-
冠层高度是森林资源调查的重要指标,也是重要的测树因子之一,与树木长势、生长量、林分蓄积量计算等密切相关[1-2]。快速、准确估测树高对于森林资源监测,森林生物量计算具有重要意义。当前,对于树高的测定有传统地面测量和遥感数据估测2类,传统的地面测量调查依据测高仪对活立木进行树高测定,是森林资源调查中树高测量最常用的方法[3],但工作效率低,且受到人为因素、仪器质量等影响,测量精度有一定的误差[4]。现阶段出现的森林树高遥感测定技术,如干涉合成孔径雷达估算技术、机载小光斑激光雷达数据结合光数码影像技术以及利用激光雷达数据点云数据提取树高[5-7]等,能够克服外界环境因素对树高估测的影响,但存在成本相对高,在大比例尺下测定地物仍有较大误差的缺陷。随着民用无人机的兴起,无人机遥感技术也得到了发展。无人机遥感影像具有分辨率高、重叠度大、信息量大等特点,并且小型民用无人机使用成本低、操作便捷、采集周期灵活等特点在很大程度上弥补了现有遥感估测树高的不足[8-13]。基于无人机平台搭载不同传感器,能够获取多光谱、高光谱、激光点云等多种类型的高精度数据,为遥感技术在森林资源调查和动态监测中的应用提供了新的发展思路[14-17],也将推动小型无人机在林业方面的普及应用[18]。杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata是中国重要的速生树种和用材树种,在森林资源中占有重要的地位[19-20]。快速、可靠地获取杉木的树高对于森林生物量的计算具有重要意义。为此,本研究选择福建省闽清县白云山国有林场的杉木林为对象,利用无人机多光谱影像数据,开展杉木人工林冠层高度遥感估测,以期为无人机在森林资源的调查应用提供理论借鉴和参考。
HTML
-
福建省闽清县白云山国有林场(26°24′06.42″~26°28′44.10″N,118°49′11.53″ ~118°55′46.19″E),海拔为800~1 200 m,坡度为26~35°。林场气候温和偏凉,年平均气温为19.5 ℃,雨水充沛,年均降水量约为1 800.0 mm,湿度大,适宜营造杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata,马尾松Pinus massoniana,湿地松Pinus elliottii,秃杉Taiwania flousiana,柳杉Cyptomeria fortunei等用材树种。该林场经营总面积为3 858.3 hm2,森林覆盖率为85.3%,林木蓄积量为58万m3,其中生态公益林面积为2 316.1 hm2,占林场经营面积60.0%。在白云山林场3个以杉木为主要树种的人工林小班(004林班-25大班-040,050,070小班,分别简称为A小班,B小班,C小班)开展无人机遥感树高估测研究,3块小班总面积约11 hm2,优势树种为杉木,西部林分密度较东部小,坡度约为25°,东、东南坡向,高程西高东低。
-
2018年1月16日,利用Eco Drone-UA无人机搭载的多光谱镜头[蓝(380~500 nm),绿(500~600 nm),红(600~760 nm),红边(红光范围680~760 nm内反射光谱的一阶导数最大值所对应的光谱位置)和近红外(760~860 nm)等5个光谱波段]获取遥感影像,利用地面控制站软件Mission Planner设置飞行相对航高为120 m,航带重叠度50%以及航程、航时、飞行航线等一系列参数。
-
随机选取研究区内的60株树,利用激光测高仪(型号TruPulse200)测量树高,作为杉木实测高度;利用手持全球定位系统(GPS)采集研究区高程数据。地面数据还包括白云山林场二类调查小班数据、地形图、林场概况等其他辅助资料。
1.1. 研究区概况
1.2. 无人机遥感数据获取
1.3. 地面数据获取
-
无人机影像获取过程中,受像素高、数量大以及气流扰动等因素影响,影像会产生几何畸变[7, 21],需进行信息检测、拼接及几何校正等预处理。预处理分为3个阶段。一是利用人工手段初步检验,剔除无关影像数据。二是将筛选好的原始影像导入Pix4D Mapper软件进行检测,完成覆盖研究区的影像拼接;为满足制作高精度数字表面模型(DSM)影像精度要求,本次处理使用原始数据影像2 078张,各影像的校准率为99%,重叠度为50%,初始焦距与最终焦距的相对差为1.69%,地理定位均方根误差X为1.26%,Y为0.71%,Z为1.33%,同时基于无人机获取的多幅正射照片生成研究区数字正射影像(DOM)[21]。三是利用空中三角测量,自动计算、识别同名地物点,求得像方坐标,得到研究区DSM影像[22],实现遥感影像校正。
-
冠层高度数据提取关键在于树冠顶点的识别。首先利用无人机遥感影像的纹理特征和光谱信息,面向对象分类筛选样木,通过遥感图像处理平台(ENVI)将数字正射影像信息分为森林、道路、林隙3类,得到研究区实际森林覆盖区域。其次基于块统计分析原理(即统计生成的值会赋予指定邻域的最小外接矩形中的所有像元,各邻域间无重叠),根据研究对象的树冠特征,将邻域设置为圆形,利用地图单位结合DOM目视判定半径,反复试验后,确定邻域半径为1.5 m。据指定的半径值计算出准确的圆面积,再计算出另外2个圆面积值,一个是指定半径值向下舍入后的圆面积,另一个是指定半径值向上舍入后的圆面积。这2个面积分别与用指定半径计算出的准确面积值进行比较,两者中更为接近准确值的一个将被用于运算过程中(图 1)。最后利用DSM块统计后新的影像与原始DSM影像相减,结合邻域分析块统计原理,搜索目标区中的最大值,并认定为潜在树顶点(图 2);对于判定混合的点,选取归一化植被指数(NDVI),比值植被指数(SR),增强植被指数(EVI),大气阻抗植被指数(ARVI)等植被指数,以及红、绿、蓝、红边、近红外5个波段进行树冠顶点识别,采用随机森林算法对冠顶点特征差异识别的指标重要性进行排序,获取实际树冠顶点作为提取冠层的基础数据。
-
用DSM表示研究区林分树冠表面的海拔变化,用DEM表示立木基部的海拔高度变化,两者相减即为数字冠层高度模型(CHM)[23],可作为杉木树高基础数据(图 3)。构建CHM模型,以研究区1:10 000地形图(图 4)为基础,在地理信息系统软件(GIS)上生成不规则三角网(TIN),利用TIN的转栅格功能,重采样生成与DSM像元大小一致的DEM影像,即像元0.15 m[24-26];DSM模型的实现则基于DOM影像利用计算机相邻影像匹配,量测每个像素的视差,利用空中三角测量,自动计算、识别同名地物点,求得其像方坐标,经解算获得物方空间坐标DSM[27-29],然后将DSM影像进行配准和裁剪,生成覆盖研究区的DSM影像。
2.1. 数据预处理
2.2. 无人机遥感杉木树高提取
2.2.1. 单木树冠顶点识别
2.2.2. 杉木树高的判定
-
基于邻域分析得到的潜在树冠顶点,结合无人机获取的DOM影像,通过目视抽样的方法检测随机森林算法的训练集,再利用不同指数在训练集的树冠顶点识别中重要性进行排序,得到归一化植被指数(NDVI)>比值植被指数(SR)>大气阻抗植被指数(ARVI)>近红外波段(NIR)>蓝色波段(BLUE)>增强植被指数(EVI)>红色波段(RED)>绿色波段(GREEN)>红边波段(REDEDGE)(图 5)。选择重要性较大的NDVI,SR,ARVI和NIR作为树冠顶点识别指标,叠加随机森林算法识别的树顶点分类结果,剔除伪树冠顶点(图 6),得到真实树冠顶点(图 7)。试验共得到潜在树顶点6 629个,其中伪树冠顶点1 483个,真树冠顶点5 146个;C小班的潜在树冠顶点和伪树冠顶点数量均最多,分别为3 549个和977个,A小班最少,分别为984个和101个,基本实现潜在树顶点的准确分类。结合研究区概况可知,A小班海拔高程较高,林分密度较小,C小班总体海拔高程低,而林分密度较大;由此推测,真实树冠顶点识别的效果可能与林分密度和海拔高程有关。
-
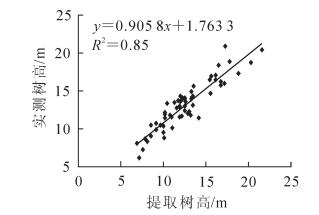
基于无人机遥感影像判定杉木的真实树冠顶点及样地的DEM信息,提取随机选取的60株杉木冠层高度信息,并将高度信息与实测的杉木高度进行比较分析,显著性值小于0.000 01,表明提取树高与实测树高显著相关,树高相关性分析具有统计学意义。以无人机遥感影像提取数据为自变量,外业实测数据为因变量,建立线性函数关系(图 8);相关性分析得到决定系数R2为0.85,提取树高与实测树高的相对误差最小值为0.81%,最大值为23.48%,计算得到标准误差(RMSE)为1.48 m,树高估测精度为90.8%。由此可知:提取效果较佳,利用无人机高分辨率影像实现树高估测的方法具有可行性。
-
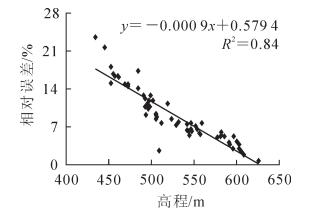
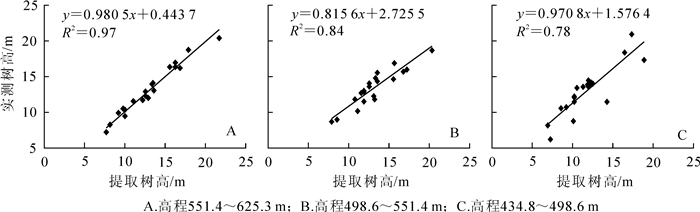
对60株样木树高实测值和提取值的相对误差与对应的DEM值作相关性分析,得到R2为0.84;树高相对误差随着高程的变化而变化(图 9),两者具有显著相关性。基于60株样木的不同高度信息,将其按高程划分为A组(551.4~625.2 m),B组(498.6~551.4 m)和C组(434.8~498.6 m)3组,20株·组-1,研究不同高程对杉木树高无人机估测的影响。通过计算不同高程的树高标准误差和决定系数发现,高程对树高提取有影响,3组树高值的误差分别为0.67,1.17和1.99 m;表现为随着高程的降低树高估测的标准误差明显增大。对3组树高的测量值与真实值进行拟合(图 10),其决定系数分别为0.97,0.84和0.78;表明在相同影像空间分辨率下,高程较高的杉木由于距离无人机较近,提取精度更高,山坳或者山谷的杉木则不容易分辨。对采集到的影像进行分析发现,高程较低的区域林分密度较大,伪树冠顶点总体增多,这些因素也是提取杉木树高时精度存在较大差异的原因。
3.1. 树冠顶点的识别
3.2. 冠层高度估测结果分析
3.3. 高程对冠层高度提取的影响
-
以杉木人工林为对象,利用无人机获取遥感影像,通过随机森林算法结合DSM多光谱波段和植被指数识别真实树冠顶点,叠加DSM数据和地面DEM数据差值来构建CHM模型,实现杉木树高提取。结果表明:①树冠顶点识别的过程存在非树冠顶点错分现象;利用随机森林算法结合植被指数和DSM多光谱波段可剔除错分的树冠顶点,同时可避免点云分割算法在提取树冠顶点中的繁琐运算,提高了树冠顶点提取效率及精度。C小班的伪树冠顶点数量最多,A小班最少,各小班伪树冠顶点均为山坳处多,高程较低处多;分析原因是C小班的高程较低,地势较为平坦,人工林的森林密度大,树冠顶点识别错误的可能性增加;A小班的高程较高,不利于杉木人工林生长,造成森林密度较小,因而伪树冠顶点误分的概率减小;山坳和高程较低处距离无人机较远,影像易产生形变,树冠顶点识别偏差。②点云数据生成DEM时,常因遮挡无法获取完整的地面信息,精度误差大[30]。本研究基于冠层高度模型等于数字表明模型与数字高程模型之差的估测思路,以根据地形图生成的DEM作为树高提取的基础数据之一,很大程度上改善了DEM对树高提取所带来的影响;结合无人机获取的DSM,有效实现杉木树高的提取。提取树高值与实测树高值的偏差[31],更多归因于同一像元值的平均化,并非树冠顶点真实值的反映,因而树高估测中低值高估,高值低估的现象仍然存在;同时由于树冠的遮挡,无人机搭载的多光谱镜头无法获取林冠层以下的影像数据,只能将林分的最高点当作林木的树高,是估测值存在一定误差的另一原因。本试验中提取树高的决定系数R2为0.85,精度为90.8%,在总体上满足林业对于树高估测的精度要求[32]。③高程与估测树高的相对误差分析结果表明,高程与树高相对误差具有显著相关性,其决定系数为0.84;不同高程下树高的提取值与实测值存在相关性,A组(625.2~551.4 m),B组(551.4~498.6 m),C组(498.6~434.8 m)的决定系数分别是0.97,0.84和0.78,标准误差分别是0.67,1.17和1.99 m。由此可知,高程变化对树高提取精度有影响,高程越高相对误差越小,其原因是高程对无人机获取样木影像的完整度和森林密度有影响。以上分析可以看出,DEM在南方丘陵山区数据应用上存在一定局限,因此将来可以使用与实际地形相似度更高的DEM数据进行树高估测;DSM精度也是影响树高提取精度的要素之一,改进DSM提取方法对提高树高的提取精度具有重要意义。
基于无人机获取的高分辨率遥感影像,经过模型构建、空间分析、技能算法识别等一系列处理,实现树高遥感估测,能够为高精度林木树高估测提供有效途径,表明高精度无人机遥感系统在林业调查中具有可行性,能够快捷、有效且准确地获取森林特征参数数据。



















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: