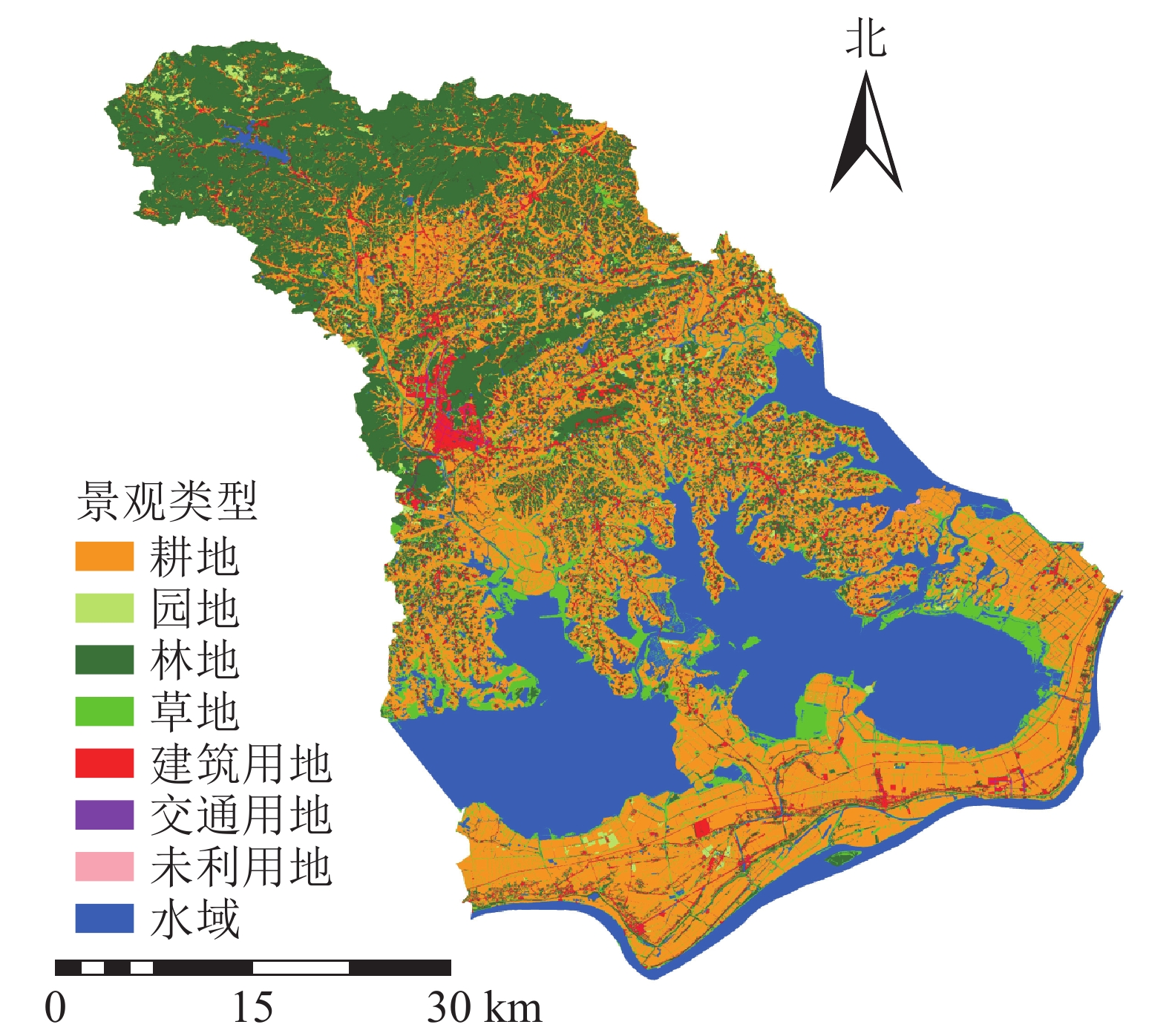
-
土地资源是人类社会赖以生存发展的基础,近年来,随着城市化进程不断加快,耕地流失和土地破碎化问题日益严重,区域景观生态风险评价已成为全球环境变化的研究热点[1-3]。日益频繁的人类活动及高强度的开发建设,使得土地景观趋于破碎化,结构趋于复杂化,威胁着人地关系的和谐[4]。景观生态风险评价方法主要分为景观指数法和基于风险源-汇的理论分析法。研究对象多集中在生态环境敏感脆弱和人为干扰剧烈的区域,如城镇[5-7]、流域[8]、海岸带[9]、矿区[10-11]、自然保护区[12]、道路沿线[13]、湿地[14]等,数据源多为人工解译方法获得的遥感解译数据或土地利用现状图矢量图[10-14]。如HAYES等[15]利用GIS技术对生境模型的空间数据进行编译和对比,直观评估出华盛顿西北部近海岸海洋环境的生态风险空间分布状况。张莹等[12]以扎龙自然保护区为研究对象,基于研究区景观格局变化特点构建景观生态风险指数,总结了1995−2010年保护区多尺度下景观生态风险的时空变化特征。刘炎序等[16]以深圳市社会-生态系统为评价研究对象,借助GIS空间分析手段,制作出“忽视风险情景”“正常风险情景”“重视风险情景”等景观生态风险图。王涛等[17]运用景观生态学理论,综合选取指数构建了景观生态风险评价模型,定量化总结1985−2015年杞麓湖流域的景观生态风险分布特征。景观具有高度空间异质性,存在一定的空间分布规律,在景观生态风险评价体系中引入景观指数法,不仅能增加景观异质性的关注度和空间定量描述,还能使风险评价摆脱传统方法中由于某一特定风险因子表征区域状态所造成的局限性[18]。宿松县地处大别山南麓,地理位置特殊,山区和湖泊面积占总面积的86%,生态环境敏感脆弱。人类活动的干扰导致该地区林地面积不断退化,农田城镇化明显,生态系统的基本结构和功能够遭到破坏,景观生态风险日益加剧。本研究从土地景观生态安全角度重新审视该区域的环境和发展问题,通过探究县域景观结构的变化动态,构建最佳粒度下景观指数的生态风险评价模型,进行景观生态风险评价研究,以期为县域尺度景观生态风险的管理提供理论和技术支持。
-
宿松县(29°47′20′′~30°25′30′′N,115°52′52′′~116°34′40′′E)位于安徽省西南方向,是安徽、湖北、江西三省的交界处,也是八县结合部,地处长江下游北岸的顶端。全县东西宽约67 km,南北长约72 km,总面积达2 394 km2;东北接壤太湖县,西边紧邻湖北省的蕲春县和黄梅县,东南角连接望江县,南边隔江相望于江西省湖口县和彭泽县;属北亚热带湿润季风气候,四季分明,季风性明显;年平均气温16.6 ℃,由于地势原因,境内温度自西北方向至东南逐渐增高;季节性降水较明显,城区为暴雨多发地区;光照充足,年均无霜期254 d。
-
标准采用2017年的GQJC 03−2017《基础性地理国情监测内容与指标》,与2015年标准不同的是,2017年新标准将耕地、园地合并为种植土地;林地、草地合并为了林草覆盖。本研究以2015、2017年的地理国情普查成果为依据,结合研究目标,参考GB/T 21010−2017《土地利用现状分类》,根据土地实际用途以及地物意义,将普查数据中的地表覆盖分类重新划分为耕地、园地、林地、草地、建筑用地(房屋建筑区、构筑物、人工堆掘地)、交通用地(道路)、水域、未利用地(荒漠与裸露地表)八大土地景观类型[19](图1)。通过ArcGIS对划分后的土地斑块类型进行分类、合并处理。选取宿松县景观格局变化研究的最佳粒度值100 m[20],利用Arc GIS重采样功能得出2015、2017年宿松县土地景观栅格分布图。
-
本研究从类型和景观水平共选取5个景观指数(表1),从面积与结构、形状、多样性等3个方面对宿松县2015−2017年土地利用格局的动态变化进行研究,并利用FRAGSTATS软件计算出相关值。
表 1 不同水平下选取的土地利用景观指数
Table 1. Land use landscape index selected at different levels
景观特征 景观指数 水平类型 含义 面积与结构 斑块面积(CA) 类型 描述某斑块类型的
总面积斑块类型面积比例指数(PLAND) 类型 描述某斑块类型所占整个景观面积比例 形状 景观形状指数(LSI) 类型/景观 描述斑块形状边界
形状的复杂性多样性 Simpson 多样性指数(SIDI) 景观 描述斑块类型多样性程度 Simpson 均匀度指数(SIEI) 景观 描述斑块类型均匀性程度 -
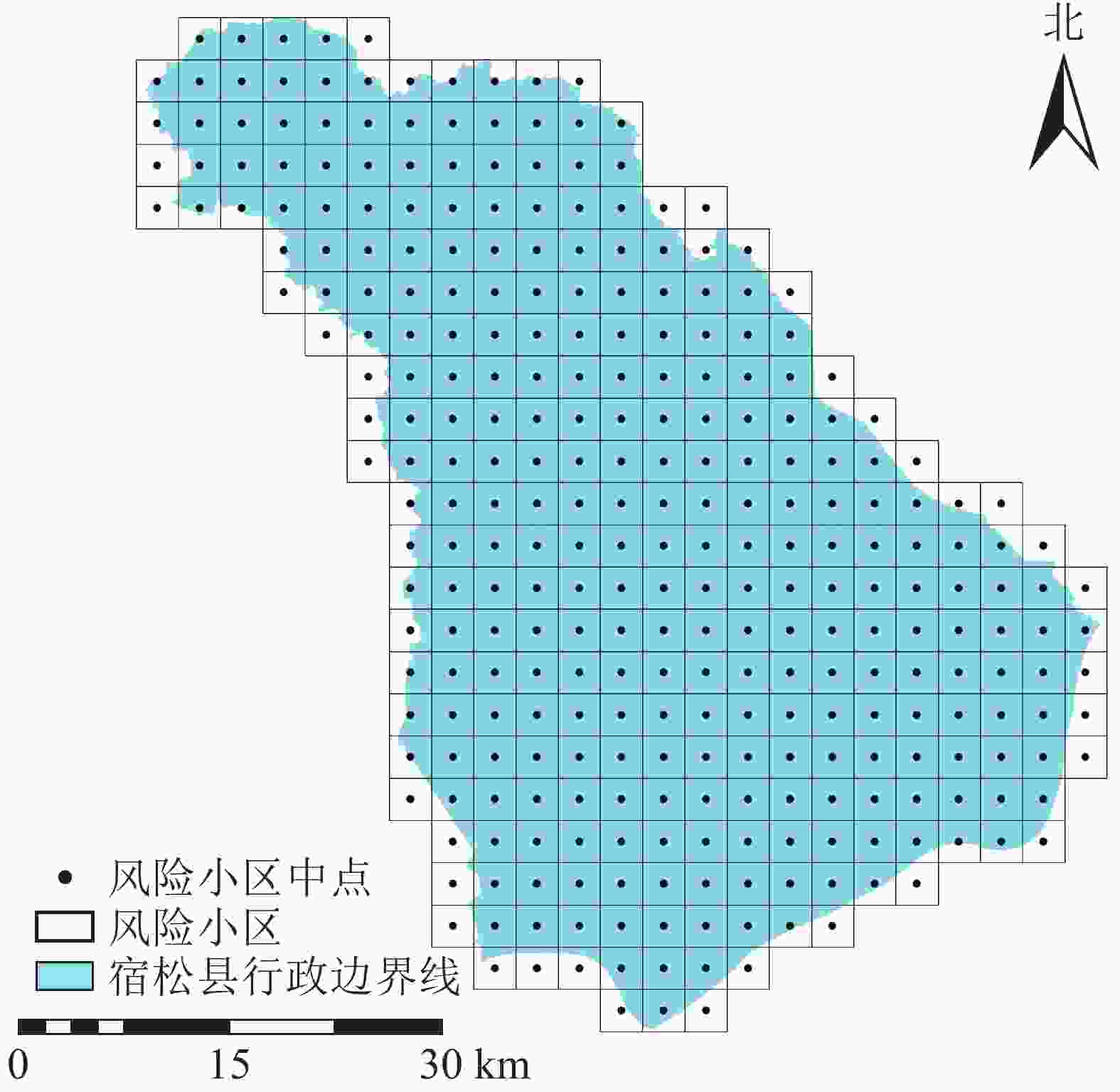
样方面积的大小需满足研究区景观斑块平均面积的2~5倍,样本才能综合反映采样地点周围综合景观格局信息[21]。2015和2017年景观斑块平均面积分别为1.872 7、1.862 6 km2,确定风险小区边长选择区间为1.930 0~3.064 5 km,考虑单元格划分既要保证足够多的单元数来反映研究区景观格局的分布规律,又要避免计算强度和精度等问题,因此本研究以3 km×3 km风险小区为评价单元,采用等间距采样方法,将研究区划分为308个风险小区,网格中心点为景观生态风险指数的采样点(图2)。
-
生态风险是生态系统结构和功能在响应外界干扰时保持本身处在低能量平衡的一种可能性[22]。景观生态风险由外部的扰动强度和内部的脆弱性来衡量。本研究选取景观干扰度指数和景观脆弱度指数对景观生态风险进行定量分析,该方法能够快速有效识别土地资源异质性带来地干扰度和生态系统自身的脆弱程度[23]。
-
景观干扰度指数(Gi)表示i类土地景观抵抗外界的干扰能力和自我恢复能力,景观格局所受的人为和自然的干扰强度越大,则整个土地景观生态系统敏感性越强,其景观生态风险越大。选取景观破碎度指数(Pi)、景观分离度指数(Di)、景观分维度指数(Fi)来构建景观干扰度指数,计算公式为:
$$G_i = W_1 \times P_i + W_2 \times D_i + W_3 \times F_i \text{。}$$ (1) 式(1)中:W1、W2、W3分别为景观破碎度、景观分离度、景观分维度等3个景观指数的权重值,结合相关研究成果分别赋值0.5、0.3、0.2;i为特定的土地覆盖类型[24-25]。
-
景观脆弱度数值大小与区域景观抵抗外界干扰能力的程度成反比。本研究依据各土地类型结构组成形成的土地利用稳定性,和自身的敏感性、脆弱性及分布集中性程度,参考相关研究成果[26-27],将各土地利用类型的脆弱度值进行赋值,并归一化处理,结果见表2。
表 2 景观脆弱度值归一化结果
Table 2. Normalized results of landscape vulnerability values
景观类型 脆弱度值 归一化值 建设用地 1 0.028 交通用地 2 0.056 林地 3 0.083 园地 4 0.111 耕地 5 0.139 水域 6 0.167 草地 7 0.194 未利用地 8 0.222 -
不同的土地利用方式对区域生态风险的贡献程度不同,为了定量分析土地景观结构变化带来的景观生态风险,将景观干扰度指数(外部)和景观脆弱度指数(内部)引入景观生态风险指数(ERI)概念能够使其更具针对性,能够结合采样方法将土地利用格局转化为空间化的生态风险变量。公式如下[28-29]:
$${E_{{\rm{RI}}k}} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\frac{{{A_{ki}}}}{{{A_k}}}} ({G_i} \times {R_i}) \text{。}$$ (2) 式(2)中:ERIk为第k个风险小区景观生态风险指数,Aki为第k个风险小区i类景观类型面积的总和,Ak为第k个风险小区n类景观类型面积的总和。Gi为i类景观类型的景观干扰度指数,Ri为i类景观类型的景观脆弱度指数。
最后用空间采样及普通克里金插值法进行分析,根据风险值的范围,采用自然间断法将生态风险程度划分为5个等级:低生态风险区、较低生态风险区、中等风险区、较高风险区、和高生态风险区。
-
根据表3~4可见:2015−2017年景观结构发生了变化,景观形状呈复杂化趋势,多样化程度和均匀度不断加强。耕地、林地、水域、草地等优势景观类型面积有所减少,而与人类活动密切相关的建筑用地、园地、交通用地面积有所增加。优势景观类型面积的减少,弱势景观类型面积的增高造成斑块类型分布不断均匀化,同时多样指数的提高说明研究区景观类型的丰富度有所增高,破碎化程度进一步加深。其中林地面积减少的最多,为969 hm2,减少的林地面积与增加的建设用地面积几乎相等,建设用地景观形状指数增幅最大。且2017年比2015人口增长0.31%,城镇人口增长21.11%,建筑业生产总值增长11 000万元。说明宿松县的城市化进程,尤其是城镇建设和农房面积的扩张是导致大量林地面积减少和建设用地形状复杂化的主要原因;耕地主要分布于城镇村庄周围,随着农业科技自动化水平的提高和城镇面积进一步扩张,城镇村庄周围的农业用地都逐渐转化为非农业用地,导致耕地面积有所减少,园地面积有所增加;由于耕地为主体景观类型且分布广泛,交通用地主要贯穿于城镇村庄内部,随着建设用地的大幅度增加,交通用地呈现增加趋势,造成草地、未利用地面积有所减少,耕地斑块形状变得更加复杂。综上,经济发展在一定程度上加剧了景观格局的不稳定状态。
表 3 2015和2017年类型水平上的格局指数
Table 3. Pattern index values at the type level in 2015 and 2017
景观类型 年份 CA/hm2 PLAND/% LSI 林地 2015 54 007 22.785 6 72.819 4 2017 53 038 22.376 7 72.817 8 耕地 2015 86 614 36.542 5 81.321 4 2017 86 367 36.438 2 82.403 7 建设用地 2015 11 000 4.640 9 73.838 1 2017 12 084 5.098 2 76.163 6 园地 2015 2 328 0.982 2 27.247 4 2017 2 380 1.004 1 27.479 6 交通用地 2015 1 984 0.837 1 41.677 8 2017 2 164 0.913 0 43.414 9 草地 2015 18 324 7.730 9 87.638 4 2017 18 278 7.711 5 86.273 1 水域 2015 62 615 26.417 3 30.990 0 2017 62 580 26.402 5 31.503 0 未利用地 2015 151 0.063 7 9.160 0 2017 132 0.055 7 9.869 6 说明:CA为斑块类型面积,PLAND为斑块面积比例,LSI 为景观形状指数 表 4 2015和2017年景观水平上的格局指数
Table 4. Pattern index values at the landscape level in 2015 and 2017
年份 LSI SIDI SIEI 2015 74.329 6 0.736 7 0.842 0 2017 75.241 8 0.739 0 0.844 5 说明:LSI为景观形状指数,SIDI为Simpson 多样性指数, SIEI为Simpson 均匀度指数 -
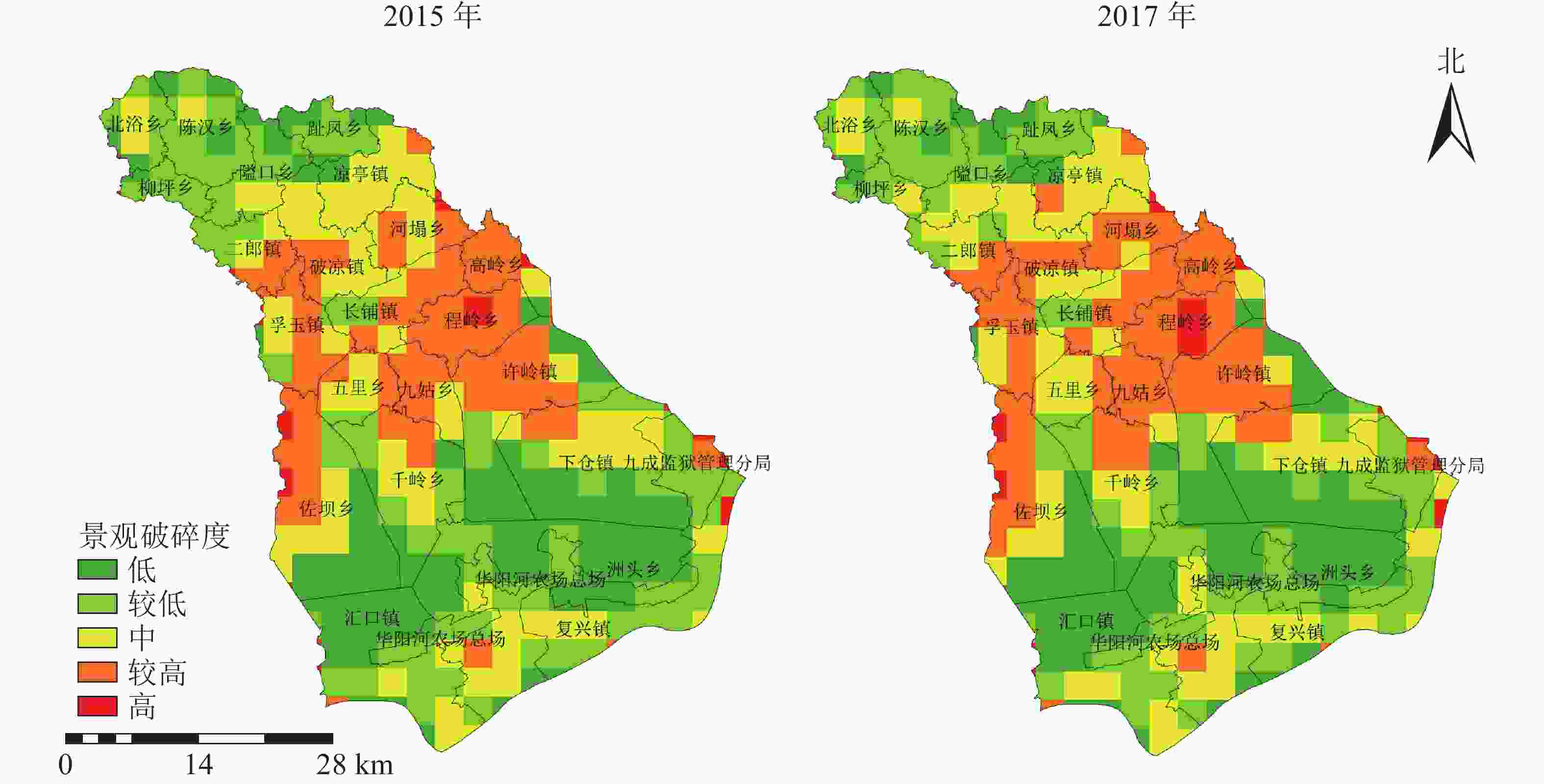
图3表明:西北部和东南部景观破碎程度较低,中部较高。由于宿松县地处大别山山脉,西北部主体景观类型为林地;东南部华阳河农场总场、汇口镇北部、洲头乡北部为主要的农业区,主体景观类型为耕地和水域,且均呈集聚状态分布,景观破碎程度较低;中部破碎化均较高且呈现由东向西的扩张趋势,其中程岭乡的破碎化程度最大,且高破碎度区域依然呈增加趋势,这与中部的景观类型为建筑用地、耕地、草地密切相关,虽然耕地依然为主体景观类型,但是由于受到错综复杂的交通用地、建设用地等其他土地类型的分割,造成中部耕地类型破碎化程度较大。
-
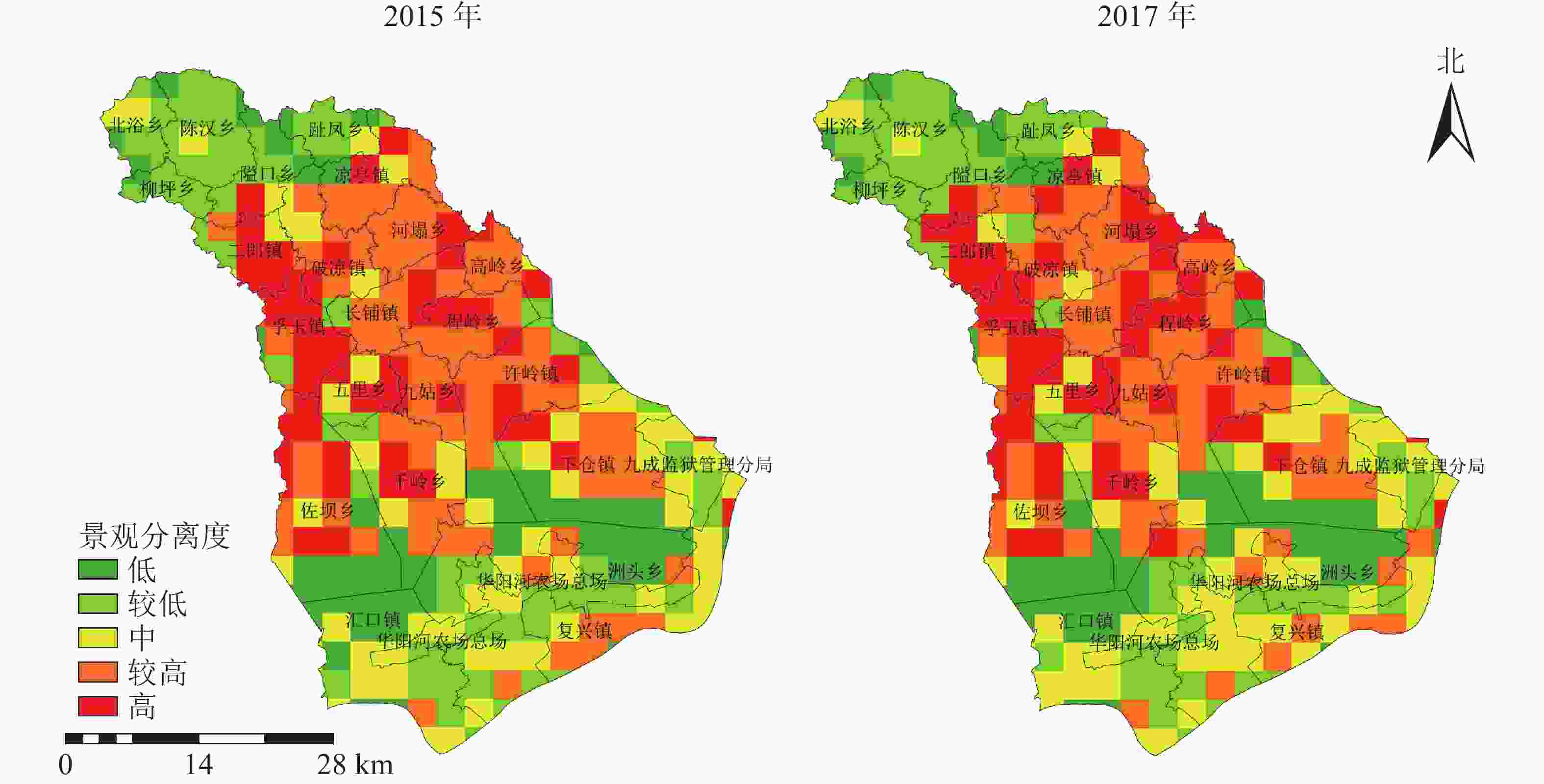
图4表明:西北部山区景观分离度较低,东南部农业区次之,景观分布较简单,中部地区景观分离度较高,景观分布复杂。2015−2017年西北部北浴乡、陈汉乡、柳坪乡主体景观类型为林地且位于山区,景观分离度未发生明显改变,分离度低于0.602 4;东南部复兴镇、洲头乡南部景观分离度虽发生轻微变化,但变化范围不大;中部西侧二郎镇、孚玉镇,及程岭乡西北部分离度最高、变化最为剧烈,呈现自东向西的扩张趋势。
-
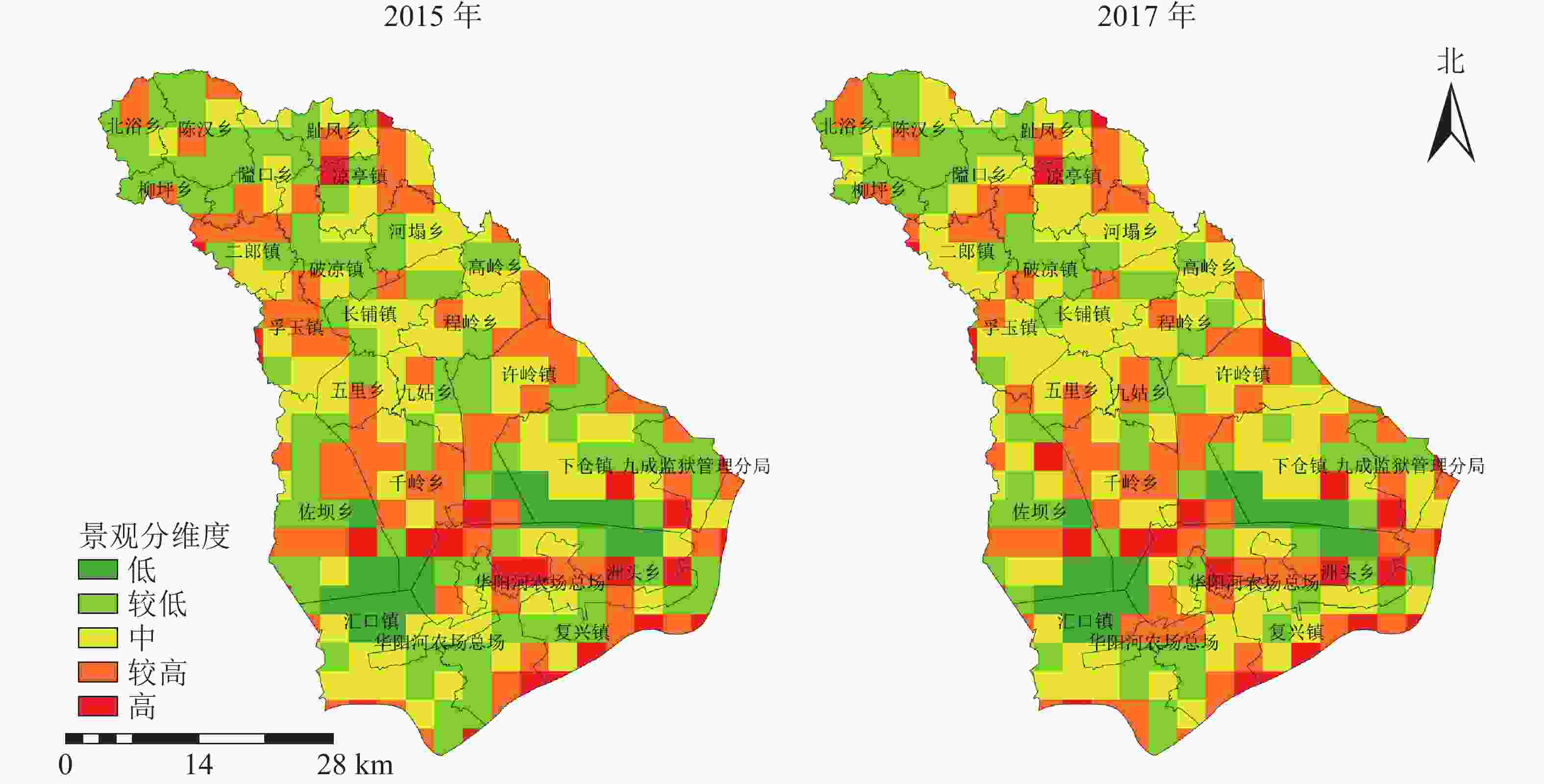
图5表明:西北部分维度最低,景观形状简单,中部中等区域所占比例较大,且较高级有向中等和高级分离度转化的趋势,高区域集中于东南部,景观形状较复杂。西北部分维度较低,主要是由于该地位于大别山区,主体景观类型由斑块较大的乔木林地组成;与之相对应分维度高区域为中部九姑乡、孚玉镇及东南部华阳河农场地区,原因是由于九姑乡存在较多分散的草地面积,一条自然水系贯穿孚玉镇,且水系形状较复杂,华阳河农场主体景观类型农业用地耕地,其形状均较不规则。综上所述,分维度指数与地貌形态、人类活动的制约和影响有着密切的联系。
-
图6表明:宿松县景观生态风险空间分布呈明显区位性和异质性特征的景观结构分布规律。低风险区主要集中于西北部山地地带,受其他生态风险等级的胁迫,研究期间面积有所下降,优势景观类型为林地且连片集中分布,景观结构稳定,景观破碎度和分离度较低;较低生态风险区位于西北部林地边缘和黄湖、龙湖南部地带,2015−2017年较低生态风险区有边缘向中部萎缩的趋势,以集中连片的深水域、耕地、和破碎化林地为主,景观结构较为完善,但也是人类主要活动区域的边缘地带,存在一定程度的风险;中等风险区和较高生态风险区主要分布于中部,以及东南部湖泊、长江边缘地带,优势景观类型主要以耕地、水域、林地、草地为主,耕地主要位于山地丘陵地带,自身形状复杂,水网密布且草地、林地的破碎化程度较高造成景观的动态变化较大,生态风险进一步加剧;高生态风险区主要分布于西南和东部边缘地带,2017年中部九姑乡出现大片的高生态风险区,高岭乡高生态风险面积逐渐内部扩张,而其余边缘高生态风险区面积均有所降低,表明高生态风险区有从边缘向中部发展的趋势。综上所述,宿松县的生态风险分布呈现明显的阶梯状态,与研究区内的地势从西北到东南逐渐降低,山区、丘陵、湖泊、平原依次分布的地貌有密切关系。
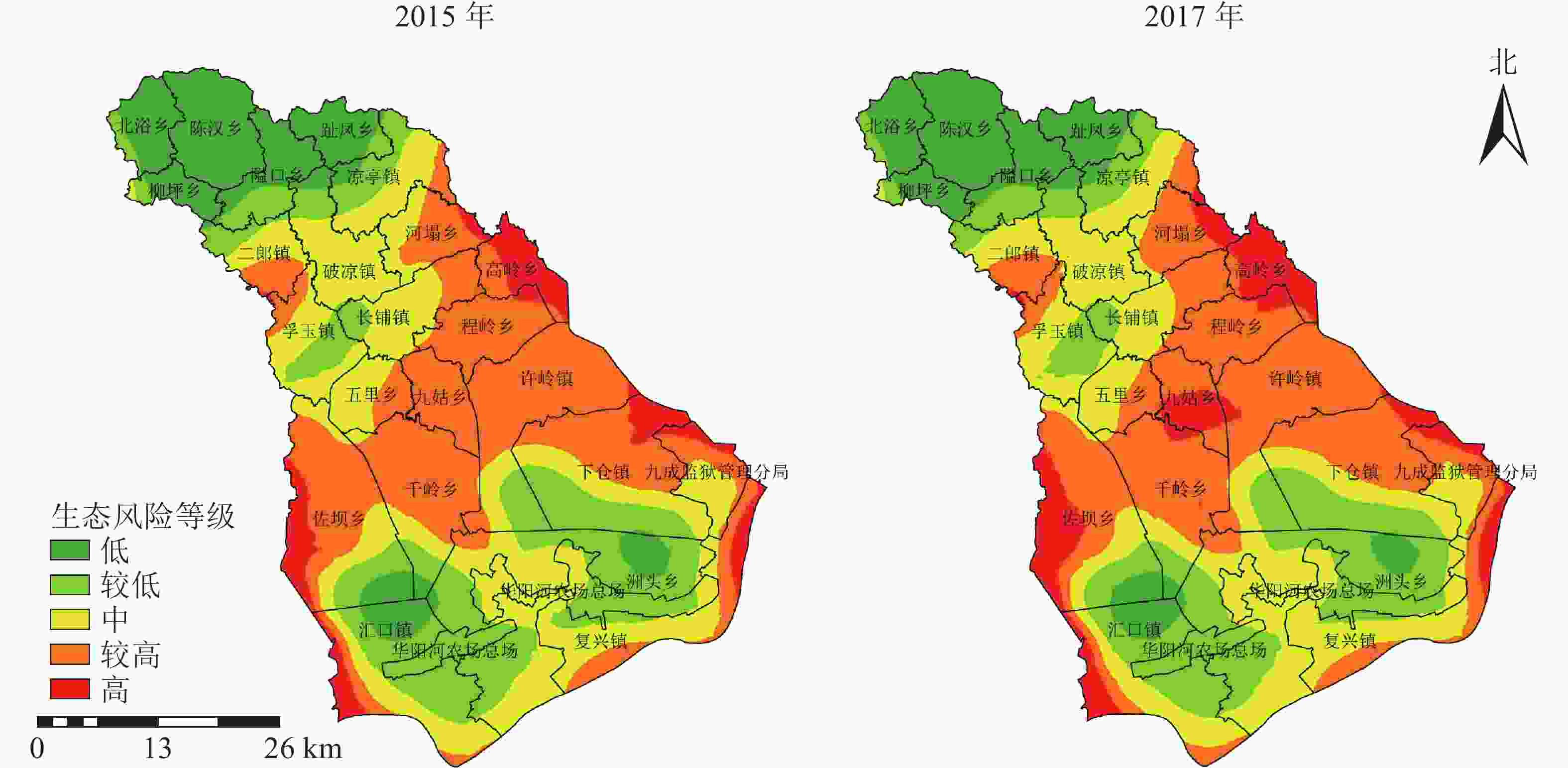
图 6 2015和2017年宿松县景观生态风险指数空间分布示意图
Figure 6. Spatial distribution map of landscape ecological risk index in Susong County in 2015 and 2017
利用ArcGIS对2015和2017年不同等级的土地景观生态风险面积统计(表5)表明:2015−2017年风险面积占比从高到低依次为较高生态风险区、中等生态风险区、较低生态风险区、低生态风险区、高生态风险区。研究区以较高生态风险区和中等生态风险区为主,2017年二者占比分别为31.22%、27.10%,合计超过总面积的一半。生态等级表现为低等级向相邻高等级转化,风险程度逐渐增加。低生态风险、较低生态风险区面积均有所降低,其中较低生态风险区面积主要由低生态风险区转入和转出为中等生态风险区的面积决定,面积减少了23.174 km2;中等生态风险面积降低幅度较明显,减少了45.605 km2,降幅占2015年中等风险区总面积的6.63%;较高生态风险区、高生态风险区的面积均有所增加,其中高生态风险面积在2 a间增加了65.326 km2,占2015年高风险区总面积的49.73%。根据各等级转化趋势可以得出,宿松县应进一步加大土地利用的治理,减少人为干扰强度,降低破碎化程度,避免较高生态风险区,进一步向高生态风险区转化。
表 5 2015和2017年各级生态风险面积及其占比
Table 5. Areas and percentages of ecological risks at all levels in 2015 and 2017
生态风险等级 2015年 2017年 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 低 315.329 13.31 309.537 13.06 较低 504.786 21.30 481.612 20.32 中 687.981 29.02 642.376 27.10 较高 730.788 30.83 740.033 31.22 高 131.350 5.54 196.676 8.30 -
为了进一步对宿松县的景观生态风险进行分析,依据地形地貌、社会经济条件等限制因素,将宿松县24个乡镇分为五大类,山地旅游区、交通枢纽镇、鱼米之乡、农业区、矿产资源区,统计出各类型地区的风险等级面积(表6)。图5和表6表明:2015−2017年除矿产资源区外,各类地区低生态风险、较低生态风险、中等生态风险面积均呈降低趋势;鱼米之乡、矿产资源区的较高生态风险区面积,由于转化为高生态风险面积而有所降低。低生态风险区集中于西北部山地旅游地区,其中陈汉乡完全处于低生态风险区,风险程度最低,隘口乡旅游资源丰富,2017年出现中等生态风险区,面积为0.389 km2,表明旅游业在一定程度上促进了中等生态风险区从中部向西北部扩张;2015−2017年中部交通枢纽镇二郎镇、孚玉镇的较高生态风险面积增长6.316 km2,且邻乡破凉镇中三乡交界处出现较高生态风险区,表明以城镇为中心的城镇扩张进一步加剧了生态风险;中等生态风险区集中于农业区复兴镇、破凉镇等,2015−2017生态风险增加程度较大为复兴镇,增加面积为3.119 km2,这与复兴镇滨江依湖的地理位置有着密切的关系,表明水域的脆弱性比耕地大,更易受到人为干扰;高生态风险区主要位于有“鱼米之乡”之称的高岭乡和佐坝乡,2017年这2个乡镇的高生态风险面积占总高生态风险区面积的47%,与2个乡镇河网分布错综复杂,渔业活动频繁有着密切的关系;矿产资源区九姑乡含有丰富的石灰石资源,2017年高生态风险区出现,中等风险区面积消失,高生态风险面积为21.715 km2,占该乡总面积的42.6%,表明矿产资源区潜在生态风险程度最大。综上所述,宿松县的潜在生态风险由高到低依次为矿产资源区、鱼米之乡、交通枢纽镇、农业区、山地旅游区。
表 6 2015和2017年宿松县各类乡镇不同等级的生态风险区面积
Table 6. Ecological risk area of different grades in various township of Susong County in 2015 and 2017
类别 乡镇 年份 不同等级生态风险区面积/ km2 低 较低 中等 较高 高 山地旅游区 北浴乡、柳坪乡、陈汉乡、隘口乡、趾凤乡、凉亭镇 2015 249.104 69.701 43.759 8.108 0.016 2017 247.286 68.742 41.539 11.401 1.720 农业区 河塌乡、五里乡、复兴镇、下仓镇、破凉镇、华阳河农场、长铺镇 2015 7.043 155.911 323.446 187.567 35.868 2017 6.904 147.139 299.386 221.214 35.192 交通枢纽镇 二郎镇、孚玉镇、九成监狱 2015 0.731 36.072 98.160 50.707 9.616 2017 0.057 33.934 90.754 59.559 10.982 鱼米之乡 高岭乡、程岭乡、千岭乡、佐坝乡、
许岭镇、洲头乡、汇口镇2015 58.451 243.102 222.531 433.498 85.850 2017 55.290 231.797 210.697 418.581 127.067 矿产资源区 九姑乡 2015 0 0 0.085 50.908 0 2017 0 0 0 29.278 21.715 -
景观生态风险评价是研究区域生态环境的有效手段。本研究表明:由于经济的发展,人类活动强度的增加,城镇用地的扩张,土地利用的景观生态风险等级有明显的变化趋势,呈低等级向高等级转变,这与张双双等[5]、白舒婷[29]、闻国静等[30]、王涛等[31]的结论类似。目前相关研究多集中于大区域[6-9]的生态风险讨论。县域为中国主要的行政单元,更是连接城市与乡村的节点[32],利用高分影像下采集的地理国情数据具有精度高、尺度细的优点,更能进一步提高生态风险评价结果的精度。本研究表明:乡镇经济的发展程度与景观生态风险的等级大小为正相关关系,即发展程度越高,景观生态风险越大,这与傅微等[23]的研究结果相似。通过对单一景观指数的生态风险分析及乡镇角度的生态风险评价,能进一步针对研究区的地貌、经济特征提出合理化的建议和对策。因此,本研究针对宿松县经济发展中带来的景观生态风险问题,为防止由于建设用地、交通用地的盲目扩张,造成林地、耕地流失,景观生态系统结构遭到破坏等现象的继续发生,提出了以下建议:①低生态风险区和较低生态风险主要位于西北部山区和黄湖、龙湖的中心等区域,景观类型以林地、和水域为主,是生物生长最优栖息地和水源涵养区,景观生态风险指数虽然低,但依然是重点保护对象。因此该区域应充分利用山地景观资源和水源资源,在现有自然保护区和旅游景区的基础上,划出一定的保护区域,扩大相邻林地和水域的面积,使其集中连片,保证生态环境的质量,降低景观破碎度,提高生态系统抗风险能力。②中等生态风险区主要位于宿松县中部的农业大乡,景观类型以耕地为主。由于宿松县是农业大县,耕地资源的保护和利用十分重要,建议对耕地质量等级划分,在保证耕地质量的基础上对质量差的耕地实施退耕还林政策。针对山区耕地,大力推广高效节水灌溉技术,适量推广种植经济价值高、耗水少的药材,减少水资源的浪费,保证区域农业用水。③较高生态风险区主要位于河网密布的鱼米之乡以及交通运输的枢纽镇。区域内存在大量生态稳定性脆弱的湿地,应建立湿地公园等自然保护区,并在河道周围加强林草工程维护,减少土地流失,降低水系破碎度,提高生态系统稳定性。此外还需控制该区域的人口数量,减少建设用地的扩张对耕地资源的占用。④高生态风险区主要位于矿产资源开发区等地。应严格控制对矿产资源的开采,减少矿山企业数量。充分利用遥感技术手段对矿山环境数据进行调查和监测,建立档案,编制相应的矿山环境治理方案,提高矿山修复效率,减少水土流失滑坡等自然灾害的发生。尤其是九姑山,需对矿产资源开采进行严格的管理和控制,降低人类活动的干扰强度。
-
2015−2017年宿松县土地景观结构存在一定变化,景观形状呈复杂化趋势,多样化程度和均匀度不断增强,生态风险结果与地貌特征、经济发展存在明显关联性,呈阶梯状分布,经济发展一定程度上造成了景观格局的不稳定。西北部以林地为主的山地旅游区景观,景观破碎度、分离度、分维度均较低,景观多样化水平低,景观生态风险较低。中部和东南部以耕地、建设用地、河网为主的农业区、交通枢纽镇、鱼米之乡景观,景观破碎度、分离度、分维度较高,景观分布结构较为复杂,景观生态风险较高,其中矿产资源区九姑乡的潜在生态风险程度最大。宿松县以较高生态风险区和中等风险区为主,2015−2017年低生态风险区、较低生态风险区、中等生态风险区面积呈降低趋势,而较高生态风险区和高生态风险区面积呈增加趋势,生态等级表现为低等级向相邻高等级转化。
Landscape ecological risk assessment of county
-
摘要:
目的 利用地理国情数据,定量化研究县域尺度下景观生态风险的变化趋势。 方法 以2015和2017年安徽省宿松县国情数据分类合并后的景观分布图为数据源,在地理信息系统(GIS)技术和Fragstats 4.2软件支持下,基于景观指数,采用地统计学方法,定量化分析2015−2017年宿松县土地景观动态变化、生态风险的时空变化及人类干扰活动对其的影响。 结果 宿松县景观破碎化程度不断增高, 多样化程度不断增强,景观分布呈复杂趋势;西北部景观破碎度、分离度、分维度均较低,景观多样化水平低,景观生态风险较低,中部和东南部景观破碎度、分离度、分维度较高,景观分布结构较为复杂,景观生态风险较高;宿松县低生态风险区、较低生态风险区、中等生态风险区面积呈降低趋势,而较高生态风险区和高生态风险区面积呈增加趋势。 结论 宿松县景观生态风险程度有所增加,生态等级表现为低等级向相邻的高等级转化,潜在生态风险程度从高到低排序为矿产资源区、鱼米之乡、交通枢纽镇、农业区、山地旅游区。图6表6参32 Abstract:Objective The geographic national conditions data was used to quantitatively study the change trend of landscape ecological risk at the county scale. Method Based on the geographic and national conditions data supported by the GIS technology and Fragstats 4.2 software, the landscape index were selected and the geo-statistical methods were used to analyzed the dynamic changes of landscape, spatial-temporal changes of landscape ecological risks and human disturbance activities in Susong County from 2015 to 2017. Result In the northwest, landscape fragmentation, landscape separation, landscape fractional dimension, the level of landscape diversity and landscape ecological risks were all lower; In the central and southeast, landscape fragmentation, landscape separation, and landscape sub-dimension were higher which shows that the landscape distribution structure was more complicated, and the landscape ecological risk was higher; The low ecological risk areas, lower ecological risk areas, and medium ecological risk areas were decreasing, while the areas of higher ecological risk areas and high ecological risk areas were increasing. Conclusion From 2015 to 2017, the degree of landscape ecological risk in Susong County increased, and the ecological risk level was transformed from a lower level to an adjacent higher level. The ecological risk levels of mineral resource areas, fish and rice towns, transportation hub towns, agricultural areas, and mountain tourist areas were arranged in order from high to low. [Ch, 6 fig. 6 tab. 32 ref.] -
Key words:
- landscape index /
- land use /
- geographical conditions /
- ecological risk /
- Susong County
-
表 1 不同水平下选取的土地利用景观指数
Table 1. Land use landscape index selected at different levels
景观特征 景观指数 水平类型 含义 面积与结构 斑块面积(CA) 类型 描述某斑块类型的
总面积斑块类型面积比例指数(PLAND) 类型 描述某斑块类型所占整个景观面积比例 形状 景观形状指数(LSI) 类型/景观 描述斑块形状边界
形状的复杂性多样性 Simpson 多样性指数(SIDI) 景观 描述斑块类型多样性程度 Simpson 均匀度指数(SIEI) 景观 描述斑块类型均匀性程度 表 2 景观脆弱度值归一化结果
Table 2. Normalized results of landscape vulnerability values
景观类型 脆弱度值 归一化值 建设用地 1 0.028 交通用地 2 0.056 林地 3 0.083 园地 4 0.111 耕地 5 0.139 水域 6 0.167 草地 7 0.194 未利用地 8 0.222 表 3 2015和2017年类型水平上的格局指数
Table 3. Pattern index values at the type level in 2015 and 2017
景观类型 年份 CA/hm2 PLAND/% LSI 林地 2015 54 007 22.785 6 72.819 4 2017 53 038 22.376 7 72.817 8 耕地 2015 86 614 36.542 5 81.321 4 2017 86 367 36.438 2 82.403 7 建设用地 2015 11 000 4.640 9 73.838 1 2017 12 084 5.098 2 76.163 6 园地 2015 2 328 0.982 2 27.247 4 2017 2 380 1.004 1 27.479 6 交通用地 2015 1 984 0.837 1 41.677 8 2017 2 164 0.913 0 43.414 9 草地 2015 18 324 7.730 9 87.638 4 2017 18 278 7.711 5 86.273 1 水域 2015 62 615 26.417 3 30.990 0 2017 62 580 26.402 5 31.503 0 未利用地 2015 151 0.063 7 9.160 0 2017 132 0.055 7 9.869 6 说明:CA为斑块类型面积,PLAND为斑块面积比例,LSI 为景观形状指数 表 4 2015和2017年景观水平上的格局指数
Table 4. Pattern index values at the landscape level in 2015 and 2017
年份 LSI SIDI SIEI 2015 74.329 6 0.736 7 0.842 0 2017 75.241 8 0.739 0 0.844 5 说明:LSI为景观形状指数,SIDI为Simpson 多样性指数, SIEI为Simpson 均匀度指数 表 5 2015和2017年各级生态风险面积及其占比
Table 5. Areas and percentages of ecological risks at all levels in 2015 and 2017
生态风险等级 2015年 2017年 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 低 315.329 13.31 309.537 13.06 较低 504.786 21.30 481.612 20.32 中 687.981 29.02 642.376 27.10 较高 730.788 30.83 740.033 31.22 高 131.350 5.54 196.676 8.30 表 6 2015和2017年宿松县各类乡镇不同等级的生态风险区面积
Table 6. Ecological risk area of different grades in various township of Susong County in 2015 and 2017
类别 乡镇 年份 不同等级生态风险区面积/ km2 低 较低 中等 较高 高 山地旅游区 北浴乡、柳坪乡、陈汉乡、隘口乡、趾凤乡、凉亭镇 2015 249.104 69.701 43.759 8.108 0.016 2017 247.286 68.742 41.539 11.401 1.720 农业区 河塌乡、五里乡、复兴镇、下仓镇、破凉镇、华阳河农场、长铺镇 2015 7.043 155.911 323.446 187.567 35.868 2017 6.904 147.139 299.386 221.214 35.192 交通枢纽镇 二郎镇、孚玉镇、九成监狱 2015 0.731 36.072 98.160 50.707 9.616 2017 0.057 33.934 90.754 59.559 10.982 鱼米之乡 高岭乡、程岭乡、千岭乡、佐坝乡、
许岭镇、洲头乡、汇口镇2015 58.451 243.102 222.531 433.498 85.850 2017 55.290 231.797 210.697 418.581 127.067 矿产资源区 九姑乡 2015 0 0 0.085 50.908 0 2017 0 0 0 29.278 21.715 -
[1] 曾辉, 刘国军. 基于景观结构的区域生态风险分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 1999, 19(5): 454 − 457. ZENG Hui, LIU Guojun. Analysis of regional ecological risk based on landscape structure [J]. China Environ Sci, 1999, 19(5): 454 − 457. [2] 许学工, 林辉平, 付在毅, 等. 黄河三角洲湿地区域生态风险评价[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 37(1): 111 − 120. XU Xuegong, LIN Huiping, FU Zaiyi, et al. Regional ecological risk assessment of wetland in the Huanghe River Delta [J]. Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekinensis, 2001, 37(1): 111 − 120. [3] 彭建, 党威雄, 刘焱序, 等. 景观生态风险评价研究进展与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70(4): 664 − 667. PENG Jian, DANG Weixiong, LIU Yanxu, et al. Review on landscape ecological risk assessment [J]. Acta Geogr Sin, 2015, 70(4): 664 − 667. [4] 曹祺文, 张曦文, 马洪坤, 等. 景观生态风险研究进展及基于生态系统服务的评价框架: ESRISK[J]. 地理学报, 2018, 73(5): 843 − 885. CAO Qiwen, ZHANG Xiwen, MA Hongkun, et al. Review of landscape ecological risk and an assessment framework based on ecological services: ESRISK [J]. Acta Geogr Sin, 2018, 73(5): 843 − 885. [5] 张双双, 董斌, 高祥, 等. 基于地理国情数据的合肥市城镇扩展及其景观生态风险研究[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2019, 46(5): 826 − 833. ZHANG Shuangshuang, DONG Bin, GAO Xiang, et al. Urbanization expansion and ecological risk in Hefei City based on geographical national conditions data [J]. J Anhui Agric Univ, 2019, 46(5): 826 − 833. [6] 陈晶晶, 李天宏. 基于PSR模型和投影寻踪法的荆州市景观生态风险评价[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(4): 731 − 740. CHEN Jingjing, LI Tianhong. Landscape ecological risk analysis for Jingzhou City based on PSR model and projection pursuit method [J]. Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekinensis, 2017, 53(4): 731 − 740. [7] 张甜, 刘焱序, 彭建, 等. 深圳市景观生态风险多尺度关联分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(9): 2478 − 2486. ZHANG Tian, LIU Yanxu, PENG Jian, et al. Correlation of the landscape ecological risk on multi-scales in Shenzhen City [J]. Chin J Ecol, 2016, 35(9): 2478 − 2486. [8] 奚世军, 安裕伦, 李阳兵, 等. 基于景观格局的喀斯特山区流域生态风险评估——以贵州省乌江流域为例[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(3): 712 − 721. XI Shijun, AN Yulun, LI Yangbing, et al. Ecological risk assessment of karst mountain watershed based on landscape pattern: a case study of Wujiang River Basin in Guizhou Province [J]. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin, 2019, 28(3): 712 − 721. [9] 李加林, 徐谅慧, 杨磊, 等. 浙江省海岸带景观生态风险格局演变研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2016, 30(1): 293 − 299, 314. LI Jialin, XU Lianghui, YANG Lei, et al. Study on spatial pattern changes of landscape ecological risk on coastalzone of Zhejiang Province [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2016, 30(1): 293 − 299, 314. [10] 郭美楠. 矿区景观格局分析、生态系统服务价值评估与景观生态风险研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2014. GUO Meinan. Landscape Pattern Analysis, Ecosystem Services Value Assessment and Landscape Ecological Risk Research on Mining Area[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2014. [11] 吴健生, 乔娜, 彭建, 等. 露天矿区景观生态风险空间分异[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(12): 3816 − 3824. WU Jiansheng, QIAO Na, PENG Jian, et al. Spatial variation of landscape eco-risk in open mine area [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2013, 33(12): 3816 − 3824. [12] 张莹, 雷国平, 林佳, 等. 扎龙自然保护区不同空间尺度景观格局时空变化及其生态风险[J]. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(5): 1250 − 1256. ZHANG Ying, LEI Guoping, LIN Jia, et al. Spatiotemporal change and its ecological risk of landscape pattern in different spatial scales in Zhalong Nature Reserve [J]. Chin J Ecol, 2012, 31(5): 1250 − 1256. [13] 毕恺艺, 牛铮, 黄妮, 等. 道路网络对景观生态风险的影响——以“中国-中南半岛经济走廊”为例[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2019, 36(3): 347 − 357. BI Kaiyi, NIU Zheng, HUANG Ni, et al. Effects of road network on landscape ecological risk: a case study of“China and Indochina Peninsula Economic Corridor” [J]. J Univ Chin Acad Sci, 2019, 36(3): 347 − 357. [14] 章蛰. 黄河三角洲景观格局变化与生态风险评价研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2016. ZHANG Zhe. The Study on Landscape Pattern Change and Ecological Risk Assmennt of Yellow River Delta[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong Normal University, 2016. [15] HAYES E H, LANDIS W G. Regional ecological risk assessment of a near shore marine environment: Cherry Point, WA [J]. Hum Ecol Risk Assess, 2004, 10(2): 299 − 325. [16] 刘焱序, 王仰麟, 彭建, 等. 基于生态适应性循环三维框架的城市景观生态风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70(7): 1052 − 1067. LIU Yanxu, WANG Yanglin, PENG Jian, et al. Urban landscape ecological risk assessment based on the 3D framework of adaptive cycle [J]. Acta Geogr Sin, 2015, 70(7): 1052 − 1067. [17] 王涛, 肖彩霞, 刘娇, 等. 杞麓湖流域景观时空格局演变及其对景观生态风险的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(6): 219 − 225. WANG Tao, XIAO Caixia, LIU Jiao, et al. Evolution of spatial and temporal patterns of landscape and its impact on landscape ecological risk in Qilu Lake Basin [J]. Res Soil Water Conserv, 2019, 26(6): 219 − 225. [18] 许妍, 高俊峰, 赵家虎, 等. 流域生态风险评价研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(1): 284 − 292. XU Yan, GAO Junfeng, ZHAO Jiahu, et al. The research progress and prospect of watershed ecological risk assessment [J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2012, 32(1): 284 − 292. [19] 杨晓红, 张双双, 汪鑫. 基于地理国情数据的土地利用景观格局分析[J]. 地理空间信息, 2019, 17(10): 32 − 36. YANG Xiaohong, ZHANG Shuangshuang, WANG Xin. Land use landscape pattern analysis based on geographical conditions data [J]. Geospat Inf, 2019, 17(10): 32 − 36. [20] 崔杨林, 董斌, 位慧敏, 等. 县域尺度下景观指数的粒度效应[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(4): 778 − 786. CUI Yanglin, DONG Bin, WEI Huimin, et al. Granularity effect of landscape index at county scale [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2020, 37(4): 778 − 786. [21] 李小燕, 柳书俊, 王志杰. 南水北调中线汉中市水源地景观生态风险评价与特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(5): 181 − 187. LI Xiaoyan, LIU Shujun, WANG Zhijie. Landscape ecological risk characteristics of water source site in Hanzhong City of the middle route of the South-to-North water transfer project of China [J]. Res Soil Water Conserv, 2019, 26(5): 181 − 187. [22] GONG Jian, YANG Jianxin, TANG Wenwu. Spatially explicit landscape level ecological risks induced by land use and land cover change in a national ecologically representative region in China [J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2015, 12(11): 14192 − 14215. [23] 傅微, 吕一河, 傅伯杰, 等. 陕北黄土高原典型人类活动影响下景观生态风险评价[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019, 35(3): 290 − 299. FU Wei, LÜ Yihe, FU Bojie, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment under the influence of typical human activities in Loess Plateau, Northern Shaanxi [J]. J Ecol Rural Environ, 2019, 35(3): 290 − 299. [24] 谢花林. 基于景观结构的土地利用生态风险空间特征分析——以江西兴国县为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2011, 31(4): 688 − 695. XIE Hualin. Spatial characteristic analysis of land use eco-risk based on landscape structure: a case study in the Xingguo County, Jiangxi Province [J]. China Environ Sci, 2011, 31(4): 688 − 695. [25] 臧淑英, 梁欣, 张思冲. 基于GIS的大庆市土地利用生态风险分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2005, 14(4): 141 − 145. ZANG Shuying, LIANG Xin, ZHANG Sichong. GIS-based analysis of ecological risk on land-use in Daqing City [J]. J Nat Disasters, 2005, 14(4): 141 − 145. [26] 岳万艳, 周长威. 黔中城市群景观生态风险时空动态研究[J]. 贵州科学, 2019, 37(5): 52 − 59. YUE Wanyan, ZHOU Changwei. Space-time dynamic analysis of landscape ecological risk of urban agglomeration in central Guizhou [J]. Guizhou Sci, 2019, 37(5): 52 − 59. [27] 刘迪, 陈海, 张敏, 等. 生态脆弱区景观生态风险时空分异及其地形梯度分析——以陕西省米脂县为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(4): 239 − 244, 251. LIU Di, CHEN Hai, ZHANG Min, et al. Analysis of spatial-temporal distribution of landscape ecological risk in ecologically vulnerable areas and its terrain gradient: a case study of Mizhi County of Shannxi Province [J]. Res Soil Water Conserv, 2019, 26(4): 239 − 244, 251. [28] 陈爱莲, 朱博勤, 陈利顶, 等. 双台河口湿地景观及生态干扰度的动态变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(5): 1120 − 1128. CHEN Ailian, ZHU Boqin, CHEN Liding, et al. A dynamic changes of landscape pattern and eco-disturbance degree in Shuangtai estuary wet land of Liaoning Province, China [J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2010, 21(5): 1120 − 1128. [29] 白舒婷. 基于土地利用变化的吉林西部景观生态风险评价研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019. BAI Shuting. Study on Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment of Western Jilin based on Land Use Change[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019. [30] 闻国静, 刘云根, 王妍, 等. 普者黑湖流域景观格局及生态风险时空演变[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2017, 34(6): 1095 − 1103. WEN Guojing, LIU Yungen, WANG Yan, et al. Temporal and spatial evolution of landscape patterns and ecological risk in the Puzhehei Lake basin [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2017, 34(6): 1095 − 1103. [31] 王涛, 肖彩霞, 刘娇, 等. 云南高原湖泊杞麓湖动态演变及景观生态风险评价[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(1): 9 − 17. WANG Tao, XIAO Caixia, LIU Jiao, et al. Dynamic evolution and landscape ecological risks assessment of Qilu Lake in Yunnan Plateau [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2020, 37(1): 9 − 17. [32] 王彦军, 杨月. 基于地理国情普查成果的城市景观格局分析[J]. 现代测绘, 2018, 41(2): 27 − 30. WANG Yanjun, YANG Yue. Analysis on landscape pattern of city based on the survey of geographical conditions [J]. Modern Surv Mapp, 2018, 41(2): 27 − 30. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200461







 下载:
下载: