-
农业生产中大量施用化肥,人为地增加了土壤的含盐量,使园艺作物受到盐害,导致产量、品质下降。因此,可通过改良土壤,或者提高植物耐盐性来解决产品质量下降的问题。盐胁迫可以引发植物体内盐分的过度积累,导致植物产生离子毒害、膜系统氧化损伤、渗透调节失衡,轻者影响花卉的品质,重者直接导致植株死亡[1]。月季Rosa chinensis不仅是中国的传统名花,也是重要的切花材料,具有极高的市场价值[2]。但在月季栽培过程中,盐胁迫往往会降低月季开花期、开花量,降低花香、花色等品质,导致月季不具有经济价值。褪黑素(melatonin, MT)属于吲哚杂环类化合物,其化学名是N-乙酰基-5甲氧基色胺,具有清除活性氧、自由基,维护细胞膜结构,降低过氧化物含量的功能[3]。最近研究表明:外源褪黑素处理可以有效减轻盐胁迫对平邑甜茶Malus hupehensis的氧化胁迫伤害,增强苹果Malus domestica砧木的抗盐能力[4];同时外源褪黑素处理也可以提高番茄Solanum lycopersicum盐分胁迫下的果实品质[5]和缓解盐分对猕猴桃Actinidia chinensis幼苗的伤害[6];对切花月季保鲜也具有积极的作用[7]。但到目前为止,关于外源褪黑素处理对月季盐胁迫下生理特性还缺乏深入研究。本研究以中国古老月季‘月月粉’Rosa chinensis ‘Old Blush’为材料,采用根灌褪黑素的方法,分析测定盐胁迫下月季幼苗叶片生理指标的变化,探讨褪黑素影响月季苗盐胁迫响应的生理机制,为合理利用褪黑素,解决月季栽培中的盐害问题提供理论依据。
-
以中国古老月季‘月月粉’90 d扦插苗为材料,栽培基质为V(泥炭)∶V(椰壳)∶V(珍珠岩)=1∶1∶1,置于人工气候箱培养,光照时间为 16 h光照/8 h黑暗,培养温度为(23±2) ℃。研究共分5组,其中3组分别连续5 d在8:00对根部浇灌50 mL浓度分别为0、5、10和20 μmol·L−1的褪黑素溶液,其余2组以清水为对照。在最后1次浇灌褪黑素溶液后的第2天开始盐胁迫处理。任选1组浇灌清水的植株作为空白对照(ck),即继续浇灌清水,其余4组植株均每隔5 d浇灌50 mL浓度分别为200 mmol·L−1的氯化钠,连续浇灌20 d。5个处理分别为清水(ck)、200 mmol·L−1氯化钠(T)、5 μmol·L−1褪黑素+200 mmol·L−1氯化钠(S1)、10 μmol·L−1褪黑素+200 mmol·L−1氯化钠(S2)和20 μmol·L−1褪黑素+200 mmol·L−1氯化钠(S3),各处理6盆,重复3次。
-
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性采用氮蓝四唑(NBT)法测定,过氧化物酶(POD)活性采用愈创木酚法测定,过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性采用紫外吸收法测定,丙二醛(MDA)质量摩尔浓度采用硫代巴比妥酸法测定,可溶性蛋白质采用BCA法测定,抗坏血酸采用分光光度计法测定[8],相对电导率采用DDB-303A型电导率仪测定。
-
采用SAS软件进行方差分析(one-way ANOVA),采用Duncan法进行多重比较分析(P<0.05)。
-
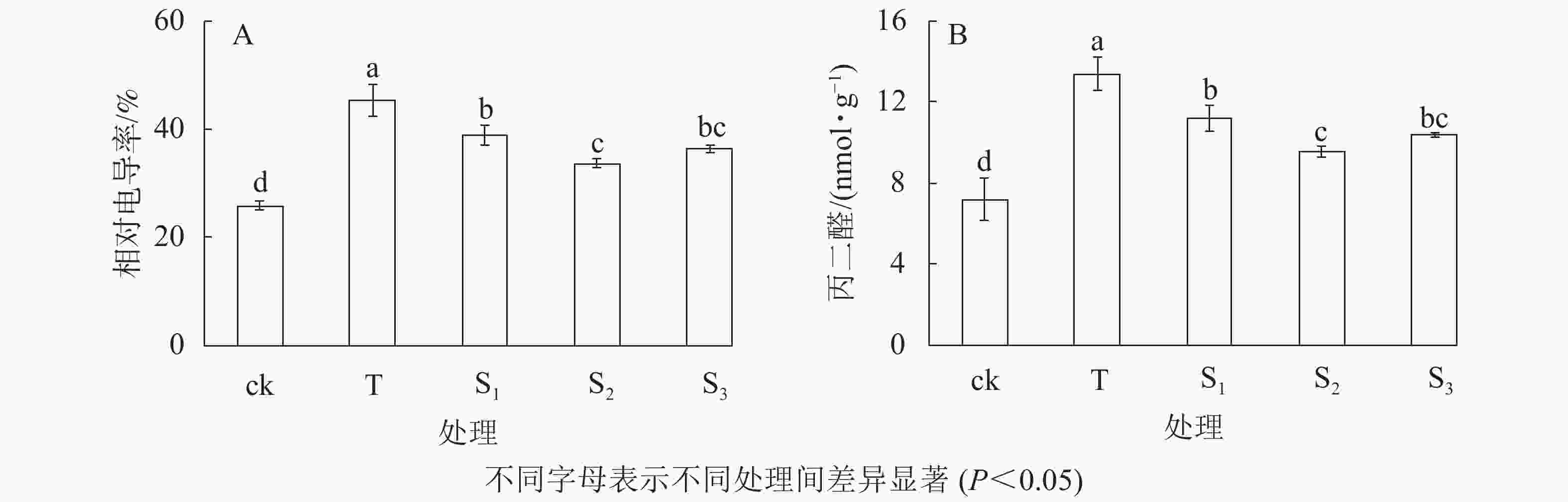
相对电导率是衡量植物细胞膜通透性的一个重要指标。由图1A可知:在盐胁迫下,月季苗叶片的相对电导率显著升高,其中200 mmol·L−1氯化钠(T)处理的相对电导率最高,达45.34%;不同浓度外源褪黑素处理下,月季叶片的相对电导率显著低于T处理(P<0.05),特别是10 μmol·L−1褪黑素(S2)处理下,相对电导率最低,为33.58%(图1A)。表明外源褪黑素处理可以显著抑制盐胁迫条件下月季苗叶片相对电导率的升高,保护细胞膜的完整性,其中10 μmol·L−1褪黑素处理抑制效果最明显。丙二醛质量摩尔浓度作为脂质过氧化指标,表示细胞膜脂质过氧化程度和植物对逆境反应的强弱,细胞受损越严重,其含量越高。由图1B可知:在盐胁迫下,月季苗叶片的丙二醛(MDA)质量摩尔浓度显著升高,其中T处理最高(P<0.05),为13.37 nmol·g−1;然而不同浓度外源褪黑素处理下,月季苗叶片的MDA质量摩尔浓度显著低于T处理(P<0.05),特别是10 μmol·L−1褪黑素(S2)处理下,MDA质量摩尔浓度最低,为9.50 nmol·g−1。表明褪黑素处理可有效抑制盐胁迫下月季叶片丙二醛质量摩尔浓度的增加,从而缓解膜脂质的过氧化。
-
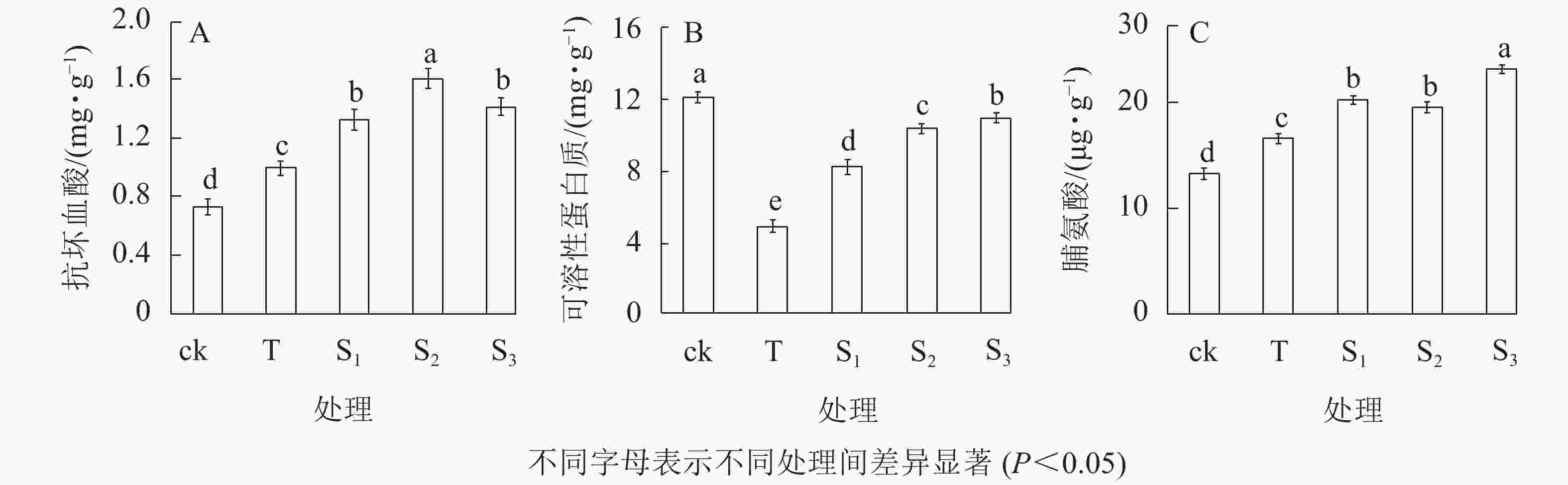
抗坏血酸(AsA)是植物体内重要的非酶促抗氧化剂,在清除植物体内活性氧和缓解膜脂过氧化对细胞的损伤方面具有积极的作用。由图2A可知:在盐胁迫下月季苗叶片AsA质量分数显著增加,为0.99 mg·g−1;不同浓度外源褪黑素处理下,其AsA质量分数均显著高于ck和T处理(P<0.05),特别是10 μmol·L−1褪黑素(S2)处理下,其AsA质量分数为1.60 mg·g−1。表明外源褪黑素处理能显著增加月季苗盐胁迫过程中的AsA质量分数,从而提高植株的抗盐胁迫能力。盐胁迫下月季苗叶片中可溶性蛋白质质量分数显著低于ck(P<0.05),其中T处理的可溶性蛋白质最低,为4.57 mg·g−1(图2B);而外源褪黑素处理,可以显著减少月季苗叶片可溶性蛋白质质量分数的降低,特别是20 μmol·L−1褪黑素处理下,可溶性蛋白质质量分数为10.33 mg·g−1。盐胁迫下,随褪黑素浓度的增加,月季苗叶片脯氨酸质量分数逐渐增加。当褪黑素浓度为20 μmol·L−1时,其质量分数最高为23.20 μg·g−1(图2C)。表明外源褪黑素处理可以显著增加盐胁迫下月季叶片中抗坏血酸、可溶性蛋白质和脯氨酸的质量分数。
-
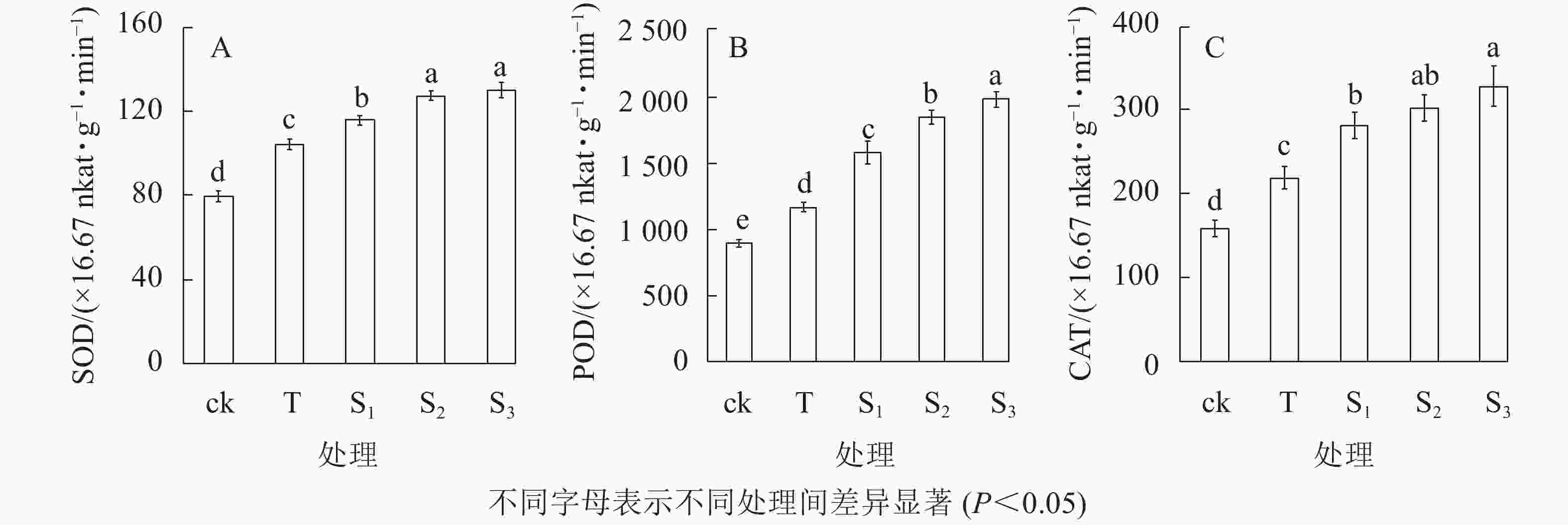
抗氧化酶系统作为植物逆境条件下重要的防御体系,可有效清除细胞中的活性氧,从而维持植株正常的生理活动。由图3可知:盐胁迫下月季叶片中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性均增强,而外源褪黑素处理可以使抗氧化酶的活性显著高于ck和T处理。盐胁迫下,SOD活性显著高于ck;当外源褪黑素浓度增加时,SOD活性呈上升趋势,S3处理的活性显著高于S1、T和ck处理(P<0.05),但是S3与S2处理之间没有显著差异(图3A)。盐处理下,POD的活性显著高于ck和T处理;当外源褪黑素浓度增加时,其活性逐渐增加;S3处理的活性是T处理的1.7倍;S1和S2处理的POD活性显著高于ck和T处理(P<0.05)(图3B)。此外,盐胁迫可以显著增加CAT的活性,S3处理的活性显著高于ck、T和S1处理(P<0.05),与S2处理没有显著差异(图3C)。表明外源褪黑素处理可以增强月季盐胁下的抗氧化酶活性,从而减少活性氧的积累,缓解盐胁迫下细胞的氧化伤害,维持细胞的完整性。
-
盐胁迫是影响植物生长发育的重要外界因素之一[9]。近年来,褪黑素作为生理调节剂,对缓解植物在干旱、高温、低温、重金属等逆境下氧化胁迫伤害具有积极作用[10−12]。本研究表明:外源褪黑素预处理可有效降低盐胁迫下月季苗叶片丙二醛质量摩尔浓度,增加抗坏血酸、脯氨酸和可溶性蛋白质质量分数,增强抗氧化酶(SOD、POD、CAT)的活性,从而缓解月季苗的盐分胁迫伤害。
正常植物细胞内的钠离子、钾离子与钙离子处于平衡状态,从而使细胞保持完整性和通透性[13]。而一旦植物遭受盐分胁迫,通常会使细胞内钠离子浓度增加,打破离子平衡,迫使改变细胞的膜透性[14]。此外,盐胁迫会诱导植物细胞积累大量的活性氧(ROS),导致膜脂发生过氧化,产生MDA,破坏膜的通透性[15]。本研究通过外源褪黑素处理,可以显著抑制盐胁迫条件下月季叶片MDA的积累(P<0.05),保护细胞膜的通透性。其作用机理可能是褪黑素作为一种信号分子,参与活性氧的清除,防止膜脂发生过氧化。
脯氨酸和可溶性蛋白质是植物体内的重要渗透调节物质,在抵制活性氧的细胞伤害中具有积极的作用[16]。植物体内的脯氨酸可以增强细胞原生质的亲水性,提高植物组织细胞的持水性,防止植物细胞脱水,保护细胞质膜的完整性。张娜等[17]研究发现:在盐胁迫条件下外源褪黑素处理狼尾草Pennisetum alopecuroides种子,其发芽势和发芽率显著高于单独盐胁迫处理,且脯氨酸显著增加,因此盐胁迫所造成的渗透伤害显著降低。可溶性蛋白质的增加和积累能提高植物细胞的保水能力,对细胞的生命物质及生物膜起到保护作用[18]。本研究表明:在盐胁迫条件下月季幼苗叶片中可溶性蛋白质质量分数降低,而外源褪黑素处理可以使叶片中可溶性蛋白质质量分数显著增加(P<0.05),这可能是因为褪黑素作为一种信号物质参与可溶性蛋白质的合成。
抗坏血酸作为植物体内重要的的抗氧化剂,在胁迫条件下能够抑制活性氧的形成和积累,缓解植物的胁迫伤害[19]。本研究表明:褪黑素处理可以显著提高盐胁迫下月季幼苗叶片抗坏血酸质量分数(P<0.05)。可能原因是外源褪黑素处理诱导抗坏血酸的合成,增加抗坏血酸质量分数,而抗坏血酸的增加可以提高月季清除活性氧的能力,避免脂质过氧化。综上所述,盐胁迫下外源褪黑素处理可以提高月季叶片抗坏血酸质量分数,增强月季耐盐性,缓解盐胁迫的伤害。
植物在逆境条件下,会积累大量活性氧(ROS),从而导致细胞膜脂过氧化,对生物膜的结构和功能造成损伤。SOD、POD和CAT是植物体内重要的抗氧化酶,它们可以清除细胞内ROS,减少ROS的积累,防止脂质过氧化[20]。高帆等[21]发现:外源褪黑素处理可以增强盐胁迫下美味猕猴桃Aclinidia deliciosa苗抗氧化酶的活性,从而缓解盐胁迫伤害。本研究表明:外源褪黑素处理可以显著增加盐胁迫下月季叶片SOD、POD和CAT的活性(P<0.05),从而增强月季清除ROS的能力,缓解月季盐分胁迫伤害。可能因为外源褪黑素处理诱导激活抗氧化酶系统,使SOD、POD和CAT的活性大大增强,提高了月季的耐盐性。
Alleviation of exogenous melatonin on rose seedlings under salt stress
-
摘要:
目的 研究外源褪黑素(MT)处理对盐胁迫下中国古老月季‘月月粉’ Rosa chinensis ‘Old Blush’的缓解效应及其机制,为解决月季栽培中的盐害问题提供理论依据。 方法 以90 d扦插苗为材料,分别通过根部浇灌0、5、10和20 μmol·L−1褪黑素进行预处理5 d后,再对根部浇灌200 mmol·L−1氯化钠溶液进行盐胁迫处理20 d,以浇灌清水的植株为空白对照,研究了外源褪黑素处理对月季盐胁迫的缓解效应。 结果 与空白对照相比,不同浓度外源褪黑素处理可显著降低盐胁迫下月季叶片的相对电导率和丙二醛质量摩尔浓度(P<0.05),同时可显著提高可溶性蛋白质、抗坏血酸和脯氨酸的质量分数(P<0.05),特别是显著提高了超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)的活性,从而增强了活性氧的清除能力。 结论 外源褪黑素处理可增强月季‘月月粉’的抗氧化酶活性以及渗透调节物质的质量分数,从而抑制活性氧的积累,防止膜脂过氧化,提高耐盐性。图3参21 Abstract:Objective To provide a theoretical basis for solving salt damage of rose, the effect of exogenous melatonin (MT) on the physiological characteristics of rose seedlings (Rosa chinensis ‘Old Blush’) with the NaCl stress was investigated. Method 90 d rose cutting seedlings were watered with 0, 5, 10 and 20 μmol·L−1 melatonin of exogenous melatonin solution respectively for 5 days before they were treated with 20 d 200 mmol·L−1 NaCl while the control group was treated with water to study the alleviation of exogenous melatonin on rose seedlings under salt stress with the physiological and biochemical indexes determined after the salt treatment. Result With the exposure to salt stress, rose seedlings with the alleviation of exogenous melatonin of different concentrations present a significant decrease in electrical conductivity and mass molar concentration of malondialdehyde(P<0.05) while a significant increase in the content of soluble protein, proline and ascorbic acid (P<0.05). In particular, the activity of superoxide dismutase(SOD), catalase(CAT) and peroxidase(POD)(P<0.05)has been significantly promoted, which helps enhance the scavenging activity of reactive oxygen species(ROS) under salt stress. Conclusion The exogenous melatonin treatment could enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes and increase the osmotic substance content to avoid lipid peroxidation and improve rose salt tolerant ability. [Ch, 3 fig. 21 ref.] -
Key words:
- plant physiology /
- Rosa chinensis ‘Old Blush’ /
- melatonin /
- salt stress /
- alleviation
-
-
[1] YAO Yuxin, DONG Qinglong, ZHAI Heng, et al. The functions of an apple cytosolic malate dehydrogenase gene in growth and tolerance to cold and salt stresses [J]. Plant Physiol Biochem, 2011, 49(3): 257 − 264. [2] YAN Huijun, SHI Shaochuan, MA Nan, et al. Graft-accelerated virus-induced gene silencing facilitates functional genomics in rose flowers [J]. J Integrative Plant Biol, 2018, 60(1): 34 − 44. [3] 王伟香, 张锐敏, 孙艳, 等. 外源褪黑素对硝酸盐胁迫条件下黄瓜幼苗抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(4): 695 − 703. WANG Weixiang, ZHANG Ruimin, SUN Yan, et al. Effect of exogenous melatonin on the antioxidant system of cucumber seedlings under nitrate stress [J]. Acta Hortic Sin, 2016, 43(4): 695 − 703. [4] LI Chao, WANG Ping, WEI Zhiwei, et al. The mitigation effects of exogenous melatonin on salinity-induced stress in Malus hupehensis [J]. J Pineal Res, 2012, 53(3): 298 − 306. [5] 杜天浩, 周小婷, 朱兰英, 等. 褪黑素处理对盐胁迫下番茄果实品质及挥发性物质的影响[J]. 食品科学, 2016, 37(15): 69 − 76. DU Tianhao, ZHOU Xiaoting, ZHU Lanying, et al. Effect of melatonin treatment on tomato fruit quality and volatile compounds under salt stress [J]. Food Sci, 2016, 37(15): 69 − 76. [6] 倪知游, 夏惠, 高帆, 等. 外源褪黑素对猕猴桃幼苗盐胁迫的缓解作用[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2017, 35(4): 535 − 539. NI Zhiyou, XIA Hui, GAO Fan, et al. Alleviation of exogenous melatonin on kiwifruit seedlings under salt stress [J]. J Sichuan Agric Univ, 2017, 35(4): 535 − 539. [7] 罗彤彤, 庞天虹, 马骥, 等. 褪黑素对切花月季“卡罗拉”保鲜效应的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2018, 35(5): 981 − 986. LUO Tongtong, PANG Tianhong, MA Ji, et al. Melatonin for cut flower preservation with Rosa hybrida ‘Corolla’ [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2018, 35(5): 981 − 986. [8] 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. [9] 靳娟, 鲁晓燕, 王依. 果树耐盐性研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(9): 1761 − 1776. JIN Juan, LU Xiaoyan, WANG Yi. Advances in the studies on salt tolerance of fruit trees [J]. Acta Hortic Sin, 2014, 41(9): 1761 − 1776. [10] 徐向东, 孙艳, 郭晓芹, 等. 高温胁迫下外源褪黑素对黄瓜幼苗抗坏血酸代谢系统的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(10): 2580 − 2586. XU Xiangdong, SUN Yan, GUO Xiaoqin, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on ascorbate metabolism system in cucumber seedlings under high temperature stress [J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2010, 21(10): 2580 − 2586. [11] 张娜, 张海军, 杨荣超, 等. 褪黑素在植物中的功能研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(9): 16 − 20. ZHANG Na, ZHANG Haijun, YANG Rongchao, et al. Research progress on the function of melatonin in plants [J]. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2012, 28(9): 16 − 20. [12] WANG Ping, SUN Xun, LI Chao, et al. Long-term exogenous application of melatonin delays drought-induced leaf senescence in apple [J]. J Pineal Res, 2013, 54(3): 292 − 302. [13] 李娜, 陈红, 裴孝伯. 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下黄瓜幼苗耐盐性的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 2013, 34(7): 1359 − 1364. LI Na, CHEN Hong, PEI Xiaobo. Effects of extraneous spermidine on the salt tolerance in cucumber seedlings under salt stress [J]. Chin J Trop Crops, 2013, 34(7): 1359 − 1364. [14] 韩志平, 郭世荣, 尤秀娜, 等. 盐胁迫对西瓜幼苗活性氧代谢和渗透调节物质含量的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2010, 30(11): 2210 − 2218. HAN Zhiping, GUO Shirong, YOU Xiuna, et al. Metabolism of reactive oxygen species and contents of osmotic substances in watermelon seedlings [J]. Acta Bot Boreali-Occident Sin, 2010, 30(11): 2210 − 2218. [15] 陈莎莎, 兰海燕. 植物对盐胁迫响应的信号转导途径[J]. 植物生理学报, 2011, 47(2): 119 − 128. CHEN Shasha, LAN Haiyan. Signal transduction pathways in response to salt stress in plants [J]. Plant Physiol J, 2011, 47(2): 119 − 128. [16] HU Yonghua, Chen C M, XU Lian, et al. Postharvest application of 4-methoxy cinnamic acid for extending the shelf life of mushroom(Agaricus bisporus) [J]. Postharvest Biol Technol, 2015, 104: 33 − 41. [17] 张娜, 蒋庆, 李殿波, 等. 外源施加褪黑素对NaCl胁迫下狼尾草种子萌发及相关生理指标的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2014, 19(4): 54 − 60. ZHANG Na, JIANG Qing, LI Dianbo, et al. Effect of exogenous melatonin on germination of Pennisetum alopecuroides under NaCl stress [J]. J China Agric Univ, 2014, 19(4): 54 − 60. [18] SUN Qianqian, ZHANG Na, WANG Jinfang, et al. Melatonin promotes ripening and improves quality of tomato fruit during postharvest life [J]. J Exp Bot, 2015, 66(3): 657 − 668. [19] 徐芳, 周海鹏, 郭早霞, 等. 植物褪黑素及其抗逆性研究[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2013, 32(2): 260 − 266. XU Fang, ZHOU Haipeng, GUO Zaoxia, et al. The melatonin and its resistance to stress in plants [J]. Genomics Appl Biol, 2013, 32(2): 260 − 266. [20] 罗青红, 寇云玲, 史彦江, 等. 6种杂交榛对新疆盐碱土的生理适应性研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(9): 1867 − 1873. LUO Qinghong, KOU Yunling, SHI Yanjiang, et al. Physiological characteristics of adaptability of six hybrid hazelnuts to saline-alkali land in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Bot Boreali-Occident Sin, 2013, 33(9): 1867 − 1873. [21] 高帆, 谢玥, 沈妍秋, 等. 外源褪黑素对氯化钠胁迫下美味猕猴桃实生苗抗氧化物酶和渗透调节物质的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2018, 35(2): 291 − 297. GAO Fan, XIE Yue, SHEN Yanqiu, et al. Exogenous melatonin for NaCl stress with antioxidant enzymes and osmotic substances of Aclinidia deliciosa seedlings [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2018, 35(2): 291 − 297. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190604






 下载:
下载: