-
湖北贝母Fritillaria hupehensis为百合科Liliaceae贝母属Fritillaria植物,以干燥鳞茎入药,含多种异甾体、甾体类生物碱,具有化痰止咳、散结的功效,是恩施州大力发展药材之一[1]。由于野生资源日趋匮乏,目前多为人工栽培。如何提高湖北贝母产量和品质,成为湖北贝母种植亟需解决的问题。氮(N)、磷(P)、钾(K)是植物生长必需的矿质元素,对植物生长和品质形成有重要影响。研究表明:适量施用磷肥可增强浙贝母F. thunbergii抗逆性,有利于生物碱类物质质量分数及产量的提高[2]。不同品种钾肥配施可促进浙贝母的养分吸收,显著提高浙贝母鳞茎的生物量及其生物碱的积累量,且硫酸钾对生物碱质量分数的提升作用优于氯化钾[3]。陈天德等[4]研究发现:施用240 kg·hm−2氮、105 kg·hm−2五氧化二磷(P2O5)、135 kg·hm−2氧化钾 (K2O)为浙贝母最佳施肥量。陆中华等[5]认为:施用300 kg·hm−2氮、80 kg·hm−2五氧化二磷、180 kg·hm−2氧化钾为露天环境中浙贝母获得高产且贝母素总量较高的施肥方案。上述施肥量差异可能受土壤肥力、种植密度及作物品种等因素的影响。近年来有关施肥对贝母产量与品质影响的研究多以浙贝母为主,针对湖北贝母养分需求规律及有效成分积累的研究未见系统报道。
氮是植物体内蛋白质、代谢酶、核酸及生物碱等次生代谢产物的重要物质组成成分,氮肥通过影响药用植物的养分吸收与代谢转化等过程,成为限制中药材产量与品质的关键因素[6−7],并且药用植物在不同生育期对养分的需求及有效成分的积累均存在显著差异[8−9]。鉴于此,本研究以湖北贝母为供试材料,研究不同氮施用量对各生育期湖北贝母鳞茎氮磷钾吸收及生物碱动态积累的影响,以期明确湖北贝母不同生育期矿质元素的吸收规律及主要生物碱的积累特征,为湖北贝母规范化生产及科学施肥提供理论依据。
-
取样地点位于湖北省恩施市新塘乡境内,属亚热带季风湿润型山地气候,年均无霜期为260.0 d,年均气温为15.5 ℃。境内雨量充沛,年均降雨量为1 000.0~2 000.0 mm。采样地土壤的主要化学性质:pH 为6.60,有机质为33.91 g·kg−1,硝态氮为 17.05 mg·kg−1,有效磷为 4.01 mg·kg−1,速效钾为 205.66 mg·kg−1。
-
湖北贝母种质由湖北省农业科学院中药材研究所提供,于2021年9月21日播种,种植密度为15 cm×20 cm,种植前未施用肥料。试验中氮肥为尿素(含质量分数为 46.4%的氮),磷肥为过磷酸钙(含质量分数为16.0%的五氧化二磷),钾肥为硫酸钾(含质量分数为54.0%的氧化钾)。试验设置4个氮水平:不施氮肥(N0)、 氮肥用量为58.0 kg·hm−2(N1)、氮肥用量为116.0 kg·hm−2(N2)、氮肥用量为174.0 kg·hm−2(N3);均另施102.4 kg·hm−2五氧化二磷和86.4 kg·hm−2氧化钾。试验所用肥料分4次施用,分别于2021年9月10日施基肥(氮施用量的20%,五氧化二磷施用量的70%,氧化钾施用量的20%),2022年1月3日施腊肥(氮施用量的40%,五氧化二磷施用量的30%,氧化钾施用量的40%),2022年3月23日施苗肥(氮施用量的20%,氧化钾施用量的20%),2022年4月23日施花肥(氮施用量的20%,氧化钾施用量的20%)。所有处理磷、钾肥用量均相同。每个处理重复3次,随机区组排列,四周设置保护行。
-
采用刨根法分别在湖北贝母苗期(2022年4月1日)、花期(2022年5月1日)、收获期(2022年6月10日)采集生长健壮、长势一致、无病虫害的植株作为供试材料。将湖北贝母按茎秆、叶片、鳞茎等器官分开,测量不同处理组的叶长、叶宽、叶型指数(叶长/叶宽)、株高、茎粗、鳞茎鲜质量等生长指标。鳞茎洗净晾干表面水分后称鲜质量,烘干后称量并计算折干率。鳞茎折干率 =干质量/鲜质量。鳞茎用 H2SO4-H2O2 消煮后,分别用凯氏定氮法、钼锑抗比色法及火焰光度法测定氮、磷、钾质量分数[10];总生物碱质量分数采用酸性染料比色法测定[11]。参照王路伟等[12]的方法提取湖北贝母中贝母素甲、贝母素乙、贝母辛、湖贝甲素。采用液相色谱串联质谱法测定4种物质质量分数。色谱条件:Poroshell 120 SB-C18色谱柱(2.1 mm ×150.0 mm,2.7 µm),体积分数为0.1%甲酸水溶液为流动相A,乙腈为流动相B,进行梯度洗脱,流速为0.4 mL·min−1,进样量为2 µL,柱温为40 ℃。质谱条件:电喷雾离子源正离子模式(ESI),扫描模式为多反应监测(MRM)模式,雾化温度为500 ℃,气帘气压力为0.207 MPa,喷雾电压为5.5 kV,雾化气及辅助气压力均为0.345 MPa。
-
本研究中氮磷比(N∶P)、 氮钾比(N∶K)、 钾磷比(K∶P) 均为质量比。采用Origin 9.0作图,采用 SPSS 17.0进行单因素方差分析及相关性分析,采用最小显著性差异法(LSD)进行多重比较,运用Pearson进行相关性分析。
-
由表1可知:不同氮肥用量对湖北贝母幼苗叶长、叶宽、株高、茎粗等生长指标影响有较大差异。随着氮肥用量的增加,苗期、花期幼苗的叶长、叶宽、株高、茎粗总体呈增加趋势,且均在N2处理时达到峰值。各生育期湖北贝母鳞茎的鲜质量及干质量均随氮肥用量增加显著增加(P<0.05),且均在N2处理时达到峰值;但各生育期内不同氮肥处理时鳞茎的折干率总体差异不显著。相同氮肥处理下,苗期至花期湖北贝母鳞茎干质量的增长量为0.53~2.72 g·株−1,增长率为22.36%~83.44%;花期至收获期湖北贝母鳞茎干质量增长量为0.30~1.85 g·株−1,增长率为10.34%~50.82%。此结果表明:湖北贝母鳞茎干物质积累速率在苗期至花期较快,此后其产量增长量减缓。
表 1 不同氮肥施用量时湖北贝母的生长指标
Table 1. Growth indices of F. hupehensis under different nitrogen dosages
生育期 处理 叶长/cm 叶宽/cm 叶型指数 株高/cm 茎粗/cm 苗期 N0 11.15±0.12 b 1.03±0.06 c 10.88±0.56 a 19.70±0.92 c 0.50±0.01 b N1 11.33±0.12 b 1.33±0.05 b 8.55±0.29 b 29.30±1.00 b 0.53±0.02 ab N2 11.45±0.19 a 1.55±0.10 a 7.39±0.25 d 33.90±3.11 a 0.55±0.03 a N3 11.00±0.19 b 1.42±0.06 b 7.76±0.21 c 32.85±0.95 a 0.50±0.02 b 花期 N0 11.77±0.10 b 1.72±0.10 b 6.86±0.48 a 36.45±0.58 b 0.50±0.02 b N1 11.90±0.07 b 1.80±0.11 a 6.61±0.39 a 38.00±0.94 b 0.55±0.02 b N2 14.20±0.08 a 2.10±0.10 b 6.76±0.51 a 40.50±1.16 a 0.65±0.03 a N3 12.00±0.20 b 1.70±0.12 b 7.06±0.61 a 37.60±2.02 b 0.51±0.04 b 收获期 N0 - - - - - N1 - - - - - N2 - - - - - N3 - - - - - 生育期 处理 鳞茎鲜质量/(g·株−1) 鳞茎干质量/(g·株−1) 折干率/% 鳞茎干质量产量/(g·m−2) 苗期 N0 7.11±0.12 d 2.37±0.06 d 33.30±0.62 b - N1 7.60±0.22 c 2.63±0.09 c 34.65±1.51 ab - N2 11.28±0.17 a 4.00±0.13 a 35.43±1.75 ab - N3 8.85±0.16 b 3.26±0.17 b 36.86±2.50 a - 花期 N0 10.32±0.17 c 2.90±0.07 d 28.14±1.13 b - N1 10.52±0.29 c 3.64±0.22 c 35.24±1.19 a - N2 20.49±0.98 a 6.82±0.13 a 33.32±1.00 a - N3 16.75±0.78 b 5.98±0.14 b 35.78±2.53 a - 收获期 N0 11.72 ±0.59 d 3.20±0.20 d 27.31±0.83 c 64.00±3.91 c N1 16.67±0.69 c 5.49±0.27 c 32.93±0.47 b 109.89±5.88 b N2 21.83±1.02 a 8.26±0.27 a 37.93±3.02 a 165.20±4.69 a N3 18.25±0.48 b 7.22±0.18 b 39.57±0.08 a 144.38±4.00 a 说明:-表示无此项。数值为平均值±标准差(n=3)。不同小写字母表示同一生育期不同氮肥施用量间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
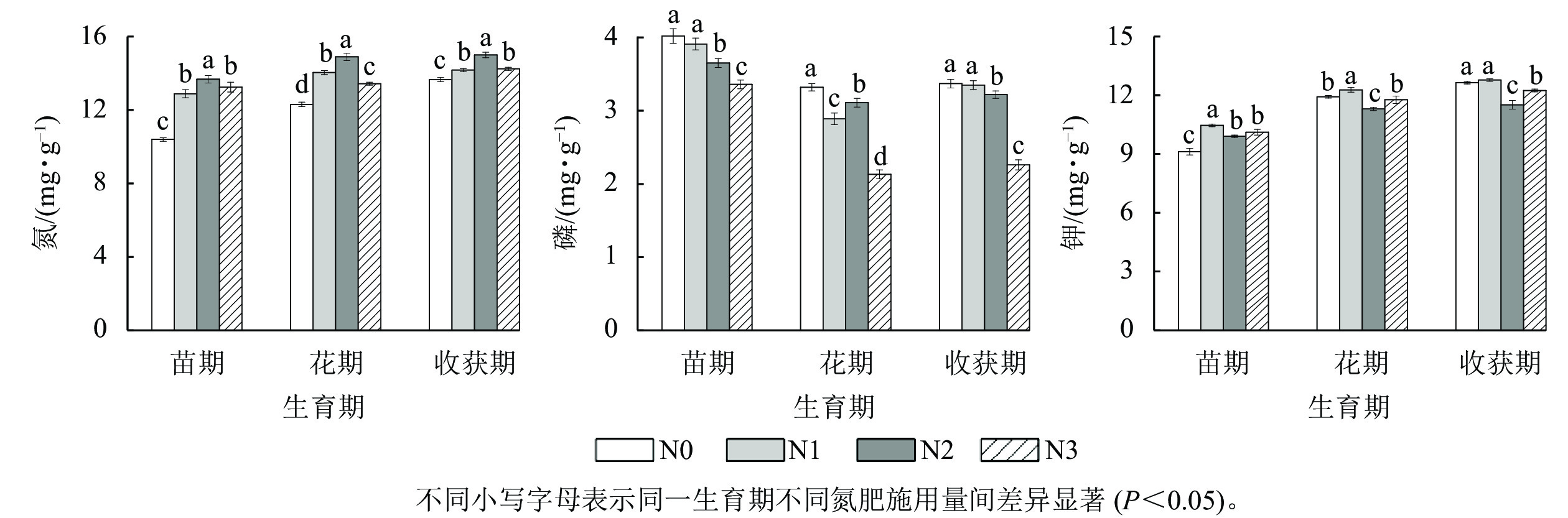
由图1可知:随氮肥用量增加,苗期、花期及收获期湖北贝母鳞茎中氮质量分数较N0处理的增幅分别为2.49~3.28、1.13~2.59、0.52~1.34 mg·g−1,均在N2处理时达到峰值,且贝母鳞茎中氮质量分数与其干质量显著正相关(P<0.01)。随氮肥用量增加,各生育期内贝母鳞茎中磷质量分数与N0处理相比总体呈降低趋势,且鳞茎中磷质量分数与其干质量显著负相关(P<0.05)。各生育期内湖北贝母鳞茎中钾质量分数均在N1处理时达到峰值。苗期时,N2、N3处理中贝母鳞茎钾质量分数均显著高于N0处理(P<0.05);花期和收获期,N2、N3处理中贝母鳞茎钾质量分数均小于N0处理,且均在N2处理时最小。相关性分析表明:湖北贝母鳞茎中氮与钾的质量分数显著正相关(P<0.05)。相同氮肥施用量时,湖北贝母鳞茎中氮、钾质量分数均随生育期延长逐渐增加,但磷质量分数均为苗期时最高,花期时最低。
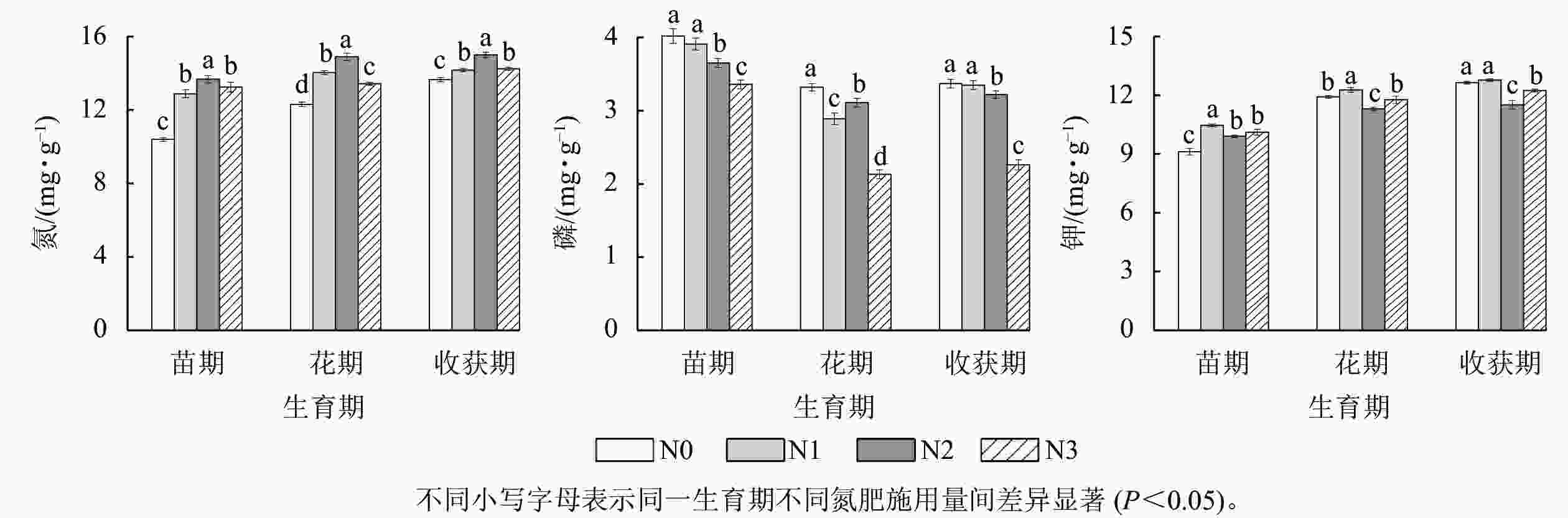
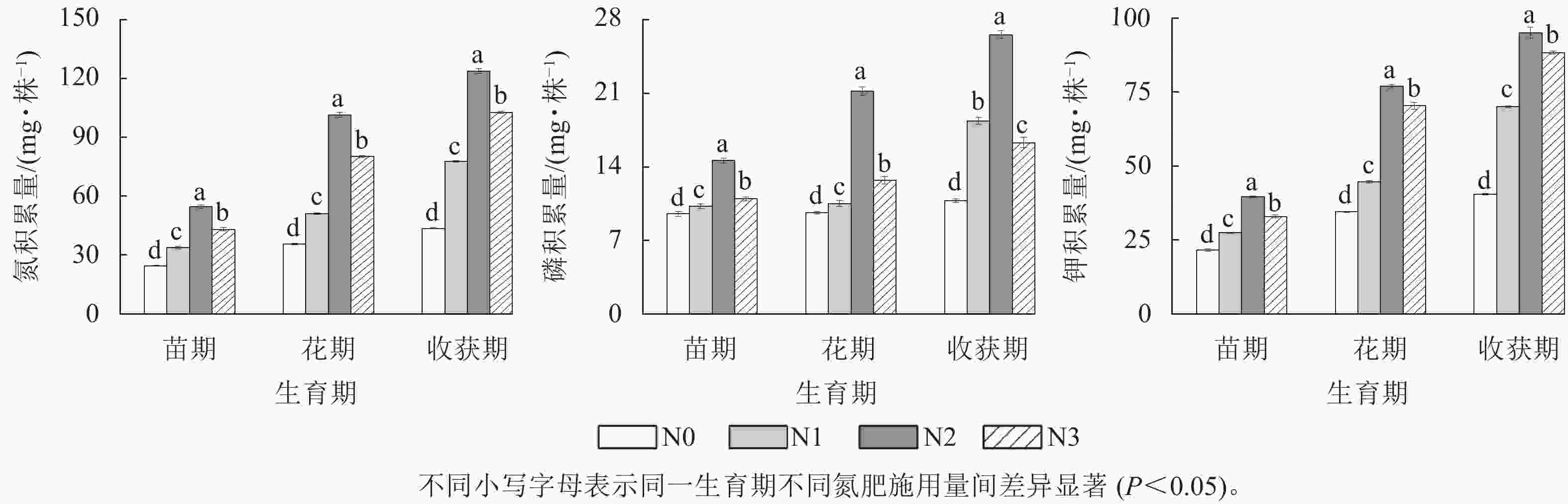
图 1 不同氮肥施用量对湖北贝母鳞茎氮、磷、钾质量分数的影响
Figure 1. Effects of different nitrogen dosages on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in F. hupehensis bulbs under different nitrogen
由图2可知:在同一生育期内,随氮肥用量增加,湖北贝母鳞茎中氮、磷、钾的积累量显著增加(P<0.05),且均在N2处理时达到峰值。相关性分析表明:单株湖北贝母鳞茎干质量与氮、磷、钾积累量均显著正相关(P<0.05),相关系数分别为0.997、0.890、0.988。相同氮肥施用量时,苗期至花期,湖北贝母鳞茎中氮、钾积累量分别增长11.05~46.87、12.95~37.47 mg·株−1,增长率分别为44.86%~85.72%、59.93%~113.55%;花期至收获期,湖北贝母鳞茎中氮、钾积累量分别增长8.01~22.27、5.88~25.44 mg·株−1,增长率分别为21.93%~52.22%、17.01%~56.97%。总体而言,4种氮肥用量处理时苗期至花期湖北贝母鳞茎中氮、钾的积累量及增长率均高于花期至收获期,此变化趋势与湖北贝母鳞茎干质量的增长规律相同。这一结果表明:苗期至花期是湖北贝母增产的关键时期,重施氮、钾肥对于鳞茎生长至关重要。
-
表2为不同氮肥用量时各生育期湖北贝母鳞茎中氮、磷、钾的化学计量比。总体而言,贝母鳞茎的氮磷比均小于14.0,苗期湖北贝母鳞茎中钾磷比小于3.4,花期及收获期鳞茎中钾磷比均大于3.4。在同一生育期内,随氮肥用量增加,湖北贝母鳞茎的氮磷比、钾磷比呈增加趋势。相同氮肥用量处理下,苗期至花期湖北贝母鳞茎的氮磷比、钾磷比均增加,花期至收获期湖北贝母鳞茎的氮磷比、钾磷比均呈降低趋势,且降幅减小。此结果可能与花期湖北贝母鳞茎中磷质量分数最低有关。在湖北贝母整个生育期内,鳞茎中氮钾比均小于2.1;在同一生育期内,随氮肥用量增加,湖北贝母鳞茎的氮钾比均先增加后降低,且在N2处理时达到峰值;相同氮肥用量处理下,随生育期延长,湖北贝母鳞茎中氮钾比总体呈降低趋势,说明湖北贝母由营养生长向生殖生长过渡时,鳞茎对钾的需求不断增强,可适量增施钾肥。
表 2 不同氮肥用量时湖北贝母鳞茎氮、磷、钾的化学计量比
Table 2. Stoichiometric ratio of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium in F. hupehensis bulbs under different nitrogen dosages
时期 处理 氮磷比 氮钾比 钾磷比 时期 处理 氮磷比 氮钾比 钾磷比 苗期 N0 2.58±0.07 d 1.14±0.03 d 2.27±0.03 c 花期 N2 4.79±0.08 b 1.32±0.02 a 3.63±0.05 c N1 3.29±0.10 c 1.23±0.03 c 2.68±0.04 b N3 6.31±0.17 a 1.14±0.02 b 5.53±0.22 a N2 3.75±0.07 b 1.38±0.02 a 2.71±0.02 b N3 3.94±0.09 a 1.31±0.01 b 3.01±0.07 a 收获期 N0 4.05±0.07 c 1.08±0.01 c 3.75±0.08 bc N1 4.23±0.06 c 1.11±0.01 c 3.81±0.08 b 花期 N0 3.70±0.02 c 1.00±0.01 c 3.59±0.03 c N2 4.66±0.02 b 1.30±0.03 a 3.57±0.09 c N1 4.86±0.10 b 1.14±0.01 b 4.25±0.08 b N3 6.30±0.17 a 1.16±0.01 b 5.42±0.20 a 说明:不同小写字母表示同一生育期不同氮肥施用量间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
由图3可知:湖北贝母鳞茎中各生物碱质量分数由高到低依次为贝母素乙、贝母素甲、贝母辛、湖贝甲素。在湖北贝母各生育期内,鳞茎中总生物碱质量分数均随氮肥用量增加而降低,但4种生物碱质量分数的变化各异。随氮肥用量增加,苗期及收获期湖北贝母鳞茎中贝母素甲、贝母素乙、湖贝甲素质量分数均降低,花期鳞茎中贝母素甲、贝母素乙质量分数呈增加趋势。苗期及花期,鳞茎中贝母辛质量分数随氮肥用量增加而增加,收获期贝母辛质量分数随氮肥用量增加而降低。相同氮肥施用量时,随生育期延长,湖北贝母鳞茎中总生物碱、贝母素甲、贝母素乙、湖贝甲素质量分数从高到低依次均为收获期、苗期、花期,贝母辛质量分数为苗期较高,花期最低。

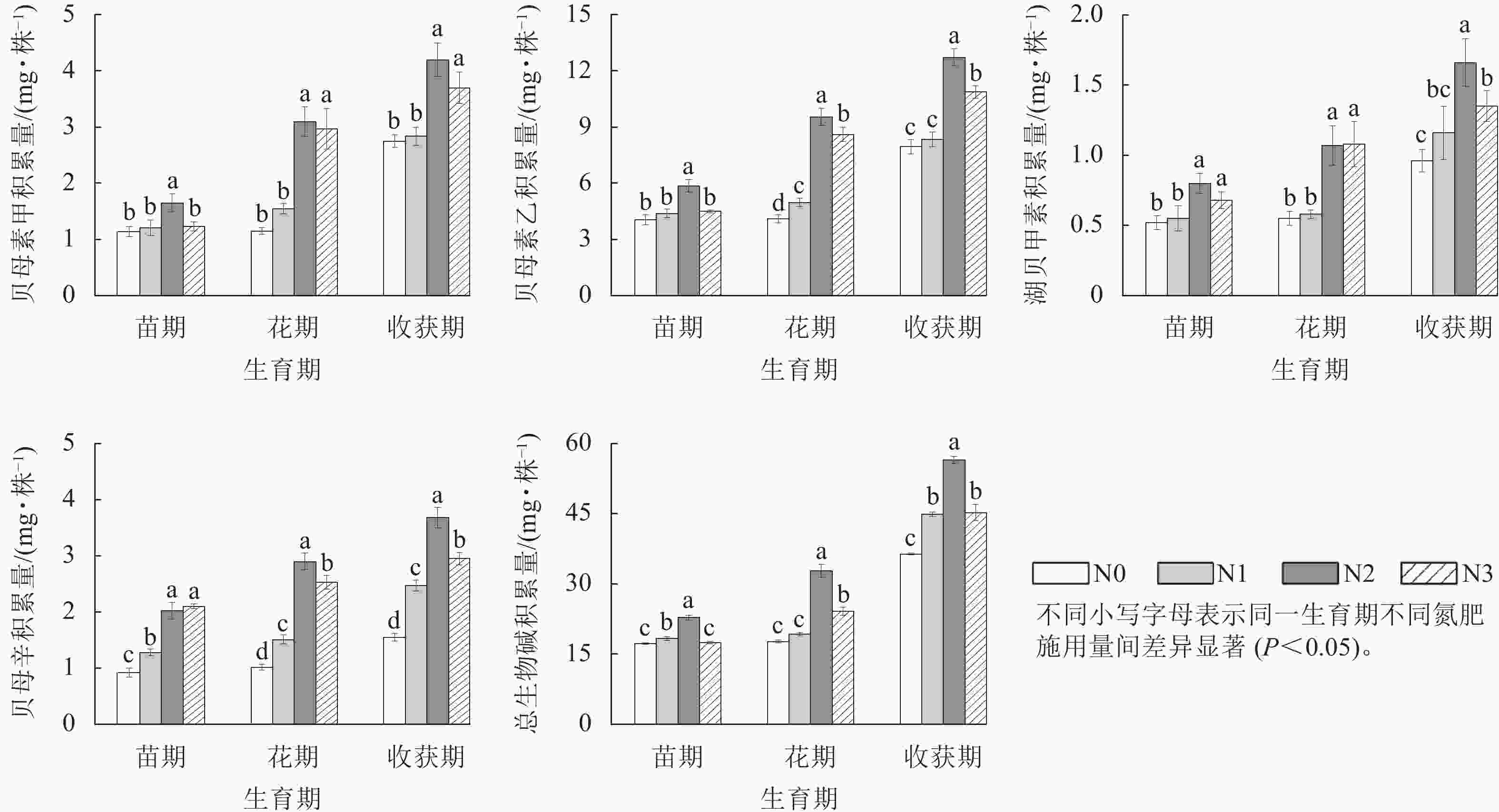
图 3 不同氮肥施用量对湖北贝母鳞茎生物碱的影响
Figure 3. Effects of different nitrogen dosages on concentration of alkaloids in F. hupehensis bulbs
由图4可知:在同一生育期内,随氮肥用量增加,贝母鳞茎中总生物碱、贝母素甲、贝母素乙、湖贝甲素、贝母辛的积累量显著增加(P<0.05),且均在N2处理时达到峰值。相关分析表明:单株湖北贝母鳞茎干质量与上述5种生物碱的积累量均显著正相关(P<0.05),相关系数分别为0.813、0.925、0.943、0.931、0.959。湖北贝母鳞茎中氮、磷、钾的积累量与上述5种生物碱的积累量也均显著正相关(P<0.05)。鳞茎中氮积累量与上述5种生物碱积累量的相关系数分别为0.825、0.925、0.945、0.931、0.964,磷积累量与上述5种生物碱积累量的相关系数分别为0.833、0.813、0.855、0.867、0.897,钾积累量与上述5种生物碱积累量的相关系数分别为0.844、0.944、0.949、0.936、0.930。氮肥用量相同时,苗期至花期鳞茎中总生物碱积累量增长仅为0.47~9.96 mg·株−1,花期至收获期鳞茎中总生物碱积累量增长为18.70~25.62 mg·株−1。此结果表明:花期至收获期为湖北贝母鳞茎总生物碱的快速积累时期。当氮施用量小于116.0 kg·hm−2(N2)时,花期至收获期鳞茎中贝母素甲、贝母素乙、湖贝甲素、贝母辛积累量的增幅高于苗期至花期的变化;当氮肥用量达到N2处理水平时,花期至收获期鳞茎中贝母素甲、贝母素乙、贝母辛积累量的增幅低于苗期至花期的变化。这种差异表明:氮肥用量对湖北贝母鳞茎中各生物碱的积累至关重要,过量施用氮肥不利于上述生物碱的合成。
-
施肥是提高人工栽培药用植物产量和品质的重要手段,不合理的施肥会对产量和品质造成影响[13−14]。本研究结果表明:各生育期湖北贝母鳞茎的干质量均随氮肥用量增加显著增加,且均在N2处理时达到峰值;氮肥用量超过N2水平时鳞茎的干质量显著降低。李林宏等[15]研究施肥对川贝母F. cirrhosa产量的影响时也发现这一规律。这可能与氮肥过量施用引起植株地上部徒长,使鳞茎养分供应不足有关,同时氮肥过量也易导致鳞茎腐烂而减产。本研究发现:湖北贝母鳞茎的干物质积累速率在苗期至花期较快,此后增长减缓。孟培等[16]研究矿质养分对丹参Salvia miltiorrhiza干物质积累的影响时也发现:不同生育期干物质积累量差异显著,生长旺盛期干物质积累能力最强,幼苗期其次,生长转折期最弱。植株干物质积累与养分吸收密切相关。在湖北贝母生长发育过程中,根不断从土壤中吸收氮、磷、钾等营养物质以满足其代谢对养分的需求。随氮肥用量增加,各生育期湖北贝母鳞茎中磷、钾质量分数较不施氮肥处理总体呈降低趋势,这可能与湖北贝母鳞茎干质量增加,产生“养分稀释效应”有关。湖北贝母鳞茎中氮、钾质量分数呈显著正相关;相同氮肥施用量时,磷质量分数均为苗期最高,花期最低。崔迪等[17]研究也发现:浙贝母鳞茎对磷的吸收与积累是苗期高于中后期,茎和叶中磷质量分数在盛花期最高。本研究供试土壤中速效钾质量分数为205.66 mg·kg−1,钾肥用量均为86.4 kg·hm−2,可为湖北贝母生长发育提供充足的钾素。钾在植物细胞中主要以离子态存在,在植物体内移动性较大,可被植物再吸收和利用。同时,氮磷钾元素间存在互作效应,钾在磷质量分数充足时发挥作用,钾也可提高氮肥效应[18]。因此,本研究中湖北贝母鳞茎的氮、钾质量分数呈现相似的变化趋势。此外,氮、磷、钾是影响植物生长的必需矿质元素,其化学计量比可反映植物的生长策略及环境养分限制,氮磷比、氮钾比、 钾磷比可作为植株营养元素限制的诊断指标[19]。本研究发现:随生育期延长,湖北贝母鳞茎的氮磷比均小于14.0,氮钾比均小于2.1。当氮磷比小于14.0,氮是限制植物生长的主要因素;当氮磷比大于 16.0时,主要受磷的限制;当氮磷比为14.0~16.0时,受到氮、磷的共同限制;当氮钾比大于2.1,钾磷比小于3.4时,植物生长主要受钾的限制[20]。供试土壤中有效氮质量分数较低,速效钾质量分数相对丰富,这可能是造成氮限制湖北贝母生长,但鳞茎未表现出缺钾的重要因素。同时,随氮肥用量增加,苗期湖北贝母鳞茎中钾磷比小于3.4,花期及收获期湖北贝母鳞茎中钾磷比均大于3.4;相同氮肥用量时,随生育期延长,湖北贝母鳞茎中氮钾比总体呈降低趋势。上述结果表明:湖北贝母由营养生长向生殖生长过渡时,鳞茎对钾的积累不断增强。钾是糖降解过程中的重要活化剂,协调光合产物的合成、运输和转化[21]。在湖北贝母鳞茎膨大期,鳞茎中钾的分配比例上升有利于营养物质的转移,提高产量。
生物碱是贝母属植物的主要药用成分,大部分生物碱为含氮化合物,氮素对生物碱的合成与积累有促进作用。本研究发现:花期湖北贝母鳞茎中贝母素甲、贝母素乙、贝母辛质量分数随氮肥用量增加呈上升趋势。丁丽洁等[22]发现在一定氮素范围内,黄檗Phellodendron amurense中小檗碱、药根碱质量分数随氮肥用量增加而增加。朱孟炎等[23]研究表明:长春花Catharanthus roseus叶片中文朵灵、长春碱质量分数与添加氮肥用量正相关。本研究结果表明:在苗期及收获期,湖北贝母鳞茎中总生物碱、贝母素甲、贝母素乙、湖贝甲素质量分数均随氮肥用量增加而降低。在本研究中,同一生育期内,单株湖北贝母鳞茎的质量随氮肥用量增加而递增,说明在一定范围内颗粒越小,有效成分越高。此结果与吴广等[24]的研究结论一致。也有研究表明:适当低氮胁迫能够显著增加喜树Camptotheca acuminata幼苗中喜树碱的质量分数[25]。这可能是由于低氮水平刺激了植物体内某些次生代谢物质的合成,使部分生物碱质量分数增加。相同氮肥施用量时,随生育期延长,湖北贝母鳞茎中总生物碱、贝母素甲、贝母素乙、湖贝甲素质量分数从高到低均为收获期、苗期、花期,且各生物碱质量分数均为花期最低。崔迪等[17]研究施钾对浙贝母生物碱积累的影响时发现:在盛花期鳞茎生物碱质量分数最低,仅为0.13%~0.21%,进入生殖生长后,生物碱快速上升,至临枯期达到0.18%~0.36%。但也有研究表明:平贝母F. usuriensis中贝母素乙质量分数在萌芽期较高,随生育期延长,其质量分数降低,花期达到峰值,临枯期最低[26]。本研究也发现:氮肥用量相同时,花期至收获期湖北贝母鳞茎中总生物碱的积累量显著上升;当氮肥用量达到N2水平时,花期至收获期鳞茎中贝母素甲、贝母素乙、贝母辛的积累量较苗期至花期相比呈降低趋势。对浙贝母生物碱积累规律的研究也表明:浙贝母中贝母素甲的积累对钾肥施用量的需求存在临界值,缺钾条件下植物体内的生物碱有所上升[27−28]。在不同物候期,湖北贝母中生物碱的积累是动态变化的过程,因此,研究湖北贝母不同生育期对土壤矿质元素的养分需求规律,明确土壤矿质元素对湖北贝母生物碱合成的影响机制,可为进一步提升湖北贝母产量,改善品质提供理论依据。
-
随生育期延长,不同氮肥用量下湖北贝母鳞茎对氮、磷、钾的吸收及鳞茎中生物碱的积累差异较大。苗期至花期,湖北贝母鳞茎的干物质积累速率较快,此后其产量增长减缓;花期至收获期鳞茎中总生物碱的积累能力较强。湖北贝母产量及各生物碱积累量均最高的施肥量为:116.0 kg·hm−2氮、102.4 kg·hm−2五氧化二磷、86.4 kg·hm−2氧化钾。氮是限制湖北贝母生长的主要因素,且氮钾元素间存在互作效应,重施氮、钾肥对于湖北贝母鳞茎增产有重要意义。湖北贝母由营养生长向生殖生长过渡时,鳞茎对钾的需求增强,宜增施钾肥。氮肥用量对湖北贝母鳞茎中各生物碱的积累至关重要,过量施用氮肥不利于生物碱的合成。
Effects of nitrogen application on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium absorption and alkaloid accumulation in Fritillaria hupehensis
-
摘要:
目的 分析湖北贝母Fritillaria hupehensis鳞茎中氮、磷、钾质量分数及积累量的年变化规律,探讨不同氮肥用量对湖北贝母干物质及各生物碱积累的影响,为湖北贝母合理施肥提供科学依据。 方法 以湖北省恩施市新塘乡境内种植的湖北贝母为材料,在磷肥(五氧化二磷)、钾肥(氧化钾)用量均为102.4和86.4 kg·hm−2的条件下,设置4个氮肥处理:不施氮肥(N0)、氮肥用量为58.0 kg·hm−2(N1)、氮肥用量为116.0 kg·hm−2(N2)、氮肥用量为174.0 kg·hm−2(N3),分别于苗期、花期、收获期取样,测定不同生育期湖北贝母鳞茎中氮、磷、钾及各生物碱质量分数。 结果 随氮肥用量增加,单株湖北贝母鳞茎的干物质,鳞茎中氮、磷、钾及总生物碱,贝母素甲,贝母素乙,湖贝甲素,贝母辛的积累量显著增加(P<0.05),且均在氮肥用量为116.0 kg·hm−2时达到峰值。随氮肥用量增加,湖北贝母苗期鳞茎中钾磷比小于3.4,花期及收获期贝母鳞茎中钾磷比均大于3.4;整个生育期内湖北贝母鳞茎中氮磷比小于14.0,氮钾比小于2.1。苗期及收获期,湖北贝母鳞茎中总生物碱、贝母素甲、贝母素乙、湖贝甲素质量分数均随氮肥用量增加而降低;花期湖北贝母鳞茎中贝母素甲、贝母素乙、贝母辛质量分数随氮肥用量增加呈上升趋势。氮肥用量为116.0 kg·hm−2时,湖北贝母鳞茎中总生物碱、贝母素甲、贝母素乙、湖贝甲素、贝母辛积累量的峰值分别为56.50、4.20、12.73、1.66、3.68 mg·株−1。相同氮肥用量时,随生育期延长,除贝母辛外,其余各生物碱质量分数均为收获期最高,花期最低。氮肥用量为116.0 kg·hm−2时,花期至收获期鳞茎中贝母素甲、贝母素乙、贝母辛的积累速率降低。苗期至花期,湖北贝母鳞茎的干物质积累速率较快,花期至收获期鳞茎中总生物碱的积累能力较强。 结论 氮肥用量对湖北贝母产量及品质影响显著,过量施用氮肥不利于鳞茎干物质及各生物碱的积累。湖北贝母在不同物候期鳞茎干物质及生物碱的积累是动态的过程,营养生长期以产量提升为主,生殖生长阶段以生物碱积累为主。图4表2参28 Abstract:Objective This study aims to analyze the annual variation of the concentration and accumulation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in Fritillaria hupehensis bulbs, and explore the impacts of different nitrogen dosages on the accumulation of dry matter and alkaloids of F. hupehensis, so as to provide scientific basis for rational fertilization of F. hupehensis. Method F. hupehensis obtained from Xintang township, Enshi City, Hubei Province was used as the material. Under the conditions of 102.4 kg·hm−2 phosphorus pentoxide and 86.4 kg·hm−2 potassium oxide for both phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, 4 nitrogen fertilizer treatments were set up: no nitrogen fertilizer (N0), 58.0 kg·hm−2 nitrogen fertilizer (N1), 116.0 kg·hm−2 nitrogen fertilizer (N2), and 174.0 kg·hm−2 nitrogen fertilizer (N3). Samples were collected at seedling, flowering and harvest stages to determine the concentration of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and various alkaloids in the bulbs of F. hupehensis at different growth stages. Result The accumulation of dry matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, total alkaloid, verticine, verticinone, peimissine and hupehenine in F. hupehensis bulbs significantly increased with increasing nitrogen application (P<0.05), and all reached their peak at a nitrogen fertilizer application of 116.0 kg·hm−2. With the increase of nitrogen application, potassium to phosphorus ratio in F. hupehensis bulbs was less than 3.4 at seedling stage, while that during the flowering and harvesting periods was more than 3.4. Throughout the entire growth period, nitrogen to phosphorus ratio in F. hupehensis bulbs was less than 14.0, and nitrogen to potassium ratio was less than 2.1. During the seedling and harvest stages, the concentration of total alkaloid, verticine, verticinone, and hupehenine in F. hupehensis bulbs all decreased with increasing nitrogen application. During the flowering period, the concentration of verticine, verticinone and peimissine in F. hupehensis bulbs showed an increasing trend with the increase in nitrogen application. When the nitrogen fertilizer application amount was 116.0 kg·hm−2, the peak accumulation of total alkaloid, verticine, verticinone, hupehenine and peimissine in F. hupehensis bulbs were 56.50, 4.20, 12.73, 1.66, and 3.68 mg·plant−1, respectively. When the same amount of nitrogen fertilizer was applied, with the extension of growth period, except for peimissine, the concentration of all other alkaloids was the highest during the harvest period and the lowest during the flowering period. When the nitrogen fertilizer application amount was 116.0 kg·hm−2, the accumulation rate of verticine, verticinone and peimissine in bulbs decreased from flowering to harvest stage. The dry matter accumulation rate was relatively fast from seedling to flowering stage, and the accumulation ability of total alkaloids in the bulb during the flowering to harvest period was strong. Conclusion The amount of nitrogen fertilizer significantly affects the yield and quality of F. hupehensis. Excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer is not conducive to the accumulation of dry matter and alkaloids in bulbs. The accumulation of dry matter and alkaloids in bulbs of F. hupehensis at different growth stages is a dynamic process. Yield increase is predominant at vegetative growth stage, while alkaloids accumulation is dominant at productive growth stage. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 28 ref.] -
表 1 不同氮肥施用量时湖北贝母的生长指标
Table 1. Growth indices of F. hupehensis under different nitrogen dosages
生育期 处理 叶长/cm 叶宽/cm 叶型指数 株高/cm 茎粗/cm 苗期 N0 11.15±0.12 b 1.03±0.06 c 10.88±0.56 a 19.70±0.92 c 0.50±0.01 b N1 11.33±0.12 b 1.33±0.05 b 8.55±0.29 b 29.30±1.00 b 0.53±0.02 ab N2 11.45±0.19 a 1.55±0.10 a 7.39±0.25 d 33.90±3.11 a 0.55±0.03 a N3 11.00±0.19 b 1.42±0.06 b 7.76±0.21 c 32.85±0.95 a 0.50±0.02 b 花期 N0 11.77±0.10 b 1.72±0.10 b 6.86±0.48 a 36.45±0.58 b 0.50±0.02 b N1 11.90±0.07 b 1.80±0.11 a 6.61±0.39 a 38.00±0.94 b 0.55±0.02 b N2 14.20±0.08 a 2.10±0.10 b 6.76±0.51 a 40.50±1.16 a 0.65±0.03 a N3 12.00±0.20 b 1.70±0.12 b 7.06±0.61 a 37.60±2.02 b 0.51±0.04 b 收获期 N0 - - - - - N1 - - - - - N2 - - - - - N3 - - - - - 生育期 处理 鳞茎鲜质量/(g·株−1) 鳞茎干质量/(g·株−1) 折干率/% 鳞茎干质量产量/(g·m−2) 苗期 N0 7.11±0.12 d 2.37±0.06 d 33.30±0.62 b - N1 7.60±0.22 c 2.63±0.09 c 34.65±1.51 ab - N2 11.28±0.17 a 4.00±0.13 a 35.43±1.75 ab - N3 8.85±0.16 b 3.26±0.17 b 36.86±2.50 a - 花期 N0 10.32±0.17 c 2.90±0.07 d 28.14±1.13 b - N1 10.52±0.29 c 3.64±0.22 c 35.24±1.19 a - N2 20.49±0.98 a 6.82±0.13 a 33.32±1.00 a - N3 16.75±0.78 b 5.98±0.14 b 35.78±2.53 a - 收获期 N0 11.72 ±0.59 d 3.20±0.20 d 27.31±0.83 c 64.00±3.91 c N1 16.67±0.69 c 5.49±0.27 c 32.93±0.47 b 109.89±5.88 b N2 21.83±1.02 a 8.26±0.27 a 37.93±3.02 a 165.20±4.69 a N3 18.25±0.48 b 7.22±0.18 b 39.57±0.08 a 144.38±4.00 a 说明:-表示无此项。数值为平均值±标准差(n=3)。不同小写字母表示同一生育期不同氮肥施用量间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 不同氮肥用量时湖北贝母鳞茎氮、磷、钾的化学计量比
Table 2. Stoichiometric ratio of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium in F. hupehensis bulbs under different nitrogen dosages
时期 处理 氮磷比 氮钾比 钾磷比 时期 处理 氮磷比 氮钾比 钾磷比 苗期 N0 2.58±0.07 d 1.14±0.03 d 2.27±0.03 c 花期 N2 4.79±0.08 b 1.32±0.02 a 3.63±0.05 c N1 3.29±0.10 c 1.23±0.03 c 2.68±0.04 b N3 6.31±0.17 a 1.14±0.02 b 5.53±0.22 a N2 3.75±0.07 b 1.38±0.02 a 2.71±0.02 b N3 3.94±0.09 a 1.31±0.01 b 3.01±0.07 a 收获期 N0 4.05±0.07 c 1.08±0.01 c 3.75±0.08 bc N1 4.23±0.06 c 1.11±0.01 c 3.81±0.08 b 花期 N0 3.70±0.02 c 1.00±0.01 c 3.59±0.03 c N2 4.66±0.02 b 1.30±0.03 a 3.57±0.09 c N1 4.86±0.10 b 1.14±0.01 b 4.25±0.08 b N3 6.30±0.17 a 1.16±0.01 b 5.42±0.20 a 说明:不同小写字母表示同一生育期不同氮肥施用量间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 潘晓燕, 吕晓, 范寅仲, 等. 湖北贝母内生真菌Curreya pityophila 化学成分及其生物活性研究 [J]. 中南民族大学学报 (自然科学版), 2023, 42(2): 196 − 200. PAN Xiaoyan, LÜ Xiao, FAN Yinzhong, et al. The chemical constituents from endophytic fungus Curreya pityophila of Fritillaria hupehensis [J]. Journal of South-Central Minzu University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 42(2): 196 − 200. [2] 罗静, 文明, 王骞, 等. 不同磷源及其浓度水平对浙贝母产量和品质的影响 [J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(8): 1818 − 1824. LUO Jing, WEN Ming, WANG Qian, et al. Effects of different phosphate fertilizers and application levels on yield and quality of Fritillary thunberg [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2020, 43(8): 1818 − 1824. [3] 邬小红, 周浓, 侯瑶, 等. 不同钾肥品种及配施对浙贝母产量和品质的影响 [J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2020, 39(8): 6 − 12. WU Xiaohong, ZHOU Nong, HOU Yao, et al. Effects of different potassium fertilizers and application on yield and quality of Fritillaria thunbergii Miq. [J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2020, 39(8): 6 − 12. [4] 陈天德, 金天寿, 倪顺尧, 等. 浙贝母最佳氮、磷、钾施肥量初探 [J]. 浙江农业科学, 2009, 50(2): 308 − 310. CHEN Tiande, JIN Tianshou, NI Shunyao, et al. Optimal nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium application on Fritillaria thunberg [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 50(2): 308 − 310. [5] 陆中华, 姜娟萍, 陈爱良, 等. 浙贝母优质高产关键技术试验 [J]. 浙江农业科学, 2015, 56(8): 1193 − 1195. LU Zhonghua, JIANG Juanping, CHEN Ailiang, et al. Experiment on improving quality and production of Fritillaria thunberg [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 56(8): 1193 − 1195. [6] 罗静, 母茂君, 王骞, 等. 不同氮素形态和浓度水平对浙贝母产量和品质的影响 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(16): 168 − 174. LUO Jing, MU Maojun, WANG Qian, et al. Effect of different nitrogen forms and concentrations on yield and quality of Fritillaria thunbergii [J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2020, 26(16): 168 − 174. [7] 隋利, 王康才, 易家宁, 等. 不同氮素形态对紫苏生长及品质的影响 [J]. 土壤通报, 2018, 49(3): 667 − 672. SUI Li, WANG Kangcai, YI Jianing, et al. Effect of different nitrogen forms on growth and quality of Perilla frutescens (L. ) Britt [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2018, 49(3): 667 − 672. [8] 王新月, 王业, 邬洁, 等. 花期追肥对川贝母产量和品质的影响 [J]. 世界中医药, 2022, 17(13): 1789 − 1796. WANG Xinyue, WANG Ye, WU Jie, et al. Effects of topdressing in the flowering stage on yield and quality of Fritillaria cirrhosa D. Don [J]. World Chinese Medicine, 2022, 17(13): 1789 − 1796. [9] 王华, 何美军, 穆森, 等. 贝母属植物生物碱累积研究进展 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(34): 128 − 129, 131. WANG Hua, HE Meijun, MU Sen, et al. Advances in alkaloids accumulation of Fritillaria [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(34): 128 − 129, 131. [10] 郭丽, 史建硕, 王丽英, 等. 滴灌水肥一体化条件下施氮量对夏玉米氮素吸收利用及土壤硝态氮含量的影响 [J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(5): 668 − 676. GUO Li, SHI Jianshuo, WANG Liying, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rate on nitrogen absorption and utilization in summer maize and soil \begin{document}${\mathrm{NO}}_3^- $\end{document} [11] 姚德中, 闵会, 何厚洪, 等. 不同产地浙贝母总生物碱含量测定与比较 [J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2014, 31(10): 1249 − 1251. YAO Dezhong, MIN Hui, HE Houhong, et al. Determination and comparison of total alkaloids content of Fritiliariae thunbergh bulbus from different habitats [J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2014, 31(10): 1249 − 1251. [12] 王路伟, 沈晨薇, 张水利, 等. 不同炮制方法对浙贝母药材3种生物碱含量的影响 [J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2018, 35(1): 80 − 84. WANG Luwei, SHEN Chenwei, ZHANG Shuili, et al. Effects of different processing methods on the contents of 3 alkaloids in Fritillaria thunbergii bulbus [J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2018, 35(1): 80 − 84. [13] 关佳莉, 王刚, 张梦蕊, 等. 不同氮素供应水平对菘蓝生长及药材质量的影响 [J]. 核农学报, 2019, 33(10): 2077 − 2085. GUAN Jiali, WANG Gang, ZHANG Mengrui, et al. Effect of different nitrogen supply levels on the growth of Isatis indigotica Fort. and quality of medicinal materials [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 33(10): 2077 − 2085. [14] 周水灯, 孙健, 江建铭, 等. 不同生育期施肥对浙贝母产量和品质的影响 [J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2023, 40(4): 756 − 764. ZHOU Shuideng, SUN Jian, JIANG Jianming, et al. Effects of fertilization at different growth stages on yield and quality of Fritillaria thunbergii [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2023, 40(4): 756 − 764. [15] 李林宏, 叶本贵, 龚盼竹, 等. 不同施肥方式对川贝母产量及质量的影响 [J]. 华西药学杂志, 2019, 34(3): 266 − 269. LI Linhong, YE Bengui, GONG Panzhu, et al. Effects of different fertilization methods on yield and quality of Fritillaria cirrhosa [J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2019, 34(3): 266 − 269. [16] 孟培, 王建华, 宋振巧, 等. 丹参氮、磷、钾积累分配特点及其与干物质、丹酚酸B积累的关系 [J]. 植物营养育肥料学报, 2013, 19(4): 940 − 945. MENG Pei, WANG Jianhua, SONG Zhenqiao, et al. Accumulation and distribution of N, P and K in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. and their relations to the dry matter production and Salvianolic acid B [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2013, 19(4): 940 − 945. [17] 崔迪, 崔培章, 陈红方. 施钾对浙贝母氮磷钾吸收分配与生物碱积累的影响研究 [J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(9): 2095 − 2098. CUI Di, CUI Peizhang, CHEN Hongfang. Effect of potassium application on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium absorption, distribution and alkaloid accumulation of Fritillary thunbergii [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2020, 43(9): 2095 − 2098. [18] 邓秋林, 杨正明, 陈雨, 等. 氮磷钾配施对瓦布贝母产量及总生物碱质量分数的影响 [J]. 西北农业学报, 2019, 28(7): 1138 − 1146. DENG Qiulin, YANG Zhengming, CHEN Yu, et al. Effects of combined application of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on the yield and total alkaloid mass fraction of Fritillaria unibracteata var. wabuensis [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2019, 28(7): 1138 − 1146. [19] 姜利, 洪娟, 陈法志, 等. 油用牡丹‘凤丹’不同生育期养分吸收和积累规律 [J]. 经济林研究, 2022, 40(1): 112 − 122. JIANG Li, HONG Juan, CHEN Fazhi, et al. Regularity of the adsorption and accumulation of nutrients at different growth stages of Paeonia ostii Feng Dan [J]. Non-wood Forest Research, 2022, 40(1): 112 − 122. [20] 孙雪娇, 常顺利, 宋成程, 等. 雪岭云杉不同器官 N、P、K化学计量特征随生长阶段的变化 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(5): 1291 − 1298. SUN Xuejiao, CHANG Shunli, SONG Chengcheng, et al. Age-related N, P, and K stoichiometry in different organs of Picea schrenkiana [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(5): 1291 − 1298. [21] 平文超, 徐婧, 曹平平, 等. 外源钾对盐胁迫下植物生长和生理特征影响的研究进展 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(9): 100 − 105. PING Wenchao, XU Jing, CAO Pingping, et al. Effects of exogenous potassium on growth and physiological characteristics of plants under salt stress: a review [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(9): 100 − 105. [22] 丁丽洁, 李霞, 刘强. 氮素浓度对黄檗幼苗主要次生代谢产物的影响 [J]. 人参研究, 2013, 25(4): 39 − 41. DING Lijie, LI Xia, LIU Qiang. Effects of nitrogen concentration on the main secondary metabolites of corktree seedlings [J]. Ginseng Research, 2013, 25(4): 39 − 41. [23] 朱孟炎, 于博帆, 陈华峰. 外源硝态氮水平对长春花生理代谢的影响 [J]. 植物研究, 2016, 36(4): 535 − 541. ZHU Mengyan, YU Bofan, CHEN Huafeng. Effects of nitrate nitrogen levels on physiological metabolism of Catharanthus roseus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(4): 535 − 541. [24] 吴广, 谢柏艳, 张勇慧, 等. 不同环境对湖北贝母总生物碱含量与指纹图谱的影响 [J]. 医药导报, 2008, 27(6): 707 − 710. WU Guang, XIE Baiyan, ZHANG Yonghui, et al. Effects of different habitats on total alkaloids and HPLC fingerprints of Fritillaria hupehensis [J]. Herald of Medicine, 2008, 27(6): 707 − 710. [25] 孙世芹, 阎秀峰. 氮素水平对喜树幼苗喜树碱含量的影响 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2008, 33(4): 356 − 359. SUN Shiqin, YAN Xiufeng. Effect of nitrogen on camptothecin content in Camptotheca acuminata seedlings [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2008, 33(4): 356 − 359. [26] 王振月, 侯素云, 王志林, 等. 不同产地不同物候期平贝母的贝母乙素含量研究 [J]. 中药材, 2006, 29(11): 1135 − 1136. WANG Zhenyue, HOU Suyun, WANG Zhilin, et al. Research on verticinone of Fritillaria ussurieusis from different habitats and growth stages [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2006, 29(11): 1135 − 1136. [27] 卢晓, 毕艳孟, 霍亚珍, 等. 不同施肥和覆盖措施对浙贝母产量和有效成分的影响 [J]. 中国现代中药, 2018, 20(5): 576 − 580. LU Xiao, BI Yanmeng, HUO Yazhen, et al. Effect of different fertilization and cover treatments on yield and active constituents of Fritillaria thunbergii Miqi [J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2018, 20(5): 576 − 580. [28] GREMIGNI P, WONG M T F, EDWARDS N K, et al. Potassium nutrition effects on seed alkaloid concentrations, yield and mineral content of lupins (Lupinus angustifolius) [J]. Plant and Soil, 2001, 234: 131 − 142. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240217






 下载:
下载: