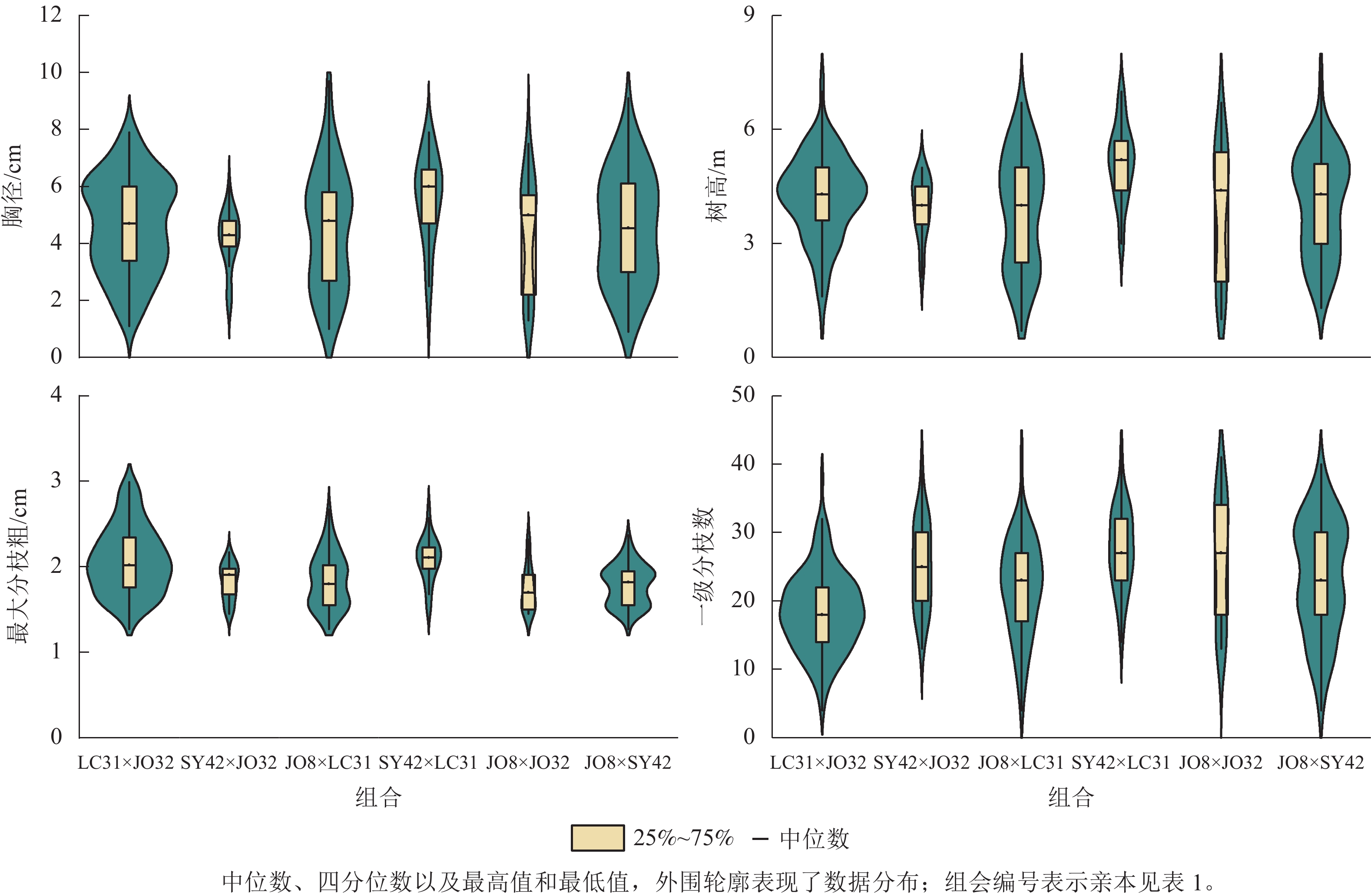
-
进行林木育种时,及时精确地估算主要经济性状的遗传参数对育种策略的制定和实施起着至关重要的作用[1]。杂交育种可以将双亲控制的不同优良性状结合于一体,从而创造出适合生产上需要的特殊性状,获得超级杂种[2]。自从SPRAGUE等[3]在玉米Zea mays杂交育种研究中首次提出一般配合力(GCA)和特殊配合力(SCA)的概念以后,配合力育种在林木遗传改良中得到了广泛应用。配合力分析不仅可用以评价育种亲本,而且可以了解林木重要经济性状所受的遗传控制式样,从而为科学制定林木遗传改良策略提供重要的理论依据。其中一般配合力是亲本在杂交后代中的平均表现,是目标性状在代际遗传中可以固定的遗传效应,在林木育种中占有相对重要的地位;而特殊配合力是等位基因间的相互作用,被认为是能遗传但不能被固定的遗传效应,是产生特殊配合力效应的主导因素[4−6]。对杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata杂交亲本配合力的研究发现:杂交子代的生长主要受一般配合力影响;对于已测评过一般配合力的材料,要加强特殊配合力的测定[7−8]。湿地松Pinus elliottii 在一般配合力大于特殊配合力的前提下,胸径、材积、基本密度等以加性效应为主,而树高则以显性效应为主[9]。相对针叶树,阔叶树种的育种进程相对缓慢。水曲柳Fraxinus mandshurica是一般配合力较高的材料,在任意亲本组合中都会增加子代苗高表现[10]。尾巨桉Eucalyptus urophylla × E. grandis杂交子代性状主要由显性和加性效应共同决定,且显性效应占主导地位[11]等。以上研究可为林木的高世代育种改良提供丰富的科学依据。
木荷Schima superba为山茶科Theaceae木荷属Schima的常绿阔叶大乔木,是亚热带常绿阔叶林的主要建群种,也是中国南方最主要的造林树种之一,其木材坚重致密,结构均匀,力学性质好,是建筑、器材、木制工艺品等珍贵优质阔叶用材。木荷育种始于2001年,通过前期研究初步揭示了木荷生长和形质的遗传变异规律。如辛娜娜等[12−13]利用福建建瓯和江西永丰两地5年生自由授粉家系的遗传测定林,揭示了木荷生长性状受中等偏强的遗传控制,而分枝性状则受中等偏弱的遗传控制,分枝性状与树高、胸径呈极显著遗传正相关,认为速生的木荷家系须加强早期修枝,以培育优质干材。10年生优树自由授粉家系生长性状的遗传效应随年龄增强,且胸径受到的遗传控制强于树高,木材基本密度受到较强的遗传控制,但与生长性状相关性较小,可与生长性状独立选择[14−17]。这些研究均基于半同胞家系的生长和形质开展,而对全同胞家系的研究较少。为了进一步了解木荷的生长性状和分枝性状的遗传规律,揭示木荷全同胞子代配合力,明确不同性状的加性效应遗传分量、显性遗传效应分量及两者相对值等,本研究利用不同来源的4个木荷优树亲本控制授粉,开展木荷全同胞家系生长和分枝性状的遗传变异与效应分析研究,为木荷高世代育种提供科学理论依据。
-
木荷亲本选自福建建瓯、福建连城、江西上犹的木荷天然林中所选的优树(表1)。子代测定林采用4×4半双列交杂设计(表2),随机完全区组,5次重复, 5株小区,株行距为2.5 m×3.0 m。木荷子代测定林于2015年营建于浙江龙泉(28°03′N,119°06′E),海拔为250 m。试验地年平均气温为17.6 ℃,7月平均气温为27.8 ℃,1月平均气温为6.5 ℃,年平均降水量为1 699.4 mm,无霜期为263 d,属中亚热带湿润季风气候。造林地坡向西南,坡度约15°,立地条件中等。
表 1 参试亲本来源
Table 1. The source of parent of S. superba
产地 编号 纬度(N) 经度(E) 海拔/m 年龄/a 树高/m 胸径/cm 福建建瓯 JO8 26°57′ 118°22′ 141 25 16 21.3 JO32 26°57′ 118°22′ 141 25 15 19.2 福建连城 LC31 25°13′ 116°32′ 800 40 15 34.0 江西上犹 SY42 25°42′ 114°01′ 483 28 16 23.5 表 2 4×4半双列组合设计表
Table 2. 4×4 semi-diallel combination design
母本 父本 JO32 LC31 SY42 JO8 JO32 LC31 × SY42 × × JO8 × × × 说明:×表示亲本的杂交组合。 -
2020年11月底进行全林调查,指标包括生长性状:胸径(DBH),树高(H);分枝性状:冠幅(CW),枝下高(CBH),一级分枝数(PBN),最大分枝角(MBA),最大分枝粗(MBD)等。利用R (v4.1.0)中的MASS、pastecs、dplyr、corrplot、lme 4、Sommer等程序包分别进行正态分布检测、描述性分析、方差分析、相关分析及配合力计算等,利用SAS (v8.0)中GLM程序计算协方差,同时,利用Excel对所有数据进行模型评估核验和补充[2],保证分析结果的可靠性。
性状分析使用混合线性模型:Yijk=μ+bi+mj+fk+xjk+xjkbi+eijk。其中:Yijk为单株观察值;μ为群体平均值;bi为第 i 个重复效应值(固定);mj为母本效应值(随机);fk为父本效应值(随机);xjk为第 j 亲本与第k 亲本杂交组合效应值(随机);xjkbi为亲本组合与重复的互作效应值(随机);eijk为残差[18]。表型变异系数(VCP): VCP=S /$ \overline{X}\times 100\mathrm{\%} $,其中:S为性状标准差,$ \overline{X} $为性状均值。遗传变异系数(VCG): VCG=$ \sqrt{{\sigma }^{2}} $/$ \overline{X}\times 100\mathrm{\%} $,其中:σ2为遗传方差分量,$ \overline{X} $为性状均值。
父本家系遗传率[19]、母本家系遗传率[19]、家系遗传率[20]、单株遗传率[21]的计算分别参照文献[19-21]。若亲本组合间差异显著,按 Griffing 双列杂交方法Ⅳ,按模型Ⅱ(随机模型)以重复平均值进行配合力方差分析,并按随机模型估算一般配合力、特殊配合力效应及其遗传方差分量[2, 6, 22]。一般配合力和特殊配合力的计算参照文献[22]。表型相关系数、遗传相关系数和遗传增益的计算参见文献[17, 19, 23]
-
由表3和图1可见:木荷全同胞子代生长和分枝性状变异丰富且存在极显著的遗传差异(P<0.01)。生长性状中,胸径变幅及变异系数较大,而分枝性状枝下高、分枝数和最大分枝粗变异系数较大。这几个指标与速生优质干型密切相关,在速生优质目标选育上木荷全同胞子代具有较大的变异基础。方差分析结果显示:亲本效应间存在极显著差异(P<0.01),其中生长性状的父本效应均方较大,而分枝性状的母本效应均方较大,说明生长性状受父本效应影响较大,而分枝性状受母本效应影响较大。除枝下高与最大分枝角外,性状存在显著的组合×重复互作效应(P<0.05)。木荷的生长性状(胸径和树高)在亲本组合间存在极显著差异(P<0.01),且变异系数较大,说明亲本组合间生长性状的遗传变异丰富,在速生性方面具有较大的选择潜力。
表 3 木荷全同胞子代的生长与分枝性状的方差分析
Table 3. ANOVA analysis of growth and branching traits of crossing progeny
项目 胸径/cm 树高/m 冠幅/m 枝下高/m 一级分枝数 最大分枝角/(°) 最大分枝粗/cm 均值 4.87 4.27 2.24 0.43 23.87 80.90 2.13 变幅 0.90~9.70 0.70~7.60 0.35~3.80 0.10~1.30 4.00~46.00 30.00~120.00 0.60~7.80 变异系数/% 39.17 31.47 28.66 47.84 35.05 19.59 52.77 均方 母本(随机) 13.70** 9.76** 5.82** 0.33** 838.43** 4 814.07** 18.71** 父本(随机) 17.46** 14.82** 3.27** 0.30** 63.11 166.41 6.18** 重复(固定) 165.23** 80.55** 14.94** 0.12* 1 611.67** 378.52 15.29** 组合(随机) 3.89** 4.40** 0.20 0.03 26.96** 50.96 1.65 组合×重复(随机) 1.72** 1.52** 0.25** 0.03 98.65** 258.87 1.71** 残差 0.29 0.31 0.12 0.04 24.36 186.55 0.75 说明:**表示P<0.01;*表示P<0.05。母本、父本、重复、组合、组合×重复的自由度分别为2、2、4、5、20。 -
木荷全同胞子代的生长和分枝性状受较强的遗传控制(全同胞遗传率为0.86~0.93)(表4)。其中,生长性状(胸径和树高)的父本家系遗传率比母本家系分别高出8%和27%,主要受父本的遗传控制较强,胸径的单株遗传率为0.79,说明生长性状受父本影响更大,即父本对交配子代的高径生长贡献更大,在创制大径材优良杂种时应重点考虑父本家系的影响。分枝性状则主要受母本家系的遗传控制。枝下高在父本和母本家系中遗传率接近,亲本间差异不大。一级分枝数、最大分枝角和最大分枝粗则受母本影响更大。一般情况下,分枝性状对生长起到制约作用,因此,在创制速生优良全同胞子代时,亲本的选择在参考分枝性状的基础上应重点考虑母本家系的分枝参数。
表 4 木荷全同胞子代生长与分枝性状的遗传率估算
Table 4. Heritability estimation of growth and branching traits of crossing progeny of S. superba
性状 母本遗传率 父本遗传率 全同胞遗传率 单株遗传率 性状 母本遗传率 父本遗传率 全同胞遗传率 单株遗传率 胸径 0.72 0.78 0.93 0.79 一级分枝数 0.97 0.57 0.86 0.70 树高 0.55 0.70 0.86 0.50 最大分枝角 0.98 0.69 0.91 0.94 枝下高 0.91 0.90 0.88 0.76 最大分枝粗 0.91 0.73 0.89 0.77 生长、分枝性状在亲本组合间的配合力方差分析结果显示:木荷一般配合力和特殊配合力在性状间存在显著(P<0.05)或极显著(P<0.01)差异(表5)。其中,胸径、树高、一级分枝数和最大分枝角的一般配合力、特殊配合力存在显著(P<0.05)水平以上的差异,而冠幅、枝下高和最大分枝粗的特殊配合力并未达到显著水平,说明可以通过亲本的交配设计来获得速生性状的优势材料。加性方差分量/显性方差分量比估算结果显示:胸径和树高的加性效应方差和显性效应方差差异不显著,受加性和显性效应共同影响。冠幅、枝下高和最大分枝粗受基因加性效应控制较强,一级分枝数和最大分枝角则受显性效应控制较强。这说明,木荷在幼龄期的生长性状受基因的加性和显性效应共同控制,而分枝性状则更多受到基因的加性效应控制。因此,可以通过育种手段来降低分枝性状对速生性状的影响。
表 5 木荷生长分枝性状的配合力方差分析及方差分量
Table 5. Analysis and variance components of combining ability for growth and branching traits of crossing progeny of S. superba
变异来源 胸径 树高 冠幅 枝下高 一级分枝数 最大分枝角 最大分枝粗 一般配合力 0.28** 0.27** 0.12** 0.010 2** 8.55** 45.87** 0.33** 特殊配合力 0.19* 0.18* 0.02 0.001 6 12.15** 43.92** 0.08 机误 0.05 0.05 0.01 0.000 9 1.87 4.97 0.02 加性分量∶显性分量 1.0∶1.4 1.0∶1.6 11.0∶1.0 12.3∶1.0 1.0∶10 1.0∶20.0 5.0∶1.0 说明:一般配合力和特殊配合力的自由度分别为3和2。 **表示P<0.01;*表示P<0.05。 -
木荷生长和分枝性状的表型相关系数大于遗传相关系数(表6),胸径、树高和冠幅、一级分枝数、最大分枝角和最大分枝粗间呈极显著的表型正相关(r=0.20~0.87,P<0.01),说明树高和胸径生长量大的家系分枝多、树冠大,且具有较粗的分枝。胸径与树高存在极显著的遗传正相关(r=0.87, P<0.01),与枝下高和一级分枝数存在显著遗传相关(r=0.67~0.70, P<0.05),与最大分枝粗不相关,说明胸径生长主要受分枝数和枝下高的遗传影响,可独立于最大分枝粗的影响进行选择。除冠幅外,树高则与其他分枝性状不存在显著的遗传相关。因此,做选择时,应重点考虑胸径指标。
表 6 木荷全同胞子代生长和分枝性状的表型相关系数与遗传相关系数
Table 6. Phenotypic and genetic correlation coefficients of growth and branching traits of crossing progeny of S. superba
性状 胸径 树高 冠幅 枝下高 一级分枝数 最大分枝角 最大分枝粗 胸径 0.87** 0.78* 0.02 0.67** 0.20** 0.49** 树高 0.87** 0.74** 0.03 0.65** 0.24** 0.40** 冠幅 0.30 0.64* 0.15 0.42** 0.06 0.67** 枝下高 0.61* −0.13 0.56 −0.11 −0.02 0.13 一级分枝数 0.70* 0.47 −0.32 −0.61* 0.43** 0.05 最大分枝角 0.09 0.01 −0.33 −0.30 0.77* −0.22** 最大分枝粗 0.05 0.45 0.85** 0.51 −0.64* −0.83** 说明:对角线以上为表型相关系数;对角线以下为遗传相关系数。 **表示极显著相关(P<0.01);*表示显著相关(P<0.05)。 -
通过亲本组合间的配合力分析,发现生长性状一般配合力较高的亲本为LC31和SY42 (表7),其中LC31亲本胸径、树高的一般配合力最大,一级分枝数和枝下高的一般配合力为负值,最大分枝粗的一般配合力为正值,其交配子代具有速生径粗的优势;SY42亲本胸径和树高的一般配合力较大,一级分枝数和枝下高的一般配合力较大,最大分枝粗的一般配合力为负值,其交配子代虽然具有速生径粗的优势,但会受到分枝数和枝下高的影响。通过组合间特殊配合力的结果,发现SY42×LC31与JO8×JO32组合的特殊配合力较大。以高出均值的前20%为标准进行优良组合的选择,选出的组合是SY42×LC31,该组合胸径、树高的遗传增益分别18.20%和19.55%。综上评估并结合各性状数据结构,认为SY42×LC31是比较理想的亲本组合,其交配子代胸径(5.53 cm)和树高(5.13 m)分别高于全同胞群体均值(4.62 cm、4.17 m) 20%和23%。从6个杂交组合中,筛选胸径、树高高于群体均值,一级分枝数和最大分枝粗低于群体均值的优良交配单株6株,其中胸径和树高分别为4.90~9.10 cm和4.50~5.90 m,材积增益平均为108.5% ,一级分枝数和最大分枝粗均低于均值的11.0%。
表 7 木荷不同亲本及组合配合力估算
Table 7. Variance effects of combining ability of different parents and combinations of S. superba
变异来源 胸径 树高 冠幅 枝下高 一级分枝数 最大分枝角 最大分枝粗 一般配合力 JO8 −0.26 −0.40 −0.29 −0.09 2.07 −0.47 −0.25 SY42 0.17 0.30 0.16 0.07 5.69 −0.04 −0.05 LC31 0.44 0.33 0.25 −0.03 −4.89 0.52 0.13 JO32 −0.35 −0.23 −0.12 0.05 −2.88 −0.01 0.17 母本一般配合力 LC31 −0.02 −0.05 0.06 0.04 −4.97 −9.99 0.47 SY42 0.01 0.23 0.17 0.05 2.84 6.95 −0.02 JO8 0.01 −0.18 −0.23 −0.08 2.13 3.04 −0.45 父本一般配合力 JO32 −0.34 −0.10 0.07 0.08 −4.25 −6.47 0.38 LC31 −0.01 0.05 0.13 −0.02 −0.49 2.22 0.10 SY42 −0.50 −0.28 −0.11 0.04 −0.56 3.59 −0.33 特殊配合力 JO8×SY42 −0.02 −0.03 −0.05 0.05 −2.30 −5.22 0.15 JO8×LC31 −0.27 −0.33 −0.10 −0.05 −0.20 1.38 −0.20 JO8×JO32 0.28 0.27 0.05 0.00 2.60 3.83 0.05 SY42×LC31 0.33 0.32 0.05 −0.05 2.60 3.88 0.05 SY42×JO32 −0.32 −0.28 −0.10 0.00 −0.20 1.33 −0.20 LC31×JO32 0.03 0.02 0.05 0.00 −2.40 −5.17 0.15 说明:组合编号所表示亲本见表1。 -
林木的遗传变异是遗传改良的前提,有效的遗传变异决定了物种在育种过程中的改良潜力。掌握林木遗传变异规律,是育种策略的基础[19]。本研究表明:木荷全同胞子代生长性状和分枝性状在各亲本组合间皆存在极显著差异,受较强的遗传控制。生长性状的父本家系遗传率高于母本家系遗传率,主要受父本的遗传控制较强;分枝性状则主要受母本家系的遗传控制较强。
一般配合力和特殊配合力的相对重要性受性状、测试材料、地点和年龄等因素的影响。一般认为,经过一般配合力测定的材料,则需要进行特殊配合力的选择和测定,而未经过一般配合力测定与选择的材料,则其一般配合力的选择较特殊配合力更为重要[19−20]。估算一般配合力、特殊配合力是判断性状遗传控制的重要方法,亲本的利用价值与其一般配合力效应值有关[18]。本研究结果显示:木荷全同胞子代的生长性状和分枝性状的一般配合力存在极显著差异,其中,LC31和SY42亲本的生长性状一般配合力较大,同时特殊配合力效应值大于其他组合,因此,认为以这2个优树无性系作为亲本,能得到速生性状优良的子代。组合间特殊配合力的分析发现:不同组合同一性状以及同一性状不同组合间特殊配合力差异较大。以SY42做母本,LC31做父本的组合,如SY42×JO32和JO8×LC31,其生长性状的特殊配合力较小,分枝性状的特殊配合力较大。一般配合力效应值高的2个亲本其子代的特殊配合力效应值不一定高,而一般配合力效应值低的2个亲本,其子代的特殊配合力效应值不一定低[21−23] 。比如本研究中的JO8×JO32,存在亲本的一般配合力不高,其组合的特殊配合力会有不错的效果,但是考虑其结果不稳定因素太高,不能选择作为优良的组合。
木荷全同胞子代幼龄期生长性状的特殊配合力效应明显大于一般配合力效应,与谭小梅等[20]对马尾松Pinus massoniana幼龄期测定结果一致。同时,木荷全同胞子代的生长性状主要受加性和显性基因效应共同控制,分枝性状主要受加性基因效应控制。马尾松杂交育种研究认为:未经过一般配合力选择和测定的材料,早期生长性状(树高和胸径)主要受显性基因效应控制,随着年龄的增长,加性基因效应逐渐占据主导地位[24−25]。因此,以一般配合力作为基础,结合特殊配合力的选择是选择优良品种的重要途径。
性状间的遗传相关性是亲本选择的重要依据,而分枝性状是影响阔叶树形态和速生性的重要指标,因此,生产上应尽量减少分枝性状对速生性状产生的负面效应[ 26−27] 。木荷全同胞子代胸径生长与枝下高和分枝数存在显著的遗传相关,因此在速生性状选择的时候,亲本还应考虑枝下高和分枝数这2个重要的分枝性状。枝下高受加性效应控制较强,可通过亲本选择减弱该性状的负效应,而分枝数受显性效应控制较强,则可通过人工修剪,以排除该性状对速生性的影响。最大分枝粗也是一个重要的分枝性状指标,但其与生长性状的遗传相关不显著,与表型相关显著,因此可独立于生长性状进行考虑。由于该性状在母本中表现的遗传率较大,属于加性效应,因此,母本选择时,尽量选择最大分枝粗较低的亲本选配,可对子代速生性状进行优化。
亲本选择和亲本组合选配关系到木荷育种的成败,仅根据亲本表现型进行组配具有一定的局限性和盲目性,通过遗传测定可为亲本组合的合理选配提供可靠依据,同时也为种子园去劣疏伐提供了参考。本研究筛选出的优良亲本无性系SY42和LC31可作为种子园建园无性系选用,SY42×LC31杂交子代胸径和树高的遗传增益分别高达18.20%和19.55%,显著优于其他组合,与木荷10年生半同胞筛选出的优良家系胸径遗传增益(16.08%)相比[16],该组合的生长遗传增益得到显著提升。选出的6株优良全同胞子代具有速生优质效果,可选作2代育种亲本及推广应用。由于林木生长周期较长,现阶段全同胞家系试验林仍处于幼龄阶段,生长、形质和材性指标尚未稳定,今后仍需要开展连续的跟踪观测。此外,木荷为两性花,花朵小,花粉不易储存,花期同步性较差,人工控制授粉困难,再加上木荷种子需2 年成熟等导致木荷交配设计育种受到诸多限制,因此,较难获得更多杂交组合数量的全同胞子代试验林。本研究结果可以作为亲本组合设计及后续跟踪观察的参考。今后仍需加强杂交育种的研究,以期进一步揭示木荷全同胞家系的遗传变异规律。
-
木荷6年生全同胞子代生长和分枝性状存在极显著的遗传变异,性状受较强的家系遗传控制,生长性状父本遗传率较高,分枝形状母本遗传率较高。木荷全同胞子代的生长性状和分枝性状的一般配合力存在极显著的差异,生长性状主要受基因加性和显性效应共同控制,分枝性状主要受基因加性效应控制。胸径与树高生长遗传正相关,且胸径生长与分枝数、枝下高显著遗传相关。根据一般配合力和特殊配合力的结果,认为SY42×LC31组合具有速生性特殊配合力效应。综合分析评价认为:亲本SY42和LC31可作为种子园建园优良无性系材料,6株优良全同胞子代可用于2代育种亲本的补充。
Genetic variation and effect of growth and branching traits in full-sib families of Schima superba
-
摘要:
目的 揭示木荷Schima superba F1代全同胞家系的生长与分枝性状的遗传变异规律,为木荷科学育种提供依据。 方法 以2015年在浙江龙泉营建的4 × 4半双列交配设计的木荷全同胞家系测定林为研究对象,对木荷亲本组合生长与分枝性状的遗传变异参数、一般配合力(GCA)和特殊配合力(SCA)等进行分析。 结果 6年生木荷全同胞家系间的生长和分枝性状存在极显著差异(P<0.01)。生长和分枝性状的变异系数为20%~53%。木荷的生长和分枝性状受较强的遗传控制(全同胞遗传率为0.86~0.93),其中,生长性状的父本遗传率更高,受基因加性和显性效应共同控制;分枝性状的母本遗传率更高,受基因加性效应控制。相关分析表明:木荷全同胞子代生长和分枝性状存在极显著的表型相关(r=0.20~0.87,P<0.01),胸径生长与一级分枝数、枝下高呈极显著遗传相关(r=0.67~0.70, P<0.01)。生长和分枝性状的GCA和SCA效应均达到显著(P<0.05)和极显著(P<0.01)水平。根据GCA和SCA的结果,认为江西上犹和福建连城的优树为优良亲本,两者组合具有速生性状的特殊配合力效应,初选的6株优良全同胞子代可作为2代育种亲本材料。 结论 6年生木荷全同胞家系生长和分枝性状受较强遗传控制,生长性状父本控制力更强,分枝性状母本控制力更强。根据生长性状和分枝性状分别对亲本进行选配,可以得到速生优质的超级亲本组合。图1表7参27 Abstract:Objective This study aims to reveal the heredity and variation of the growth and branching traits of the full-sib families of Schima superba and provide reference for scientific breeding. Method Taking a 4 × 4 half diallel mating design that was conducted in Longquan of Zhejiang Province in 2015 as the research object, the genetic variation parameters, general combining ability (GCA), and special combining ability (SCA) of the growth and branching characters were analyzed. Result The growth and branching traits differed significantly across the 6-year-old full-sib families (P<0.01). The coefficient of variation for the growth and branching traits ranged from 20% to 53%. The growth and branching traits were under strong genetic control, and the heritability of full-sib families was 0.86−0.93. The paternal heritability of the growth traits was higher, which was jointly controlled by gene additive and dominant effects. The maternal heritability of branching traits was higher, which was controlled by gene additive effect. The correlation analysis showed that there was a significant phenotypic correlation between the growth and branching traits (r=0.20−0.87, P<0.01), and there was a significant genetic correlation between DBH growth and bole height and primary branch number (r=0.67−0.70, P<0.01). The GCA and SCA effects of the growth and branching traits reached significant (P<0.05) and extremely significant (P<0.01) levels. According to the results of GCA and SCA, SY42 in Shangyou of Jiangxi and LC31 in Liancheng of Fujian were considered as excellent parents, and SY42 × LC31 combination had special combining ability with fast-growing characters. In addition, the six super-crossing progenies could be used as parent materials for the second-generation breeding. Conclusion The growth and branching traits of full-sib families of S. superba are under strong genetic control, with stronger paternal control over growth traits and stronger maternal control over branching traits. Parents can be selected according to the growth and branching traits, and the super parent combination with fast growth and high quality can be obtained. [Ch, 1 fig. 7 tab. 27 ref.] -
Key words:
- full-sib families /
- half diallel /
- heritability /
- combining ability /
- Schima superba
-
表 1 参试亲本来源
Table 1. The source of parent of S. superba
产地 编号 纬度(N) 经度(E) 海拔/m 年龄/a 树高/m 胸径/cm 福建建瓯 JO8 26°57′ 118°22′ 141 25 16 21.3 JO32 26°57′ 118°22′ 141 25 15 19.2 福建连城 LC31 25°13′ 116°32′ 800 40 15 34.0 江西上犹 SY42 25°42′ 114°01′ 483 28 16 23.5 表 2 4×4半双列组合设计表
Table 2. 4×4 semi-diallel combination design
母本 父本 JO32 LC31 SY42 JO8 JO32 LC31 × SY42 × × JO8 × × × 说明:×表示亲本的杂交组合。 表 3 木荷全同胞子代的生长与分枝性状的方差分析
Table 3. ANOVA analysis of growth and branching traits of crossing progeny
项目 胸径/cm 树高/m 冠幅/m 枝下高/m 一级分枝数 最大分枝角/(°) 最大分枝粗/cm 均值 4.87 4.27 2.24 0.43 23.87 80.90 2.13 变幅 0.90~9.70 0.70~7.60 0.35~3.80 0.10~1.30 4.00~46.00 30.00~120.00 0.60~7.80 变异系数/% 39.17 31.47 28.66 47.84 35.05 19.59 52.77 均方 母本(随机) 13.70** 9.76** 5.82** 0.33** 838.43** 4 814.07** 18.71** 父本(随机) 17.46** 14.82** 3.27** 0.30** 63.11 166.41 6.18** 重复(固定) 165.23** 80.55** 14.94** 0.12* 1 611.67** 378.52 15.29** 组合(随机) 3.89** 4.40** 0.20 0.03 26.96** 50.96 1.65 组合×重复(随机) 1.72** 1.52** 0.25** 0.03 98.65** 258.87 1.71** 残差 0.29 0.31 0.12 0.04 24.36 186.55 0.75 说明:**表示P<0.01;*表示P<0.05。母本、父本、重复、组合、组合×重复的自由度分别为2、2、4、5、20。 表 4 木荷全同胞子代生长与分枝性状的遗传率估算
Table 4. Heritability estimation of growth and branching traits of crossing progeny of S. superba
性状 母本遗传率 父本遗传率 全同胞遗传率 单株遗传率 性状 母本遗传率 父本遗传率 全同胞遗传率 单株遗传率 胸径 0.72 0.78 0.93 0.79 一级分枝数 0.97 0.57 0.86 0.70 树高 0.55 0.70 0.86 0.50 最大分枝角 0.98 0.69 0.91 0.94 枝下高 0.91 0.90 0.88 0.76 最大分枝粗 0.91 0.73 0.89 0.77 表 5 木荷生长分枝性状的配合力方差分析及方差分量
Table 5. Analysis and variance components of combining ability for growth and branching traits of crossing progeny of S. superba
变异来源 胸径 树高 冠幅 枝下高 一级分枝数 最大分枝角 最大分枝粗 一般配合力 0.28** 0.27** 0.12** 0.010 2** 8.55** 45.87** 0.33** 特殊配合力 0.19* 0.18* 0.02 0.001 6 12.15** 43.92** 0.08 机误 0.05 0.05 0.01 0.000 9 1.87 4.97 0.02 加性分量∶显性分量 1.0∶1.4 1.0∶1.6 11.0∶1.0 12.3∶1.0 1.0∶10 1.0∶20.0 5.0∶1.0 说明:一般配合力和特殊配合力的自由度分别为3和2。 **表示P<0.01;*表示P<0.05。 表 6 木荷全同胞子代生长和分枝性状的表型相关系数与遗传相关系数
Table 6. Phenotypic and genetic correlation coefficients of growth and branching traits of crossing progeny of S. superba
性状 胸径 树高 冠幅 枝下高 一级分枝数 最大分枝角 最大分枝粗 胸径 0.87** 0.78* 0.02 0.67** 0.20** 0.49** 树高 0.87** 0.74** 0.03 0.65** 0.24** 0.40** 冠幅 0.30 0.64* 0.15 0.42** 0.06 0.67** 枝下高 0.61* −0.13 0.56 −0.11 −0.02 0.13 一级分枝数 0.70* 0.47 −0.32 −0.61* 0.43** 0.05 最大分枝角 0.09 0.01 −0.33 −0.30 0.77* −0.22** 最大分枝粗 0.05 0.45 0.85** 0.51 −0.64* −0.83** 说明:对角线以上为表型相关系数;对角线以下为遗传相关系数。 **表示极显著相关(P<0.01);*表示显著相关(P<0.05)。 表 7 木荷不同亲本及组合配合力估算
Table 7. Variance effects of combining ability of different parents and combinations of S. superba
变异来源 胸径 树高 冠幅 枝下高 一级分枝数 最大分枝角 最大分枝粗 一般配合力 JO8 −0.26 −0.40 −0.29 −0.09 2.07 −0.47 −0.25 SY42 0.17 0.30 0.16 0.07 5.69 −0.04 −0.05 LC31 0.44 0.33 0.25 −0.03 −4.89 0.52 0.13 JO32 −0.35 −0.23 −0.12 0.05 −2.88 −0.01 0.17 母本一般配合力 LC31 −0.02 −0.05 0.06 0.04 −4.97 −9.99 0.47 SY42 0.01 0.23 0.17 0.05 2.84 6.95 −0.02 JO8 0.01 −0.18 −0.23 −0.08 2.13 3.04 −0.45 父本一般配合力 JO32 −0.34 −0.10 0.07 0.08 −4.25 −6.47 0.38 LC31 −0.01 0.05 0.13 −0.02 −0.49 2.22 0.10 SY42 −0.50 −0.28 −0.11 0.04 −0.56 3.59 −0.33 特殊配合力 JO8×SY42 −0.02 −0.03 −0.05 0.05 −2.30 −5.22 0.15 JO8×LC31 −0.27 −0.33 −0.10 −0.05 −0.20 1.38 −0.20 JO8×JO32 0.28 0.27 0.05 0.00 2.60 3.83 0.05 SY42×LC31 0.33 0.32 0.05 −0.05 2.60 3.88 0.05 SY42×JO32 −0.32 −0.28 −0.10 0.00 −0.20 1.33 −0.20 LC31×JO32 0.03 0.02 0.05 0.00 −2.40 −5.17 0.15 说明:组合编号所表示亲本见表1。 -
[1] 欧阳芳群, 祁生秀, 范国霞, 等. 青海云杉自由授粉家系遗传变异与基于BLUP的改良代亲本选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(6): 53 − 59. OUYANG Fangqun, QI Shengxiu, FAN Guoxia, et al. Genetic variation and improved parents selection of open pollination families of Picea crassifolia Kom. basing one BLUP method [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 43(6): 53 − 59. [2] 王明庥. 林木育种学概论[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1989. WANG Mingxiu. Introduction to Forest Breeding Science [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 1989. [3] SPRAQUE O K, TATUM L A. General verses specific combining ability in single crosses of corn [J]. Journal of the American Society of Agronomy, 1942, 34: 923 − 932. [4] JONES G, LIZINIEWICV M, ADAMOPOULOS S, et al. Genetic parameters of stem and wood traits in full-sib silver birch families[J/OL]. Forests, 2021, 12(2): 159[2022-09-10]. doi: 10.3390/f12020159. [5] MUNEERA PARVEEN A B, MUTHUPANDI M, KUMAR N, et al. Quantitative genetic analysis of wood property traits in biparental population of Eucalyptus camaldulensis × E. tereticornis [J]. Journal of Genetics, 2021, 100(46): 1 − 11. [6] VÁZQUEZ-GONZÁLEZ C, GOLDAR L X, ALÍA R, et al. Genetic variation in resin yield and covariation with tree growth in maritime pine [J/OL]. Forest Ecology and Managemen, 2021, 482(2)[2022-09-10]. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118843. [7] 李力, 施季森, 陈孝丑, 等. 杉木两水平双列杂交亲本配合力分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报, 2000, 24(5): 9 − 13. LI Li, SHI Jisen, CHEN Xiaochou, et al. Combining ability analyses of parents in two-level diallel cross experiment of Chinese fir [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 2000, 24(5): 9 − 13. [8] 齐明. 杉木育种中 GCA 与 SCA 的相对重要性[J]. 林业科学研究, 1996, 9(5): 498 − 503. QI Ming. Relative importance of GCA and SCA in genstic breeding of Chinese fir [J]. Forest Research, 1996, 9(5): 498 − 503. [9] 赵奋成, 张应中, 李宪政, 等. 湿地松半双列子代遗传分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2001, 14(6): 641 − 647. ZHAO Fencheng, ZHANG Yingzhong, LI Xianzheng, et al. Genetic analysis of half diallel progeny of slash pine [J]. Forest Research, 2001, 14(6): 641 − 647. [10] 曹士晗, 张桂芹, 赵兴江, 等. 水曲柳种子园半双列杂交配合力测定初报[J]. 林业科技, 2013, 38(5): 22 − 24. CAO Shihan, ZHNAG Guiqin, ZHAO Xingjiang, et al. The determination of half diallel cross combining ability of Fraxinus mandshurica seed orchard [J]. Forestry Science &Technology, 2013, 38(5): 22 − 24. [11] 沈乐, 徐建民, 李光友, 等. 尾叶桉与巨桉杂种F1代生长性状遗传分析[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(7): 68 − 76. SHEN Le, XU Jianmin, LI Guangyou, et al. Genetic parameters for growth traits in Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis F1 crossings [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2019, 55(7): 68 − 76. [12] 辛娜娜, 张蕊, 范辉华, 等. 5年生木荷生长和形质性状的家系变异和选择[J]. 林业科学研究, 2014, 27(3): 316 − 322. XIN Nana, ZHANG Rui, FAN Huihua, et al. Family variation and selection of growth and quality characteristics of 5-year-old Schima superba seedlings [J]. Forest Research, 2014, 27(3): 316 − 322. [13] 辛娜娜, 张蕊, 徐肇友, 等. 木荷F1代育种群体遗传多样性分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2015, 28(3): 332 − 338. XIN Nana, ZHANG Rui, XU Zhaoyou, et al. Genetic diversity among breeding parents of Schima superba revealed by SSR [J]. Forest Research, 2015, 28(3): 332 − 338. [14] 王云鹏, 张蕊, 周志春, 等. 木荷优树自由授粉家系早期生长性状遗传变异动态规律[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(9): 77 − 86. WANG Yunpeng, ZHANG Rui, ZHOU Zhichun, et al. Dynamic patterns of genetic variation in early growth traits of the open-pollinated families of Schima superba plus tree [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2020, 56(9): 77 − 86. [15] 徐肇友, 王云鹏, 肖纪军, 等. 不同产地木荷优树无性系表型多样性[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2021, 49(2): 5 − 10, 17. XU Zhaoyou, WANG Yunpeng, XIAO Jijun, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis of Schima superba superior clones from different locations [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2021, 49(2): 5 − 10, 17. [16] 王云鹏, 张蕊, 周志春, 等. 10年生木荷生长和材性性状家系变异及选择[J]. 南京林业大学学报 (自然科学版), 2020, 44(5): 85 − 92. WANG Yunpeng, ZHANG Rui, ZHOU Zhichun, et al. A variation and selection of growth and wood traits for 10-year-old Schima superba [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 2020, 44(5): 85 − 92. [17] YANG Hanbo, ZHANG Rui, SONG Ping, et al. The floral biology, breeding system and pollination efficiency of Schima superba Gardn. et Champ. (Theaceae)[J/OL]. Forests, 2017, 8(11)[2022-09-10]. doi: 10.3390/f8100404. [18] 翟虎渠, 王建康. 应用数量遗传[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2007. ZHAI Huqu, WANG Jiankang. Applied Quantitative Inheritance [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2007. [19] 朱之悌. 林木遗传学基础[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1990. ZHU Zhiti. Genetic Basis of Forest Trees [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 1990. [20] 谭小梅, 金国庆, 周志春. 马尾松3代种质苗高生长参数的配合力分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 2011, 24(5): 663 − 667. TAN Xiaomei, JIN Guoqing, ZHOU Zhichun. Combining ability analysis on seedling shoot elongation and growth parameters for the third generation germplasm of Pinus massoniana [J]. Forest Research, 2011, 24(5): 663 − 667. [21] 赵颖, 周志春, 金国庆. 马尾松苗木生长和根系性状的GCA/SCA及磷素环境影响[J]. 林业科学, 2009, 45(6): 27 − 33. ZHAO Ying, ZHOU Zhichun, JIN Guoqing. GCA/SCA of seedling growth and root parameters in Pinus massoniana and the phosphorus environment influence [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2009, 45(6): 27 − 33. [22] 董虹妤, 刘青华, 周志春, 等. 马尾松子代生长杂种优势与亲本配合力、遗传距离的相关性[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(2): 65 − 75. DONG Hongyu, LIU Qinghua, ZHOU Zhichun, et al. Correlation between heterosis in the growth of progeny and combining ability and genetic distance of the parents for Pinus massoniana [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(2): 65 − 75. [23] YANG Yong, SUN Miao, LI Shanshan, et al. Germplasm resources and genetic breeding of Paeonia: a systematic review[J/OL]. Horticulture Research, 2020, 7(1): 107[2022-09-10]. doi: org/10.1038/s41438-020-0332-2. [24] 金国庆, 秦国峰, 刘伟宏, 等. 马尾松测交系杂交子代生长性状遗传分析[J]. 林业科学, 2008, 44(1): 70 − 76. JIN Guoqing, QIN Guofeng, LIU Weihong, et al. Genetic analysis of growth traits on tester strain progeny of Pinus massoniana [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2008, 44(1): 70 − 76. [25] 刘青华, 金国庆, 储德裕, 等. 基于马尾松测交系子代的生长、干形和木材密度的配合力分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(2): 8 − 14. LIU Qinghua, JIN Guoqing, CHU Deyu, et al. Genetic analysis on combining ability of growth, stem form and wood basic density of Pinus massoniana by testcross mating design [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 35(2): 8 − 14. [26] 张振, 金国庆, 余启新, 等. 马尾松三代测定林抽梢性状的遗传效应及与针叶氮磷钾养分的遗传相关[J]. 林业科学, 2017, 53(8): 26 − 34. ZHANG Zhen, JIN Guoqing, YU Qixin, et al. Genetic effects of shoot growth and its genetic correlation with N, P and K contents in needles of the third generation trial plantation of Pinus massoniana [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2017, 53(8): 26 − 34. [27] 齐明, 王海蓉, 叶金俊, 等. 杉木全双列杂交试验的遗传分析及优良品种的选择[J]. 林业科技通讯, 2019(12): 8 − 11. QI Ming, WANG Hairong, YE Jinjun, et al. Cunninghamia lanceolata, complete diallel cross experiment of genetic analysis and the selection of good varieties [J]. Forest Science and Technology, 2019(12): 8 − 11. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220634






 下载:
下载: