-
近年来,随着工农业的发展及人类的活动,重金属对土壤的污染越来越严重。2014年发布的《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》显示,全国土壤重金属总的超标率为16.1%。土壤污染防治需要的资金量非常大,“土壤污染防治行动计划”的发布预计带动5.7万亿元投资。针对中国及世界上严重的土壤重金属污染问题,有着众多的研究方法,如物理化学和生物方法[1]。生物方法又分为动物修复、植物修复和微生物修复[2],其中植物修复是新兴的一种绿色环保的修复技术[3]。近年来,在植物修复过程中对于超累积植物的研究比较多[4],而速生林木相对比较少[5]。速生林木相对超累积植物,生物量大、生长迅速,且不与食物链相连,但对重金属的吸收能力相对较弱。针对速生林木的优缺点,如果在吸收量上得到有效强化,将大大提升植物修复的效率。因此,展开对速生林木的强化研究具有重要的研究意义。
-
目前,在植物修复方面研究的超累积植物主要是草本植物,如东南景天Sedum alfredii[6-7],龙葵Solanum nigrum[8-9],蜈蚣草Pteris vittata[10]和商陆Phytolacca acinosa[11]等。超累积植物对重金属的富集和转运能力强,但它们的生物量低、植株矮小、生长缓慢,主根系不发达等因素,限制了在植物修复中的应用。
速生林木生物量大、生长迅速、对金属胁迫耐性较强,且不与食物链相连,能吸收多种重金属,能够修复大面积污染土壤,修复重金属后还可以在回收重金属及建材等多方面的利用,具有一定的经济效益。能源林及用材林等速生林木是土壤重金属修复的主要材料,其中柳树Salix spp.,杨树Populus spp.是国内外研究最多的2种林木,且杨树和柳树在中国分布最广,无性繁殖率高,稍加管理便能成活[12]。目前,速生林木修复重金属污染土壤的研究主要集中在植物对重金属的吸收转运、累积分布、胁迫抗性和强化修复这几方面。
速生林木资源丰富、生长迅速,尤其在幼年期,如柳树幼苗在速生期苗高生长量占总生长量的60.5%,地径生长量占总生长量的64.0%[12];杨树经过6 a的生长,地上部生物量达到112.8 t·hm-2,而干木材蓄积量达到237.5 m3·hm-2[13]。速生林木不仅可以修复重金属,还能吸收其他污染、净化空气和水的作用,美化环境,被广泛运用于园林绿化和植树造林,资源化利用前景广阔。
-
国外运用速生林木修复重金属污染土壤起步相对较早。瑞典在镉污染的耕地中种植大面积的柳树来修复,并将收获的柳树作为能源来利用[14];SLYCKEN等[15]在被冶炼厂所导致的铅、锌、镉等重金属污染的农田土壤中种植柳树,镉、锌的去除能力达到69 g·hm-2·a-1和1 911 g·hm-2·a-1。在中国,利用速生林木修复重金属污染土壤大多还在试验阶段。赖发英等[16]在A和B不同实验区的重金属污染的土壤中种植杨树,B土壤中的铜、铅、锌、镉含量分别下降了22.15%,19.61%,36.64%,2.03%。李金花等[17]对受到铅、锌、铜、镉重金属污染的土壤种植杨树,其中对镉的富集系数最大,其值达到16,具有良好的去除镉的能力。
在植物修复重金属污染土壤的过程中采用的试验方法一般有水培试验、土培试验以及田间试验,如表 1所示。在水培和土培试验中,研究材料主要是速生林木的种子或幼苗,且研究重点在重金属胁迫下的生理生化影响,抗性和富集以及快速初步地进行筛选植物修复材料,而田间试验则是进一步的验证修复土壤重金属材料的筛选。
表 1 在不同研究方法及处理水平上对重金属污染土壤研究情况
Table 1. Research of heavy metal contaminated soil in different research methods and treatment levels

-
种子萌发与植物的受耐性相关,研究重金属对速生林木种子萌发的影响可以在一定程度上反映植物耐重金属胁迫能力[38]。研究表明:在不同浓度铅离子(Pb2+)和镉离子(Cd2+)对毛竹Phyllostachys edulis种子萌发和幼苗早期生长的影响下,随着Pb2+和Cd2+浓度的增加,毛竹种子的发芽率呈现出先升高后降低的趋势,发芽指数、活力指数均与浓度呈负相关关系[39]。这表明,某些重金属在低浓度下对植物有促进作用,而高浓度下则抑制。也有研究表明:银杏Ginkgo biloba种子经重金属处理后,在种子萌发初期对银杏的蛋白质代谢和氨基酸代谢有着促进作用,但随着种子萌发的进行,在高浓度重金属下对银杏种子生理代谢产生了抑制效应[40]。
重金属胁迫对植物生长发育也有一定的影响,其生物量的变化反应植物对重金属的耐性。研究表明:低浓度重金属对樟树Cinnamomum camphora和栾树Koelreuteria paniculata幼苗生长没有明显伤害,甚至可以促进生长;高浓度重金属导致幼株长势衰弱,叶片发黄枯萎,生长量下降,侧须根生长受阻,幼苗生长缓慢,甚至死亡[41],也表现出“低促高抑”现象。温瑀等[42]研究表明:随重金属处理浓度的增加,小叶丁香Syringa microphylla,红瑞木Swida alba,辽东水蜡Ligustrum obtusifolium,杞柳Salix integra等4种绿化植物株高和地径的增加都受到抑制,浓度越高,抑制越明显。
-
重金属影响着林木的生理生化特性,对植物的光合作用、酶活性以及细胞膜透性产生影响[43-45]。在重金属镉的胁迫下,杨树Populus canescens幼苗表现出一定的毒害症状,叶片失绿,甚至出现坏死斑,根生长受阻,而光合速率、蒸腾速率和气孔导数显著降低[46]。石贵玉等[47]研究泥栽培实验发现:当培养液中镉浓度为0.6 mmol·L-1时,桐花树Aegiceras corniculatum和白骨壤Aricennia marina幼苗生长正常,叶绿素含量和光合速率变化不大。杨卫东等[48]通过水培方法,添加不同浓度镉对旱柳Salix matsudana光合作用和内肽酶变化活性影响发现:镉处理降低了总叶绿素、叶绿素a和叶绿素b质量分数,核酮糖-1, 5-二磷酸羧化酶、加氧酶(rubisco)活性随着介质中镉浓度增加而降低;镉抑制根和叶磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧化酶(PEPC)活性;同对照相比,根中游离氨基酸质量分数没有显著变化;而叶中游离氨基酸质量分数增加;不同浓度镉处理降低根的内肽酶活性,高浓度镉使叶内肽酶活力增加。李艳丽等[49]研究表明:随着重金属铅胁迫浓度的增加,旱柳的比叶质量、株高与地径生长受到抑制,叶绿素质量分数及根系活力呈下降的趋势,叶片游离脯氨酸质量分数与细胞膜透性呈逐渐增加趋势。
-
速生林木在重金属环境中长期生长以及环境的适应,对重金属产生了一定的耐性[50]。杨卫东等[51]研究发现:旱柳叶片中有65%~69%的镉富集于细胞壁中;而根中的镉也集中在细胞壁,占59%~66%。植物体内的一些螯合物质在植物对重金属的解毒过程中起到作用,因此,螯合也是植物对细胞内重金属解毒的主要方式之一[52]。当部分金属离子穿过细胞壁和细胞膜进入细胞后,能和细胞质中的蛋白质、谷肤甘肚、有机酸等形成复杂的稳定螯合物,它们能使重金属的毒性降低[53]。ANNEGRET等[54]研究表明:小黑杨Populus trichocarpa×deltoides金属硫蛋白(MT)基因的表达增强了对重金属的耐性。植物体内的酶系统的保护也能增强植物对重金属的抗性。有研究表明[23]:在铅胁迫质量分数不超过2 000 mg·kg-1时,桐花树幼苗叶片中的过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶活性高于对照,且随铅质量分数的升高而上升,说明在一定胁迫浓度下,过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶已被激活,能对铅胁迫起防御作用,提高了植物抗铅的能力。
-
速生林木的根系发达,对土壤中的重金属具有强烈的吸收作用[55]。根系也可通过呼吸释放二氧化碳与水形成碳酸或向外分泌柠檬酸、苹果酸等有机酸来活化,并进一步加以吸收[56-57]。重金属进入根系后,一部分被运输到地上部,重金属进入根内部运输至导管后随蒸腾作用运输到地上部。重金属可通过质外体或共质体进入根内部,质外体运输时,当达到内皮层时,由于内皮层上存在凯氏带,在运输中被阻挡而不能通过,最终通过共质体向内运输至导管[55]。重金属可通过木质部向上运输,也可以从木质部横向运输到韧皮部。在馒头柳Salix matsudana中,镉从根到地上部的长距离运输主要通过韧皮部完成的[58]。
-
朱宇恩等[59]研究旱柳体内铜迁移特征中发现:不同组织富集能力顺序为根>叶>茎,且SEM-EDAX分析发现,根内铜主要存在于表皮、中柱及维管束部分,茎内铜则主要分布在皮层、韧皮部和木质部。董方平等[36]研究发现:锑矿区构树Broussonetia papyrifera根、枝、茎、叶各器官累积重金属锑、砷、铅的顺序为叶>枝>茎>根,累积锌的顺序为叶>枝>根>茎。重金属锑、锌、铅、砷主要富集在构树的叶、枝部。锑矿区重金属污染地构树整株累积的锑为155.85 mg·kg-1,锌为150.12 mg·kg-1,铅为7.56 mg·kg-1,砷为18.90 mg·kg-1,其中85%的重金属累积在构树的地上部分,且60%以上累积在构树的叶部。吴海燕等[58]在馒头柳对镉的研究中发现馒头柳地上部有非常强的持续富集能力;地上部富集的镉占植株吸收总镉量的52%~62%,且主要集中在叶片。杨树中金属含量最低是树干,最高是衰老叶片,因此,清除落叶是必要的,以防止重金属对土壤造成二次污染[60]。
-
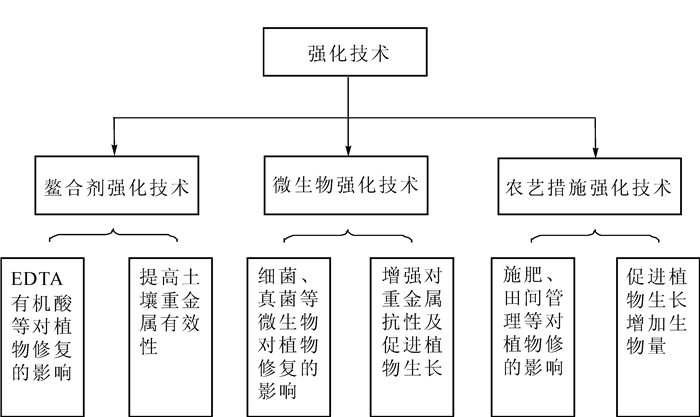
速生林木的生物量大、根系发达,但吸收能力较弱。速生林木强化技术主要在螯合剂强化、微生物强化及农艺措施强化等方面。通过强化技术可提高土壤中重金属活性或促进植物生长来增强对重金属的吸收累积,具体如图 1所示。
-
在污染土壤中施加乙二胺四乙酸、柠檬酸、苹果酸等螯合剂,可与土壤中一些重金属发生配位反应,使不溶态转化为可溶态,提高重金属在土壤中的生物有效性,从而促进植物的吸收。金诚等[61]通过盆栽实验发现投加螯合剂显著提高了土壤中水提态铅的含量,且乙二胺四乙酸相比于乙二醇双(2-氨基乙醚)四乙酸和柠檬酸,更有助于杨树对土壤中铅的吸收和积累,但过量的乙二胺四乙酸会对植物产生一定的毒性,降低其生物量[62]。ZHIVOTOVSKY等[63]观察柳树在盆栽试验和田间试验的吸收和转运铅差异中发现乙二胺四乙酸的使用能使铅大量地向地上部转移,转移量超过1 000 mg·kg-1。尽管螯合剂对重金属污染土壤修复具有强化作用,但螯合剂的使用也存在着一定的风险,主要表现在淋失与地下水的污染,残留的螯合物也有可能产生新的污染[64]。因此,使用可生物降解、对植物无毒害和对环境影响小的螯合剂修复重金属污染土壤具有重要的意义。
-
根际微生物可提高重金属的生物有效性来促进重金属在植物中的累积[65]。目前,研究的微生物主要是真菌、细菌等[66-67]。丛枝菌根(arbuscular mycorrhizal, AM)真菌能与林木形成良好的共生关系,促进植物的生长和根的活动,从而提高植物对重金属的吸收及修复,同时也提高对重金属的抗性[68]。BOJARCZUK等[69]在研究灰杨Populus×canescens在重金属铜和铅污染土壤生长中,发现在接种丛枝菌根真菌的灰杨比未接种的灰杨更好地生存在重金属污染的土壤中,且可有效降低土壤中的重金属浓度。在重金属污染条件下,丛枝菌根真菌能与植物形成良好的共生关系,且丛枝菌根真菌能够显著促进植物吸收磷,增加植物生物量,同时改变植物重金属吸收及分配,减少重金属的生理毒害[70],也增加了植物体内抗氧化酶的活性,提高了对重金属的抗性[71-72]。李霞等[73]研究发现,丛枝菌根真菌降低了翅英木Zenia insignis体内铁、铜、锌和铅浓度,同时增加了铁、铜、锌和铅累积量。
-
农艺措施是强化植物修复重金属的基本措施,主要是促进植物的生长,提高生物量来增加对重金属的累积,包括施肥、增加二氧化碳浓度和田间管理等。肥料的施加改变了土壤的环境,为植物提供营养物质,促进植物生长和吸收重金属的能力。其中,氮是植物体内蛋白质、酶、叶绿素、维生素等的重要组成元素,氮肥在植物对重金属的解毒中起到重要的作用,可以降低重金属对植物的毒害作用。ZHANG等[74]通过盆栽试验对镉胁迫下杨树扦插苗施加氮肥,高浓度镉处理下施加氮肥不仅增加了植株的生长,并且体内的叶绿体结构完整,在重金属胁迫中起到解毒作用。二氧化碳浓度的升高也增加了植物对重金属的抗性,提高植物的生物量,进而提高了植物对重金属的修复。有研究表明:在镉处理下,二氧化碳浓度的增加有效地刺激了杨树和柳树生长。随着光合作用的增强,增加了抗氧化酶活性,提高了杨树和柳树对镉的抗性[75],并且增加了隔在杨树和柳树中的累积[76]。定期地将林木进行地上部的短期轮伐及对落叶的清理可有效地清除重金属,提高植物的修复效率[77]。
-
能源林及用材林等速生林木在修复重金属污染后的回收利用具有一定的经济效益,比如重金属的回收、植物能源的利用以及建材方面的利用[78]。在重金属回收和能源利用方面,欧美国家首先把植物修复和能源生产结合起来,达到一定的生态和经济效益。将富集重金属的林木进行焚烧处理,大大减少了约90%以上的质量和体积,而焚烧后的底灰可用作农田和林地肥料,产生的热能用于所需要的电能[79]。在建材方面,速生林木被广泛运用于建筑、煤矿、家具等产业。在一些行业中,林木会长期的暴露在自然环境中,经受风吹、日晒、雨淋和虫蛀而腐蚀。为了防止进一步被腐蚀,人们采用防腐剂渗透到林木内部达到防腐、防虫效果,节约林木资源。目前市场上防腐剂主要以活性成分二价铜离子和硼酸盐类化合物为主[80-81]。含有重金属的林木如果能运用到防腐中,具有积极的应用价值。在中轻度重金属污染下生长的林木可用作于生物能源、纸浆及工艺品的生产,在使用过程中必须考虑是否会对环境和人们带来影响。针对速生林木生物量大的优点,进行修复重金属材料的资源化利用具有重大的意义。林木资源具有多方面的利用,深入处理的修复材料可应用于能源和建材工程等领域,具有重要的经济效益和社会效益。
-
目前,针对重金属污染土壤,在植物修复方面研究的超累积植物较多,但对速生林木的研究较少,且对速生林木的研究大多数是幼苗在重金属胁迫下生理生化的影响以及重金属在体内的累积分布,没有像超累积植物一样进行深入研究。今后应从以下几个方面对速生林木修复重金属污染展开研究。①在速生林木对重金属的吸收转运及耐性机制方面,重点围绕重金属在林木体内的耐性/解毒机制及吸收转运机制,根际微生物的作用机理对重金属的根际吸收及重金属在木质部的转运情况进行研究,达到细胞层次。②在强化修复土壤重金属技术方面,由于速生林木对重金属的吸收能力相对较弱,在其对重金属的吸收量上得到一定的强化,提高对重金属的吸收及转运,具有重要的应用价值。在今后的研究中,应将螯合剂、微生物和农艺措施等强化技术结合起来进行重金属污染土壤修复,并应用在大田试验中。③速生林木修复重金属后具有很大的生物质能,针对速生林木的特点,将速生林木修复重金属后的材料进行资源化利用,深入地开展修复材料在应用于能源和建材工程领域,以及吸收重金属后材料防腐、防虫效果的研究,具有重要的生态效益和经济效益。
Research progress of heavy metal phytoremediation technology of fast-growing forest trees in soil
-
摘要: 植物修复技术是目前国际上常用的一种用于修复重金属污染土壤的绿色环保技术。目前研究的修复材料主要集中在重金属超积累植物上面,而对速生林木方面的研究相对较少,且研究重点主要侧重于对修复材料的筛选。一般超积累植物主要集中在草本植物,它们对重金属具有吸收和转运能力, 但其生物量小,生长缓慢,根系不发达等因素限制了在植物修复中的运用。速生林木相比超积累植物,具有生物量大,生长迅速等特点,将其应用在植物修复中可为大面积修复重金属污染土壤提供选择。综述了速生林木用于重金属土壤修复的特点,从对重金属的胁迫耐性、吸收转运、累积分布、强化技术及修复材料的回收利用方面进行论述,并为今后速生林木修复土壤重金属污染提供了新的研究思路。Abstract: Phytoremediation is a green and environmental technology used for heavy metal contaminated soil remediation which is commonly used in the world currently. However, the research materials are mainly concentrated on hyperaccumulating plants especially for the screening of remediation species, and less research focus on the fast-growing trees. Hyperaccumulators mainly concentrated in herbaceous plants and had strong ability of absorption and transport of heavy metals because of their ability, but due to the reason of smaller size, low biomass, slow growth rate and undeveloped root the application was limited. Compared with the hyperaccumulators, the fast-growing trees have the advantages of high biomass and rapid growth, etc. The application of fast-growing trees in phytoremediation provides a choice for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil of large area. This paper reviews the characteristics of fast-growing trees used for heavy metal contaminated soil remediation. At the same times, the tolerance, absorption, transportation, accumulation, distribution, strengthening technology and recycling of fast-growing trees as a remediation materials are also discussed in this paper, which could provides a new research viewpoint in the future.
-
Key words:
- soil biology /
- phytoremediation /
- heavy metal /
- soil /
- fast-growing forest trees /
- review
-
表 1 在不同研究方法及处理水平上对重金属污染土壤研究情况
Table 1. Research of heavy metal contaminated soil in different research methods and treatment levels

-
[1] 赵风兰, 高原, 刘彩玲.土壤重金属污染及修复方法研究进展[J].环境科学与技术, 2013, 36(12M): 232-235. ZHAO Fenglan, GAO Yuan, LIU Cailing. Research progress on soil of heavy metal pollution and remediation method [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2013, 36(12M): 232-235. [2] 李飞宇.土壤重金属污染的生物修复技术[J].环境科学与技术, 2011, 34(12H): 148-151. LI Feiyu. Bioremediation in heavy metals contaminated soils [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2011, 34(12H): 148-151. [3] SALT D E, BLAYLOCK M, KUMAR N P, et al. Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants [J]. Bioltechnolgy, 1995, 13(5): 468-474. [4] 宋想斌, 方向京, 李贵祥, 等.重金属污染土壤植物联合修复技术研究进展[J].广东农业科学, 2014, 41(24): 58-62. SONG Xiangbin, FANG Xiangjing, LI Guixiang, et al. Research progress of phytoremediation combination technology to remediate heavy metal contaminated soil [J]. Guangdong Agric Sci, 2014, 41(24): 58-62. [5] LIU Xihua, LIN Xianju, XING Jianhong, et al. Advances in application of forest trees as hyperaccumulators of heavy metal [J]. J Henan Agric Sci, 2011, 40(11): 13-16. [6] 廉梅花, 孙丽娜, 胡筱敏, 等.土壤pH对东南景天修复镉和锌污染土壤的影响[J].生态学杂志, 2014, 33(11): 3068-3074. LIAN Meihua, SUN Lina, HU Xiaomin, et al. Effect of soil pH on phytoremediation of Sedum alfredii Hance in Cd and Zn contaminated soil [J]. Chin J Ecol, 2014, 33(11): 3068-3074. [7] ZHANG Xincheng, LIN Li, CHEN Mingyue, et al. A nonpathogenic Fusarium oxysporum strain enhances phytoextraction of heavy metals by the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance [J]. J Hazard Mater, 2012, 229/230(3): 361-370. [8] 殷永超, 吉普辉, 宋雪英, 等.龙葵(Solanum nigrum L.)野外场地规模Cd污染土壤修复试验[J].生态学杂志, 2014, 33(11): 3060-3067. YIN Yongchao, JI Puhui, SONG Xueying, et al. Field experiment on phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated soils using Solanum nigrum L. [J]. Chin J Ecol, 2014, 33(11): 3060-3067. [9] LIU Hui, YUAN Ming, TAN Shiyun, et al. Enhancement of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (Glomus versiforme) on the growth and Cd uptake by Cd﹣hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum [J]. Appl Soil Ecol, 2015, 89: 44-49. [10] 朱启红, 夏红霞.蜈蚣草对Pb, Zn复合污染的响应[J].环境化学, 2012, 31(7): 1029-1035. ZHU Qihong, XIA Hongxia. Study on response of Pteris vittata to Pb and Zn combined pollution [J]. Environ Chem, 2012, 31(7): 1029-1035. [11] 黄五星, 高境清, 黄宇, 等.商陆对镉锌铜胁迫的生理响应与金属积累特性[J].环境科学与技术, 2010, 33(1): 77-79. HUANG Wuxing, GAO Jingqing, HUANG Yu, et al. Bioaccumulation and physiological response to cadmium, zinc and copper stress in Phytolacca acinosa [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2010, 33(1): 77-79. [12] 沈惠娟.国外主要速生树种快速繁殖的进展[J].世界林业研究, 1996(1): 21-27. SHEN Huijuan. Progress of rapid propagation of fast-growing woody species at abroad [J]. World For Res, 1996(1): 21-27. [13] FORTIER J, GAGNON D, TRUAX B, et al. Biomass and volume yield after 6 years in multiclonal hybrid poplar riparian buffer strips [J]. Biom Bioen, 2010, 34(7): 1028-1040. [14] BERNDES G, FREDTIKSON F, BÖRJESSON P. Cadmium accumulation and Salix-based phytoextraction on arable land in Sweeden [J]. Agric Ecosyst Environ, 2004, 103(1): 207-223. [15] SLYCKEN S V, WITTERS N, MEIRESONNE L, et al. Field evaluation of willow under short rotation coppice for phytomanagement of metal-polluted agricultural soils [J]. Int J Phytorem, 2013, 15(7): 677-689. [16] 赖发英, 赖明, 曾小钦, 等.立体式植物修复受重金属污染农田土壤的探讨[J].环境污染与防治, 2005, 27(5): 382-384, 319. LAI Faying, LAI Ming, ZENG Xiaoqin, et al. Three-dimensional solid phytoremediation of heavy-metal polluted soil [J]. Environ Poll Control, 2005, 27(5): 382-384, 319. [17] 李金花, 何燕, 段建平, 等. 107杨对土壤重金属的吸收和富集[J].林业科学研究, 2012, 25(1): 65-70. LI Jinhua, HE Yan, DUAN Jianping, et al. Absorption and accumulation of heavy metal from soil by leaves of Populus × euramericana 'Neva' plantation [J]. For Res, 2012, 25(1): 65-70. [18] 高建欣, 张文辉, 王校锋. Cd2+处理对5个柳树无性系气体交换参数及叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2013, 33(9): 1874-1884. GAO Jianxin, ZHANG Wenhui, WANG Xiaofeng. Effects Cd2+ stresst on photosynthetic and fluorescent parameters of five willow clones [J]. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 2013, 33(9): 1874-1884. [19] 王树凤, 施翔, 孙海菁, 等.镉胁迫下杞柳对金属元素的吸收及其根系形态构型特征[J].生态学报, 2013, 33(19): 6065-6073. WANG Shufeng, SHI Xiang, SUN Haijing, et al. Metal uptake and root morphological changes for two varieties of Salix integra under cadmium stress [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2013, 33(19): 6065-6073. [20] 孙晓灿, 魏虹, 谢小红, 等.水培条件下秋华柳对重金属Cd的富集特性及光合响应[J].环境科学研究, 2012, 25(2): 220-225. SUN Xiaocan, WEI Hong, XIE Xiaohong, et al. Bioaccumulation and photosynthesis response of Salix variegate to cadmium under hydroponic culture [J]. Res Environ Sci, 2012, 25(2): 220-225. [21] YANG Weidong, ZHAO Fengliang, ZHANG Xincheng, et al. Variations of cadmium tolerance and accumulation among 39 Salix clones: implications for phytoextraction [J]. Environ Earth Sci, 2015, 73(7): 3263-3274. [22] POLLE A, KLEIN T, KETTNER C. Impact of cadmium on young plants of Populus euphratica and P. × canescens, two poplar species that differ in stress tolerance [J]. New For, 2011, 44(1): 13-22. [23] 蔡建秀, 王慧云, 王春风.铅胁迫对桐花树幼苗根叶蛋白质及根抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(6): 2903-2905. CAI Jianxiu, WANG Huiyun, WANG Chunfeng. The effects of Pb stress on roots and leaves protein and root antioxidant enzyme activity of Aegiceras corniculatum seedlings [J]. J Anhui Agric Sci, 2010, 38(6): 2903-2905. [24] 赵素贞, 洪华龙, 严重玲.钙对镉胁迫下秋茄叶片光合作用及超微结构的影响[J].厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 53(6): 875-882. ZHAO Suzhen, HONG Hualong, YAN Chongling. Effect of calcium supply on photosynthesis and ultrastructure of cell of Kandelia obovata (S. L.)Yong under cadmium stress [J]. J Xiamen Univ Nat Sci, 2014, 53(6): 875-882. [25] 刘旭辉, 李月兰, 李秋明, 等.锌和镉胁迫下的桑树幼苗盆栽试验[J].江苏农业科学, 2012, 40(4): 335-339. LIU Xuhui, LI Yuelan, LI Qiuming, et al. Pot experiment of mulberry seedlings under zinc and cadmium stress [J]. Jiangsu Agric Sci, 2012, 40(4): 335-339. [26] LIU Dan, CHEN Junren, MAHMOOD Q, et al. Effect of Zn toxicity on root morphology, ultrastructure, and the ability to accumulate Zn in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) [J]. Environ Sci Poll Res, 2014, 21(23): 13615-13624. [27] 汪庆兵, 陈光才, 房娟, 等.速生柳树苗对土壤铅的耐性、积累与分配特性研究[J].植物研究, 2014, 34(5): 626-633. WANG Qingbing, CHEN Guangcai, FANG Juan, et al. Characteristics of soil lead tolerance, accumulation and distribution in Salix babylonica Linn. and Salix jiangsuensis J172 [J]. Bull Bot Res, 2014, 34(5): 626-633. [28] 王校锋, 张文辉, 崔豫川.瑞典能源柳4个无性系对土壤Hg2+胁迫的生理响应[J].西北植物学报, 2013, 33(3): 555-563. WANG Xiaofeng, ZHANG Wenhui, CUI Yuchuan. Physiological response of four energy willow clones to soil Hg2+ stress [J]. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 2013, 33(3): 555-563. [29] 张春燕, 王瑞刚, 范稚莲, 等.杨树和柳树富集Cd, Zn, Pb的品种差异性[J].农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(3): 530-538. ZHANG Chunyan, WANG Ruigang, FAN Zhilian, et al. Difference in cadmium, zinc and lead accumulation of poplar and willow species [J]. J Agro-Environ Sci, 2013, 32(3): 530-538. [30] JAKDVLJEVIC T, REDOVNIKOVIC I R, CVJETKO M, et al. The potential of poplar (Populus nigra var. italica) in the phytoremediation of cadmium [J]. Sumarski List, 2015, 139(5): 223-232. [31] 陈良华, 徐睿, 杨万勤, 等.镉污染条件下香樟和油樟对镉的吸收能力和耐性差异[J].生态环境学报, 2015, 24(2): 316-322. CHEN Lianghua, XU Rui, YANG Wanqin, et al. Interspecific differences between Cinnamomum camphora and C. longepaniculatum in Cd absorption and tolerance under two levels of Cd pollution [J]. Ecol Environ Sci, 2015, 24(2): 316-322. [32] 王锦文, 白秀, 陈锦峰, 等.复合重金属Pb, Zn对香樟生理特征的影响[J].安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(21): 10253-10254. WANG Jinwen, BAI Xiu, CHEN Jinfeng, et al. Effect of complex heavy metals Pb/Zn on the physiological characteristics of Cinnamomum camphora [J]. J Anhui Agric Sci, 2009, 37(21): 10253-10254. [33] 秦芳, 胥晓, 刘刚, 等.桑树(Morus alba)幼苗对铅污染的生理耐性和积累能力的性别差异[J].环境科学学报, 2014, 34(10): 2615-2623. QIN Fang, XU Xiao, LIU Gang, et al. Sexual differences in physiological tolerance and accumulation capacity against lead pollution in Morus alba seedlings [J]. Acta Sci Circumst, 2014, 34(10): 2615-2623. [34] 田胜尼, 张静, 孙庆业, 等.铜尾矿自然定居腺柳对重金属吸收及分布的研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(9): 1771-1777. TIAN Shengni, ZHANG Jing, SUN Qingye, et al. Heavy metals absorption and distribution by Salix chaenomeloides settled naturally on the copper tailings [J]. J Agro-Environ Sci, 2013, 32(9): 1771-1777. [35] 王新, 贾永锋.杨树、落叶松对土壤重金属的吸收及修复研究[J].生态环境, 2007, 16(2): 432-436. WANG Xin, JIA Yongfeng. Study on absorption and remediation by poplar and larch in the soil contaminated with heavy metals [J]. Ecol Environ, 2007, 16(2): 432-436. [36] 童方平, 龙应忠, 杨勿享, 等.锑矿区构树富集重金属的特性研究[J].中国农学通报, 2010, 26(14): 328-331. TONG Fangping, LONG Yingzhong, YANG Wuxiang, et al. Study on the characteristics of heavy metal accumulation in Broussonetia papyrifera in an antimony mine [J]. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2010, 26(14): 328-331. [37] 张兴, 王冶, 揭雨成, 等.桑树对矿区土壤中重金属的原位去除效应研究[J].中国农学通报, 2012, 28(7): 59-63. ZHANG Xing, WANG Ye, JIE Yucheng, et al. Effect of heavy metal home position elimination on the mulberry in mining area soil [J]. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2012, 28(7): 59-63. [38] 陈俊任, 柳丹, 吴家森, 等.重金属胁迫对毛竹种子萌发及其富集效应的影响[J].生态学报, 2014, 34(22): 6501-6509. CHEN Junren, LIU Dan, WU Jiasen, et al. Seed germination and metal accumulation of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) under heavy metal exposure [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2014, 34(22): 6501-6509. [39] 张大鹏, 蔡春菊, 范少辉, 等.重金属Pb2+和Cd2+对毛竹种子萌发及幼苗早期生长的影响[J].林业科学研究, 2012, 25(4): 500-504. ZHANG Dapeug, CAI Chunju, FAN Shaohui, et al. Effects of Pb2+, Cd2+ on germination and seedling early growth of moso bamboo(Phyllostachys edulis) seed [J]. For Res, 2012, 25(4): 500-504. [40] 朱宇林, 曹福亮, 汪贵斌, 等. Cd, Pb处理对银杏种子萌发的影响[J].种子, 2006, 25(3): 35-37. ZHU Yulin, CAO Fuliang, WANG Guibin, et al. Effects of cadmium and lead treatment on the germination of Ginkgo biloba seeds [J]. Seed, 2006, 25(3): 35-37. [41] 王利宝, 朱宁华, 鄂建华. Pb, Zn等重金属对樟树、栾树幼苗生长的影响[J].中南林业科技大学学报, 2010, 30(2): 44-47. WANG Libao, ZHU Ninghua, E Jianhua. Effects of heavy matels lead, zinc and copper on young seedling growth of Cinnamomum camphora and Koelreuteria paniculata [J]. J Cent South Univ For Technol, 2010, 30(2): 44-47. [42] 温瑀, 穆立蔷.土壤铅、镉胁迫对4种绿化植物生长、生理及积累特性的影响[J].水土保持学报, 2013, 27(5): 234-239. WEN Yu, MU Liqiang. Effects of soil Pb, Cd stress on the growth, physiological and accumulating characteristics of four ornamental trees [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2013, 27(5): 234-239. [43] 高建欣, 张文辉, 王校锋. Cd2+处理对5个柳树无性系气体交换参数及叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2013, 33(9): 1874-1884. GAO Jianxin, ZHANG Wenhui, WANG Xiaofeng. Effects of Cd2+ stress on photosynthetic and fluorescent parameters of five willow clones [J]. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 2013, 33(9): 1874-1884. [44] 杨斌, 张文辉, 高建欣. 5种速生柳无性系对Pb2+胁迫的生理抗性比较[J].西北植物学报, 2015, 35(6): 1182-1189. YANG Bin, ZHANG Wenhui, GAO Jianxin. Physiological resistance of five fast-growing willow clones to lead(Pb) stress [J]. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 2015, 35(6): 1182-1189. [45] 杨卫东, 陈益泰.镉胁迫对旱柳细胞膜透性和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].西北植物学报, 2008, 28(11): 2263-2269. YANG Weidong, CHEN Yitai. Membrane leakage and antioxidant enzyme activities in roots and leaves of Salix matsudana with cadmium stress [J]. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 2008, 28(11): 2263-2269. [46] 张莹, 魏安智, 杨途熙, 等.锌胁迫对灰杨幼苗生长和光合特性的影响[J].东北林业大学学报, 2011, 39(3): 19-21. ZHANG Ying, WEI Anzhi, YANG Tuxi, et al. Effect of zinc stress on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Populus canescens [J]. J Northeast For Univ, 2011, 39(3): 19-21. [47] 石贵玉, 康浩, 段文芳.重金属镉对红树植物白骨壤和桐花树幼苗生理特性的影响[J].广西植物, 2009, 29(5): 644-647. SHI Guiyu, KANG Hao, DUAN Wenfang. Effect of cadmium on physiological characteristics of mangrove Avicennia marina and Aegiceras corniculatum seedlings [J]. Guihaia, 2009, 29(5): 644-647. [48] 杨卫东, 陈益泰, 王树凤.镉胁迫对旱柳光合作用和内肽酶变化的影响[J].植物研究, 2009, 29(4): 428-432. YANG Weidong, CHEN Yitai, WANG Shufeng. Influences of cadmium stress on photosynthesis and endopeptidase activities in Salix matsudana [J]. Bull Bot Res, 2009, 29(4): 428-432. [49] 李艳丽, 李永杰.土壤铅胁迫对旱柳生长及相关生理特性的影响[J].北方园艺, 2011(13): 168-170. LI Yanli, LI Yongjie. Effect of lead stress on the growth and some physiological characteristics in Salix matsudana seedling [J]. Northern Hortic, 2011(13): 168-170. [50] KATAYAMA H, BANBA N, SUGIMURA Y, et al. Subcellular compartmentation of strontium and zinc in mulberry idioblasts in relation to phytoremediation potential [J]. Environ Exp Bot, 2013, 85(1): 30-35. [51] 杨卫东, 陈益泰, 屈明华.镉在旱柳中亚细胞分布及存在的化学形态[J].西北植物学报, 2009, 29(7): 1394-1399. YANG Weidong, CHEN Yitai, QU Minghua. Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Salix matsudana [J]. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 2009, 29(7): 1394-1399. [52] 邬飞波, 张国平.植物螯合肽及其在重金属耐性中的作用[J].应用生态学报, 2003, 14(4): 632-636. WU Feibo, ZHANG Guoping. Phytochelatin and its function in heavy metal tolerance of higer plants [J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2003, 14(4): 632-636. [53] BACCIO D D, KOPRIVA S, SEBASTIANI L, et al. Does glutathione metabolism have a role in the defence of poplar against zinc excess? [J]. New Phytol, 2005, 167(1): 73-80. [54] KOHLER A, BLAUDEZ D, CHALOT M, et al. Cloning and expression of multiple metallothioneins from hybrid poplar [J]. New Phytol, 2004, 164(1): 83-93. [55] 李合生.现代植物生理学[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2012. [56] 刘子雄, 朱天辉, 张建.林木根系分泌物与根际微生物研究进展[J].世界林业研究, 2005, 18(6): 25-31. LIU Zixiong, ZHU Tianhui, ZHANG Jian. Research advances in root exudates and rhizosphere microorganisms of forest trees [J]. World For Res, 2005, 18(6): 25-31. [57] 张豆豆, 梁新华, 王俊.植物根系分泌物研究综述[J].中国农学通报, 2014, 30(35): 314-320. ZHANG Doudou, LIANG Xinhua, WANG Jun. A review of plant root exudates [J]. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2014, 30(35): 314-320. [58] 吴海燕, 台培东, 李培军, 等.馒头柳对镉的耐性、运输途径和累积特征[J].生态学杂志, 2011, 30(6): 1222-1228. WU Haiyan, TAI Peidong, LI Peijun, et al. Cadmium tolerance of and cadmium transportation and accumulation in Salix matsudana [J]. Chin J Ecol, 2011, 30(6): 1222-1228. [59] 朱宇恩, 赵烨, 徐东昱, 等.旱柳(Salix matsudana Koidz)体内Cu迁移特征的水培模拟研究[J].环境科学学报, 2011, 31(12): 2740-2747. ZHU Yuen, ZHAO Ye, XU Dongyu, et al. Investigation on the characteristics of copper migration in different tissues of Salix matsudana Koidz based on hydroponic experiment [J]. Acta Sci Circumst, 2011, 31(12): 2740-2747. [60] LAUREYSENS I, BLUST R, de TEMMERMAN L, et al. Clonal variation in heavy metal accumulation and biomass production in a poplar coppice culture (I) seasonal variation in leaf, wood and bark concentrations [J]. Environ Poll, 2004, 131(3): 485-494. [61] 金诚, 南忠仁, 胡亚虎, 等.螯合剂强化下新疆杨对干旱区Pb污染农田土壤的修复[J].农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(12): 2340-2344. JIN Cheng, NAN Zhongren, HU Yahu, et al. Chelator-enhanced phytoremediation of Pb from contaminated arable soil in arid region by Populus bolleana Lauch [J]. J Agro-Environ Sci, 2012, 31(12): 2340-2344. [62] CHATURVEDI N, DHAL N K, PATRA H K. EDTA and citric acid-mediated phytoextraction of heavy metals from iron ore tailings using Andrographis paniculata: a comparative study [J]. Int J Min Reclam Environ, 2014, 29(1): 33-46. [63] ZHIVOTOVSKY O P, KUZOVKINA Y A, SCHULTHESS C P, et al. Lead uptake and translocation by willows in pot and field experiments [J]. Int J Phytoremed, 2011, 13(8): 731-749. [64] 丁竹红, 胡忻, 尹大强.螯合剂在重金属污染土壤修复中应用研究进展[J].生态环境学报, 2009, 18(2): 777-782. DING Zhuhong, HU Xin, YIN Daqiang. Application of chelants in remediation of heavy metals-contaminated soil [J]. Ecol Environ Sci, 2009, 18(2): 777-782. [65] 王海鸥, 徐海洋, 钟广蓉, 等.根际微生物对植物修复重金属污染土壤作用的研究进展[J].安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(30): 14832-14834. WANG Haiou, XU Haiyang, ZHONG Guangrong, et al. Progress in effect of rhizosphere microbeson phytoremediation of soil pollutedby heavy metal [J]. J Anhui Agric Sci, 2009, 37(30): 14832-14834. [66] ZHU Donglin, OUYANG Liming, XU Zhaohui, et al. Rhizobacteria of Populus euphratica promoting plant growth against heavy metals [J]. Int J Phytoremed, 2015, 17(10): 973-980. [67] 廖妤婕, 谈宇, 付旺, 等.丛枝菌根真菌作用下桉树对铅的耐受机制研究[J].基因组学与应用生物学, 2014, 33(3): 633-639. LIAO Yujie, TAN Yu, FU Wang, et al. Study on the Pb-tolerance mechanism of Eucalyptus under the role of Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi [J]. Gen Appl Biol, 2014, 33(3): 633-639. [68] YANG Yurong, LIANG Yan, GHOSH A, et al. Assessment of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi status and heavy metal accumulation characteristics of tree species in a lead-zinc mine area: potential applications for phytoremediation [J]. Environ Sci Poll Res, 2015, 22(17): 13179-13193. [69] BOJARCZUK K, KARLINSKI L, HAZUBSKA-PRZYBYL T, et al. Influence of mycorrhizal inoculation on growth of micropropagated Populus × canescens lines in metal-contaminated soils [J]. New For, 2015, 46(2): 195-215. [70] 黄艺, 李婷, 姜学艳.锌对外生菌根植物苏格兰松幼苗锌积累和光合作用的影响[J].环境科学学报, 2004, 24(3): 508-514. HUANG Yi, LI Ting, JIANG Xueyan. Effects of Zn on Zn accumulation and photosynthesis of ectomycorrhizal Pinus sylvestris seedlings [J]. Acta Sci Circumst, 2004, 24(3): 508-514. [71] FERREIRA P A A, CERETTA C A, SORIANI H H, et al. Rhizophagus clarus and phosphate alter the physiological responses of Crotalaria juncea cultivated in soil with a high Cu level [J]. Appl Soil Ecol, 2015, 91: 37-47. [72] 谢翔宇, 翁铂森, 赵素贞, 等. Cd胁迫下接种丛枝菌根真菌对秋茄幼苗生长与抗氧化酶系统的影响[J].厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 52(2): 244-253. XIE Xiangyu, WEND Bosen, ZHAO Suzhen, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation and Cd stress on the growth and antioxidant enzyme system of Kandelia obovata [J]. J Xiamen Univ Nat Sci, 2013, 52(2): 244-253. [73] 李霞, 彭霞薇, 伍松林, 等.丛枝菌根对翅荚木生长及吸收累积重金属的影响[J].环境科学, 2014, 35(8): 3142-3148. LI Xia, PENG Xiawei, WU Songlin, et al. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizae on growth, heavy metal uptake and accumulation of Zenia insignis Chun seedlings [J]. Environ Sci, 2014, 35(8): 3142-3148. [74] ZHANG Fan, WAN Xueqin, ZHONG Yu. Nitrogen as an important detoxification factor to cadmium stress in poplar plants [J]. J Plant Interact, 2014, 9(1): 249-258. [75] GUO Baohua, DAI Songxiang, WANG Ruigang, et al. Combined effects of elevated CO2 and Cd-contaminated soil on the growth, gas exchange, antioxidant defense, and Cd accumulation of poplars and willows [J]. Environ Exp Bot, 2015, 115: 1-10. [76] WANG Ruigang, DAI Songxiang, TANG Shirong, et al. Growth, gas exchange, root morphology and cadmium uptake responses of poplars and willows grown on cadmium-contaminated soil to elevated CO2 [J]. Environ Earth Sci, 2012, 67(1): 1-13. [77] 刘艳丽, 吴凤霞, 徐莹, 等.杨树修复重金属污染土壤的研究进展[J].林业科学, 2012, 48(9): 139-144. LIU Yanli, WU Fengxia, XU Ying, et al. Research progress in the remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils with populus [J]. Sci Silv Sin, 2012, 48(9): 139-144. [78] LICHT L A, ISEBRANDS J G. Linking phytoremediated pollutant removal to biomass economic opportunities [J]. Biom Bioen, 2005, 28(2): 203-218. [79] DELPLANQUE M, COLLET S, GRATTA F D, et al. Combustion of Salix used for phytoextraction: the fate of metals and viability of the processes [J]. Biom Bioen, 2013, 49(2): 160-170. [80] 施振华.大力发展木材防腐, 节约木材[J].木材工业, 2001, 15(4): 6-8. SHI Zhenhua. Developing wood preservation with great strength for the economical use of wood [J]. China Wood Ind, 2001, 15(4): 6-8. [81] 蒋明銜, 陈奶荣, 林巧佳.木材防腐的研究进展[J].福建林业科技, 2013, 40(1): 207-213. JIANG Mingxian, CHEN Nairong, LIN Qiaojia. Research progress in preservative-treated wood [J]. J Fujian For Sci Technol, 2013, 40(1): 207-213. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2016.05.024







 下载:
下载: