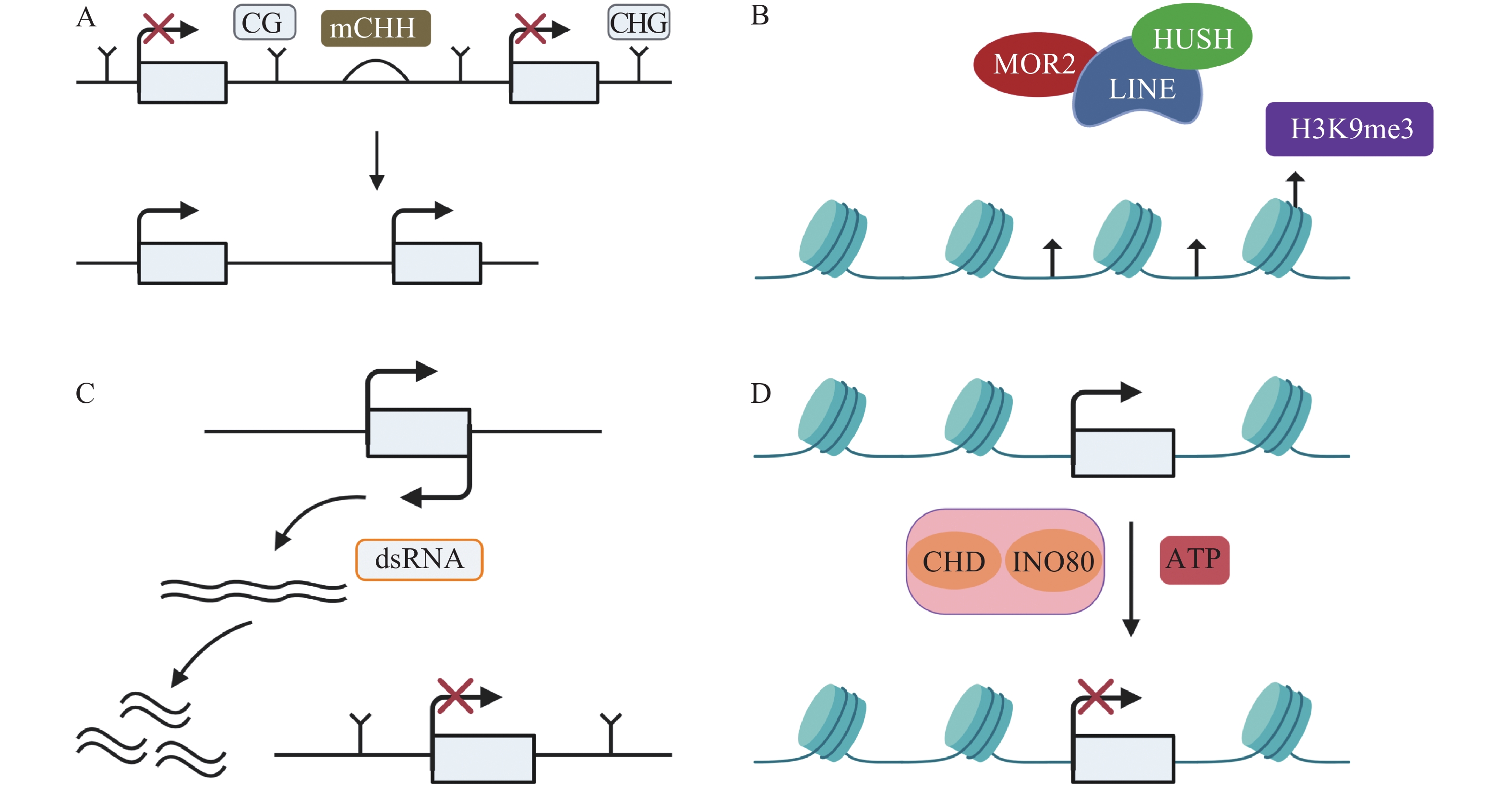
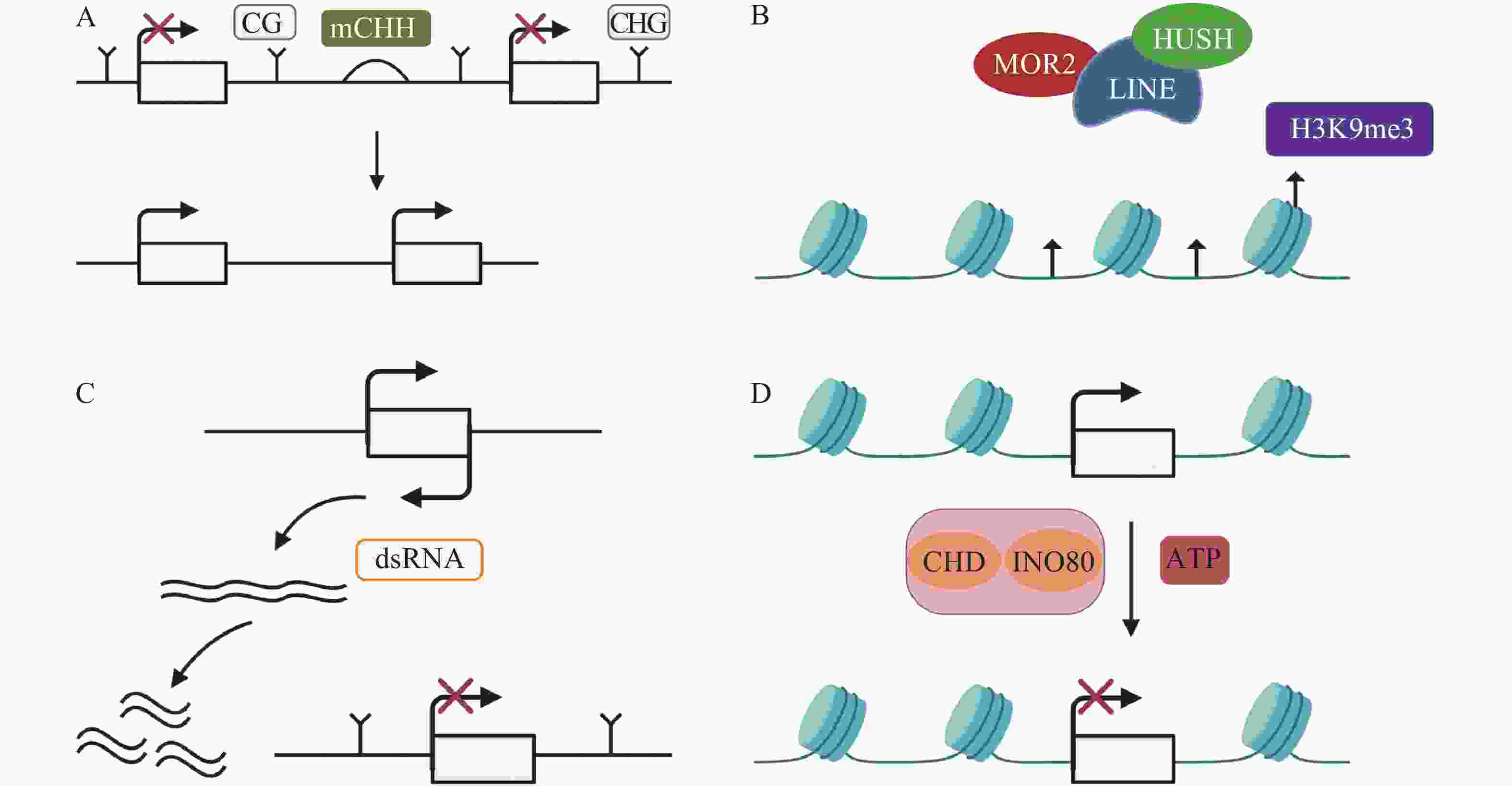
TEs沉默分为检测、扩增和抑制3个部分[33],保持TEs沉默通常受DNA甲基化、抑制性组蛋白修饰、小RNA途径以及染色质途径的调控。(1)例如,在玉米基因组中,mCHH甲基化岛常常插入活跃基因与沉默转座子之间,去甲基化会导致沉默的转座子表达上调,RNA指导的DNA甲基化(RNA-directed DNA methylation,RdDM)能够维持转座子的沉默[34],mCHH甲基化岛缺失会导致CG、CHG的丢失,同时上调TEs活性(图1A)。DNMT1在hNPCs (human neural progenitor cells)维持DNA甲基化,通过CRISPR-Cas9技术去除DNMT1后,导致CPG甲基化水平降低,激活LINE-1,进一步影响与精神疾病有关的基因[35]。(2)抑制性组蛋白修饰是另一个沉默TEs的途径。通常认为组蛋白H3的赖氨酸9和27的三甲基化H3K9me3 (histone H3 Lys9 trimethylation)、H3K27me3 (histone H3 Lys27 trimethylation)能够沉默TEs。MORC2蛋白和HUSH (human silencing hub)与在进化上较年轻的全长LINE-1结合,诱导组蛋白H3K9me3富集,从而沉默TEs(图1B)[36]。水稻的H3K4特异性脱甲基酶蛋白JMJ703介导H3K4脱甲基,当JMJ703活性受到影响时,增加H3K4me3积累,2个LINE元素被激活转座[37]。(3)小RNA途径同样是沉默TEs的有效途径。AT(alternative transposition)产生的CIs(composite insertions)的反向复制被转录生成dsRNA(double-stranded RNA),等位基因P1-WW-ID1和P1-WW-ID4上富集21、22、24 nt (nucleotide) siRNA,然后siRNA介导玉米Ac/Ds转座子沉默(图1C)。这是首次提出TEs自主介导的沉默[38]。RNA与Piwi (P-element-induced wimpy testis)蛋白相互作用结合形成piRNAs,Hsp70伴侣蛋白是piRNAs生物合成的主要参与者,在果蝇Drosophila生物体中,Hsp70伴侣蛋白遭受热激胁迫导致piRNAs的合成被破坏,因此在转录后水平增加了TEs的表达[39]。(4)染色质途径对TEs的沉默同样也很重要。染色质重塑复合物(chromatin remodelers)包括CHD、SWI/SNF、INO80、SWR1等,它能利用ATP水解的能量移动或者重组核小体,从而沉默TEs(图1D)[40-41]。SWI/SNF家族中SWI3B协同HDA6 (histone deacetylase 6)增加H3K9me2水平,沉默TEs,同时,MET1和SUVH4/5/6也参与增加H3K9me2以及DNA甲基化维持TEs沉默[42]。
-
DNA甲基化在TEs沉默中的作用已被很多研究证实。毛竹Phyllostachys edulis的DNA甲基化水平经过甲基化抑制剂5-氮杂胞苷和γ射线的处理后显著降低,具有转座活性的MITEs家族转座子PhTst-3-79的转座频率相比野生型对照显著增加,并且DNA甲基化随甲基化抑制剂浓度和γ射线辐照剂量增加而下降,TEs的转座频率也随之增加[43]。ZHOU等[44]鉴定的毛竹基因组全长LTR反转录转座子PHRE2(Phyllostachys edulis retrotransposon 2)经过脱落酸(ABA)、水杨酸(SA)、γ射线处理后,甲基化水平显著降低,而拷贝数显著增加。
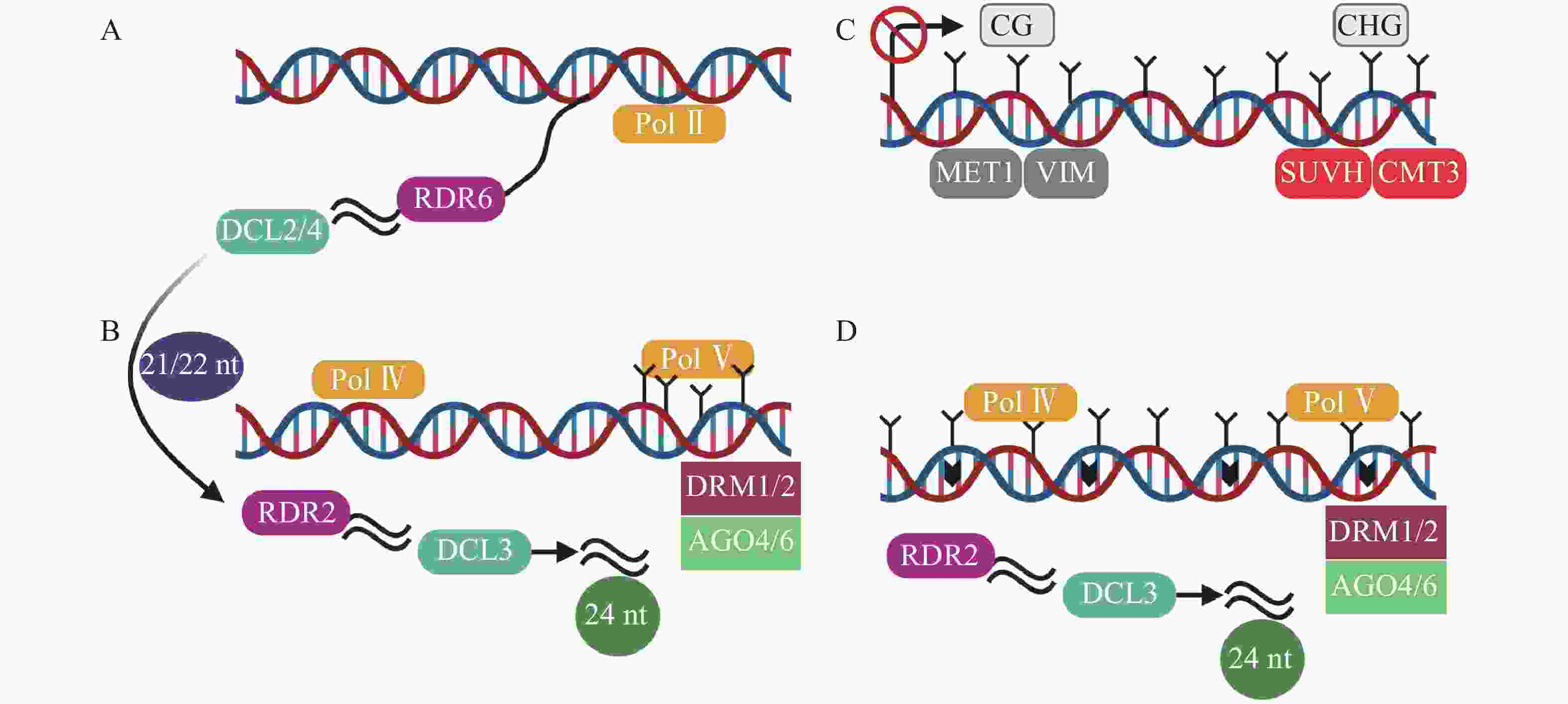
转录后基因沉默(post-transcriptional gene silencing,PTGS)以RDR6合成的双链RNA为起始,然后在由DCL2/4(dicer-like 2/4)介导产生21~22 nt (nucleotide) sRNA(图2A),招募DRM1/2产生5-甲基胞嘧啶(5mC)[45]。其中,21 nt sRNA在转录后水平和24 nt sRNA在转录水平指导TEs沉默[46]。RdDM是开花植物维持TEs沉默的主要机制[47]。RdDM是由RNA聚合酶Ⅳ (RNA polymerase Ⅳ,Pol Ⅳ)介导RNA转录起始,依赖RNA的RNA聚合酶2 (RDR2)合成双链RNA,然后双链RNA在RDR2和DCL3(dicer-like 3)作用下,降解为24 nt sRNA,AGO4/6 (ARGONAUTE 4/6)蛋白与24 nt sRNA结合,最终由DRM1/2介导DNA甲基化(图2B)[31, 48-49]。最新的关于植物non-CG甲基化的研究中,在转座子失活的3个阶段基础上,提出了第4个阶段[45]。在番茄基因组中,第1阶段为转录后基因沉默,LTR反转座子在Pol II(RNA polymerase II)等参与下,生成21~22 nt sRNA(small RNA)(图2A)。第2阶段是RdDM的短暂参与,LTR拷贝数增加,RdDM导向LTR甲基化(图2B)。第3阶段不包含RdDM途径,而是由MET1和CMT3维持沉默(图2C)[50]。第4阶段中,沉默的LTR反转座子失去转座能力,不再受MET1和CMT3的靶向,再次开始转录,RdDM第2次增加LTR反转座子甲基化水平(图2D)。
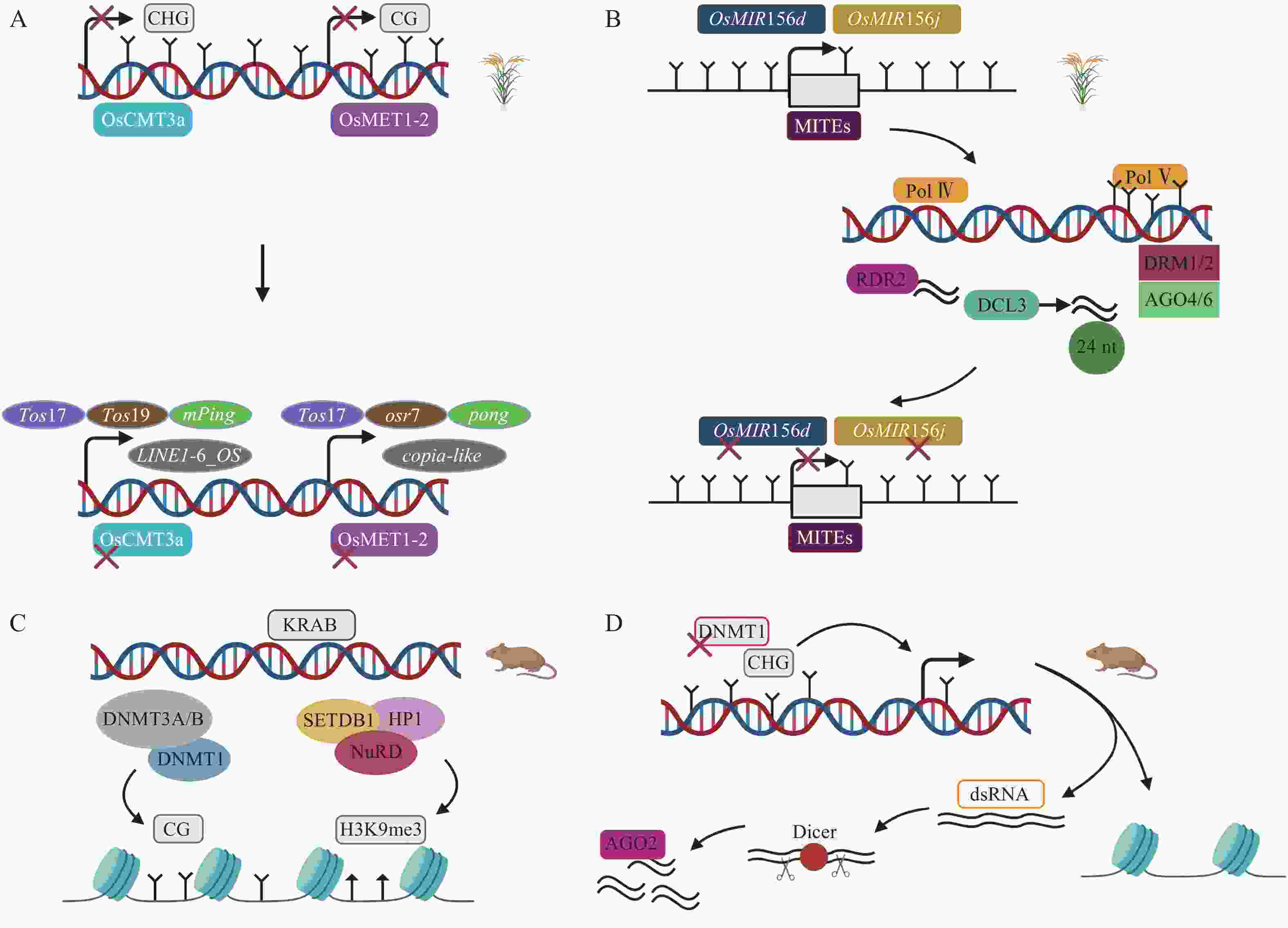
甲基化酶对DNA甲基化的维持是非常重要的,间接调控TEs的活性。在水稻基因组中,染色体甲基化酶OsCMT3a维持CHG甲基化维持TEs沉默,转座子Tos17处理的OsCMT3a突变体甲基化水平降低,繁殖阶段时,8个TEs家族发生转座,其中包括1个LINE,1个MITE等[51]。关于水稻基因组甲基化水平下调而沉默TEs的研究中,在DNA甲基转移酶OsMET1-2纯合突变体中发现,CG甲基化损失激活包括低拷贝LTR反转座子copia-like在内的TEs[52](图3A)。在拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana中,关于RdDM通路的研究已有很多,但很少有明显RdDM通路介导的发育表型变化。RdDM途径影响水稻TEs表达从而导致水稻表型发生变化。OsMIR156d和OsMIR156j是水稻中促进分蘖的基因,其启动子区域的MITEs被RdDM介导甲基化,抑制OsMIR156d和OsMIR156j基因的表达,从而调控水稻的分蘖[49](图3B)。这在表观遗传水平上对调控农艺性状的表达具有重要意义。另一个沉默TEs的关键通路涉及KRAB-ZFPs(krüppel-associated box-zinc-finger proteins)。在小鼠胚胎发生早期,KRAB-ZFPs特异识别TEs,KAP1(KRAB-associated protein 1)作为辅助因子,在组蛋白甲基转移酶SETDB1(SET domain bifurcated 1)、HP1(heterochromatin protein 1)以及组蛋白去乙酰化酶复合物NuRD(nucleosome remodeling deacetylase)等作用下形成压制性染色质结构,维持H3K9me3,抑制内源性逆转录病毒(endogenous retrovirus,ERVs),胚胎干细胞(embryonic stem cells,ESCs)KAP1缺失将导致ERVs的上调,并且,DNMT1、DNMT3A/B也参与沉默ERVs,但是敲除DNMT1、DNMT3a/b后,KRAB-ZFPs仍然维持绝大多数ERVs的沉默[53-55](图3C)。小RNA途径可以作为TEs激活后的快速防御,而抑制性组蛋白修饰作为接下来的缓慢防御。小鼠ESCs中,DNMT1缺失导致CPG甲基化水平从85%降到20%,DNA去甲基化诱导TEs激活,这是因为低甲基化时的反义TEs转录,核酸内切酶Dicer切割dsRNA,接下来AGO2(ARGONAUTE2)与小RNA结合,基于endosiRNA(endogenous short interfering RNAs)的抑制机制沉默甲基化丧失激活的TEs[56](图3D)。
无论Ⅰ类或Ⅱ类TEs的活性,都与DNA甲基化水平密切相关。En/Spm DNA家族转座子也称CACTA转座子[57]。在红肉萝卜Raphanus sativus中,CACTA转座子高度甲基化导致其拷贝数下降,同时甲基化扩散至花青素合成基因RsMYB1启动子区域,导致基因RsMYB1表达下调,影响花青素的积累[58]。有研究通过分析癌症数据库,发现400多个TEs表达上调,其中包括HERVs (human endogenous retroviral)、LINE、SINE等,接近2/3的TEs表达上调似乎是由于邻近区域DNA甲基化的损失导致的[59]。敲除番茄基因组中对CHG甲基化起关键作用的KYP和CMT3基因后,LTR反转座子富集在上调基因的启动子区域[45]。DNA糖基化酶介导的主动去甲基化同样可以激活水稻反转座子[60]。反转录转座子MRL (multiretrotransposon-like)插入大麦Hordeum vulgare基因组启动子区域,可以极大增强HvAACT1基因的表达,从而增强大麦抵抗铝毒害的能力。但是MRL的插入通常伴随着高甲基化,因此只有MRL转座子去甲基化才能增强大麦耐铝性[61]。水稻中,LTR反转座子的插入导致有害的异位重组,高度甲基化抑制LTR反转座子的活性,从而抑制这种有害作用[62]。在小鼠中,胞嘧啶甲基化在缺乏DNMT1的胚胎中下调,导致内源性逆转录病毒ERVs(endogenous retrovirus)上调,这是首次证明DNA甲基化在小鼠中沉默TEs的研究[63]。丝状真菌Neurospora crassa中的Ⅰ类TEs在胞嘧啶甲基化信号诱导下发生甲基化,下调了TEs的表达[64]。在斑马鱼Danio rerio基因组中,DNA低甲基化上调RNA转座子表达[65]。
-
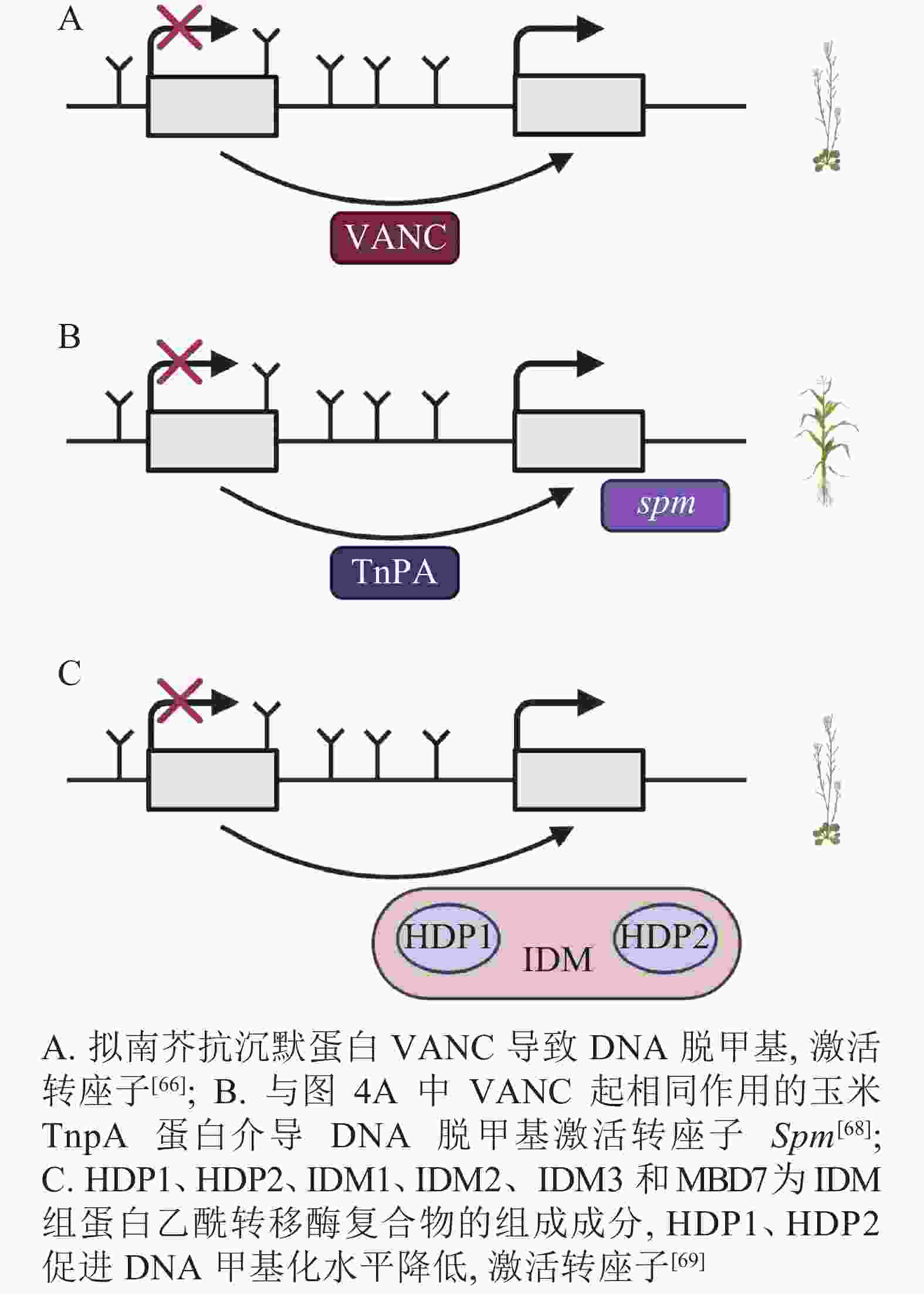
DNA甲基化是当TEs对宿主产生有害影响时的防御机制,但在拟南芥中,进化出转座子Hi (Hiun)编码的抗沉默蛋白VANC,上调被DNA甲基化沉默的TEs表达。这种抗沉默蛋白VANC不仅可以诱导低甲基化,增加TEs的拷贝数,而且能够把对宿主的不利影响降到最小[66-67](图4A)。与抗沉默蛋白VANC一样诱导低甲基化的还有玉米转座子编码蛋白TnpA,TnpA介导玉米转座子Spm DNA脱甲基化,这是由TnpA结合到Spm上,在脱甲基底物和脱甲基酶的参与下进行的DNA去甲基化[68](图4B)。在拟南芥中,Harbinger转座子编码的2个蛋白HDP1(H arbinger-derived protein 1)和HDP2(H arbinger-derived protein 2)的正常表达可以维持低甲基化和内源TEs的沉默,HDP1、HDP2、IDM1(increased DNA methylation 1)、IDM2等作为IDM(increased DNA methylation)组蛋白乙酰转移酶复合物的组成成分,任一结合因子的突变都会升高甲基化水平和影响TEs的表达。HDP1、HDP2突变后下调了AT1TE46455、AT1TE36115和AT1TE35325的表达[69-70](图4C)。
-
生物或非生物胁迫会导致DNA甲基化发生改变,例如,强烈的锌缺乏会导致拟南芥全基因组的DNA甲基化水平发生变化[71]。在CG对称环境中,缺磷对甲基化水平影响较小,但缺氮会导致玉米根甲基化水平降低[72]。水稻在遭受盐胁迫时,盐敏感的IR29缺乏改变DNA甲基化水平的能力,而耐盐水稻能降低甲基化水平[73]。双生病毒干扰植物DNA甲基转移酶MET1和CMT3,导致DNA去甲基化[74]。连作胁迫导致大豆Glycine max基因组DNA去甲基化酶ROS1和DML增加表达,从而降低基因组DNA甲基化水平[75]。
环境胁迫会降低DNA甲基化水平,可能诱导TEs激活。用鞭毛蛋白衍生肽flg22(flagellin peptide 22)处理拟南芥叶片,会触发DNA去甲基化,导致某些TEs转录增加[76]。在棉花Gossypium hirsutum基因组中,高温胁迫导致DNA甲基化水平降低,甲基化程度较高的TEs被激活增加拷贝数[77]。在拟南芥的精子伴细胞(vegetative cell,VC)中,H1组蛋白缺失会使转录起始位点发生去甲基化,从而激活TEs[78]。用去甲基化剂5-azaC处理水稻种子后,激活Dart1-24 DNA转座子,同时验证了转座子拷贝数增加是5′区域的核苷酸去甲基化导致的[79]。在磷酸盐缺乏的环境中,水稻基因组DNA甲基化水平优先在TEs中瞬时变化,在抑制TEs方面发挥潜在的作用。磷酸盐不足的压力环境诱导高甲基化,从而沉默TEs[80]。
-
通常,TEs对宿主不利影响是由于TEs的插入破坏启动子区域或基因区域,导致基因组重排,以及引起的缺失、重复、倒位等基因组结构变异[81-82]。调控TEs表达对维持基因组稳定性具有重要意义,DNA修饰是物种进化过程中普遍采用的调控TEs表达的方式。现阶段,基因组学和表观基因组学的快速发展推动了DNA修饰的研究,其中,DNA甲基化是最主要的调控机制之一。然而,DNA修饰的这种作用具有不稳定性,包括在亲缘关系很近的物种中也存在变异[31]。并且,DNA甲基化水平变化涉及特定酶的参与,影响甲基化酶发挥作用的因素也在间接影响TEs表达。因此,与DNA甲基化相关的酶和基因的作用被进一步发现,可以明确DNA甲基化调控TEs表达的机制。生物或非生物胁迫导致的甲基化水平降低以及主动去甲基化上调TEs,TEs抵抗由DNA甲基化介导的沉默,编码了例如VANC、TnpA等抗沉默蛋白,促进DNA脱甲基从而增加TEs拷贝数[67-68]。宿主在遗传进化过程中更好适应环境的前提就是基因组的稳定,TEs的表达则是破坏基因组稳定的重要因素,环境因子诱导DNA甲基化水平发生变化,进一步影响TEs的表达。DNA甲基化和TEs响应环境因子的互作机制,以及最终调控宿主基因表达的机制是未来研究的方向。
On transposon silencing and DNA methylation
-
摘要: 转座子(transposable elements,TEs)在生物体基因组可以通过转座或逆转座移动,它拷贝数的大规模增加是基因组不稳定的重要因素,因此,维持TEs沉默是宿主进化的方向。DNA甲基化被认为是沉默TEs的可遗传表观遗传修饰方式,同时也在维持基因组稳定、基因印迹、调节基因表达中发挥作用。本研究综述了TEs对生物基因组进化和基因表达的影响,重点总结了以DNA甲基化为主的转座子沉默机制的最新研究进展,归纳了环境因素通过DNA去甲基化调控转座子跳跃的机理。图4参82Abstract: Transposable elements (TEs) can be moved by means of transposition or reverse transposition in the genome of an organism, whose copy number in large numbers is an important factor for genome instability. Therefore, it is the direction of host evolution to maintain TEs silence. DNA methylation, generally considered to be a heritable epigenetic modification method for silencing TEs, plays a role in the maintainance of genome stability, genetic imprinting and the regulation of gene expression. This study is aimed at an overview of the impact of TEs on the evolution of biological genome and gene expression, a summary of the latest research progress of transposon silencing mechanism dominated by DNA methylation, and an investigation of the mechanism of environmental factors that regulate transposon jumping via DNA demethylation. [Ch, 4 fig. 82 ref.]
-
Key words:
- botany /
- transposon /
- transposon silence /
- DNA methylation /
- stress
-
图 3 DNA甲基化与转座子作用机制
A. 水稻OsCMT3a发生突变,DNA甲基化的丧失导致Tos17、Tos19、mPing、Dasheng、Osr4、Osr13、DaiZ、LINE1-6_OS上调;OsMET1-2突变,DNA甲基化的丧失导致Tos17、Osr7、Ping/Pong、mPing上调[51-52]。B. RdDM途径沉默转座子MITEs、OsMIR156d和OsMIR156j基因失去活性,调控水稻表型变化[49]。C. KRAB-ZFPs通路涉及SETDB1、HP1元件,形成压制性染色质结构沉默TEs,TEs也能被DNMT1、DNMT3A/B维持的CG甲基化沉默,丧失CG甲基化后只有少部分TEs上调[53]。D. 去甲基化上调TEs,核酸内切酶Dicer切割dsRNA产生的小RNA与AGO2蛋白结合沉默TEs[56]
Figure 3 DNA methylation and transposon mechanism
-
[1] MITA P, BOEKE J D. How retrotransposons shape genome regulation [J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2016, 37: 90 − 100. [2] FINNEGAN D J. Eukaryotic transposable elements and genome evolution [J]. Trends Genet, 1989, 5(4): 103 − 107. [3] WICKER T, SABOT F, HUA-VAN A, et al. A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements [J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2007, 8(12): 973 − 982. [4] SCHULMAN A H. Retrotransposon replication in plants [J]. Curr Opin Virol, 2013, 3(6): 604 − 614. [5] OROZCO-ARIAS S, ISAZA G, GUYOT R. Retrotransposons in plant genomes: structure, identification, and classification through bioinformatics and machine learning [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(15): 3837. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153837. [6] GONZALEZ J, PETROV D A. Evolution of genome content: population dynamics of transposable elements in flies and humans[C]//ANISIMOVA M. Evolutionary Genomics. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols), vol 855. Totowa: Humana Press, 2012: 361 − 383. [7] de KONING A P J, GU Wanjun, CASTOE T A, et al. Repetitive elements may comprise over two-thirds of the human genome[J]. PLoS Genet, 2011, 7(12): e1002384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002384. [8] SAVAGE A L, SCHUMANN G G, BREEN G, et al. Retrotransposons in the development and progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2019, 90(3): 284 − 293. [9] LANDER E S, LINTON L M, BIRREN B, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome [J]. Nature, 2001, 409(6822): 860 − 921. [10] YANG Fang, WANG P J. Multiple LINEs of retrotransposon silencing mechanisms in the mammalian germline [J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2016, 59: 118 − 125. [11] CHOULET F, WICKER T, RUSTENHOLZ C, et al. Megabase level sequencing reveals contrasted organization and evolution patterns of the wheat gene and transposable element spaces [J]. Plant Cell, 2010, 22(6): 1686 − 1701. [12] SONG Xianwei, CAO Xiaofeng. Transposon-mediated epigenetic regulation contributes to phenotypic diversity and environmental adaptation in rice [J]. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2017, 36: 111 − 118. [13] SASAKI T. The map-based sequence of the rice genome [J]. Nature, 2005, 436(7052): 793 − 800. [14] JIAO Yinping, PELUSO P, SHI Jinghua, et al. Improved maize reference genome with single-molecule technologies [J]. Nature, 2017, 546(7659): 524 − 527. [15] SCHNABLE P S, WARE D, FULTON R S, et al. The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics [J]. Science, 2009, 326(5956): 1112 − 1115. [16] ENNOS R A, CLEGG M T. Flower color variation in the morning glory, Ipomoea purpurea [J]. J Hered, 1983, 74(4): 247 − 250. [17] BUTELLI E, LICCIARDELLO C, ZHANG Yang, et al. Retrotransposons control fruit-specific, cold-dependent accumulation of anthocyanins in blood oranges [J]. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(3): 1242 − 1255. [18] LISCH D. How important are transposons for plant evolution? [J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2013, 14(1): 49 − 61. [19] BENOIT M, DROST H G, CATONI M, et al. Environmental and epigenetic regulation of Rider retrotransposons in tomato[J]. PLoS Genet, 2019, 15(9): e1008370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008370. [20] SANCHEZ D H, GAUBERT H, YANG Weibing. Evidence of developmental escape from transcriptional gene silencing in MESSI retrotransposons [J]. New Phytol, 2019, 223(2): 950 − 964. [21] KUBOTA S, ISHIKAWA T, KAWATA K, et al. Retrotransposons manipulating mammalian skeletal development in chondrocytes[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(5): 1564. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051564. [22] BUNDO M, TOYOSHIMA M, OKADA Y, et al. Increased l1 retrotransposition in the neuronal genome in schizophrenia [J]. Neuron, 2014, 81(2): 306 − 313. [23] 陈文充, 贾宁, 董昂, 等. 山核桃甲基化敏感扩增多态体系的建立与甲基化初步分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(3): 468 − 478. CHEN Wenchong, JIA Ning, DONG Ang, et al. A protocol for methylation-sensitive amplified polymorphism markers and its application to a methylation analysis in Carya cathayensis [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2019, 36(3): 468 − 478. [24] HANCKS D C, KAZAZIAN H H. Roles for retrotransposon insertions in human disease[J]. Mob DNA, 2016, 7: 9. doi: 10.1186/s13100-016-0065-9. [25] SCOTT E C, GARDNER E J, MASOOD A, et al. A hot L1 retrotransposon evades somatic repression and initiates human colorectal cancer [J]. Genome Res, 2016, 26(6): 745 − 755. [26] MAO Hude, WANG Hongwei, LIU Shengxue, et al. A transposable element in a NAC gene is associated with drought tolerance in maize seedlings [J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6(1): 1 − 13. [27] MOLARO A, MALIK H S. Hide and seek: how chromatin-based pathways silence retroelements in the mammalian germline [J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2016, 37: 51 − 58. [28] CHOI Y J, LIN C P, RISSO D, et al. Deficiency of microRNA miR-34a expands cell fate potential in pluripotent stem cells [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6325): eaag1927. doi: 10.1126/science.aag1927. [29] HUTCHISON C A, MERRYMAN C, SUN Lijie, et al. Polar effects of transposon insertion into a minimal bacterial genome [J]. J Bacteriol, 2019, 201(19): e00185-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00185-19. [30] FURNER I J, MATZKE M. Methylation and demethylation of the Arabidopsis genome [J]. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2011, 14(2): 137 − 141. [31] DENIZ Ö, FROST J M, BRANCO M R. Author correction: regulation of transposable elements by DNA modifications [J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2019, 20(7): 432 − 432. [32] CHAN S W L, HENDERSON I R, JACOBSEN S E. Gardening the genome: DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2005, 6(5): 351 − 360. [33] GIRARD A, HANNON G J. Conserved themes in small-RNA-mediated transposon control [J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2008, 18(3): 136 − 148. [34] LI Qing, GENT J I, ZYNDA G, et al. RNA-directed DNA methylation enforces boundaries between heterochromatin and euchromatin in the maize genome [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2015, 112(47): 14728 − 14733. [35] JÖNSSON M E, BRATTÅS P L, GUSTAFSSON C, et al. Activation of neuronal genes via LINE-1 elements upon global DNA demethylation in human neural progenitors [J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10: 3182. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11150-8. [36] LIU Nian, LEE C H, SWIGUT T, et al. Selective silencing of euchromatic L1s revealed by genome-wide screens for L1 regulators [J]. Nature, 2018, 553(7687): 228 − 232. [37] CUI Xiekui, JIN Ping, CUI Xia, et al. Control of transposon activity by a histone H3K4 demethylase in rice [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2013, 110(5): 1953 − 1958. [38] WANG Dafang, ZHANG Jianbo, ZUO Tao, et al. Small RNA-mediated De Novo silencing of Ac/Ds transposons is initiated by alternative transposition in maize [J]. Genetics, 2020, 215(2): 393 − 406. [39] CAPPUCCI U, NORO F, CASALE A M, et al. The Hsp70 chaperone is a major player in stress-induced transposable element activation [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2019, 116(36): 17943 − 17950. [40] BARTHOLOMEW B. Regulating the chromatin landscape: structural and mechanistic perspectives [J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 2014, 83: 671 − 696. [41] HORVÁTH V, MERENCIANO M, GONZÁLEZ J. Revisiting the relationship between transposable elements and the eukaryotic stress response [J]. Trends Genet, 2017, 33(11): 832 − 841. [42] JIE Yang, YUAN Lianyu, YEN M R, et al. SWI3B and HDA6 interact and are required for transposon silencing in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant J, 2019, 102(4): 809 − 822. [43] 陈昂. 毛竹微型反向重复转座子(MITEs)鉴定及对宿主基因表达的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2016. CHEN Ang. Identification of Miniature Inverted Repeat Transposable Elements (MITEs) from Phyllostachys edulis and Their Effects on Host Gene Expression[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A&F University, 2016. [44] ZHOU Mingbing, LIANG Linlin, HÄNNINEN H. A transposition-active Phyllostachys edulis long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposon [J]. J Plant Res, 2018, 131(2): 203 − 210. [45] WANG Zhengming, BAULCOMBE D C. Transposon age and non-CG methylation [J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 1221. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14995-6. [46] ZHANG Huiming, LANG Zhaobo, ZHU Jiankang. Dynamics and function of DNA methylation in plants [J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018, 19(8): 489 − 506. [47] KIM M Y, ZILBERMAN D. DNA methylation as a system of plant genomic immunity [J]. Trends Plant Sci, 2014, 19(5): 320 − 326. [48] CZECH B, HANNON G J. One loop to rule them all: the ping-pong cycle and piRNA-guided silencing [J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2016, 41(4): 324 − 337. [49] XU Le, YUAN Kun, YUAN Meng, et al. Regulation of rice tillering by RNA-Directed DNA methylation at miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements [J]. Mol Plant, 2020, 13(6): 851 − 863. [50] MIROUZE M, REINDERS J, BUCHER E, et al. Selective epigenetic control of retrotransposition in Arabidopsis [J]. Nature, 2009, 461(7262): 427 − 430. [51] CHENG Chaoyang, TARUTANI Y, MIYAO A, et al. Loss of function mutations in the rice chromomethylase Os CMT 3a cause a burst of transposition [J]. Plant J, 2015, 83(6): 1069 − 1081. [52] HU Lanjuan, LI Ning, ZHANG Zhibin, et al. CG hypomethylation leads to complex changes in DNA methylation and transpositional burst of diverse transposable elements in callus cultures of rice [J]. Plant J, 2020, 101: 188 − 203. [53] ROWE H M, JAKOBSSON J, MESNARD D, et al. KAP1 controls endogenous retroviruses in embryonic stem cells [J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7278): 237 − 240. [54] MATSUI T, LEUNG D, MIYASHITA H, et al. Proviral silencing in embryonic stem cells requires the histone methyltransferase ESET [J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7290): 927 − 931. [55] IMBEAULT M, HELLEBOID P Y, TRONO D. KRAB zinc-finger proteins contribute to the evolution of gene regulatory networks [J]. Nature, 2017, 543(7646): 550 − 554. [56] BERRENS R V, ANDREWS S, SPENSBERGER D, et al. An endosiRNA-based repression mechanism counteracts transposon activation during global DNA demethylation in embryonic stem cells [J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2017, 21(5): 694 − 703. [57] NOUROZ F, NOREEN S, HESLOP-HARRISON J S. Identification and evolutionary dynamics of CACTA DNA transposons in brassica [J]. Pak J Bot, 2017, 49(2): 789 − 798. [58] WANG Qingbiao, WANG Yanping, SUN Honghe, et al. Transposon-induced methylation of the RsMYB1 promoter disturbs anthocyanin accumulation in red-fleshed radish [J]. J Exp Bot, 2020, 71(9): 2537 − 2550. [59] KONG Yu, ROSE C M, CASS A A, et al. Transposable element expression in tumors is associated with immune infiltration and increased antigenicity [J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10: 5228. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13035-2. [60] LA Honggui, DING Bo, MISHRA G P, et al. A 5-methylcytosine DNA glycosylase/lyase demethylates the retrotransposon Tos17 and promotes its transposition in rice [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2011, 108(37): 15498 − 15503. [61] KASHINO-FUJII M, YOKOSHO K, YAMAJI N, et al. Retrotransposon insertion and DNA methylation regulate aluminum tolerance in European barley accessions [J]. Plant Physiol, 2018, 178(2): 716 − 727. [62] CHOI J Y, PURUGGANAN M D. Evolutionary epigenomics of retrotransposon-mediated methylation spreading in rice [J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2018, 35(2): 365 − 382. [63] WALSH C P, CHAILLET J R, BESTOR T H. Transcription of IAP endogenous retroviruses is constrained by cytosine methylation [J]. Nat Genet, 1998, 20(2): 116 − 117. [64] ZHOU Y, CAMBARERI E, KINSEY J. DNA methylation inhibits expression and transposition of the neurospora tad retrotransposon [J]. Mol Genet Genomics, 2001, 265(4): 748 − 754. [65] CHERNYAVSKAYA Y, MUDBHARY R, ZHANG Chi, et al. Loss of DNA methylation in zebrafish embryos activates retrotransposons to trigger antiviral signaling [J]. Development, 2017, 144(16): 2925 − 2939. [66] HOSAKA A, SAITO R, TAKASHIMA K, et al. Evolution of sequence-specific anti-silencing systems in Arabidopsis [J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 2161. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02150-7. [67] FU Yu, KAWABE A, ETCHEVERRY M, et al. Mobilization of a plant transposon by expression of the transposon-encoded anti-silencing factor [J]. EMBO J, 2013, 32(17): 2407 − 2417. [68] CUI Hongchang, FEDOROFF N V. Inducible DNA demethylation mediated by the maize suppressor-mutator transposon-encoded TnpA protein [J]. Plant Cell, 2002, 14(11): 2883 − 2899. [69] DUAN Chengguo, WANG Xingang, XIE Shaojun, et al. A pair of transposon-derived proteins function in a histone acetyltransferase complex for active DNA demethylation [J]. Cell Res, 2017, 27(2): 226 − 240. [70] QIAN Weiqiang, MIKI D, ZHANG Heng, et al. A histone acetyltransferase regulates active DNA demethylation in Arabidopsis [J]. Science, 2012, 336(6087): 1445 − 1448. [71] CHEN Xiaochao, SCHÖNBERGER B, MENZ J, et al. Plasticity of DNA methylation and gene expression under zinc deficiency in Arabidopsis roots [J]. Plant Cell Physiol, 2018, 59(9): 1790 − 1802. [72] MAGER S, LUDEWIG U. Massive loss of DNA methylation in nitrogen-, but not in phosphorus-deficient Zea mays roots is poorly correlated with gene expression differences [J]. Front Plant Sci, 2018, 9: 497. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00497. [73] FERREIRA L J, AZEVEDO V, MAROCO J, et al. Salt tolerant and sensitive rice varieties display differential methylome flexibility under salt stress [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(5): e0124060. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124060. [74] RODRÍGUEZ-NEGRETE E, LOZANO-DURÁN R, PIEDRA-AGUILERA A, et al. Geminivirus Rep protein interferes with the plant DNA methylation machinery and suppresses transcriptional gene silencing [J]. New Phytol, 2013, 199(2): 464 − 475. [75] LIANG Xiong, HOU Xue, LI Jianying, et al. High-resolution DNA methylome reveals that demethylation enhances adaptability to continuous cropping comprehensive stress in soybean [J]. BMC Plant Biol, 2019, 19(1): 79. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1670-9. [76] YU A, LEPÈRE G, JAY F, et al. Dynamics and biological relevance of DNA demethylation in Arabidopsis antibacterial defense [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2013, 110(6): 2389 − 2394. [77] ZHANG Meng, ZHANG Xuexian, GUO Liping, et al. Single-base resolution methylomes of cotton CMS system reveal epigenomic changes in response to high-temperature stress during anther development [J]. J Exp Bot, 2019, 71(3): 951 − 969. [78] HE S, VICKERS M, ZHANG J, et al. Natural depletion of histone H1 in sex cells causes DNA demethylation, heterochromatin decondensation and transposon activation [J]. eLife, 2019, 8: e42530. doi: 10.7554/eLife.42530.002. [79] NISHIMURA H, HIMI E, EUN C H, et al. Transgenerational activation of an autonomous DNA transposon, Dart1-24, by 5-azaC treatment in rice [J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2019, 132(12): 3347 − 3355. [80] SECCO D, WANG Chuang, SHOU Huixia, et al. Stress induced gene expression drives transient DNA methylation changes at adjacent repetitive elements [J]. eLife, 2015, 4: e09343. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09343.001. [81] KOFLER R. Dynamics of transposable element invasions with piRNA clusters [J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2019, 36(7): 1457 − 1472. [82] GRAY Y H M. It takes two transposons to tango: transposable-element-mediated chromosomal rearrangements [J]. Trends Genet, 2000, 16(10): 461 − 468. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200338






 下载:
下载: