-
自然界许多生物能对环境变化做出反应,改变自身的颜色,这种颜色被称为结构色[1−2],是由光子晶体的微结构周期性排列,通过光干涉效应产生的[3]。这种根据环境产生颜色的功能可用于智能材料的开发,在防伪商标[4]、化学传感[5]和生物技术[6]等领域具有广阔的应用潜力。纤维素纳米晶体(CNC)可由木质纤维素经强酸水解法、酶水解法、磷酸水热法和2, 2, 6, 6 -四甲基哌啶氧化物(TEMPO)氧化法等[7]方法获得,具有精细的纳米结构、丰富的表面活性基团、优异的力学性能以及可再生和降解的特点[8−9],是一种重要的生物基纳米材料。CNC悬浮液达到某一临界浓度时,会自发进行有序排列,形成手性向列相液晶结构[10]。通过溶剂蒸发的方法制备CNC薄膜,手性向列相结构得以保留。随着溶剂的蒸发,CNC的浓度逐渐增大,螺距减小,最大反射光波长(λmax)蓝移至可见光范围,赋予薄膜结构色[11],因此,CNC是一种生物质光子晶体材料,成为近期的研究热点。
CNC光子材料的螺距会随环境湿度变化,从而影响其光学性质及结构色,具有湿度敏感性[12−15]。纯CNC液晶薄膜,由于CNC的刚性,非常脆,还存在薄膜湿度灵敏度低,结构色变化不均匀的缺点。为了提高CNC液晶薄膜的韧性,YOUSSEF等[16]将聚乙二醇(PEG)和CNC自组装,形成了具有均匀结构色且柔性的复合膜,在不同的湿度条件下,复合膜的结构色发生可逆均匀改变,由于PEG与CNC良好的相容性,在提升液晶薄膜韧性的基础上,PEG还提升了薄膜的湿度敏感性。研究者们向CNC体系中引入水溶性聚合物,如PEG[12]、聚乙烯醇(PVA)[17]、水性聚氨酯(WPU)[18]等,研究复合CNC液晶薄膜力学和湿度响应行为。
目前针对CNC复合薄膜湿度响应方面的研究主要关注于湿度-结构-变色之间的构效关系,对CNC复合薄膜湿度响应速度和重复性研究不够深入,因此,本研究以CNC为原料,通过将PEG与CNC共组装,制备具有手性向列结构的虹彩色PEG/CNC复合液晶薄膜,系统考察PEG质量分数对复合液晶薄膜的微观结构、显色、力学性能以及吸湿行为的影响,通过饱和电解质溶液控制环境湿度,重点考察复合薄膜在不同湿度下的吸湿-解湿过程和性能变化,阐明PEG/CNC复合薄膜湿度响应机制,为制备低成本、可重复使用和高灵敏度的PEG/CNC复合薄膜湿度传感器提供理论基础。
-
木质纤维素纳米晶体(CNC,美国缅因大学),从木浆中提取并通过硫酸水解,固含量为10.3% (质量分数),含质量分数为1.1%的硫和钠离子;PEG 4000、氯化锂(LiCl)、氯化钠(NaCl)、溴化钠(NaBr)和氯化镁(MgCl2)均为分析纯。
-
首先按照所需比例称取一定质量的CNC与PEG,加入一定量的去离子水稀释后,用玻璃棒搅拌2 min,再用超声波细胞粉碎机超声5 min,得CNC与PEG的混合液,混合液的流动性较好,在剪切速率为1 s−1时,黏度为0.01~0.02 Pa·s。随后,将混合液倒入塑料培养皿,置于35 ℃烘箱中干燥约36 h,得PEG/CNC液晶薄膜。在溶液浇筑过程中控制固含量,控制所得复合薄膜的厚度约为150 μm。制备CNC悬浮液质量分数分别为3%、5%和7%的CNC液晶薄膜,分别标记为3%CNC、5%CNC和7%CNC; PEG/CNC复合体系中,CNC悬浮液质量分数为5%,添加的PEG质量分数分别为0%、5%、10%和15%,分别标记为5%CNC 、5%CNC+5%PEG、5%CNC+10%PEG和5%CNC+15%PEG。
-
采用透射电子显微镜(JEM-1200EX)观察CNC的形貌。用滴管吸取1滴待测CNC悬浮液,滴在电镜铜网上,用体积分数为2%醋酸双氧铀染色,干燥2 min后进行观察并拍摄图像。再使用ImageJ软件处理图像,统计CNC悬浮液微粒的长度与宽度,最终得出长径比分布。
-
使用偏光显微镜(Nikon ECLIPSE LV100ND)拍摄液晶薄膜的显微照片。用裁刀剪取少许CNC液晶薄膜,置于载玻片上,随后将载玻片放置在POM上观察。
-
采用紫外可见分光光度计(UV2400)对所制备液晶薄膜的λmax进行测试,波长范围为200~800 nm。
-
采用冷场发射扫描电子显微镜(SU8010)观察所制得液晶薄膜截面的微观结构。通过液氮淬断的方法制备薄膜样品横截面,并将其安装在样品支架上,成像前样品需喷金45~60 s,电子加速电压为5 kV。
-
采用微机控制电子万能试验机(CMT6104)表征添加不同质量分数的PEG的CNC液晶薄膜的拉伸性能。将样品薄膜剪裁成长度约25 mm,宽度约5 mm的样条,安装样条于试验机上,以2 mm·min−1拉伸速率测试,测定样条断裂时的拉伸强度、弹性模量和断裂伸长率等。
-
在密闭空间中,过饱和盐溶液可以调控环境相对湿度。采用饱和LiCl、MgCl2、NaBr和NaCl溶液分别调控环境相对湿度为20%、40%、60%与80%。①湿度响应时间。将样品薄膜剪裁成样条状,分别放置于不同相对湿度的密闭环境中,每隔一段时间,采用紫外可见分光光度计测定其λmax,得出达到平衡状态下的λmax及所需时间。②吸湿-解湿响应行为研究。将样品薄膜剪裁成样条状,放置于相对湿度为80%的密闭环境中2 h,采用紫外可见分光光度计测定其λmax;随后放入烘箱中干燥2 h,再次测定其λmax,多次重复此过程即可得到其循环性能。
-
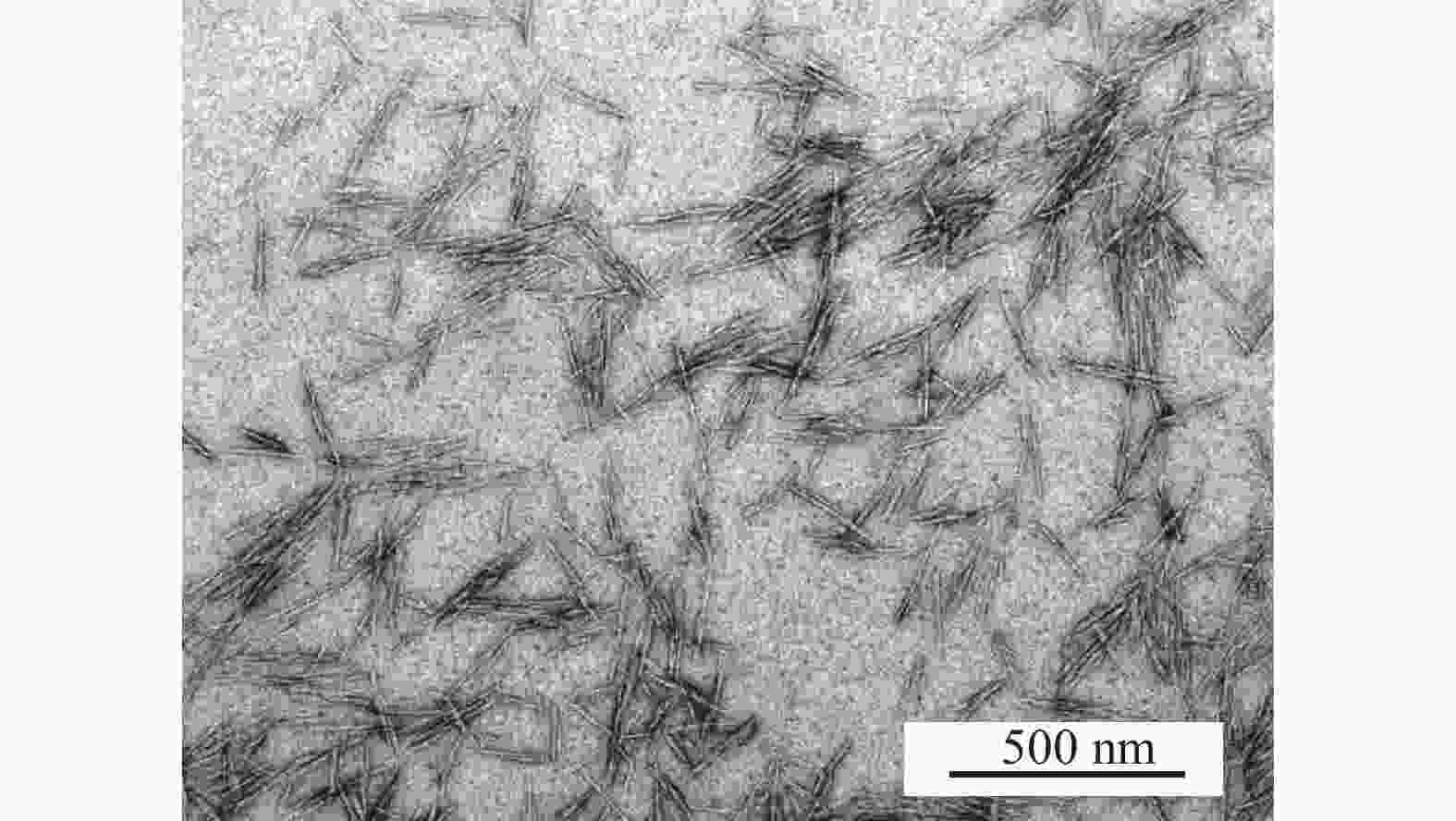
由图1可知:经过醋酸双氧铀染色后的CNC在TEM中呈现均匀的棒状结构,彼此之间排列松散,未出现明显的团聚现象,经统计:CNC的长度为(163.6 ± 60.0) nm,宽度为(8.6 ± 3.2) nm,长径比约19。
-
采用溶液浇筑的手段,可获得具有手性向列结构的虹彩色薄膜。由图2A和图2B1可知:所得薄膜都具有光滑表面及虹彩色,其中,3%CNC和5%CNC所得的薄膜颜色为橙红色,分别对应的λmax为596.5和597.0 nm,7%CNC所得的薄膜部分表现出蓝绿色,对应的λmax为511.0 nm。这是因为随着CNC质量分数的提高,CNC排列更加紧密,分子层间距离减小,从而导致螺距减小,λmax发生蓝移[19]。
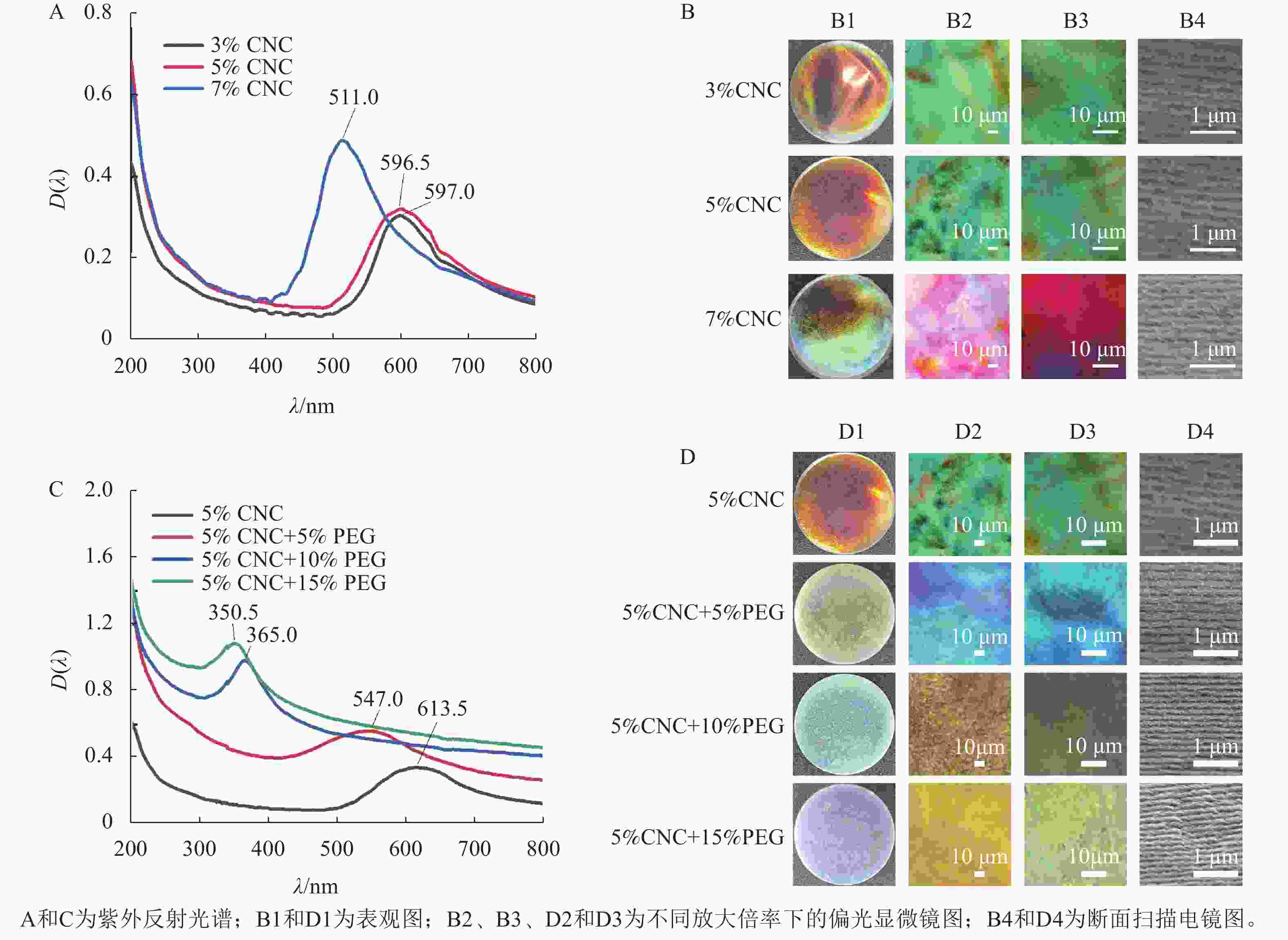
图 2 CNC和PEG/CNC液晶薄膜的UV-vis及图像
Figure 2. UV-vis absorbance spectra and images of CNC and PEG/CNC liquid crystal films
由图2B2和B3观察到:3种不同质量分数的CNC薄膜都表现出显著的双折射特性,在高倍率下可以观察到手性向列相液晶特有的指纹织构。指纹织构出现的原因是CNC的螺旋轴与显微镜基片平行,观测到明暗相间的指纹状衍射条纹,形成了像指纹一样的织构图案[20]。图2B4为CNC液晶薄膜断面的SEM图,所有液晶薄膜都呈现出手性向列相液晶特有的层状螺旋结构,相邻层之间的距离是螺距的一半[21]。测量统计100段CNC液晶薄膜的螺距,3%CNC、5%CNC和7%CNC所得的螺距分别为401.0、394.0、335.0 nm。手性光子晶体的λmax与螺距(P)的关系可以用布拉格方程来描述[22]:$ {\lambda }_{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}}=nP\mathrm{sin}\theta $。其中,n为平均折射率,θ为反射光与平面夹角。以5%CNC液晶薄膜为例,n=1.52,θ=90°,因此λmax=599.0 nm,橙色的可见光波长范围为580.0~610.0 nm,液晶薄膜的颜色与之对应,这与UV-vis测得的λmax基本符合。
-
由图2C和图2D1可知:所有薄膜都具有光滑表面和均匀的虹彩色,随着PEG质量分数的增加,所制得的液晶薄膜的颜色由橙红色转变为黄绿色、蓝绿色,最后变为蓝紫色,复合薄膜的λmax从613.5 nm下降到350.5 nm,这是由于PEG分子中含有大量的羟基,羟基之间会形成氢键,进而形成微交联结构,使CNC分子层间距离减小,导致螺距减小,λmax发生显著蓝移[23]。与纯CNC液晶薄膜相比,PEG/CNC复合薄膜的颜色更均匀。
由图2D2和D3可见:与纯CNC液晶薄膜相同,复合薄膜也表现出双折射特性,且能观察到手性向列相指纹织构;由图2D4可见:与纯CNC液晶薄膜相同,所有液晶薄膜都能呈现出手性向列相液晶特有的层状螺旋结构。POM和SEM的结果都表明:PEG的加入保留了CNC的手性向列相特征。测量统计100段PEG/CNC液晶薄膜的螺距,PEG质量分数为0、5%、10%和15%的液晶薄膜螺距分别为394.0、361.0、263.0、244.0 nm。以PEG质量分数为5%的CNC液晶薄膜为例,n=1.52,θ=90°,因此λmax=549.0 nm,而黄绿色的可见光波长范围为540.0~570.0 nm,液晶薄膜的颜色与之对应,这与UV-vis测得的λmax基本符合。
-
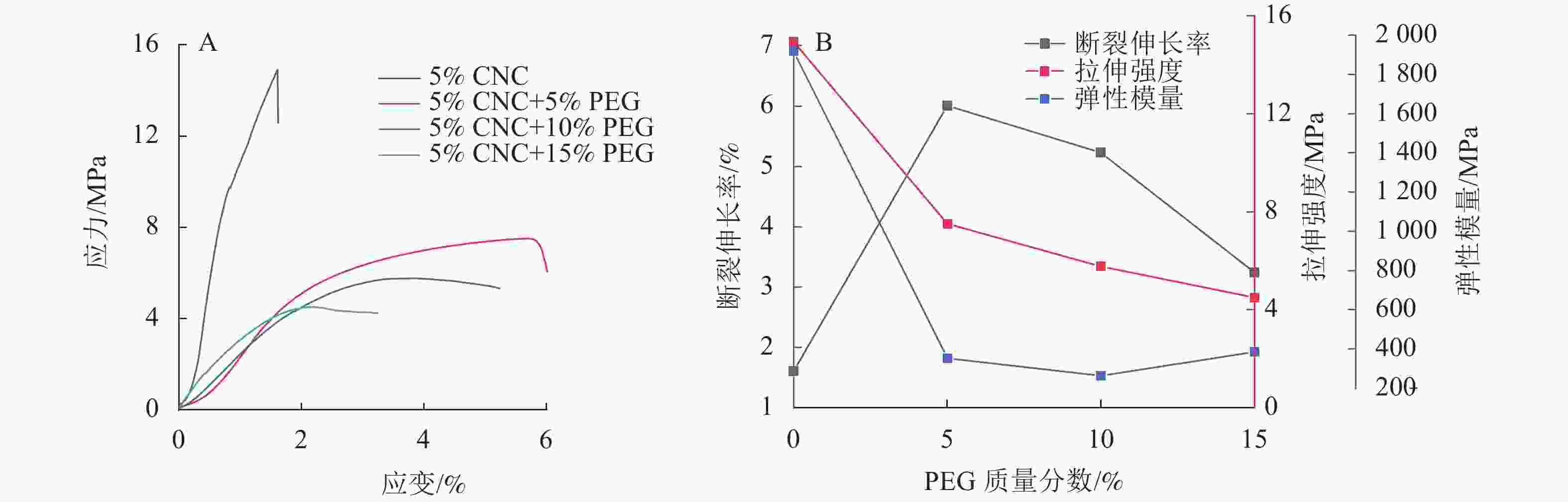
由图3可见:5%CNC液晶薄膜的断裂伸长率为1.60%,添加PEG显著提升CNC液晶薄膜断裂伸长率,5%CNC+5%PEG液晶薄膜的断裂伸长率为6.00%,对应力-应变曲线进行积分可得断裂能,断裂能为31.9 J·m−2,较纯CNC薄膜提升了138%,这主要是由于PEG能与CNC形成氢键,构成三维网络结构,进而提高薄膜的韧性[24]。然而,随着PEG质量分数的增加,CNC液晶薄膜的断裂伸长率会有所下降,5%CNC+15%PEG断裂伸长率下降到3.20%,断裂能较5%CNC+5%PEG 降低了65.4%,这是由于过量加入PEG在一定程度上破坏了复合薄膜的手性向列结构[25]。虽然PEG提升了CNC复合薄膜韧性,但使其拉伸强度及弹性模量下降,5%CNC+5%PEG 薄膜的拉伸强度下降了49.7 %,弹性模量下降了81.6%。
-
由图4可知:在所有环境湿度下,随时间增加,薄膜的λmax会发生红移,到达一定时间后,λmax恒定,因此,可以估算PEG/CNC液晶薄膜的湿度响应时间。此外,对于同一个PEG/CNC液晶薄膜,环境相对湿度越大,λmax红移程度就越明显,这是随着环境相对湿度提高,进入PEG/CNC液晶薄膜的水汽增多所致[13],也表明PEG/CNC液晶薄膜具有优异的湿度响应性。图5显示:PEG/CNC液晶薄膜纤维素表面存在大量的羟基,当环境湿度增加,水汽进入CNC液晶薄膜,使单个CNC分子之间的距离增大,螺距增大,λmax出现了红移[23]。
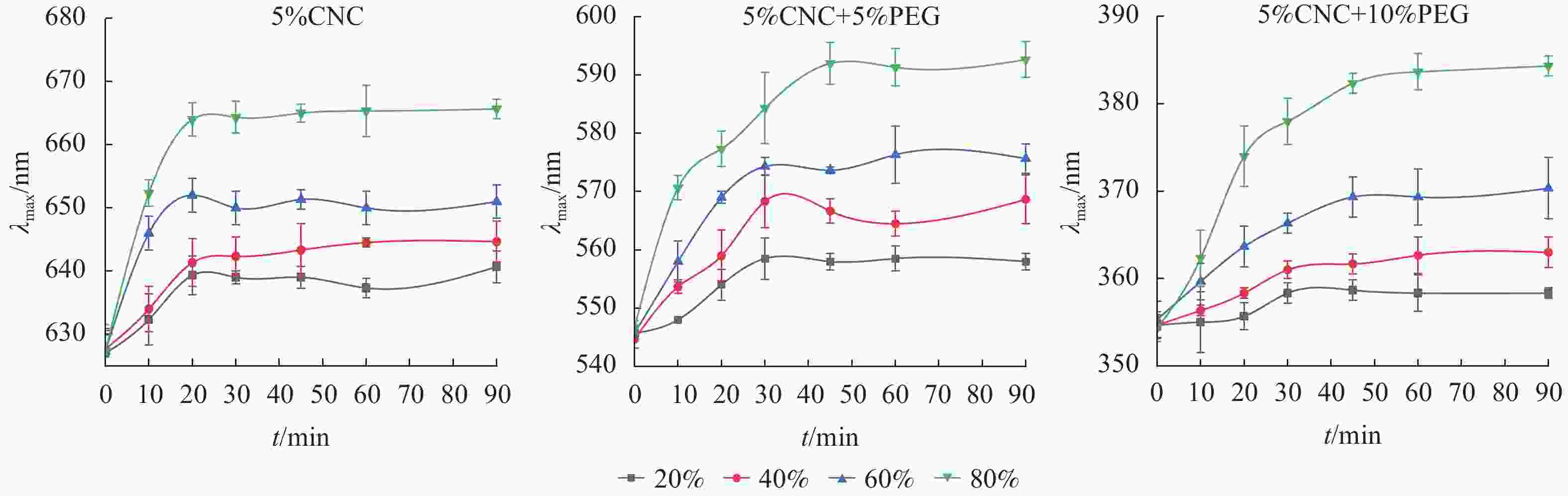
图 4 不同湿度环境下PEG/CNC液晶薄膜λmax随时间的变化
Figure 4. Changes of λmax over time of PEG/CNC liquid crystal films in different humidity environments

图 5 水汽浸入及螺距变化机制示意图
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of water vapor immersion and pitch variation mechanism
由图6A可知,随着PEG质量分数的提高,薄膜的λmax发生蓝移,这与2.3.1中的研究结果相一致。所有种类的薄膜均随环境湿度的提高而发生红移,说明其具有湿度响应性能。由图6B可知:随着PEG质量分数和湿度的增加,平衡时间增加,这是因为PEG/CNC液晶薄膜的湿度响应来自于CNC螺距的变化,PEG的加入限制了CNC分子的运动,因此需要更多的时间才能观察到平衡;同时周围环境的相对湿度越高,PEG/CNC液晶薄膜达到平衡波长所需要的时间也越长,这是由于薄膜需要吸收更多的水汽达到平衡所致。
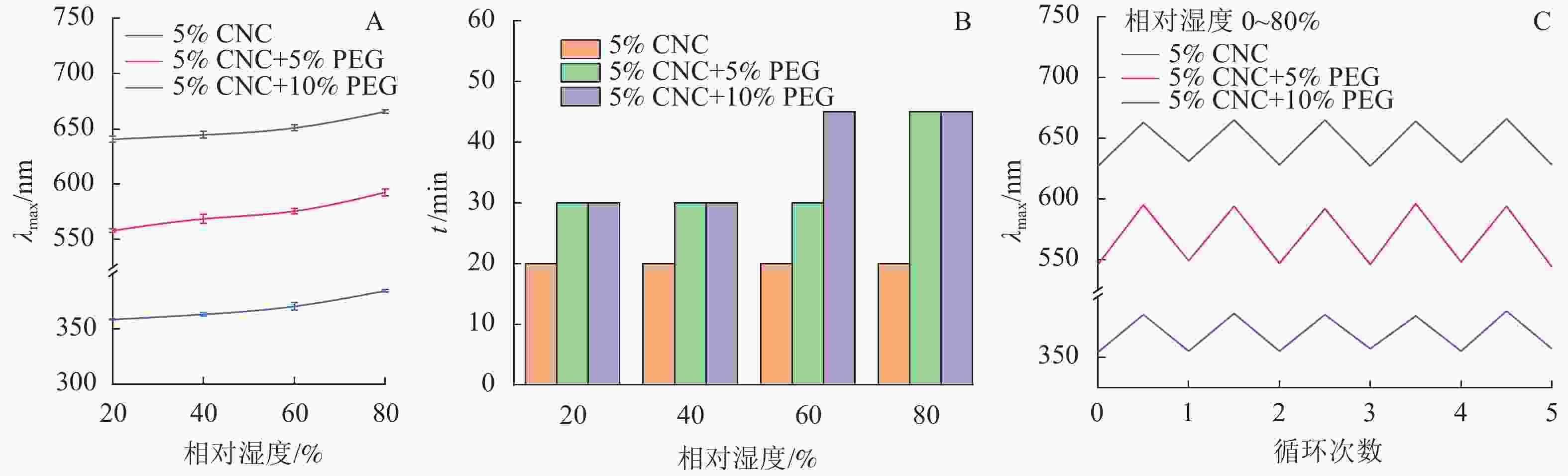
图 6 不同湿度环境下PEG/CNC液晶薄膜λmax变化(A)、达到平衡波长所需时间(B)及湿度响应(C)
Figure 6. λmax variation (A) and time for PEG/CNC liquid crystal films to reach the equilibrium wavelength (B) in different humidity environments, and humidity response (C)
随着环境相对湿度的提高,水汽能够进入CNC液晶薄膜中,λmax发生红移;在干燥过程中,进入CNC液晶薄膜的水汽又重新蒸发出来,λmax回复到原始状态[23]。由图6C可知,CNC和PEG/CNC液晶薄膜经过5次反复吸湿-解湿实验,均表现出良好的湿度响应重复性,平衡波长的变化率小于0.6%,说明其湿度响应性能很稳定。
-
本研究将木质CNC与PEG共组装,制备了一种对湿度具有敏感响应的虹彩色光子液晶薄膜。PEG可以调控复合薄膜螺距,从而起到调节结构色的作用。随着PEG质量分数的增加,复合薄膜螺距减小,结构色发生蓝移。PEG还可以提高复合薄膜的韧性,当PEG质量分数为5%时,所制得的液晶薄膜具有最大的断裂伸长率及韧性,断裂能提高了138%。PEG/CNC液晶薄膜具有良好的湿度响应性能,随环境相对湿度变化,复合薄膜的颜色相应改变,其中PEG质量分数为5%的复合薄膜的颜色变化最显著,λmax由545.0 nm变为595.0 nm。另外,随着PEG质量分数的增加,复合薄膜对湿度的响应时间增加,但不影响吸湿-解湿重复响应行为,因此,这种基于木质CNC的低成本响应光子材料在湿度监测领域具有重要的潜在应用。
Microstructure and humidity response of polyethylene glycol/cellulose nanocrystal composite liquid crystal films
-
摘要:
目的 探索聚乙二醇(PEG)对纤维素纳米晶体(CNC)液晶薄膜湿度响应的影响,阐明其响应机制,旨在为开发低成本、可重复使用和高灵敏度的PEG/CNC复合薄膜湿度传感器提供理论基础。 方法 将CNC与PEG共组装,制备了一种具有湿度响应性能的虹彩色手性向列相光子液晶薄膜,系统考察了PEG质量分数对液晶薄膜的微观结构、显色、力学性能及湿度响应的影响,在此基础上,研究了PEG/CNC复合液晶薄膜在不同湿度条件下的响应循环性能。 结果 对于纯CNC体系,CNC质量分数由3%增加到7%,CNC液晶薄膜的螺距减小,最大反射光波长由596.5 nm蓝移至511.0 nm;对于添加PEG的CNC体系,随着PEG质量分数的增加,PEG/CNC复合液晶薄膜的螺距由394.0 nm减小到244.0 nm,最大反射光波长由613.5 nm蓝移至350.5 nm,韧性先提升后下降,PEG质量分数为5%时为最佳,断裂能为31.9 J·m−2,较纯CNC薄膜提升了138%;液晶薄膜经过5次吸湿-解湿,表现出良好的湿度响应重复性,平衡波长的变化率小于0.6%。 结论 制备了一种对湿度具有敏感响应的虹彩色光子PEG/CNC复合液晶薄膜,PEG可以调控复合薄膜螺距,起到调节结构色的作用。图6参25 Abstract:Objective Cellulose nanocrystalline (CNC) liquid crystal film, as a kind of photonic crystal with special optical properties, has a promising prospect in the fields of anti-counterfeiting technology, photoelectric functional materials and humidity responsive functional materials. This study, with an exploration of the influence of polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the humidity response of CNC liquid crystal films, is aimed to explain its response mechanism to provide a theoretical basis for the development of low-cost, reusable and highly sensitive PEG/CNC composite film humidity sensors. Method The chiral nematic photonic liquid crystal films with humidity response were prepared by evaporation-induced self-assembly of PEG/CNC suspension, and the effects of PEG content on the microstructure, color evolution, mechanical properties and humidity response of the PEG/CNC films were investigated. Then, the cyclic properties of PEG/CNC liquid crystal films under different humidity conditions were studied. Result For pure CNC film system, with the increase of CNC content from 3% to 7%, the pitch of CNC liquid crystal film decreased, and the maximum wavelength of reflected light shifted from 596.5 nm to 511.0 nm. For PEG/CNC films, with the increase of PEG content, the pitch of PEG/CNC composite liquid crystal film decreased from 394.0 nm to 244.0 nm while the maximum wavelength of reflected light moved from 613.5 nm to 350.5 nm. The toughness increased first and then decreased, the optimal PEG addition amount was 5%, the breaking energy was 31.9 J·m−2 which was 138% higher than that of pure CNC film. After 5 hygroscopic and dehumidifying experiments, the PEG/CNC film showed good humidity response repeatability with the change rate of the equilibrium wavelength being lower than 0.6%. Conclusion An iridescent photonic PEG/CNC liquid crystal film for humidity sensing were prepared, and it was found that PEG can regulate the structural colour by modulate the pitch of the composite film. [Ch, 6 fig. 25 ref.] -
-
[1] 安邦, 徐明聪, 马春慧, 等. 纤维素纳米晶体手性复合材料: 结构色的调控与应用[J]. 高分子学报, 2022, 53(3): 211 − 226. AN Bang, XU Mingcong, MA Chunhui, et al. Tuning and application of structural color of cellulose nanocrystals chiral composite materials [J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2022, 53(3): 211 − 226. [2] DUAN Ran, LIU Mengli, TANG Ruiqi, et al. Structural color controllable humidity response chiral nematic cellulose nanocrystalline film [J/OL]. Biosensors, 2022, 12(9) : 707[2023-03-20]. doi:10.3390/bios12090707. [3] ROBERT J M, ASHLIE M, JOHN N, et al. Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(7): 3941 − 3994. [4] 万轩, 张亚运, 孙誉飞, 等. 抗静电纤维素纳米晶体彩虹防伪标签膜的制备[J]. 包装工程, 2017, 38(9): 53 − 58. WAN Xuan, ZHANG Yayun, SUN Yufei, et al. Preparation of iridescence anti-counterfeiting label films of anti-electrostatic nanocrystaline celluloses [J]. Packaging Engineering, 2017, 38(9): 53 − 58. [5] 林涛, 王乐, 魏潇瑶, 等. 基于纤维素纳米晶体的比色传感器研究进展[J]. 中国造纸, 2022, 41(6): 95 − 102. LIN Tao, WANG Le, WEI Xiaoyao, et al. Research progress of colorimetric sensors based on cellulose nanocrystal [J]. China Pulp &Paper, 2022, 41(6): 95 − 102. [6] GRAY D G. Recent advances in chiral nematic structure and iridescent color of cellulose nanocrystal films [J/OL]. Nanomaterials, 2016, 6(11): 213[2023-03-20]. doi:10.3390/nano6110213. [7] 李金召, 李政, 庄旭品, 等. 纤维素纳米晶体的制备及其在复合材料中的应用[J]. 化学进展, 2021, 33(8): 1293 − 1310. LI Jinzhao, LI Zheng, ZHUANG Xupin, et al. Preparation of cellulose nanocrystalline and their applications in composite materials [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2021, 33(8): 1293 − 1310. [8] ZHAO Guoming, HUANG Yanping, MEI Changtong, et al. Chiral nematic coatings based on cellulose nanocrystals as a multiplexing platform for humidity sensing and dual anticounterfeiting [J/OL]. Small, 2021, 17(50): e2103936[2023-03-20]. doi: 10.1002/smll.202103936. [9] 卿彦, 王礼军, 吴义强, 等. 纤维素纳米晶体胆甾相液晶形成与应用[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(4): 152 − 159. QING Yan, WANG Lijun, WU Yiqiang, et al. Formation and application of cellulose nanocrystalline cholesteric liquid crystals [J]. Forestry Science, 2019, 55(4): 152 − 159. [10] MARCHESSAULT R H, MOREHEAD F F, WALTER N M. Liquid crystal systems from fibrillar polysaccharides [J]. Nature, 1959, 184(4686): 632 − 633. [11] WANG Peixi, MACLAXHLAN M J. Liquid crystalline tactoids: ordered structure, defective coalescence and evolution in confined geometries [J]. Philosophical Transactions Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences, 2018, 376(2112): 20170042[2023-07-03]. doi:10.1098/rsta.2017.0042. [12] AMIN B, BISHNU A. Humidity-responsive photonic films and coatings based on tuned cellulose nanocrystals/glycerol/polyethylene glycol [J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(21): 3695[2023-07-03]. doi: 10.3390/polym13213695. [13] CHEN Huanghuang, HOU Aiqin, ZHENG Changwu, et al. Light and humidity-responsive chiral nematic photonic crystal films based on cellulose nanocrystals [J]. ACS Applied Materials &Interfaces, 2020, 12(21): 24505 − 24511. [14] LIN Maoqi, SINGH R V, CHRISTINE B, et al. Tailoring the humidity response of cellulose nanocrystal-based films by specific ion effects [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 629(PB): 694 − 704. [15] 张亚运, 万轩, 莫梦敏, 等. 纤维素纳米晶体膜及胆甾型液晶图案的制备[J]. 林业工程学报, 2017, 2(4): 103 − 108. ZHANG Yayun, WAN Xuan, MO Mengmin, et al. Preparation of cellulose nanocrystal film and cholesteric liquid crystal pattern [J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2017, 2(4): 103 − 108. [16] YOUSSEF H, LUCIAN A L, ORLANDO J R. Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(6): 3479 − 3500. [17] ZHANG Pengju, WANG Qian, GUO Rui, et al. Self-assembled ultrathin film of CNC/PVA liquid metal composite as a multifunctional Janus material [J]. Materials Horizons, 2019, 6(8): 1643 − 1653. [18] 王大伟. 基于纳米晶纤维素手性液晶薄膜的制备与研究 [D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021. WANG Dawei. Preparation and Study of Chiral Liquid Crystal Films Based on Cellulose Nanocrystal [D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021. [19] 陈戴玮, 白绘宇, 王大伟. 具有手性液晶特性的纳米晶纤维素在智能包装材料中的应用展望[J]. 塑料包装, 2021, 31(4): 7 − 10, 30. CHEN Daiwei, BAI Huiyu, WANG Dawei, et al. Application prospects of nanocrystals cellulose with chiral liquid crystal characteristics in smart packaging materials [J]. Plastic Packaging, 2021, 31(4): 7 − 10, 30. [20] 郭梦娜. 胆甾相纤维素纳米晶的手性光学调控 [D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2022. GUO Mengna. Chiral Optical Regulation of Cholesteric Cellulose Nanocrystals [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2022. [21] 黄伟杰, 高萌, 张正健, 等. 纤维素纳米晶手性向列液晶在颜色防伪中的应用[J]. 包装工程, 2019, 40(23): 85 − 93. HUANG Weijie, GAO Meng, ZHANG Zhengjian, et al. Application of cellulose nanocrystal chiral nematic liquid crystal in color anti-counterfeiting [J]. Packaging Engineering, 2019, 40(23): 85 − 93. [22] 王释玉, 李海明. CNC手性向列型液晶结构的形成、调控与应用[J]. 大连工业大学学报, 2022, 41(4): 261 − 268. WANG Shiyu, LI Haiming. Formation, tuning, and application of chiral nematic liquid crystal structure of cellulose nanocrystal [J]. Journal of Dalian Polytechnic University, 2022, 41(4): 261 − 268. [23] 于佳酩. 纳米晶纤维素胆甾型液晶相的结构色及光学性能调控 [D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2021. YU Jiaming. Regulation of Structure Color and Optical Properties of Cholesteric Liquid Crystal Phase Based on Nanocrystalline Cellulose [D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2021. [24] HUANG Yiyan, CHEN Gaowen, LIANG Qianmin, et al. Multifunctional cellulose nanocrystal structural colored film with good flexibility and water-resistance [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 149: 819 − 825. [25] ANDREW J L, WALTERS M C, HAMAMD Y W, et al. Coassembly of cellulose nanocrystals and neutral polymers in iridescent chiral nematic films [J]. Biomacromolecules, 2023, 24(2): 896 − 908. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230236






 下载:
下载: