-
紫葳科Bignoniaceae梓属Catalpa落叶乔木楸树Catalpa bungei是中国重要的乡土树种,广泛分布于长江流域和黄河流域,生长速度快,木材品质优良,具有很强的适应性[1-2]。楸树自花不育,实生苗繁殖困难,营养繁殖中嫁接苗根系质量差,易出现风折、病虫等危害,扦插育苗是当前楸树快速繁殖的重要方法[3]。研究发现:插穗内营养物质在扦插生根过程中起着关键性的作用[4]。对橄榄Canarium album[5]、油茶Camellia oleifera[6]等的研究发现:生根能力大小与插穗内的可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白质密切相关,如油茶中易生根的‘Arbequina’品种可溶性糖含量高于较难生根的‘Kalamata’品种,杂种落叶松Larix olgensis × L. kaempferi插穗的可溶性蛋白质与根原基的发生、分化有关[7]。插穗内碳氮比(C/N)越高,插穗生根率也越高[8]。酶活性对植物不定根的产生和生长有间接或者直接影响。仿栗Sloanea hemsleyana扦插试验中,插穗在愈伤组织形成期及不定根形成期,超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性都呈明显上升趋势,促进了仿栗插穗的生根[9]。过氧化物酶(POD)、多酚氧化酶(PPO)等也在扦插过程中呈现规律性的曲线波动[10]。对于较难生根的树种,插穗中存在生根抑制物质。季孔庶等[11]通过对插穗物质浸提、萃取后的高效液相色谱分离,认为插穗内的黄酮类物质和苯酚类物质可能是导致马尾松Pinus massoniana扦插生根率低的原因之一。而核桃楸Juglans mandshurica插穗内大多数抑制物质是酸性物质,如单宁及酚类等[12]。目前,楸树扦插育苗中存在较多问题,扦插生根困难,成活率、保苗率低,许多楸树品种(系)生根时间长(30~45 d),易腐烂,生根率仅为20%~40%[13]。本研究选择楸树良种‘8611’,研究它在插穗生根过程中根系发生特点及插穗内生理生化指标的变化规律,筛选与生根相关指标,探索楸树生根困难的制约因素,为建立楸树扦插育苗繁殖技术体系提供理论依据。
-
楸树良种‘8611’插穗采自南京林业大学白马教学科研基地楸树资源圃。参照相关材料,以V(泥炭)∶V(珍珠岩)=1∶1[14]混合均匀后装入32孔育苗穴盘(6.0 cm×6.0 cm×11.0 cm),并用质量分数0.5%的高锰酸钾消毒。扦插池配置自动间歇喷雾装置,上方设遮阳网。
插穗直径为0.2~0.5 cm,长度为5.0~7.0 cm,每穗至少带2个芽;留叶1~2片,每片叶保留1/3大小。根据前期研究结果[15],插穗用1 000 mg·kg−1 ABT生根粉1号(GGR-6)(北京艾比蒂研究开发中心生产)浸泡,设3个区组,各区组500个插穗,以蒸馏水浸泡为对照。用于各指标观察及测定。
试验于2018年6月中旬开始,边采边插。为减少高温天气下插穗腐烂,提高嫩枝扦插的成活率,扦插后立刻间歇喷雾,外覆小拱棚,控制温度为25~30 ℃[16-17]。生根前保持扦插池内相对湿度80%~90%,生根后保持相对湿度60%~70%,每隔1周喷施1次多菌灵。待地上部抽生新叶后,及时清除杂草,适时灌溉。
-
扦插后3 d取样1次,每次取10个插穗。采样后清洗干净,统计穗条生根过程各阶段(大量愈伤组织形成期、不定根发生期、不定根大量形成期)出现时间,拍照留存;生根后统计生根率。
扦插后5 d取样1次,每次取15个插穗。将插穗的韧皮部与木质部分离,取基部(下切口以上)2.0~3.0 cm韧皮部,之后将15个样品混匀,用于测定不同生根阶段的生理生化指标。采用蒽酮比色法测定可溶性糖质量分数[18];采用考马斯亮蓝法测定可溶性蛋白质质量分数[19];采用硫酸-高氯酸消煮法测定总氮质量分数[20]。采用氯化硝基氮蓝四唑法测定SOD活性[21];采用愈创木酚比色法测定POD活性[22];采用焦儿茶酚比色法测定PPO活性[23]。各指标测定均重复3次。采用气相色谱质谱联用仪(GC-MS)测定内源抑制物质。
分别于大量愈伤组织形成期、不定根发生期、不定根大量形成期随机取3个GGR-6处理的插穗,取基部(下切口往上2.0 cm)韧皮部,称取2 g,液氮充分磨碎后,加入体积分数为99.6%甲醇密闭浸提24 h;浸提液以8 000 r·min−1离心30 min,取上清液;旋转蒸发仪上浓缩蒸馏,并定容至5 mL,备用。
选用30.00 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm的Rtx-5MS毛细管柱,流速1 mL·min−1氦气进行气相色谱检测。色谱条件为:进样口温度为250 ℃,分流比为20∶1。升温程序为:35 ℃保持3 min,以6 ℃·min−1升至300 ℃后保持10 min。离子源的温度为220 ℃,接口温度为260 ℃,溶剂切除时间3 min,离子扫描(m/z)范围45~500,进样量为1 μL。由计算机控制库存信息检查质谱图并与标准图库谱图核对。
-
使用SPSS 20.0软件对数据进行统计并作方差分析。
-
不同处理对楸树插穗的生根进程具有较大的影响。根据楸树‘8611’扦插的前期研究,其生根进程可分为大量愈伤组织出现期、不定根发生期、不定根大量形成期等3个阶段[15]。由表1可知:不同处理条件下,3个阶段出现的时间存在差异。GGR-6处理的插穗,扦插后约8 d形成大量愈伤组织,从形成大量愈伤组织到不定根的形成约需7 d,从不定根开始形成到不定根大量形成约需要8 d。对照在扦插约2周后出现大量的愈伤组织,从形成大量愈伤组织到不定根发生约需7 d,从出现不定根到不定根大量形成需13 d。说明GGR-6处理可促进楸树生根,缩短了不定根出现到大量形成的时间。与对照相比,GGR-6处理使插穗愈伤组织形成提前(P<0.05),插穗生根率极显著提高(P<0.01)。
表 1 不同处理对插穗生根进程的影响
Table 1. Rooting morphology of cuttings with different treatments
大量愈伤组织出现/d 不定根发生/d 不定根大量形成/d 生根率/% GGR-6 8.34 ± 1.94 b 15.43 ± 0.51 a 23.20 ± 1.02 a 82.04 ± 0.71 a 对照 14.24 ± 0.16 a 21.93 ± 1.64 a 34.54 ± 0.63 a 66.21 ± 3.57 b F 8.550 0.077 13.727 20.675 P 0.018 0.926 0.307 <0.001 说明:F表示组间和组内的离差平方和与自由度的比值,同列不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05) -
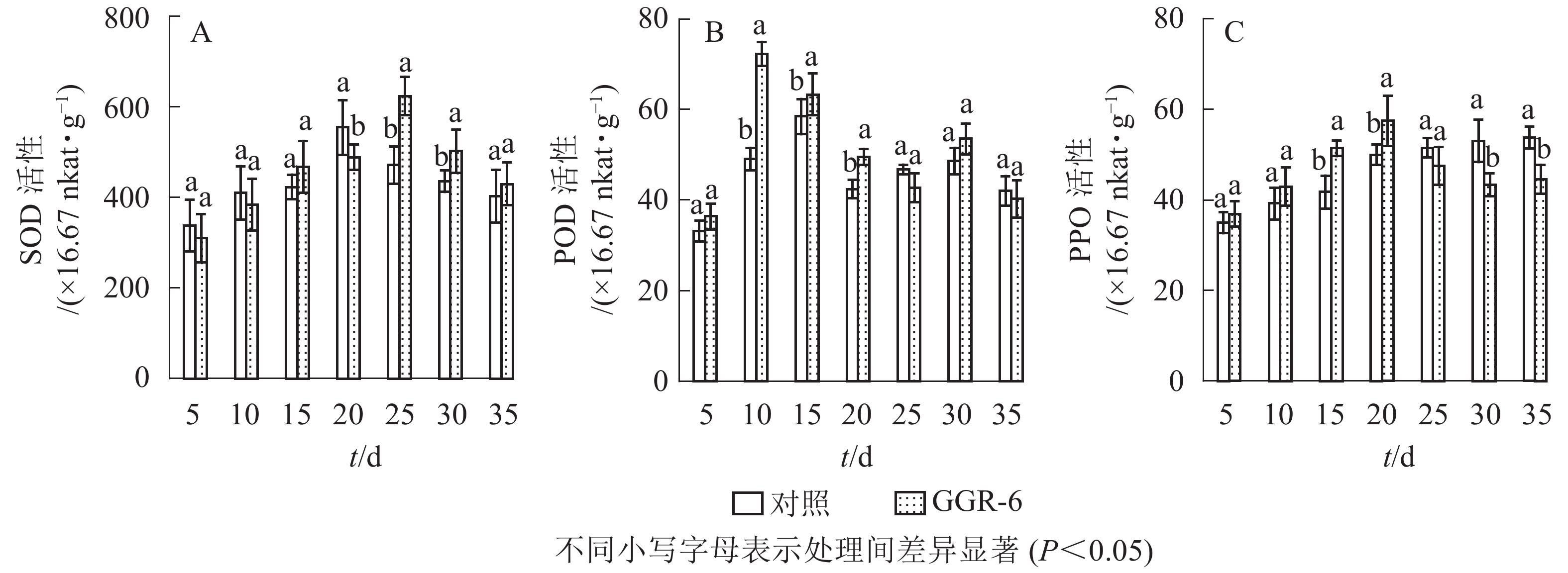
SOD可催化超氧化物阴离子自由基发生歧化反应,是生物体抗氧化系统的第1道防线。由图1A可知:SOD活性随着扦插时间的延长,先增大后减小,与对照相比,GGR-6处理的插穗在扦插后25 d时SOD活性出现最大值(623.33×16.67 nkat·g−1),两者差异显著(P<0.05)。结合生根过程的观察,25 d是插穗不定根大量形成期;说明SOD增加有利于楸树插穗快速生根。
-
POD与插穗生根有着密切的联系,对植物的细胞发育起着重要的作用。由图1B可知:扦插后POD活性呈先增加再下降后趋于平稳的趋势。GGR-6处理的插穗,扦插后5~10 d,POD活性显著增加,10 d达最大值(72.30×16.67 nkat·g−1),之后显著下降,至25 d时降到42.75×16.67 nkat·g−1,接近扦插后5 d的水平,之后又略上升。与对照相比,整个扦插过程中,GGR-6处理的插穗POD活性均高于对照,且在扦插后10 d达到显著差异(P<0.05)。扦插后10 d是插穗大量愈伤组织产生时期,说明POD活性与愈伤组织形成有关。
-
PPO是具有催化作用的酚类物质,和吲哚乙酸(IAA)生成“IAA-酚酸复合物”,可促进插穗不定根形成。由图1C可知:GGR-6处理后,插穗内PPO活性呈上升趋势,20 d时达到最大值(57.44×16.67 nkat·g−1);在5~20 d,GGR-6处理的插穗PPO活性高于对照组,且在15和20 d时达到显著差异(P<0.05)。此阶段是不定根大量形成阶段,推断PPO增加促进了插穗生根。
-
由表2可知:POD、PPO活性与插穗生根率都有很高的相关性,插穗生根率与PPO活性呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与POD活性呈显著正相关(P<0.05),但与SOD活性的相关性未达到显著水平(P>0.05)。
表 2 SOD、POD、PPO活性与生根率的相关性
Table 2. Correlation of SOD, POD, PPO activity and rooting rate
指标 生根率 SOD活性 POD活性 PPO活性 生根率 1 SOD活性 0.68 1 POD活性 0.87* 0.98** 1 PPO活性 0.93** 0.76 0.94** 1 说明:*和**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上显著相关 -
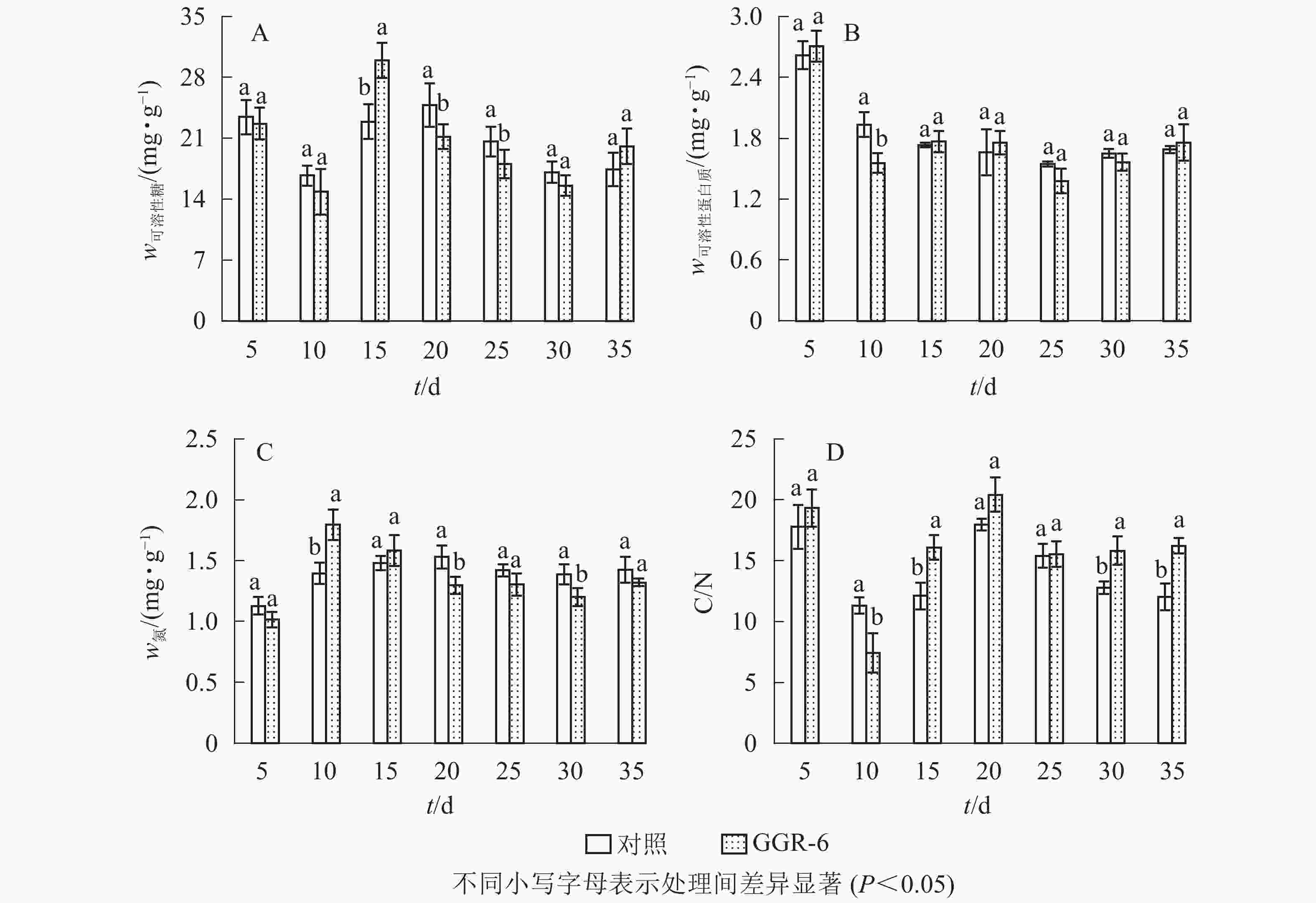
可溶性糖是植物体生命活动最直接的能量来源,为插穗不定根的形成提供所需的营养,有利于插穗的生根。由图2A可知:可溶性糖质量分数表现为快速下降再上升,之后又下降的特点,GGR-6处理与对照均在扦插10 d时降到最低值,此时为愈伤组织出现期,说明营养物质被大量消耗。GGR-6处理后插穗可溶性糖在扦插后15 d达到最大值(29.96 mg·g−1),且与对照达到显著差异(P<0.05),之后明显下降;说明可溶性糖是扦插阶段主要能量来源。扦插后35 d后可溶性糖质量分数略有升高,认为与此时根系形成、地上部分光合能力恢复有关。
-
可溶性蛋白质对插穗内细胞生长分化起调节作用,是插穗生长发育必需的营养物质。由图2B可知:扦插后5~10 d,GGR-6处理组可溶性蛋白质质量分数急剧减少,由最初的2.71 mg·g−1降为1.56 mg·g−1,降低了42%左右,与对照差异显著(P<0.05);15~20 d又小幅升高,但均低于初始值。对照插穗可溶性蛋白质也呈下降趋势,但其变化幅度小于GGR-6处理组。
-
由图2C可知:扦插5~10 d,GGR-6处理插穗总氮质量分数逐渐上升,扦插后10 d达到最大值(1.80 mg·g−1),之后明显降低;与对照相比,处理插穗扦插后10 d,总氮质量分数显著增加(P<0.05)。插穗内总氮质量分数在扦插过程中表现为下降趋势,GGR-6处理下降幅度大于对照,说明总氮快速消耗有利于不定根的形成。
-
C/N与插穗的生根率有关。由图2D可知:扦插后5~10 d,GGR-6处理插穗内C/N急剧下降,10 d时达到最小值(7.43),之后又快速上升,在扦插后20 d达到最大值(20.41)。对照也出现相似变化趋势,但上升的幅度小于GGR-6处理组。在10~15 d时处理与对照间差异显著(P<0.05)。生根前碳水化合物消耗多于氮,C/N明显下降,进入大量生根阶段(15~20 d),氮素消耗增加,C/N显著增加;反映在生根阶段,较高的C/N能促进根系的形成。
-
插穗内营养物质质量分数与插穗生根率之间有着紧密的联系,是插穗生根的必要条件之一。对各因素的相关性分析表明(表3):插穗生根率与可溶性蛋白质、可溶性糖、C/N均正相关,与总氮负相关。C/N与可溶性糖、总氮间也表现为显著相关。
表 3 营养物质质量分数与生根率的相关性
Table 3. Correlation of nutrient content and rooting rate
指标 生根率 w可溶性糖 w可溶性蛋白质 w总氮 C/N 生根率 1 w可溶性糖 0.82* 1 w可溶性蛋白质 0.96** 0.61 1 w总氮 −0.69 −0.44 −0.78 1 C/N 0.83* 0.94** 0.66 −0.81* 1 说明:*和**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上显著相关 -
生根不同阶段插穗的甲醇提取物经GC-MS鉴定分析,筛选出总离子流色谱中峰面积较大、质谱图与计算机检索谱库图吻合性较好的主要有机化合物。由表4可知:插穗扦插前期可明确鉴定出9种物质,其中峰面积较大、相似度较高的有6种,分别为棕榈酸(14.69%)、维生素E(12.07%)、亚油酸(11.05%)、邻苯二甲酸(10.87%)、6-叔丁基苯酚(9.43%)和槲皮素(8.37%),相对含量较高;其次是硬脂酸(6.48%)、乙酸十八脂(6.47%)和植物甾醇(3.28%),相对含量较低;其中维生素E、乙酸十八脂仅出现于扦插前期。愈伤组织形成期,亚油酸、硬脂酸、棕榈酸、槲皮素相对含量均明显下降,6-叔丁基苯酚、植物甾醇的相对含量增加;至扦插生根期,亚油酸、棕榈酸、槲皮素相对含量继续下降,植物甾醇的相对含量由愈伤组织时期的6.96%上升到35.22%,在整个生根的过程中呈现逐渐上升的趋势。新出现十六碳三烯酸甲酯、邻苯三酚、2-羟基苯乙酸等物质,而硬脂酸、6-叔丁基苯酚未检测到。
表 4 有机化合物种类及相对含量
Table 4. Types and relative contents of the organic compounds
阶段 邻苯二甲酸/% (9E,12E)-亚油酸/% 硬脂酸/% 乙酸十八脂/% 棕榈酸/% 6-叔丁基苯酚/% 槲皮素/% 植物甾醇/% 扦插前期 10.87 11.05 6.48 6.47 14.69 9.43 8.37 3.28 愈伤期 8.15 2.08 6.33 13.21 4.56 6.96 生根期 2.65 4.45 3.74 2.92 35.22 阶段 维生素E/% 十六碳三烯酸甲酯/% 硬脂腈/% 邻苯三酚/% 二十烷 2-羟基苯乙酸/% 未知/% 扦插前期 12.07 愈伤期 5.65 6.16 8.01 生根期 28.86 2.99 7.44 -
植物生长调节剂能够提高插穗生根率[23]。本研究中,GGR-6对楸树生根率有明显促进作用,插穗平均生根率达到82%以上,显著缩短了不定根的出现到大量形成的时间。
酶保护系统是植物在逆境条件下对有害物质消长变化的响应机制,对根原基和愈伤组织的形成起积极作用。有研究表明:植物生长调节剂浸泡可以提高插穗内SOD、POD活性,且最大值出现在不定根发生阶段[24]。本研究发现:楸树嫩枝扦插过程中,SOD、PPO的峰值均出现在不定根形成期,分别在扦插后第25天和第20天。扦插初期,SOD活性增强,抗逆性增加,保护了楸树扦插生根环境,促进了不定根的发生;扦插生根后,SOD活性下降,与新叶形成后光合作用恢复、自由基含量下降有关[9]。PPO通过与IAA互作合成大量生根辅助因子,促进了插穗生根[10]。POD活性在5~10 d显著增强,之后大幅下降。POD活性增加,可清除过氧化氢等物质,增强细胞壁强度和细胞发育,促进愈伤组织形成[25]。
充足的营养物质是插穗扦插生根的必要条件之一。赵爽等[26]发现:山木通Clematis finetiana生根过程中,可溶性糖质量分数在不定根诱导期下降,在根系表达期和生长后期回升;可溶性蛋白质质量分数在扦插后逐渐下降,至插穗大量生根期低至谷值。本研究发现:插穗生根率与可溶性糖质量分数、C/N显著正相关,与可溶性蛋白质极显著正相关。扦插10 d后愈伤组织大量形成,此时可溶性糖比扦插5 d时降低约30%,说明可溶性糖是植物体生命活动最直接的能量来源。整个生根阶段可溶性蛋白质质量分数均处于较低水平,反映它在提供插穗营养方面作用明显。但也有研究[27]发现:可溶性糖质量分数在侧柏Platycladus orientalis古树愈伤组织形成期有不同程度的升高,推测与树木年龄及树种遗传特性有关。本研究发现C/N最大值出现在扦插后20 d,认为前期消耗碳水化合物较氮素多,在进入大量生根期时,氮素的消耗增加,C/N也逐渐增加,与张应团[28]对紫玉兰Magnolia liliflora绿枝扦插研究结果一致。
有研究表明[29]:亚油酸、棕榈酸抑制细胞增值,类黄酮类物质槲皮素抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性,某些酚醇类物质(植物甾醇)可能是内源生长素的增效剂。魏树强[30]在对杂交鹅掌楸Liriodendron chinensis进行扦插繁殖时发现:其韧皮部浸出液抑制白菜Brassica pekinensis籽发芽生长,推测这些物质可能是杂交鹅掌楸扦插生根的抑制物质。王顺财[31]在研究楸树嫩枝扦插繁殖时发现:金丝楸Catalpa bungei韧皮部生根抑制物质较多。朱鹏等[32]利用气相色谱测定了扦插过程中酚类和醇类等物质的变化,发现这些物质质量浓度与抑制强度基本一致;认为扦插生根困难的树种,其插穗韧皮部中存在抑制生根的物质。本研究发现:楸树扦插过程中植物甾醇相对含量上升,槲皮素、亚油酸、棕榈酸的相对含量下降,推断植物甾醇为楸树生根促进物质,槲皮素、亚油酸、棕榈酸为生根抑制物质。
关于生根抑制物质的作用机制目前尚无定论,推测其主要作用包括2个方面:一是抑制物质削弱了生长素的促进作用,二是部分抑制物质如树脂和单宁类等,容易在切口表面堵塞,影响插穗的营养物质和水分的运输,从而降低了扦插生根率。本研究仅对GGR-6处理的样品进行检测,分离的化合物种类偏少,结合楸树扦插过程中根系形成进程,初步推测其在楸树生根过程中的功能。后期研究还需要改进样品提取方法,提高纯度,通过质谱检验分析及外源处理等,掌握相关物质在楸树扦插生根过程中的作用机制,为解决楸树扦插生根困难等问题提供更有效的理论依据。
Cutting test of Catalpa bungei and change analysis of cutting contents
-
摘要:
目的 探索楸树Catalpa bungei扦插生根机制,研究插穗生根过程的形态特征和生理生化特性。 方法 采用ABT生根粉1号(GGR-6)浸泡处理楸树插穗,以蒸馏水浸泡为对照,测定扦插生根不同阶段相关酶活性、营养物质及生根抑制物质的变化规律。 结果 GGR-6处理显著促进插穗生根,生根率达到82.04%,高于对照(P<0.01)。生根过程中,超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和多酚氧化酶(PPO)活性在大量愈伤组织形成期均上升;SOD、PPO最大值出现在不定根大量形成期,分别为623.33×16.67和57.44×16.67 nkat·g−1,POD在不定根大量形成期下降;3种酶均与生根率成显著正相关。插穗可溶性糖、碳氮比(C/N)在大量愈伤组织形成期急剧下降,仅为扦插初时的40%左右,扦插20 d时达到最大值。可溶性蛋白质、总氮质量分数总体呈下降趋势,25~30 d时为最小值;GGR-6处理下插穗内营养物质变化幅度大,且最大值均高于对照;总氮质量分数与生根率负相关(P<0.05),可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白质、C/N均与生根率显著正相关(P<0.05);气相色谱质谱联用仪(GC-MS)鉴定出4种与生根相关的物质,其中3种可能抑制生根,1种可能促进生根。 结论 插穗抗氧化酶活性的提高促进了楸树不定根的发生;可溶性糖与可溶性蛋白质是插穗生根的主要营养物质;初步推断槲皮素、亚油酸、棕榈酸抑制插穗生根,植物甾醇促进插穗生根。图2表4参32 Abstract:Objective The objective of this study is to explore the rooting mechanism of Catalpa bungei, as well as the morphological characteristics and physiological and biochemical characteristics of cuttings during rooting process. Method The cuttings of C. bungei were treated with dissolved GGR-6 to promote rooting, and the enzyme activities, nutrients and rooting inhibitors in different rooting stages were measured. Result GGR-6 treatment significantly promoted the rooting of cuttings, and the rooting rate reached 82.04%, higher than that of the control treatment (P<0.01). During the rooting process, the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD) and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) increased during the formation of a large number of callus, and the maximum values of SOD and PPO were 623.33×16.67 and 57.44×16.67 nkat·g−1, respectively. POD activity decreased during the formation of adventitious roots, and the three enzymes were positively correlated with the rooting rate. The soluble sugar and C/N ratio in cuttings decreased sharply at the callus stage, only about 40% of the initial value, and reached the maximum at 20 days of cutting. The soluble protein and total nitrogen showed a decreasing trend, and reached the minimum at 25−30 days. Under GGR-6 treatment, the change range of nutrients in cuttings was large, and the maximum values were higher than those of the control. Total nitrogen content was negatively correlated with rooting rate (P<0.05), while soluble sugar, soluble protein and C/N were significantly positively correlated with rooting rate (P<0.05). GC-MS analysis identified four rooting related substances, three of which might inhibit rooting and one might promote rooting. Conclusion The increase of antioxidant enzyme activities of cuttings can promote the occurrence of adventitious roots of C. bungei. Soluble sugar and soluble protein are the main nutrients of cuttings. Quercetin, linoleic acid and palmitic acid may inhibit the rooting of cuttings and phytosterol may promote the rooting of cuttings. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 32 ref.] -
Key words:
- Catalpa bungei /
- cuttings /
- enzymes /
- nutrients /
- rooting inhibitor
-
表 1 不同处理对插穗生根进程的影响
Table 1. Rooting morphology of cuttings with different treatments
大量愈伤组织出现/d 不定根发生/d 不定根大量形成/d 生根率/% GGR-6 8.34 ± 1.94 b 15.43 ± 0.51 a 23.20 ± 1.02 a 82.04 ± 0.71 a 对照 14.24 ± 0.16 a 21.93 ± 1.64 a 34.54 ± 0.63 a 66.21 ± 3.57 b F 8.550 0.077 13.727 20.675 P 0.018 0.926 0.307 <0.001 说明:F表示组间和组内的离差平方和与自由度的比值,同列不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05) 表 2 SOD、POD、PPO活性与生根率的相关性
Table 2. Correlation of SOD, POD, PPO activity and rooting rate
指标 生根率 SOD活性 POD活性 PPO活性 生根率 1 SOD活性 0.68 1 POD活性 0.87* 0.98** 1 PPO活性 0.93** 0.76 0.94** 1 说明:*和**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上显著相关 表 3 营养物质质量分数与生根率的相关性
Table 3. Correlation of nutrient content and rooting rate
指标 生根率 w可溶性糖 w可溶性蛋白质 w总氮 C/N 生根率 1 w可溶性糖 0.82* 1 w可溶性蛋白质 0.96** 0.61 1 w总氮 −0.69 −0.44 −0.78 1 C/N 0.83* 0.94** 0.66 −0.81* 1 说明:*和**分别表示在0.05和0.01水平上显著相关 表 4 有机化合物种类及相对含量
Table 4. Types and relative contents of the organic compounds
阶段 邻苯二甲酸/% (9E,12E)-亚油酸/% 硬脂酸/% 乙酸十八脂/% 棕榈酸/% 6-叔丁基苯酚/% 槲皮素/% 植物甾醇/% 扦插前期 10.87 11.05 6.48 6.47 14.69 9.43 8.37 3.28 愈伤期 8.15 2.08 6.33 13.21 4.56 6.96 生根期 2.65 4.45 3.74 2.92 35.22 阶段 维生素E/% 十六碳三烯酸甲酯/% 硬脂腈/% 邻苯三酚/% 二十烷 2-羟基苯乙酸/% 未知/% 扦插前期 12.07 愈伤期 5.65 6.16 8.01 生根期 28.86 2.99 7.44 -
[1] 郭从俭著. 楸树栽培[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1988. [2] 王改萍, 岑显超, 彭方仁, 等. 不同楸树品种的抗旱性鉴定[J]. 浙江林学院学报, 2009, 26(6): 815 − 821. WANG Gaiping, CEN Xianchao, PENG Fangren, et al. Drought resistance in seedlings of Catalpa bungei cultivars [J]. J Zhejiang For Coll, 2009, 26(6): 815 − 821. [3] 梁有旺, 杜旭华, 王顺才, 等. 楸树嫩枝扦插生根的主要影响因子分析[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2008, 17(4): 46 − 50. LIANG Youwang, DU Xuhua, WANG Shuncai, et al. Analysis of main influence factors on rooting of two cutting of Catalpa bungei [J]. J Plant Resour Environ, 2008, 17(4): 46 − 50. [4] DRUEGE U, KADNER R. Response of post-storage carbohydrate levels in pelargonium cuttings to reduced air temperature during rooting and the relationship with leaf senescence and adventitious root formation [J]. Postharvest Biol Technol, 2008, 47(1): 126 − 135. [5] KIM J W, KIM T S. Rooting promotion in cutting propagation of tea [J]. Korean J Med Crop Sci, 1995, 3(3): 195 − 199. [6] 王瑞, 陈永忠, 彭邵锋, 等. 油茶扦插生根过程的生理生化基础研究[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2013, 30(4): 615 − 619. WANG Rui, CHEN Yongzhong, PENG Shaofeng, et al. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of Camellia oleifera during root cutting establishment [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2013, 30(4): 615 − 619. [7] 刘桂丰, 庄振东, 由香铃, 等. 杂种落叶松扦插生根过程中可溶性蛋白的比较分析[J]. 植物研究, 2003, 23(2): 195 − 197. LIU Guifeng, ZHUANG Zhendong, YOU Xiangling, et al. The soluble protein analysis of hybrid larch during cutting rootings [J]. Bull Bot Res, 2003, 23(2): 195 − 197. [8] 郭素娟, 凌宏勤, 李凤兰. 白皮松插穗生根的生理生化基础研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2004, 26(2): 43 − 47. GUO Sujuan, LIN Hongqin, LI Fenglan. Physiological and biochemical basis of rooting of Pinus bungeana cuttings [J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2004, 26(2): 43 − 47. [9] 刘延青. 仿栗扦插繁殖技术及其生根机理的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2010. LIU Yanqing. Studies on the Cutting Propagation Technique and Rooting Mechanism of Sloanea hemsleyana [D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2010. [10] 付喜玲, 郭先锋, 康晓飞, 等. IBA 对芍药扦插生根的影响及生根过程中相关酶活性的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2009, 36(6): 849 − 854. FU Xiling, GUO Xianfeng, KANG Xiaofei, et al. Effects of IBA on stem cutting and activity of related enzymes during rooting of Paeonia lactiflora Pall [J]. Acta Hortic Sin, 2009, 36(6): 849 − 854. [11] 季孔庶, 王章荣, 陈天华, 等. 马尾松种源与内源生根抑制物的相关性[J]. 南京林业大学学报, 2002, 26(2): 24 − 28. JI Kongshu, WANG Zhangrong, CHEN Tianhua, et al. A study on variation of the endogenous inhibitors in Pinus massoniana cuttings [J]. J Nanjing For Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2002, 26(2): 24 − 28. [12] 徐程杨, 张忠辉, 李绍臣. 核桃揪枝条、插穗中生根抑制物质的含量[J]. 吉林林学院学报, 1998, 14(4): 212 − 215. XU Chengyang, ZHANG Zhonghui, LI Shaochen. Dynamic state of rooting inhibitor in branches and cuttings of Juglans mandshurica [J]. J Jilin For Univ, 1998, 14(4): 212 − 215. [13] 王良桂, 杜旭华, 王顺财, 等. 不同揪树品种(类型)嫩枝扦插生根能力及扦插繁殖技术[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 32(5): 127 − 130. WANG Lianggui, DU Xuhua, WANG Shuncai, et al. Study on the rooting ability of different varieties (types) Catalpa spp. and its unlignified branch cutting technique [J]. J Nangjing For Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2008, 32(5): 127 − 130. [14] 张博, 兰再平, 马可, 等. 不同激素处理和基质配方对楸树嫩枝扦插生根的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2011, 24(6): 749 − 753. ZHANG Bo, LAN Zaiping, MA Ke, et al. Rooting response of Catalpa bungei softwood cutting to different hormone treaments and medium mixture [J]. For Res, 2011, 24(6): 749 − 753. [15] 王改萍, 王良桂, 王晓聪, 等. 楸树嫩枝扦插生根发育及根系特征分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(6): 94 − 102. WANG Gaiping, WANG Lianggui, WANG Xiaocong, et al. Dynamic characteristics of cutting rooting of Catalpa bungei with tender branches [J]. J Nangjing For Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2020, 44(6): 94 − 102. [16] 陈向珍, 杨小林. 温度对藏川杨扦插生根的影响[J]. 西部林业科学, 2016, 45(1): 53 − 56, 61. CHEN Xiangzhen, YANG Xiaolin. Effects of temperatures on the rooting of Populus szechuanica var. tibetica cutting [J]. J West China For Sci, 2016, 45(1): 53 − 56, 61. [17] 任恒泽. 茶树全光照弥雾嫩枝扦插育苗技术研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2018. REN Hengze. Study on the Rapid Propagation Technique of Softwood Cutting of Tea Plant under the Condition of Full-Illumination and Mist[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2018. [18] 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理与技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. [19] BRADFORD M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing theprinciple of protein-dye binding [J]. Anal Biochem, 1976, 72(suppl 1/2): 248 − 254. [20] 庞夫花, 赵密珍, 王钰, 等. ‘宁玉’草莓花芽分化及其生化物质的变化[J]. 果树学报, 2014, 31(6): 1117 − 1122. PANG Fuhua, ZHAO Mizhen, WANG Yu, et al. Studies on floral bud differentiation and biochemical changes of‘Ningyu’strawberry [J]. J Fruit Sci, 2014, 31(6): 1117 − 1122. [21] WINTERBOURN C C, HAWKINS R E, BRIAN M, et al. The estimation of red cell superoxide dismutase activity [J]. J Lab Clin Med, 1975, 85(2): 337 − 341. [22] IORI R, CAVALIERI B, PALMIERI S. Cathodic peroxidases of durum wheat flour [J]. Cereal Chem, 1995, 72(2): 176 − 181. [23] 赵翔, 李清莹, 姜清彬, 等. 不同基质和促根剂对灰木莲嫩枝扦插生根的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(2): 23 − 30. ZHAO Xiang, LI Qingying, JIANG Qingbin, et al. Effects of substrates and rooting regulators on rooting of cuttings in Mahglietia cohifera Dandy [J]. J Nangjing For Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2019, 43(2): 23 − 30. [24] 何崇单, 姚锐, 黄瑞春, 等. 外源K-IBA对北美香柏扦插生根和内源激素含量变化的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2017, 37(10): 7 − 12. HE Chongdan, YAO Rui, HUANG Ruichun, et al. Effects of K-IBA treatments on adventitious rooting and endogenous hormones contents of shoot cuttings of Thuja occidentals L. [J]. J Cent South Univ For Technol, 2017, 37(10): 7 − 12. [25] 张丹丹, 范俊俊, 赵明明, 等. 外施植物生长调节剂对细柄阿丁枫扦插生根的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(1): 41 − 47. ZHANG Dandan, FAN Junjun, ZHAO Mingming, et al. Effects of plant growth regulator on cuttings rooting of Altingia gracilipessl [J]. J Nangjing For Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2018, 42(1): 41 − 47. [26] 赵爽, 刘志高, 冯彬, 等. 山木通扦插繁殖及生根机制[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2017, 34(5): 955 − 962. ZHAO Shuang, LIU Zhigao, FENG Bin, et al. Cutting propagation technology and rooting of Clematis finetiana [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2017, 34(5): 955 − 962. [27] 魏黔春, 江泽平, 刘建锋, 等. 侧柏古树扦插试验及插穗营养物质变化[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(1): 63 − 71. WEI Qianchun, J1ANG Zeping, LIU Jianfeng, et al. Effects of several factors on rooting of cutting propagation of ancient Platycladus orierrtalias and the changes of nutritive material [J]. J Nanjing For Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2020, 44(1): 63 − 71. [28] 张应团. 紫玉兰绿枝扦插生根率与采条时期的关系[J]. 江苏林业科技, 2000, 27(2): 16 − 19. ZHANG Yingtuan. A study on the relationship between Magnolia liliflora Desr. green branch cuttage rooting rate and cutting time [J]. J Jiangsu For Sci Technol, 2000, 27(2): 16 − 19. [29] 李明, 黄卓烈, 谭绍满, 等. 难易生根桉树多酚氧化酶、吲哚乙酸氧化酶活性及其同工酶的比较研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2000, 13(5): 493 − 500. LI Ming, HUANG Zhuolie, TAN Shaoman, et al. Comparison on the activities and isoenzymes of polyphenol oxidase and indoleacetic acid oxidase of difficult and easy-to-root Eucalyptus species [J]. For Res, 2000, 13(5): 493 − 500. [30] 魏树强, 高捍东, 王章荣, 等. 杂交鹅掌揪插穗提取物对白菜种子萌发的影响[J]. 江苏林业科技, 2009, 36(3): 9 − 13. WEI Shuqiang, GAO Handong, WANG Zhangrong, et al. Effects of extract matter from the cutting of Liriodendron chinense×L. tulipifera on the germination of Chinese cabbage seeds [J]. J Jiangsu For Sci Technol, 2009, 36(3): 9 − 13. [31] 王顺财. 楸树嫩枝扦插繁殖技术及其生根机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2007. WANG Shuncai. Study on Softwood Cutting Techniques of Catalpa bungei and Its Rooting Mechanism [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2007. [32] 朱鹏, 徐建民. 邓恩桉组织材料生根抑制物研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2007, 35(32): 10236 − 10238, 10560. ZHU Peng, XU Jianmin. Research on rooting inhibitor of Eucalyptus dunnii's tissue [J]. J Anhui Agric Sci, 2007, 35(32): 10236 − 10238, 10560. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200313






 下载:
下载: