-
生态环境是人类社会可持续发展的基础,随着气候变化和社会经济的快速发展,土地退化、水土流失、生物多样性锐减等生态环境问题日益凸显[1],这些问题直接威胁到区域的可持续发展。生态安全是人类不受生态破坏与环境污染等影响的保障程度,具有2个方面的内涵:一是自然和半自然生态系统的安全;二是在人的生活、健康、基本权利、社会次序等方面不受威胁的状态[2]。生态安全作为经济繁荣、民生改善最为基础和牢固的构成要素,其以生态环境系统为目标,旨在分析和评价人类活动与自然环境之间的交互作用及其影响[3]。目前,关于生态安全问题的研究,学者们常用的评价方法主要有综合指数法[4]、层次分析法[5]、主成分分析法[6]、变异系数法[7]等;评价模型则主要包括压力-状态-响应模型(PSR模型)[8]及其改进形式的DPSIR、DPSIRM等[9];同时也有从自然-经济-社会(NES)[9]和经济-环境-社会(EES)[10]等维度构造评价模型。其中,PSR模型是由经济合作与发展组织(OECD)与联合国环境规划署(UNEP)共同提出[11],用于研究人类与自然环境的关系。PSR模型由于其逻辑思路清晰、理论框架成熟,且考虑了生态系统结构和功能的完整性,以及恢复力、压力和响应水平[12−13],因此在国内外生态环境评价中运用广泛[14],并在可持续发展研究环境指标体系的构建方面产生了极好的反响。
在中国当前生态文明建设、新型城镇化建设的新阶段,生态文明的核心理念是人类社会发展必须遵循“人-自然-社会”和谐发展这一规律[15−16]。由于干旱区生态系统具有较为脆弱且易受人为干扰的特点,其平衡极易被打破,这使得干旱区成为了中国生态文明建设的重点关注区域[17]。天山-帕米尔地区作为典型的中国西北内陆干旱区,其独特的地理位置和丰富多样的生态系统将在中国生态安全方面发挥重要的屏障作用,同时天山-帕米尔地区也是丝绸之路经济带、中巴经济走廊起始端的核心区域,其建设对“一带一路”国家的经济发展具有强大的推动作用[18]。在此背景下,如何准确评价区域生态安全状况,并有效针对区域内生态环境问题提出综合解决措施,促进天山-帕米尔地区生态文明和绿色发展的有序推进具有重要的现实意义。
鉴于此,本研究基于PSR模型,以天山-帕米尔地区为研究区,运用熵权法及地理探测器等方法,开展天山-帕米尔地区生态安全评价并揭示影响区域生态安全的关键因子。这即是绿色丝绸之路建设高度关注的研究主题,又是可持续发展的重要议题,同时可为该区域的生态保护与生态建设以及协同发展提供科学依据。
-
天山-帕米尔地区(34°18′26″~45°24′08″N,73°27′58″~96°27′36″E)地处准噶尔盆地南部、帕米尔高原东部、塔里木盆地西南缘,包含新疆维吾尔自治区中部和西南部地区,涵盖了4个地级市、13个县级市、34个县、5个自治县,合计56个行政单元,研究区面积约74.38×104 km2。该区域属温带大陆性气候,干旱少雨,由于自然条件的制约,各区域受人类活动的影响程度有所差异[18]。然而由于旅游业的兴起、工业的发展、政策以及社会人文条件等因素的改变,生态环境也随之受到一定影响,放牧等活动使得草地退化,荒漠化加剧[19],导致区域内生态安全度降低。天山-帕米尔地区所在的天山北坡经济带,属于新疆社会经济发展的增长极,在国家“一带一路”建设中具有重要的战略地位。天山-帕米尔地区2018年人口为1 551.27万人,区域生产总值为10 300.57亿元。
-
涉及的社会经济、人口、生态建设、环境保护等数据,主要通过《新疆维吾尔自治区统计年鉴》、新疆维吾尔自治区《国民经济和社会发展统计公报》等提供的数据计算获得,选取1990、2000、2010、2018年的数据。所需的1∶10万土地利用矢量数据集,包含6个大类(耕地、林地、草地、湿地、人工表面、其他),分类体系参考土地覆盖分类系统(LCCS)和联合国政府间气候变化专门委员会(IPCC)分类体系,与中国土地覆被数据集所用分类体系一致[20]。采用分区分层的决策树法,结合土地覆被实际变化,借助e-Cognition遥感解译软件和人工解译等完成,通过样点验证最终精度达93%。
运用极差标准化对数据进行常规预处理。将选取的指标依据对环境的影响划分为正向和负向,正向指标值越大越好,负向指标值越小越好。计算公式为:
$$ {Z_i} = \frac{{{X_i} - {X_{\min }}}}{{{X_{\max }} - {X_{\min }}}} \text{;} $$ (1) $$ {Y_i} = \frac{{{X_{\max }} - {X_i}}}{{{X_{\max }} - {X_{\min }}}} 。 $$ (2) 式(1)~(2)中:Zi、Yi为标准化后该项指标(Xi)在i时段的正向评价指标和负向评价指标;Xi为i时段的指标值;Xmin、Xmax为Xi的最小值和最大值。
-
生态环境质量受到自然和人文2个方面的影响,因此,评价区域生态环境应综合考虑环境、资源、人口、社会经济等多方面的因素。PSR模型的研究思路为人类对生态环境会造成一定的“压力”,在这种“压力”下自然环境发生改变并呈现相应的“状态”,当产生不利的状况时,社会通过政策、法规以及行为规范等做出“响应”。
天山-帕米尔地区是西北干旱区典型的生态脆弱区,以绿洲农业为主,旅游资源丰富,因此在生态安全评价指标选取方面更加侧重人口、旅游收入、耕地用肥等指标。借鉴已有研究成果基础[21−26],遵循天山-帕米尔地区的区域特点、数据的可获取性以及科学性等原则,共选取20个指标(表1)。
表 1 天山-帕米尔地区生态安全评价体系
Table 1. Evaluation system of ecological security in Tianshan-Pamir region
目标层 准则层 要素层 指标层 指标属性 生态安全综合指数 压力(P) 社会经济压力 人口密度/(人·km−2) 负 人口自然增长率/% 负 人均国内生产总值(GDP)/元 负 国内游客数量增长率/% 负 资源环境压力 单位耕地化肥使用量/(t·hm−2) 负 单位面积废水排放量/(t·km−2) 负 湿地覆盖率/% 正 状态(S) 社会经济状态 区域开发指数/% 负 经济密度/(万元·km−2) 负 旅行社数量增长率/个 负 资源环境状态 草地覆盖率/% 正 森林覆盖率/% 正 原煤消耗/(t·万元−1) 负 人均水资源量/(m3·人−1) 正 响应(R) 社会经济响应 旅游收入占GDP比例/% 负 第三产业占GDP比例/% 正 城镇化水平/% 负 拥有卫生技术人员/人 正 资源环境响应 单位面积环保投入/(万元·km−2) 正 自然保护区数量/个 正 -
目前熵权法、层次分析法以及Delphi法等为常用的赋值方法,为有效地克服专家打分的主观性,本研究采用熵权法对指标进行赋值,根据信息量的大小来确定权重,以避免人为因素带来的误差。具体公式为:
$$ {H_{{i}}} = {{ - }}\frac{{\text{1}}}{{\ln n}}\sum\limits_{j = 1}^n {{X_{ij}}} \ln {X_{ij}} \text{;} $$ (3) $$ {W_i} = \frac{{1 - {H_i}}}{{m - \displaystyle \sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {{H_i}} }} 。 $$ (4) 式(3)~(4)中:
$ {H_i} $ 为第$ i $ 个指标的信息熵;$ {W_i} $ 为第$ i $ 个指标的熵权;$ {X_{ij}} $ 为第$ i $ 个指标下第j个样本的指标占比;$ m $ 为评价指标总数;n为研究单元数量。 -
综合指数法在生态安全的评价中应运最为广泛且成熟,因此采用综合指数法计算天山-帕米尔地区的生态安全综合指数,计算公式如下:
$$ {E_{\rm{S}}}_{{i}} = \sum\limits_{j = 1}^m {{W_j}} {P_{ij}} 。 $$ (5) 式(5)中:ESi为第
$ i $ 研究单元的生态安全综合值;$ {W_j} $ 为第$ j $ 个指标的熵权;$ {P_{ij}} $ 为第$ i $ 研究单元第$ j $ 项指标标准化后的指标值;$ m $ 为指标的数量。为对比反映区域内生态安全的状态和差异,采用自然断裂点法(Jenks)将天山-帕米尔地区区域生态安全划分为5个分级[24−25]。但若每个时期的分类标准不同,则无法比较分析[26]。因此,1990、2000、2010、2018年均采用1990年的分级标准(表2)。
表 2 天山-帕米尔地区生态安全分级标准
Table 2. Classification standard of ecological security in Tianshan-Pamir region
等级 安全等级 生态安全综合指数 生态安全特征描述 Ⅰ 不安全 [0.00~0.19) 压力极大,环境极差,存在严重生态环境问题 Ⅱ 较不安全 [0.19~0.23) 压力较大,环境较差,生态环境处于不稳定状态 Ⅲ 临界安全 [0.23~0.31) 压力接近阈值,环境一般,能发挥基本生态系统功能 Ⅳ 较安全 [0.31~0.49) 压力较小,环境较好,但仍存在部分限制性因素 Ⅴ 安全 [0.49~0.72) 压力很小,环境优越,生态系统功能、结构完善 -
地理探测器用于探测空间分异性,是揭示其驱动因子的一种新的统计学方法,共包括4个因子探测器[27−29]。本研究运用因子探测器来分析20个因子(X)在多大程度上揭示了生态安全的空间分异性(Y)。其表达式为[28−29]:
$$ q = 1 - \frac{{\displaystyle \sum\limits_{h = 1}^L {{N_h}\sigma _h^2} }}{{N{\sigma ^2}}} 。 $$ (6) 式(6)中:
$ h = 1, \cdot \cdot \cdot $ ,L;L为变量Y或因子X的分类或分层;$ {N_h} $ 、$ N $ 分别为层$ h $ 和全区单元数,$ \sigma _h^2 $ 为层$ h $ 的方差、$ {\sigma ^2} $ 为全区$ Y $ 值的方差。q为因子X对变量Y的解释度,取值范围为[0, 1],值越大说明分异性越明显,解释力就越强,反之则越小。 -
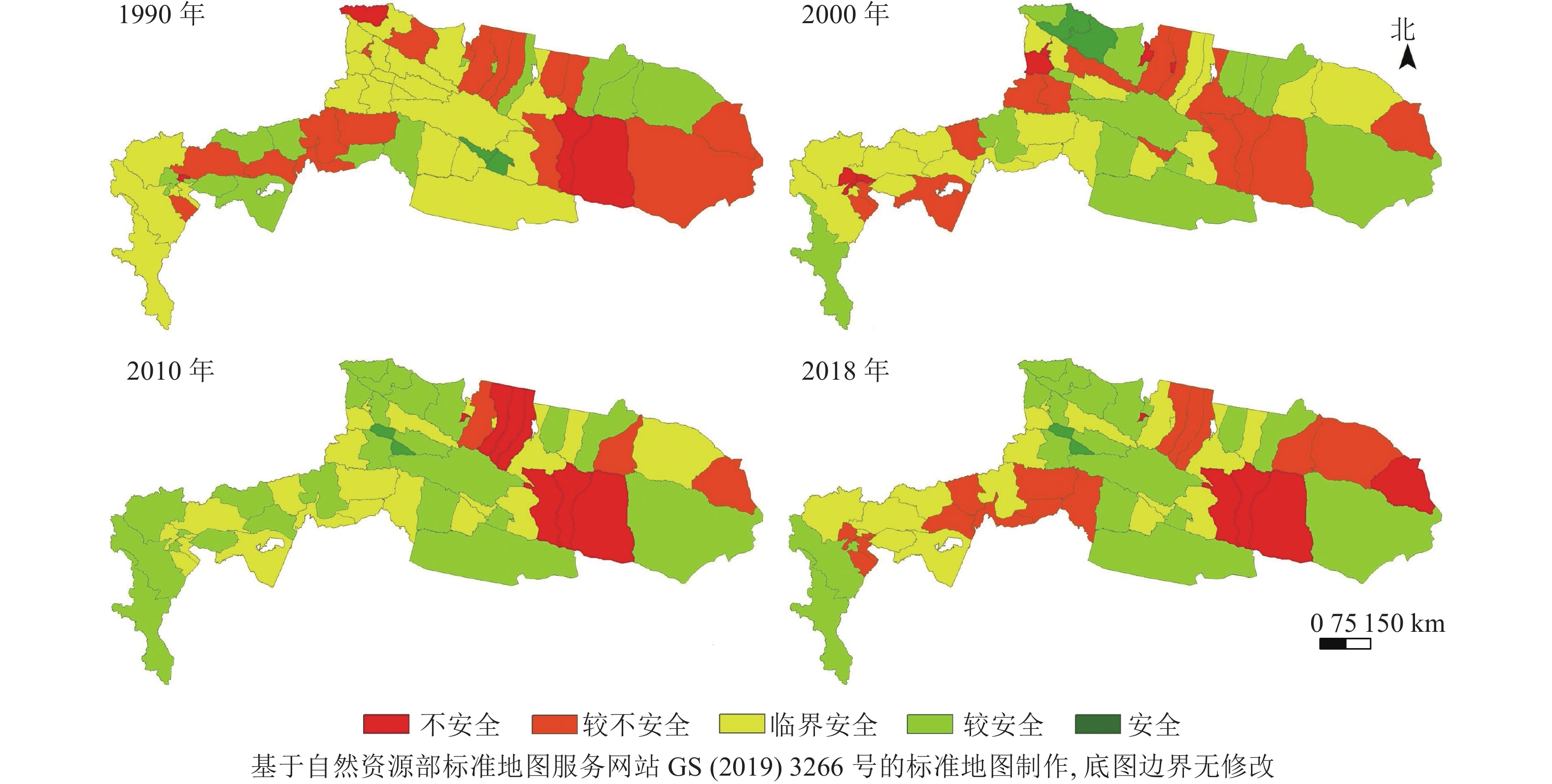
通过计算生态安全综合指数,得到天山-帕米尔地区生态安全时空格局分布图(图1)。从空间上来看,1990年大部分地区生态安全等级处于临界安全及以下,2000年生态安全综合指数略微上升;2010年区域综合指数最高,生态状况最好,生态环境状况改善最为明显,主要发生在帕米尔高原地区;2018年研究区西部地区的生态安全综合值有所下降,其他地区则较稳定。不同行政单元间生态安全等级在空间上的表现差异较大,但由于天山-帕米尔地区的地形地貌并未发生大尺度的变化,因此地区生态安全的分布格局并没有发生明显变化。
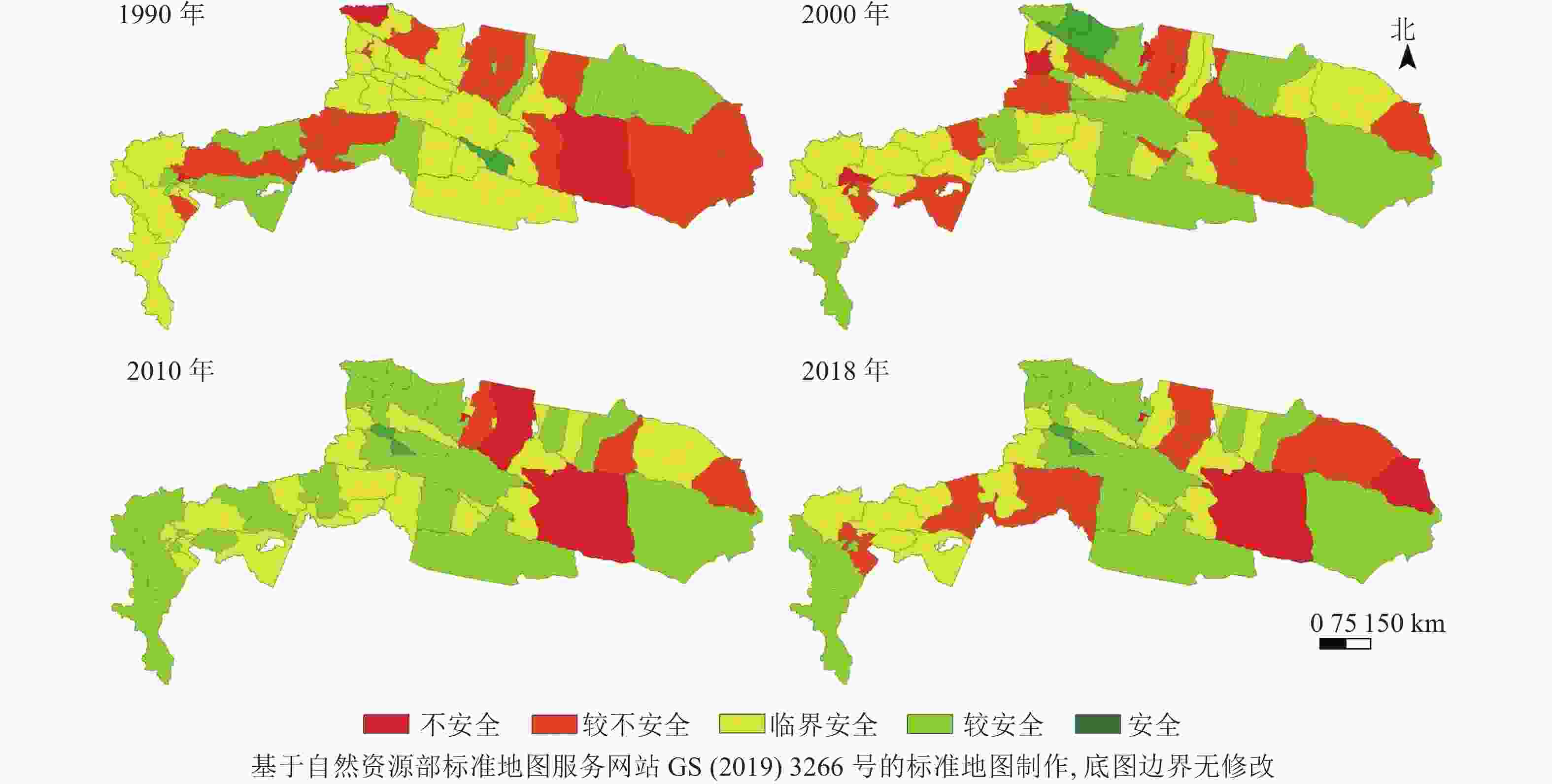
图 1 天山-帕米尔地区生态安全时空格局示意图
Figure 1. Spatio-temporal pattern of ecological security in Tianshan-Pamir region
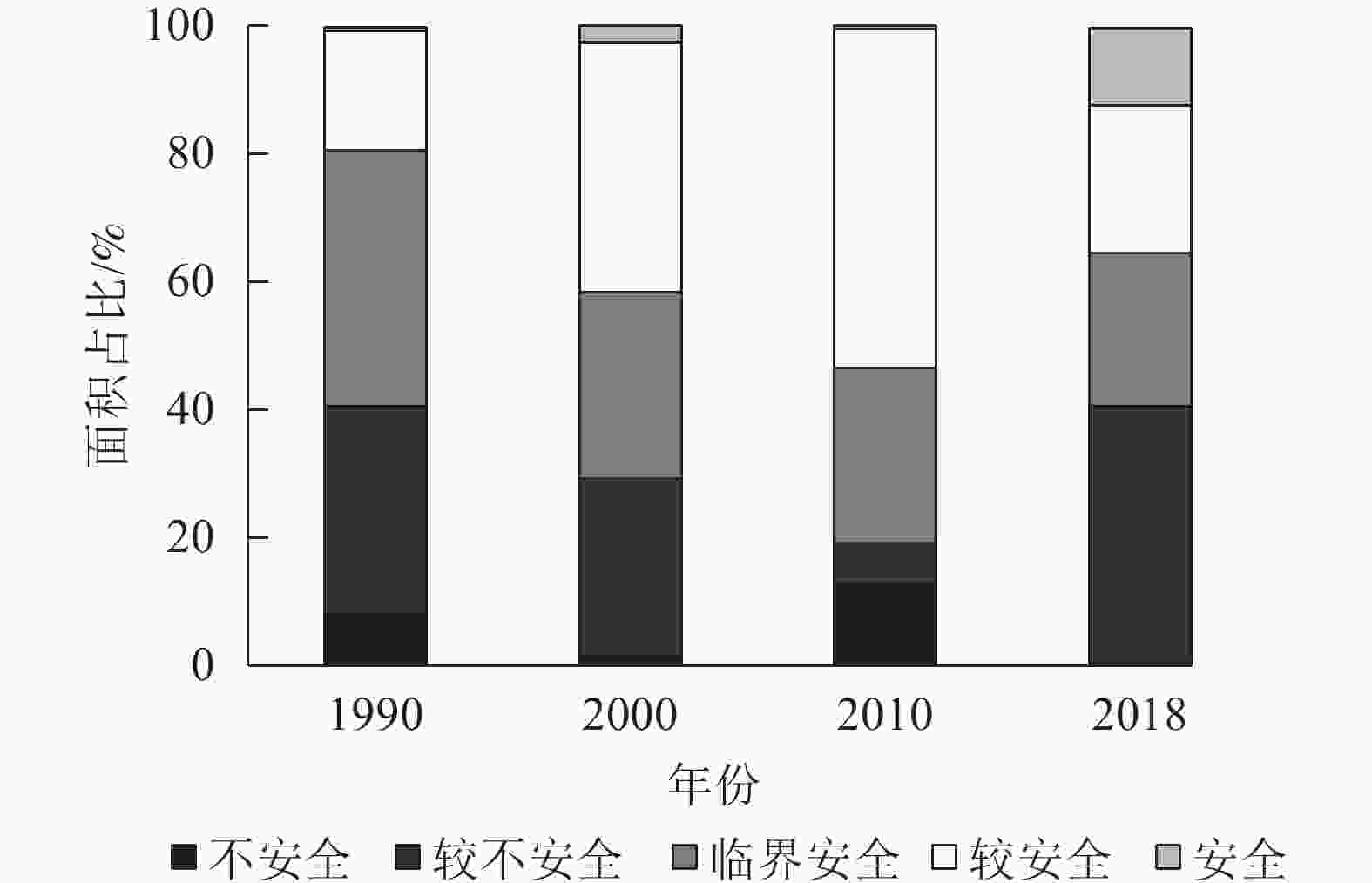
从时间序列上看,1990—2000年研究区处于较安全级的面积增加,临界安全及以上的面积占70%,这说明1990—2000年天山-帕米尔地区生态安全状况在改善;至2010年临界安全及以上的面积占比达80%,处于较安全等级的面积增加约1.5倍,生态环境质量改善尤为明显;2010—2018年安全级面积增加,但较不安全级的面积呈明显的增加趋势,表明2010—2018年生态环境有恶化的趋势(图2)。28 a间,天山-帕米尔地区生态安全的临界安全级及以上的安全级面积占比始终在60%以上,表明生态安全状况总体上处于安全状态,但城市化、工业化、绿洲扩张以及旅游业的发展等行为给生态环境带来的压力不可避免,也存在一些生态破坏的现象。
-
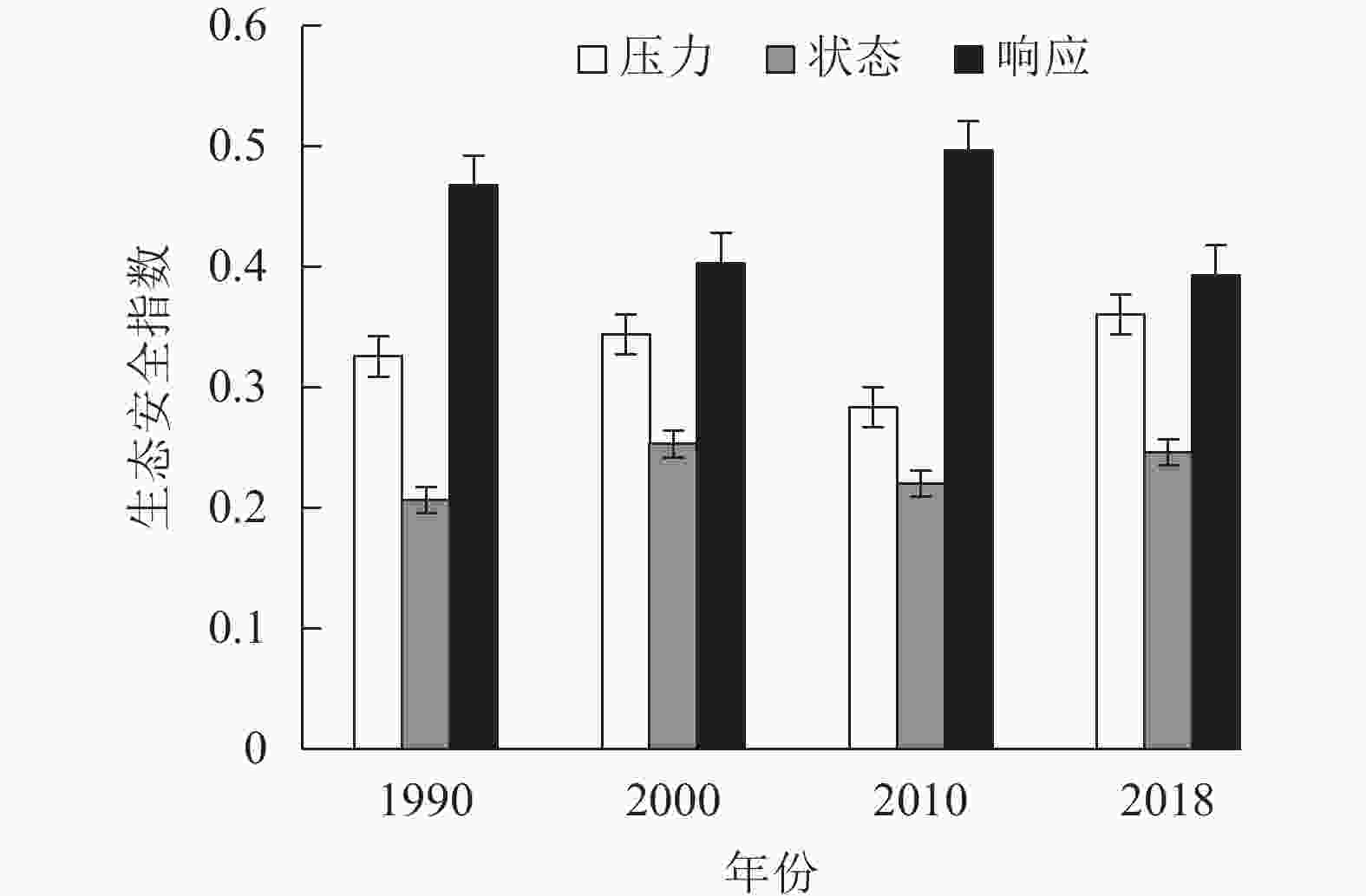
天山-帕米尔地区总体区域生态安全处于临界安全以及较安全状态,全区域平均生态安全综合值变化可分为2个阶段(表3):第1阶段为1990—2010年,区域平均生态安全综合值上升;第2阶段为2010年以后,全区域平均生态安全综合值略微下降。整体来看,从1990—2018年,天山-帕米尔地区总体区域生态安全呈缓慢上升趋势。
表 3 天山-帕米尔地区生态安全综合指数描述性统计
Table 3. Descriptive statistics of ecological security index in Tianshan-Pamir region
年份 生态安全综合指数 变异系数/% 平均值 最小值 最大值 标准差 1990 0.275 0.171 0.712 0.091 33.14 2000 0.277 0.140 0.523 0.095 34.34 2010 0.307 0.151 0.507 0.083 26.84 2018 0.297 0.165 0.529 0.094 31.82 从3个子系统来说,对区域生态安全的贡献具有明显的规律性,从大到小依次为响应、压力、状态(图3)。1990—2018年,生态安全压力指数呈现出上升—下降—上升的波动变化特征,说明人类活动对生态安全的压力有所上升,经济社会发展的同时忽略了环境保护与治理;生态安全状态指数的变化趋势与生态安全压力指数相似,但状态指数的变化相较于压力指数的变化则相对稳定,表明天山-帕米尔地区生态环境状态对压力的变化反映敏感;而生态安全响应指数则呈现出下降—上升—下降的变化特征,这与国家和地方政府增加了产业结构调整和生态环境保护力度有关。
-
天山-帕米尔地区生态安全在空间上呈现不同的表现力,为进一步探究其影响因素,采用地理探测器来识别关键影响因子[30]。选取q>0.2的因素作为主导影响因子,得到天山-帕米尔地区生态安全q变化(表4)。结果显示:国内游客数量增长率、人均水资源量、原煤消耗、旅游收入占GDP比例、拥有卫生技术人员数等5个因子对天山-帕米尔地区生态安全的影响较为稳定,这与天山-帕米尔地区旅游业的兴起、工业的发展以及社会人文条件的改善有关。对天山-帕米尔地区生态安全变化产生影响的因子中,压力层占3个,状态层占3个,响应层占4个,表明社会响应对生态安全的影响较大,且对生态安全的提高也最为重要,因此,要更加重视响应反映的速度以及响应建设的牢固程度,这对天山-帕米尔地区生态安全的提升将起到重要的作用。
表 4 不同年份主要影响因子探测结果
Table 4. Detection results of main influencing factors in different years
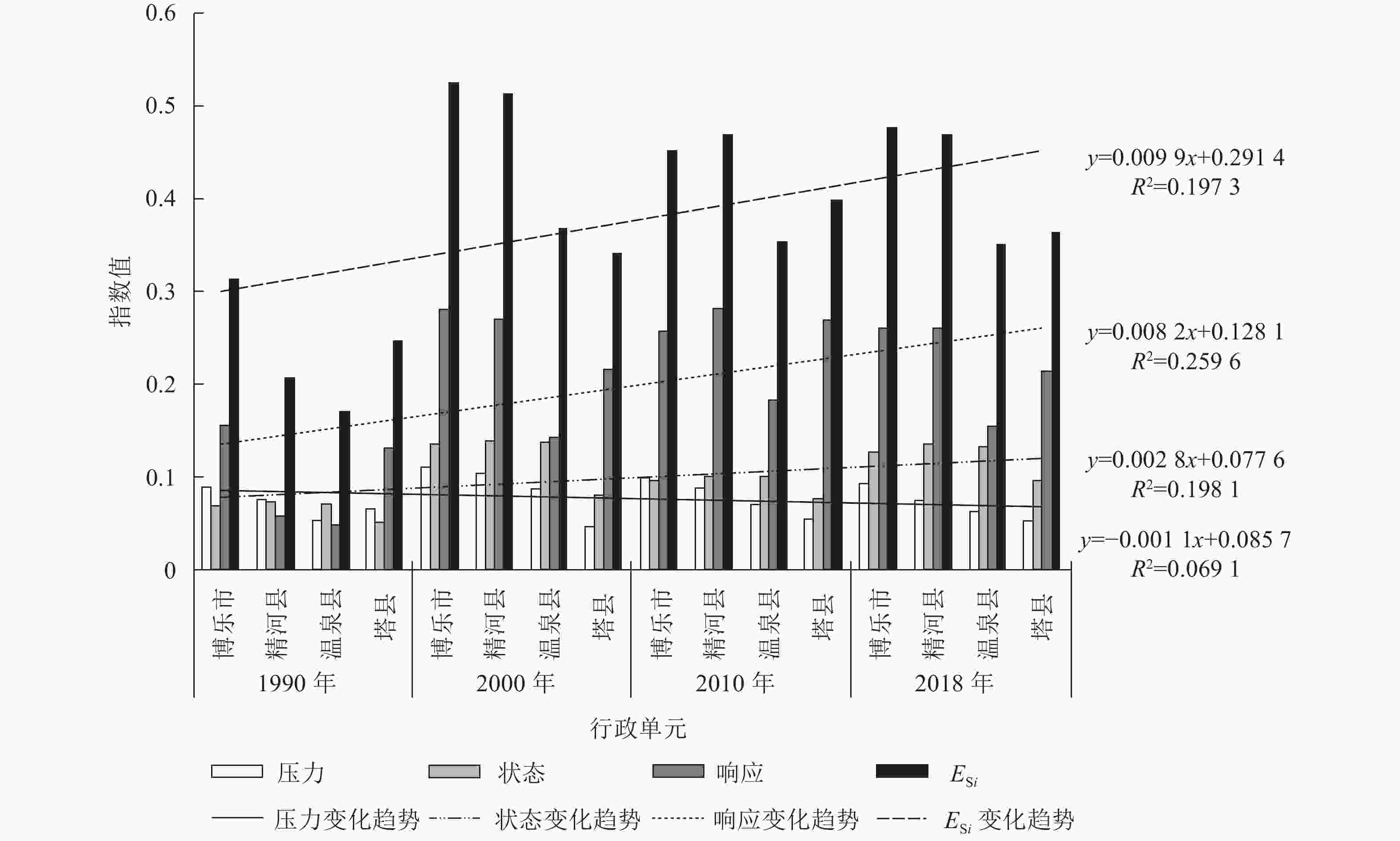
影响因子 (X) q (Y) 1990年 2000年 2010年 2018年 国内游客数量增长率 0.29 0.46 0.47 0.50 人均GDP − − 0.24 − 湿地覆盖率 0.45 0.23 − 0.22 人均水资源量 0.28 0.45 0.42 0.50 原煤消耗 0.29 0.46 0.47 0.51 旅行社数量增长率 − 0.26 − 0.34 旅游收入占GDP比例 0.29 0.46 0.467 0.51 第三产业占GDP比例 − 0.20 − − 拥有卫生技术人员数 0.29 0.47 0.48 0.51 自然保护区数量 − − − 0.66 说明:−表示q<0.20 天山-帕米尔地区生态环境的变化是自然和人为因子相互作用的结果,这与前人的研究结论一致[31−32]。其中研究区内的博乐市、精河县、温泉县、塔什库尔干塔吉克自治县(以下简称“塔县”)作为中国新疆干旱区的典型代表城市,生态系统具有脆弱性和敏感性。但在1990—2018年,这些市(县)的生态安全状况都发生了较大转变(图4),其中博乐市、精河县、温泉县、塔县生态安全状态全部呈现上升趋势,生态安全状态改善显著。从3个子系统变化趋势来看,对生态安全的贡献从大到小依次为响应、状态、压力,与全区域的趋势有所不同。2000年以来,在国家政策方针的指引以及生态文明建设的大力推进下,对环境、医疗卫生、水利工程等投入开始增加,城镇化水平不断提高,第三产业占比逐步提高,自然保护区数量增加,管理力度加强,响应能力的提高缓解了人类活动对环境的压力,从而提高了生态安全等级。
-
本研究显示:不同行政单元间生态安全等级在空间上的表现差异较大,但由于天山-帕米尔地区的地形地貌并未发生大尺度的变化,因此地区生态安全的分布格局并没有发生明显变化。从时间序列上看,天山-帕米尔地区生态安全的临界安全级及以上的面积占比始终在60%以上,表明生态安全总体上处于安全状态;从生态安全指数动态变化分析来看,1990—2018年天山-帕米尔地区区域生态安全总体呈缓慢上升趋势。基于地理探测器方法的分析结果显示:天山-帕米尔地区生态安全在空间上呈现不同的表现力,国内游客数量增长率、人均水资源量、原煤消耗、旅游收入占GDP比例、拥有卫生技术人员数等5个因子对天山-帕米尔地区生态安全的影响较为稳定,主要受到天山-帕米尔地区旅游业的兴起、工业的发展以及社会人文条件的改善等影响。
-
1990—2018年,天山-帕米尔地区生态安全总体上处于安全状态,且呈缓慢上升趋势。为进一步提升天山-帕米尔地区的生态安全,构建生态文明理念下的生态安全格局,要结合当前生态文明建设进程及区域生态与资源本底状况,应继续深入贯彻落实“绿水青山就是金山银山”的理念,在水资源利用红线、生态环境红线等“无形之手”和国家土地政策“有形之手”的共同作用下,维持耕地扩张在可控范围[15−16];加强统筹山水林田湖草沙系统治理,推进以国家公园为主体的自然保护地体系建设[19];合理有序发展区域内旅游业,完善相关的政策法规,减轻因旅游业发展而带来的生态压力;建立生态环境监测体系,对工业排放的废弃物等进行实时监测和定期评价;加大生态环保的投资力度,引导资源型城市的转型,以绿色、可持续发展产业代替[18];将生态文明建设的理念融入经济建设、文化建设和社会建设中,实现天山-帕米尔地区的可持续发展。
Spatio-temporal evolution of ecological security pattern and its influencing factors in Tianshan-Pamir region
-
摘要:
目的 天山-帕米尔地区以其独特的地理位置和丰富多样的生态系统,在中国生态安全方面发挥着重要的屏障作用,但近30 a来区域经济和生态环境发生了很大变化,开展基于自然及人为压力状态下天山-帕米尔地区生态安全格局时空演变及其影响因素研究,为区域生态保护、生态建设以及协同发展提供科学依据。 方法 以天山-帕米尔地区作为研究区,运用压力-状态-响应(PSR)模型以及地理探测器方法,选取20个关键指标,对天山-帕米尔地区1990—2018年的生态安全及其影响因素进行分析。 结果 天山-帕米尔地区区域生态安全的分布格局并没有发生显著变化,但不同市(县)的生态安全等级差异较大;1990—2018年天山-帕米尔地区生态安全处于Ⅲ级及以上的面积占比始终在60%及以上,2010年达80%,区域生态环境改善显著;其中有5个因子对天山-帕米尔地区生态安全的影响较为稳定,其他各因子的影响各有差异;3个子系统影响从大到小依次为响应、压力、状态,状态指数和压力指数变化趋势相似。 结论 天山-帕米尔地区生态安全状况逐步向好,但也存在一些生态破坏的现象。其中博乐市、精河县、温泉县、塔什库尔干塔吉克自治县生态安全状态改善显著,响应能力的提高对缓解生态压力具有较大贡献。图4表4参32 Abstract:Objective Tianshan-Pamir region, with its unique geographical location and rich and diverse ecosystems, plays an important role as a barrier to China’s ecological security. However, great changes had taken place in the regional economy and ecological environment in the past 30 years, and it is urgent to carry out research on the spatiotemporal evolution of ecological security pattern and its influencing factors in Tianshan-Pamir region under natural and human pressure. Method Taking Tianshan-Pamir region as the study area, 20 key indicators were selected to analyze the ecological security and its influencing factors in the region from 1990 to 2018 by using the pressure-state-response (PSR) model and geographical detector method. Result The distribution pattern of regional ecological security in this region did not change significantly, but the ecological security levels of different cities and counties varied greatly. From 1990 to 2018, the area with ecological security of level Ⅲ or above accounted for 60% or more and reached 80% in 2010, indicating significant improvement of regional ecological environment. 5 factors among them had a relatively stable impact on the ecological security of the region, while other factors had different impacts. The influence of the 3 subsystems from large to small was response, pressure and state, and the change trend of state index and pressure index was similar. Conclusion The ecological security in Tianshan-Pamir region is gradually improving, but there are still some damage phenomena. Among them, Bole City, Jinghe County, Wenquan County, and Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County have significantly improved their ecological security status, and the improvement of response capacity has a great contribution to alleviating ecological pressure. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 32 ref.] -
Key words:
- ecological security /
- PSR model /
- geographic detector /
- Tianshan-Pamir region
-
表 1 天山-帕米尔地区生态安全评价体系
Table 1. Evaluation system of ecological security in Tianshan-Pamir region
目标层 准则层 要素层 指标层 指标属性 生态安全综合指数 压力(P) 社会经济压力 人口密度/(人·km−2) 负 人口自然增长率/% 负 人均国内生产总值(GDP)/元 负 国内游客数量增长率/% 负 资源环境压力 单位耕地化肥使用量/(t·hm−2) 负 单位面积废水排放量/(t·km−2) 负 湿地覆盖率/% 正 状态(S) 社会经济状态 区域开发指数/% 负 经济密度/(万元·km−2) 负 旅行社数量增长率/个 负 资源环境状态 草地覆盖率/% 正 森林覆盖率/% 正 原煤消耗/(t·万元−1) 负 人均水资源量/(m3·人−1) 正 响应(R) 社会经济响应 旅游收入占GDP比例/% 负 第三产业占GDP比例/% 正 城镇化水平/% 负 拥有卫生技术人员/人 正 资源环境响应 单位面积环保投入/(万元·km−2) 正 自然保护区数量/个 正 表 2 天山-帕米尔地区生态安全分级标准
Table 2. Classification standard of ecological security in Tianshan-Pamir region
等级 安全等级 生态安全综合指数 生态安全特征描述 Ⅰ 不安全 [0.00~0.19) 压力极大,环境极差,存在严重生态环境问题 Ⅱ 较不安全 [0.19~0.23) 压力较大,环境较差,生态环境处于不稳定状态 Ⅲ 临界安全 [0.23~0.31) 压力接近阈值,环境一般,能发挥基本生态系统功能 Ⅳ 较安全 [0.31~0.49) 压力较小,环境较好,但仍存在部分限制性因素 Ⅴ 安全 [0.49~0.72) 压力很小,环境优越,生态系统功能、结构完善 表 3 天山-帕米尔地区生态安全综合指数描述性统计
Table 3. Descriptive statistics of ecological security index in Tianshan-Pamir region
年份 生态安全综合指数 变异系数/% 平均值 最小值 最大值 标准差 1990 0.275 0.171 0.712 0.091 33.14 2000 0.277 0.140 0.523 0.095 34.34 2010 0.307 0.151 0.507 0.083 26.84 2018 0.297 0.165 0.529 0.094 31.82 表 4 不同年份主要影响因子探测结果
Table 4. Detection results of main influencing factors in different years
影响因子 (X) q (Y) 1990年 2000年 2010年 2018年 国内游客数量增长率 0.29 0.46 0.47 0.50 人均GDP − − 0.24 − 湿地覆盖率 0.45 0.23 − 0.22 人均水资源量 0.28 0.45 0.42 0.50 原煤消耗 0.29 0.46 0.47 0.51 旅行社数量增长率 − 0.26 − 0.34 旅游收入占GDP比例 0.29 0.46 0.467 0.51 第三产业占GDP比例 − 0.20 − − 拥有卫生技术人员数 0.29 0.47 0.48 0.51 自然保护区数量 − − − 0.66 说明:−表示q<0.20 -
[1] 冯琰玮, 甄江红, 马晨阳. 内蒙古生态承载力评价及生态安全格局优化[J]. 地理研究, 2021, 40(4): 1096 − 1110. FENG Yanwei, ZHEN Jianghong, MA Chenyang. Evaluation of ecological carrying capacity and optimization of ecological security pattern in Inner Mongolia [J]. Geographical Research, 2021, 40(4): 1096 − 1110. [2] 肖笃宁, 陈文波, 郭福良. 论生态安全的基本概念和研究内容[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(3): 354 − 358. XIAO Duning, CHEN Wenbo, GUO Fuliang. On the basic concepts contents of ecological security [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(3): 354 − 358. [3] 崔杨林, 高祥, 董斌, 等. 县域景观生态风险评价[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(3): 541 − 551. CUI Yanglin, GAO Xiang, DONG Bin, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment of county [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2021, 38(3): 541 − 551. [4] GAO Sheng, SUN Huihui, ZHAO Lin, et al. Dynamic assessment of island ecological environment sustainability under urbanization based on rough set, synthetic index and catastrophe progression analysis theories [J/OL]. Ocean and Coastal Management, 2019, 178: 104790[2022-06-28]. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2019.04.017. [5] SONG Guoba, CHEN Yu, TIAN Meirong, et al. The ecological vulnerability evaluation in southwestern mountain region of China based on GIS and AHP method [J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2010, 2: 465 − 475. [6] 徐涵秋. 城市遥感生态指数的创建及其应用[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(24): 7853 − 7862. XU Hanqiu. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(24): 7853 − 7862. [7] WANG Qiang, LI Siqi, LI Rongrong. Evaluating water resource sustainability in Beijing, China: combining PSR model and matter-element extension method [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 206: 171 − 179. [8] BAI Xiaorui, TANG Jingchun. Ecological security assessment of Tianjin by PSR model [J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2010, 2: 881 − 887. [9] RUAN Wenqi, LI Yongquan, ZHANG Shuning, et al. Evaluation and drive mechanism of tourism ecological security based on the DPSIR-DEA model [J]. Tourism Management, 2019, 75: 609 − 625. [10] 王晶, 原伟鹏, 刘新平. 哈尔滨城市土地生态安全时序评价及预测分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2018, 41(4): 885 − 892. WANG Jing, YUAB Weipeng, LIU Xinping. Time series evaluation and prediction analysis of urban land ecological security in Harbin City [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2018, 41(4): 885 − 892. [11] 汤旭, 郑洁, 冯彦, 等. 云南省县域森林生态安全评价与空间分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2018, 35(4): 684 − 694. TANG Xu, ZHENG Jie, FENG Yan, et al. Country-level forest ecological security evaluation and spatial analysis in Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2018, 35(4): 684 − 694. [12] HAN Baolong, LIU Hongxiao, WANG Rusong. Urban ecological security assessment for cities in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan region based on fuzzy and entropy methods [J]. Ecological Modelling, 2015, 318(24): 217 − 225. [13] SUN Tengteng, LIN Wenpeng, CHEN Guangsheng, et al. Wetland ecosystem health assessment through integratingremote sensing and inventory data with an assessment model for the Hangzhou Bay [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 566/567: 627 − 640. [14] LIU Delin, HAO Shilong. Ecosystem health assessment at county-scale using the pressure-state-response framework on the Loess Plateau, China [J/OL]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14: 2[2022-07-01]. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14010002. [15] 李琛, 高彬嫔, 吴映梅, 等. 基于PLUS模型的山区城镇景观生态风险动态模拟[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(1): 84 − 94. LI Chen, GAO Binpin, WU Yingmei, et al. Dynamic simulation of landscape ecological risk in mountain towns based on PLUS model [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2022, 39(1): 84 − 94. [16] 于贵瑞, 杨萌, 陈智, 等. 大尺度区域生态环境治理及国家生态安全格局构建的技术途径和战略布局[J]. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(4): 1141 − 1153. YU Guirui, YANG Meng, CHEN Zhi, et al. Technical approach and strategic plan for large-scale ecological and environmental governance and national ecological security pattern construction [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(4): 1141 − 1153. [17] 艾克旦·依萨克, 满苏尔·沙比提, 阿曼妮萨·库尔班, 等. 阿克苏河流域绿洲生态安全评价及影响因子分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(7): 217 − 223. Akida Essak, Mansur Sabit, Amannisa Kurban, et al. Ecological security evaluation and impact factor analysis of oasis in Aksu River Basin [J]. Environmental Science &Technology, 2020, 43(7): 217 − 223. [18] 王昌博, 李爱农, 张晓荣, 等. 基于遥感和GIS的中巴经济走廊多发展情景生态风险综合评价[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2021, 36(1): 65 − 78. WANG Changbo, LI Ainong, ZHANG Xiaorong, et al. Comprehensive assessment of ecological risk in multi-scenarios of China-Pakistan economic corridor based on RS and GIS [J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2021, 36(1): 65 − 78. [19] 田浩, 刘琳, 张正勇, 等. 天山北坡经济带关键性生态空间评价研究[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(1): 401 − 414. TIAN Hao, LIU Lin, ZHANG Zhengyong, et al. Evaluation on the critical ecological space of the economic belt of Tianshan northslope [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(1): 401 − 414. [20] 李鹏辉, 徐丽萍, 刘笑, 等. 基于三维生态足迹模型的天山北麓绿洲生态安全评价[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(5): 1337 − 1345. LI Penghui, XU Liping, LIU Xiao, et al. Ecological security evaluation of an oasis in the north of the Tianshan Mountains based on three-dimensional ecological footprint model [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(5): 1337 − 1345. [21] 张磊, 吴炳方, 李晓松, 等. 基于碳收支的中国土地覆被分类系统[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(24): 7158 − 7166. ZHANG Lei, WU Bingfang, LI Xiaosong, et al. Classification system of China land cover for carbon budget [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(24): 7158 − 7166. [22] 徐浩田, 周林飞, 成遣. 基于PSR模型的凌河口湿地生态系统健康评价与预警研究[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(24): 8264 − 8274. XU Haotian, ZHOU Linfei, CHENG Qian. Study on ecosystem health evaluation and risk assessment for Linghekou wetlands based on a PSR model [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(24): 8264 − 8274. [23] CHEN Yun, WANG Jinliang. Ecological security early-warning in central Yunnan Province, China, based on the gray model [J/OL]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 111: 106000[2022-07-02]. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.106000. [24] HU Mengmeng, LI Zhaotian, YUAN Mengjiao, et al. Spatial differentiation of ecological security and differentiated management of ecological conservation in the Pearl River Delta, China [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 104: 439 − 448. [25] 李建春, 袁文华. 基于GIS格网模型的银川市土地生态安全评价研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2017, 32(6): 988 − 1001. LI Jianchun, YUAN Wenhua. Assessment of urban land ecological security in Yinchuan city based on the Grid method [J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2017, 32(6): 988 − 1001. [26] 田璐, 邱思静, 彭建, 等. 基于PSR框架的内蒙古自治区沙漠化敏感性评估[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(12): 1682 − 1692. TIAN Lu, QIU Sijing, PENG Jian, et al. Desertification sensitivity evaluation in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region based on PSR framework [J]. Progress in Geography, 2018, 37(12): 1682 − 1692. [27] 王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1): 116 − 134. WANG Jinfeng, XU Chengdong. Geodetector: principle and prospective [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(1): 116 − 134. [28] 黄木易, 方斌, 岳文泽, 等. 近20 a来巢湖流域生态服务价值空间分异机制的地理探测[J]. 地理研究, 2019, 38(11): 2790 − 2803. HUANG Muyi, FANG Bin, YUE Wenze, et al. Spatial differentiation of ecosystem service values and its geographical detection in Chaohu Basin during 1995−2017 [J]. Geographical Research, 2019, 38(11): 2790 − 2803. [29] WANG Haiying, QIN Fen, XU Chengdong, et al. Evaluating the suitability of urban development land with a Geodetector [J/OL]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 123: 107339[2022-07-05]. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107339. [30] MA Rui, LIANG Lizhong, KONG Yunfeng, et al. Hotspot detection and socio-ecological factor analysis of asthma hospitalization rate in Guangxi, China [J/OL]. Environmental Research, 2020, 183: 109201[2022-07-05]. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109201. [31] 袁烨城, 刘海江, 李宝林, 等. 2000—2010年新疆陆地生态系统变化格局与分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2015, 17(3): 300 − 308. YUAN Yecheng, LIU Haijiang, LI Baolin, et al. Study on the change of ecosystem in Xinjiang from 2000 to 2010 [J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2015, 17(3): 300 − 308. [32] 宋文杰, 张清, 刘莎莎, 等. 基于LUCC的干旱区人为干扰与生态安全分析——以天山北坡经济带绿洲为例[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018, 35(1): 235 − 242. SONG Wenjie, ZHANG Qing, LIU Shasha, et al. LUCC-based human disturbance and ecological security in arid area: a case study in the economic zone on northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2018, 35(1): 235 − 242. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220458






 下载:
下载: