-
木材在中国可再生资源中占有很大的比例。随着国民经济逐步增长,木材市场不断扩大。目前,由于优质木材频频出现供需不平衡、木材造假等问题,因此采用多种识别技术来甄别木材种类已成为必然。木材种类识别除了依照形态学处理外,还可以使用计算机图像识别、DNA识别等方法[1-3],但是这些方法和传统的取样方法一样[4],都需要对树木进行剖析和制样,对于一些珍贵的木材会造成不必要的浪费,甚至会降低本身的价值。近红外光谱分析技术是20世纪70年代兴起的一种新的木材识别分析技术。它作为一种常用的测量工具,具有快速、无损、在线分析等优势。近几年,学者们应用近红外光谱技术对木材种类进行了识别研究[5],如王学顺等[6]利用近红外光谱技术,结合主成分分析(PCA)和BP神经网络对不同木材种类进行了识别研究,效果良好。谭念等[7]基于近红外光谱技术,联合PCA和支持向量机实现了木材种类的有效鉴别。
目前,近红外光谱分析技术用于木材种类识别大多采用PCA进行特征提取,实现数据降维,但这种方法的特征值筛选有一定的局限性,仅凭累计贡献率决定特征值的个数,无法通过参数化等方法对处理过程进行干预,效率和物理实用性不高。连续投影算法(SPA)是一种常用的特征波长筛选算法。它能够利用向量的投影分析,寻找含有最低限度冗长信息的变量组,通过参数调整可实现较强物理实用性的数据压缩。陈远哲等[8]基于SPA构建了最小偏二乘法回归模型,适用于淡水鱼储藏期质构品质的快速无损检测。郭文川等[9]通过比较不同特征提取方式,得出采用SPA和随机森林识别准确率最高。遗传算法(GA)用于寻优,广泛应用于机器学习等领域。
本研究将SPA和GA联用,在运用SPA获得特征值后,应用GA进一步寻找最佳特征参数,以提升木材识别的效率和准确率。本研究以红檀Swartizia spp.、刺猬紫檀Pterocarpus erinaceus、巴里黄檀Dalbergia bariensis、大果紫檀Pterocarpus macrocarpus、红檀香Myroxylon balsamu、破布木Cordia dichotoma、豆瓣香Osmanthus delavayi、檀香紫檀Pterocarpus santalinus、中美洲黄檀Dalbergia granadillo和黑檀Dalbergia nigra为研究对象,应用可见/近红外光谱仪采集10种木材的光谱图,运用不同的预处理方式叠加进行降噪分析,以BP神经网络为木材种类的分类识别算法,探讨经GA优化的SPA较之常规特征提取算法的优越性,为更精确高效的木材识别提供参考。
-
数据采集:参与试验的木材共10种,试样为6 cm×5 cm×2 cm的木块。每种木材制备5块样本,共计50块。每块木材分10个点采集光谱,以木块横向等分2份,纵向等分5份,取每份的中心点作为标记进行采样,每个点采集10组数据,取平均值作为此样点的实验数据,即1块试样采集10组实验数据,10种木材共计采集500组实验数据。样点采集遵循以下原则:①采谱过程中每15 min进行1次空白校正,以保证光谱的稳定性。②每块木材样本大小、薄厚和形状均保持一致,确保样点在每块样本木块上的属性相同,最大程度缩小误差。
主要仪器:LabSpec 5000光谱仪(ASD公司,美国),波长为350~2 500 nm。用光谱仪配套的软件Indico Pro Version 3.1采集光谱数据。
-
PCA是一种常用的波段降维手段。主成分通常表示为原始变量的某种线性组合,它们不仅能够代表原始变量绝大多数的信息,还可以一定程度上去除噪声,压缩数据,对高维数据进行降维,减少预测变量的个数[10]。
-
SPA是一种使矢量空间共线性最小化的前向变量选择算法,在降低共线信息的研究和有效信息获取的研究中取得较好的成效[11-12]。本研究应用SPA在光谱全波段中筛选出少量几个特征波段,不仅能够减少参与识别的光谱波段个数,并且可以保证特征波段之间的共线性最小,进而提高识别正确率和速度。
-
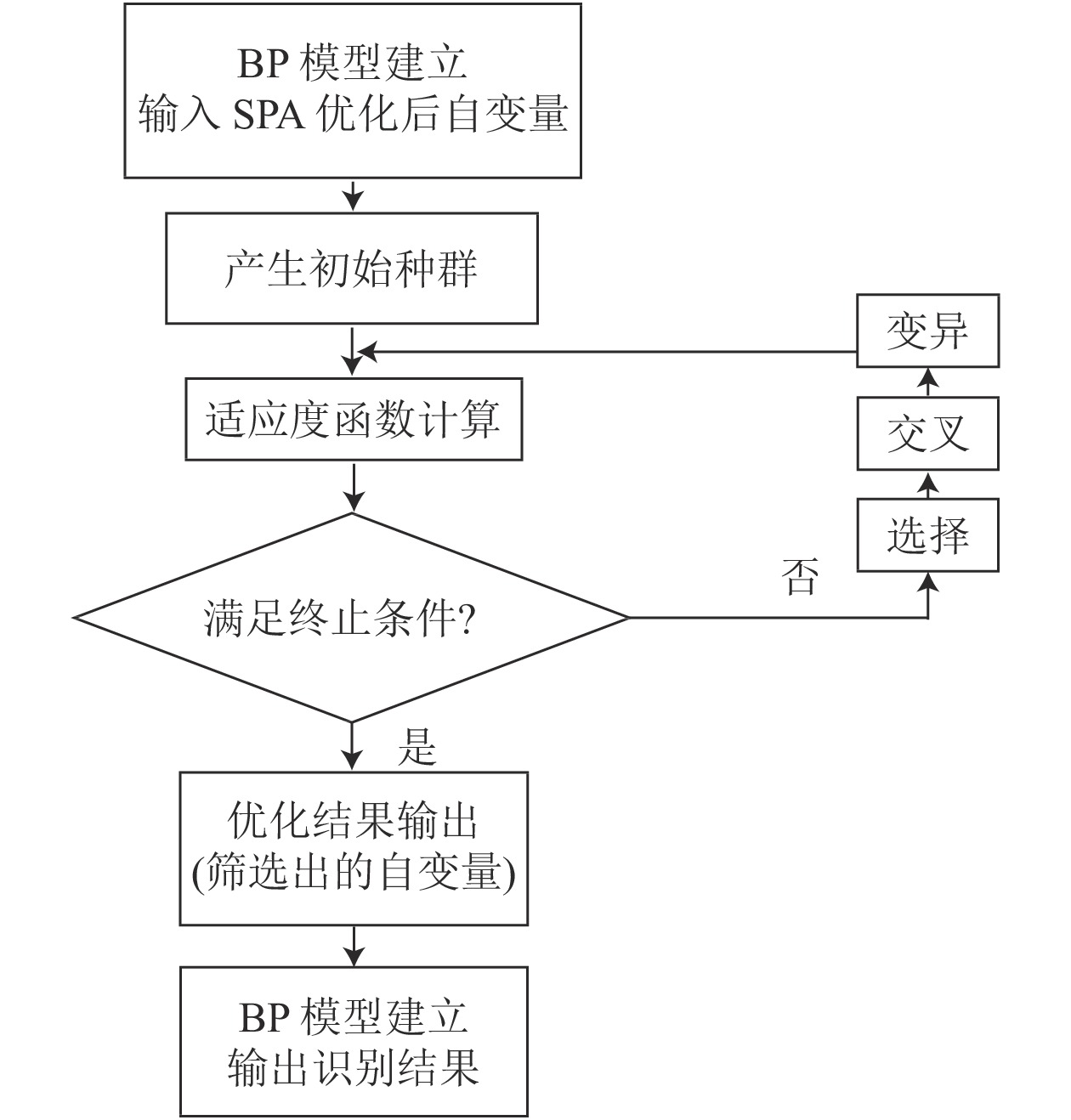
当SPA筛选后的输入自变量较多且不是相互独立时,利用BP神经网络容易出现过拟合的现象,从而导致所建立的模型精度低、建模时间长等问题,因此,在构建模型前,有必要对输入自变量进行优化,选择最能反映输入与输出关系的自变量参与建模。GA优化能较好解决上述问题。利用GA进行优化计算,需要将解空间映射到编码空间,每个编码对应问题的1个解。本研究将编码长度设计为10,木材光谱特征的每位对应1个输入自变量,每一位的基因取值只能是“1”和“0”,如果一位值为“1”,表示该位对应的输入自变量参与最终的建模;反之,则表示“0”对应的输入自变量不作为最终的建模自变量。选取测试集数据均方误差的倒数作为GA的适应度函数,这样,经过不断的迭代进化,最终筛选出最具代表性的输入自变量参与建模[13-14]。GA优化的设计步骤主要为:首先产生初始种群,对适应度函数进行计算,其次进行选择、交叉和变异的基础操作,最后优化结果输出,构建其模型。设计步骤如图1所示。
-
应用LabSpec 5000光谱仪采集10种木材的原始光谱图,其中选取红檀的50个样本进行对比分析(图2)。
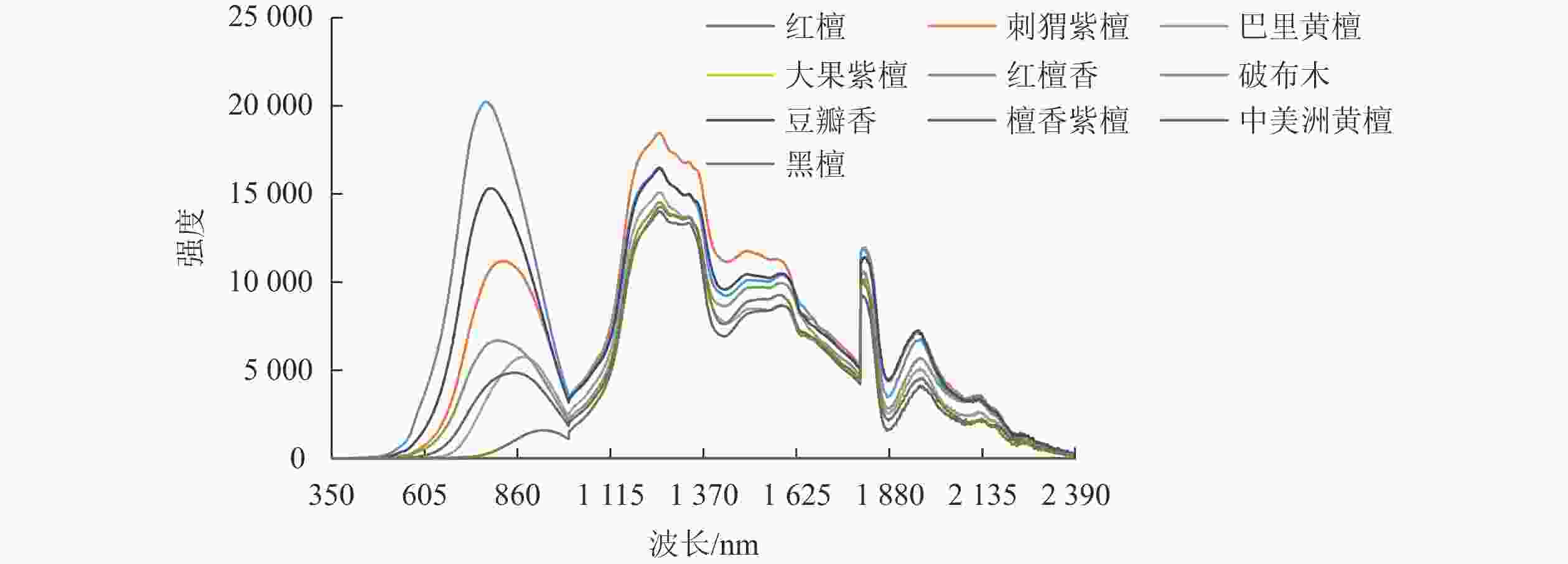
为了更直观地对比10种木材光谱图的差异,分别取10种木材中第1组数据进行绘图分析(图3)。由图3可见:大果紫檀、红檀和檀香紫檀的强度数值过小,几乎与x轴重叠。
由图2和图3可以看出:同一种木材光谱图的波形基本一致,但强度值略有差异;刺猬紫檀、巴里黄檀、红檀香、破布木、豆瓣香、中美洲黄檀这6种木材的光谱图从波峰、形状上相似性均较高,黑檀与这6种木材的光谱图也较相似,仅在第1个波谷处形状上略有差异。
-
原始光谱图往往带有一定的噪声,影响BP神经网络识别的正确率,因此有必要对光谱数据进行预处理[15-17]。数据的预处理方法较多,本研究分别采用了移动平均法、移动平均法+多元散射校正(MSC)、移动平均法+标准正态变量变换(SNV)、Savitzky-Golay卷积平滑算法(S-G滤波器)、S-G滤波器+MSC和S-G滤波器+SNV对10种木材的原始光谱进行了预处理,通过对比分析以确定最佳的预处理方法。
针对上述的几种预处理方法,分别进行主成分特征提取。以累计贡献率达95%及以上为主成分个数的选取标准。以选取的主成分为输入向量,40个样本作为训练,10个样本作为测试(后文测试数据均与此相同,不再赘述)。应用BP神经网络进行木材种类识别测试,经过20次的随机试验,获得各种预处理下BP神经网络的平均识别结果(表1)。由表1可以看出:采用S-G滤波器+SNV预处理时,BP 神经网络获得的平均识别率最高,达到了84.7%。
表 1 不同预处理的PCA-BP神经网络识别率
Table 1. PCA-BP neural network recognition with different preprocessing
检测方式 预处理方法 累计贡
献率/%主成分
个数/个平均识
别率/%可见/近红外光谱 对照组 95 12 80.2 移动平均法 95 14 81.4 移动平均法+MSC 95 10 82.1 移动平均法+SNV 95 11 83.5 S-G滤波器 95 12 81.3 S-G滤波器+MSC 95 13 82.9 S-G滤波器+SNV 95 15 84.7 为了方便对比10种木材各自的识别效果,整理了S-G滤波器+SNV预处理时10种木材的BP神经网络识别结果:10种木材的识别效果相差不大,最低为豆瓣香(83.1%),最高为刺猬紫檀(85.8%)。
-
针对2.2节中的几种预处理方法进行SPA的BP神经网络识别探讨,以确定最佳的预处理方法。为了对比预处理的效果,针对SPA方法中的起始波段和特征值个数进行了随机设置。令SPA方法中的起始波段(Winitial)为15 nm,特征值个数(Ntot)为10,对各种预处理后的数据进行SPA特征提取,应用BP神经网络进行20次的随机识别,得出10种木材的平均识别率(表2)。由表2可以看出:对于不同的预处理方式,SPA-BP的正确识别率有所不同,移动平均法+SNV的预处理方法最佳,正确率可达88.2%,因此,后续在分析SPA-BP神经网络识别木材时,本研究仅针对移动平均法和SNV叠加的预处理方法进行分析。
表 2 不同预处理的SPA-BP神经网络平均识别率
Table 2. Average recognition rate of SPA-BP neural network with different pretreatments
预处理方法 平均识
别率/%预处理方法 平均识
别率/%对照组 86.1 S-G滤波器 86.4 移动平均法 87.2 S-G滤波器+MSC 86.8 移动平均法+MSC 86.5 S-G滤波器+SNV 87.3 移动平均法+SNV 88.2 -
影响SPA特征提取的因素通常有2个,分别是Winitial和Ntot。随着Winitial和Ntot的改变,提取的特征波长分布会有所不同,从而影响最终BP神经网络的正确识别率,此处探讨最佳Winitial的选取方法。光谱图中的特征吸收峰对被分析物质是很关键的特征,因此首先考虑分别以木材的吸收峰和非吸收峰作为起始波段,通过对比分析,确定最佳起始波段。①吸收峰作为起始波段的选取。光谱图中分布了大小不一的波峰,选取波峰特征较明显的吸收峰进行分析,以波峰点为中心点,取宽度相等的波段区间(每个波段均取51个数据)作为吸收峰的集中分布波段,10种木材的吸收峰集中波段如表3所示。由表3可以看出:10种木材的吸收峰重叠的波段有1 230~1 260、1 780~1 810、1 940~1 970 nm。分别取3个波段的中位数作为起始波段值,即1 245、1 795和1 955 nm。因为Winitial的数值表示为序列号,所以在此基础上减去初始波段350 nm,Winitial最终取值分别为895、1 445、1 605 nm。②非吸收峰作为起始波段的选取。将全波段350~2 500 nm等分成5份,分别在每个等分波段中随机选取1个非吸收峰作为起始波段。本研究随机选取的5个波段的波长分别为365、1 145、1 345、1 700、2 300 nm。在此基础上减去初始波段350 nm,Winitial最终取值分别为15、795、995、1350、1 950。分别以上述的吸收峰和非吸收峰为起始波段值,即以15、795、895、995、1 350、1 445、1 605、1 950 nm作为SPA的起始波段。SPA的特征值个数统一取10,进行BP神经网络识别,经过20次的随机试验,10种木材提取的特征波长分布和平均识别率如表4所示。由表4可以看出:以吸收峰作为起始波段时,特征波长分布大多追溯在吸收峰附近。对比表4的识别率可见,起始波段为1 445 nm时最高,达90.4%,其余按照1605、895、795、995、1 350、1 950和15 nm的顺序依次递减。不难看出,吸收峰作为起始波段的识别率普遍优于非吸收峰。
表 3 10种木材吸收峰个数和集中波段
Table 3. Number of absorption peaks and concentrated bands of 10 species of wood
木材种类 吸收峰个数/个 集中分布波段/nm 红檀 7 920~970、1 010~1 060、1 210~1 260、1 570~1 620、1 779~1 829、1 921~1 971、2 122~2 172 大果紫檀 7 930~980、1 020~1 070、1 220~1 270、1 580~1 630、1 780~1 830、1 920~1 970、2 120~2 170 檀香紫檀 7 932~982、1 023~1 073、1 221~1 271、1 568~1 618、1 777~1 827、1 921~1 971、2 123~2 173 刺猬紫檀 9 763~813、1 222~1 272、1 308~1 358、1 461~1 511、1 548~1 598、1 760~1 810、1 931~1 981、
2 092~2 142、2 211~2 261巴里黄檀 9 765~815、1 221~1 271、1 307~1 357、1 466~1 516、1 545~1 595、1 769~1 819、1 930~1 980、
2 087~2 137、2 219~2 269红檀香 9 753~803、1 223~1 273、1 309~1 359、1 463~1 513、1 558~1 608、1 771~1 821、1 932~1 982、
2 092~2 142、2 212~2 262破布木 9 763~813、1 222~1 272、1 317~1 367、1 463~1 513、1 551~1 601、1 772~1 822、1 933~1 983、
2097~2147、2214~2264豆瓣香 9 766~816、1230~1280、1317~1367、1468~1518、1554~1604、1775~1825、1940~1990、
2095~2145、2 216~2 266中美洲黄檀 9 753~803、1 218~1 268、1 305~1 355、1 457~1 507、1 544~1 594、1 769~1 819、1 928~1 978、
2 084~2 134、2 209~2 259黑檀 9 881~931、1 218~1 268、1 305~1 355、1 452~1 502、1 557~1 607、1 772~1 822、1 923~1 973、
2 092~2 142、2 218~2 268表 4 不同起始波段的SPA-BP神经网络平均识别率
Table 4. Average recognition rate of SPA-BP neural network with different starting bands
特征值数/个 起始波段/nm 10种木材提取特征波长分布/nm 平均识别率/% 10 895 364~368、2 141~2 144;402~410;418~426;324、2 135~2 142;375~383;432~440;400~408;476~484;420~428;1 452~1 460 89.7 10 1 445 478~586;410~418;423~431;500~508;405~413;436~444;418~426;693~701;891~899;888~896 90.4 10 1 605 133~135、2 137~2 142;891~899;891~899;2 135~2 142、2 132;419~427;819~827;420~428;446~454;892~990;893~901 90.1 10 15 2133~135、2 137~2 142;2 133~2 135、2 137~2 142;408~416;292、22 135~2 142;375~383;430~438;414~422;461~469;420~428;890~898 88.3 10 795 61~64、2 139~2 143;405~413;420~428;326、2 135~2 142;378~386;527~535;403~411;478~486;420~422、1 453~1 458;1 350~1 358 89.5 10 995 203~209、2 141~2 142;399~407;418~426;349~352、2 138~2 142;3381~389;434~442;421~429;485~493;527~535;1 452、1 454~ 1458、1 461~1 463 89.2 10 1 350 82~90;891~899;434~442;519~527;416~424;886~894;420~428;694~702;891~899;888~896 88.9 10 1 950 13、2 135~2 142;379~387;407~415;281、2 135~2 142;293~301;428~436;
1 058~1 066;450~458;413、1 452~1 459;1 452~1 46088.6 说明:木材依次为红檀、大果紫檀、檀香紫檀、刺猬紫檀、巴里黄檀、红檀香、破布木、豆瓣香、中美洲黄檀、黑檀 -
将起始波段固定为最佳,即Winitial=1 445 nm,探讨Ntot取不同数值时,对BP神经网络识别木材的影响。从图3的光谱图可以看出:红檀、大果紫檀、檀香紫檀3种木材样本的吸收峰有7个,刺猬紫檀、巴里黄檀、红檀香、破布木、豆瓣香、中美洲黄檀和黑檀有9个。考虑吸收峰能更好地反映木材光谱图的特征,Ntot分别取了7和9,同时参考SPA的相关文献[18-21],且基于BP神经网络输入向量过多也会影响识别精度,又分别取了5、8、10、20、25进行了对比分析。基于以上特征数,分别应用BP神经网络进行木材识别,每个状态仍随机运行20次,获得的结果如表5所示。分析表5可知:整体上,当特征值个数取7和9时正确率偏高,说明特征值个数的取值和吸收峰值有关;当特征值个数取9时识别率最高,达93.2%,说明特征值个数和单个木材的吸收峰无关,应由整体的吸收峰来确定。
表 5 同一起始波段不同特征波段的SPA-BP神经网络平均识别率
Table 5. Average recognition rate of SPA-BP neural network with the same starting band and different characteristic bands
起始波
段/nm特征值
数/个平均识
别率/%起始波
段/nm特征值
数/个平均识
别率/%1 445 5 92.3 1 445 10 90.6 1 445 7 93.0 1 445 20 92.7 1 445 9 93.2 1 445 25 91.2 1 445 8 91.6 -
基于最佳预处理方式(移动平均法+SNV)、最佳起始波段(Winitial=1 445 nm)和最佳特征值个数(Ntot=9),整理出SPA-BP神经网络识别10种木材各自的识别结果(表6)。由表6可以看出:在最佳参数设置下,SPA-BP神经网络的识别率较高,大果紫檀、红檀香、中美洲黄檀和黑檀的平均识别率均为100.0%,其他木材的平均识别率最低达90.7%,最高达95.1%。
表 6 同一预处理方式10种木材的SPA-BP神经网络平均识别率
Table 6. Average recognition rate of SPA-BP neural network for 10 species of wood with the same pretreatment method
木材种类 平均识
别率/%木材种类 平均识
别率/%木材种类 平均识
别率/%红檀 90.9 巴里黄檀 94.2 中美洲黄檀 100.0 大果紫檀 100.0 红檀香 100.0 黑檀 100.0 檀香紫檀 90.7 破布木 94.6 平均 95.7 刺猬紫檀 95.1 豆瓣香 91.0 说明:预处理方式为移动平均法+SNV,起始波段为1 445 nm, 特征值数为9个 -
针对SPA的最佳预处理方式(移动平均法+SNV)、最佳起始波段(Winitial=1 445 nm)和最佳特征值个数(Ntot=9),基于SPA-GA的BP神经网络识别方法随机运行20次,采用GA优化前后建模时间明显缩短;大果紫檀、红檀香、中美洲黄檀和黑檀在采用GA优化前后正确识别率均为100.0%,说明这4种木材在采用SPA特征提取时,识别率较高,采用GA优化后对正确识别率影响不大;其他6种木材采用SPA特征提取时均有一定的误判,运用GA优化后识别率有一定的提高。其中破布木的识别率由90.0%提升到了100.0%,巴里黄檀由88.9%提升到了100.0%,刺猬紫檀由90.9%提升到了100.0%。虽然每次仅提升1种木材,但通过多次运行,可达到整体提升的效果。
针对上述20次运行结果,获得10种木材各自的识别结果:大果紫檀、中美洲黄檀、刺猬紫檀、巴里黄檀、红檀香、破布木和黑檀平均识别正确率高达100.0%,其他3种木材的平均识别率最低达91.5%,最高达95.7%,10种木材的平均识别率达98.0%。
已有的木材识别研究的特征提取方法主要集中于主成分分析[22]、导数处理[23]等,主成分分析的平均识别率为70.0%~95.3%,导数处理识别率达98.6%。虽然这些研究识别率较高,但这些研究参与识别的木材种类大多仅为4~5个,对于同时识别10种木材未见尝试。经研究,参与识别的木材种类越多,识别率越难保证。本研究的主成分分析法识别10种木材,平均识别率仅为84.7%。本研究采取SPA-GA联合的特征提取方法,识别对象为10种木材,通过调整吸收峰、特征值等参数,最终7种木材的平均识别率达100.0%,且识别速度提高为原来的2~3倍。为了进一步验证识别率的鲁棒性,本研究还采用多种预处理的方式,使得原始数据表现出良好的稳定性和容错性。最后实验数据均为随机20次运行的结果,说明训练好的模型可以随时间和频次迁移应用,识别性能不会降低。
-
研究结果表明:①SPA-GA法识别木材时,选择移动平均法+SNV的预处理方式效果最佳。②对于参数的选择,起始波段选取吸收峰比选取非吸收峰识别率更高,特征值个数结合光谱图的峰值个数选取更恰当。本研究分别选取起始波段为1 445 nm,特征值个数为9个。③SPA-GA提取光谱图特征时识别性能最佳。SPA特征值经GA寻优后,特征个数大多减少为原来的一半左右,优化后BP神经网络的平均识别速度显著提升,大果紫檀、中美洲黄檀、刺猬紫檀、巴里黄檀、红檀香、破布木和黑檀等7种木材的平均识别正确率均高达100.0%,总体识别率较SPA显著提高。
本研究仅选择了红檀、刺猬紫檀、巴里黄檀、大果紫檀、红檀香、破布木、豆瓣香、檀香紫檀、中美洲黄檀和黑檀这10种木材样本进行了探讨,对于其他木材的识别有待进一步研究验证。
Visible/near infrared spectrum wood identification based on SPA-GA-BP neural network
-
摘要:
目的 基于可见/近红外光谱技术,以10种木材为研究对象,探索不同预处理和特征提取方法下BP神经网络识别木材的效果。 方法 利用美国ASD公司生产的LabSpec 5000光谱仪采集10种木材的光谱图,分别进行移动平均法处理、移动平均法+多元散射校正(MSC)、移动平均法+标准正态变量变换(SNV)、Savitzky-Golay卷积平滑算法(S-G滤波器)、S-G滤波器+MSC和S-G滤波器+SNV的预处理,运用主成分分析法(PCA)、连续投影算法(SPA)、SPA和遗传算法(GA)联合分别进行特征提取,将提取的特征结合BP神经网络进行木材识别试验。 结果 以SPA和GA联合提取光谱特征时,移动平均法+SNV的预处理效果最佳,以吸收峰为起始波段(Winitial=1 445 nm)、吸收峰个数为特征个数(Ntot=9)时,识别率较高,特征个数大部分减少为SPA提取特征值个数的一半左右。BP神经网络的平均识别速度提升明显。10种木材的平均识别率为98.0%,其中7种木材的识别率达到了100.0%。 结论 在移动平均法+SNV的预处理下,SPA和GA联合提取光谱图的特征,既可提高BP神经网络识别木材的正确率,又可提升识别速度。图3表6参23 Abstract:Objective The purpose of this study is to explore the effect of BP neural network identification under different pretreatment and feature extraction methods based on visible/near infrared spectroscopy technology, with 10 wood species as objects. Method The LabSpec 5000 spectrometer produced by American ASD company was used to collect the spectrograms of 10 species of wood, which were pretreated by moving average method, moving average method + multiplicative scattering correction(MSC), average method+standard normal variable transformation (SNV), Savitzky-Golay convolution smoothing algorithm (S-G filter), S-G filter+MSC and S-G filter+SNV. Meanwhile, principal component analysis(PCA), successive projections algorithm(SPA), and SPA combined with genetic algorithm(GA) were used for feature extraction respectively. The extracted features were combined with BP neural network for wood identification test. Result When SPA and GA were combined to extract spectral features, the moving average+SNV method had the best preprocessing effect. When absorption peak was used as the initial waveband (Winitial=1 445 nm) and the number of absorption peaks (Ntot=9) as the number of features, the identification rate was high, and the number of features mostly decreased to about 1/2 of the number of feature values extracted by SPA. The average identification speed of BP neural network significantly increased. The average identification rate of the 10 wood species was 98.0%, and the identification rate of 7 of them reached 100.0%. Conclusion Under the pretreatment of moving average method+SNV, the combined use of SPA and GA in spectral feature extraction can improve not only the accuracy of wood identification by BP neural network, but also the identification speed. [Ch, 3 fig. 6 tab. 23 ref.] -
表 1 不同预处理的PCA-BP神经网络识别率
Table 1. PCA-BP neural network recognition with different preprocessing
检测方式 预处理方法 累计贡
献率/%主成分
个数/个平均识
别率/%可见/近红外光谱 对照组 95 12 80.2 移动平均法 95 14 81.4 移动平均法+MSC 95 10 82.1 移动平均法+SNV 95 11 83.5 S-G滤波器 95 12 81.3 S-G滤波器+MSC 95 13 82.9 S-G滤波器+SNV 95 15 84.7 表 2 不同预处理的SPA-BP神经网络平均识别率
Table 2. Average recognition rate of SPA-BP neural network with different pretreatments
预处理方法 平均识
别率/%预处理方法 平均识
别率/%对照组 86.1 S-G滤波器 86.4 移动平均法 87.2 S-G滤波器+MSC 86.8 移动平均法+MSC 86.5 S-G滤波器+SNV 87.3 移动平均法+SNV 88.2 表 3 10种木材吸收峰个数和集中波段
Table 3. Number of absorption peaks and concentrated bands of 10 species of wood
木材种类 吸收峰个数/个 集中分布波段/nm 红檀 7 920~970、1 010~1 060、1 210~1 260、1 570~1 620、1 779~1 829、1 921~1 971、2 122~2 172 大果紫檀 7 930~980、1 020~1 070、1 220~1 270、1 580~1 630、1 780~1 830、1 920~1 970、2 120~2 170 檀香紫檀 7 932~982、1 023~1 073、1 221~1 271、1 568~1 618、1 777~1 827、1 921~1 971、2 123~2 173 刺猬紫檀 9 763~813、1 222~1 272、1 308~1 358、1 461~1 511、1 548~1 598、1 760~1 810、1 931~1 981、
2 092~2 142、2 211~2 261巴里黄檀 9 765~815、1 221~1 271、1 307~1 357、1 466~1 516、1 545~1 595、1 769~1 819、1 930~1 980、
2 087~2 137、2 219~2 269红檀香 9 753~803、1 223~1 273、1 309~1 359、1 463~1 513、1 558~1 608、1 771~1 821、1 932~1 982、
2 092~2 142、2 212~2 262破布木 9 763~813、1 222~1 272、1 317~1 367、1 463~1 513、1 551~1 601、1 772~1 822、1 933~1 983、
2097~2147、2214~2264豆瓣香 9 766~816、1230~1280、1317~1367、1468~1518、1554~1604、1775~1825、1940~1990、
2095~2145、2 216~2 266中美洲黄檀 9 753~803、1 218~1 268、1 305~1 355、1 457~1 507、1 544~1 594、1 769~1 819、1 928~1 978、
2 084~2 134、2 209~2 259黑檀 9 881~931、1 218~1 268、1 305~1 355、1 452~1 502、1 557~1 607、1 772~1 822、1 923~1 973、
2 092~2 142、2 218~2 268表 4 不同起始波段的SPA-BP神经网络平均识别率
Table 4. Average recognition rate of SPA-BP neural network with different starting bands
特征值数/个 起始波段/nm 10种木材提取特征波长分布/nm 平均识别率/% 10 895 364~368、2 141~2 144;402~410;418~426;324、2 135~2 142;375~383;432~440;400~408;476~484;420~428;1 452~1 460 89.7 10 1 445 478~586;410~418;423~431;500~508;405~413;436~444;418~426;693~701;891~899;888~896 90.4 10 1 605 133~135、2 137~2 142;891~899;891~899;2 135~2 142、2 132;419~427;819~827;420~428;446~454;892~990;893~901 90.1 10 15 2133~135、2 137~2 142;2 133~2 135、2 137~2 142;408~416;292、22 135~2 142;375~383;430~438;414~422;461~469;420~428;890~898 88.3 10 795 61~64、2 139~2 143;405~413;420~428;326、2 135~2 142;378~386;527~535;403~411;478~486;420~422、1 453~1 458;1 350~1 358 89.5 10 995 203~209、2 141~2 142;399~407;418~426;349~352、2 138~2 142;3381~389;434~442;421~429;485~493;527~535;1 452、1 454~ 1458、1 461~1 463 89.2 10 1 350 82~90;891~899;434~442;519~527;416~424;886~894;420~428;694~702;891~899;888~896 88.9 10 1 950 13、2 135~2 142;379~387;407~415;281、2 135~2 142;293~301;428~436;
1 058~1 066;450~458;413、1 452~1 459;1 452~1 46088.6 说明:木材依次为红檀、大果紫檀、檀香紫檀、刺猬紫檀、巴里黄檀、红檀香、破布木、豆瓣香、中美洲黄檀、黑檀 表 5 同一起始波段不同特征波段的SPA-BP神经网络平均识别率
Table 5. Average recognition rate of SPA-BP neural network with the same starting band and different characteristic bands
起始波
段/nm特征值
数/个平均识
别率/%起始波
段/nm特征值
数/个平均识
别率/%1 445 5 92.3 1 445 10 90.6 1 445 7 93.0 1 445 20 92.7 1 445 9 93.2 1 445 25 91.2 1 445 8 91.6 表 6 同一预处理方式10种木材的SPA-BP神经网络平均识别率
Table 6. Average recognition rate of SPA-BP neural network for 10 species of wood with the same pretreatment method
木材种类 平均识
别率/%木材种类 平均识
别率/%木材种类 平均识
别率/%红檀 90.9 巴里黄檀 94.2 中美洲黄檀 100.0 大果紫檀 100.0 红檀香 100.0 黑檀 100.0 檀香紫檀 90.7 破布木 94.6 平均 95.7 刺猬紫檀 95.1 豆瓣香 91.0 说明:预处理方式为移动平均法+SNV,起始波段为1 445 nm, 特征值数为9个 -
[1] LEE H T, SOON L L, KEVIN K N, et al. DNA extraction from dry wood of Neobalanocarpus heimii (Diperocarpaceae)for forensic DNA profiling and timeber tracking [J]. Wood Sci Technol, 2012, 46(5): 813 − 815. [2] 陈利顶, 李秀珍, 傅伯杰, 等. 中国景观生态学发展历程与未来研究重点[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(12): 3129 − 3141. CHEN Liding, LI Xiuzhen, FU Bojie, et al. Development history and future research priorities of landscape ecology in China [J]. J Ecol, 2014, 34(12): 3129 − 3141. [3] JIAO Lichao, YIN Yafang, XIAO Fuming, et al. Comparative analysis of two DNA extraction protocols from fresh and dried wood of Cunninghamia lanceolata(Taxodiaceae) [J]. J Iawa, 2012, 4(33): 441 − 456. [4] 王宪, 沈华杰, 于清琳, 等. 基于IAWA的3种简易木材识别方法探究[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2019, 39(6): 167 − 172. WANG Xian, SHEN Huajie, YU Qinglin, et al. Research on 3 simple timber identification methods based on IAWA [J]. J Southwest For Univ, 2019, 39(6): 167 − 172. [5] MUECHER S, KLIJN J A, WASCHER D, et al. A new European landscape clasification(LANMAP): a transparent, flexible and user-oriented methodology to distinguish landscapes [J]. Ecol Indic, 2010, 10(1): 87 − 103. [6] 王学顺, 黄安民, 孙一丹, 等. 基于BP神经网络的木材近红外光谱树种识别[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(12): 82 − 85, 89. WANG Xueshun, HUANG Anmin, SUN Yidan, et al. Back propagation artificial neural network combine with near infrared spectroscopy for timber recognition [J]. J Northeast For Univ, 2015, 43(12): 82 − 85, 89. [7] 谭念, 孙一丹, 王学顺, 等. 基于主成分分析和支持向量机的木材近红外光谱树种识别研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(11): 3370 − 3374. TAN Nian, SUN Yidan, WANG Xueshun, et al. Research on near infrared spectrum with principal component analysis and support vector machine for timber identification [J]. Spectrosc Spectral Anal, 2017, 37(11): 3370 − 3374. [8] 陈远哲, 王巧华, 高升, 等. 基于近红外光谱的淡水鱼贮藏期质构品质的无损检测模型[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(12): 491 − 499. CHEN Yuanzhe, WANG Qiaohua, GAO Sheng, et al. Nondestructive testing model for textural quality of freshwater fish instorage usingnear-infrared spectroscopy [J]. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2021, 58(12): 491 − 499. [9] 郭文川, 朱德宽, 张乾, 等. 基于近红外光谱的掺伪油茶籽油检测[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(9): 350 − 357. GUO Wenchuan, ZHU Dekuan, ZHANG Qian, et al. Detection on adulterated oil-tea camellia seed oil based on near-infrared spectroscopy [J]. J Agric Mach, 2020, 51(9): 350 − 357. [10] 潘拓, 马鑫, 谢安, 等. 利用主成分分析法优化BP神经网络模型在砂砾岩岩性识别中的应用[J]. 新疆地质, 2020, 38(3): 417 − 420. PAN Tuo, MA Xin, XIE An, et al. Application of the optimized BP neural network model based on principal component analysis in lithology identification of glutenite reservoirs [J]. Xinjiang Geol, 2020, 38(3): 417 − 420. [11] ZHU Hongyan, CHU Bingquan, FAN Yangyang, et al. Hyperspectral imaging for predicting the internal quality of kiwifruits based on variable selection algorithms and chemometric models [J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 1 − 13. [12] ARAÚJO M C U, SALDANHA T C B, GALVÃO R K H, et al. The successive projections algorithm for variable selection in spectroscopic multicomponent analysis [J]. Chemometrics Intell Lab Syst, 2001, 57(2): 65 − 73. [13] 董蒙, 栾希亭, 吴宝元, 等. 基于自适应遗传算法的电液伺服系统控制[J]. 机床与液压, 2019, 47(14): 78 − 83. DONG Meng, LUAN Xiting, WU Baoyuan, et al. Control of electro-hydraulic servo system control based on adaptive genetic algorithm [J]. Mach Tools Hydraul, 2019, 47(14): 78 − 83. [14] 冯国红, 朱玉杰, 徐华东, 等. 应用遗传算法-主成分分析-反向传播神经网络的近红外光谱识别树种效果[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2020, 48(6): 56 − 60. FENG Guohong, ZHU Yujie, XU Huadong, et al. Using near infrared spectrum to identify tree species by GA-PCA-BP neural network [J]. J Northeast For Univ, 2020, 48(6): 56 − 60. [15] 许锋, 付丹丹, 王彬, 等. 基于MCCV-CARS-RF建立红提糖度和酸度的可见-近红外光谱无损检测方法[J]. 食品科学, 2018, 39(8): 149 − 154. XU Feng, FU Dandan, WANG Bin, et al. Nondestructive detection of sugar content and acidity in red globe table grapes using visible near infrared spectroscopy based on Monte-Carlo Cross Validation-Competitive Adaptive Reweighted Sampling-Random Forest (MCCV-CARS-RF) [J]. Food Sci, 2018, 39(8): 149 − 154. [16] ROMERO-TORRES S, PÉREZ-RAMOS J D, MORRIS K R. Raman spectroscopic measurement of tablet-to-tablet coating variability [J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2005, 38(2): 270 − 274. [17] 于慧伶, 门洪生, 梁浩, 等. SA-PBT-SVM的实木表面缺陷近红外光谱识别[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(6): 1724 − 1728. YU Huiling, MEN Hongsheng, LIANG Hao, et al. Near, infrared spectroscopy identification method of wood surface defects based on SA-PBT-SVM [J]. Spectrosc Spectral Anal, 2018, 38(6): 1724 − 1728. [18] 殷勇, 王光辉. 连续投影算法融合信息熵选择霉变玉米高光谱特征波长[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(2): 356 − 362. YIN Yong, WANG Guanghui. Hyperspectral characteristic wavelength selection method for moldy maize based on continuous projection algorithm fusion information entropy [J]. J Nucl Agric Sci, 2020, 34(2): 356 − 362. [19] 朱淑鑫, 顾兴健, 杨宸, 等. K均值算法结合连续投影算法应用于土壤速效钾含量的高光谱分析[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2020, 36(2): 358 − 365. ZHU Shuxin, GU Xingjian, YANG Chen, et al. K-means algorithm combined with successive projection algorithm for hyperspectral analysis of soil available potassium content [J]. J Jiangsu Agric Sci, 2020, 36(2): 358 − 365. [20] 陈伟, 李创, 唐荣年. 应用间隔随机蛙结合连续投影算法检测橡胶树叶片氮含量[J]. 河南科技大学学报, 2019, 40(5): 51 − 56. CHEN Wei, LI Chuang, TANG Rongnian. Application of interval randomfrog combined with successive projections algorithm to detecting nitrogen content in rubber tree leaves [J]. J Henan Univ Sci Technol Nat Sci, 2019, 40(5): 51 − 56. [21] 熊智新, 房桂干, 梁龙, 等. 近红外光谱结合连续投影算法检测综纤维素含量[J]. 中国造纸学报, 2019, 34(4): 46 − 51. XIONG Zhixin, FANG Guigan, LIANG Long, et al. Full cellulose content in composite optical fibrous in combination with continuous projection algorithm [J]. Transac China Pulp Paper, 2019, 34(4): 46 − 51. [22] 明曼曼, 陈芳, 孙恺琦, 等. 基于集群算法优化BP神经网络的NIRS树种识别研究[J]. 西部林业科学, 2020, 49(5): 124 − 128. MING Manman, CHEN Fang, SUN Kaiqi, et al. NIRS tree species identification based on cluster algorithm optimized BP neural network [J]. J West China For Sci, 2020, 49(5): 124 − 128. [23] 汪紫阳, 尹世逵, 李耀翔, 等. 基于可见/近红外光谱识别东北地区常见木材[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(1): 162 − 169. WANG Ziyang, YIN Shikui, LI Yaoxiang, et al. Identification of common wood species in northeast China using Vis/NIR spectroscopy [J]. J Zhejiang A&F Univ, 2019, 36(1): 162 − 169. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210377







 下载:
下载: