-
梅花Prunus mume为蔷薇科Rosaceae李属Prunus植物,是中国十大传统名花之一,具有悠久的栽培和应用历史[1]。与李属其他植物相比,梅花具有独特的香气[2]。梅花品种繁多,目前在全世界范围内已登录486个梅花品种[3]。陈俊愉等[4]提出了梅花分类的新方案,将梅花分为11个品种群,其中有9个品种群来源于原真梅系,其余2个品种群来源于梅的种间杂交。梅花不同品种具有不同的香气,这些香气成分对香精、香料工业具有潜在的应用价值[5−6]。
植物花香是花朵散发出的挥发性低分子量化合物,这些物质不仅能参与植物体内的次生代谢,还能在植物抵御外来侵略方面起到作用[7]。迄今为止,已鉴定了超过2 100种天然花香物质[8−9]。按照花香物质的代谢途径,可将其分为萜烯类化合物、苯丙烷类/苯环型化合物和脂肪族化合物三大类[10]。蔷薇科植物主要释放苯环及苯丙烷类化合物,如苯甲醛、苯甲醇、乙酸苯甲酯、苯甲酸苯甲酯、丁子香酚、异丁子香酚等[11]。植物种类不同,其花朵释放的挥发物种类与含量也不同,产生的香气也具有植物个体特异性[12]。梅花香气物质在不同品种间具有一定的差异,在梅花中共鉴定出几十种化合物,最主要的香气物质包括乙酸苯甲酯、丁子香酚、苯甲醛、苯甲醇、乙酸肉桂酯等[13−17]。然而,不同梅花品种的花香多样性尚未被确定。鉴于此,本研究采用顶空固相微萃取法(HS-SPME)结合气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)对6个品种群20个梅花品种的花香成分差异进行研究,筛选对梅花花香有较大贡献特征的香气物质,以期为梅花花香的代谢释放机制研究和深度经济价值(如精油、梅花茶等)开发提供参考。
-
所有梅花品种保存于浙江农林大学梅花种质资源圃。选取株龄相同、长势一致的梅花品种,共20个品种,6个品种群。其中:朱砂品种群有6个品种,分别为‘晨晖朱砂’‘Chenhui Zhusha’‘粉红朱砂’‘Fenhong Zhusha’‘红颜朱砂’‘Hongyan Zhusha’‘先春朱砂’‘Xianchun Zhusha’‘银红朱砂’‘Yinhong Zhusha’‘大盃’‘DaBei’;宫粉品种群有5个品种,分别为‘粉皮宫粉’‘Fenpi Gongfen’‘粉晕宫粉’‘Fenyun Gongfen’‘晓红宫粉’‘Xiaohong Gongfen’‘早花宫粉’‘Zaohua Gongfen’‘春意早宫粉’‘Chunyizao Gongfen’;绿萼品种群有3个品种,分别为‘变绿萼’‘Bian Lve’‘小绿萼’‘Xiao Lve’‘素玉绿萼’‘Suyu Lve’;玉蝶品种群有3个品种,分别为‘乔妆玉蝶’‘Qiaozhuang Yudie’‘月光玉蝶’‘Yueguang Yudie’‘长蕊玉蝶’‘Changrui Yudie’;垂枝品种群有1个品种,为‘单粉垂枝’‘Danfen Chuizhi’;跳枝品种群有2个品种,分别为‘单粉跳枝’‘Danfen Tiaozhi’和‘筋入春日野’‘Jinruchunriye’。所用试剂为C7~C30正构烷烃混合标准品(Sigma公司,德国)。
-
用镊子取下3朵盛开期的梅花,将其快速转移至22 mL的采样瓶,封口膜密封瓶盖,平衡10 min,将固相微萃取SPME纤维头(Supelco公司,美国)插入花朵上方2 cm处的采样瓶中吸附30 min。将吸附完花香的萃取头插入GC-MS联用仪的进样口进行分析,3次平行重复实验。GC-MS分析条件:色谱柱HP-5MS (30.00 m×250.00 μm×0.25 μm),载入氦气,流速1.2 mL·min−1;起始柱温为45 ℃,保持3 min,以5 ℃·min−1升至120 ℃,然后以6 ℃·min−1升温至260 ℃,保持3 min,离子电离能量70 eV,离子阱温度为230 ℃。每个品种3次生物学重复。
-
在相同分析条件下,测定C7~C30正构烷烃混合标准品,计算待鉴定化合物的保留指数,并结合GC-MS联用仪计算机的NIST05a.L/NIST11.L标准谱库自动检索分析各组分。保留指数计算公式[18]为IR=100n+100(t−tn)/(tn+1−tn)。其中:IR为保留指数,n和n+1分别为目标化合物出峰前后正构烷烃的碳原子数,tn和tn+1分别为相应正构烷烃的保留时间,t为待鉴定化合物在谱图中的保留时间(tn<t<tn+1)。依据总离子流各色谱峰平均峰面积,并通过面积归一化方法计算各香气成分的相对含量。
通过文献查找主要花香化合物的香气阈值,结合花香化合物的相对含量计算其香气贡献值,相对含量与香气阈值的比值即为香气贡献值。使用Origin 2021绘制花香成分的聚类分析图。
-
在20个梅花品种中共鉴定出43种挥发性成分,包括苯环/苯丙烷类化合物23种,萜烯类化合物7种,脂肪酸衍生物9种,烷烃类4种(表1)。朱砂品种群检测到的成分最多,有35种,包括苯环/苯丙烷类16种,萜烯类7种,脂肪酸衍生物9种,烷烃类3种;宫粉品种群共检测到30种成分,包括苯环/苯丙烷类20种,萜烯类4种,脂肪酸衍生物3种,烷烃类3种;玉蝶品种群共检测到20种成分,包括苯环/苯丙烷类13种,萜烯类3种,脂肪酸衍生物4种;绿萼品种群共检测到23种成分,包括苯环/苯丙烷类15种,萜烯类3种,脂肪酸衍生物5种;跳枝品种群共检测到28种成分,包括苯环/苯丙烷类15种,萜烯类6种,脂肪酸衍生物7种;垂枝品种群共检测到17种成分,包括苯环/苯丙烷类9种,萜烯类4种,脂肪酸衍生物4种。不同类型化合物的相对含量也存在较大差异,苯环/苯丙烷类的相对含量最高,为87.01%~99.87%,脂肪酸衍生物的相对含量为0~6.95%,萜烯类物质的相对含量为0~6.15%。
表 1 不同梅花品种群的挥发性成分类型及相对含量
Table 1. Category and relative content of volatile components in six cultivar groups of P. mume
品种群 苯环/苯丙
烷类/种萜烯类/
种脂肪酸衍
生物/种烷烃/
种总数/
种朱砂 16 7 9 3 35 宫粉 20 4 3 3 30 玉蝶 13 3 4 − 20 绿萼 15 3 5 − 23 跳枝 15 6 7 − 28 垂枝 9 4 4 − 17 总数/种 23 7 9 4 43 总相对含量/% 87.01~99.87 0~6.15 0~6.95 0~0.18 说明:−表示未检测到。 -
如表2所示:‘晨晖朱砂’中乙酸苯甲酯(44.97%)、苯甲醇(41.83%)、丁子香酚(5.98%)和苯甲醛(2.84%)等相对含量较高。‘粉红朱砂’与‘晨晖朱砂’相似,其最主要的花香成分为乙酸苯甲酯(48.25%)、苯甲醇(34.21%)、丁子香酚(5.25%)和苯甲醛(5.24%)等。‘红颜朱砂’中苯甲醇(72.86%)、丁子香酚(7.37%)、肉桂醇(5.97%)和苯甲醛(5.61%)等相对含量较高。‘先春朱砂’中苯甲醇(63.15%)、肉桂醇(13.67%)、苯甲醛(8.72%)和丁子香酚(7.59%)等相对含量较高。‘银红朱砂’的挥发性成分为乙酸苯甲酯(50.48%)、苯甲醇(39.96%)和丁子香酚(3.93%)等相对含量较高。‘大盃’中乙酸苯甲酯(25.56%)、苯甲醛(17.53%)、草蒿脑(12.44%)、丁子香酚(10.50%)、4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚(9.66%)和乙酸-2-己烯酯(4.63%)等相对含量较高。
表 2 朱砂品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 2. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Cinnabar Purple group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘晨晖朱砂’ ‘粉红朱砂’ ‘红颜朱砂’ ‘先春朱砂’ ‘银红朱砂’ ‘大盃’ 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 2.75±0.57 3.08±0.37 2.08±0.78 3.24±0.88 1.64±0.45 5.20±1.61 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 2.84±1.24 5.24±4.44 5.61±3.08 8.72±5.64 1.18±0.25 17.53±1.20 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 41.83±1.67 34.21±1.57 72.86±5.64 63.15±8.15 39.96±2.62 5.78±1.69 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 44.97±4.91 48.25±3.64 1.16±0.12 1.47±0.16 50.48±3.16 25.56±8.21 水杨酸甲酯 methyl salicylate 1 197 − − − − − 0.08±0.07 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 0.08±0.04 − 0.26±0.10 − − 12.44±3.57 3,4-二甲氧基甲苯 3,4-dimethoxytoluene 1 242 − − − − − 0.07±0.05 3-苯丙醇 3-phenylpropanol 1 233 − − 0.37±0.18 0.40±0.13 − − 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 − 0.16±0.09 0.22±0.07 0.21±0.08 − 9.66±3.34 反式肉桂醛 cinnamaldehyde, (E)- 1 272 − − 0.35±0.11 0.75±0.29 0.07±0.06 − 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 1 307 − 1.36±0.58 5.97±1.67 13.67±4.18 1.04±0.48 − 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 5.98±2.00 5.25±1.61 7.37±1.95 7.59±1.37 3.93±0.71 10.50±1.68 丁酸-3-苯丙酯 3-phenylpropyl butyrate 1 373 − 0.07±0.01 − − 0.08±0.01 − 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 0.15±0.05 − 0.30±0.11 0.07±0.05 − 0.46±0.09 乙酸肉桂酯 cinnamyl acetate 1 447 − 1.33±0.34 0.20±0.05 0.59±0.13 0.77±0.21 − 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 0.19±0.08 − 0.79±0.53 − − − 苯基/苯丙烷类合计
total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids98.79 98.95 97.55 99.87 99.15 87.01 莰烯 camphene 963 0.15±0.12 − 1.32±0.18 − − 1.52±0.54 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮 sulcatone 1 003 − − − − − 0.07±0.05 柠檬烯 limonene 1 038 − − − − − 0.17±0.04 3-蒈烯 3-carene 1 056 − − − − − 3.82±2.51 γ-松油烯 γ-terpinene 1 066 − − − − − 0.03±0.02 莰酮 camphor 1 149 − − 0.36±0.05 − − 0.22±0.03 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 0.11±0.09 − 0.13±0.03 − 0.05±0.03 0.32±0.08 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 0.26 0.00 1.82 0.00 0.05 6.15 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 801 − − − − − 0.16±0.12 己醛 hexanal 845 0.10±0.05 − − − − − 乙酸戊酯 n-amylacetate 935 − − − − − 0.17±0.15 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 0.17±0.04 0.30±0.05 − − 0.39±0.11 1.37±0.18 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 0.46±0.14 0.75±0.16 − − 0.42±0.30 4.63±0.76 壬醛 nonanal 1 109 − − − − − 0.05±0.04 癸醛 decanal 1 208 − − − − − 0.07±0.05 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯
2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate1 369 0.21±0.13 − 0.65±0.11 − − − 月桂酸甲酯 methyl laurate 1 525 − − − − − 0.04±0.03 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 0.95 1.05 0.65 0.00 0.81 6.49 十三烷 tridecane 1 300 − − − − − 0.08±0.05 十九烷 nonadecane 1 900 − − − 0.08±0.01 − − 二十一烷 heneicosane 2 100 − − − 0.05±0.03 − − 烷烃类合计 total alkanes 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.13 0.00 0.08 说明:−表示未检测到。 对梅花香气贡献率(表3)的计算发现:β-紫罗兰酮、肉桂醇、丁子香酚和甲基丁香酚对朱砂品种群梅花的香气的贡献率较高。由于β-紫罗兰酮的香气阈值很低,所以其在梅花花朵香气中的贡献率最高。
表 3 朱砂品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 3. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Cinnabar Purple group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘晨晖朱砂’ ‘粉红朱砂’ ‘红颜朱砂’ ‘先春朱砂’ ‘银红朱砂’ ‘大盃’ 苯甲醛
benzaldehyde0.350~3.500 0.810~8.110 1.640~16.380 1.600~16.030 2.490~24.910 0.340~3.370 5.010~50.090 苯甲醇
benzyl alcohol80.000 0.523 0.428 0.911 0.789 0.500 0.072 乙酸苯甲酯
benzyl acetate2.600 17.297 18.558 0.445 0.567 19.415 9.831 草蒿脑
estragole0.016 5.000 − 16.250 − − 777.500 丁子香酚
eugenol0.006~0.030 199.330~996.670 175.000~875.000 245.670~1 228.330 253.000~1 265.000 131.000~655.000 350.000~1 750.000 甲基丁香酚
methyleugenol0.001 146.667 − 296.667 66.667 − 180.000 β-紫罗兰酮
β-ionone0.000 15 238.095 − 19 047.619 − 6 666.667 46 190.476 壬醛
nonanal0.001 − − − − − 53.333 癸醛
decanal0.001~0.002 − − − − − 35.000~70.000 肉桂醇
cinnamyl alcohol0.001 − 1 700.000 7 466.667 17 087.500 1 295.833 − 异戊醇
isoamyl alcohol0.006 − − − − − 25.683 乙酸叶醇酯
cis-3-hexe-nylacetate0.009 19.259 33.704 − − 43.333 151.852 说明:−表示未检测到。 -
如表4所示:‘粉皮宫粉’中苯甲醇(53.90%)、肉桂醇(16.19%)、苯甲醛(11.44%)和丁子香酚(9.35%)等相对含量较高。‘粉晕宫粉’与‘粉皮宫粉’相似,其中苯甲醇(54.94%)、肉桂醇(19.83%)、丁子香酚(9.57%)和苯甲醛(5.10%)等是其主要的花香成分。‘晓红宫粉’中乙酸苯甲酯(53.19%)、苯甲醇(30.57%)和丁子香酚(7.13%)等相对含量较高。‘早花宫粉’中苯甲醇(30.31%)、乙酸苯甲酯(25.32%)、乙酸肉桂酯(9.94%)、丁子香酚(9.15%)、苯甲醛(8.74%)和肉桂醇(7.42%)等为主要的香气成分。‘春意早宫粉’中乙酸苯甲酯(46.72%)、苯甲醇(40.05%)、丁子香酚(7.13%)和苯甲醛(4.06%)等为主要的香气物质。
表 4 宫粉品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 4. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Pink Double group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘粉皮宫粉’ ‘粉晕宫粉’ ‘晓红宫粉’ ‘早花宫粉’ ‘春意早宫粉’ 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 2.00±0.08 2.89±0.61 5.38±3.15 4.17±1.33 1.80±0.24 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 11.44±1.89 5.10±3.94 2.45±1.37 8.74±1.64 4.06±1.31 苄甲醚 benzyl methyl ether 999 − − − − 0.04±0.03 对甲苯甲醚 p-methylanisole 1 029 0.56±0.12 0.51±0.15 − − − 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 53.90±3.71 54.94±9.98 30.57±6.39 30.31±4.00 40.05±1.42 对甲酚 p-cresol 1 080 0.06±0.05 0.07±0.05 − − − 苯甲酸甲酯 methyl benzoate 1 099 − − − 0.57±0.35 − 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 1.54±0.11 1.20±0.13 53.19±8.71 25.32±4.67 46.72±1.19 2-甲氧基-4-甲基苯酚 creosol 1 195 0.07±0.01 − − 0.05±0.04 − 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 0.17±0.05 0.15±0.04 − 0.12±0.02 0.05±0.00 3-苯丙醇 3-phenylpropanol 1 233 0.38±0.08 0.65±0.24 − 0.12±0.05 0.07±0.00 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 0.23±0.03 0.32±0.16 0.09±0.04 0.63±0.22 − 反式肉桂醛 cinnamaldehyde, (E)- 1 272 0.89±0.28 1.07±0.50 − 1.22±0.36 0.09±0.02 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 1 307 16.19±5.50 19.83±9.73 − 7.42±1.96 1.46±0.17 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 9.35±0.92 9.57±1.02 7.13±0.90 9.15±1.09 3.33±0.30 丁酸-3-苯丙酯 3-phenylpropyl butyrate 1 373 − − − − 0.17±0.02 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 0.17±0.02 0.17±0.02 0.05±0.03 0.09±0.02 0.11±0.03 乙酸肉桂酯 cinnamyl acetate 1 447 0.81±0.08 0.77±0.10 − 9.94±1.43 1.13±0.11 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 − 0.19±0.06 − 0.03±0.02 − 苯甲酸苯甲酯 benzyl benzoate 1 771 0.40±0.04 0.31±0.09 − 0.35±0.02 − 苯基/苯丙烷类合计 total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids 98.15 97.75 98.86 98.21 99.07 莰烯 camphene 963 0.61±0.49 0.67±0.56 0.23±0.18 0.23±0.13 0.24±0.06 3-蒈烯 3-carene 1 056 0.86±0.58 1.03±0.87 − − − 莰酮 camphor 1 149 0.13±0.07 0.16±0.08 0.16±0.07 0.17±0.14 0.07±0.03 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 0.25±0.12 0.19±0.12 − − 0.08±0.01 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 1.85 2.04 0.39 0.40 0.39 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 − − 0.26±0.13 0.18±0.02 0.26±0.02 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 − − 0.49±0.07 1.01±0.33 0.28±0.03 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate 1 369 − 0.20±0.04 − − − 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 0.00 0.20 0.75 1.19 0.54 十五烷 pentadecane 1 500 − − − 0.11±0.03 − 十九烷 nonadecane 1 900 − − − 0.02±0.02 − 二十一烷 heneicosane 2 100 − − − 0.05±0.04 − 烷烃类合计 total alkanes 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.18 0.00 说明:−表示未检测到。 如表5所示:在‘粉晕宫粉’和‘粉皮宫粉’中,香气贡献值从高到低依次是β-紫罗兰酮、肉桂醇、对甲苯甲醚、丁子香酚和甲基丁香酚,未检测到乙酸叶醇酯。‘晓红宫粉’香气贡献值从高到低依次是丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚、乙酸叶醇酯和乙酸苯甲酯。‘早花宫粉’香气贡献值从高到低依次是肉桂醇、丁子香酚和甲基丁香酚。在‘春意早宫粉’中,香气贡献值从高到低依次是β-紫罗兰酮、肉桂醇、丁子香酚和甲基丁香酚。
表 5 宫粉品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 5. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Pink Double group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘粉皮宫粉’ ‘粉晕宫粉’ ‘晓红宫粉’ ‘早花宫粉’ ‘春意早宫粉’ 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 0.350~3.500 3.270~32.690 1.460~14.570 0.700~7.000 2.500~24.970 1.160~11.600 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 80.000 0.674 0.687 0.382 0.379 0.501 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 2.600 0.594 0.462 20.458 9.737 17.969 草蒿脑 estragole 0.016 10.417 9.375 − 7.708 3.333 丁子香酚 eugenol 0.006~0.030 311.670~1558.330 319.000~1595.000 237.670~1 188.330 305.000~1525.000 111.000~555.000 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 0.001 166.667 173.333 46.667 90.000 110.000 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 0.000 35 714.286 27 142.857 − − 10 952.381 对甲苯甲醚 p-methylanisole 0.000 2 800.000 2 566.667 − − − 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 0.001 20 241.667 24 787.500 − 9 270.833 1 825.000 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 0.009 − − 29.259 20.370 28.889 说明:−表示未检测到。 -
如表6所示:‘乔妆玉蝶’中乙酸苯甲酯(62.67%)、苯甲醇(24.35%)、丁子香酚(5.36%)和苯甲醛(4.42%)等相对含量较高。‘月光玉蝶’中乙酸苯甲酯(72.90%)、苯甲醛(7.83%)、苯甲醇(7.73%)和丁子香酚(3.06%)等相对含量较高。‘长蕊玉蝶’中乙酸苯甲酯(62.63%)、苯甲醇(18.80%)、丁子香酚(6.17%)和苯甲醛(5.94%)等相对含量较高。
表 6 玉蝶品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 6. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Alboplena group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘乔妆玉蝶’ ‘月光玉蝶’ ‘长蕊玉蝶’ 乙基苯 ethylbenzene 889 − 0.10±0.08 − 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 2.10±0.19 2.66±0.82 1.71±0.96 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 4.42±0.44 7.83±2.17 5.94±4.00 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 24.35±6.23 7.73±2.29 18.80±5.01 苯甲酸甲酯 methyl benzoate 1 099 0.14±0.05 − − 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 62.67±4.41 72.90±6.01 62.63±5.69 水杨酸甲酯 methyl salicylate 1 197 − − 0.06±0.05 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 − 0.13±0.05 1.09±1.22 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 0.13±0.11 − 1.01±1.21 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 5.36±0.93 3.06±0.50 6.17±1.95 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 − 0.38±0.02 0.28±0.10 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 − 0.11±0.10 0.22±0.18 苯甲酸苯甲酯 benzyl benzoate 1 771 − 0.13±0.12 − 苯基/苯丙烷类合计 total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids 99.17 95.02 97.92 莰烯 camphene 963 0.24±0.08 0.07±0.06 0.38±0.25 莰酮 camphor 1 149 0.13±0.04 − 0.05±0.04 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 − − 0.05±0.04 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 0.38 0.07 0.49 乙酸戊酯 n-amylacetate 935 − 0.15±0.04 − 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 0.07±0.06 1.69±0.66 0.64±0.39 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 0.38±0.19 2.95±1.10 0.66±0.49 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate 1 369 − 0.12±0.11 0.29±0.24 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 0.45 4.91 1.59 说明:−表示未检测到。 如表7所示:在‘长蕊玉蝶’中,香气贡献值从高到低依次是β-紫罗兰酮、丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚、乙酸叶醇酯、乙酸苯甲酯和草蒿脑。在‘月光玉蝶’中,香气贡献值从高到低依次是丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚、乙酸叶醇酯和乙酸苯甲酯,未检测到β-紫罗兰酮。‘乔妆玉蝶’中香气贡献值从高到低是丁子香酚和乙酸苯甲酯。
表 7 玉蝶品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 7. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Alboplena group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘乔妆玉蝶’ ‘月光玉蝶’ ‘长蕊玉蝶’ 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 0.350~3.500 1.260~12.630 2.240~22.370 1.700~16.970 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 80.000 0.304 0.097 0.235 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 2.600 24.103 28.037 24.090 草蒿脑 estragole 0.016 − 8.125 68.333 丁子香酚 eugenol 0.006~0.030 178.670~893.330 102.000~510.000 205.670~1 028.330 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 0.001 − 376.667 276.667 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 0.000 − − 7 619.048 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 0.009 7.778 187.778 71.481 说明:−表示未检测到。 -
如表8所示:‘变绿萼’中乙酸苯甲酯(57.43%)、苯甲醛(14.67%)、苯甲醇(8.26%)、对甲苯甲醚(5.41%)和丁子香酚(5.34%)等相对含量较高。‘小绿萼’中乙酸苯甲酯(65.13%)、苯甲醇(23.37%)和丁子香酚(3.74%)等相对含量较高。‘素玉绿萼’中乙酸苯甲酯(59.20%)、苯甲醇(24.56%)、丁子香酚(5.81%)和苯甲醛(5.45%)等相对含量较高。
表 8 绿萼品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 8. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Green Calyx group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘变绿萼’ ‘小绿萼’ ‘素玉绿萼’ 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 2.49±1.74 1.57±0.59 0.73±0.22 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 14.67±3.77 2.73±0.41 5.45±1.16 对甲苯甲醚 p-methylanisole 1 029 5.41±1.57 − − 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 8.26±1.41 23.37±5.36 24.56±0.85 对甲酚 p-cresol 1 080 0.05±0.04 − − 苯甲酸甲酯 methyl benzoate 1 099 0.33±0.10 − − 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 57.43±4.67 65.13±4.33 59.20±1.79 水杨酸甲酯 methyl salicylate 1 197 0.25±0.08 − − 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 0.81±0.18 0.09±0.07 1.26±0.30 3,4-二甲氧基甲苯 3,4-dimethoxytoluene 1 242 0.09±0.07 − − 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 0.27±0.18 − 0.89±0.33 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 5.34±0.44 3.74±1.54 5.81±0.61 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 0.46±0.21 0.28±0.17 0.31±0.03 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 0.12±0.09 0.35±0.26 − 苯甲酸苯甲酯 benzyl benzoate 1 771 1.93±0.49 − − 苯基/苯丙烷类合计 total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids 97.90 97.26 98.21 莰烯 camphene 963 − 0.40±0.20 0.16±0.05 莰酮 camphor 1 149 − 0.28±0.18 − β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 − 0.14±0.06 − 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 0.00 0.82 0.16 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 801 0.31±0.27 − − 乙酸戊酯 n-amylacetate 935 0.17±0.06 − 0.07±0.01 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 1.41±0.77 0.70±0.25 0.41±0.14 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 − 1.11±0.58 1.04±0.73 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate 1 369 0.19±0.07 0.12±0.09 0.11±0.09 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 2.09 1.93 1.63 说明:−表示未检测到。 如表9所示:‘变绿萼’中香气贡献值从高到低依次是对甲苯甲醚、丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚、乙酸叶醇酯和异戊醇,未检测到β-紫罗兰酮。在‘小绿萼’中,香气贡献值从高到低依次是β-紫罗兰酮、丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚、乙酸叶醇酯和乙酸苯甲酯。在‘素玉绿萼’中,香气贡献值从高到低依次是丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚、乙酸叶醇酯和草蒿脑,未检测到β-紫罗兰酮。
表 9 绿萼品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 9. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Green Calyx group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘变绿萼’ ‘小绿萼’ ‘素玉绿萼’ 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 0.350~3.500 4.190~41.910 0.780~7.800 1.560~15.570 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 80.000 0.103 0.292 0.307 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 2.600 22.087 25.050 22.769 草蒿脑 estragole 0.016 50.833 5.833 78.750 丁子香酚 eugenol 0.006~0.030 178.000~890.000 124.670~623.330 193.670~968.330 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 0.001 460.000 280.000 310.000 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 0.000 − 19523.810 − 对甲苯甲醚 p-methylanisole 0.000 27050.000 − − 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 0.006 51.366 − − 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 0.009 157.037 77.407 45.556 说明:−表示未检测到。 -
如表10所示:‘单粉跳枝’中苯甲醇(59.78%)、苯甲醛(17.58%)、丁子香酚(5.50%)和肉桂醇(4.14%)等相对含量较高。‘筋入春日野’中乙酸苯甲酯(63.54%)、苯甲醇(12.20%)、苯甲醛(9.12%)和乙酸-2-己烯酯(4.31%)等相对含量较高。‘单粉垂枝’中乙酸苯甲酯(55.42%)、苯甲醛(16.53%)、苯甲醇(13.88%)、丁子香酚(4.88%)和乙酸-2-己烯酯(3.02%)等相对含量较高。
表 10 跳枝和垂枝品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 10. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Versicolor group and Pendulous Mei group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘单粉跳枝’ ‘筋入春日野’ ‘单粉垂枝’ 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 5.92±0.62 4.67±0.99 2.87±0.66 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 17.58±0.46 9.12±2.60 16.53±3.54 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 59.78±1.26 12.20±5.77 13.88±4.66 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 1.36±0.13 63.54±9.56 55.42±1.57 2-甲氧基-4-甲基苯酚 creosol 1 195 − 0.16±0.06 − 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 0.40±0.05 0.16±0.04 0.25±0.08 3,4-二甲氧基甲苯 3,4-dimethoxytoluene 1 242 − 0.11±0.02 − 3-苯丙醇 3-phenylpropanol 1 233 0.24±0.06 − − 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 0.19±0.01 − 0.22±0.04 反式肉桂醛 cinnamaldehyde, (E)- 1 272 0.34±0.07 − − 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 1 307 4.14±1.34 − − 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 5.50±0.16 2.59±0.48 4.88±0.85 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 0.09±0.03 0.22±0.06 0.18±0.12 乙酸肉桂酯 cinnamyl acetate 1 447 0.14±0.10 − − 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 0.57±0.36 0.13±0.11 0.36±0.16 苯基/苯丙烷类合计 total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids 96.25 92.92 94.58 莰烯 camphene 963 1.99±0.59 − 1.02±0.08 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮 sulcatone 1 003 − 0.08±0.06 − 柠檬烯 limonene 1 038 0.14±0.10 − 0.10±0.01 3-蒈烯 3-carene 1 056 − 0.06±0.04 − 莰酮 camphor 1 149 0.83±0.09 − 0.08±0.01 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 0.14±0.07 − 0.08±0.07 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 3.10 0.13 1.28 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 801 0.05±0.03 − − 己醛 hexanal 845 − 0.14±0.13 − 乙酸戊酯 n-amylacetate 935 − − 0.08±0.06 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 − 2.36±1.43 0.81±0.23 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 − 4.31±2.65 3.02±0.77 壬醛 nonanal 1 109 0.11±0.03 − − 癸醛 decanal 1 208 0.12±0.02 − − 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate 1 369 0.34±0.13 0.14±0.10 0.24±0.19 月桂酸甲酯 methyl laurate 1 525 − − − 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 0.61 6.95 4.15 说明:−表示未检测到。 如表11所示:在‘单粉跳枝’中,香气贡献值从高到低依次是β-紫罗兰酮、肉桂醇、丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚、壬醛和癸醛。‘筋入春日野’中香气贡献值最高的依次是丁子香酚、乙酸叶醇酯和甲基丁香酚。‘单粉垂枝’香气贡献值最高的依次是β-紫罗兰酮、丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚和乙酸叶醇酯。
表 11 跳枝和垂枝品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 11. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Versicolor group and Pendulous Mei group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘单粉跳枝’ ‘筋入春日野’ ‘单粉垂枝’ 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 0.350~3.500 5.020~50.230 2.610~26.060 4.720~47.230 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 80.000 0.747 0.153 0.174 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 2.600 0.523 24.440 21.314 草蒿脑 estragole 0.016 24.792 9.729 15.833 丁子香酚 eugenol 0.006~0.030 183.330~916.670 86.330~431.670 162.670~813.340 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 0.001 93.333 223.667 176.667 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 0.000 20 000.000 − 11 428.571 壬醛 nonanal 0.001 113.333 − − 癸醛 decanal 0.001~0.002 60.000~120.000 − − 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 0.001 5 175.000 − − 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 0.006 7.650 − − 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 0.009 − 262.296 90.000 说明:−表示未检测到。 -
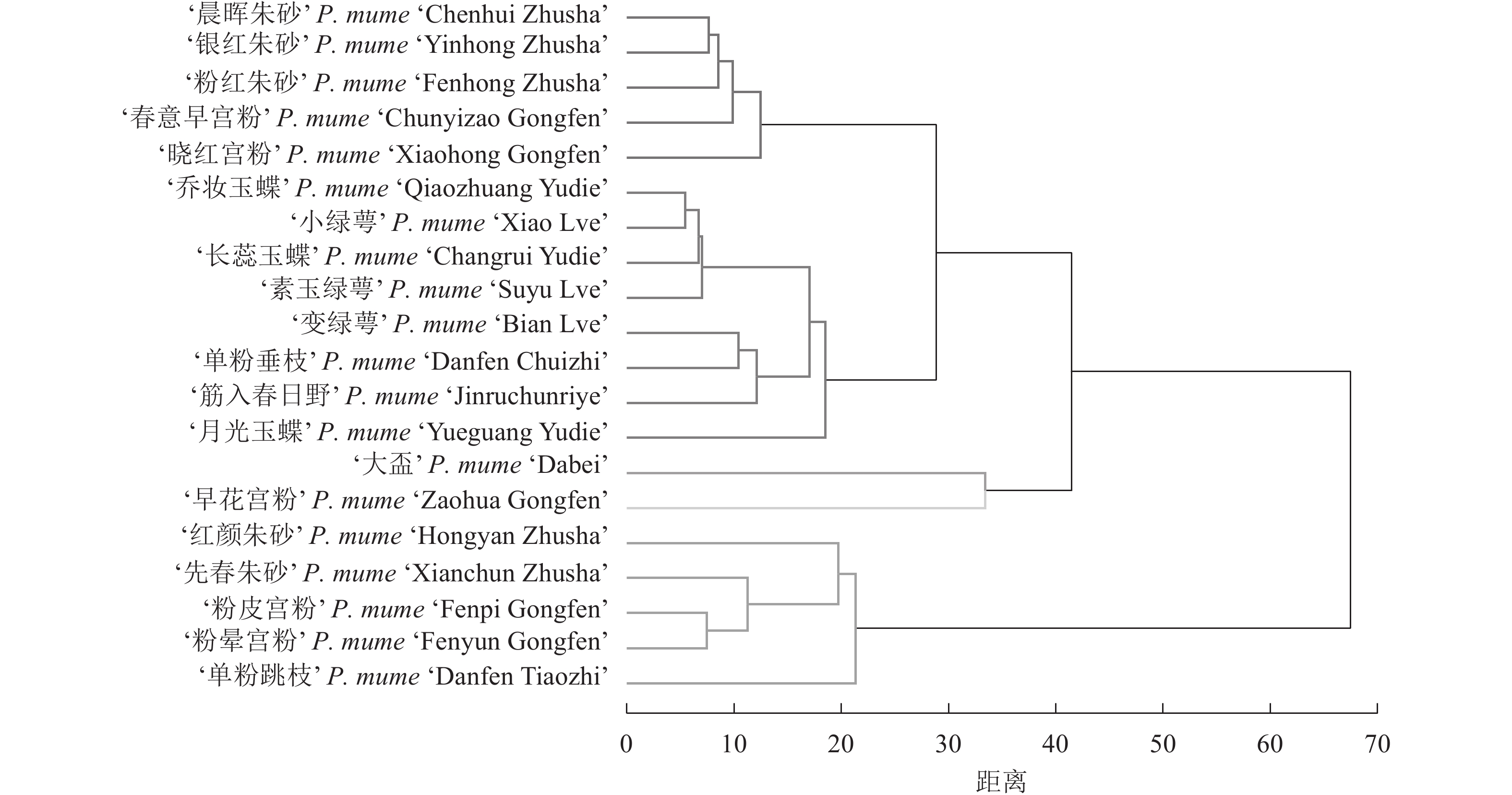
如图1所示:20个梅花品种依据花香成分组成及相对含量,被分为5类。第1类为‘晨晖朱砂’‘银红朱砂’‘粉红朱砂’‘春意早宫粉’和‘晓红宫粉’,其花香成分特点是乙酸苯甲酯和苯甲醇相对含量较高,且相近。第2类为‘单粉垂枝’‘筋入春日野’、玉蝶品种群及绿萼品种群,其花香特点是乙酸苯甲酯相对含量最高,其次是苯甲醇,且苯甲醇相对含量远低于乙酸苯甲酯。第3类仅包括朱砂品种群的‘大盃’,其花香特点是乙酸苯甲酯、苯甲醛、草蒿脑相对含量均较高且相近,萜烯类物质相对含量也较高。第4类仅包括宫粉品种群的‘早花宫粉’,其花香特点是苯甲醇和乙酸苯甲酯相对含量最高,其次是乙酸肉桂酯、丁子香酚和苯甲醛。第5类包括‘红颜朱砂’‘先春朱砂’‘粉皮宫粉’‘粉晕宫粉’和‘单粉跳枝’,其花香成分组成特点是苯甲醇相对含量最高,均高于50%,其次是苯甲醛,而乙酸苯甲酯相对含量极低,均低于2%。
-
梅花是中国拥有第1个国际登录权的物种,目前已有超过400个梅花品种被登录[19]。郝瑞杰等[20]研究表明:决定梅花香气的主要成分是苯环/苯丙烷类化合物,其中以乙酸苯甲酯、苯甲醇、苯甲醛和丁子香酚等为主。本研究结果与郝瑞杰等[20]的研究结果一致,苯环/苯丙烷类化合物是梅花花香的主要成分,其中乙酸苯甲酯、苯甲醛、苯甲醇和丁子香酚占比最高,还含有少量萜烯类和脂肪酸类物质。ZHANG等[21]对8个不同花色梅花品种的花香成分进行了分析,表明苯基/苯丙烷类化合物占总排放量的95%以上。白花品种的花香挥发物以乙酸苯甲酯为主,品种间差异较小,粉花品种的花香挥发物组成存在差异。本研究发现:梅花不同品种群间香气种类及相对含量有明显差异,朱砂和宫粉品种群花香化合物数量最多,其次是跳枝和绿萼品种群,玉蝶和垂枝品种群花香化合物数量较少。
花朵香气特征并不完全由香气物质的种类与相对含量决定,还与香气物质的香气阈值有关,相对含量越高且阈值越小,香气强度就越大,对香气的贡献值就越大[14]。LI等[22]分析了6个梅花品种的花香及挥发性代谢组的差异,根据花香化合物的香气阈值筛选出了6种促进梅花不同品种香气差异的成分,包括苯甲醛、苯甲酸甲酯、乙酸苯甲酯、丁子香酚、反式肉桂醇、4-烯丙基苯酚、2-壬烯醛、3,4-二甲氧基甲苯和反式-β-紫罗兰酮。本研究通过计算梅花主要花香成分的香气贡献值,发现β-紫罗兰酮、丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚、肉桂醇、对甲苯甲醚、草蒿脑、苯甲醛和乙酸苯甲酯等对梅花花香贡献较大。
苯甲醇具清香、果香和甜香味[23],苯甲醛具有苦杏仁、木香、樱桃香味,乙酸苯甲酯具有茉莉香、浓甜香味,在蜡梅中,乙酸苯甲酯与芳樟醇共同构成其特征香气[24]。丁子香酚有强烈的丁香气味,有抗虫、杀菌的效果。在矮牵牛Petunia hybrida中,丁子香酚的挥发部位主要是花瓣和雄蕊[25]。β-紫罗兰酮具有紫罗兰Matthiola incana、水果、鸢尾花Iris tectorum香味,是紫花含笑Michelia crassipes初花期的特征挥发性物质,也是四季桂Osmanthus fragrans‘Fragrans Group’和金桂Osmanthus fragrans var. thunbergii的主要花香成分[26−27]。其香气阈值极低,在花朵中仅存在少量就能释放出强烈的香气。草蒿脑呈大茴香香气,存在于欧洲越橘Vaccinium padifolium、龙蒿Artemisia dracunculus、茴香Foeniculum vulgare等中[28]。本研究分析了不同类型梅花花香的成分组成,通过香气阈值计算出主要成分的香气贡献值,从而明确其主要贡献成分。
-
不同梅花品种,其香气成分、相对含量和气味品质差异较大。朱砂和宫粉品种群花香化合物种类最多,且苯环/苯丙烷类化合物种类最多。其次是跳枝品种群、绿萼品种群、玉蝶品种群和垂枝品种群。依据梅花主要花香成分的差异,可将20个梅花品种分为5种不同香气类型。本研究鉴定分析了梅花不同品种的花香物质,明确了主要香气成分。后期可进一步明确决定梅花花香差异的主要物质,并结合转录组分析梅花花香的代谢机制。
Identification and analysis of floral scent compounds of Prunus mume cultivars
-
摘要:
目的 比较梅花Prunus mume不同品种间的花香成分差异,了解梅花花香成分组成,为梅花花香代谢途径关键酶基因挖掘和分子育种提供参考。 方法 以不同品种群为材料,采用顶空固相微萃取法和气相色谱质谱联用技术(HS-SPME-GC-MS)测定了20个梅花品种的花香成分,明确梅花花香的特征香气物质,分析梅花不同品种群的花香成分及相对含量差异,并按照花香成分组成对梅花品种进行聚类分析。 结果 在20个梅花品种中共鉴定出43种挥发物,其中苯环/苯丙烷类化合物种类最多且相对含量最高,在梅花各品种中的相对含量均高于85%。乙酸苯甲酯、苯甲醇、丁子香酚、甲基丁香酚、苯甲醛和肉桂醇是梅花花香的主要成分,朱砂和宫粉品种群花香化合物数量最多,其次是跳枝和绿萼品种群,玉蝶和垂枝品种群花香化合物数量较少。聚类分析表明:根据花香成分的种类及相对含量,20个梅花品种可分为5类。 结论 梅花不同品种群的香气成分及其相对含量均有差异,不同花香成分对不同品种梅花香气的贡献也有差异。图1表11参28 Abstract:Objective This study, with a comparison of the different floral scent compounds of different cultivars of Prunus mume, is aimed to investigate the floral composition of P. mume so as to lay a foundation for mining the key enzyme genes in the pathway of floral aroma metabolism and molecular breeding in the future. Method With 20 cultivars of P. mume from different groups selected as experimental materials, headspace solid phase microextraction method and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS) were employed to determine the floral components of 20 cultivars of P. mume and identify the characteristic aroma substances of P. mume before an analysis was conducted of the floral components and relative content differences of P. mume in different cultivars groups whereas a cluster analysis was conducted of the cultivars in accordance with the floral components. Result A total of 43 volatiles were identified from 20 cultivars of P. mume, among which benzene/phenylpropane compounds were the most diverse and had the highest content, and their relative content in all cultivars was higher than 85%. Among the volatiles, the benzyl acetate, benzyl alcohol, eugenol, methyl eugenol, benzaldehyde and cinnamyl alcohol were the main components of P. mume flower fragrance, the number of floral compounds in Cinnabar Purple and Pink Double group was the highest, followed by that in Versicolor and Green Calyx group, and the number of floral compounds in Alboplena and Pendulous Mei group was relatively smaller. Cluster analysis showed that 20 cultivars of P. mume could be divided into 5 categories according to the types and contents of flower aroma components. Conclusion The aroma components and relative contents of different cultivars of P. mume were different, so was the contribution of different floral components to the aroma of different cultivars of P. mume. [Ch, 1 fig. 11 tab. 28 ref.] -
Key words:
- Prunus mume /
- cultivars /
- floral scent compounds
-
表 1 不同梅花品种群的挥发性成分类型及相对含量
Table 1. Category and relative content of volatile components in six cultivar groups of P. mume
品种群 苯环/苯丙
烷类/种萜烯类/
种脂肪酸衍
生物/种烷烃/
种总数/
种朱砂 16 7 9 3 35 宫粉 20 4 3 3 30 玉蝶 13 3 4 − 20 绿萼 15 3 5 − 23 跳枝 15 6 7 − 28 垂枝 9 4 4 − 17 总数/种 23 7 9 4 43 总相对含量/% 87.01~99.87 0~6.15 0~6.95 0~0.18 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 2 朱砂品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 2. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Cinnabar Purple group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘晨晖朱砂’ ‘粉红朱砂’ ‘红颜朱砂’ ‘先春朱砂’ ‘银红朱砂’ ‘大盃’ 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 2.75±0.57 3.08±0.37 2.08±0.78 3.24±0.88 1.64±0.45 5.20±1.61 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 2.84±1.24 5.24±4.44 5.61±3.08 8.72±5.64 1.18±0.25 17.53±1.20 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 41.83±1.67 34.21±1.57 72.86±5.64 63.15±8.15 39.96±2.62 5.78±1.69 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 44.97±4.91 48.25±3.64 1.16±0.12 1.47±0.16 50.48±3.16 25.56±8.21 水杨酸甲酯 methyl salicylate 1 197 − − − − − 0.08±0.07 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 0.08±0.04 − 0.26±0.10 − − 12.44±3.57 3,4-二甲氧基甲苯 3,4-dimethoxytoluene 1 242 − − − − − 0.07±0.05 3-苯丙醇 3-phenylpropanol 1 233 − − 0.37±0.18 0.40±0.13 − − 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 − 0.16±0.09 0.22±0.07 0.21±0.08 − 9.66±3.34 反式肉桂醛 cinnamaldehyde, (E)- 1 272 − − 0.35±0.11 0.75±0.29 0.07±0.06 − 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 1 307 − 1.36±0.58 5.97±1.67 13.67±4.18 1.04±0.48 − 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 5.98±2.00 5.25±1.61 7.37±1.95 7.59±1.37 3.93±0.71 10.50±1.68 丁酸-3-苯丙酯 3-phenylpropyl butyrate 1 373 − 0.07±0.01 − − 0.08±0.01 − 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 0.15±0.05 − 0.30±0.11 0.07±0.05 − 0.46±0.09 乙酸肉桂酯 cinnamyl acetate 1 447 − 1.33±0.34 0.20±0.05 0.59±0.13 0.77±0.21 − 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 0.19±0.08 − 0.79±0.53 − − − 苯基/苯丙烷类合计
total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids98.79 98.95 97.55 99.87 99.15 87.01 莰烯 camphene 963 0.15±0.12 − 1.32±0.18 − − 1.52±0.54 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮 sulcatone 1 003 − − − − − 0.07±0.05 柠檬烯 limonene 1 038 − − − − − 0.17±0.04 3-蒈烯 3-carene 1 056 − − − − − 3.82±2.51 γ-松油烯 γ-terpinene 1 066 − − − − − 0.03±0.02 莰酮 camphor 1 149 − − 0.36±0.05 − − 0.22±0.03 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 0.11±0.09 − 0.13±0.03 − 0.05±0.03 0.32±0.08 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 0.26 0.00 1.82 0.00 0.05 6.15 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 801 − − − − − 0.16±0.12 己醛 hexanal 845 0.10±0.05 − − − − − 乙酸戊酯 n-amylacetate 935 − − − − − 0.17±0.15 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 0.17±0.04 0.30±0.05 − − 0.39±0.11 1.37±0.18 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 0.46±0.14 0.75±0.16 − − 0.42±0.30 4.63±0.76 壬醛 nonanal 1 109 − − − − − 0.05±0.04 癸醛 decanal 1 208 − − − − − 0.07±0.05 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯
2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate1 369 0.21±0.13 − 0.65±0.11 − − − 月桂酸甲酯 methyl laurate 1 525 − − − − − 0.04±0.03 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 0.95 1.05 0.65 0.00 0.81 6.49 十三烷 tridecane 1 300 − − − − − 0.08±0.05 十九烷 nonadecane 1 900 − − − 0.08±0.01 − − 二十一烷 heneicosane 2 100 − − − 0.05±0.03 − − 烷烃类合计 total alkanes 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.13 0.00 0.08 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 3 朱砂品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 3. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Cinnabar Purple group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘晨晖朱砂’ ‘粉红朱砂’ ‘红颜朱砂’ ‘先春朱砂’ ‘银红朱砂’ ‘大盃’ 苯甲醛
benzaldehyde0.350~3.500 0.810~8.110 1.640~16.380 1.600~16.030 2.490~24.910 0.340~3.370 5.010~50.090 苯甲醇
benzyl alcohol80.000 0.523 0.428 0.911 0.789 0.500 0.072 乙酸苯甲酯
benzyl acetate2.600 17.297 18.558 0.445 0.567 19.415 9.831 草蒿脑
estragole0.016 5.000 − 16.250 − − 777.500 丁子香酚
eugenol0.006~0.030 199.330~996.670 175.000~875.000 245.670~1 228.330 253.000~1 265.000 131.000~655.000 350.000~1 750.000 甲基丁香酚
methyleugenol0.001 146.667 − 296.667 66.667 − 180.000 β-紫罗兰酮
β-ionone0.000 15 238.095 − 19 047.619 − 6 666.667 46 190.476 壬醛
nonanal0.001 − − − − − 53.333 癸醛
decanal0.001~0.002 − − − − − 35.000~70.000 肉桂醇
cinnamyl alcohol0.001 − 1 700.000 7 466.667 17 087.500 1 295.833 − 异戊醇
isoamyl alcohol0.006 − − − − − 25.683 乙酸叶醇酯
cis-3-hexe-nylacetate0.009 19.259 33.704 − − 43.333 151.852 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 4 宫粉品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 4. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Pink Double group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘粉皮宫粉’ ‘粉晕宫粉’ ‘晓红宫粉’ ‘早花宫粉’ ‘春意早宫粉’ 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 2.00±0.08 2.89±0.61 5.38±3.15 4.17±1.33 1.80±0.24 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 11.44±1.89 5.10±3.94 2.45±1.37 8.74±1.64 4.06±1.31 苄甲醚 benzyl methyl ether 999 − − − − 0.04±0.03 对甲苯甲醚 p-methylanisole 1 029 0.56±0.12 0.51±0.15 − − − 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 53.90±3.71 54.94±9.98 30.57±6.39 30.31±4.00 40.05±1.42 对甲酚 p-cresol 1 080 0.06±0.05 0.07±0.05 − − − 苯甲酸甲酯 methyl benzoate 1 099 − − − 0.57±0.35 − 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 1.54±0.11 1.20±0.13 53.19±8.71 25.32±4.67 46.72±1.19 2-甲氧基-4-甲基苯酚 creosol 1 195 0.07±0.01 − − 0.05±0.04 − 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 0.17±0.05 0.15±0.04 − 0.12±0.02 0.05±0.00 3-苯丙醇 3-phenylpropanol 1 233 0.38±0.08 0.65±0.24 − 0.12±0.05 0.07±0.00 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 0.23±0.03 0.32±0.16 0.09±0.04 0.63±0.22 − 反式肉桂醛 cinnamaldehyde, (E)- 1 272 0.89±0.28 1.07±0.50 − 1.22±0.36 0.09±0.02 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 1 307 16.19±5.50 19.83±9.73 − 7.42±1.96 1.46±0.17 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 9.35±0.92 9.57±1.02 7.13±0.90 9.15±1.09 3.33±0.30 丁酸-3-苯丙酯 3-phenylpropyl butyrate 1 373 − − − − 0.17±0.02 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 0.17±0.02 0.17±0.02 0.05±0.03 0.09±0.02 0.11±0.03 乙酸肉桂酯 cinnamyl acetate 1 447 0.81±0.08 0.77±0.10 − 9.94±1.43 1.13±0.11 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 − 0.19±0.06 − 0.03±0.02 − 苯甲酸苯甲酯 benzyl benzoate 1 771 0.40±0.04 0.31±0.09 − 0.35±0.02 − 苯基/苯丙烷类合计 total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids 98.15 97.75 98.86 98.21 99.07 莰烯 camphene 963 0.61±0.49 0.67±0.56 0.23±0.18 0.23±0.13 0.24±0.06 3-蒈烯 3-carene 1 056 0.86±0.58 1.03±0.87 − − − 莰酮 camphor 1 149 0.13±0.07 0.16±0.08 0.16±0.07 0.17±0.14 0.07±0.03 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 0.25±0.12 0.19±0.12 − − 0.08±0.01 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 1.85 2.04 0.39 0.40 0.39 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 − − 0.26±0.13 0.18±0.02 0.26±0.02 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 − − 0.49±0.07 1.01±0.33 0.28±0.03 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate 1 369 − 0.20±0.04 − − − 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 0.00 0.20 0.75 1.19 0.54 十五烷 pentadecane 1 500 − − − 0.11±0.03 − 十九烷 nonadecane 1 900 − − − 0.02±0.02 − 二十一烷 heneicosane 2 100 − − − 0.05±0.04 − 烷烃类合计 total alkanes 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.18 0.00 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 5 宫粉品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 5. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Pink Double group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘粉皮宫粉’ ‘粉晕宫粉’ ‘晓红宫粉’ ‘早花宫粉’ ‘春意早宫粉’ 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 0.350~3.500 3.270~32.690 1.460~14.570 0.700~7.000 2.500~24.970 1.160~11.600 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 80.000 0.674 0.687 0.382 0.379 0.501 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 2.600 0.594 0.462 20.458 9.737 17.969 草蒿脑 estragole 0.016 10.417 9.375 − 7.708 3.333 丁子香酚 eugenol 0.006~0.030 311.670~1558.330 319.000~1595.000 237.670~1 188.330 305.000~1525.000 111.000~555.000 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 0.001 166.667 173.333 46.667 90.000 110.000 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 0.000 35 714.286 27 142.857 − − 10 952.381 对甲苯甲醚 p-methylanisole 0.000 2 800.000 2 566.667 − − − 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 0.001 20 241.667 24 787.500 − 9 270.833 1 825.000 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 0.009 − − 29.259 20.370 28.889 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 6 玉蝶品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 6. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Alboplena group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘乔妆玉蝶’ ‘月光玉蝶’ ‘长蕊玉蝶’ 乙基苯 ethylbenzene 889 − 0.10±0.08 − 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 2.10±0.19 2.66±0.82 1.71±0.96 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 4.42±0.44 7.83±2.17 5.94±4.00 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 24.35±6.23 7.73±2.29 18.80±5.01 苯甲酸甲酯 methyl benzoate 1 099 0.14±0.05 − − 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 62.67±4.41 72.90±6.01 62.63±5.69 水杨酸甲酯 methyl salicylate 1 197 − − 0.06±0.05 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 − 0.13±0.05 1.09±1.22 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 0.13±0.11 − 1.01±1.21 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 5.36±0.93 3.06±0.50 6.17±1.95 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 − 0.38±0.02 0.28±0.10 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 − 0.11±0.10 0.22±0.18 苯甲酸苯甲酯 benzyl benzoate 1 771 − 0.13±0.12 − 苯基/苯丙烷类合计 total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids 99.17 95.02 97.92 莰烯 camphene 963 0.24±0.08 0.07±0.06 0.38±0.25 莰酮 camphor 1 149 0.13±0.04 − 0.05±0.04 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 − − 0.05±0.04 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 0.38 0.07 0.49 乙酸戊酯 n-amylacetate 935 − 0.15±0.04 − 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 0.07±0.06 1.69±0.66 0.64±0.39 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 0.38±0.19 2.95±1.10 0.66±0.49 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate 1 369 − 0.12±0.11 0.29±0.24 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 0.45 4.91 1.59 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 7 玉蝶品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 7. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Alboplena group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘乔妆玉蝶’ ‘月光玉蝶’ ‘长蕊玉蝶’ 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 0.350~3.500 1.260~12.630 2.240~22.370 1.700~16.970 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 80.000 0.304 0.097 0.235 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 2.600 24.103 28.037 24.090 草蒿脑 estragole 0.016 − 8.125 68.333 丁子香酚 eugenol 0.006~0.030 178.670~893.330 102.000~510.000 205.670~1 028.330 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 0.001 − 376.667 276.667 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 0.000 − − 7 619.048 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 0.009 7.778 187.778 71.481 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 8 绿萼品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 8. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Green Calyx group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘变绿萼’ ‘小绿萼’ ‘素玉绿萼’ 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 2.49±1.74 1.57±0.59 0.73±0.22 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 14.67±3.77 2.73±0.41 5.45±1.16 对甲苯甲醚 p-methylanisole 1 029 5.41±1.57 − − 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 8.26±1.41 23.37±5.36 24.56±0.85 对甲酚 p-cresol 1 080 0.05±0.04 − − 苯甲酸甲酯 methyl benzoate 1 099 0.33±0.10 − − 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 57.43±4.67 65.13±4.33 59.20±1.79 水杨酸甲酯 methyl salicylate 1 197 0.25±0.08 − − 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 0.81±0.18 0.09±0.07 1.26±0.30 3,4-二甲氧基甲苯 3,4-dimethoxytoluene 1 242 0.09±0.07 − − 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 0.27±0.18 − 0.89±0.33 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 5.34±0.44 3.74±1.54 5.81±0.61 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 0.46±0.21 0.28±0.17 0.31±0.03 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 0.12±0.09 0.35±0.26 − 苯甲酸苯甲酯 benzyl benzoate 1 771 1.93±0.49 − − 苯基/苯丙烷类合计 total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids 97.90 97.26 98.21 莰烯 camphene 963 − 0.40±0.20 0.16±0.05 莰酮 camphor 1 149 − 0.28±0.18 − β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 − 0.14±0.06 − 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 0.00 0.82 0.16 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 801 0.31±0.27 − − 乙酸戊酯 n-amylacetate 935 0.17±0.06 − 0.07±0.01 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 1.41±0.77 0.70±0.25 0.41±0.14 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 − 1.11±0.58 1.04±0.73 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate 1 369 0.19±0.07 0.12±0.09 0.11±0.09 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 2.09 1.93 1.63 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 9 绿萼品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 9. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Green Calyx group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘变绿萼’ ‘小绿萼’ ‘素玉绿萼’ 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 0.350~3.500 4.190~41.910 0.780~7.800 1.560~15.570 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 80.000 0.103 0.292 0.307 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 2.600 22.087 25.050 22.769 草蒿脑 estragole 0.016 50.833 5.833 78.750 丁子香酚 eugenol 0.006~0.030 178.000~890.000 124.670~623.330 193.670~968.330 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 0.001 460.000 280.000 310.000 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 0.000 − 19523.810 − 对甲苯甲醚 p-methylanisole 0.000 27050.000 − − 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 0.006 51.366 − − 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 0.009 157.037 77.407 45.556 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 10 跳枝和垂枝品种群花香成分及其相对含量
Table 10. Aromatic compounds and the relative content of Versicolor group and Pendulous Mei group of P. mume
化合物 保留指数 相对含量/% ‘单粉跳枝’ ‘筋入春日野’ ‘单粉垂枝’ 对二甲苯 p-xylene 896 5.92±0.62 4.67±0.99 2.87±0.66 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 973 17.58±0.46 9.12±2.60 16.53±3.54 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 1 041 59.78±1.26 12.20±5.77 13.88±4.66 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 1 171 1.36±0.13 63.54±9.56 55.42±1.57 2-甲氧基-4-甲基苯酚 creosol 1 195 − 0.16±0.06 − 草蒿脑 estragole 1 201 0.40±0.05 0.16±0.04 0.25±0.08 3,4-二甲氧基甲苯 3,4-dimethoxytoluene 1 242 − 0.11±0.02 − 3-苯丙醇 3-phenylpropanol 1 233 0.24±0.06 − − 4-(2-丙烯基)苯酚 phenol-4-(2-propenyl)- 1 255 0.19±0.01 − 0.22±0.04 反式肉桂醛 cinnamaldehyde, (E)- 1 272 0.34±0.07 − − 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 1 307 4.14±1.34 − − 丁子香酚 eugenol 1 360 5.50±0.16 2.59±0.48 4.88±0.85 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 1 406 0.09±0.03 0.22±0.06 0.18±0.12 乙酸肉桂酯 cinnamyl acetate 1 447 0.14±0.10 − − 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 dimethyl phthalate 1 458 0.57±0.36 0.13±0.11 0.36±0.16 苯基/苯丙烷类合计 total phenylpropanoids/ benzenoids 96.25 92.92 94.58 莰烯 camphene 963 1.99±0.59 − 1.02±0.08 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮 sulcatone 1 003 − 0.08±0.06 − 柠檬烯 limonene 1 038 0.14±0.10 − 0.10±0.01 3-蒈烯 3-carene 1 056 − 0.06±0.04 − 莰酮 camphor 1 149 0.83±0.09 − 0.08±0.01 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 1 490 0.14±0.07 − 0.08±0.07 萜烯类合计 total terpenoids 3.10 0.13 1.28 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 801 0.05±0.03 − − 己醛 hexanal 845 − 0.14±0.13 − 乙酸戊酯 n-amylacetate 935 − − 0.08±0.06 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 1 018 − 2.36±1.43 0.81±0.23 乙酸-2-己烯酯 2-hexen-1-ol acetate 1 027 − 4.31±2.65 3.02±0.77 壬醛 nonanal 1 109 0.11±0.03 − − 癸醛 decanal 1 208 0.12±0.02 − − 二乙二醇丁醚醋酸酯 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)-ethanol acetate 1 369 0.34±0.13 0.14±0.10 0.24±0.19 月桂酸甲酯 methyl laurate 1 525 − − − 脂肪酸衍生物合计 total fatty acid derivatives 0.61 6.95 4.15 说明:−表示未检测到。 表 11 跳枝和垂枝品种群梅花花香化合物香气贡献值
Table 11. Aroma contribution value of floral scent compounds from Versicolor group and Pendulous Mei group of P. mume
化合物 香气阈值 香气贡献值/% ‘单粉跳枝’ ‘筋入春日野’ ‘单粉垂枝’ 苯甲醛 benzaldehyde 0.350~3.500 5.020~50.230 2.610~26.060 4.720~47.230 苯甲醇 benzyl alcohol 80.000 0.747 0.153 0.174 乙酸苯甲酯 benzyl acetate 2.600 0.523 24.440 21.314 草蒿脑 estragole 0.016 24.792 9.729 15.833 丁子香酚 eugenol 0.006~0.030 183.330~916.670 86.330~431.670 162.670~813.340 甲基丁香酚 methyleugenol 0.001 93.333 223.667 176.667 β-紫罗兰酮 β-ionone 0.000 20 000.000 − 11 428.571 壬醛 nonanal 0.001 113.333 − − 癸醛 decanal 0.001~0.002 60.000~120.000 − − 肉桂醇 cinnamyl alcohol 0.001 5 175.000 − − 异戊醇 isoamyl alcohol 0.006 7.650 − − 乙酸叶醇酯 cis-3-hexe-nylacetate 0.009 − 262.296 90.000 说明:−表示未检测到。 -
[1] 唐桂梅, 黄国林, 曾斌, 等. 梅花种质资源研究进展[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2020(5): 108 − 111, 114. TANG Guimei, HUANG Guolin, ZENG Bin, et al. Research progress of germplasm resources of Prunus mume [J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2020(5): 108 − 111, 114. [2] HAO Ruijie, DU Dongliang, WANG Tao, et al. A comparative analysis of characteristic floral scent compounds in Prunus mume and related species [J]. Bioscience,Biotechnology,and Biochemistry, 2014, 78(10): 1640 − 1647. [3] 陈瑞丹, 包满珠, 张启翔. 国际梅品种登录工作19年——业绩与前景[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(增刊1): 1 − 4. CHEN Ruidan, BAO Manzhu, ZHANG Qixiang. Nineteen years in international registration for mei flower (Prunus mume): achievements and prospects [J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(suppl 1): 1 − 4. [4] 陈俊愉, 陈瑞丹. 中国梅花品种群分类新方案并论种间杂交起源品种群之发展优势[J]. 园艺学报, 2009, 36(5): 693 − 700. CHEN Junyu, CHEN Ruidan. A new system for classifying China mei cultivar groups, with special reference to developing superiorities of interspecific hybrid originated groups [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2009, 36(5): 693 − 700. [5] 赵印泉, 周斯建, 彭培好, 等. 不同类型梅花品种及近缘种山桃挥发性成分分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(26): 16164 − 16165. ZHAO Yinquan, ZHOU Sijian, PENG Peihao, et al. Analysis of volatile component in different species of plum varieties and its related specie: prunus plum [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(26): 16164 − 16165. [6] 王爽, 董彬, 王艺光, 等. 不同梅品种花果特性分析与评价[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2024, 41(1): 113 − 123. WANG Shuang, DONG Bin, WANG Yiguang, et al. Analysis and evaluation of flower and fruit characteristics of different Prunus mume cultivars [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2024, 41(1): 113 − 123. [7] DONG Fang, FU Xiumin, WATANABE N, et al. Recent advances in the emission and functions of plant vegetative volatiles [J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(2): 1 − 10. [8] MUHLEMANN J K, KLEMPIEN A, DUDAREVA N. Floral volatiles: from biosynthesis to function [J]. Plant Cell Environment, 2014, 37(8): 1936 − 1949. [9] DUDAREVA N, KLEMPIEN A, MUHLEMANN J K, et al. Biosynthesis, function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile organic compounds [J]. New Phytologist, 2013, 198(1): 16 − 32. [10] RAMYA M, AN H R, BAEK Y S, et al. Orchid floral volatiles: biosynthesis genes and transcriptional regulations [J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2018, 235: 62 − 69. [11] 李海燕, 李火根, 杨秀莲, 等. 植物花香物质合成与调控研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2018, 16(1): 123 − 129. LI Haiyan, LI Huogen, YANG Xiulian, et al. Advances studies on the synthesis and regulation of floral substances in plant [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(1): 123 − 129. [12] 王文静, 吕思佳, 汪庆昊, 等. 植物花香物质代谢与调控研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(22): 7612 − 7617. WANG Wenjing, LÜ Sijia, WANG Qinghao, et al. Research advance on the metabolism and regulation of plant floral fragrance [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(22): 7612 − 7617. [13] WANG Xueqin, WU Yanyan, ZHU Huanhuan, et al. Headspace volatiles and endogenous extracts of Prunus mume cultivars with different aroma types [J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(23): 1 − 12. [14] 赵印泉, 潘会堂, 张启翔, 等. 不同类型梅花品种挥发性成分的研究[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2010, 18(3): 310 − 315. ZHAO Yinquan, PAN Huitang, ZHANG Qixiang, et al. Studies on the volatile constituents from cultivars of Prunus mume [J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2010, 18(3): 310 − 315. [15] 曹慧, 李祖光, 王妍, 等. 两种梅花香气成分的分析及QSRR研究[J]. 分析科学学报, 2009, 25(2): 130 − 134. CAO Hui, LI Zuguang, WANG Yan, et al. Study on quantitative structure-retention relationships for volatile fragrance compounds in fresh flowers of Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc [J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2009, 25(2): 130 − 134. [16] 金荷仙, 陈俊愉, 金幼菊. 南京不同类型梅花品种香气成分的比较研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2005, 32(6): 1139. JIN Hexian, CHEN Junyu, JIN Youju. Comparision of different cultvars of Prunus mume’s major gas ingredinets [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2005, 32(6): 1139. [17] 王利平, 刘扬岷, 袁身淑. 梅花香气成分初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2003, 30(1): 42. WANG Liping, LIU Yangming, YUAN Shenshu. Fragrance of the Prunus mume [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2003, 30(1): 42. [18] 雷春妮, 王波, 孙苗苗, 等. GC-MS-AMDIS结合保留指数在玫瑰花露香气成分准确定性分析中的应用[J]. 质谱学报, 2022, 43(1): 109 − 120. LEI Chunni, WANG Bo, SUN Miaomiao, et al. Application of GC-MS-AMDIS combined with retention index in the accurate qualitative analysis of aroma components in rose water [J]. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2022, 43(1): 109 − 120. [19] 杨亚会, 李庆卫, 陈俊愉. 梅学术和产业化研究进展[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2012, 34(增刊1): 164 − 170. YANG Yahui, LI Qingwei, CHEN Junyu. Advances in academic and industrial research on Prunus mume studies. [J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2012, 34(suppl 1): 164 − 170. [20] 郝瑞杰, 张启翔, 杨炜茹, 等. 梅花与远缘子代特征花香成分差异原因分析[J]. 核农学报, 2014, 28(5): 808 − 816. HAO Ruijie, ZHANG Qixiang, YANG Weiru, et al. Study on the difference in characteristic scent between Prunus mume and its interspecific hybrids [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 28(5): 808 − 816. [21] ZHANG Tengxun, BAO Fei, YANG Yongjuan, et al. A comparative analysis of floral scent compounds in intraspecific cultivars of Prunus mume with different corolla colours [J]. Molecules, 2019, 25(1): 1 − 11. [22] LI Ting, ZHAO Xi, CAO Xueli. Volatile metabolome and aroma differences of six cultivars of Prunus mume blossoms [J]. Plants, 2023, 12(2): 1 − 18. [23] 周琦, 赵峰, 张慧会, 等. 香水莲花花香测试条件优化及不同部位挥发性物质成分研究[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 2022-04-22[2023-04-20]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220421.1642.025.html. ZHOU Qi, ZHAO Feng, ZHANG Huihui, et al. Optimization of test conditions and the study on volatile components in different parts of Nymphaea hybrid [J/OL]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022-04-22[2023-04-20]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220421.1642.025.html. [24] 冯楠. 蜡梅花香挥发物测定及2个萜烯合酶基因功能初步研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. FEN Nan. Determination of Floral Volatile Components and Preliminary Study on Function of Two Terpene Synthases in Wintersweet [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. [25] 刘璐, 肖志娜, 刘菲, 等. 矮牵牛花香生物合成及其调控研究进展[J]. 北方园艺, 2016(1): 181 − 185. LIU Lu, XIAO Zhina, LIU Fei, et al. Floral scent biosynthesis and its regulation in Petunia [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2016(1): 181 − 185. [26] 施婷婷, 杨秀莲, 王良桂. ‘波叶金桂’花香成分的释放规律[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(2): 97 − 104. SHI Tingting, YANG Xiulian, WANG Lianggui. Study on the aroma component emission pattern of Osmanthus fragrans ‘Boye Jingui’ [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2018, 42(2): 97 − 104. [27] 杨秀莲, 施婷婷, 文爱林, 等. 3个四季桂品种花瓣挥发性成分的GC-MS分析[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2015, 35(10): 127 − 133. YANG Xiulian, SHI Tingting, WEN Ailin, et al. Analysis of volatile compounds from petals of three species Osmanthaus fragrans asiaticus group cultivars by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry &Technology, 2015, 35(10): 127 − 133. [28] 魏泉增, 胡旭阳. 不同产地小茴香香气成分差异分析[J]. 中国调味品, 2018, 43(5): 74 − 79. WEI Quanzeng, HU Xuyang. Differential analysis for the aroma compounds of fennel from different places of origin [J]. China Condiment, 2018, 43(5): 74 − 79. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230279






 下载:
下载: