-
物种多样性是森林自然恢复状况和森林生态系统健康的重要标志[1],生物量是群落功能稳定性的重要表现形式,探讨物种多样性与生物量之间的关系是阐明物种多样性对生态系统功能作用的重要途径[2-5]。城市化进程的加快促使人为活动对生态环境干扰程度加深,人为干扰导致环境变量发生改变,引起物种多样性空间分布重新配置,从而改变生态系统的结构与功能演化[4, 6-7]。长期持续、高频度的干扰对植被的破坏具有累加和放大的作用[8],影响植被的自然修复和林地生产力水平,致使生态系统严重退化。人为干扰在自然界和生态系统过程中的作用越来越明显,已作为生态学研究的一个重要内容[9-10]。随着社会的加速发展,人为干扰对林地的影响在逐渐加深。城市林地时常遭受道路绿化施工、游人踩踏破坏、日常维护管理和抚育采伐等活动的干扰,探讨城市化背景下植物多样性以及群落生物量水平具有重要意义[11-13]。四川省雅安市苍坪山公园桉树Eucalyptus grandis人工林属于生态景观林,具有调节气候、涵养水源、防风保土、降噪滞尘等生态服务功能。本研究以苍坪山公园桉树人工林为研究对象,同时结合桉树人工林的生态问题[14-15],分析和讨论不同人为干扰强度对桉树人工林物种组成、物种多样性及其与生物量关系的影响,以期为桉树人工林生物多样性和生产力的恢复与维持提供科学依据。
-
研究区苍坪山公园位于四川省雅安市雨城区(29°40′~30°15′N;102°51′~103°12′E),地处四川盆地西缘,成都平原向青藏高原过渡带,地势西南高东北低,为中低山带。该地为亚热带季风性湿润气候类型,冬无严寒,夏无酷暑,雨量充沛。年平均气温为16.1 ℃,最冷月1月平均气温6.1 ℃,最热月7月平均气温25.3 ℃;该区年均雨日218.0 d,降水量达1 732.0 mm,有“天漏”之称;日照偏少,年日照率为23%;湿度较大,年平均湿度为79%。雨城区自然植被结构属于季雨式山地次生常绿阔叶林,森林覆盖率71.94%,植物种类繁多,结构复杂。苍坪山公园地处海拔1 000 m以下低山区,土壤为紫色土。桉树人工林乔木层中桉树、女贞Ligustrum lucidum、绢毛稠李Padus wilsonii、水杉Metasequoia glyptostroboides和桢楠Phoebe zhennan等植物占据重要空间,其中水杉、桢楠等植物是原林地保留下来的混植树种。灌木层中八角枫Alangium chinense、绢毛稠李、桢楠、高粱泡Rubus lambertianus和萝芙木Rauvolfia verticillata等植物占据林下空间;草本层有鸭跖草科Commelinaceae、桑科Moraceae、葫芦科Cucurbitaceae、茄科Solanaceae、商陆科Phytolaccaceae和蕨类植物等。
-
研究区内设有烈士陵园、气象台、雷达站。因道路绿化施工等对林木进行了采伐,对靠近道路和施工地的林木和林下植被造成了破坏。苍坪山桉树人工林均为1980年栽植,原林地分散保留有桢楠、水杉、二球悬铃木Platanus acerifolia、喜树Camptotheca acuminata等树种;栽植初期伐除生长不良、干形差的植株。抚育措施包括进行疏枝、补植、割藤、除草割灌、伐除病害木等。人工林平时受到游人和当地居民踩踏、攀折以及遛狗、野餐、挖野菜、收走凋落物等活动干扰。经踏查发现,人为干扰强度主要与道路的距离密切相关。本研究以人工林遭受的人为活动频率、施工和抚育强度来划分干扰区[10, 13]。
重度干扰(A):靠近游道和道路,遭受过施工破坏和抚育干扰,受游人和当地居民的践踏、挖野菜、攀折等活动频繁,植被破坏严重,垃圾较多。郁闭度0.4~0.5。
中度干扰(B):没有遭受施工破坏,遭受过除补植外的抚育干扰,人为活动频率较低,植被遭一定破坏,有少量垃圾。郁闭度0.5~0.6。
轻度干扰(C):远离道路,除前期进行不良木伐除外未进行抚育和采伐破坏,少有人为活动,植被无破坏,无垃圾。郁闭度0.7。
参照方精云等[16]、郝建锋等[10]的方法,采用典型选样法,在桉树人工林群落内布设12块20 m×20 m林相整齐、立地条件相似的典型样地,其中重度、中度和轻度干扰样地各4块。将每个样地等分为4 个10 m×10 m 的乔木样方,并在每个样地中沿对角线选取6个5 m×5 m 的灌木样方,12个1 m×1 m 的草本样方。实测并记录乔木层(树高≥3 m) 物种、株数、胸径、树高、冠幅,灌木层(树高<3 m,包括木质藤本和乔木更新苗)物种、株(丛)数、株高、冠幅和草本层物种、株数、高度、盖度等指标。同时记录各样地的海拔高度、坡度、坡向等概况(表1)。植物均鉴定到种。
表 1 样地概况
Table 1. Information about the sampling plots
样地号 干扰强度 海拔/m 坡度/(°) 坡向/(°) 平均胸径/cm 平均树高/m 密度/(株·hm-2) 郁闭度 1~4 重度干扰 610~616 20.6~24.7 SW228.5~SW236.0 14.3~16.9 10.0~11.3 1 001 0.4~0.5 5~8 中度干扰 620~624 34.8~37.2 NW27.4~NW29.0 18.6~20.1 13.8~15.2 783 0.5~0.6 9~12 轻度干扰 617~619 30.5~33.5 NW27.2~NW28.1 17.3~18.8 12.1~14.1 905 0.7 -
① 计算各样地各物种的重要值(VI)。乔木层:VI=(相对多度+相对显著+相对频度)/3;灌木层、草本层:VI=(相对多度+相对盖度+相对频度)/3。② 采用α多样性测度方法[10]测定以下指数。丰富度指数(D):D=S;Simpson指数:
$H'=1 - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^S {\mathop P\nolimits_i^2 } $ ;Shannon-Wiener指数:H=$ - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^S {\mathop P\nolimits_i } \log \mathop P\nolimits_i $ ;Pielou均匀度指数:$\mathop J\nolimits_{{\rm{sw}}} = \dfrac{{ - \sum\limits_{i=1}^S {\mathop P\nolimits_i \log \mathop P\nolimits_i } }}{{\log \mathop S\nolimits_{} }}$ 。其中:Pi为第i个物种的个体数ni占所有物种个体总数n的比例;i=1,2,3,$\cdots $ ,S;S为物种数。 -
通过株数、树干横断面积和形高计算乔木层的蓄积量[17]。依据杨昆等[18]的森林林下植被生物量模型,利用冠幅求算出每株灌木(丛)的冠幅直径来计算灌木层的生物量。采用“全株收获法”测定生物量,在每个样地内随机选取4个1 m×1 m的样方,将样方内的草本全部收获,称取鲜质量后带回实验室置于105 ℃的烘箱中杀青30 min,然后调烘箱温度至65 ℃烘干至恒量。将收获的草本植物干质量单位换算成g·m−2。
-
运用Excel 2007、DPS 7.05、Origin7.5统计软件对数据进行整理与统计分析,采用单因素方差分析法(one-way ANOVA)分析不同干扰程度下各多样性指数、生物量间的差异,运用相关分析计算物种多样性生与物量之间的相关性。
-
桉树人工林内共调查到维管束植物55科82属87种。乔木层21科23属23种;灌木层25科33属35种,其中层间植物2科2种,分别是豆科Leguminosae葛Pueraria lobata,五加科Araliaceae常春藤Hedera sinensis;草本层27科38属40种,其中蕨类植物4科4种。调查发现,样地内植被天然更新良好,但林下无桉树的幼树、幼苗。不同干扰强度下,桉树人工林物种数从少到多依次为重度干扰区、中度干扰区、轻度干扰区。如表2所示:乔木层重要值靠前的桢楠、女贞、绢毛稠李和八角枫,在灌木层也占据相当重要的位置。这些均为雨城区常见的乡土树种,传播繁殖能力强,幼树幼苗更新速度快。混植在林内的水杉、柳杉Cryptomeria fortunei、桢楠和二球悬铃木重要值靠前。刺槐Robinia pseudoacacia为喜光造林树种,在林内并不占优势。灌木层高粱泡、石海椒Reinwardtia indica、朴树Celtis sinensis幼树均在微碱性土壤上生长良好,稍耐阴,在林下重要值靠前。林下分布的葛、刺槐具固氮功能,有改良土壤的作用。草本层优势种多为多年生草本,对土壤的适应性强。白花紫露草Tradescantia fluminensis原产南美,生性强健,抗干扰能力强,干扰程度越强分布面越广,在不同干扰下重要值均占第1位;重要值靠前的垂序商陆Phytolacca americana和葎草Humulus scandens,适生幅度宽,具有保持水土的能力,分布面随着干扰的增强而减少;里白Diplopterygium glaucum在轻度干扰区内没有分布,可能轻度干扰区环境过于荫蔽不适宜其生长。铁线蕨Adiantum capillus-veneri喜半阴润环境,是钙质土指示植物,样地内均有分布,重度干扰区分布最广。朴树、水麻Debregeasia orientalis、紫麻Oreocnide frutescens、透茎冷水花Pilea pumila等植物在重度干扰区没有分布。这可能与其抗干扰能力的大小和对生境的要求有关。
表 2 不同干扰下桉树人工林各层次物种及其重要值
Table 2. Important values of species in different layers of E. grandis plantation in different levels of interference
层次 干扰强度 物种及其重要值 乔木层 重度干扰 桉树(0.251 1)+女贞(0.159 8)+水杉(0.136 7)+绢毛稠李(0.139 4)+桢楠(0.062 5)+二球悬铃木(0.086 0)+柳杉(0.0413) 中度干扰 桉树(0.297 3)+女贞(0.097 2)+水杉(0.183 4)+绢毛稠李(0.052 6)+桢楠(0.197 5)+八角枫 (0.053 9) 轻度干扰 桉树(0.217 2)+女贞(0.154 7)+水杉(0.071 6)+绢毛稠李(0.143 5)+喜树(0.083 8)+二球悬铃木(0.057 2)+银木 Cinnamomum septentrionale(0.050 6) 灌木层 重度干扰 桢楠(0.177 4)+绢毛稠李(0.147 1)+高粱泡 (0.099 0)+石海椒 (0.076 8)+刺槐 (0.072 8)+八角枫(0.067 8)+女贞(0.066 0)+ 朴树 (0.043 3) 中度干扰 萝芙木 (0.209 7)+高粱泡(0.129 4)+桢楠(0.108 8)+绢毛稠李(0.098 8)+紫麻(0.0556)+女贞(0.048 6)+朴树(0.048 8)+ 常春藤 (0.048 8) 轻度干扰 绢毛稠李(0.177 8)+润楠Machilus nanmu(0.134 0)+桢楠(0.072 1)+水麻 (0.092 3)+石海椒(0.067 8)+女贞(0.041 6)+朴 树(0.051 0)+苦竹Pleioblastus amarus(0.041 1) 草本层 重度干扰 白花紫露草 (0.553 9)+铁线蕨(0.073 4)+钮子瓜Zehneria maysorensis(0.042 5) 中度干扰 白花紫露草(0.491 6)+里白 (0.117 4)+垂序商陆(0.055 2)+毛茛Ranunculus japonicus (0.054 0) 轻度干扰 白花紫露草(0.413 8)+垂序商陆(0.100 5)+葎草 (0.079 8)+透茎冷水花 (0.086 8)+白英Solanum lyratum(0.051 9) 说明:括号中数值为重要值 -
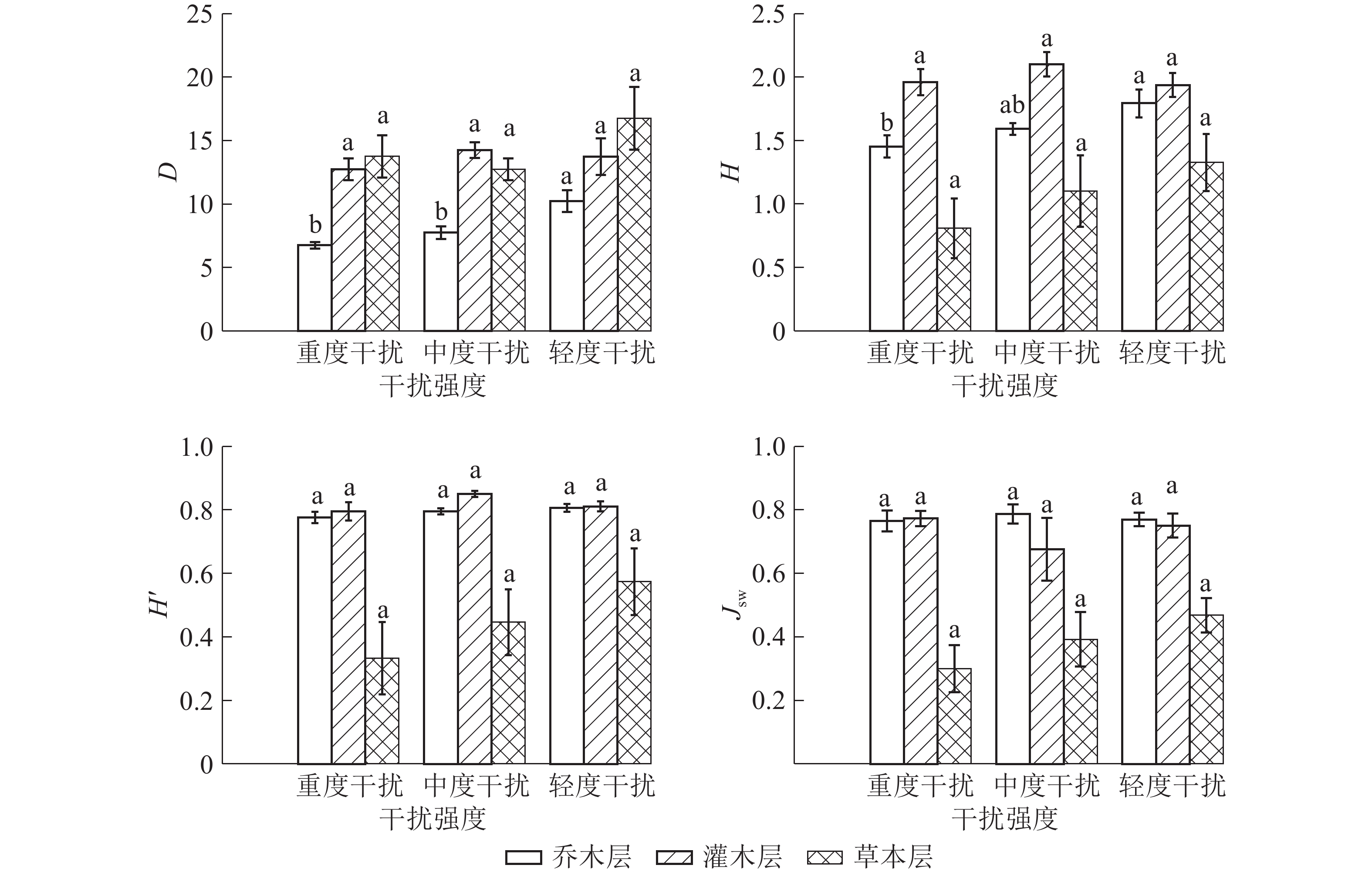
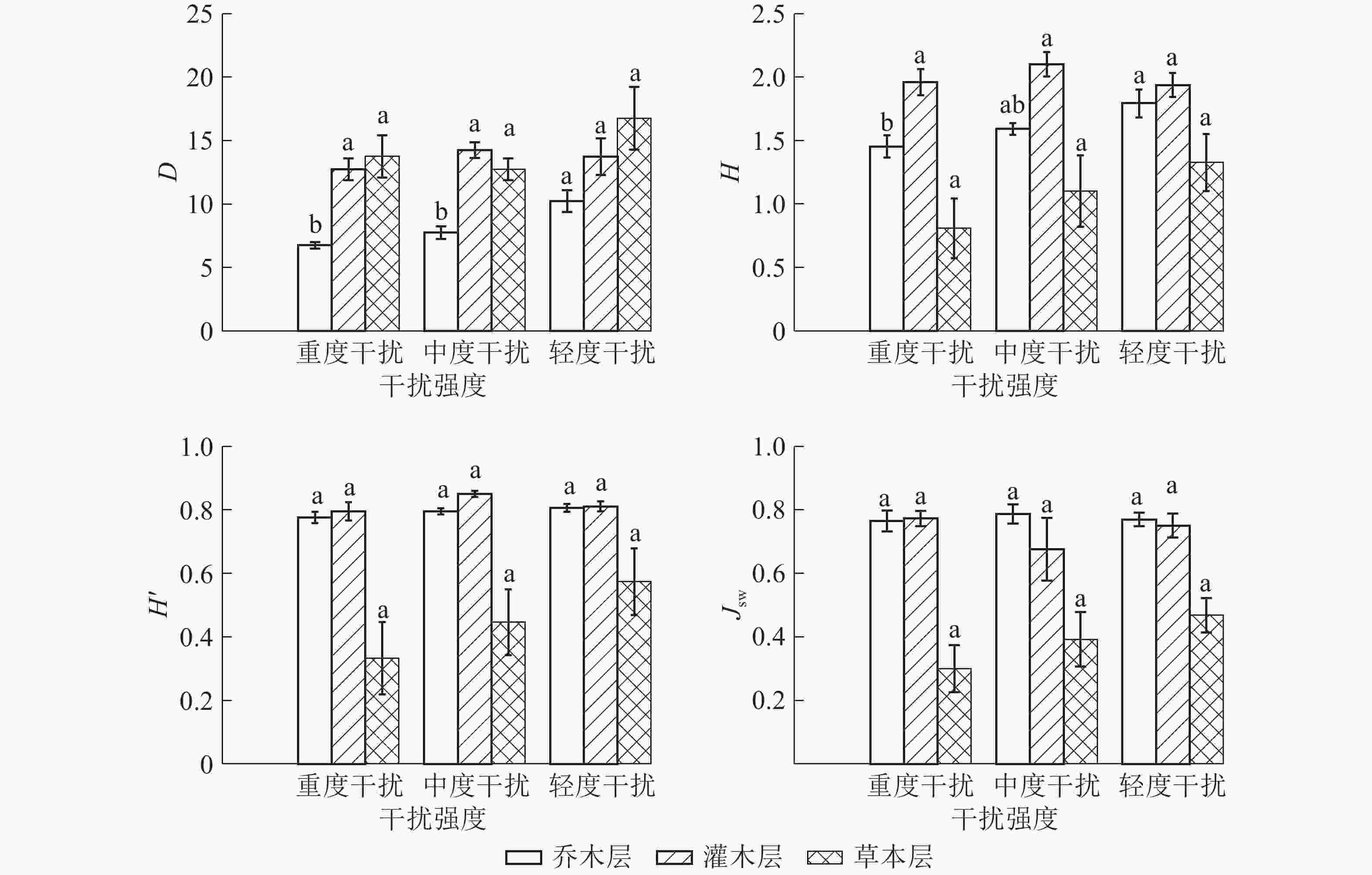
人为干扰引起的环境条件变化常常对林下植物的生长更新和分布产生制约,表现出在空间分布上的差异[19]。如图1所示:桉树人工林内D值从大到小依次为草本层、灌木层、乔木层,轻度干扰区、中度干扰区、重度干扰区;重度干扰区和中度干扰区乔木层D显著较低(P<0.05),重度干扰区乔木层H显著低于轻度干扰区(P<0.05),其余不同干扰程度下植物的物种多样性差异均不显著。人为干扰对乔木层物种多样性的影响较大,灌木层的物种样性水平仍较高。乔本层和草本层的D、H、H'在不同干扰区变化顺序表现一致,轻度干扰区最高,重度干扰区最低;乔木层和草本层Jsw在重度干扰区最低。不同干扰强度下,灌木层D、H、H'从大到小依次表现为中度干扰区、轻度干扰区、重度干扰区,中度干扰区最高,Jsw在中度干扰区最低,虽然中度干扰区物种数和株数最大,但分布均匀度最差。综合分析可知:重度干扰区植物各层次的物种多样性最低,优势物种最不突出,种群的空间分布均匀性较差,群落稳定性较差。
-
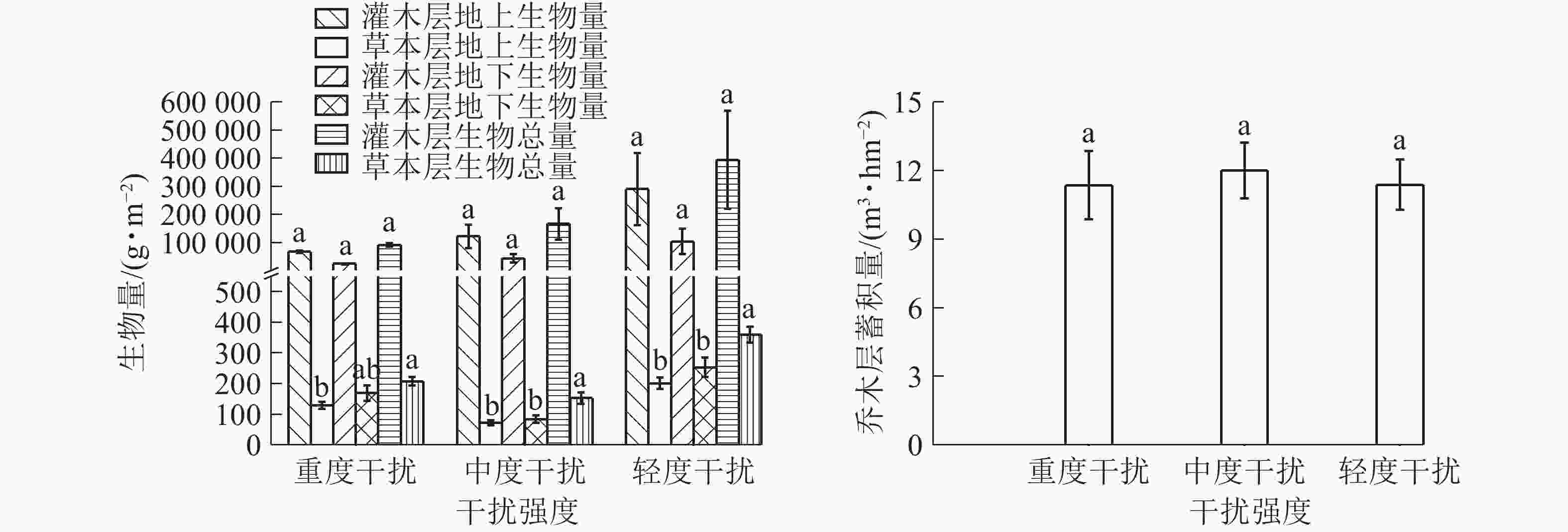
图2表明:乔木层蓄积量从大到小总体依次为中度干扰区、轻度干扰区、重度干扰区,受人为干扰的影响不显著,在中度干扰下表现出了较强的生产力。这符合竞争排斥原理,在有限资源的基础上种内种间竞争达到某种平衡,促使最大生物量的产生[5],也可能与中度干扰区混植有较大树龄的其他树种有关。灌木层生物量地上部分高于地下部分,灌木层生物总量、地上部分生物量和地下部分生物量从大到小均表现为轻度干扰区、中度干扰区、重度干扰区,可见,灌木层的生物量随着干扰强度的增加而减弱;灌木层在中度干扰下生物量处于中等水平,而物种多样性最高。草本层地上部分干质量均小于地下部分干质量,这应与多数草本植物的根部为肉质根、须根系发达有关,如铁线蕨和里白均有粗壮的根状茎;垂序商陆有肥大的纺锤状根茎;麦冬Ophiopogon japonicus根较粗,有膨大的小块根等。草本层生物总量、地上部分干质量和地下部分干质量从大到小排列均为轻度干扰、重度干扰、中度干扰,轻度干扰区的生物量最高,重度干扰区次之,中度干扰区最低,可能由于重度干扰区群落的优势物种突出,其繁衍力强,应对干扰环境而充分利用资源聚集生长,比中度干扰下产生更多的生物量。
-
表3表明:乔木层D与草本层地上生物量、生物总量呈显著正相关(P<0.05),相关系数分别是0.61和0.57;乔木层Jsw与整体群落生物量呈负相关;乔木层D、H、H'与灌木层生物量相关性极小。草本层地上生物量和生物总量受上层乔木的影响显著(P<0.05)。灌木层H、H'、Jsw与灌木层、草本层的生物量均成负相关;灌木层D与整体群落生物量相关性小,与乔木层蓄积量呈负相关。林内生物总量随灌木层物种多样性的增加呈减少趋势,灌木层物种多样性越大,数量繁多的优势种,抢占过多生存资源,可能会促使群落整体生物量的减少。草本层H'与草本层地上生物量、生物总量呈显著正相关(P<0.05),草本层Jsw与草本层生物总量呈显著正相关(P<0.05);草本层物种多样性与乔木层、灌木层的生物量无显著相关;草本层物种多样性与其生物量相关系数为0.35~0.59。草本层的物种多样性对自身生物量的影响明显,草本植物的均匀分布能够更充分利用林下资源,促使生物量的增长。
表 3 桉树人工林下的物种多样性指数与生物量的相关系数
Table 3. Correlation between species diversity index and biomass of E. grandis plantation
层次 项目 多样性指数 乔木层 灌木层 草本层 D H H' JSW D H H' JSW D H H' JSW 乔木层 森林蓄积量 0.00 −0.10 0.26 −0.17 −0.24 0.12 0.48 −0.20 −0.05 0.05 0.00 0.05 灌木层 地上生物量 0.20 −0.01 −0.02 −0.41 0.05 −0.46 −0.34 −0.14 −0.02 0.01 0.00 0.04 地下生物量 0.20 −0.01 −0.02 −0.41 0.05 −0.46 −0.34 −0.14 −0.02 0.01 0.00 0.04 生物总量 0.20 −0.01 −0.02 −0.41 0.05 −0.46 −0.34 −0.14 −0.02 0.01 0.00 0.04 草本层 地上生物量 0.61* 0.35 0.37 −0.34 0.14 −0.32 −0.16 −0.28 0.40 0.53 0.59* 0.55 地下生物量 0.44 0.20 0.21 −0.37 0.00 −0.54 −0.29 −0.35 0.35 0.46 0.44 0.49 生物总量 0.57* 0.30 0.31 −0.39 0.08 −0.46 −0.24 −0.34 0.41 0.53 0.56* 0.56* 说明:* 表示显著相关(P<0.05) -
本研究得出:随着人为干扰强度的加大,物种数呈递减趋势,这与郝建锋等[10]的研究结论较为一致。桉树人工林乔木层和草本层D、H、H'随干扰强度的增大而减少,与吕浩荣等[19]研究得出的风水林下木本植物D、H、H'随着人为干扰强度的增大而增加的结论相左,这可能与不同的气候环境、林分以及干扰强度的标准等因素有关。灌木层D、H、H'在中度干扰下达到最高,符合“中度干扰假说”[20],适度的人为干扰会增加物种多样性,加速林下乔木幼苗的生长更新,增加灌木层的物种多样性;利于喜光植物的侵入定居或外界活动对植物的带入,如干扰区多见分布的柑橘Citrus reticulata、柚C. maxima和枇杷Eriobotrya japonica等果树。重度干扰区的物种多样性水平最低,物种在群落中分布不均匀,群落稳定性差,对环境波动的缓冲功能减弱[1],生态系统容易遭受病虫害和极端天气的侵害。不同的干扰强度会使物种产生适应性进化,影响其组成与空间分布,适当的干扰会对林地产生增益性,而严重的干扰会对林地物种多样性乃至生态系统产生不利影响。
桉树人工林下的物种多样性比其他树种的纯林和自然林(次生林)都弱,作为外来种短时期内不能在引种地形成完善的生态系统和生物多样性的生境,国内粗放的经营模式下,桉树林生物多样性减弱、地力衰退、生态环境恶劣[21]。虽然桉树本身对资源具有较大的竞争力,但研究区桉树人工林内的物种数仍较为可观[13],生态林下阳性树种少,中性树种居多。这可能与雨城区多雨、少日照的环境条件有关,中国桉树栽植区的雨量多在1 000 mm以上,降水的淋溶、稀释,都会减弱桉树化感作用,使其可以与绝大多数林下植物共生[14, 21];也可能与研究区本身物种丰富有关。桉树人工林下多分布适应性强的乡土树种和草本植物,其中石海椒喜石灰岩土壤,铁线蕨是钙质土指示植物,在研究区内均有分布,且在重度干扰区分布最广。人为干扰的加强可能加重林地土壤碱化程度,不利于植物生长发育。
乔木层蓄积量受人为干扰的影响较小,灌木层和草本层生物量受人为干扰的影响较大,但差异均不显著,这可能与重度干扰区和中度干扰区的补植抚育和林下植物生长旺盛有关。林下植被遭受的干扰比乔木层更为直接频繁,所以灌木层和草本层遭受更大的干扰影响。生物量与物种多样性的关系主要表现为线性、单峰和没有显著关系[5]。本研究中草本层生物总量随乔木层物种丰富度、草本层物种多样性的增加而增加;灌木层生物总量随其物种多样性的增加而减少,关系不显著;乔木层相关关系不显著。这与高艳等[5]、王勇军等[22]、郑晓翾等[23] 等研究得出的线性关系和没有显著关系的结论相一致,符合在自然生态系统中,多样性和生产力的关系受到自然条件和人类活动干扰而改变,并没有固定关系的说法[24-25]。王勇军等[22]研究得出:灌木层生物总量随物种多样性的增加而增大,且关系显著。与本研究恰好相反,这可能与本研究区灌木处于人工林下,多样性的增加反而加大了物种间的竞争关系,导致灌木层生物总量的减少。森林生物量是研究和评价森林生态系统结构与功能过程最基本的参数,能反映生态系统功能的强弱[3]。研究区物种数低于雅安市境内马尾松Pinus massoniana人工林[25]的物种数;乔木层蓄积量与桉树林第 20 个轮伐期后的年均生长量相近[15]。对于速生丰产树种,这可能与本研究区日照偏少和林地类型有关。这种较低的物种多样性与植被生物量反映了桉树人工林较为脆弱的生态特性[22]。
轻度干扰区较接近半自然状态,林下物种丰富、分布均匀,群落结构较稳定,群落生物量和物种多样性水平优于干扰强度大的区域,能促进林地稳定和健康演变。所以因“树”制宜,减少人为干扰,筛选本地适应性强、有生态功能或珍贵的乡土树种进行地带性桉树人工混交林营造,利用自然力调控,实现桉树人工林的健康、持续发展。建议加强苍坪山桉树人工林的管理保护力度,限制林下游玩活动和樵采破坏行为以便于地被植物的恢复;减少抚育强度,对灌木层可适当割除,优化群落组成结构,促进林内生态系统修复,并积极发挥地方公益林主导功能。
Effects of human interference on species diversity and biomass of Eucalyptus grandis plantation in Cangping Mountain Park in Ya’an
-
摘要:
目的 揭示不同人为干扰强度对桉树Eucalyptus grandis人工林物种多样性和生物量的影响。 方法 以四川省雅安市苍坪山公园桉树人工林为研究对象,采用典型样地法,设置12块20 m × 20 m不同干扰程度的样地,对林内物种组成、物种多样性水平(丰富度指数D、Shannon-Wiener指数H、Simpson优势度指数 H'、Pielou均匀度指数 Jsw)和植物层生物量进行调查研究。 结果 共调查到维管植物87种,隶属55科82属,桉树人工林物种数随着干扰的加强而减少;乔木层与草本层D、H、H'随着干扰强度的增加而降低,灌木层D、H、H'在中度干扰下达到最大值,乔木层的D、H变化差异显著(P<0.05)。随着干扰强度的增加,植物各层生物量呈不同变化趋势:中度干扰下乔木层蓄积量(12.01 m3·hm−2)最高;轻度干扰下灌木层生物量(394.533 kg·m−2)和草本层生物量(359.680 g·m−2)最高。乔木层D、草本层H'与草本层地上生物量和生物总量呈显著正相关(P<0.05);草本层Jsw与草本层生物总量呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。 结论 适度的干扰会促使桉树人工林物种多样性和生物量增加;物种多样性和生物量的关系受人为干扰和自然条件而改变,没有固定关系。图2表3参25 Abstract:Objective This study aims to reveal the effects of human interference on species diversity and biomass in E. grandis plantations. Method 12 sample plots of E. grandis plantations (20 m×20 m) with different interference intensities were set up by typical plot method in Cangping Mountain Park in Ya’an City of Sichuan Province, to investigate the species composition, species diversity(richness index D, Shannon-Wiener index H, Simpson dominance index H', Pielou evenness index Jsw), and plant layer biomass. Result There were 87 species of vascular plants belonging to 55 families and 82 genera. The number of species in E. grandis plantation decreased with increasing interference. The D, H and H' indices of tree layer and herb layer decreased with the increase of interference intensity. The D, H and H' indices of shrub layer reached the maximum under moderate disturbance. The difference of D and H indices in tree layer was significant (P<0.05). With the increase of disturbance intensity, the biomass of each plant layer showed different changing trends. The tree layer had the highest volume (12.01 m3·hm−2) under moderate disturbance, while the biomass of shrub layer (394.533 kg·m−2) and herb layer (359.680 g·m−2) was the highest under light disturbance. The D index of tree layer and H' index of herb layer were significantly positively correlated with aboveground biomass and total biomass of herb layer (P<0.05). The Jsw index of herb layer was significantly positively correlated with total biomass of herb layer (P<0.05). Conclusion Moderate disturbance will increase species diversity and biomass in E. grandis plantation. The relationship between species diversity and biomass is subject to human interference and natural conditions, and there is no fixed relationship. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 25 ref.] -
Key words:
- forest ecology /
- human interference /
- Eucalyptus grandis plantation /
- species diversity /
- biomass
-
表 1 样地概况
Table 1. Information about the sampling plots
样地号 干扰强度 海拔/m 坡度/(°) 坡向/(°) 平均胸径/cm 平均树高/m 密度/(株·hm-2) 郁闭度 1~4 重度干扰 610~616 20.6~24.7 SW228.5~SW236.0 14.3~16.9 10.0~11.3 1 001 0.4~0.5 5~8 中度干扰 620~624 34.8~37.2 NW27.4~NW29.0 18.6~20.1 13.8~15.2 783 0.5~0.6 9~12 轻度干扰 617~619 30.5~33.5 NW27.2~NW28.1 17.3~18.8 12.1~14.1 905 0.7 表 2 不同干扰下桉树人工林各层次物种及其重要值
Table 2. Important values of species in different layers of E. grandis plantation in different levels of interference
层次 干扰强度 物种及其重要值 乔木层 重度干扰 桉树(0.251 1)+女贞(0.159 8)+水杉(0.136 7)+绢毛稠李(0.139 4)+桢楠(0.062 5)+二球悬铃木(0.086 0)+柳杉(0.0413) 中度干扰 桉树(0.297 3)+女贞(0.097 2)+水杉(0.183 4)+绢毛稠李(0.052 6)+桢楠(0.197 5)+八角枫 (0.053 9) 轻度干扰 桉树(0.217 2)+女贞(0.154 7)+水杉(0.071 6)+绢毛稠李(0.143 5)+喜树(0.083 8)+二球悬铃木(0.057 2)+银木 Cinnamomum septentrionale(0.050 6) 灌木层 重度干扰 桢楠(0.177 4)+绢毛稠李(0.147 1)+高粱泡 (0.099 0)+石海椒 (0.076 8)+刺槐 (0.072 8)+八角枫(0.067 8)+女贞(0.066 0)+ 朴树 (0.043 3) 中度干扰 萝芙木 (0.209 7)+高粱泡(0.129 4)+桢楠(0.108 8)+绢毛稠李(0.098 8)+紫麻(0.0556)+女贞(0.048 6)+朴树(0.048 8)+ 常春藤 (0.048 8) 轻度干扰 绢毛稠李(0.177 8)+润楠Machilus nanmu(0.134 0)+桢楠(0.072 1)+水麻 (0.092 3)+石海椒(0.067 8)+女贞(0.041 6)+朴 树(0.051 0)+苦竹Pleioblastus amarus(0.041 1) 草本层 重度干扰 白花紫露草 (0.553 9)+铁线蕨(0.073 4)+钮子瓜Zehneria maysorensis(0.042 5) 中度干扰 白花紫露草(0.491 6)+里白 (0.117 4)+垂序商陆(0.055 2)+毛茛Ranunculus japonicus (0.054 0) 轻度干扰 白花紫露草(0.413 8)+垂序商陆(0.100 5)+葎草 (0.079 8)+透茎冷水花 (0.086 8)+白英Solanum lyratum(0.051 9) 说明:括号中数值为重要值 表 3 桉树人工林下的物种多样性指数与生物量的相关系数
Table 3. Correlation between species diversity index and biomass of E. grandis plantation
层次 项目 多样性指数 乔木层 灌木层 草本层 D H H' JSW D H H' JSW D H H' JSW 乔木层 森林蓄积量 0.00 −0.10 0.26 −0.17 −0.24 0.12 0.48 −0.20 −0.05 0.05 0.00 0.05 灌木层 地上生物量 0.20 −0.01 −0.02 −0.41 0.05 −0.46 −0.34 −0.14 −0.02 0.01 0.00 0.04 地下生物量 0.20 −0.01 −0.02 −0.41 0.05 −0.46 −0.34 −0.14 −0.02 0.01 0.00 0.04 生物总量 0.20 −0.01 −0.02 −0.41 0.05 −0.46 −0.34 −0.14 −0.02 0.01 0.00 0.04 草本层 地上生物量 0.61* 0.35 0.37 −0.34 0.14 −0.32 −0.16 −0.28 0.40 0.53 0.59* 0.55 地下生物量 0.44 0.20 0.21 −0.37 0.00 −0.54 −0.29 −0.35 0.35 0.46 0.44 0.49 生物总量 0.57* 0.30 0.31 −0.39 0.08 −0.46 −0.24 −0.34 0.41 0.53 0.56* 0.56* 说明:* 表示显著相关(P<0.05) -
[1] 龚艳宾. 天然阔叶红松林下植被物种多样性及生物量研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2016. GONG Yanbin. Understory Species Diversity and Biomass of Natural Broad-leaved Korean Pine Forest[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2016. [2] NERFA L, RHEMTULLA J M. Changes in tree species diversity, composition and aboveground biomass in areas of fuelwood harvesting in miombo woodland ecosystems of southern Malawi [J]. For Trees Livelihoods, 2019, 28(3): 176 − 193. [3] 杨路存, 赵玉红, 徐文华, 等. 青海省高寒灌丛物种多样性、生物量及其关系[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(1): 309 − 315. YANG Lucun, ZHAO Yuhong, XU Wenhua, et al. Species diversity, biomass and their relationships of alpine shrubberies in Qinghai Province [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2018, 38(1): 309 − 315. [4] 李尚益, 方晰, 陈金磊, 等. 人为干扰对中亚热带森林生物量及其空间分布格局的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(17): 6111 − 6124. LI Shangyi, FANG Xi, CHEN Jinlei, et al. Effects of different degrees of anthropogenic disturbance on biomass and spatial distribution in subtropical forests in central southern China [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2018, 38(17): 6111 − 6124. [5] 高艳, 杜峰, 王雁南. 黄土丘陵区撂荒群落地上生物量和物种多样性关系[J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(3): 96 − 102. GAO Yan, DU Feng, WANG Yannan. Relationship between aboveground biomass and species diversity of abandoned communities in loess hilly area [J]. Res Soil Water Conserv, 2017, 24(3): 96 − 102. [6] CATHERINE M, JENNIFER M F. Species traits as generalized predictors of forest community response to human disturbance [J]. For Ecol Manage, 2009, 257(2): 723 − 730. [7] RGRAMONT A R E, SERGIO F M, GAVA-BERNAL G, et al. Effect of human disturbance on the structure and regeneration of forests in the Nevado de Toluca National Park, Mexico [J]. J For Res, 2012, 23(1): 39 − 44. [8] 张希彪, 上官周平. 人为干扰对黄土高原子午岭油松人工林土壤物理性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(11): 3685 − 3695. ZHANG Xibiao, SHANGGUAN Zhouping. Effects of Human-induced disturbance on physical properties of soil in artificial Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. forests of the Loess Plateau [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2006, 26(11): 3685 − 3695. [9] 方茹意, 吴炜, 鲁翔, 等. 不同强度人为干扰对毛竹林植物多样性的影响[J]. 世界竹藤通讯, 2017, 15(6): 1 − 5. FANG Ruyi, WU Wei, LU Xiang, et al. Effects of different artificial disturbances intensities on plant siversity in moso bamboo forest [J]. World Bamboo Rattan Commun, 2017, 15(6): 1 − 5. [10] 郝建锋, 王德艺, 唐永彬, 等. 人为干扰对江油地区马尾松人工林群落结构和物种多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(5): 729 − 735. HAO Jianfeng, WANG Deyi, TANG Yongbin, et al. Effects of human disturbance on species diversity of Pinus massoniana plantation in Jiangyou district, Sichuan Province [J]. J Ecol Environ, 2014, 23(5): 729 − 735. [11] 周光兵, 龙翠玲. 人为干扰对城市近郊区森林植物多样性的影响: 以贵阳市乌当区为例[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 36(5): 98 − 103. ZHOU Guangbing, LONG Cuiling. Effects of human-induced disturbance on plant diversity in urban area: a case study of Wudang area in Guiyang, Guizhou Province [J]. J Southwest Norm Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2011, 36(5): 98 − 103. [12] 吴思思, 鲁小珍, 王馨悦, 等. 2种类型人为干扰对城市风景林植物多样性的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(5): 128 − 134. WU Sisi, LU Xiaozhen, WANG Xinyue, et al. Effects of two types of artificial interferences on plant diversity of urban landscape forests [J]. J Nanjing For Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2019, 43(5): 128 − 134. [13] 艾训儒, 易咏梅, 姚兰, 等. 旅游区人为干扰对森林群落物种多样性的影响[J]. 浙江林学院学报, 2010, 27(2): 178 − 184. AI Xunru, YI Yongmei, YAO Lan, et al. Effects of human disturbance on species diversity of Pinus massoniana-Cunninghamia lanceolata mixed forest in Suobuya Stone Forest [J]. J Zhejiang For Coll, 2010, 27(2): 178 − 184. [14] 许晓东, 莫晓勇, 邓海燕, 等. 桉树人工林抚育间伐优化模型[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 49(3): 341 − 347. XU Xiaodong, MO Xiaoyong, DENG Haiyan, et al. Optimizing models of tending and thinning for Eucalyptus plantation [J]. J Fujian A&F Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2020, 49(3): 341 − 347. [15] 潘辉, 黄石德, 张金文, 等. 试论福建省桉树人工林的生态问题及其对策[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(3): 605 − 609. PAN Hui, HUANG Shide, ZHANG Jinwen, et al. Ecological defects and countermeasures of Eucalyptus plantation in Fujian Province [J]. Chin J Eco-Agric, 2009, 17(3): 605 − 609. [16] 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 等. 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(6): 533 − 548. FANG Jingyun, WANG Xiangping, SHEN Zehao, et al. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory [J]. Biodiversity Sci, 2009, 17(6): 533 − 548. [17] 高凌寒. 基于ArboLiDAR的多源遥感数据融合的林分参数估测[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2017. GAO Linghan. Forest Parameters Estimate of Multi-remote Sensing Data Based on ArboLiDAR[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2017. [18] 杨昆, 管东生. 森林林下植被生物量收获的样方选择和模型[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(2): 705 − 714. YANG Kun, GUAN Dongsheng. Selection of gaining quadrat for harvesting the undergrowth vegetation and its biomass estimation modeling in forest [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2007, 27(2): 705 − 714. [19] 吕浩荣, 刘颂颂, 朱剑云, 等. 人为干扰对风水林群落林下木本植物组成和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(5): 458 − 467. LÜ Haorong, LIU Songsong, ZHU Jianyun, et al. Effects of human disturbance on understory woody species composition and diversity in Fengshui forests [J]. Biodiver Sci, 2009, 17(5): 458 − 467. [20] 姚小兰, 郝建锋, 齐锦秋, 等. 人为干扰对川西碧峰峡木荷次生林群落结构和物种多样性的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(11): 18 − 26. YAO Xiaolan, HAO Jianfeng, QI Jinqiu, et al. Effects of human disturbance on community structure and species diversity of Schima superba secondary forest in Bifengxia, western Sichuan [J]. J Northwest A&F Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2017, 45(11): 18 − 26. [21] 于福科, 黄新会, 王克勤, 等. 桉树人工林生态退化与恢复研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(2): 393 − 398. YU Fuke, HUANG Xinhui, WANG Keqin, et al. An overview of ecological degradation and restoration of Eucalyptus plantation [J]. Chin J Eco-Agric, 2009, 17(2): 393 − 398. [22] 王勇军, 黄从德, 张健, 等. 岷江干旱河谷灌丛物种多样性、生物量及其关系[J]. 干旱区研究, 2010, 27(4): 567 − 572. WANG Yongjun, HUANG Congde, ZHANG Jian, et al. Species diversity, biomass and their relationship of shrubberies in an arid valley of the Minjiang River [J]. Arid Zone Res, 2010, 27(4): 567 − 572. [23] 郑晓翾, 王瑞东, 靳甜甜, 等. 呼伦贝尔草原不同草地利用方式下生物多样性与生物量的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(11): 5392 − 5400. ZHENG Xiaoxuan, WANG Ruidong, JIN Tiantian, et al. Relationships between biodiversity and biomass under different regimes of grassland use in Hulunbeir, Inner Mongolia [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2008, 28(11): 5392 − 5400. [24] LONNIE W, ROBERT A, JASON P. Is the productivity of vegetation plots higher or lower when there are more species? Variable predictions from interaction of the‘sampling effect’and‘competitive dominance effect’on the habitat templet [J]. Oikos, 2003, 102(2): 427 − 432. [25] 姚俊宇, 伍炫蓓, 孙千惠, 等. 林窗大小对川西马尾松人工林林下物种多样性和生物量的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2018, 24(2): 214 − 220. YAO Junyu, WU Xuanbei, SUN Qianhui, et al. Effects of canopy gap size on understory species diversity and biomass in a Pinus massoniana plantation in western Sichuan [J]. Chin J Appl Environ Biol, 2018, 24(2): 214 − 220. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.20950756.20200312






 下载:
下载: