-
火是生态系统中重要的干扰因子之一,具有双重性,它虽然会威胁森林及其周边生态安全,但也能给森林带来益处[1−2]。周期性低强度计划烧除不仅能预防森林大火,还能促进森林生态系统的物质交换和能量交换,是科学预防森林火灾的重要手段[3]。计划烧除能经济有效、快捷方便地清除林地危险可燃物(枯草、凋落物及半分解物),能有效降低森林燃烧性,也能为林分更新提供有利条件[1]。FINNEY等[4]分析了 2002 年2起发生在美国亚利桑那州的森林火灾卫星图像和计划烧除记录,表明计划烧除可有效降低火灾的严重程度。SCHMIDT等[5]指出:在针阔混交林中运用计划烧除可以显著减少可燃物的积累。森林资源丰富的国家,如美国、加拿大、澳大利亚等广泛开展计划烧除,这些实践工作证明:开展大面积计划烧除是成效最显著的措施[6−9]。中国内蒙古地区从1980年起开始施行林冠下计划烧除[10]。1988年起,马志贵等[11]在四川省攀西地区开展了云南松Pinus yunnanensis计划烧除试验研究和技术推广工作,效果显著。王秋华等[12]认为:滇中地区云南松林对周期性的火产生了一定的适应性,能够开展周期性的计划火烧。戚书玮等[13]发现:计划烧除前后云南松生物量的重要值等无显著差异,表明在该地区计划烧除对云南松生长影响很小。杨馥羽等[14]研究发现:高频率、低强度的计划火烧使土壤表层抗水蚀能力下降,但对深层土壤基本无影响。马志贵等[15]对计划烧除引起的水土流失进行了定量研究,发现计划烧除林地的土壤侵蚀量远低于国家规定的最低允许流失量(200 t·km−2·a−1)。计划烧除的目的就是干扰或阻断林火发生或蔓延条件[16−17],以小火防大火,由被动防火转为主动防火[18]。计划烧除的开展时间一般选在森林防火期的初期,此时细小可燃物很干燥,但粗大可燃物含水率仍较高, 能够控制住火势[19]。
云南松是中国西南林区的主要用材树种,大多分布于山区。云南松分布区气候主要受高空西风环流、西南印度洋季风和东南太平洋季风等3种气流所控制,立体气候特征明显,是西南林区火灾多发区[20]。本研究以云南省玉溪市新平县照壁山云南松林为研究对象,进行了连续6 a (2017—2022年,其中2020和2021年由于政策原因,云南全省未开展计划烧除)的定位、跟踪研究,开展云南松林计划烧除火烧试验,测定云南松林地表可燃物燃烧火行为特征,对火蔓延速度、火线强度和火焰高度等进行相关性分析,评估烧除迹地的烧除效果,以期为滇中云南松林地表可燃物综合调控和管理提供依据。
-
研究区位于云南省玉溪市新平县(23°38′15″~24°26′05″N,101°16′30″~102°16′50″E)。县域地势西北高、东南低,局部为深谷,最高海拔为3 165.9 m,最低海拔为422.0 m。土壤类型以红壤和赤红壤为主。林地和农田为县域内主要的土地利用方式,草地次之[21]。县域内立体气候明显,年最高气温为32.8 ℃,年最低气温为1.3 ℃,年平均气温为18.0 ℃,年降水量为869.0 mm,年日照时数为2 838.0 h,无霜期为316.0 d。全县天然林面积为21.9万hm2,蓄积量为1 898.0万m3,人工林(含飞播林)面积为9.6万hm2,蓄积量为531.0万m3,飞播林结构与树种组成较为简单,多为云南松[22−23]。由于云南松针叶、小枝条和树皮油脂含量高、易燃,因此云南松林属于易燃林分类型,但树皮较厚,具有一定的耐火和抗火能力[24]。该县已经对云南松林开展了近20 a的计划烧除,很少跑火。
-
2022年1月11—14日在新平县照壁山云南松林连续分布区,沿海拔每隔10 m平行设置3~5个20 m×20 m的样地,每个样地内梅花状布置5个1 m×1 m的小样方,合计10个样地,50个样方。记录每个样地内的经纬度、坡度、坡向、坡位和郁闭度等信息,对胸径≥2 cm的乔木进行每木检尺并测量树高和枝下高。采用全收获法收获每个小样方内的松针凋落物、草本凋落物和枯死的蕨类,称其质量。所选样地均位于阳坡中上坡位,坡度为15°~25°。根据地表可燃物类型的不同,将地表细小可燃物主要是蕨类和松针的云南松林称为蕨类云南松林,将地表细小可燃物主要是禾本科Gramineae草类和松针的云南松林称为禾本云南松林。
-
云南省的森林防火期为每年12月1日到第2年的6月15日,防火紧要期为每年3—4月。2022年2月12日下午本次计划烧除在1月所设样地内开始。气象观测:计划烧除前、烧除过程中用手持气象仪现场观测气温、相对湿度等气象参数。点烧方法:以现有防火道路为依托,使用风力灭火机把道路上的凋落物吹到山下一侧,形成良好的防火隔离带。沿着防火隔离带,用滴油式点火器点下山火。火中观测:沿着火线蔓延方向,当燃烧相对稳定时,测量火焰高度、温度和蔓延速度。①火焰高度的测量。当样方过火时,用钢卷尺测定4个顶点和对角线交叉点共5个位置的火焰高度,取平均值。②火焰温度的测量。用手持式非接触红外线测温仪(DTM-T1)对样方若干点进行测量,取平均值。③火蔓延速度的测量。采用线速度方法测定火头在小样方内蔓延1 m所需时间,每个样方设置3组计时点,取平均值。火后评估:计划烧除结束后第2天测定火烧后样地内可燃物载量与分布特征,调查火烧迹地花脸率。采集样方内可燃物样本带回实验室测定热值,每组测3次,最终取固定值20 MJ·kg−1为计划烧除地表凋落物的热值。
火线强度(I)计算公式(即拜拉姆公式): I=0.007HWR。其中:I为火线强度(kW·m−1);H为热值(J·g−1);W为有效可燃物载量(t·hm−2);R为蔓延速度(m·min−1)。采用上式得到的火线强度为潜在最大值。烧除率(R)计算公式:R=(W0−W1)/W0×100%。其中:W0为烧除前可燃物载量(t·hm−2);W1为烧除后可燃物载量(t·hm−2)。花脸率(r)计算公式:r=(A1/A0)×100%。其中:A0为计划烧除面积(m2);A1为未过火面积(m2)。
-
用Excel 2018进行数据汇总、整理和初步分析,用Origin 2018绘图,用SPSS 18.0对云南松林地表可燃物燃烧特征进行方差分析。
-
滇中高原的云南松林是季风常绿阔叶林被破坏后所形成的次生林,新平县照壁山云南松林为20世纪80年代飞播造林后自然生长形成的半天然林[25]。经过30余a的人工抚育和自然稀疏,研究区的云南松林分结构稳定,蕨类云南松林和禾本云南松林受海拔影响,林分特征差异如表1所示。云南松林为中龄林,上层林木郁闭度为0.6,枝下高度平均大于7 m。缺乏梯状可燃物,低强度地表火难以形成树冠火。云南松林地表可燃物含水率为12%,地表可燃物载量平均为0.68 kg·m–2(6.8 t·hm−2)。有研究表明[1, 26]:当直径<7.6 cm的可燃物少于10 t·hm−2时,应在含水率为10%~12%时点烧。对2组样地的林分特征进行成对t检验表明:2种可燃物类型的林分特征无显著差异,长势较一致。
表 1 不同可燃物类型云南松林林分特征
Table 1. Stand characteristics of P. yunnanensis forest of different fuel types
可燃物类型 坡度/(°) 郁闭度 密度/(株·hm−2) 树高/m 枝下高/m 胸径/cm 含水率/% 载量/(kg·m−2) 蕨类云南松林 17 0.60 1 240±473 a 11.5±1.6 a 7.9±1.0 a 14.5±3.1 a 11.99 a 0.67±0.14 a 禾本云南松林 14 0.55 1 152±436 a 12.1±1.6 a 8.5±1.4 a 17.1±3.8 a 12.06 a 0.69±0.19 a 说明:数据为平均值±标准差。同列不同小写字母表示不同可燃物类型间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
已有研究表明[27]:实行计划烧除的最佳气象因素指标为风速<6.0 m·s−1,空气湿度为30%~50%,气温为−5.0~10.0 ℃,可燃物含水率为7%~20%,大气气团应相对稳定。由于地表可燃物燃烧释放出大量热量,需随时记录气象数据有助于提前部署扑救力量,防止跑火。本次计划烧除的气象条件为多云天气,气温为14.0~16.0 ℃,相对湿度为40%~45%,林缘平均风速为0.5 m·s−1,阵风最高风速为1.2 m·s−1。各项技术指标符合《云南省森林防火计划烧除规程》和《云南松林计划烧除技术规范》。为了随时准确地把握林地气象因子的变化情况,隔30 min测定气温、相对湿度和风速(表2)。计划烧除开始后,林内气温明显升高,最高达24.0 ℃,比林外高3.5~6.0 ℃。
表 2 计划烧除时云南松林内气象概况
Table 2. Weather conditions in P. yunnanensis forest during prescribed burning
时段 风速/(m·s−1) 气温/℃ 相对湿度/% 11:00—12:00 0.5~0.8 14.0~16.0 38~42 12:00—13:00 0.8~1.5 16.0~19.0 33~36 13:00—14:00 1.7~2.4 17.0~22.0 30~34 14:00—15:00 2.0~3.2 18.0~24.0 29~33 15:00—16:00 2.2~2.8 17.0~20.0 32~38 -
计划烧除在阳坡实施,试验样地选取在靠近防火隔离带的安全位置。由表3可知:蕨类云南松林地表可燃物燃烧时的火焰高度为(80.20±7.50) cm,是禾本云南松林地表可燃物火焰高度的2倍,两者差异显著(P<0.05)。由于蕨类植物株高较高,平均高度达0.6 m,且冬天枯死后立于地表不倒伏,因此在蕨类云南松林地表可燃物进行计划烧除时火焰高度最高可达0.9 m。可燃物的高度对于火烧类型从地表火向树冠火过渡起决定性作用[28]。一般而言,安全用火的平均火焰高度不得高于1.5 m,在此标准内执行火烧,扑火队员可利用扑火机具(如风力灭火机和背负式水枪)控制火场。
表 3 云南松林计划烧除火行为参数
Table 3. Fire behavior characteristics of prescribed burning in P. yunnanensis forest
可燃物类型 火焰高
度/cm火焰温
度/℃火焰蔓延速度/
(m·min−1)火线强度/
(kW·m−1)蕨类云南松林 80.20±7.50 a 513±65 a 0.25±0.04 a 262±70 a 禾本云南松林 43.40±5.94 b 463±77 a 0.17±0.03 b 188±41 b 说明:数据为平均值±标准差。同列不同小写字母表示不同可燃物类型间差异显著(P<0.05)。 2种不同可燃物类型的火焰温度相差不大,温差保持在10%以内,原因是2种地表可燃物均以松针凋落物为主,蕨类云南松林燃烧时的温度略高于禾本云南松林燃烧,但无显著差异。
火场立地条件影响林火蔓延速度,林火蔓延是由一个封闭曲线扩增成另一个封闭曲线的过程,坡度越陡,林火蔓延的速度越快[29−30]。结合表1和表3可知:蕨类云南松林所在坡度较大,其火线蔓延速度较禾本云南松林快30%。本研究采用下山火点烧技术,林火种类为稳进地表火(蔓延速度<4 km·h−1),可明显降低林火蔓延速度,保证用火安全[31]。
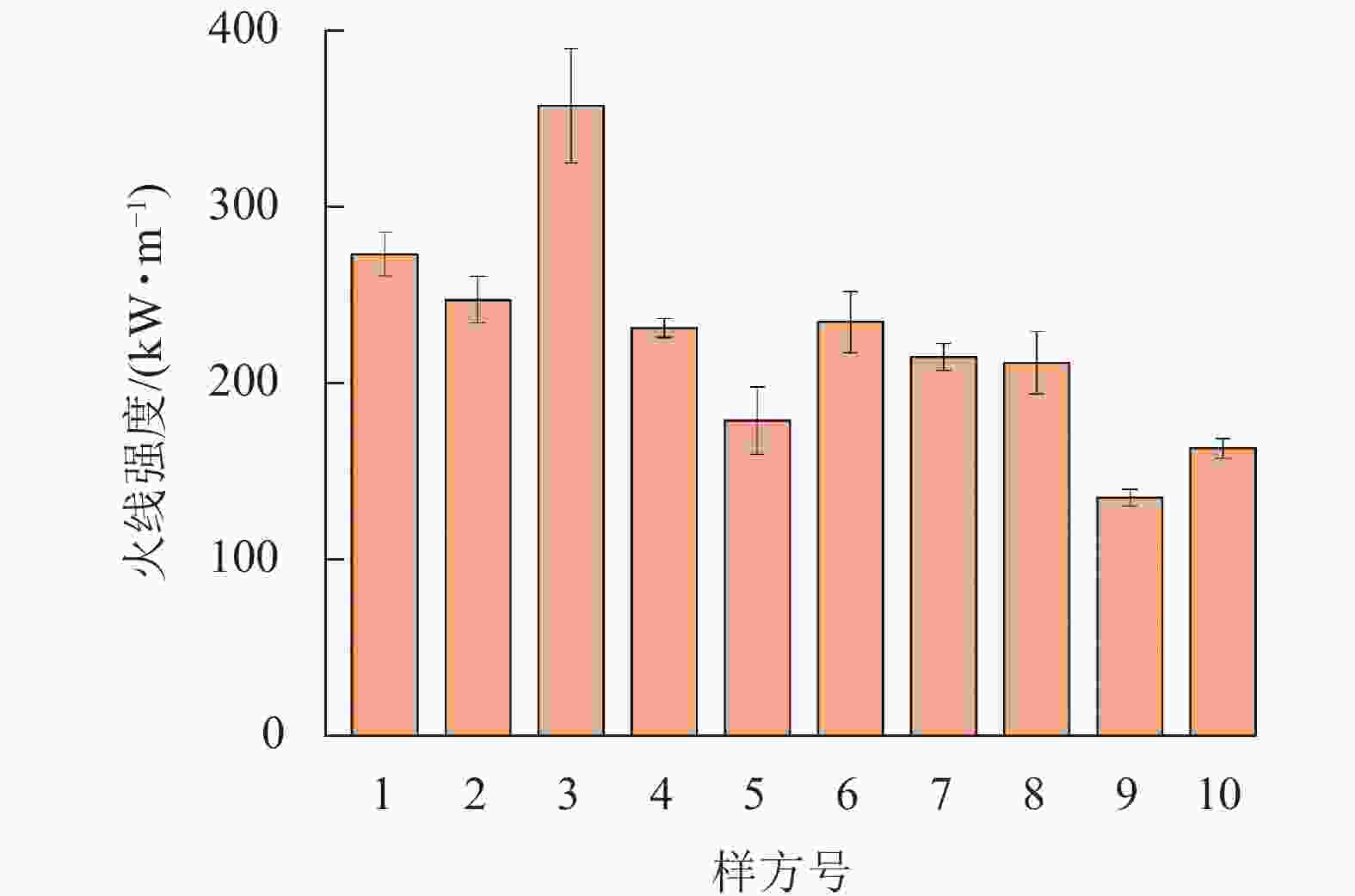
人工灭火的火强度上限为1 000 kW·m−1,通常不能超过中等强度[32−33]。由图1可以看出:试验样地的火线强度均小于750 kW·m−1,是低强度火。火线强度的大小与可燃物载量、气象、地形等因素关系密切,由于3号样方地表可燃物载量大,所处地形较陡峭,因此导致该样方出现最大火线强度。火线强度的大小也可以作为营林用火指标,以最小损失换取最大成果,即以小火防大火。
对2组样地10个小样方的火线强度、火蔓延速度和火焰高度进行相关分析表明(表4):火焰高度与火线强度和火蔓延速度呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),火蔓延速度与火线强度呈显著正相关(P<0.05),其中火焰高度与火线强度的相关系数达0.794,为最大。因此在烧除试验过程中可采用观察火焰高度来推测火线强度是否超过低强度火烧的临界标准。方差分析结果表明:2类可燃物类型的火焰高度、火焰蔓延速度和火线强度存在显著差异(P<0.05),若蕨类云南松林发生火灾,各项火行为参数偏大,扑火救援难度将提高。
表 4 云南松林计划烧除火行为之间的相关性
Table 4. Correlation between fire behaviors of P. yunnanensis forest
火行为 火线强度 火蔓延速度 火焰高度 火线强度 1 0.704* 0.794** 火蔓延速度 0.704* 1 0.779** 火焰高度 0.794** 0.779** 1 说明:*表示显著相关(P<0.05);**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。 -
研究区地表可燃物载量介于0.52~0.88 kg·m−2之间(表1)。图2A是烧除试验开展前1个月在研究区所记录的实拍图,图2B和图2C分别是烧除试验中从地面与空中拍摄,图2D是烧除后的火烧迹地。通过现场调查发现:低强度的计划烧除对乔木的影响微乎其微,只将下部枝干熏黑但并未灼伤,林冠层几乎没有任何损伤;大多数灌木层枝叶仍保持原状,部分矮灌木底部树叶被烤焦,是否烧死需另设样地后续跟踪研究;地表层凋落物过火情况明显,枯草、松针、蕨类等基本被烧光,枯枝的烧伤程度由径级决定。

图 2 云南松林计划烧除前后对比
Figure 2. Comparing characteristics before and after the prescribed burning of P. yunnanensis forest
由表5可知:云南松纯林地表可燃物计划烧除率介于59%~75%之间,烧除效果明显。火烧强度和烧除率并不是呈现简单的线性关系,例如3号样方的火线强度最高,为369.6 kW·m–1,但其相对应的烧除率并非最大值。由于采用下山火点烧技术,火焰与火头前进方向相反,会对燃烧过的可燃物进行二次燃烧,因此坡度越大烧除效果越好。对火烧迹地调查发现:样方中出现部分未被火烧的小面积植物,称为“花脸”。造成花脸的主要原因是小地形的变化,如坡地上的凹洼地,湿度大,又减缓了火蔓延速度,地表火从两旁绕过或跃过。一般来说上山火造成的花脸率远高于下山火,因为上山火蔓延速度很快导致燃烧不均匀、不彻底,留下许多未烧地块[1]。方差分析结果表明:2种可燃物的烧除效果无显著差异。在云南松纯林不同可燃物类型中开展计划烧除,均能达到清理林下可燃物的效果,且能保证一定效果的烧除率。
表 5 云南松林计划烧除效果评价
Table 5. Evaluation of prescribed burning in P. yunnanensis forest
样方
标号坡度/(°) 烧前质量/
(kg·m−2)烧后质量/
(kg·m−2)烧除
率/%花脸
率/%1~5 17 0.76±0.16 a 0.24±0.04 a 67.75±5.43 a 5.00 6~10 14 0.78±0.21 a 0.30±0.10 a 62.00±2.56 a 5.00 说明:数据为平均值±标准差。同列不同小写字母表示不同可燃物类型间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
低强度计划烧除能有效调控易燃可燃物,减少云南松林地表可燃物载量,烧除率在60%以上,实现火管理目的。本研究区云南松林为20世纪80年代的飞播林,枝下高在7 m以上,灌木很少,林下可燃物垂直连续性较差,计划烧除中最大火焰高度低于1 m,引发树冠火的概率极低,且对上层林木的生长没有明显影响。本次烧除采用下山火的点烧技术,实施过程中多项技术指标高于《云南省森林防火计划烧除规程》和《云南松林计划烧除技术规范》要求,研究结果对林火管理实践工作有一定的指导意义。计划烧除火行为特征表现为林火蔓延速度慢,保持在20 m·h–1以内,稳进地表火对细小可燃物消耗彻底;火线强度均低于750 kW·m–1,是低强度火,火势在人工可控范围内,能保证用火安全。
本研究从林火管理角度研究了在云南松纯林开展林下计划烧除过程中地表可燃物的火行为特征。尽管与云南松林大面积森林火灾的火行为有较大区别,但也能较好地反映计划烧除过程中各项火行为指标间的相关联系,可为森林火灾的安全扑救提供一定参考。计划烧除减少了危险可燃物,切断了可燃物的连续性(水平和垂直方向)分布,降低了火灾的发生率和火烧程度,是预防森林火灾的有效措施。将来研究应集中于:①持续定位研究计划烧除,创新更好的点火技术,提高烧除效率,提出科学的烧除间隔周期等。②应考虑计划烧除过程中烟气排放规律,特别是集中连片烧除产生的烟气成分及含量和迁移消散规律等,减少计划烧除造成的空气污染。③参考2021年全国第1次自然灾害风险普查中森林可燃物普查专项的调查结果,结合新一轮地区森林火险等级,确定更合适的计划烧除时间。④探讨计划烧除的长期影响,如对生物多样性和当地经济社会的影响。
Characteristics of fire behavior in prescribed burning under Pinus yunnanensis forest
-
摘要:
目的 计划烧除是当前应用最广泛有效的森林可燃物管理措施。研究云南松Pinus yunnanensis林地表可燃物进行计划烧除时的火行为特征,可有效清理林地易燃物,降低林地火烧可能性,实现林火管理以预防为主的目的。 方法 使用点烧下山火技术在云南松林开展计划烧除。森林防火期内防火前期,在滇中地区新平县照壁山云南松连续分布区进行外业调查,包括样地设置和野外计划烧除点烧试验,记录烧除过程中火行为的动态变化,包括火蔓延速度、火线强度、火焰温度和高度等,评估烧除效果。 结果 滇中地区防火前期,云南松林地表可燃物含水率为11.99%~12.06%,处于干燥、易燃状态。烧除试验表明:火蔓延速度为0.14~0.29 m·min–1,火线强度为147~332 kW·m–1,火焰温度为386~578 ℃,火焰最大高度为0.9 m。不同可燃物类型烧除时火行为参数差异显著(P<0.05),但均为低强度火。云南松林的平均枝下高达7 m以上,可燃物垂直连续性较差,林下计划烧除火焰很难蔓延到树冠,不会形成树冠火。花脸率占5.00%,整体烧除率为59.00%~75.00%,达到了预期效果,能有效调控可燃物。 结论 云南松林计划烧除火蔓延速度缓慢,为稳进地表火(蔓延速度小于4.0 km·h–1),可燃物燃烧彻底;火线强度小于750 kW·m–1,为低强度火,计划烧除为控制性火烧,不会跑火;平均烧除率为63.05%,烧除效果良好,能调控易燃可燃物载量,达到预防森林大火的目的。图2表5参33 Abstract:Objective Prescribed burning is the most widely used and effective management measure for forest fuels. This study aims to reveal the behavior characteristics of prescribed burning in Pinus yunnanensis forest, so as to effectively clean up the forest land combustibles, reduce the possibility of forest fire, and realize the goal that forest fire management should focus on prevention. Method Downhill fire technology was employed as prescribed burning in P. yunnanensis forest. In the early stage of the fire prevention period, field investigation was conducted in the continuous distribution area of P. yunnanensis in Zhaobi Hill, Xinping County in central Yunnan Province, including sample plot setting and prescribed burning test to investigate the characteristics of fuels and record dynamic changes of fire behavior during the burning process, such as fire spreading rate, fireline intensity, flame temperature and height. Result In the early stage of fire prevention, the moisture content of surface fuels in the forest was 11.99%−12.06%, which was dry and flammable. The burning test showed that the fire spreading speed was 0.14−0.29 m·min−1, the fireline intensity was 147−332 kW·m−1, the flame temperature was 386−578 ℃, and the maximum flame height was 0.9 m. The parameters of fire behavior differed significantly among different surface fuels (P<0.05), but they were all low-intensity fires. The average under-branch height of P. yunnanensis forest was more than 7 m, and the vertical continuity of surface fuels was poor, so it was difficult for the understory burning flame to spread to the canopy. The unburned land rate accounted for 5.00% and the overall burning rate was 59.00%−75.00%, which achieved the expected effect and could effectively control combustibles. Conclusion The burning and fire spreading speed in P. yunnanensis forest is slow, belonging to stable surface fire, with spreading speed less than 4 km·h−1, and the surface combustibles burn thoroughly. Fireline intensity is less than 750 kW·m−1, which is a low-intensity fire and manually controllable. The average burning rate is 63.05% and the burning effect is good, and the load of flammable and combustible materials can be regulated to prevent forest fires. [Ch, 2 fig. 5 tab. 33 ref.] -
表 1 不同可燃物类型云南松林林分特征
Table 1. Stand characteristics of P. yunnanensis forest of different fuel types
可燃物类型 坡度/(°) 郁闭度 密度/(株·hm−2) 树高/m 枝下高/m 胸径/cm 含水率/% 载量/(kg·m−2) 蕨类云南松林 17 0.60 1 240±473 a 11.5±1.6 a 7.9±1.0 a 14.5±3.1 a 11.99 a 0.67±0.14 a 禾本云南松林 14 0.55 1 152±436 a 12.1±1.6 a 8.5±1.4 a 17.1±3.8 a 12.06 a 0.69±0.19 a 说明:数据为平均值±标准差。同列不同小写字母表示不同可燃物类型间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 计划烧除时云南松林内气象概况
Table 2. Weather conditions in P. yunnanensis forest during prescribed burning
时段 风速/(m·s−1) 气温/℃ 相对湿度/% 11:00—12:00 0.5~0.8 14.0~16.0 38~42 12:00—13:00 0.8~1.5 16.0~19.0 33~36 13:00—14:00 1.7~2.4 17.0~22.0 30~34 14:00—15:00 2.0~3.2 18.0~24.0 29~33 15:00—16:00 2.2~2.8 17.0~20.0 32~38 表 3 云南松林计划烧除火行为参数
Table 3. Fire behavior characteristics of prescribed burning in P. yunnanensis forest
可燃物类型 火焰高
度/cm火焰温
度/℃火焰蔓延速度/
(m·min−1)火线强度/
(kW·m−1)蕨类云南松林 80.20±7.50 a 513±65 a 0.25±0.04 a 262±70 a 禾本云南松林 43.40±5.94 b 463±77 a 0.17±0.03 b 188±41 b 说明:数据为平均值±标准差。同列不同小写字母表示不同可燃物类型间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 4 云南松林计划烧除火行为之间的相关性
Table 4. Correlation between fire behaviors of P. yunnanensis forest
火行为 火线强度 火蔓延速度 火焰高度 火线强度 1 0.704* 0.794** 火蔓延速度 0.704* 1 0.779** 火焰高度 0.794** 0.779** 1 说明:*表示显著相关(P<0.05);**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。 表 5 云南松林计划烧除效果评价
Table 5. Evaluation of prescribed burning in P. yunnanensis forest
样方
标号坡度/(°) 烧前质量/
(kg·m−2)烧后质量/
(kg·m−2)烧除
率/%花脸
率/%1~5 17 0.76±0.16 a 0.24±0.04 a 67.75±5.43 a 5.00 6~10 14 0.78±0.21 a 0.30±0.10 a 62.00±2.56 a 5.00 说明:数据为平均值±标准差。同列不同小写字母表示不同可燃物类型间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 胡海清. 林火生态与管理[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2005: 88 − 158. HU Haiqing. Forest Fire Ecology and Management [M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2005: 88 − 158. [2] 王秋华, 舒立福, 李世友. 林火生态研究方法进展[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2009, 29(5): 78 − 82. WANG Qiuhua, SHU Lifu, LI Shiyou. Advance on research methods of ecology of forest fire [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 2009, 29(5): 78 − 82. [3] 张文文, 王秋华, 龙腾腾, 等. 周期性计划烧除对森林生态系统的影响研究综述[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 41(4): 181 − 188. ZHANG Wenwen, WANG Qiuhua, LONG Tengteng, et al. A review of the effects of periodic prescribed burning on forest ecosystems [J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Science), 2021, 41(4): 181 − 188. [4] FINNEY M A, MCHUGH C W, GRENFELL I C. Stand- and landscape-level effects of prescribed burning on two Arizona wildfires [J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2005, 35(7): 1714 − 1722. [5] SCHMIDT D A, TAYLOR A H, SKINNER C N. The influence of fuels treatment and landscape arrangement on simulated fire behavior, Southern Cascade Range, California [J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2008, 255(8/9): 3170 − 3184. [6] KOBZIAR L N, STEPHENS S L. The effects of fuels treatments on soil carbon respiration in a Sierra Nevada pine plantation [J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2006, 141(2/4): 161 − 178. [7] LOUCKS E, ARTHUR M A, LYONS J E, et al. Characterization of fuel before and after a single prescribed fire in an Appalachian hardwood forest [J]. Southern Journal of Applied Forestry, 2008, 32(2): 80 − 88. [8] POTTS J B, STEPHENS S L. Invasive and native plant responses to shrubland fuel reduction: comparing prescribed fire, mastication, and treatment season [J]. Biological Conservation, 2009, 142(8): 1657 − 1664. [9] SCHWILK D W, KEELEY J E, KNAPP E E, et al. The national fire and fire surrogate study: effects of fuel reduction methods on forest vegetation structure and fuels [J]. Ecological Applications, 2009, 19(2): 285 − 304. [10] 武来才, 韩新锁. 浅析内蒙古地区低强度计划烧除[J]. 内蒙古林业, 2005, 50(12): 14 − 15. WU Laicai, HAN Xinsuo. Analysis of low-intensity prescribed burning in Inner Mongolia [J]. Inner Mongolia Forestry, 2005, 50(12): 14 − 15. [11] 马志贵, 王金锡. 论云南松森林计划火烧三原则[J]. 四川林业科技, 1992, 13(2): 45 − 49. MA Zhigui, WANG Jinxi. On the three principles of Pinus yunnanensis forest prescribed burning [J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 1992, 13(2): 45 − 49. [12] 王秋华, 单保君, 龚家平, 等. 滇中地区云南松纯林计划烧除研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2018, 40(2): 235 − 240. WANG Qiuhua, SHAN Baojun, GONG Jiaping, et al. A study on prescribed burning in pure forest of Pinus yunnanensis Franch in central Yunnan Province [J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2018, 40(2): 235 − 240. [13] 戚书玮, 陈奇伯, 杨波, 等. 计划烧除对云南松林群落结构和物种多样性的影响研究[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 41(4): 80 − 88. QI Shuwei, CHEN Qibo, YANG Bo, et al. Effects study of prescribed burning on community structure and species diversity of Pinus yunnanensis forest [J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 2022, 41(4): 80 − 88. [14] 杨馥羽, 陈奇伯, 黎建强, 等. 计划烧除对云南松林土壤抗蚀和抗冲性的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2023, 40(1): 188 − 197. YANG Fuyu, CHEN Qibo, LI Jianqiang, et al. Effect of prescribed burning on soil anti-erodibility and anti-scourability of Pinus yunnanensis forest [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2023, 40(1): 188 − 197. [15] 马志贵, 鄢武先, 杨道贵, 等. 计划烧除引起水土流失的定量研究[J]. 四川林业科技, 2000, 21(1): 7 − 12. MA Zhigui, YAN Wuxian, YANG Daogui, et al. A quantitative study of soil and water loss resulted from planned burning [J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 2000, 21(1): 7 − 12. [16] ARTHUR M A, BLANKENSHIP B A, SCHÖRGENDORFER A, et al. Changes in stand structure and tree vigor with repeated prescribed fire in an Appalachian hardwood forest [J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2015, 340: 46 − 61. [17] 高仲亮, 舒立福, 王明玉, 等. 云南松烧除火蔓延速率预测模型研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2016, 16(4): 82 − 86. GAO Zhongliang, SHU Lifu, WANG Mingyu, et al. Model for predicting the forest fire spreading speed based on the prescriptive combustion of Pinus yunnanensis [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2016, 16(4): 82 − 86. [18] 朱政, 赵璠, 王秋华, 等. 昆明市林火驱动因子及火险区划研究[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(2): 380 − 387. ZHU Zheng, ZHAO Fan, WANG Qiuhua, et al. Driving factors of forest fire and fire risk zoning in Kunming City [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2022, 39(2): 380 − 387. [19] 李少虹, 潘颖瑛, 范彩廷, 等. 浙江省森林可燃物计划烧除与清理应用浅析[J]. 华东森林经理, 2020, 34(4): 73 − 77. LI Shaohong, PAN Yingying, FAN Caiting, et al. A brief analysis of the applicability of prescribed burning and cleaning of forest combustibles in forests in Zhejiang Province [J]. East China Forest Management, 2020, 34(4): 73 − 77. [20] 陈飞, 王健敏, 孙宝刚, 等. 云南松的地理分布与气候关系[J]. 林业科学研究, 2012, 25(2): 163 − 168. CHEN Fei, WANG Jianming, SUN Baogang, et al. Relationship between geographical distribution of Pinus yunnanensis and climate [J]. Forest Research, 2012, 25(2): 163 − 168. [21] 黄钊, 陈政, 薛传东, 等. 云南省新平县哀牢山地区富硒土壤成因及其影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(3): 609 − 617. HUANG Zhao, CHEN Zheng, XUE Chuandong, et al. Study on the genesis and influencing factors of selenium-enriched soil in the Ailaoshan Area, Xinping County, Yunnan Province [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(3): 609 − 617. [22] 杨建光. 新平县林业发展初议[J]. 内蒙古林业调查设计, 2011, 34(1): 45 − 48. YANG Jianguang. Discussion on forestry development of Xinping County [J]. Inner Mongolia Forestry Investigation and Design, 2011, 34(1): 45 − 48. [23] 查贵生. 云南省飞播造林回顾与展望[J]. 山地农业生物学报, 2003, 22(2): 151 − 154. ZHA Guisheng. Review and the prospect of aircraft seed in Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Mountain Agriculture and Biology, 2003, 22(2): 151 − 154. [24] 李世友, 李小宁, 李生红, 等. 3种针叶树种树皮的阻燃性研究[J]. 浙江林学院学报, 2007, 24(2): 192 − 197. LI Shiyou, LI Xiaoning, LI Shenghong, et al. Flame retardancy of wood bark from Keteleeria evelyniana, Pinus yunnanensis and Pinus armandii in Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 2007, 24(2): 192 − 197. [25] 李国雷, 刘勇, 郭蓓, 等. 我国飞播造林研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2006, 19(6): 45 − 48. LI Guolei, LIU Yong, GUO Bei, et al. Advances in the research of the aerial-seeding forest in China [J]. World Forestry Research, 2006, 19(6): 45 − 48. [26] 舒立福, 田晓瑞, 寇晓军. 计划烧除的应用与研究[J]. 火灾科学, 1998, 7(3): 62 − 68. SHU Lifu, TIAN Xiaorui, KOU Xiaojun. Application and research of prescribed burning and controlled burning [J]. Fire Safety Science, 1998, 7(3): 62 − 68. [27] PROGRA R A, HRINKEVICH K H, CLARK E S, et al. Prescribed burning in ponderosa pine: fuel reductions and redistributing fuels near boles to prevent injury [J]. Fire Ecology, 2017, 13(1): 149 − 161. [28] 王明玉, 舒立福, 赵凤君, 等. 北京西山可燃物特点及潜在火行为[J]. 林业科学, 2010, 46(1): 84 − 90. WANG Mingyu, SHU Lifu, ZHAO Fengjun, et al. Characteristics of forest fuel and potential fire behavior in Xishan Mountain of Beijing [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2010, 46(1): 84 − 90. [29] 王晓红, 张吉利, 金森. 林火蔓延模拟的研究进展[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2013, 33(10): 69 − 78. WANG Xiaohong, ZHANG Jili, JIN Sen. Research progress of forest fire spreading simulation [J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry &Technology, 2013, 33(10): 69 − 78. [30] 赵璠, 舒立福, 周汝良, 等. 林火行为蔓延模型研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2017, 30(2): 46 − 50. ZHAO Fan, SHU Lifu, ZHOU Ruliang, et al. A review of wildland fire spread modelling [J]. World Forestry Research, 2017, 30(2): 46 − 50. [31] 宗学政, 田晓瑞. 林火行为和扑救技术研究进展[J]. 世界林业研究, 2019, 32(6): 31 − 36. ZONG Xuezheng, TIAN Xiaorui. Research progress in forest fire behavior and suppression technology [J]. World Forestry Research, 2019, 32(6): 31 − 36. [32] 舒立福, 王明玉, 田晓瑞, 等. 关于森林燃烧火行为特征参数的计算与表述[J]. 林业科学, 2004, 46(3): 179 − 183. SHU Lifu, WANG Mingyu, TIAN Xiaorui, et al. Calculation and description of forest fire behavior characters [J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2004, 46(3): 179 − 183. [33] 张志东, 田祖为, 王伟, 等. 森林火灾蔓延强度与能量释放表述[J]. 森林防火, 2019, 37(3): 31 − 34. ZHANG Zhidong, TIAN Zuwei, WANG Wei, et al. Expressions of the burning intensity and energy release during forest fire spread [J]. Forest Fire Prevention, 2019, 37(3): 31 − 34. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220560






 下载:
下载:


