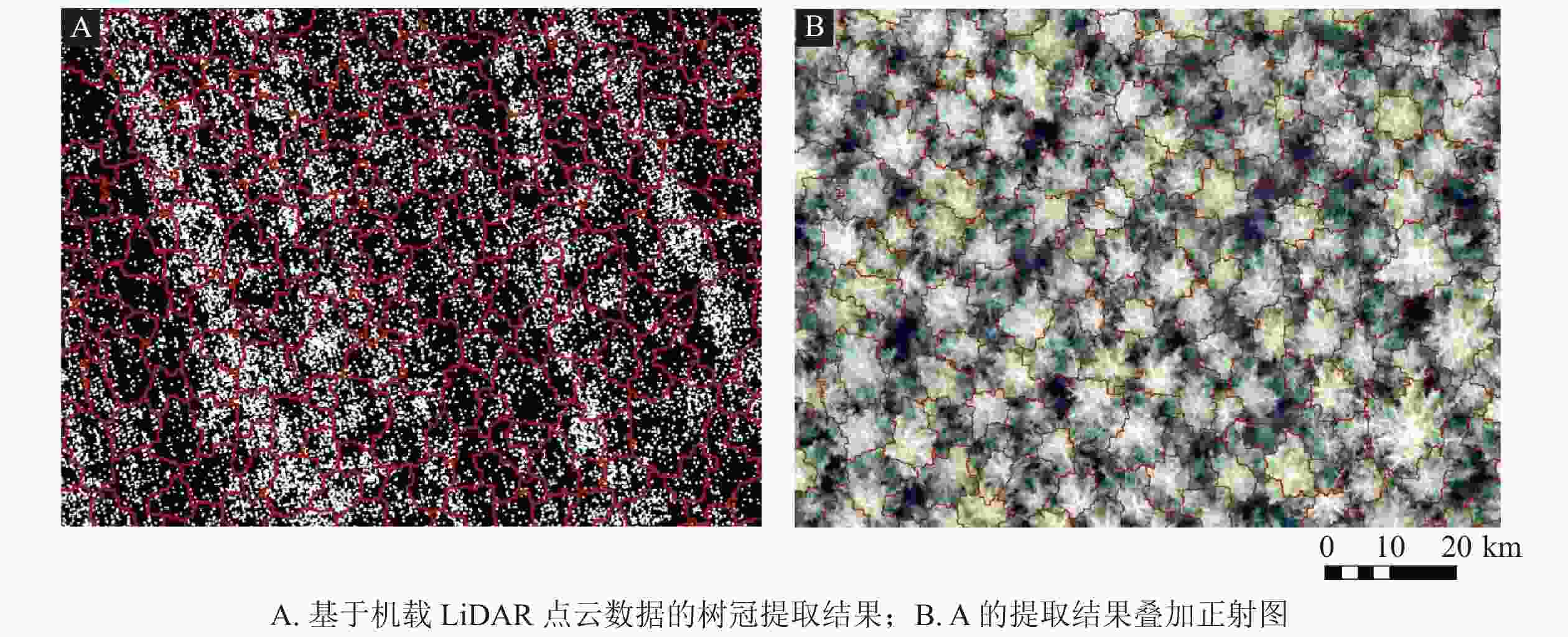
-
华北落叶松Larix principis-rupprechtii是中国华北地区第一大树种,具有较高的经济和生态价值,探讨华北落叶松单木参数的提取、林分蓄积量的估算具有重要意义[1]。高精度的单木识别是获取单木和森林结构参数的重要前提,单木识别包括单木位置识别和树冠分割[2-4]。相比高分辨率卫星影像和光学影像,机载LiDAR技术不受区域信号影响,分辨率较高,是一种主动遥感技术,能获取林木的水平和垂直结构信息[5-6]。利用机载LiDAR研究单木识别的方法主要有2类:基于冠层高度模型(CHM)识别方法和基于归一化后的点云识别方法[3]。其中基于CHM的单木位置识别方法即在灰度图像中探测单木树顶,主要实现算法包括局部最大值法和多尺度分割法。局部最大值法假设树冠顶点高于树冠边缘,通过设置固定尺寸[7-10]或动态尺寸[11-12]的搜索窗口从CHM中识别树冠顶点特征,单木位置探测率可达85%。多尺度分割法以像元为单位,根据相似特征逐渐外扩分割,关键在于最优分割尺度的选取[13-17]。基于归一化后的点云单木位置识别方法以点云的结构信息为基础,主流实现算法包括区域生长法和均值漂移法。区域生长法通过选择合适的种子点,定义距离生长准则,判别不同属类[18-20],选择的种子点和制定的距离生长规则不同,取得的单木识别精度也不同。均值漂移法是一种基于密度梯度上升的非参数方法,通过迭代运算求得同簇的数据点[21],关键在于漂移均值向量的计算。单木识别时可利用林分树冠的距离和多维特征空间为向量来完成[22-23],其在中低郁闭度林分中的单木识别精度较高,但在高郁闭度林分条件下,由于树冠重叠度增加,漂移均值向量计算会有偏差,识别结果不尽合理。为提高识别精度,结合树冠冠型特点,本研究提出基于机载LiDAR点云空间特征的高斯核函数改进的均值漂移单木位置识别方法(MSP)。为验证方法的有效性,对比了基于点云空间特征的区域生长图像分割方法(RGP)、基于CHM的局部最大值单木探测方法(LMC)和基于CHM的多尺度分割方法(MSC)等3种目前应用较为广泛的单木位置识别方法。最后,在单木位置识别结果上,进行单木树冠的提取。
-
忻州市五寨县羊圈沟林场(38º44′~39º01′N,111º48′~112º03′E)位于山西省中北部,属亚寒带大陆性气候,季节变化明显,海拔为1 350~2 700 m,年均气温为5 ℃,年降水量为453.9 mm;华北落叶松-云杉 Picea asperata天然次生林与华北落叶松人工林带状混交。本研究在华北落叶松人工林带内设置8个20 m×20 m的正方形样地,植株密度为1 875~2 925 株·hm−2,郁闭度为0.8~1.0,是典型高郁闭度森林。
-
标记并编号8个样地内胸径大于5 cm 的华北落叶松,调查记录每木冠幅、树高和胸径;利用实时动态定位和全站型电子测距仪获取每木的位置坐标。样地林分基本情况如表1。
表 1 样地林分基本特征
Table 1. Investigation results of basic characteristics of forest stand in sample plot
样地 密度/(株·hm−2) 平均树高/m 平均胸径/cm 平均冠幅/m 样地 密度/(株·hm−2) 平均树高/m 平均胸径/cm 平均冠幅/m 1 2 075 13.11 13.22 3.19 5 2 100 11.72 13.82 3.82 2 2 925 12.66 12.44 2.86 6 2 475 12.00 12.98 3.43 3 2 500 14.04 15.35 2.99 7 2 275 13.45 14.63 2.92 4 1 875 13.60 13.41 3.97 8 2 125 13.52 13.90 3.34 2018年6月2日,使用GV 1500六旋翼无人机搭载RIGEL VUX-1激光扫描仪获取机载LiDAR点云数据;设置飞行高度为200 m,飞行速度为6 m·s−1,离散点云平均密度为70个·m−2,坐标系为WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_49N。
在同一天,使用GV 120六旋翼无人机搭载传感器SONY Alpha7 RⅡ采集可见光遥感影像。通过Limapper V 2.0软件生成数字正射影像作为辅助数据,用于目视解译与可视化数据展示。
-
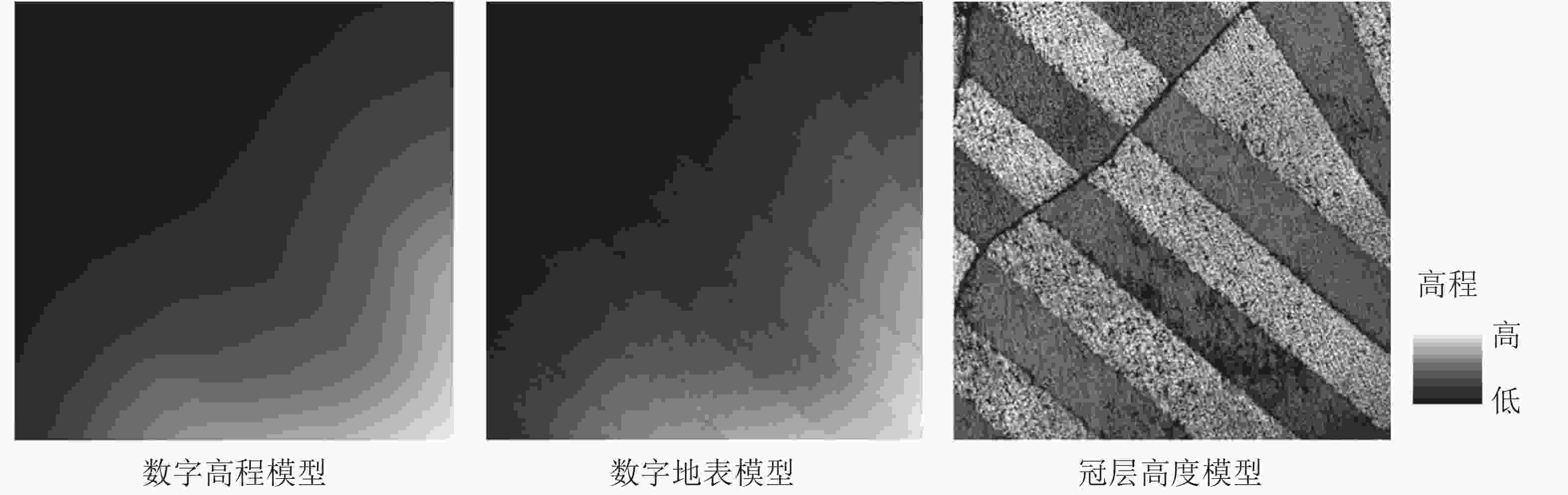
首先,对原始点云数据进行2 m缓冲带裁剪,获取8个样地。然后,对样地点云数据进行以下处理:①采用距离阈值法移除噪声点。②采用渐进加密三角网滤波算法提取地面点云。为提高后期生成数字高程模型(DEM)的精度,设置迭代距离与迭代角度为1.4 m和8º,以便分离地面点云和非地面点云。③对去噪和分类后的点云数据进行克里金插值[23]。通过定义该点邻域中采样点的距离加权平均计算像元值。对地面点云和非地面点云分别插值,得到DEM和数字地表模型(DSM),两者相减获得冠层高度模型(CHM) (图1)。图1C中,高程值较低的条带为华北落叶松人工林带,较高的为华北落叶松-云杉天然次生林。④基于LiDAR360 V 3.2软件,借助DEM对去噪后的点云进行高度信息归一化,避免地形起伏对点云高程的影响。
-
均值漂移算法是一种基于非参数概率密度梯度估计的迭代聚类过程[24-25]。单木点云分布具有与高斯核函数相似的几何形状特征,可用高斯核函数改进的均值偏移算法对点云数据进行聚类,进而获取单木位置。设置迭代运算的收敛阈值(ε),基于点云空间特征的改进均值漂移单木位置识别方法,算法如下:(1) 在点云数据点中随机选择1个点作为初始中心点,找出离中心点距离在带宽h之内的所有点,记做集合M,认为这些点属于同一类簇;(2)选用点云三维空间特征,计算中心点到集合M中每个数据点的向量之和,得到偏移向量Mh(x);(3)令中心点沿偏移向量方向移动,移动距离是偏移向量Mh(x)的模;(4)重复步骤(2)~(3),直到偏移向量小于ε,记住此时的中心点;(5)重复步骤(1)~(4),直到所有数据点都被归类;(6)提取单木位置,每一个类簇的中心点即为单木位置。
-
局部最大值法基于单木树冠顶部高程大于树冠边缘高程的假设,设置搜索窗口进行局部最大值探测。本研究将搜索窗口的起始尺寸设置为林分的平均冠幅大小,对窗口尺寸按增加或减少1个像素进行动态调整,搜索出树冠的局部最大值。基于CHM的图像分割法通过图像分割实现单木分割,根据区域中心确定单木位置。标记控制分水岭分割法是最常用的分割方法,但在本研究中分割精度不理想,因此选用面向对象的多尺度分割。利用eCognition Developer V 8.9软件的Estimation of Scale Parameter 2 (ESP2)工具包得到合适的分割尺度。本研究中,分割尺度为66,形状参数为0.8,紧致度参数为0.9,样地分割效果最好。
-
在单木位置识别的基础上,划分出同一类点云的投影范围即为该株华北落叶松的树冠范围。考虑到冠层提取过程中,林分树冠间隙部分容易产生过分割现象,需要对其结果进行区域合并[26],本研究将形状异质性作为类别之间的合并准则。选择eCognition软件对点云初始分类结果进行区域合并,分割尺度为58,形状参数和紧致度参数分别为0.8和0.8。
-
根据卫星定位测量获取坐标的定位精度,考虑树顶与树根的位置偏差,将华北落叶松位置误差预计为1 m;以真值坐标点为圆心,创建半径为1 m的缓冲区。单木位置识别结果落入此缓冲区内,则认为正确。测算正确识别的单木总数(NC)、实地调查单木实际总数(NF)、识别出的单木总数(ND)、重复识别的单木总数(NR)等数据。计算精度评价指标,并使用单因素方差分析检验不同单木位置识别方法在各个指标方面的效果。①总体精度(AO)即正确识别的单木总数占实地调查单木实际总数的比值,公式为:AO=NC/NF×100%。②识别精度(AD)即正确识别的单木总数占识别出的单木总数的比值,公式为:AD=NC/ND×100%。③漏分误差(EO)即未识别到的单木总数占实地调查单木实际总数的比值,公式为:EO=(NF−NC)/NF×100%。④错分误差(EC)即被错误识别为单木的总数占识别出的单木总数的比值,公式为:EC=(ND−NC)/ND×100%。⑤重复性误差(ER)即对同一株单木重复识别的总数占识别出的单木总数的比值,公式为:ER=NR/ND×100%。
-
采用单株冠幅提取精度(ω)来进行评价,公式为:ω=100%−∣(C1−C0)/C0∣×100%。其中:C0为实测冠幅,C1为单木对应的提取冠幅。
-
利用4种方法进行单木位置识别,空间分布图(图2)显示:4种方法均存在漏分、错分和重复性识别的现象,结合表2可知:4种方法的识别精度(AD)由高到低依次为MSP (89.30%)、LMC (85.60%)、RGP (77.50%)、MSC (70.00%);MSP法的单木位置识别效果要好于其他3种方法。4种方法的识别精度均小于总体精度(AO),说明存在单木错误识别现象;相比之下,MSP法错分误差最低(EC为8.0%),,MSC法错分误差值最高(EC为30.1%),说明依靠邻近相似特征识别单木的方法更容易产生将单木识别错误。相比RGP和MSC法,MSP法的漏分误差(EO)、错分误差(EC)和重复性误差(ER)均较低,说明高郁闭度针叶林中,按照邻域分属识别单木位置会受到树冠重叠度的影响,并不适用华北落叶松的单木位置识别。尽管LMC法和MSP法的总体精度都高于90%,但后者错分误差(Ec)较低,说明MSP法更能避免将非树对象错误识别为单木而增加识别总数的现象。
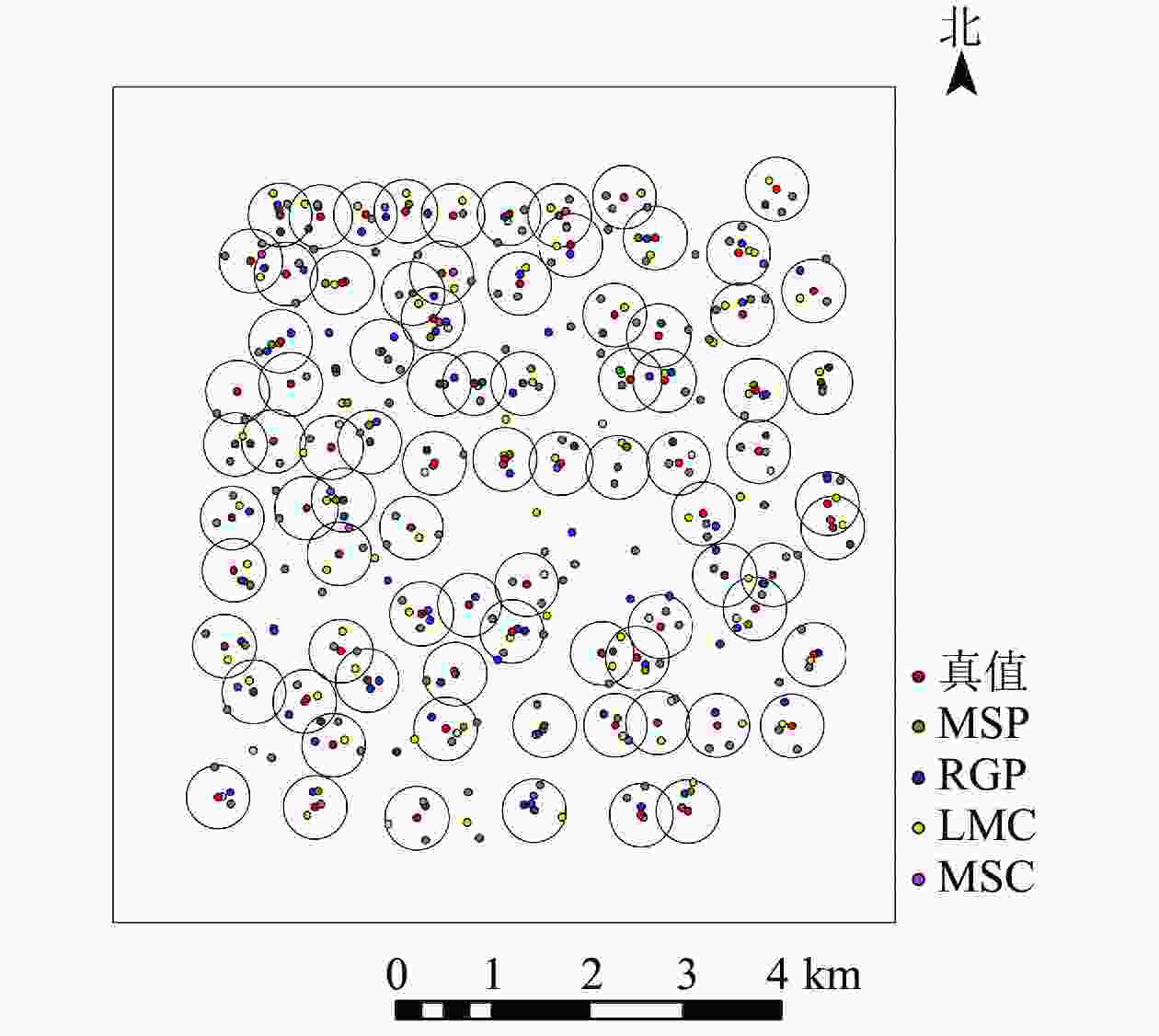
图 2 4种单木位置识别的空间分布
Figure 2. Spatial distribution of the result of individual tree position detection based on four methods
表 2 4种单木位置识别方法的精度统计
Table 2. Accuracy statistics of four methods on individual tree detection
类别 方法 AO/% AD/% EO/% EC/% ER/% 点云 MSP 91.3±3.7 a 89.3±2.5 a 8.7±3.7 b 8.0±2.5 c 5.8±1.5 b RGP 81.5±2.6 b 77.5±2.2 b 18.5±2.6 a 16.7±5.5 b 9.8±1.4 a CHM LMC 91.0±2.0 a 85.6±2.0 c 9.0±2.0 b 9.3±1.7 c 4.3±1.7 b MSC 80.8±2.1 b 70.0±1.5 d 19.2±2.1 a 30.1±5.0 a 5.0±1.4 b 说明:同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05) -
采用均值漂移方法提取华北落叶松单株树冠(图3)。以单株华北落叶松实测冠幅为真值,对利用MSP法提取的单株冠幅进行精度分析,结合表3可知:MSP法总体平均提取精度为90.18%。单株提取精度小于80%的占总体结果的10.20%,单株提取精度大于80%的占总体结果的89.80%。单株树冠分割偏小的结果占总体的62.07%,要远远高于提取冠幅偏大的结果。
表 3 MSP法提取单株冠幅精度
Table 3. Precision distribution of extracting individual canopy diameter by MSP
单株冠幅提取
精度范围/%精度范围
占比/%冠幅偏
小/%冠幅偏
大/%平均单株
提取精度/%<60 0 62.07 37.93 90.18 60~70 1.05 70~80 9.15 80~90 32.68 90~100 57.12 -
本研究提出的改进均值漂移法对高郁闭度华北落叶松林的单木提取总体精度达91.3%,这与张怡卓等[25]对中低密度人工林的研究结果(总体精度达89.0%)相似,远高于JING等[27]对加拿大高郁闭林分的总体精度(69.0%)。相比于其他3种提取方法,MSP法有2个优势。一是在林木树冠重叠的情况下,MSP法直接利用了点云空间特征,避免了生成CHM过程中产生的栅格误差;二是该方法利用统计迭代的方式确定聚类点位,根据访问频率分类,比直接比较邻域特征而进行分类稳健性更好。
本研究发现:MSP法提取单木冠幅的平均提取精度为90.18%,比同等郁闭度林分的树冠提取精度要高出很多[28],可满足森林调查需求。约10%的单株冠幅提取精度低于80%,这些点主要位于林分下层。由于上层遮挡,下层点云密度远低于上层,而点云聚类算法和点云密度息息相关,这也是本研究发现冠幅提取值偏小的原因。具体来说,由于上层冠层存在重叠,人工目视解译可以考虑到冠层重叠的影响并准确提取冠幅,而在三维点云图上,树冠界限分类时存在距离阈值类似的情况,影响提取结果;实测中,研究者往往通过东—西、南—北方向来测量冠幅,但是这只是一种理想状态下的测量,在现实中,华北落叶松林木树冠是不规则的,测量因此会存在误差;同时研究区域的坡度、地形等的限制,也会对人工测量造成影响。
-
本研究基于点云单一空间特征,引入高斯核函数简化并改进了均值漂移量的计算过程,同时所提方法不需要先验知识,算法的稳健性高,解决了高郁闭度的华北落叶松林受复杂冠层影响的问题,提高了在该林分内机载LiDAR单木识别的精度,为高郁闭度华北落叶松林单木识别提供了新的方法。
Individual tree detection in the high canopy density Larix principis-rupprechtii forest based on airborne LiDAR
-
摘要:
目的 高郁闭度华北落叶松林Larix principis-rupprechtii林木树冠交叉重叠,传统的基于高分辨影像的单木识别方法识别精度不高。利用机载LiDAR三维点云数据可提高高郁闭度华北落叶松林的单木识别精度。 方法 在点云数据预处理基础上,提出基于点云空间特征的高斯核函数改进的均值漂移单木位置识别方法(MSP),比较并分析MSP法与基于点云空间特征的区域生长点云分割方法(RGP)、基于冠层高度模型的局部最大值单木位置识别方法(LMC)和基于冠层模型的多尺度分割单木位置识别方法(MSC)的单木识别效果。 结果 4种方法单木位置识别精度从大到小依次为MSP (89.30%)、LMC (85.60%)、RGP (77.50%)和MSC (70.00%),MSP的漏分误差和错分误差最小,分别为8.7%和8.0%,平均单木冠幅提取精度为90.18%。 结论 提出的MSP法对高郁闭度华北落叶松林单木位置识别具有较好的适用性,利用机载LiDAR可为提取华北落叶松林森林结构参数提供新的途径。图3表3参28 Abstract:Objective With low identification accuracy of individual trees in Larix principis-rupprechtii forest with high canopy density employing high resolution images, this paper is aimed to confirm the strengths of airborne Laser Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) 3D point cloud data as an alternative with a workable method proposed. Method Based on the preprocessing of point cloud data, an improved Mean Shift with Gaussian kernel function (MSP) position recognition method on the basis of the spatial characteristics of airborne LiDAR point cloud was proposed. The comparison is made with other three commonly used methods: regional growing segmentation algorithm based on point cloud (RGP), local maximum method based on canopy height model (LMC) and multi-scale segmentation method based on CHM (MSC). Result Identification accuracy of the four methods is: MSP (89.30%)>LMC (85.60%)>RGP (77.50%)>MSC (70.00%), and MSC, the proposed method, displayed high average individual tree crown extraction accuracy (90.18%) and relatively low omission error and commission error rate: 8.7% and 8.0% respectively. Conclusion The proposed MSP has good applicability in high crown density L. principis-rupprechtii forest and provides a new way of extracting L. principis-rupprechtii forest structure parameters accurately on the basis of airborne LiDAR point clouds. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 28 ref.] -
表 1 样地林分基本特征
Table 1. Investigation results of basic characteristics of forest stand in sample plot
样地 密度/(株·hm−2) 平均树高/m 平均胸径/cm 平均冠幅/m 样地 密度/(株·hm−2) 平均树高/m 平均胸径/cm 平均冠幅/m 1 2 075 13.11 13.22 3.19 5 2 100 11.72 13.82 3.82 2 2 925 12.66 12.44 2.86 6 2 475 12.00 12.98 3.43 3 2 500 14.04 15.35 2.99 7 2 275 13.45 14.63 2.92 4 1 875 13.60 13.41 3.97 8 2 125 13.52 13.90 3.34 表 2 4种单木位置识别方法的精度统计
Table 2. Accuracy statistics of four methods on individual tree detection
类别 方法 AO/% AD/% EO/% EC/% ER/% 点云 MSP 91.3±3.7 a 89.3±2.5 a 8.7±3.7 b 8.0±2.5 c 5.8±1.5 b RGP 81.5±2.6 b 77.5±2.2 b 18.5±2.6 a 16.7±5.5 b 9.8±1.4 a CHM LMC 91.0±2.0 a 85.6±2.0 c 9.0±2.0 b 9.3±1.7 c 4.3±1.7 b MSC 80.8±2.1 b 70.0±1.5 d 19.2±2.1 a 30.1±5.0 a 5.0±1.4 b 说明:同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05) 表 3 MSP法提取单株冠幅精度
Table 3. Precision distribution of extracting individual canopy diameter by MSP
单株冠幅提取
精度范围/%精度范围
占比/%冠幅偏
小/%冠幅偏
大/%平均单株
提取精度/%<60 0 62.07 37.93 90.18 60~70 1.05 70~80 9.15 80~90 32.68 90~100 57.12 -
[1] 赵匡记, 王利东, 王立军, 等. 华北落叶松蓄积量及生产力研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(2): 24 − 31. ZHAO Kuangji, WANG Lidong, WANG Lijun, et al. Stock volume and productivity of Larix principis-rupprechtii in northern and northwestern China [J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2015, 37(2): 24 − 31. [2] HILL S, LATIFI H, HEURICH M, et al. Individual-tree and stand-based development following natural disturbance in a heterogeneously structured forest: a LiDAR-based approach [J]. Ecol Inf, 2017, 38: 12 − 25. [3] 李增元, 刘清旺, 庞勇. 激光雷达森林参数反演研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2016, 20(5): 1138 − 1150. LI Zengyuan, LIU Qingwang, PANG Yong. Review on forest parameters inversion using LiDAR [J]. J Remote Sensing, 2016, 20(5): 1138 − 1150. [4] 申家朋, 陈东升, 孙晓梅, 等. 基于似乎不相关回归和哑变量的日本落叶松单木生物量模型构建[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(5): 877 − 885. SHEN Jiapeng, CHEN Dongsheng, SUN Xiaomei, et al. Modeling a single-tree biomass equation by seemingly unrelated regression and dummy variables with Larix kaempferi [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2019, 36(5): 877 − 885. [5] 甄贞, 李响, 修思玉, 等. 基于标记控制区域生长法的单木树冠提取[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2016, 44(10): 22 − 29. ZHEN Zhen, LI Xiang, XIU Siyu, et al. Individual tree crown delineation using maker-controlled region growing method [J]. J Northeast For Univ, 2016, 44(10): 22 − 29. [6] 陶江玥, 刘丽娟, 庞勇, 等. 基于机载激光雷达和高光谱数据的树种识别方法[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2018, 35(2): 314 − 323. TAO Jiangyue, LIU Lijuan, PANG Yong, et al. Automatic identification of tree species based on airborne LiDAR and hyperspectral data [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2018, 35(2): 314 − 323. [7] HOLMGREN J, NILSSON M, OLSSON H. Estimation of tree height and stem volume on plots using airborne laser scanning [J]. For Sci, 2003, 49(3): 419 − 428. [8] 霍达, 邢艳秋, 田昕, 等. 基于机载LiDAR的四次多项式拟合法估测单木冠幅[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2015, 30(3): 164 − 169. HUO Da, XING Yanqiu, TIAN Xin, et al. Estimating individual tree crown diameter using fourth fegree polynomial fitting method based on airborne LiDAR [J]. J Northwest For Univ, 2015, 30(3): 164 − 169. [9] CHEN Wei, XIANG Haibing, MORIYA K. Individual tree position extraction and structural parameter retrieval based on airborne LiDAR data: performance evaluation and comparison of four algorithms [J/OL]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 12: 571[2021- 05-30]. doi: 10.3390/rs12030571. [10] 王濮, 邢艳秋, 王成, 等. 一种基于图割的机载LiDAR单木位置识别方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2019, 36(3): 385 − 391. WANG Pu, XING Yanqiu, WANG Cheng, et al. A graph cut-based approach for individual tree detection using airborne LiDAR data [J]. J Univ Chin Acad Sci, 2019, 36(3): 385 − 391. [11] 李响, 甄贞, 赵颖慧. 基于局域最大值法单木位置探测的适宜模型研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(3): 27 − 33. LI Xiang, ZHEN Zhen, ZHAO Yinghui. Suitable model of detecting the position of individual treetop based on local maximum method [J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2015, 37(3): 27 − 33. [12] CHEN Shiyue, LIANG Dan, YING Binbin, et al. Assessment of an improved individual tree detection method based on local-maximum algorithm from unmanned aerial vehicle RGB imagery in overlapping canopy mountain forests [J]. Int J Remote Sensing, 2021, 42(1): 106 − 125. [13] CHO M A, MATHIEU R, ASNER G P, et al. Mapping tree species composition in South African savannas using an integrated airborne spectral and LiDAR system [J]. Remote Sensing Environ, 2012, 125: 214 − 226. [14] 刘晓双, 黄建文, 鞠洪波. 高空间分辨率遥感的单木树冠自动提取方法与应用[J]. 浙江林学院学报, 2010, 27(1): 126 − 133. LIU Xiaoshuang, HUANG Jianwen, JU Hongbo. Research progress in the methods and application of individual tree crown’s automatic extracting by high spatial resolution remote sensing [J]. J Zhejiang For Coll, 2010, 27(1): 126 − 133. [15] LI Wenkai, GUO Qinghua, JAKUBOWSKI M K, et al. A new method for segmenting individual trees from the lidar point cloud [J]. Photogrammetric Eng Remote Sensing, 2012, 78(1): 75 − 84. [16] 李森磊, 李健平, 蒋腾平, 等. 一种基于UAV-LiDAR点云的多尺度单木分割[J]. 测绘科学技术, 2021, 9(1): 14 − 25. LI Senlei, LI Jianping, JIANG Tengping, et al. A multi-scale method for 3D individual tree extraction using UAV-LiDAR [J]. Geomatics Sci Technol, 2021, 9(1): 14 − 25. [17] NAVEED F, HU Baoxin, WANG Jianguo, et al. Individual tree crown delineation using multispectral LiDAR data [J/OL]. Sensors, 2019, 19: 5421[2021-05-30]. doi: 10.3390/s19245421. [18] 李仁忠, 刘阳阳, 杨曼, 等. 基于改进的区域生长三维点云分割[J/OL]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55: 051502[2021-05-30]. doi: 10.3788/LOP55.051502. LI Renzhong, LIU Yangyang, YANG Man, et al. Three-dimensional point cloud segmentation algorithm based on improved region growth [J/OL]. Laser Optoelectronics Prog, 2018, 55: 051502[2021-05-30]. doi: 10.3788/LOP55.051502. [19] KWONG I H Y, FUNG T. Tree height mapping and crown delineation using LiDAR, large format aerial photographs, and unmanned aerial vehicle photogrammetry in subtropical urban forest [J]. Int J Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(14): 5228 − 5256. [20] MA Zhengyu, PANG Yong, WANG Di, et al. Individual tree crown segmentation of a larch plantation using airborne laser scanning data based on region growing and canopy morphology features [J/OL]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(7): 1078[2021-05-30]. doi: 10.3389/rs12071078. [21] HU Xingbo, CHEN Wei, XU Weiyang. Adaptive mean shift-based identification of individual trees using airborne LiDAR data [J/OL]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(2): 148[2021-05-30]. doi: 10.3389/rs9020148. [22] CHEN Wei, HU Xingbo, CHEN Wen, et al. Airborne LiDAR remote sensing for individual tree forest inventory using trunk detection-aided mean shift clustering techniques [J/OL]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10: 1078[2021-05-30]. doi: 10.3389/rs10071078. [23] YAN Wanqian, GUAN Haiyan, CAO Lin, et al. A self-adaptive mean shift tree-segmentation method using UAV LiDAR data [J/OL]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12: 515[2021-05-30]. doi: 10.3389/rs12030515. [24] COMANICIU D, MEER P. Mean shift: a robust approach toward feature space analysis [J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel, 2002, 24(5): 603 − 619. [25] 张怡卓, 吕阿康, 蒋大鹏, 等. 应用高斯聚类的单木分割及树高和冠幅的提取[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(2): 54 − 59. ZHANG Yizhuo, LÜ Akang, JIANG Dapeng, et al. Single tree segmentation and extraction of tree height and crown width using gaussian clustering [J]. J Northeast For Univ, 2021, 49(2): 54 − 59. [26] 张学良, 肖鹏峰, 冯学智. 基于改进区域邻接图的遥感图像多尺度快速分割方法[J]. 遥感信息, 2011(5): 3 − 8, 46. ZHANG Xueliang, XIAO Pengfeng, FENG Xuezhi. Multi-scale fast segmentation of remotely sensed image based on improved region adjacency graph [J]. Remote Sensing Inf, 2011(5): 3 − 8, 46. [27] JING Linhai, HU Baoxin, LI Jili, et al. Automated delineation of individual tree crowns from LiDAR data by multi-scale analysis and segmentation [J]. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing, 2012, 78(12): 1275 − 1284. [28] 何祺胜, 陈尔学, 曹春香, 等. 基于LiDAR数据的森林参数反演方法研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2009, 24(7): 748 − 755. HE Qisheng, CHEN Erxue, CAO Chunxiang, et al. A study of forest parameters mapping technique using airborme LiDAR data [J]. Adv Earth Sci, 2009, 24(7): 748 − 755. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210399






 下载:
下载: