-
受市场经济背景下供需关系的影响,农作物尤其是农业经济作物的产量与价格波动之间存在着紧密联系。如何及时准确地掌握农作物的面积、产量是地方政府农业主管部门进行种植业结构调整[1]和价格宏观调控的重要依据。遥感技术具有高效、快速、动态、宏观和实施成本低等优点,目前已广泛应用于农业经济作物的面积调查[2-3]、产量估算[4-5]以及长势监测[6]等方面。农业遥感已经成为传统农业向信息化农业过渡的主要支撑技术之一[7]。与粮食、蔬菜等农作物相比,中草药具有产地区域性较强、经济价值较高、且市场需求量弹性较弱等特点,如果政府相关部门不加以引导,很容易造成与市场供求失衡相伴随的价格大幅度波动,从而对药农的经济利益和生产生活造成很大影响。这就要求相关部门须掌握时效性强且准确的产量数据。三七Panax notoginseng为五加科Araliaceae人参属Panax植物[8],为中国名贵中药材,云南文山三七因其优质和独特的道地性而著称于世,具有较高的经济价值。周应群等[9]采用5 m分辨率的SPOT 5影像和30 m分辨率的TM 5影像相配合,采用目视解译的方法分别对三七种植面积较大的文山州马关县和丘北县的三七种植面积进行提取并与相关部门的实际统计数据相对比,最终发现5 m分辨率的SPOT 5影像提取成果相对面积精度为92.7%,而30 m分辨率的TM 5影像提取成果相对面积精度为74.4%,取得了相对理想的效果。上述方法主要是在高分辨率商业影像目视解译的三七资源遥感调查,需要大量的人力和资金,成本较高,因此无法保证每年都进行1次完整的三七种植资源调查。戴晨曦等[10]基于Landsat TM/ETM+ /OLI数据,结合数字高程模型(digital elevation model,DEM)和归一化植被指数(normalized difference vegetation index,NDVI)等提出了一种基于遥感影像自动提取三七种植面积的方法,并利用该方法对云南文山、红河两州2010-2015年三七种植面积进行监测,验证了该方法的可靠性。2013年4月26日发射成功的高分1号(GF-1)卫星是中国高分辨率对地观测系统的首发星,它突破了高空间分辨率、多光谱与高时间分辨率结合的光学遥感技术[1]。目前该卫星获取的影像已被广泛应用于森林蓄积量估测[11-12]、精准农业[13-14]、国土资源调查和环境监测等方面。基于GF-1数据进行三七种植资源的调查,目前仅有少量学者做过探索:史婷婷等[15]通过对研究区内各地物的光谱特征进行分析构建了基于GF-1数据估算文山三七种植面积的决策树模型,然而并没有对该模型的提取精度进行计算和验证。本研究对史婷婷等[15]提出的决策树模型进行改进,然后基于16 m分辨率的GF-1影像对文山州4个三七主产县的三七种植面积进行提取,并通过与同时段的高分辨率谷歌影像进行抽样监测的方法对该方法的识别精度进行评价;最后以同区域内目视解译提取的三七图斑为基准,对该决策树模型的面积提取精度进行计算。
-
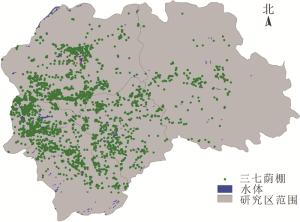
云南省文山壮族苗族自治州(22°40′~24°28′N,103°35′~106°12′E)位于云贵高原东南部,为典型的高原山地区域,北回归线贯穿全州。文山州干湿季分明,5-10月为雨季,雨量占全年的82%,11月至次年4月为干季。独特的土壤和气候条件使这里成为全国最主要的三七产区,三七种植面积和产量均占全国的90%以上。1995年文山州被命名为“中国三七之乡”[16]。文山州三七主产地主要集中在丘北、广南、砚山和文山等4个县地势相对平坦的盆地和河谷区域。本研究选取该4个县作为主要研究区域。
-
文山州的11月至次年4月为旱季,为保证影像的能见效果,结合文山州的天气和三七的耕作时段规律,本研究选取了2016年2月13日、4月15日和5月1日的3景16 m分辨率的GF-1开源数据作为基础数据。此外,还获取了覆盖该区域的6景30 m分辨率DEM数据作为辅助数据。
-
三七属于喜阴植物,光照强度对三七的生长有较大影响,人工栽培的三七一般都要架设荫棚。因此,基于遥感影像进行三七种植面积的提取主要是提取出三七荫棚的图斑。崔秀明等[17]研究发现:当荫棚的透光率为12%时,三七的单位产量达到峰值。目前大部分三七荫棚都以透光力更易于控制的黑色塑料遮阳网代替传统的枯枝棚(图 1)[18]。
-
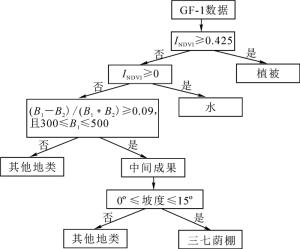
史婷婷等[15]构建了基于GF-1影像进行三七种植区提取的决策树分类模型。依据三七的生长区域一般为5°~15°的缓坡地带[14]的特点,本研究对此分类决策树模型进行改进(图 2)。在构建决策树过程中,基于预处理后的DEM构建坡度值,坡度值用变量“Slope”表示,然后通过执行决策树分类提取出三七的荫棚图斑。针对该决策树模型所完成的分类成果如图 3所示。
-
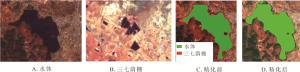
根据GF-1影像上三七荫棚和其他地物的图像机理特征的对比,可以观察到部分区域水体和三七荫棚在目视效果上可分离度不高(图 4A和图 4B)。且在三七荫棚的决策树分类成果中有部分水体的边缘区域被错分为三七荫棚(图 4C)。为剔除分类成果中被错分的部分,对分类结果进行基于GIS空间分析的精化处理。经过统计得出决策树分析提取的三七荫棚图斑中水体边缘被误判的区域平均约1.5个像元,最大约3.0个像元(约48 m),且一般而言在水域周围50 m范围内很少有三七种植区。因此,数据处理中在GIS平台上针对提取的水体图斑构建50 m缓冲区,并将缓冲区图斑与决策树分类提取的三七荫棚图斑进行叠置分析,用以剔除水体边缘被误分的区域,进而实现对提取成果的精化处理。精化前后成果对比如图 4C和图 4D所示。
-
对决策树分类所提取的三七荫棚成果进行精度验证主要包括2项内容:①三七荫棚地类识别精度验证;②专家决策树分类的三七荫棚面积提取精度验证。对决策树分类提取成果的精度验证主要是以三七荫棚的目视解译成果为基准的,在目视解译过程中对于目标判定困难的地物,进一步采用了谷歌地球(Google Earth)提供的同时段2.18 m分辨率的影像作为参考进行解译(图 5)。
-
采用专家决策树分类方法提取并经过精化处理的成果和采用目视解译方法在研究区域内勾绘的三七荫棚的图斑成果如图 6所示,研究区内各县三七荫棚图斑的提取成果统计如表 1所示。根据本研究2.18 m分辨率的同时段Google影像对三七荫棚提取成果的判定精度进行验证。具体方案为:分别在在研究区内对精化后三七荫棚的专家决策树分类成果和目视解译成果各均匀选取100组图斑作为检验样本,并与同时段的Google影像中相对应位置的图像进行对比,用以对三七荫棚判定的正确性进行检验。判定成果精度的统计如表 2所示。
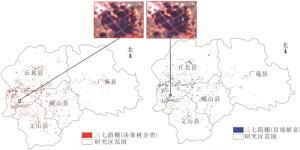
图 6 决策树分类法(A)和目视解译法(B)提取三七荫棚的成果示意图
Figure 6. Decision tree classification (A) and Visual interpretation (B) of the extracted results
表 1 实验区各县荫棚图斑提取面积精度统计
Table 1. Accuracy of statistical experimentation area shade extraction counties
区域 专家决策树分类 目视解译 重合面积So/km2 面积精度P/% 图斑数 面积/km2 图斑数 面积/km2 丘北县 1 037 23.36 993 20.05 16.32 81.4 文山县 672 11.54 611 9.05 7.09 78.3 砚山县 1 102 29.00 1 077 26.42 21.27 80.5 广南县 374 6.21 261 6.59 5.03 76.3 总计 3 185 70.11 2 942 62.11 49.71 80.0 表 2 三七荫棚地类识别精度评价
Table 2. P. notoginseng of the land intensive evaluation shed recognition
方法 检验样本数 判定正确数 判定正确率/% 决策树分类 100 87 87 目视解译 100 99 99 如表 2所示:利用决策树分析法和目视解译法对三七荫棚进行地类识别,判定正确率分布可达到87%和99%。通过总结,决策树分类法判定错误的原因一方面是由于混合像元的影响产生的,尤其是细小的荫棚斑块所形成的像元产生影响较大;另一方面是由于新旧荫棚之间的光谱特征存在差异而导致误判。目视解译法产生误判的原因主要是部分水体像元和山体阴影产生的像元与三七荫棚像元在目视判别时难以区分。
-
郭燕等[1]利用GF-1影像提取玉米Zea mays种植面积,并将提取的图斑与实测的实地面积进行对比,最终得出影像上面积的准确率达91.8%,验证了基于GF-1影像提取农作物面积的方法是可靠的。同理,为验证GF-1影像上三七荫棚面积的准确性,以相关部门在三七种植资源抽查中获取的部分实地调绘数据为基准,分别在三七种植较为集中的丘北和砚山两县各选择10块三七荫棚作为样本,在GIS平台上分别对相应地块的实地调绘图斑和GF-1影像上的目视解译图斑进行叠置分析,并统计其面积重合率。经统计,二者的平均面积重合率为丘北县85.4%,砚山县89.2%。可得出GF-1影像与实地的三七荫棚面积符合度较高,将GF-1影像用于提取三七荫棚面积的方法是可行的。因此,针对专家决策树分类提取三七荫棚的面积精度评价,本研究采用专家决策树分类提取的荫棚成果与目视解译的荫棚成果进行叠加分析,然后对两类成果的重叠部分面积进行统计。专家决策树分类提取的面积精度按下式进行计算。
$$ P=\frac{S_{\rm o}}{S_{\rm V}}。 $$ (1) 式(1)中:P为专家决策树分类提取成果的面积精度;So为2类成果重合的面积;SV为目视解译提取的三七荫棚面积。实验区内各县专家决策树分类提取的三七荫棚面积精度统计如表 1所示。通过对研究区域4个县的专家决策树分类和目视解译提取的荫棚图斑数和面积进行统计,并根据式(1)对各产区专家决策树分类提取的面积精度进行计算得出:专家决策树分类和目视解译提取的图斑数总计分别为3 185和2 942个;提取的荫棚面积总计分别为70.11 km2和62.11 m2;专家决策树分类提取的平均面积精度为80%;4个主产县的荫棚图斑面积提取精度都能达76%以上。
-
本研究基于16 m分辨率的GF-1开源影像对云南文山州4个三七主产县的三七的种植面积进行提取。在遥感提取方法上,主要考虑三七生长区域自然条件对文献[15]所构建的决策树模型进行改进,并在对决策树分类成果进行观察、分析和统计的基础上对分类成果进行精化处理。最后采用谷歌影像、实地调绘和目视解译数据相配合的方式分别对提取成果的图斑识别精度和面积提取精度进行验证。结果表明:本研究所提出的基于专家决策树和分类精化处理提取三七种植面积的方法是可行的,三七荫棚图斑识别精度可达87%,面积提取的平均识别精度可达80%。
综上所述,基于国产高分系列数据开展三七种植面积快速调查的方法虽然从技术层面而言已经日趋成熟,然而三七荫棚面积的提取精度仍有待提高,一方面是由于三七种植区域气候和其他地物信息的影响,另一方面是由于不同年份铺设的新旧三七荫棚存在一定光谱差异,这为决策树分类阈值的确定带来一定难度。因此,下一步的研究可以聚焦于2个方面:①结合地面采集数据对新旧三七荫棚和三七生长环境内的各类地物进行更有针对性和更精细化的光谱特征分析;②结合地面实测数据和光谱特征分析构建精度更高的三七种植信息分类提取模型。
GF-1 remote sensing data for Panax notoginseng planting information extraction in Wenshan, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
目的 云南文山三七Panax notoginseng作为经济价值较高的中草药,其产量多少与价格波动之间存在着较紧密的联系,实时准确地掌握三七种植面积,对于当地政府相关管理部门科学指导三七种植规模和确定价格等宏观调控具有重要意义。 方法 以文山州4个三七主产县为研究区域,基于国产16 m分辨率的高分1号(GF-1)开源影像,根据三七的生长环境特点对专家决策树模型进行改进,并通过决策树分类法提取三七的荫棚图斑。在对三七荫棚识别可靠度和面积提取精度评价中,采用了谷歌影像代替实地调绘和以目视解译结果作为图斑面积基准的方法。 结果 决策树分类成果和目视解译提取的图斑判定正确率分别为87%和99%;专家决策树分类提取的成果整体面积精度为80%。 结论 与传统基于高分辨率商业影像采用目视解译的人工勾绘图斑方法相比,基于GF-1影像的三七面积提取所采用的方法能够在保证一定精度的条件下,以较快速度开展文山三七种植资源的调查,为当地特色农产品种植的科学监管与价值估算提供基础数据与有效技术支持。 Abstract:Objective Panax notoginseng, a kind of Chinese herbal medicine with high economic value and a close relationship to price fluctuation, could be very meaningful for a government's agricultural management departments to scientifically guide its planting scale and determine the price of macro controls. The aim is to obtain P. notoginseng planting information in real time and accurately. Method Four counties which mainly produce P. notoginseng in Wenshan Prefecture were taken as the research area. According to the characteristics of P. notoginseng growth, environment construction expert decision tree, the decision tree classification method to extract P. notoginseng shade patches and a method of refining processing on classification results through GIS spatial analysis, was used. Based on these, the area of P. notoginseng from the Gaofen-1 (GF-1) remote sensing images with 16 m resolution was extracted, and the extracted results were refined. Then, Google image was used, instead of field mapping, as a method to verify the area and classification accuracy of the image in order to obtain the accuracy and reliability of identification and evaluation of the Shade shed area for P. notoginseng. Result The accuracy of decision tree classification method is 87%, and that of visual interpretation method is 99%. The area accuracy of decision tree classification can reach 80%. Conclusion Compared with the traditional method of using high-resolution commercial images and artificial drawing spots, this method of extracting the P. notoginseng area could quickly determine P. notoginseng planting resources with higher accuracy, thereby providing basic data and effective technical methods for scientific supervision and value estimation of locally cultivated agricultural products. -
Key words:
- forest mensuration /
- information extraction of planting /
- GF-1 /
- decision tree /
- precision analysis /
- Panax notoginseng
-
表 1 实验区各县荫棚图斑提取面积精度统计
Table 1. Accuracy of statistical experimentation area shade extraction counties
区域 专家决策树分类 目视解译 重合面积So/km2 面积精度P/% 图斑数 面积/km2 图斑数 面积/km2 丘北县 1 037 23.36 993 20.05 16.32 81.4 文山县 672 11.54 611 9.05 7.09 78.3 砚山县 1 102 29.00 1 077 26.42 21.27 80.5 广南县 374 6.21 261 6.59 5.03 76.3 总计 3 185 70.11 2 942 62.11 49.71 80.0 表 2 三七荫棚地类识别精度评价
Table 2. P. notoginseng of the land intensive evaluation shed recognition
方法 检验样本数 判定正确数 判定正确率/% 决策树分类 100 87 87 目视解译 100 99 99 -
[1] 郭燕, 吴喜红, 程永政, 等.用高分一号数据提取玉米面积及精度分析[J].遥感信息, 2015, 30(6):31 - 36. GUO Yan, WU Xihong, CHENG Yongzheng, et al. Maize recognition and accuracy evaluation based on high resolution remote sensing (GF-1) data[J]. Remote Sensing Inf, 2015, 30(6): 31 - 36. [2] 权文婷, 王钊.冬小麦种植面积遥感提取方法研究[J].国土资源遥感, 2013, 25(4):8 - 15. QUAN Wenting, WANG Zhao. Researches on the extraction of winter wheat planting area using remote sensing method[J]. Remote Sensing Land Resour, 2013, 25(4): 8 - 15. [3] MURTHY C S, RAJU P V, BADRINATH K V S. Classification of wheat crop with multi-temporal images: performance of maximum likelihood and artificial neural networks[J]. Int J Remote Sensing, 2003, 24(23): 4871 - 4890. [4] 张健康, 程彦培, 张发旺, 等.基于多时相遥感影像的作物种植信息提取[J].农业工程学报, 2012, 28(2):134 - 141. ZHANG Jiankang, CHENG Yanpei, ZHANG Fawang, et al. Crops planting information extraction based on multi-temporal remote sensing images[J]. Trans CSAE, 2012, 28(2): 134 - 141. [5] QUARMBY N A, TOWNSHEND J R G, SETTLE J J, et al. Linear mixture modelling applied to AVHRR data for crop area estimation[J]. Int J Remote Sensing, 1992, 13(3): 415 - 425. [6] 黄青, 唐华俊, 周清波, 等.东北地区主要作物种植结构遥感提取及长势监测[J].农业工程学报, 2010, 26(9):218 - 223. HUANG Qing, TANG Huajun, ZHOU Qingbo, et al. Remote-sensing based monitoring of planting structure and growth condition of major crops in Northeast China[J]. Trans CSAE, 2010, 26(9): 218 - 223. [7] 李根, 景元书, 王琳, 等.基于MODIS时序植被指数和线性光谱混合模型的水稻面积提取[J].大气科学学报, 2014, 37(1):119 - 126. LI Gen, JING Yuanshu, WANG Lin, et al. Extraction of paddy planting areas based on MODIS vegetation index time series and linear spectral mixture model[J]. Trans Atmos Sci, 2014, 37(1): 119 - 126. [8] 崔秀明, 雷绍武.三七规范化种植技术[M].昆明:云南科技出版社, 2015. [9] 周应群, 陈士林, 张本刚, 等.基于遥感技术的三七资源调查方法研究[J].中国中药杂志, 2005, 30(24):1902 - 1905. ZHOU Yingqun, CHEN Shilin, ZHANG Bengang, et al. Studies on the resources survey methods of Panax notogingseng based on remote sensing[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2005, 30(24): 1902 - 1905. [10] 戴晨曦, 谢相建, 徐志刚, 等.中草药材种植遥感监测与分析:以云南省文山和红河地区三七种植为例[J].国土资源遥感, 2018, 30(1):210 - 216. DAI Chenxi, XIE Xiangjian, XU Zhigang, et al. Monitoring and analyzing herbal medicine plantation via remote sensing: a case study of pseudo-ginseng in Wenshan and Honghe Prefecture of Yunnan Province[J]. Remote Sensing Land Resour, 2018, 30(1): 210 - 216. [11] 王海宾, 彭道黎, 高秀会, 等.基于GF-1 PMS影像和k-NN方法的延庆区森林蓄积量估测[J].浙江农林大学学报, 2018, 35(6):1070 - 1078. WANG Haibin, PENG Daoli, GAO Xiuhui, et al. Forest stock volume estimates in Yanqing District based on GF-1 PMS images and k-NN method[J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2018, 35(6): 1070 - 1078. [12] 向安民, 刘凤伶, 于宝义, 等.基于k-NN方法和GF遥感影像的森林蓄积量估测[J].浙江农林大学学报, 2017, 34(3):406 - 412. XIANG Anming, LIU Fengling, YU Baoyi, et al. Forest stock volume estimation based on the k-NN method and GF remote sensing data[J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2017, 34(3): 406 - 412. [13] SONG Qian, ZHOU Qingbo, WU Wenbin, et al. Mapping regional cropping patterns by using GF-1 WFV sensor data[J]. J Integrative Agric, 2017, 16(2): 337 - 347. [14] ZHOU Qingbo, YU Qiangyi, LIU Jia, et al. Perspective of Chinese GF-1 high-resolution satellite data in agricultural remote sensing monitoring[J]. J Integrative Agric, 2017, 16(2): 242 - 251. [15] 史婷婷, 张小波, 郭兰萍, 等.基于决策树模型的文山三七种植面积估算方法研究[J].中国中药杂志, 2017, 42(22):4358 - 4361. SHI Tingting, ZHANG Xiaobo, GUO Lanping. et al. Study on extraction method of Panax notoginseng plots in Wenshan of Yunnan Province based on decision tree model[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2017, 42(22): 4358 - 4361. [16] 崔秀明, 王朝梁, 贺承福, 等.三七荫棚透光度初步研究[J].中药材, 1993, 16(3):3 - 6. CUI Xiuming, WANG Chaoliang, HE Chengfu, et al. Preliminary study indicates the transmittance of Panax notoginseng[J]. Chin Herbal Med, 1993, 16(3): 3 - 6. [17] 崔秀明, 王朝梁, 陈中坚, 等.三七GAP栽培的环境质量评价[J].中草药, 2002, 33(1):77 - 79. CUI Xiuming, WANG Chaoliang, CHEN Zhongjian, et al. Estimate of environmental condition on GAP culture of Panax notoginseng[J]. Chin Tradit Herbal Drug, 2002, 33(1): 77 - 79. [18] 金航, 崔秀明, 朱艳, 等.气象条件对三七药材道地性的影响[J].西南农业学报, 2005, 18(6):825 - 828. JIN Hang, CUI Xiuming, ZHU Yan, et al. Effects of meteorological conditions on the quality of radix Notoginseng[J]. Southwest China J Agric Sci, 2005, 18(6): 825 - 828. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2020.01.017







 下载:
下载: