-
近年来,随着纳米技术的发展,碳纳米管作为一种新型吸附剂被广泛应用于多种重金属的去除[1-2]。碳纳米管表面的羧基、羟基等官能团与重金属相互作用,提高了碳纳米管对重金属的吸附和选择[3-7],是影响碳纳米管吸附重金属的重要因素。除作为吸附剂使用外,碳纳米管和重金属在环境中共存时,也会影响重金属的生态毒性。LIU等[8-9]发现:多壁碳纳米管本身对斑马鱼Danio rerio没有毒性,但却由于吸附了铅(Pb)和锌(Zn),加重了两者在斑马鱼体内的积累和毒性。MARTINEZ等[10]发现:硝酸氧化后的多壁碳纳米管加剧了Pb在鱼体中的累积。YU等[11]发现:表面未处理的多壁碳纳米管会抑制大型蚤Daphnia magna对重金属的吸收,而表面具有含氧官能团的多壁碳纳米管吸附了重金属,由于“木马效应”,重金属在大型蚤内大量积累。与其他生物相比,微生物既是生态食物链的最底层也是分解者,因此微生物的生态风险评价更为重要。WANG等[12]发现:铜(Cu)和铬(Cr)增强了碳纳米管对微生物群落的影响。付勇等[13]对3种短多壁碳纳米管和镉离子(Cd2+)的复合细菌毒性进行了初步研究,但未阐明不同官能团对碳纳米管吸附机制的影响[13]。在此基础上,本研究以未经修饰、羧基化、羟基化和氨基化多壁碳纳米管为材料,通过Cd2+吸附平衡实验和细菌毒性实验评估不同官能团多壁碳纳米管对重金属吸附及对大肠埃希菌Escherichia coli毒性的影响,从多壁碳纳米管与重金属相互作用角度揭示表面官能团在多壁碳纳米管影响重金属细菌毒性中的作用机制。
-
未经修饰(MWCNTs)、羟基化(O-MWCNTs)、羧基化(C-MWCNTs)和氨基化多壁碳纳米管(N-MWCNTs)均购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司,纯度>95%,内径为3~5 nm,外径为8~15 nm,长度约为50 μm。用超纯水配制成1 000 mg·L−1的碳纳米管悬液作为母液,使用前超声分散15 min,并用超纯水稀释至所需质量浓度。100 mg·L−1质量浓度下,4种不同官能团多壁碳纳米管的zeta电位、含氧量、电导率和pH等参数见表1。
表 1 不同官能团多壁碳纳米管的测定参数
Table 1. Determination parameters of MWCNTs with different functional groups
zeta电位/mV 含氧量/% 电导率/(μS·cm−1) pH 多壁碳纳米管 −9.14 5.654 0.87 6.57 羟基化多壁碳纳米管 −7.19 6.629 1.79 6.10 羧基化多壁碳纳米管 −12.76 11.286 2.98 5.88 氨基化多壁碳纳米管 −8.98 4.581 1.13 7.23 用分析纯四水硝酸镉[Cd(NO3)2·4H2O]配制100 mg·L−1的Cd2+储备液作为母液,使用前超纯水稀释至所需质量浓度。以分离自生活污水的大肠埃希菌(Genbank收录号:MG388227)为模型微生物,菌种保存于4 ℃冰箱中。使用前接种于LB液体培养基,37 ℃、150 r·min−1在恒温振荡器中培养过夜,然后3 000 r·min−1离心制备菌悬液。为排除盐度影响,细菌用超纯水离心洗涤2次,利用紫外-可见分光光度计调节D(600)至1.0,菌落数量约为1×109 CFU·mL−1。
-
固定多壁碳纳米管质量浓度为1 000 mg·L−1,调节Cd2+质量浓度为0 (对照)、1、2、5、10和15 mg·L−1。150 r·min−1、25 ℃恒温振荡3 h;4 000 r·min−1离心后取上清液,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤,利用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP,Prodigy7,利曼-徕伯斯公司,美国)测定滤液中Cd2+质量浓度,计算平衡吸附量,绘制吸附等温线。Langmuir吸附等温式:q=qmKlc/1+Klc。其中:q为平衡吸附量(mg·g−1),qm为单分子层饱和吸附量(mg·g−1),Kl为平衡吸附常数,c为溶液中吸附质平衡浓度(mg·g−1)。Freundlich吸附等温式:q=Kfc1/n。其中: Kf为平衡吸附常数,n为常数。用Origin 9.0绘制吸附等温线,分别用Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温式进行曲线拟合,得到qm、Kl以及Kf和n。
-
参考付勇等[13]、李梅等[14]进行细菌毒性实验,采取染毒和生长抑制实验相结合的方法。量取Cd2+母液,调节质量浓度至0(对照)、1、2、4、8、10 mg·L−1,定容至9 mL。量取各官能团多壁碳纳米管悬液母液,调节质量浓度至0(对照)、10、20、50、100、200 mg·L−1,定容至9 mL。固定Cd2+质量浓度至1 mg·L−1,分别加入0(对照)、10、20、50、100、200 mg·L−1的各官能团多壁碳纳米管悬液,定容至9 mL。往各样品中加入1 mL细菌悬液[D(600)=1.0],150 r·min−1、25 ℃恒温培养3 h进行染毒实验。染毒结束后,取1 mL混合液转移至9 mL灭菌后的LB液体培养基中,37 ℃振荡培养,每隔1 h测定混合液600 mn波长处的吸光度[D(600)]。为避免颗粒沉降造成的影响,每次吸光度测定前样品均先涡旋混合10 s。计算细菌存活率(%):S=[D(600)t-s−D(600)o-s]/[D(600)t-c−D(600)o-c]。其中:D(600)o-c为对照组初始时刻600 nm下吸光度,D(600)t-c为对照组t时刻600 nm下吸光度,D(600)o-s为样品组初始时刻600 nm下吸光度,D(600)t-s为样品组t时刻600 nm下吸光度。根据对照组迟滞期长短,t时刻选取2或3,各组取的t时刻与对照组相同。利用SPSS软件对数据进行显著性分析。
-
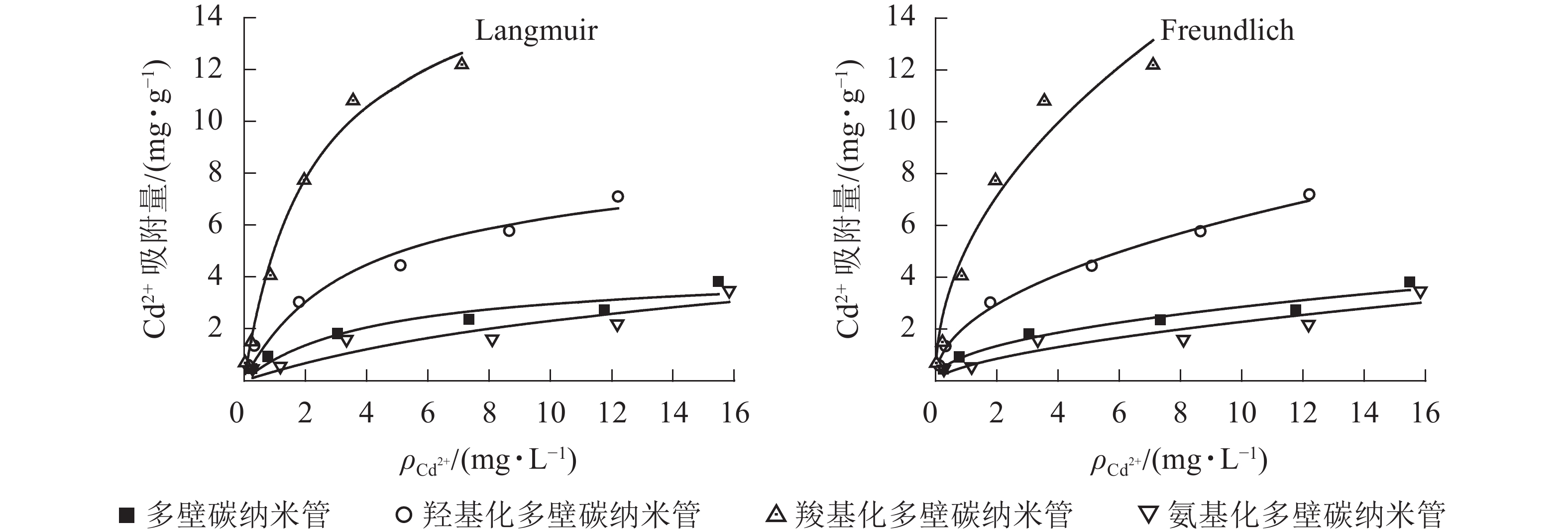
25 ℃条件下不同官能团多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附等温线见图1,Langmuir和Freundlich等温式拟合参数见表2。从图1可以看出:相同条件下,不同官能团多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附能力大小依次为羧基化多壁碳纳米管、羟基化多壁碳纳米管、多壁碳纳米管、氨基化多壁碳纳米管。结合表2可知:4种多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附均可以用Langmuir和Freundlich方程较好地拟合,其中羟基化和羧基化多壁碳纳米管的Langmuir和Freundlich拟合相关系数R2均达到了0.95以上。对于未修饰的多壁碳纳米管和氨基化多壁碳纳米管,Freundlich方程拟合效果更好。
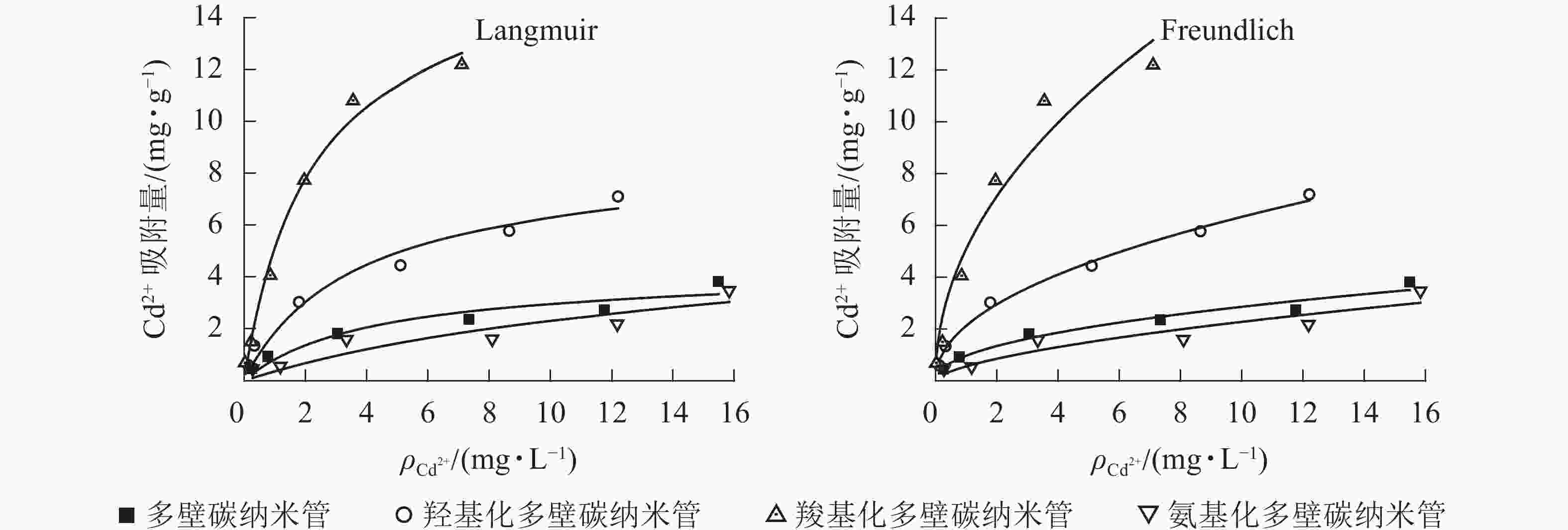
图 1 不同官能团多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附等温线
Figure 1. Adsorption isotherm of Cd2+ on MWCNTs with different functional groups
表 2 不同碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附等温线方程拟合参数
Table 2. Regression parameters of adsorption isotherms of Cd2+ onto different MWCNTs
样品 Langmuir方程 Freundlich方程 方程式 qm/(mg·g−1) Kl/(L·mg−1) R2 方程式 n Kf R2 多壁碳纳米管 q=1.002c/(1+0.238c) 4.212 0.238 0.896 q=0.976c0.467 2.108 0.976 0.954 羟基化多壁碳纳米管 q=2.346c/(1+0.273c) 8.593 0.273 0.954 q=2.131c0.473 2.113 2.131 0.994 羧基化多壁碳纳米管 q=7.442c/(1+0.451c) 16.486 0.451 0.989 q=5.103c0.483 2.071 5.103 0.950 氨基化多壁碳纳米管 q=0.386c/(1+0.066c) 5.882 0.066 0.796 q=0.564c0.607 1.647 0.564 0.852 Langmuir吸附等温式适用于表面均匀吸附剂的吸附,可预测最大吸附量,拟合相关系数R2值越接近于1,预测得到的最大吸附量将越接近于真实值。Freundlich吸附等温式适用于不均匀表面吸附剂的吸附,n值越小代表越难吸附。由表2可以看出:羧基化多壁碳纳米管吸附量最大,是羟基化多壁碳纳米管的约2倍,是未修饰多壁碳纳米管的约4倍;Langmuir吸附等温式拟合的氨基化多壁碳纳米管吸附方程对应的R2值偏低,其计算最大吸附量比实际值要大;平衡吸附常数的大小也在一定程度上代表了吸附剂的吸附性能,4种碳纳米管的Freundlich平衡吸附常数Kf与其最大吸附量相一致,说明Freundlich吸附等温式更适用于分析不同多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附。
-
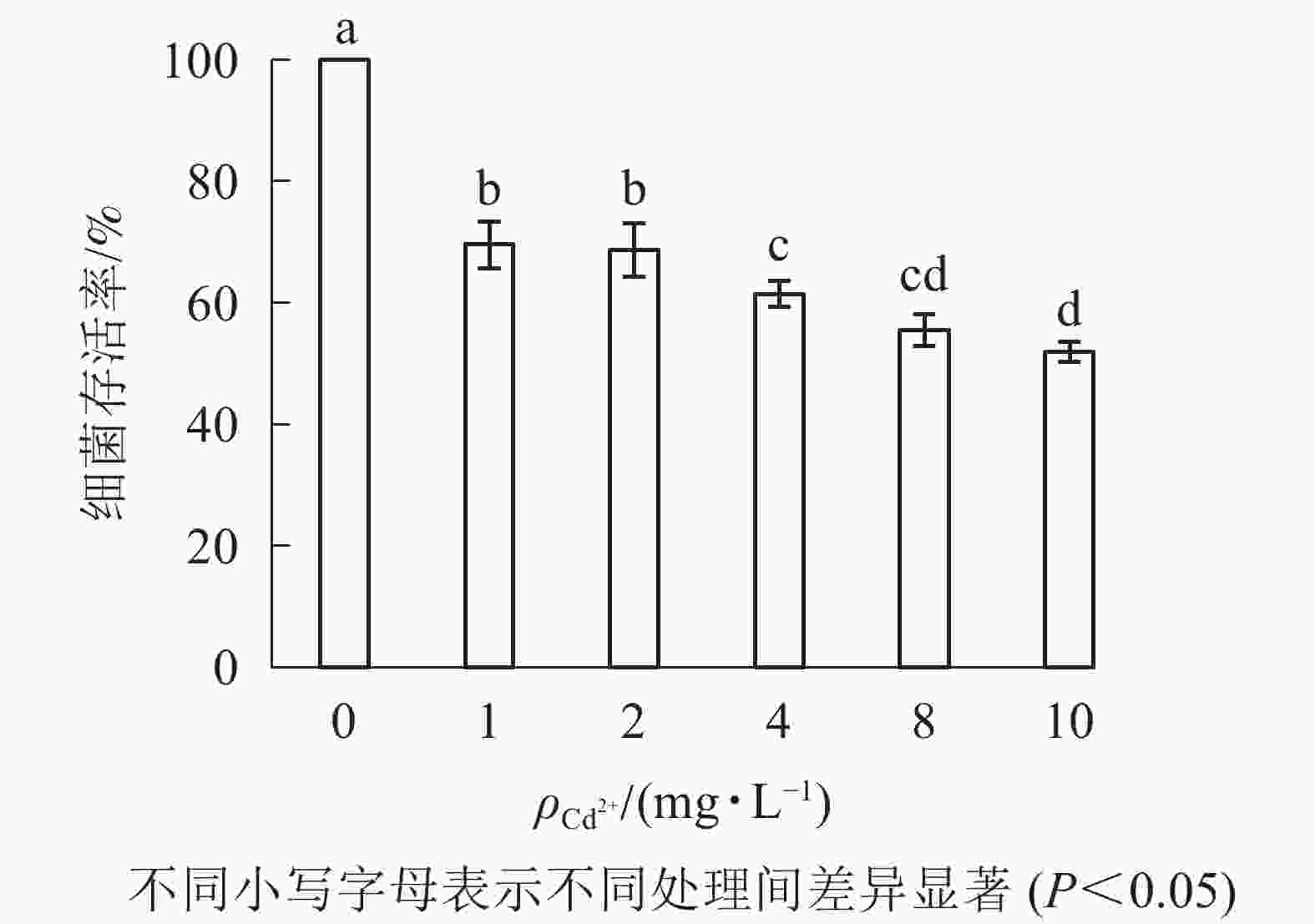
由图2可知:1 mg·L−1的Cd2+处理下,大肠埃希菌存活率约为70%;随着Cd2+质量浓度升高(10 mg·L−1),大肠埃希菌存活率缓慢但持续下降(50%)。为减少因Cd2+质量浓度变化对多壁碳纳米管毒性实验的影响,后续实验中固定Cd2+质量浓度为1 mg·L−1。
-
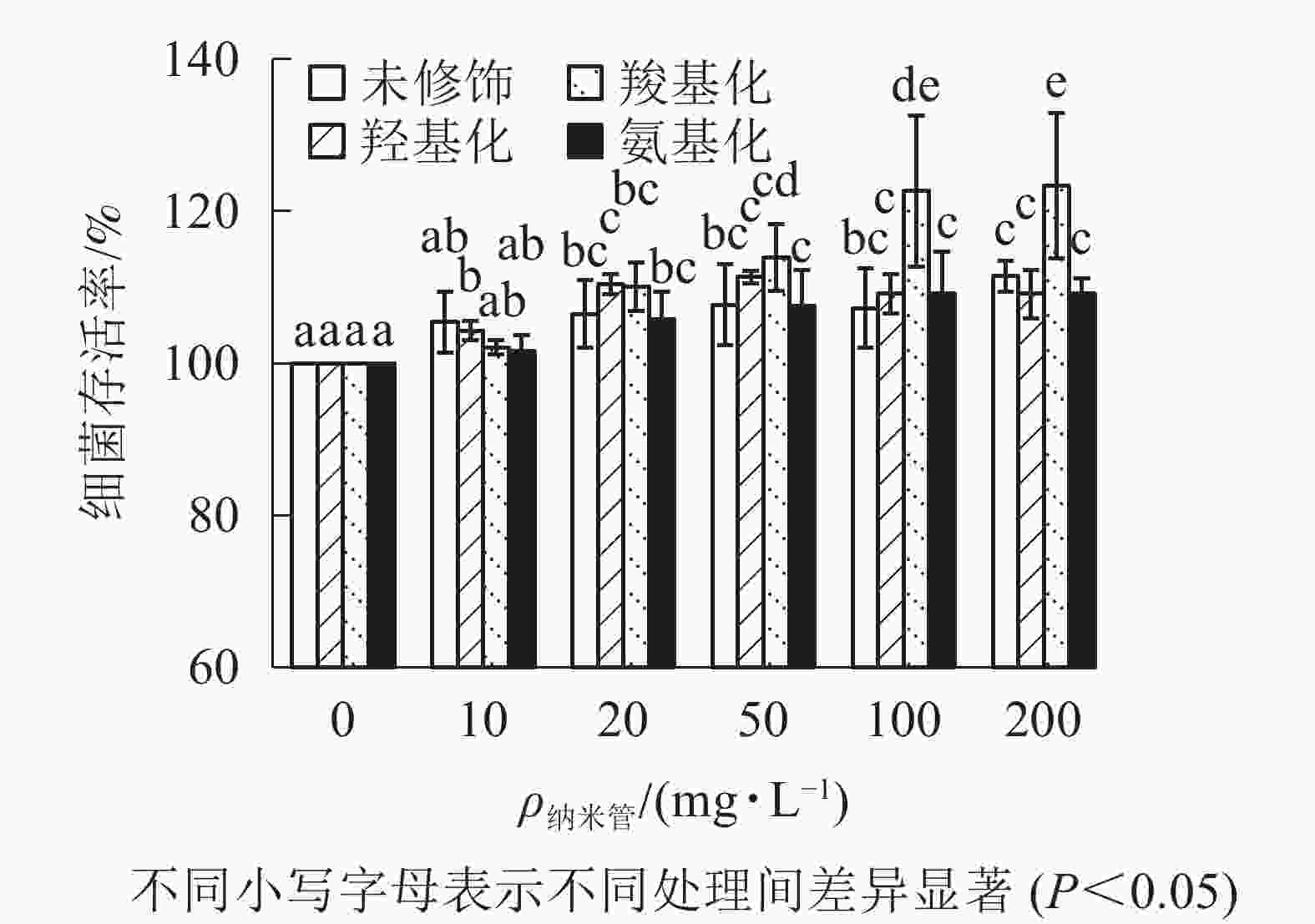
从图3可知:与对照相比,质量浓度不大于200 mg·L−1时,不同官能团多壁碳纳米管对大肠埃希菌存活不存在抑制作用,甚至不同程度提高了细菌的存活率,其中羧基化碳纳米管对大肠埃希菌的存活最有利。
-
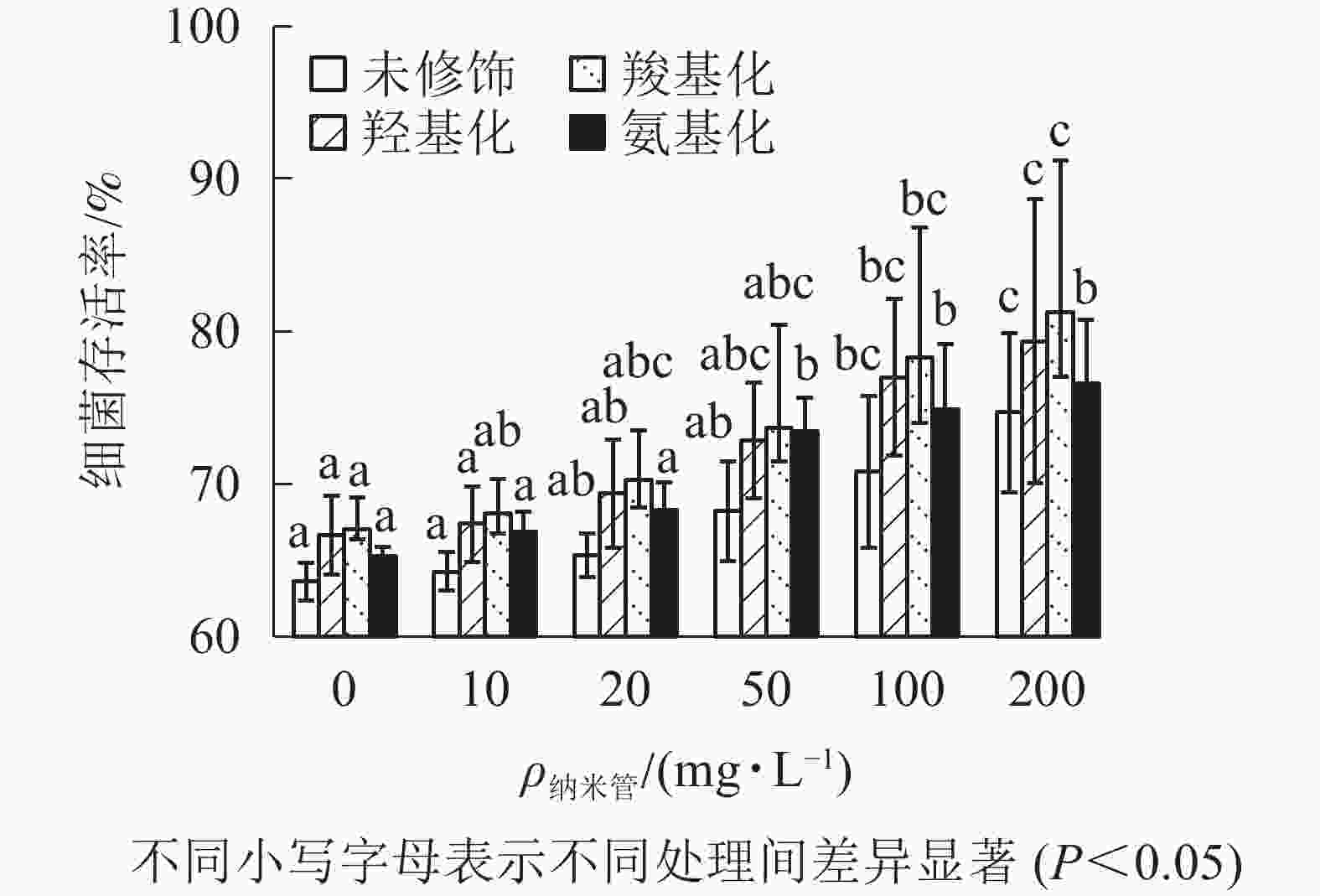
固定Cd2+质量浓度为1 mg·L−1,考察不同质量浓度的4种官能团多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+大肠埃希菌毒性的影响。从图4可以看出:随着多壁碳纳米管质量浓度的增大,4种官能团多壁碳纳米管-Cd2+复合物处理下的大肠埃希菌存活率缓慢增加。与1 mg·L−1的Cd2+相比,当复合物中多壁碳纳米管质量浓度达到200 mg·L−1时,细菌存活率提高了11%(未修饰多壁碳纳米管)~14%(羧基化多壁碳纳米管),可见4种官能团多壁碳纳米管均显著降低了Cd2+的细菌毒性。
-
碳纳米管对重金属的吸附机制包括物理吸附、静电引力、表面络合、离子交换等[15]。通常认为影响物理吸附的主要因素为吸附剂表面积,表面积越大,暴露的活性吸附点位也越多,吸附能力也越强[16]。本研究中4种多壁碳纳米管管长和管径相同,物理吸附能力(有效吸附面积,即吸附点位)主要与其在水中的分散性能有关。未修饰多壁碳纳米管和氨基化多壁碳纳米管在水中易团聚,羧基化和羟基化多壁碳纳米管分散性能较好,因此对Cd2+的物理吸附性能优于前两者。碳纳米管与Cd2+间的静电引力主要取决于碳纳米管的表面电荷。相较于其他3种多壁碳纳米管,羧基化多壁碳纳米管表面的羧基解离使-COOH变成了COO−,带负电荷更多(表1),与带正电荷的Cd2+静电吸引强,是羧基化多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附能力大的原因[17]。多壁碳纳米管含氧官能团对重金属的吸附主要通过络合作用[18-19]。XU等[20]发现:羧基化和羟基化多壁碳纳米管都可与重金属离子产生表面络合作用。本研究发现:4种多壁碳纳米管含氧量从大到小依次为羧基化多壁碳纳米管、羟基化多壁碳纳米管、多壁碳纳米管、氨基化多壁碳纳米管;结合图1可知:多壁碳纳米管含氧量越高,与Cd2+的反应就越剧烈。本研究中未修饰的多壁碳纳米管和氨基化多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附主要为物理吸附和静电引力,而羟基化和羧基化多壁碳纳米管吸附Cd2+主要为络合作用,与羟基相比,羧基与Cd2+的化学键能更强,因而络合反应也更大,即羧基化多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附性能更好。
多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附决定了水中游离Cd2+的质量浓度,一定程度上影响了Cd2+的生物可利用性。利用碳纳米管对溶解Cd2+质量浓度的影响可预测其对Cd2+细菌毒性的影响。若不考虑碳纳米管与细菌的接触,仅考虑Cd2+细菌毒性的变化,羧基化多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+细菌毒性的降低最明显,其次为羟基化多壁碳纳米管,氨基化多壁碳纳米管和未修饰的多壁碳纳米管对重金属细菌毒性影响较小。
-
超纯水中Cd2+主要以游离态存在,其致毒机制主要为与大肠埃希菌表面上的吸附位点结合,通过离子通道等途径进入大肠埃希菌内,并在某些特定部位富集[21]。实验室条件下,Cd2+细菌毒性随Cd2+质量浓度增大(1~10 mg·L−1)而增强,在菌落数为1×108 CFU·mL−1时,大肠埃希菌存活率从70%降至50%左右。
-
目前认为碳纳米管与细菌直接接触对细胞膜穿刺造成的物理损伤是碳纳米管对细菌产生毒性的重要因素[22]。碳纳米管与细菌是否能够直接接触不仅取决于碳纳米管表面电荷,还取决于碳纳米管质量浓度及分散状况。本研究中4种多壁碳纳米管表面均带负电荷,其中羧基化多壁碳纳米管负电荷最多,因此与带负电荷的细菌之间存在静电斥力,不利于接触。但羧基化多壁碳纳米管和羟基化碳纳米管分散性较好,与细菌接触机会相对更多;未修饰多壁碳纳米管和氨基化多壁碳纳米管团聚性较强,因团聚而大部分沉降,与细菌接触机会较少。同时多壁碳纳米管外径为8~15 nm,长度约为50 μm,因接触造成的物理损伤仅在细胞壁产生;因此可以认为多壁碳纳米管对细菌生长没有抑制。相反,羧基化多壁碳纳米管存在条件下,细菌存活率提高;这是由于细菌正常生长需要适合的渗透压,等渗条件下细菌抗毒能力强,低于等渗离子强度时,离子强度越大,细菌存活率越高[23]。为排除离子强度对碳纳米管影响,本研究利用超纯水为背景介质,100 mg·L−1质量浓度下,羧基化多壁碳纳米管电导率最高,表面负电荷最多,与细菌的静电斥力更强,因此羧基化多壁碳纳米管存在条件下,细菌存活率明显高于其他处理。
-
多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+毒性的影响可以从3个方面来解释。①多壁碳纳米管的毒性。多壁碳纳米管吸附Cd2+后,表面负电荷均被中和,颗粒自团聚和颗粒与细菌间的异团聚性能均增加,2种团聚对细菌的毒性影响相反,因此多壁碳纳米管吸附Cd2+前后自身毒性变化可以忽略。②游离态Cd2+的毒性。游离态Cd2+质量浓度受到多壁碳纳米管类型与质量浓度的影响[24]。对4种多壁碳纳米管的吸附等温拟合发现:同等初始质量浓度时,不同官能团多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附能力从大到小依次为羧基化多壁碳纳米管、羟基化多壁碳纳米管、多壁碳纳米管、氨基化多壁碳纳米管,而由游离态Cd2+造成的细菌毒性与其质量浓度一致。③多壁碳纳米管-Cd2+复合物的毒性。除游离态Cd2+外,体系中存在的多壁碳纳米管-Cd2+复合物也可能会对细菌产生毒性[13]。多壁碳纳米管吸附Cd2+后表面负电荷降低,导致多壁碳纳米管与细菌的接触机会增加,此时,与多壁碳纳米管结合能力弱的Cd2+将可能转移至细菌表面对细胞膜产生损伤。另外,其物理损伤将会促进Cd2+进入细菌细胞内,从而产生伤害[25-26]。未修饰多壁碳纳米管-Cd2+复合物与氨基化多壁碳纳米管-Cd2+复合物对细菌的毒性不能忽略。总体上多壁碳纳米管吸附Cd2+造成的毒性降低大于多壁碳纳米管与细菌直接接触造成的毒性增强,因此表现为多壁碳纳米管可降低环境Cd2+的细菌毒性。
-
多壁碳纳米管内外管径及长度均相同时,多壁碳纳米管吸附Cd2+性能与其表面官能团含氧量有关,含氧量越高,吸附能力越强。即4种多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+质量浓度降低程度从高到低依次为羧基化多壁碳纳米管、羟基化多壁碳纳米管、多壁碳纳米管、氨基化多壁碳纳米管。4种多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附在不同程度上降低Cd2+生物有效性,同时碳纳米管-Cd2+复合物也存在一定毒性,总体上多壁碳纳米管质量浓度越高,对Cd2+细菌毒性降低越显著,相比之下,羧基化多壁碳纳米管表现了更强的降毒能力。
Adsorption of cadmium on multi-walled carbon nanotubes with different functional groups and their bacterial toxicity
-
摘要:
目的 探讨不同官能团多壁碳纳米管对镉离子(Cd2+)的吸附作用,揭示多壁碳纳米管影响镉细菌毒性的机制。 方法 通过批量吸附平衡实验研究不同官能团(羟基化、羧基化、氨基化、未经修饰)多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)对Cd2+的吸附性能,通过细菌毒性实验评估不同官能团多壁碳纳米管和Cd2+对大肠埃希菌Escherichia coli的毒性效应。 结果 4种多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附能力从大到小依次为羧基化多壁碳纳米管、羟基化多壁碳纳米管、多壁碳纳米管、氨基化多壁碳纳米管,吸附性能与碳纳米管含氧量相关。多壁碳纳米管- Cd2+复合物细菌毒性低于游离Cd2+,随纳米管质量浓度增加(0~200 mg·L−1),羧基化多壁碳纳米管-Cd2+复合物作用下细菌存活率从67%提高到81%。 结论 不同官能团多壁碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附量与碳纳米管含氧量呈正相关;多壁碳纳米管-Cd2+复合物细菌毒性低于游离Cd2+,认为多壁碳纳米管可降低游离Cd2+的细菌毒性。图4表2参26 Abstract:Objective This study attempted to explore the adsorption properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) with different functional groups for cadmium, and to reveal the influence mechanism on the bacterial toxicity of cadmium. Method The adsorption abilities of Cd2+ on MWCNTs with different functional groups (hydroxylated, carboxylated, aminated and unmodified) were studied by batch adsorption equilibrium test. The effects of MWCNTs with different functional groups on the toxicity of Cd2+ to Escherichia coli (E. coli) were evaluated by the bacterial toxicity test. Result The order of Cd2+ adsorption capacity on the four MWCNTs were carboxylated MWCNTs, hydroxylated MWCNTs, MWCNTs, finally aminated MWCNTs, which was related to the oxygen content. The combined bacterial toxicity of MWCNTs and Cd2+ was lower than that of free Cd2+, and the bacterial survival rate increased from 67% to 81% with the increasing carboxylated MWCNTs concentration (0−200 mg·L−1). Conclusion The adsorption of Cd2+ by MWCNTs with different functional groups was positively correlated with their oxygen content. The combined bacterial toxicity of MWCNTs and Cd2+ was lower than that of free Cd2+, and it was concluded that MWCNTs could reduce the bacterial toxicity of free Cd2+. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 26 ref.] -
Key words:
- multi-walled carbon nanotubes /
- functional groups /
- cadmium /
- adsorption /
- Escherichia coli /
- toxicity
-
表 1 不同官能团多壁碳纳米管的测定参数
Table 1. Determination parameters of MWCNTs with different functional groups
zeta电位/mV 含氧量/% 电导率/(μS·cm−1) pH 多壁碳纳米管 −9.14 5.654 0.87 6.57 羟基化多壁碳纳米管 −7.19 6.629 1.79 6.10 羧基化多壁碳纳米管 −12.76 11.286 2.98 5.88 氨基化多壁碳纳米管 −8.98 4.581 1.13 7.23 表 2 不同碳纳米管对Cd2+的吸附等温线方程拟合参数
Table 2. Regression parameters of adsorption isotherms of Cd2+ onto different MWCNTs
样品 Langmuir方程 Freundlich方程 方程式 qm/(mg·g−1) Kl/(L·mg−1) R2 方程式 n Kf R2 多壁碳纳米管 q=1.002c/(1+0.238c) 4.212 0.238 0.896 q=0.976c0.467 2.108 0.976 0.954 羟基化多壁碳纳米管 q=2.346c/(1+0.273c) 8.593 0.273 0.954 q=2.131c0.473 2.113 2.131 0.994 羧基化多壁碳纳米管 q=7.442c/(1+0.451c) 16.486 0.451 0.989 q=5.103c0.483 2.071 5.103 0.950 氨基化多壁碳纳米管 q=0.386c/(1+0.066c) 5.882 0.066 0.796 q=0.564c0.607 1.647 0.564 0.852 -
[1] IHSANULLAH, ABBAS A, AL-AMER A M, et al. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution by advanced carbon nanotubes: critical review of adsorption applications [J]. Sep Purif Technol, 2016, 157(5): 141 − 161. [2] FIYADH S S, ALSAADI M A, JAAFAR W Z, et al. Review on heavy metal adsorption processes by carbon nanotubes [J]. J Clean Prod, 2019, 230(7): 783 − 793. [3] 常兰, 秦伟超. 碳纳米管表面改性及其吸附水中污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工技术与开发, 2014, 43(3): 43 − 46. CHANG Lan, QIN Weichao. Research progress in surface modification of carbon nanotubes and adsorption of pollutants in wastewater [J]. Technol Dev Chem Ind, 2014, 43(3): 43 − 46. [4] ANSARI A, MEHRABIAN M A, HASHEMIPOUR H. Zinc ion adsorption on carbon nanotubes in an aqueous solution [J]. Pol J Chem Technol, 2014, 13(1): 29 − 37. [5] 聂海瑜, 沈甘霓, 杜凤沛, 等. 碳纳米管对水体污染物吸附的研究进展[J]. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 41(3): 326 − 330. NIE Haiyu, SHEN Ganni, DU Fengpei, et al. Research progress in adsorption of contaminates from water by carbon nanotubes [J]. J Southwest Univ Natl Nat Sci Ed, 2015, 41(3): 326 − 330. [6] YANG Xiaodong, WAN Yongshan, ZHENG Yulin, et al. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metal from aqueous solutions: a critical review [J]. Chem Eng J, 2019, 366: 608 − 621. [7] 杨孝智, 高静, 贺婷婷, 等. 碳纳米管对水体重金属污染物的吸附/解吸性能研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2011, 40(4): 692 − 695. YANG Xiaozhi, GAO Jing, HE Tingting, et al. Research progress on the adsorption/desorption of heavy metal pollutants on carbon nanotubes in water [J]. Appl Chem Ind, 2011, 40(4): 692 − 695. [8] LIU Shaobin, NG A K, XU Rong, et al. Antibacterial action of dispersed single-walled carbon nanotubes on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis investigated by atomic force microscopy [J]. Nanoscale, 2010, 2(12): 2744 − 2750. [9] LIU Shaobin, WEI Li, HAO Lin, et al. Sharper and faster ‘nano darts’ kill more bacteria: a study of antibacterial activity of individually dispersed pristine single-walled carbon nanotube [J]. ACS Nano, 2009, 3(12): 3891 − 3902. [10] MARTINEZ D S T, ALVES O L, BARBIERI E. Carbon nanotubes enhanced the lead toxicity on the freshwater fish [J]. J Phys, 2013, 429: 012043. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/429/1/012043. [11] YU Zhiguo, WANG Wenxiong. Influences of ambient carbon nanotubes on toxic metals accumulation in Daphnia magna [J]. Water Res, 2013, 47(12): 4179 − 4187. [12] WANG Fei, YAO Jun, LIU Haijun, et al. Cu and Cr enhanced the effect of various carbon nanotubes on microbial communities in an aquatic environment [J]. J Hazard Mater, 2015, 292(9): 137 − 145. [13] 付勇, 裴建川, 李梅, 等. 多壁碳纳米管和重金属镉的细菌毒性及影响机制[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(2): 319 − 324. FU Yong, PEI Jianchuan, LI Mei, et al. Effects and mechanism of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the bacterial toxicity of cadmium [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2020, 37(2): 319 − 324. [14] 李梅, 裴建川, 付勇, 等. 表面活性剂对二氧化钛纳米颗粒和锌离子复合细菌毒性的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(12): 2730 − 2739. LI Mei, PEI Jianchuan, FU Yong, et al. Effect of surfactants on the combined toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles and zinc ions [J]. Environ Chem, 2018, 37(12): 2730 − 2739. [15] BASSYOUNI M, MANSI A E, ELGABRY A, et al. Utilization of carbon nanotubes in removal of heavy metals from wastewater: a review of the CNT’s potential and current challenges [J]. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Proc, 2020, 126(1): 38. doi: 10.1007/s00339-019-3211-7. [16] XU Jiang, CAO Zhen, ZHANG Yilin, et al. A review of functionalized carbon nanotubes and graphene for heavy metal adsorption from water: preparation, application, and mechanism [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 195(10): 351 − 364. [17] LI Jiaxing, CHEN Shuyu, SHENG Guodong, et al. Effect of surfactants on Pb(Ⅱ) adsorption from aqueous solutions using oxidized multiwall carbon nanotubes [J]. Chem Eng J, 2011, 166(2): 551 − 558. [18] PEREIRA R F P, VALENTE A J M, BURROWS H D. The interaction of long chains odium carboxylates and sodium dodecylsulfate with lead(Ⅱ) ions in aqueous solutions [J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2014, 414(1): 66 − 72. [19] TOFIGHY M A, MOHAMMADI T. Adsorption of divalent heavy metal ions from water using carbon nanotube sheets [J]. J Hazard Mater, 2011, 185(1): 140 − 147. [20] XU Yijun, ARRIGO R, LIU Xi, et al. Characterization and use of functionalized carbon nanotubes for the adsoption of heavy metal anions [J]. New carbon Mater, 2011, 26(1): 57 − 62. [21] 谭凌艳, 杨柳燕, 缪爱军. 人工纳米颗粒对重金属在水生生物中的富集与毒性研究进展[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2016, 52(4): 582 − 589. TAN Lingyan, YANG Liuyan, MIAO Aijun. Engineered nanoparticle effects on heavy metal bioaccumulation and toxicity in aquatic ecosystem [J]. J Nanjing Univ Nat Sci, 2016, 52(4): 582 − 589. [22] BENNETT S W, ADELEYE A, JI Zhaoxia, et al. Stability, metal leaching, photoactivity and toxicity in freshwater systems of commercial single wall carbon nanotubes [J]. Water Res, 2013, 47(12): 4074 − 4085. [23] 李梅. 水环境中ZnO纳米颗粒对大肠杆菌的毒性及影响因素[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2012. LI Mei. The Toxicity and Impact Factors of ZnO Nanoparticles to Escherichia coli in Aquatic Environment[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2012. [24] CORTES P, DENG Shuguang, SMITH G B. The toxic effects of single wall carbon nanotubes on E. coli and a spore-forming Bacillus species [J]. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett, 2014, 6(1): 26 − 30. [25] HANDY R D, OWEN R, VALSAMI-JONES E. The ecotoxicology of nanoparticles and nanomaterials: current status, knowledge gaps, challenges, and future needs [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2008, 17(5): 315 − 325. [26] QU Yuanyuan, WANG Jingwei, ZHOU Hao, et al. Concentration-dependent effects of carbon nanotubes on growth and biphenyl degradation of Dyella ginsengisoli LA-4 [J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2016, 23(3): 2864 − 2872. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200297






 下载:
下载: