-
物种在群落内的多度、个体大小、竞争关系等特征反映了其在群落中的地位,是群落演替过程中对生境长期适应的结果。研究濒危物种在群落内的地位是判断物种能否长期在群落中生存的依据,也是揭示物种濒危机制的主要途径[1-4],为针对性开展科学有效的保护措施提供基础[5]。天台鹅耳枥Carpinus tientaiensis分布区域十分狭窄,为国家Ⅱ级重点保护野生植物,被《中国生物多样性红色名录 高等植物卷》列为极危等级(CR)。前期仅在浙江省天台县天台山和磐安县大盘山共发现了24株成树,生境地群落环境复杂,物种多样性较高,天台鹅耳枥与柳杉Cryptomeria fortunei var. sinensis、黄山松Pinus taiwannensis和云锦杜鹃Rhododendron fortunei等共同组成了群落乔木层的优势树种[6-7]。天台鹅耳枥光照适应能力较强,其幼苗可以适应较强的光合有效辐射[8-10],海拔、坡度和干扰是影响群落结构和空间分布的主导环境因子[7]。天台鹅耳枥为雌雄异花植物,雄花始花期早于雌花,柱头可授期与雄花散粉的重叠时间约 15 d,授粉成功率受空气湿度和阴雨天气的影响较大;种子空壳率超过90%,自然更新困难[11]。播种育苗、扦插育苗及组织培养等人工繁育技术[12-13]对天台鹅耳枥种群更新效果不大,该物种濒危的状况未得到明显的改善。2019年5月,浙江省景宁畲族自治县上山头发现了新的天台鹅耳枥分布点,这是目前发现的面积最大的野生种群。本研究在对景宁上山头天台鹅耳枥群落结构进行充分调查的基础上,分析天台鹅耳枥种群数量特征及其与群落内其他树种的关系,以期从群落生态学的角度探讨该种群的濒危机制,为该物种的保护提供参考。
-
景宁上山头位于浙江省景宁畲族自治县县城南21 km,处于大漈乡、景南乡两地交界处,属洞宫山脉右支主峰,最高海拔为1 689.1 m,为景宁县境内最高峰。年平均气温为11.8 ℃,年平均降水量为1 918 mm,年日照时数为1 717.6 h,无霜期为196 d,森林覆盖率为96.5%。上山头分布有近70 hm2的云锦杜鹃林,胸径10~20 cm,树高2~5 m,树龄均在50 a以上。2019年5月,在云锦杜鹃林内共发现天台鹅耳枥354株,分布海拔为1 500~1 600 m,分布面积约1 hm2,是目前发现面积最大、分布海拔最高的天台鹅耳枥野生居群。
-
2019年9月,根据天台鹅耳枥实际分布情况,在上山头分布区设置140 m×60 m(样地1)和50 m×50 m (样地2)等2个样地,调查时划分成109个10 m×10 m样方。记录每个样方的木本植物(胸径≥1 cm)种类、高度、胸径。样地1和样地2中心海拔分别为1 531和1 580 m,坡度均为25º,东北坡向、上坡。土壤类型为黄壤,厚度为30~50 cm。
-
以2 cm为径级,统计每个径级的个体数目。以10 m×10 m样方尺度进行重要值和种间联结值的计算。重要值Iv=(Ra+Rp+Rf)/3。其中Ra为相对多度,Ra=(某一植物种类株数/所有植物种类株数之和)×100%;Rp为相对显著度,Rp=(某一树种的胸高断面积/所有树种的胸高断面积之和)×100%;Rf为相对频度,Rf=(某一树种的频度/所有树种的频度之和)×100%。
采用层次聚类法根据种群重要值进行聚类分析,根据距离系数划分群组。
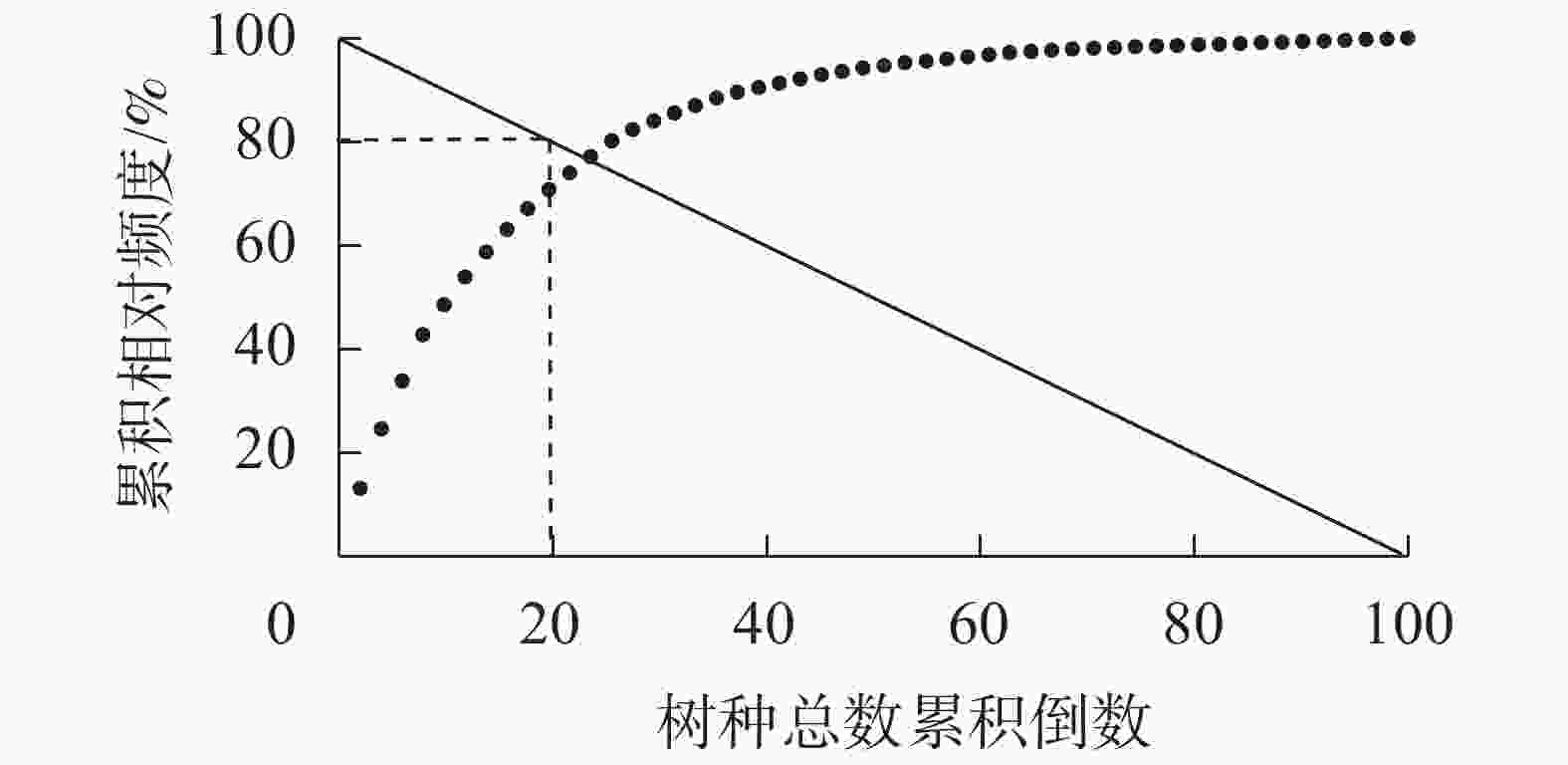
采用Godron稳定性指数评价群落稳定性。建立种百分数与累积相对频度回归方程,求回归方程与横坐标(0,100)和纵坐标(100,0)连线的交点,交点越接近种百分数与累积相对频度比值(20/80),群落就越稳定[14]。累积相对频度为乔木层出现的树种相对频度由大至小累积序列,种百分数为树种总数的倒数累积序列。建立种百分数与累积相对频度的幂函数、指数函数、二项式和Gompertz回归方程,根据R2大小选择最优模型。
采用非连续性数据的公式计算种间联结值(χ2)。公式为:
$$ \chi^{2}=\frac{(|a d-b c|-0.5 n)^{2} n}{(a+b)(a+c)(b+d)(c+d)} 。 $$ 其中:n为样方总数;a为种A和种B都出现的样地数目,b和c分别为仅有种A或种B出现的样地数目,d为种A和种B均未出现样地数目。χ2<3.841,表示种A和种B种间联结独立,两者关联性不显著(P>0.05);3.841≤χ2≤6.635,表示种A和种B种间联结显著,两者有显著关联性(P<0.05); χ2>6.635,表示种A和种B存在极显著关联性(P<0.01)。联结系数(AC)计算公式为:
ad≥bc时,AC=(ad−bc)/(a+b)(b+d);
bc≥ad且d≥a时,AC=(ad−bc)/(a+b)(a+c);
bc>ad且d<a时,AC=(ad−bc)/(b+d)(d+c)。
其中:AC为[−1,1],AC越接近1,表明种A与种B间的正联结性越强;AC越接近−1,表明种A与种B间的负联结性越强;AC越接近0,表明种A与种B间的联结性越弱;AC=0,表明种A与种B间完全独立,没有关联性。
共同出现百分率(PC)计算公式为:PC=a/(a+b+c)。其中:PC为[0,1],PC越接近1,表明种A与种B的正联结关系越强;PC越接近0,表明种A与种B的正联结关系越弱。
-
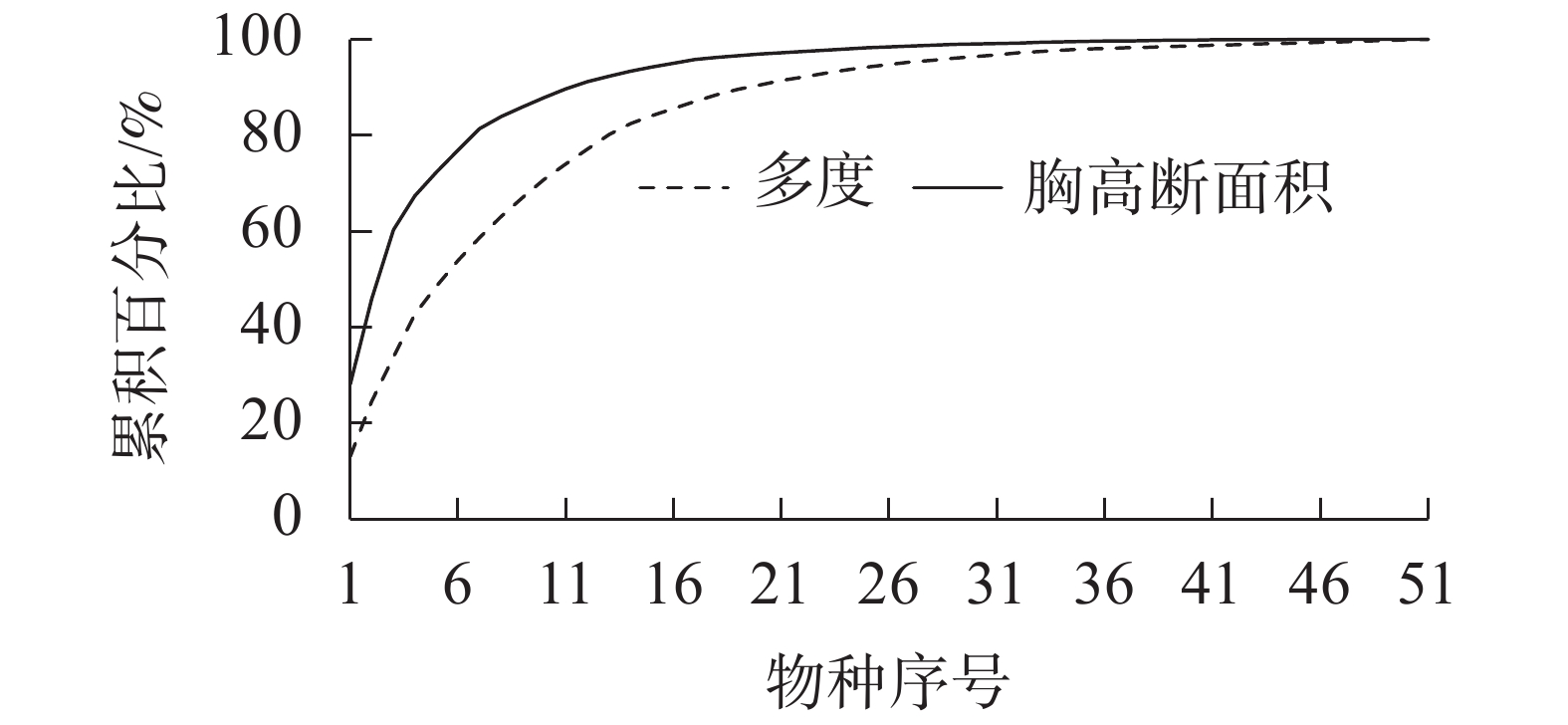
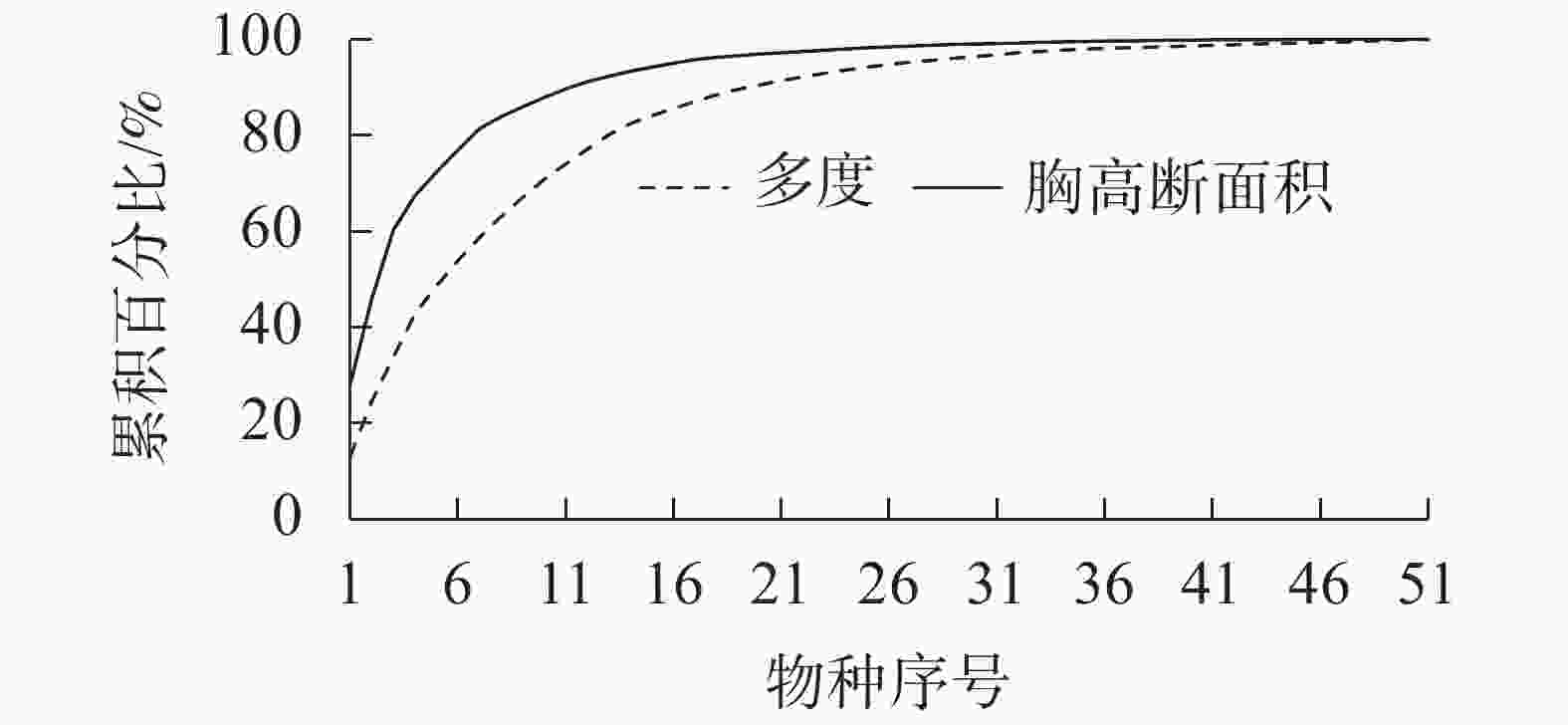
天台鹅耳枥所在群落中,云锦杜鹃重要值最大,为26.84%,其次为白檀Symplocos paniculata (12.98%),天台鹅耳枥重要值排在第3位,为12.73% (表1)。群落中胸径1 cm以上的木本植物有51种3 348株,隶属于19科,31属,裸子植物仅松科Pinaceae松属Pinus黄山松1种。群落中个体数目排在前3位的树种分别是云锦杜鹃、白檀和天台鹅耳枥,分别占个体总数的37.19%、13.39%和10.60%。个体数目最多的前9个树种,占调查到树种个体总数的80%以上,个体数较少的21个树种仅占个体总数的1%,有12个树种仅统计到1株(图1)。群落中胸高断面积最大的12个树种的累积百分比占整个群落的90%以上,胸高断面积最大的是云锦杜鹃,占28.12%,其次为天台鹅耳枥,占17.79%,黄山松占14.44%,胸高断面积较小的21个树种,累积百分比仅占不到1%(图1)。利用重要值进行聚类分析发现:天台鹅耳枥为群落的主要优势树种;51个树种根据距离系数划分为3个群组,其中群组Ⅰ仅云锦杜鹃1个物种;群组Ⅱ包括天台鹅耳枥、白檀、黄山松和微毛柃Eurya hebeclados 等4个物种,重要值为7%~13%;其余46个树种重要值<5%,归类为群组Ⅲ,包括毛果珍珠花Lyonia ovalifolia var. hebecarpa、多脉青冈Cyclobalanopsis multinervis、水青冈Fagus longipetiolata、红果山胡椒Lindera erythrocarpa和交让木Daphniphyllum macropodum等5个重要值排在前10位的树种,还有齿叶冬青Ilex crenata、湖北海棠Malus hupehensis、山樱花Cerasus serrulata等41个重要值<1%的树种。群组Ⅲ个体总数仅占27.7%,其中28个树种的个体数<10株,12个树种仅见1株,表明群组Ⅲ主要为群落伴生种和稀有种。
表 1 天台鹅耳枥所在群落重要值排前10位物种
Table 1. Top 10 tree species of importance value in C. tientaiensis communities
序号 学名 多度 重要值/% 序号 学名 多度 重要值/% 1 云锦杜鹃 1 245 26.84 6 毛果珍珠花 145 4.79 2 白檀 448 12.98 7 多脉青冈 88 4.49 3 天台鹅耳枥 354 12.73 8 水青冈 65 3.67 4 黄山松 120 8.50 9 红果山胡椒 57 3.02 5 微毛柃 255 7.79 10 交让木 44 2.60 -
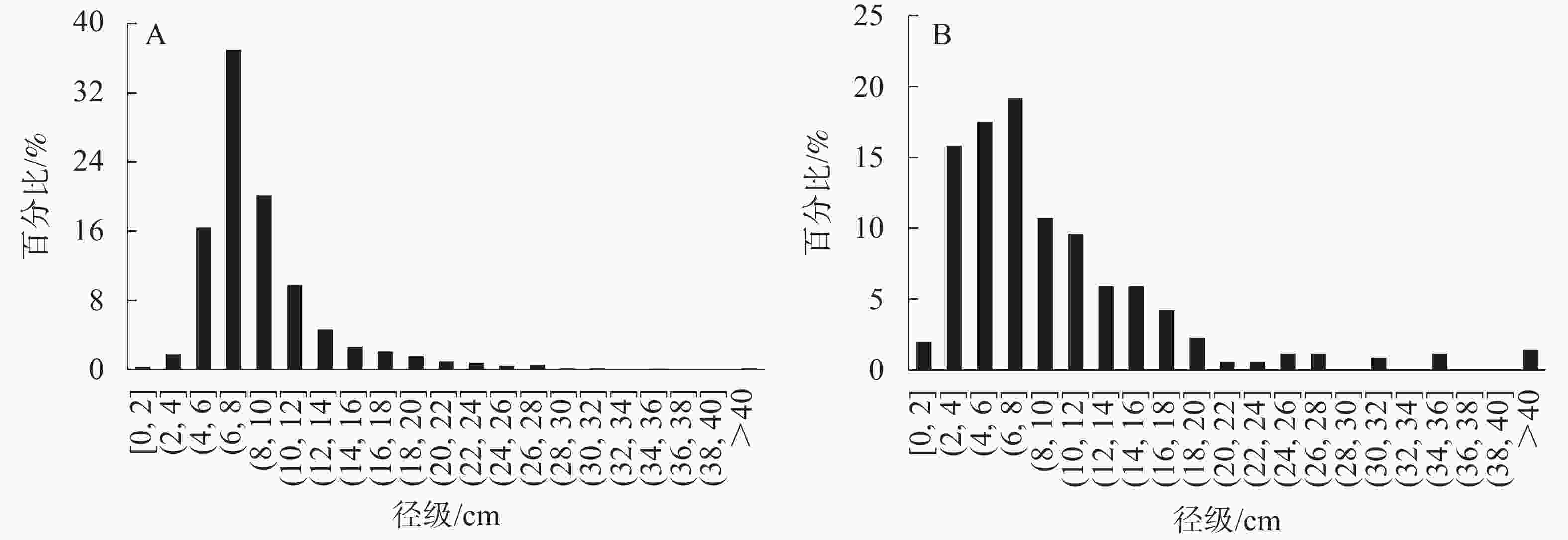
对天台鹅耳枥所在群落所有木本植物的累积相对频度与乔木总物种数累积倒数作散点图。由图2可知:最优Godron稳定性指数曲线回归结果为Gompertz曲线(y=98.14×0.179.91x,R2=0.992 5),交点坐标离群落稳定点(20,80)较近。群落径级呈偏正态分布,群落中小径级个体较少(图3A),群落结构较为稳定。具体来看,群落中4 cm及以下胸径的个体仅占个体总数的2.09%,其中天台鹅耳枥占1.88%,为所有4 cm及以下胸径个体的90%;4~20 cm胸径的个体占94.32%,其中天台鹅耳枥占7.97%;20 cm以上胸径的个体占3.58%,天台鹅耳枥占0.72%。群落中胸径30 cm以上的个体共18株,其中天台鹅耳枥11株,占61.11%,最大胸径为74.6 cm,是群落中胸径最大的个体。但在天台鹅耳枥径级分布中,4 cm及以下胸径的个体仅占18.00%,无1 cm以下胸径的个体;4~20 cm胸径的个体占75.42%;30 cm以上胸径的个体占3.39%(图3B)。
-
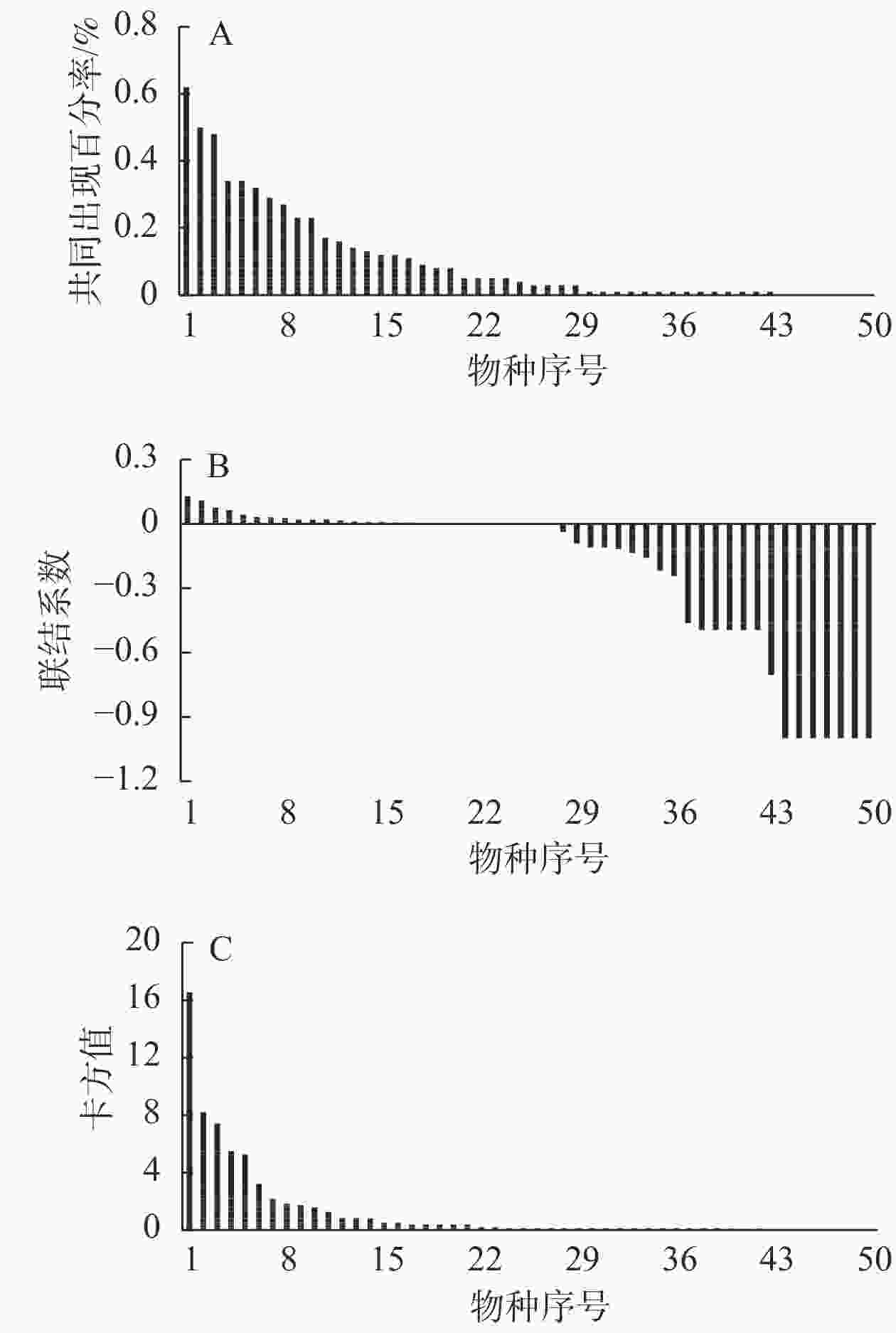
对天台鹅耳枥和群落内其他50个树种做种间联结分析。共同出现百分率(PC)分析(图4A)表明:垂丝卫矛Euonymus oxyphyllus、光叶山矾Symplocos lancifolia、闪光红山茶Camellia lucidissima、毛鸡爪槭Acer pubipalmatum、毛脉槭A. pubinerve、石灰花楸Sorbus folgneri等7个树种与天台鹅耳枥没有相关性,其他43个树种均与天台鹅耳枥表现出正相关性,其中PC>0.3的有6个树种。联结系数(AC)分析(图4B)表明:天台鹅耳枥与23个树种表现出负联结,与27个种对表现出正相关。χ2检验(图4C)表明:天台鹅耳枥与红果山胡椒、雷公鹅耳枥C. viminea、水青冈等树种极显著相关(P<0.01),与白檀、闪光红山茶等显著相关(P<0.05)。
-
天台山、大盘山和上山头,天台鹅耳枥均分布在黄壤、海拔相对较高(890~1 600 m)、坡度相对较大(15.35º~38.32º)、植被覆盖率较高的中坡至山脊上,种群更新能力差。受海拔较高影响,木本植物种类组成差异较大[6-7]。陈模舜等[7]发现:天台山和大盘山等地群落结构稳定性较差,受人为干扰的影响较大;天台山18株天台鹅耳枥在群落中的重要值排在第2位,仅次于柳杉;天台鹅耳枥自然分布植株的生长受伴生乔木的影响,同时也影响伴生树种的组成和物种多样性[6]。本研究发现:景宁上山头天台鹅耳枥所在群落结构稳定,海拔较高,受人为干扰影响较少;重要值、个体数量、胸高断面积以及群落乔木层树种重要值聚类分析等均显示:天台鹅耳枥是群落的优势树种之一。群落中4 cm及以下胸径的小径级个体和30 cm以上胸径的大径级个体在群落中具有显著的优势地位,但个体数量在其种群中的占比较小,分别占18.00%和3.39%,缺少1 cm以下胸径的个体,显示景宁上山头天台鹅耳枥存在更新限制,4~20 cm胸径的个体竞争压力较大。种间联结分析表明:与毛柄小勾儿茶Berchemiella wilsonii var. pubipetiolata[1]、白桂木Artocarpus hypargyreus[2]、云南红豆杉Taxus yunnanensis[15]、脱皮榆Ulmus lamellosa[16]、狭果秤锤树Sinojackia rehderiana[17]、对开蕨Phyllitis scolopendrium[18]和藤枣Eleutharrhena macrocarpa[19]等濒危树种在群落内表现出独立分布或随机分布的特征不同,研究区天台鹅耳枥与群落中其他树种间存在较强的种间关系,这与黄梅秤锤树S. huangmeiensis[20]的研究结果一致。群落种间关系的形成与演替过程有关,在演替初期主要种对间尚未形成一定的种间关系,随着演替的进展,逐渐表现为复杂多样的种间关系[21],但在物种丰富的热带森林中可能会出现相反的结论[22]。另外种群数量的大小和分布特征可能也会影响濒危物种与群落内其他物种的关系,如数量少、分布零散比数量相对较多且集中分布的濒危物种,其种间关系较为松散。本研究中天台鹅耳枥与群落内其他树种较为复杂的种间关系可能与数量集中分布、群落较为成熟有关。因此,从群落生态学的角度来看,天台鹅耳枥可以在适生区内作为群落的优势种长期存在,应该具有更大的分布范围。运用气象和海拔等指标对该树种潜在分布区的预测[23]也证明:天台鹅耳枥可分布在浙江南部、台湾中南部以及安徽南部等高海拔区域。
天台鹅耳枥种子空壳率极高,种子人工萌发结果非常差,空气湿度和阴雨天气影响授粉成功率[8]。目前仅在2014年采集到饱满种子约500 g,繁育了一批实生苗,而扦插和组织培养等人工繁育的效果均不理想[12-13]。天台山、大盘山和上山头3个分布区的海拔均在800 m以上,高海拔地区较大的空气湿度和降水量可能是影响种子发育的关键因素。本研究中未发现1 cm以下胸径的个体,表明种子发育障碍以及从种子到幼苗阶段的更新限制是导致该树种数量稀少、分布狭窄的主要原因。种间联结分析还显示天台鹅耳枥与群落内其他树种间存在较强的竞争关系。
陈模舜等[10,24]研究发现:天台鹅耳枥及其幼苗具有一定的阳性特征。因此在合适的气象条件下采取人工授粉可提高种子发育饱满率;可采取间伐部分4~20 cm胸径的干扰树,通过减少其竞争压力来提高群落透光率,为天台鹅耳枥幼苗生长提供条件。
本研究表明天台鹅耳枥所在群落结构稳定,其在群落构建中发挥重要的作用,但存在种群更新障碍,且中龄级个体竞争压力较大。建议通过间伐等措施改善天台鹅耳枥生长环境,提高幼苗定植成功率。后续应进一步研究天台鹅耳枥繁育特性和繁育体系,以及中龄级个体的生态需求。
Analysis of the population quantitative characteristics of Carpinus tientaiensis and its associations with other tree species
-
摘要:
目的 分析极小种群天台鹅耳枥Carpinus tientaiensis所在群落和种群数量特征及其与其他物种的种间关系,探讨其濒危原因和保护策略。 方法 采用样方法调查浙江省景宁畲族自治县上山头天台鹅耳枥群落,计算径级分布、重要值、多度和胸高断面积,测定种间联结值和群落稳定性指数。 结果 群落中天台鹅耳枥重要值排在第3位,个体数量占乔木层树种的10.6%,胸高断面积占17.79%,是群落的主要优势种之一。天台鹅耳枥最大胸径为74.6 cm,1~4 cm胸径的小径级个体和30 cm以上胸径的大径级个体分别占群落相应径级的90.00%和66.11%,但4~20 cm胸径的个体仅占群落的7.91%,且缺乏1 cm以下胸径的个体。共同出现百分率和联结系数显示:天台鹅耳枥与群落类内其他物种间关系复杂,χ2检验表明天台鹅耳枥与5个树种竞争强度较大。 结论 天台鹅耳枥在群落中具优势地位,但存在种群更新限制,且中等径级个体在群落中占比较小,受到的竞争压力较大。可采用间伐等方式适当降低天台鹅耳枥4~20 cm胸径个体的竞争压力,并为幼苗定植和生长提供必要的光环境。图4表1参24 Abstract:Objective With an analysis of the population and community characteristics of Carpinus tientaiensis, an extremely small population as well as its interactions with other trees species, this study is aimed to explore its endangerment mechanisms so as to propose workable protection strategies. Method Sampling method was first used to investigate the community characteristics in Shangshantou, Jingning She Nationality Autonomous County of Zhejiang Province, and indicators including the importance value, species abundance, distribution of the diameters at breast height (DBH) and inter-specific associations were analyzed. Result C. tientaiensis is one of the main dominant species in the community with the largest DBH 74.6 cm, ranking the third in importance value and accounting for 10.6% of the total tree species number, while 17.79% of the total basal area. Individuals with DBH of 1−4 cm and above 30 cm accounted for 90.00% and 66.11% of the total trees in the community respectively, while those with DBH of 4−20 cm only took up 7.91%. Strong inter-specific associations between C. tientaiensis and other species were found by means of association coefficient and percentage of co-occurrence whereas χ 2 test indicated that C. tientaiensis was in intense competition against 5 other tree species. Conclusion Although C. tientaiensis, is one of the dominant species in the community, it has displayed population regeneration limitation with individuals with DBH at 4−20 cm found, thus faced with strong competition from other species. It was suggested that intermediate felling measures should be taken to reduce the competitive pressure of C. tientaiensis and necessary light environment should be provided for seedling settlement and tree growth. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 24 ref.] -
表 1 天台鹅耳枥所在群落重要值排前10位物种
Table 1. Top 10 tree species of importance value in C. tientaiensis communities
序号 学名 多度 重要值/% 序号 学名 多度 重要值/% 1 云锦杜鹃 1 245 26.84 6 毛果珍珠花 145 4.79 2 白檀 448 12.98 7 多脉青冈 88 4.49 3 天台鹅耳枥 354 12.73 8 水青冈 65 3.67 4 黄山松 120 8.50 9 红果山胡椒 57 3.02 5 微毛柃 255 7.79 10 交让木 44 2.60 -
[1] 胡理乐, 江明喜, 党海山, 等. 从种间联结分析濒危植物毛柄小勾儿茶在群落中的地位[J]. 植物生态学报, 2005, 29(2): 258 − 265. HU Lile, JIANG Mingxi, DANG Haishan, et al. Community studies on the status of the endangered plant, Berchemiella wilsonii var. pubipetiolata, using interspecific association analysis [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2005, 29(2): 258 − 265. [2] 范繁荣, 马祥庆, 谢荣樟, 等. 运用种间联结分析濒危植物白桂木在群落中的地位[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 37(1): 61 − 65. FAN Fanrong, MA Xiangqing, XIE Rongzhang, et al. Community studies on the status of the endangered plant, Artocarpus hypargyreus Hance, using inter-specific association analysis [J]. J Fujian Agri For Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2008, 37(1): 61 − 65. [3] 徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 等. 植物种间联结研究内容与方法评述[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(24): 8224 − 8233. XU Manhou, LIU Min, ZHAI Datong, et al. A review of contents and methods used to analyze various aspects of plant interspecific associations [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2016, 36(24): 8224 − 8233. [4] 马晨晨, 代俊, 肖之强, 等. 极小种群物种云南肉豆蔻的群落结构及其种群现状[J]. 广西植物, 2017, 37(6): 783 − 790. MA Chenchen, DAI Jun, XIAO Zhiqiang, et al. Community structure and distribution of minimum population species of Myristica yunnanensis [J]. Guihaia, 2017, 37(6): 783 − 790. [5] 孙卫邦, 韩春艳. 论极小种群野生植物的研究及科学保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(3): 426 − 429. SUN Weibang, HAN Chunyan. Researches and conservation for plant species with extremely small populations (PSESP) [J]. Biodiversity Sci, 2015, 23(3): 426 − 429. [6] 张忠钊, 孙永涛, 季瑞炜, 等. 天台鹅耳枥自然生境植物群落调查[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2018, 38(1): 33 − 39. ZHANG Zhongzhao, SUN Yongtao, JI Ruiwei, et al. Investigation on habitat of Carpinus tientaiensis community in Tiantai [J]. J Zhejiang For Sci Technol, 2018, 38(1): 33 − 39. [7] 陈模舜, 金则新, 柯世省, 等. 极濒危物种天台鹅耳枥群落特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 林业科学, 2020, 56(9): 1 − 11. CHEN Moshun, JIN Zexin, KE Shisheng, et al. Community characteristics and their relations with environmental variables of critically endangered species Carpinus tientaiensis [J]. Sci Silv Sin, 2020, 56(9): 1 − 11. [8] 张忠钊, 季梦成, 范义荣, 等. 濒危植物天台鹅耳枥开花特性与花粉生活力测定[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2016, 36(5): 10 − 13. ZHANG Zhongzhao, JI Mengcheng, FAN Yirong, et al. Flowering properties and pollen viability of Carpinus tientaiensis [J]. J Zhejiang For Sci Technol, 2016, 36(5): 10 − 13. [9] 陈模舜, 柯世省, 杨勇宇, 等. 珍稀濒危植物天台鹅耳枥营养器官的解剖学研究[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2010, 30(5): 14 − 19. CHEN Moshun, KE Shisheng, YANG Yongyu, et al. Anatomical study on vegetative organs of Carpinus tientaiensis [J]. J Zhejiang For Sci Technol, 2010, 30(5): 14 − 19. [10] 陈模舜, 金则新, 柯世省. 不同光环境下天台鹅耳枥叶形变化的测定与分析[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(1): 54 − 63. CHEN Moshun, JIN Zexin, KE Shisheng. Measurement and analysis of leaf shape variation of Carpinus tientaiensis in different light environment [J]. Sci Silv Sin, 2018, 54(1): 54 − 63. [11] 施灵栋, 张忠钊, 季梦成, 等. 濒危植物天台鹅耳枥幼苗光合特性研究[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(19): 4949 − 4951. SHI Lingdong, ZHANG Zhongzhao, JI Mengcheng, et al. Study on seedling photosynthetic character of endangered plant Carpinus tientaiensis [J]. Hubei Agric Sci, 2016, 55(19): 4949 − 4951. [12] 邱智敏, 王国英, 袁继标. 天台鹅耳枥育苗试验初报[J]. 福建林业科技, 2013, 40(3): 131 − 133, 142. QIU Zhimin, WANG Guoying, YUAN Jibiao. Preliminary report on seedling cultivation of Carpinus tientaiensis [J]. J Fujian For Sci Technol, 2013, 40(3): 131 − 133, 142. [13] 陈珍, 陈模舜, 孙骏威, 等. 天台鹅耳枥的组织培养与快速繁殖[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2013, 40(6): 1009 − 1012. CHEN Zhen, CHEN Moshun, SUN Junwei, et al. Tissue culture and rapid propagation of Carpinus tientaiensis [J]. J Anhui Agric Univ, 2013, 40(6): 1009 − 1012. [14] 郑元润. 森林群落稳定性研究方法初探[J]. 林业科学, 2000, 36(5): 28 − 32. ZHENG Yuanrun. Comparison of methods for studying stability of forest community [J]. Sci Silv Sin, 2000, 36(5): 28 − 32. [15] 李帅锋, 刘万德, 苏建荣, 等. 滇西北云南红豆杉群落物种生态位与种间联结[J]. 植物科学学报, 2012, 30(6): 568 − 576. LI Shuaifeng, LIU Wande, SU Jianrong, et al. Niche and interspecific association of species of Taxus yunnanensis communities in northwest Yunnan Province [J]. Plant Sci J, 2012, 30(6): 568 − 576. [16] 白玉芳, 毕润成, 白玉宏, 等. 山西太岳山稀有濒危植物脱皮榆群落种间关联[J]. 广西植物, 2014, 34(1): 56 − 61. BAI Yufang, BI Runcheng, BAI Yuhong, et al. Interspecific relationship of rare and endangered Ulmus lamellose community in Taiyue Moutain of Shanxi [J]. Guihaia, 2014, 34(1): 56 − 61. [17] 周赛霞, 彭炎松, 丁剑敏, 等. 珍稀植物狭果秤锤树群落木本植物种间联结性及群落稳定性研究[J]. 广西植物, 2017, 37(4): 442 − 448. ZHOU Saixia, PENG Yansong, DING Jianmin, et al. Analysis on community stability and inter-specific correlations among dominant woody populations of the endangered plant Sinojackia rehderiana communities [J]. Guihaia, 2017, 37(4): 442 − 448. [18] 黄祥童, 王绍先, 黄炳军, 等. 珍稀植物对开蕨与其伴生物种的联结性及群落稳定性[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(1): 80 − 90. HUANG Xiangtong, WANG Shaoxian, HUANG Bingjun, et al. Analyses of community stability and inter-specific associations between the rare plant Phyllitis scolopendrium and its associated species [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2015, 35(1): 80 − 90. [19] 李帅锋, 郎学东, 黄小波, 等. 藤枣生境地木本植物种间关联性与群落稳定性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 350 − 357. LI Shuaifeng, LANG Xuedong, HUANG Xiaobo, et al. Interspecific association of woody plant species and community stability in the Eleutharrhena macrocarpa habitat [J]. Biodiversity Sci, 2020, 28(3): 350 − 357. [20] 王世彤, 吴浩, 刘梦婷, 等. 极小种群野生植物黄梅秤锤树群落结构与动态[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(7): 749 − 759. WANG Shitong, WU Hao, LIU Mengting, et al. Community structure and dynamics of a remnant forest dominated by a plant species with extremely small population (Sinojackia huangmeiensis) in central China [J]. Biodiversity Sci, 2018, 26(7): 749 − 759. [21] 周先叶, 王伯荪, 李鸣光, 等. 广东黑石顶自然保护区森林次生演替过程中群落的种间联结性分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2000, 24(3): 332 − 339. ZHOU Xianye, WANG Bosun, LI Mingguang, et al. An analysis of interspecific associations in secondary succession forest communities in Heishiding Natural Reserve, Guangdong Province [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2000, 24(3): 332 − 339. [22] 李意德, 许涵, 陈德祥, 等. 从植物种间联结探讨生态种组与功能群划分−以尖峰岭热带低地雨林乔木层数据为例[J]. 林业科学, 2007, 43(4): 9 − 16. LI Yide, XU Han, CHEN Dexiang, et al. Discussing on the ecological species groups division based on the interspecific association: a case study on the arbor layer data in tropical lowland rain forest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China [J]. Sci Silv Sin, 2007, 43(4): 9 − 16. [23] ZHAO Runan, CHU Xiaojie, HE Qianqian, et al. Modeling current and future potential geographical distribution of Carpinus tientaiensis, a critically endangered species from China [J/OL]. Forests, 2020, 11: 774[2021-04-20]. doi:10.3390/f11070774. [24] 陈模舜, 柯世省. 天台鹅耳枥叶片的解剖结构和光合特性对光照的适应[J]. 林业科学, 2013, 49(2): 46 − 53. CHEN Moshun, KE Shisheng. Acclimation of anatomical structure and photosynthesis characteristics in leaves of Carpinus tientaiensis to irradiance [J]. Sci Silv Sin, 2013, 49(2): 46 − 53. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210307






 下载:
下载: