-
随着经济的发展和人民生活水平的提高,餐饮行业迅速发展,导致餐饮废水对环境的影响日益严重[1]。餐饮废水的油含量高,且成分复杂[2],若被排放到农田里会改变土壤的物理特性,严重影响作物生产;若被排入河流,造成河水中溶解氧缺失,危害水生生物资源[3]。另外,油脂废水进入城市的排水管道,将对排水系统和污水处理厂造成巨大的压力[1]。因此,对餐饮废水中油脂的治理刻不容缓。油脂废水的治理主要有回收法和销毁法两大类。回收法适合高浓度的油脂废水,主要包括吸附[2]、混凝[2]、粗粒化法[4]和气浮法[4]等。其中,吸附法工艺简单、处理效果稳定,是当前最为有效的废水处理方法之一[5]。目前,去除废水中油脂的吸附剂主要有活性炭、聚乙烯、膨润土和橡胶等[6-7],但这些吸附材料成本较高,因此寻找价格低廉且吸附效果好的吸附材料就成为了研究的热点[2]。销毁法适合中低浓度的油脂废水,主要包括生物法[8]、催化氧化法[9]、电解法[2]等。除生物法以外的方法存在占地面积大,能源消耗大[2],需二次处理等问题。生物法通过微生物将脂类物质氧化为二氧化碳和水,避免二次污染,具有高效、对环境影响较小的特点。游离油脂降解菌株具有较高的降解效率,广泛应用于生活污水的油脂降解[10]。然而,游离态的菌株在处理含油废水的过程中,菌株分散,容易流失,相比固定化菌株而言,降解效率低,且不易回收[11]。选择合适的吸附材料作为固定降解菌株的载体,可以提高微生物对环境的适应能力[12]和降解率[13]。因此,微生物固定化技术在废水治理领域得到了很好的发展和应用。
聚氨酯海绵弹性高,孔隙率高,且成本低[14],被广泛应用于家居、建筑、日用品等领域。2020年,中国聚氨酯海绵的产量高达1 500万t,且每年以约5%的速度增长。同时,每年都会丢弃大量的废弃海绵床垫、海绵沙发等不易分解的家具产品,污染环境。常用的填埋法处理聚氨酯海绵存在既占用土地又耗费用的缺点,而焚烧法回收热能则需要严格控制燃烧条件,减少有毒气体对环境的污染。因此,寻找废弃海绵有效处理的方法显得尤为重要。有研究表明:通过改性或修饰聚氨酯海绵可以提高它的油水分离作用[15],这也为废弃海绵的利用提供了方法。基于此,本研究将废弃海绵经热解制备成吸附性能良好的海绵热解炭,用于固定降解油脂的菌株,探究其对餐饮废水中油脂的吸附-降解作用规律,实现“以废治废”,为废弃海绵资源化利用和固定化微生物技术治理餐饮废水中油脂提供新的思路和方法。
-
供试菌株:菌株源自浙江农林大学食堂厨房的油水池以及下水道管壁污泥中,以大豆油为有机污染物驯化污泥,筛选出可高效降解大豆油的菌株,经常规形态学和生理生化特征的初步鉴定,该菌株属芽孢杆属Bacillus。供试废水:供试废水包括模拟废水和实际废水。模拟废水由超纯水和大豆油配制而成,质量浓度为1~3 g·L−1;实际餐饮废水样品取自浙江农林大学东湖食堂的油水池排出口,废水颜色基本澄清透明,呈中性,废水化学需氧量为420~450 mg·L−1。
金龙鱼食用大豆油,主要含有饱和脂肪、单不饱和脂肪、多不饱和脂肪等。胰蛋白胨和酵母膏购置于上海生工生物工程有限公司,石油醚(光学纯)、硫酸铵(分析纯)、磷酸氢二钾(分析纯)、磷酸二氢钠(分析纯)、氯化钠(分析纯)、七水硫酸镁(分析纯)、盐酸(分析纯)、氢氧化钠(分析纯)购置于国药集团化学试剂有限公司。Luria-Bertani (LB)液体培养基:胰蛋白胨10.0 g,氯化钠5.0 g,酵母膏10.0 g,1.0 L超纯水,pH 7.2,121 ℃高压灭菌20 min。复筛培养基:硫酸铵2.0 g,磷酸氢二钾2.0 g,磷酸二氢钠2.0 g,氯化钠2.0 g,七水硫酸镁0.5 g,超纯水1.0 L,pH 7.2,大豆油2.0 g·L−1。
-
①海绵热解炭制备:将废弃海绵剪切成约5 mm小块,于管式炉中氮气氛围下高温热解,再以5 ℃·min−1速率加热至设定温度(400、500、600和700 ℃)保温2 h,待其冷却至室温后储存备用[16],记为SPCx,其中x是热解温度,如SPC400为热解温度为400 ℃的海绵热解炭。②海绵热解炭表征:热解炭的外观形貌特征采用冷场发射扫描电子显微镜(SU8010,日本株式会社)进行观测;表面官能团采用傅立叶红外光谱(Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS20)进行表征,溴化钾压片法,波数范围为4 000~400 cm−1;表面原子组成等使用X射线光电子能谱(Thermo Scientific K-Alpha)进行表征,键能以C1s(碳原子的1 s轨道上电子与原子核结合的能量)=284.80 eV作为参考基线进行校准。
-
挑取1环菌苔接种到LB液体培养基上,于恒温振荡器(30 ℃、150 r·min−1)中培养15 h制得菌液。称取0.002 0 g的SPC600于50 mL锥形瓶中,经灭菌锅灭菌20 min,冷却至室温后加入5 mL菌液,于恒温振荡器(30 ℃、150 r·min−1)中培养48 h至形成生物膜,即得到固定化微生物(immobilized microorganism),记为SPC600-IM,并用冷场发射扫描电子显微镜观察海绵热解炭固定微生物后的形态特征。
-
①吸附影响因素实验。在50 mL锥形瓶中加入0.002 0 g海绵热解炭和模拟废水(20 mL),调节模拟废水的pH (6~9)和温度(20~35 ℃),于恒温振荡器中吸附4 h。固液分离后,向液相中加入一定量石油醚,于振荡器上振荡萃取,重复2~3次,收集石油醚相定容于容量瓶(10 mL)中。利用紫外可见分光光度计(Alpha-1502A)在波长225 nm[17]下测定其吸光度,计算不同条件下大豆油的吸附率和吸附量。计算公式:
$$ A=\left(m-m_1\right) /m \times 100 \% $$ (1) 式(1)中:A为吸附率(%),m为原始加入大豆油的质量(g),m1为吸附结束剩余大豆油的质量(g)。
$$ q_t=\left[V\left(C_0-C_t\right)\right] / m ; $$ (2) $$ q_{\mathrm{e}}=\left[V\left(C_0-C_{\mathrm{e}}\right)\right] / m 。 $$ (3) 式(2)~(3)中:qt为t时刻的吸附量(mg·g−1),qe为吸附平衡时的吸附量(mg·g−1),C0、Ct和Ce分别为大豆油的初始质量浓度、t时刻质量浓度和平衡时质量浓度(mg·L−1),V为溶液的体积(L),m为吸附剂的质量(g)。②吸附动力学实验。称取0.001 0 g的SPC600于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入模拟废水20 mL,在20 ℃和pH 7的条件下,于恒温振荡器(150 r·min−1)中吸附一定时间(1/6、1/2、1、2、4、8、12、18和24 h),采用上述方法测定模拟废水中大豆油的质量浓度,探究分析吸附量随吸附时间的变化规律[18]。③吸附热力学实验。调节模拟废水的pH为7,恒温振荡器转速为150 r·min−1,称取0.001 0 g的SPC600,探究模拟废水中不同大豆油质量浓度(0.5、1.0、2.0和3.0 g·L−1)在20、30和40 ℃条件下的吸附情况,利用Langmuir和Freundlich模型对吸附过程进行拟合;同时,通过在不同温度和大豆油质量浓度下吸附平衡数据计算的吸附热力学参数,判断吸附反应的自发性和吸附特性。
-
将上述海绵热解炭(SPC600,0.002 0 g)固定化微生物(1.2.2)加入到复筛培养基及实际废水(调节pH 为5~8)中,置于一定温度(20、25、30和35 ℃)的恒温振荡器(150 r·min−1)中进行吸附降解(0~72 h),降解结束后处理方法与1.2.3①相同,其降解率(R)计算方法见式(1)。作为对照,取等量的游离菌株(不含SPC600)、游离菌株+SPC600(不事先固定)分别加入到复筛培养基和实际废水样中,其余条件均与实验组相同。
-
吸附动力学模型采用准一级动力学模型[式(4)]和准二级动力学模型[式(5)][18]进行分析。
$$ \ln \left(q_{\mathrm{e}}-q_t\right)=\ln q_{\mathrm{e}}-k_1 t。 $$ (4) $$ {q}_{t}=\frac{{k}_{2}{{q}_{\mathrm{e}}^{2}}t}{1+{k}_{2}{q}_{\mathrm{e}}t}\mathrm{。} $$ (5) 式(4)~(5)中:k1(min−1)为准一级吸附速率常数,k2 (g·mg−1·min−1)为准二级吸附速率常数。
-
推断污染物与吸附材料之间的相互作用关系,采用Langmuir 吸附等温模型[式(6)]和Freundlich 吸附等温模型[式(7)][18]。
$$ \frac{1}{{q}_{{\rm{e}}}}=\frac{1}{{k}_{\mathrm{L}}{q}_{\mathrm{m}}}\times \frac{1}{{C}_{\mathrm{e}}}+\frac{1}{{q}_{\mathrm{m}}} 。 $$ (6) $$ {\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}q}_{\mathrm{e}}=\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}{k}_{\mathrm{F}}+\frac{1}{n}\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}{C}_{\mathrm{e}} 。 $$ (7) 式(6)~(7)中:qm(mg·g−1)为最大吸附容量,kL为Langmuir模型常数,kF和n都是Freundlich模型常数。
吸附热力学参数计算则采用标准吉布斯自由能(ΔG0,kJ·mol−1)、标准焓变(ΔH0,kJ·mol−1)、标准熵变(ΔS0,kJ·mol−1·K−1)来判断吸附过程的自发性和热量变化情况[18]。
-
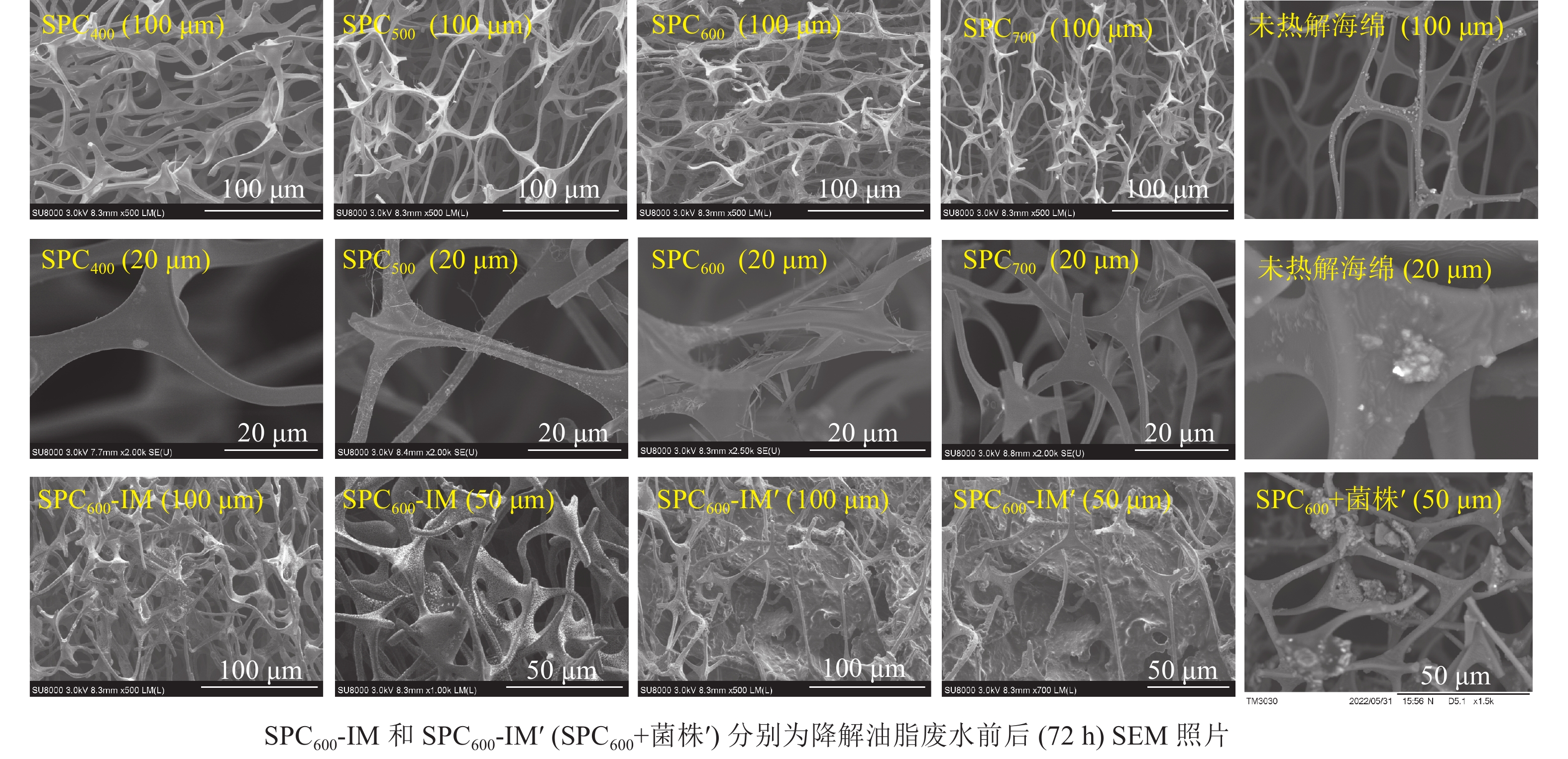
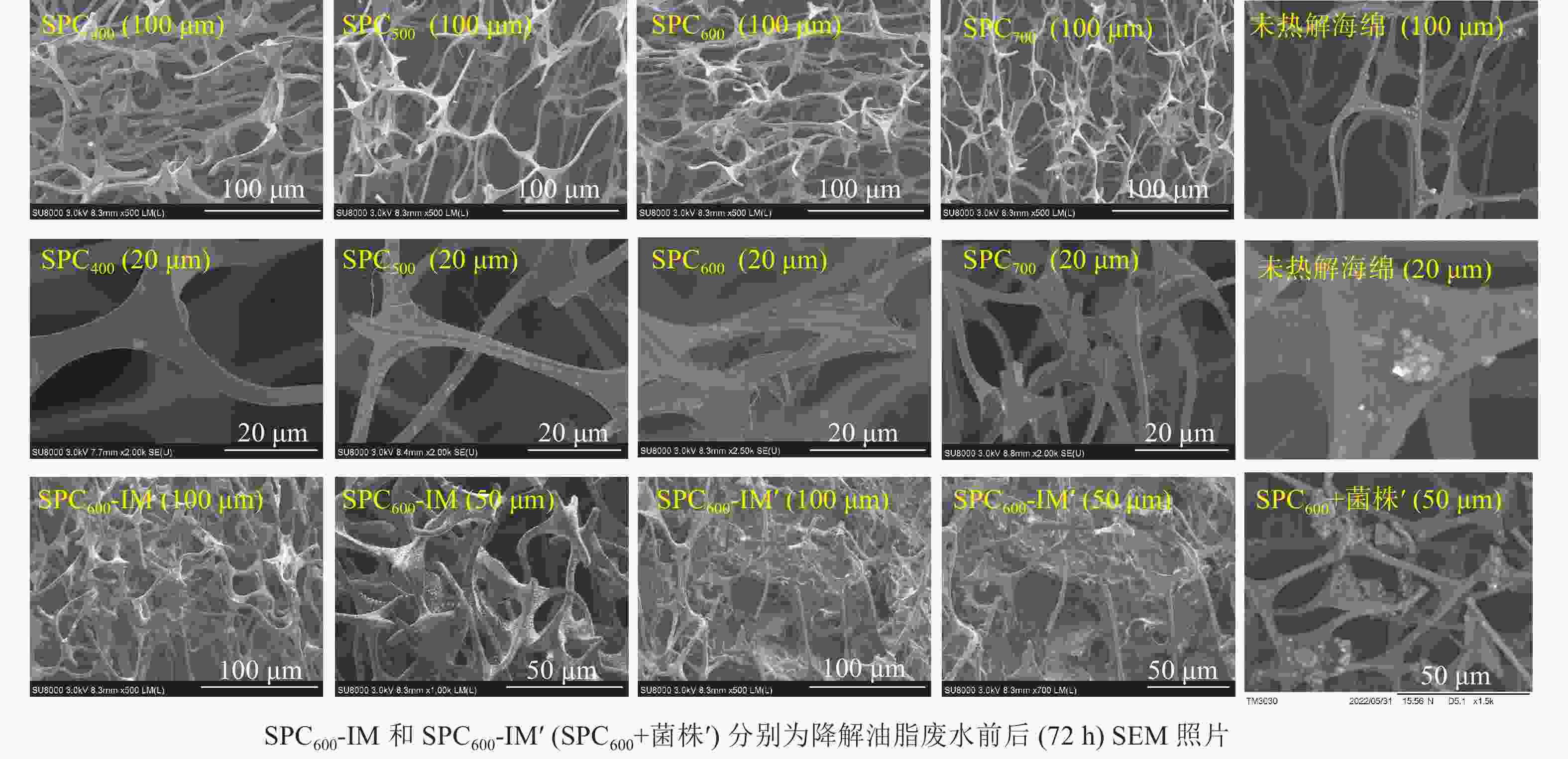
海绵热解炭及其固定化微生物的表面结构形态如图1所示。海绵热解炭具有丰富的“网络”结构,为微生物固定生长提供良好的场所[19]。从100 μm尺度来看,未热解海绵的骨架表面光滑,随着热解温度的升高,热解炭的骨架结构变得更加复杂、密实;从20 μm尺度来看,未热解海绵、SPC400和SPC700的表面光滑平整,但SPC500、SPC600的骨架开始发生断裂,表面开始出现大量细小分支,尤其SPC600的断裂分支较其他热解炭多,增加了SPC600的比表面积,有利于SPC600吸附性能的提高。固定前的海绵热解炭其“网络”结构明显,固定后大量微生物均匀地固定在海绵热解炭“网络”结构上,微生物的分泌物加强了其与海绵热解炭之间的黏合作用[20],形成了“生物膜”;而SPC600+游离菌株经3 d的降解后,只有少量的微生物在SPC600骨架上形成“菌落”。因此,海绵热解炭的分支“网络”结构为微生物生长提供了良好的场所,缓解了外部环境因素变化带来的冲击[19]。
-
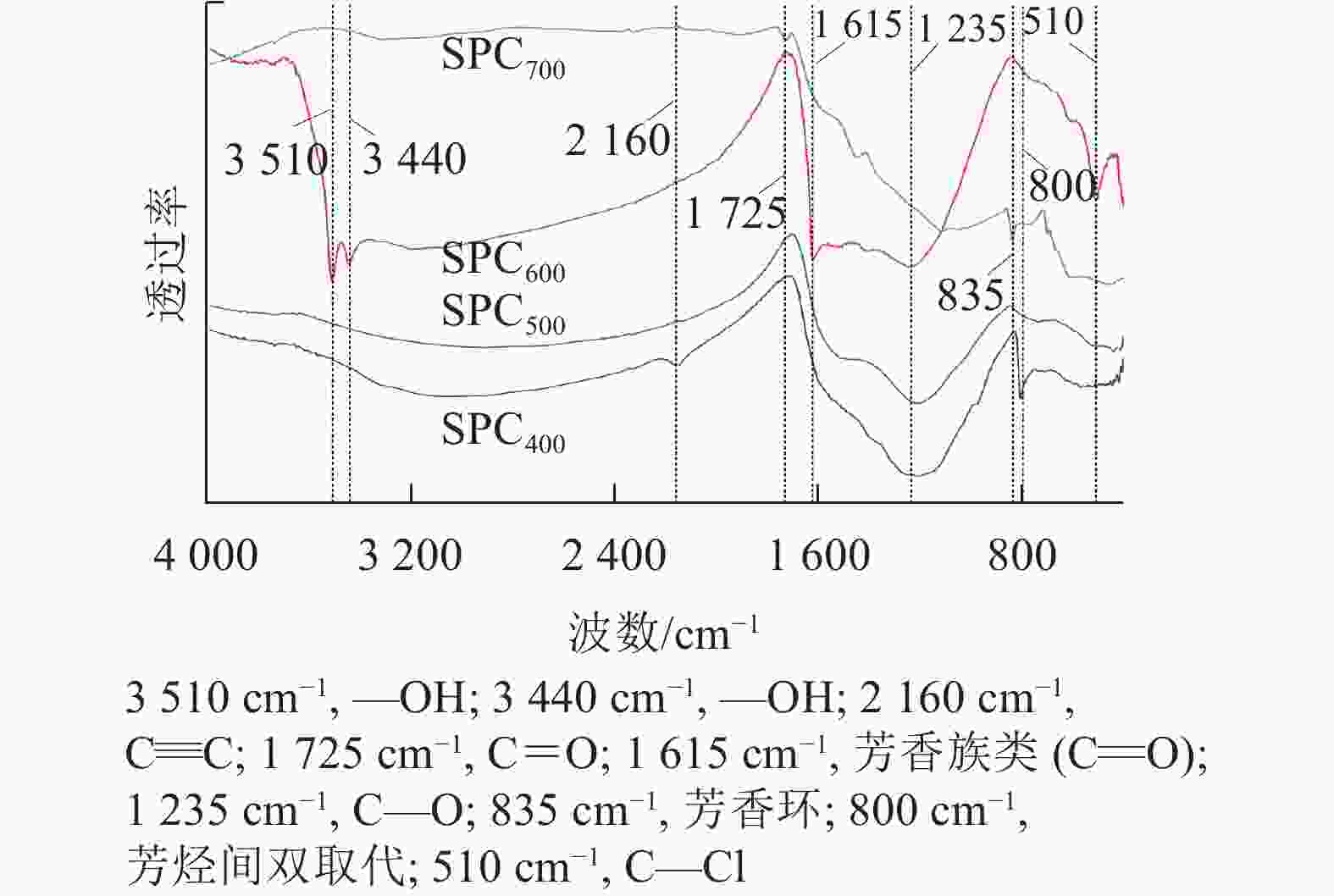
由图2可知:SPC600在3 510、3 440、1 615、1 235和510 cm−1等波数附近具有较强的吸收峰,其中3 510和3 440 cm−1附近的吸收峰归属于羟基(—OH)的伸缩振动[21],1 615 cm−1附近的吸收峰归属于羰基(C=O)的伸缩振动,1 235 cm−1附近的吸收峰归属于C—O的伸缩振动[22]。与其他热解温度的海绵热解炭相比,SPC600具有较多的含氧官能团,尤其羟基(—OH)可以提高热解炭的亲水性,有助于热解炭吸附亲水性微生物,进而提高微生物的附着率[23]。
-
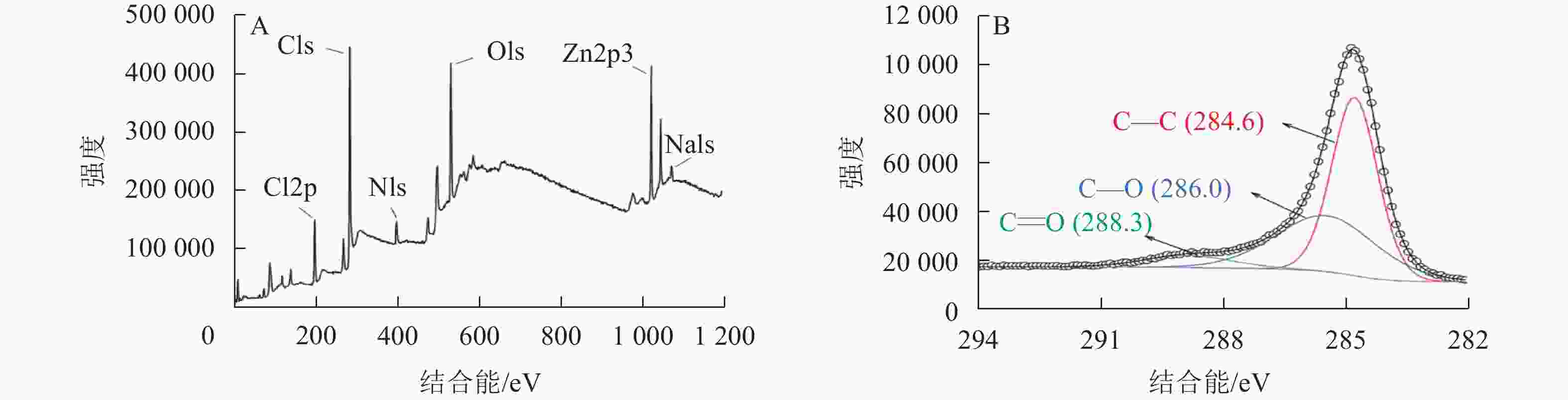
为了进一步探究热解炭的表面原子组成和含量,对SPC600进行了X射线光电子能谱分析(图3)。结果表明:SPC600主要由C、O、N、Cl和Zn等元素组成(图3A)。图3B给出了SPC600的C1s图谱,线性拟合得到C的3个特征峰,在结合能为284.6、286.0和288.3 eV的C1s峰分别归属于C—C、C—O和C=O官能团[24],与FTIR表征结果(图2)一致。SPC600表面含有多种含氧官能团,且C—O官能团含量远高于C=O官能团含量,为微生物生长提供所需要的碳源和附着位点[25]。
-
如图4A所示:随着废弃海绵的热解温度升高,SPCx对大豆油的吸附率大幅上升,从400 ℃的24.21%升至600 ℃的68.00%,但继续升高至700 ℃时,吸附率开始大幅下降至24.38%。聚氨酯海绵因本身具有一定的“网络”结构,其对油脂也具有一定吸附能力(35.33%)。根据上述表征结果,SPC600存在大量断裂分支,增加了其吸附的比表面积。在较高温度(700 ℃)下,海绵热解炭“网络”结构的收缩和碳结构的重新排列影响了其吸附效果[26]。另外,SPC600的表面官能团丰富且含氧基团较多(C—O),有利于疏水性油脂污染物的吸附,吸附量高达8 021.29 mg·g−1。
-
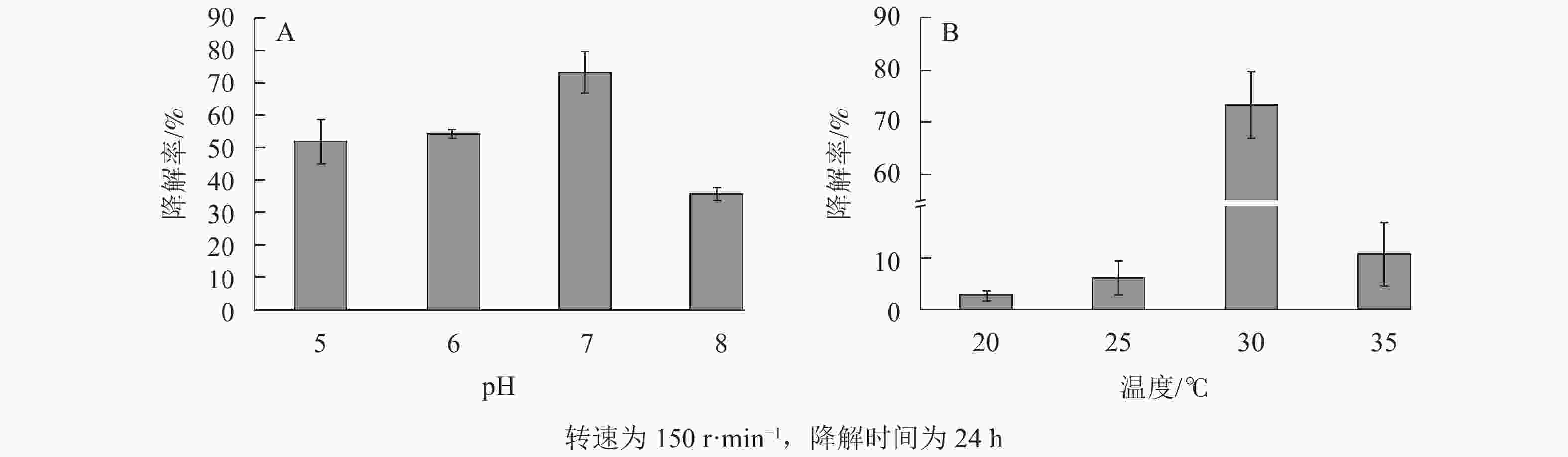
如图4B所示,随着模拟废水pH由酸到碱变化,SPC600对大豆油的吸附率先升高后降低。当pH为7时,SPC600对大豆油的吸附率最高(77.83%),此时吸附量达到8 093.07 mg·g−1。pH的影响可能与不同酸碱度下聚氨酯海绵热解炭表面基团的带电状态有关[22]:当溶液为酸性时,热解炭表面的大部分活性位点被H+所占据,不利于SPC600对油脂的吸附;当溶液为中性时,溶液中H+的数量减少,SPC600表面的活性吸附位点就会释放出来[22],有利于SPC600对油脂的吸附;当溶液为碱性时,SPC600表面的负电荷增加,静电力表现为排斥作用,导致吸附率降低[27]。
-
由图4C可知:随着模拟废水温度从20 ℃升至30 ℃,SPC600对大豆油的吸附率逐渐上升。其原因可能是低温条件下,大豆油的黏度较大,扩散系数小,不利于热解炭的吸附,当温度升至30 ℃时,SPC600对大豆油的吸附能力最佳(82.81%)。但当温度升高至35 ℃时,由于分子的运动速度加快[28],使大豆油在SPC600表面的吸附变得不稳定,吸附率又开始降低。结果表明:在30 ℃时吸附效果最佳,吸附容量达到8 051.58 mg·g−1;同时30 ℃也是降解菌株适宜生长的温度,为固定化微生物降解实验奠定了良好的基础。
-
由图5可知:SPC600在240 min左右吸附达到平衡。通过吸附动力学拟合,由表1可知:准二级动力学方程的拟合参数为0.981 1,高于准一级动力学方程(0.869 6),说明SPC600对大豆油的吸附更符合准二级动力学模型,且吸附以化学吸附为主[29]。经计算,SPC600的平衡吸附容量高达8 046.37 mg·g−1。由表2可知:与吸附性能较好的毛纤维等相比,SPC600吸附容量有一定的差距,但与常规吸附材料(生物质及其炭材料)相比, SPC600对大豆油有良好的吸附性能,且制备成本低。
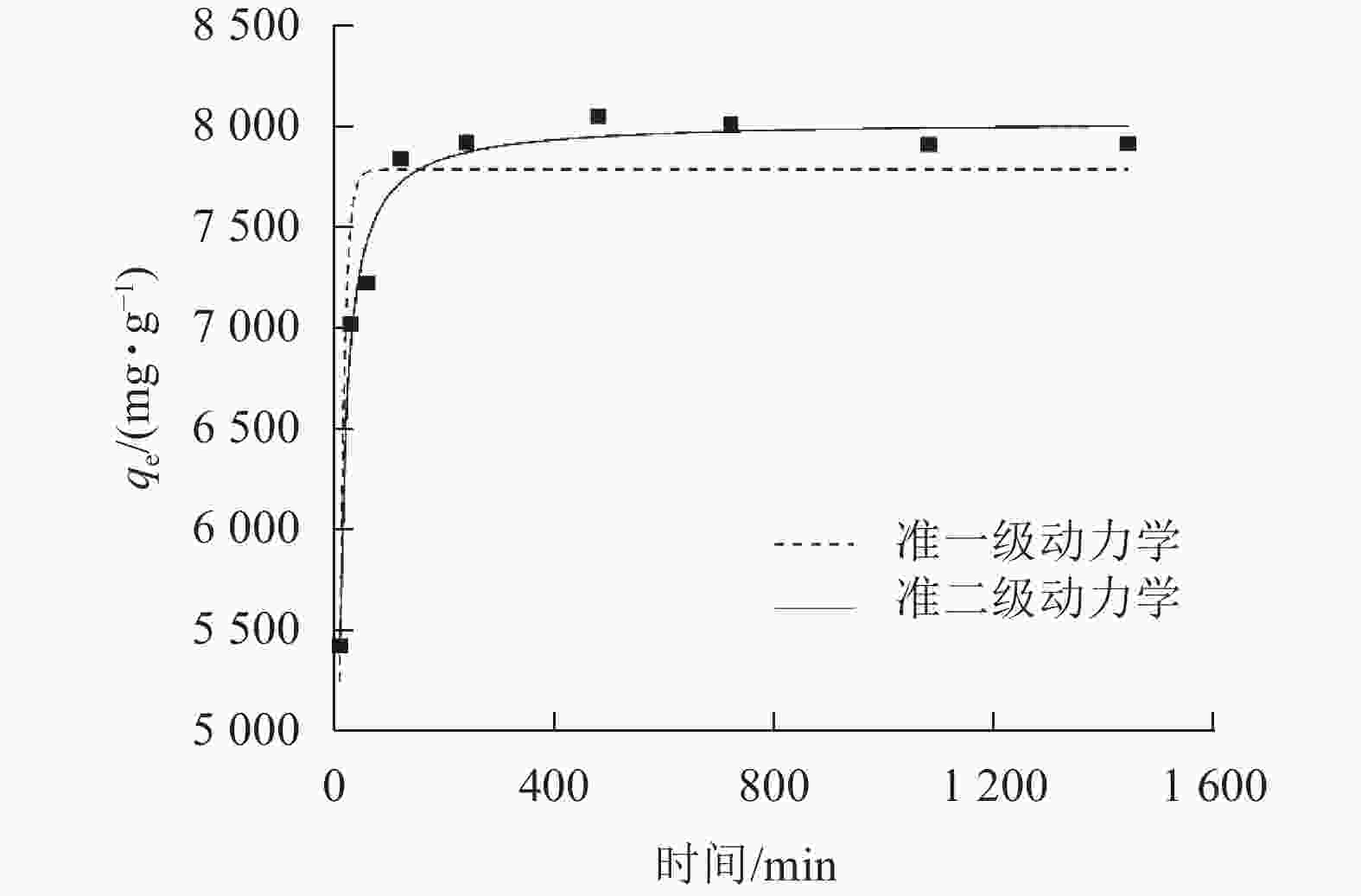
图 5 SPC600对大豆油吸附准一级和准二级动力学拟合曲线
Figure 5. Quasi-first-order and quasi-second-order kinetic curves of SPC600 adsorption of soybean oil
表 1 SPC600的吸附动力学方程式及拟合参数
Table 1. Adsorption kinetics equations and correlation coefficients for SPC600
准一级动力方程 准二级动力方程 k1 qe1/(mg·g−1) R2 k2 qe2/(mg·g−1) R2 0.112 1 7 785.6 0.869 6 0.002 6 8 027.1 0.981 1 表 2 不同吸附材料对油脂的吸附容量对比
Table 2. Comparison of oil adsorption capacity of different adsorption materials
序号 吸附材料 吸附容量/
(mg·g−1)参考
文献序号 吸附材料 吸附容量/
(mg·g−1)参考
文献序号 吸附材料 吸附容量/
(mg·g−1)参考
文献1 壳聚糖 99.9 [30] 5 甘蔗渣 6 650.0 [33] 9 松木屑生物炭 1 960.0 [36] 2 不可溶膳食纤维 1 270.0 [31] 6 萝藦种毛纤维 81 520.0 [34] 10 水稻生物炭 10 880.0 [37] 3 新鲜粽叶 1 766.4 [32] 7 辣木种子活性炭 111.1 [35] 11 磁性活性炭 1 900.0 4 改性花生壳 166.7 [28] 8 豆荚活性炭 104.2 [35] 12 海绵热解炭 8 093.1 本研究 说明:松木屑生物炭和磁性活性炭吸附石油;水稻生物炭吸附石蜡油;其余均吸附植物油脂 -
利用 Langmuir模型和Freundlich模型对吸附过程进行拟合,如图6所示。结果表明:SPC600在30 ℃下吸附效果最佳,其在大豆油质量浓度为0.5、1.0、2.0和3.0 g·L−1的平衡吸附容量分别达3 955.31、8 281.58、11 367.43和13 573.65 mg·g−1。2个模型的拟合参数(R2) (表3)通过模型拟合得出均在0.98以上,说明这2个模型能很好地反映SPC600对大豆油的吸附情况,吸附过程主要为物理吸附和化学吸附。通过计算吉布斯自由能ΔG、吸附焓变ΔH、吸附熵变ΔS来确定吸附的热力学效应,结果表明:SPC600对大豆油的吸附在30 ℃时,ΔG值最大(13 595.89 kJ·mol−1),同时ΔH为负值(−13 196.31 kJ·mol−1),说明该吸附过程是放热的,ΔS为负值(−62.17 kJ·mol−1·K−1),说明在该吸附过程中熵减小。
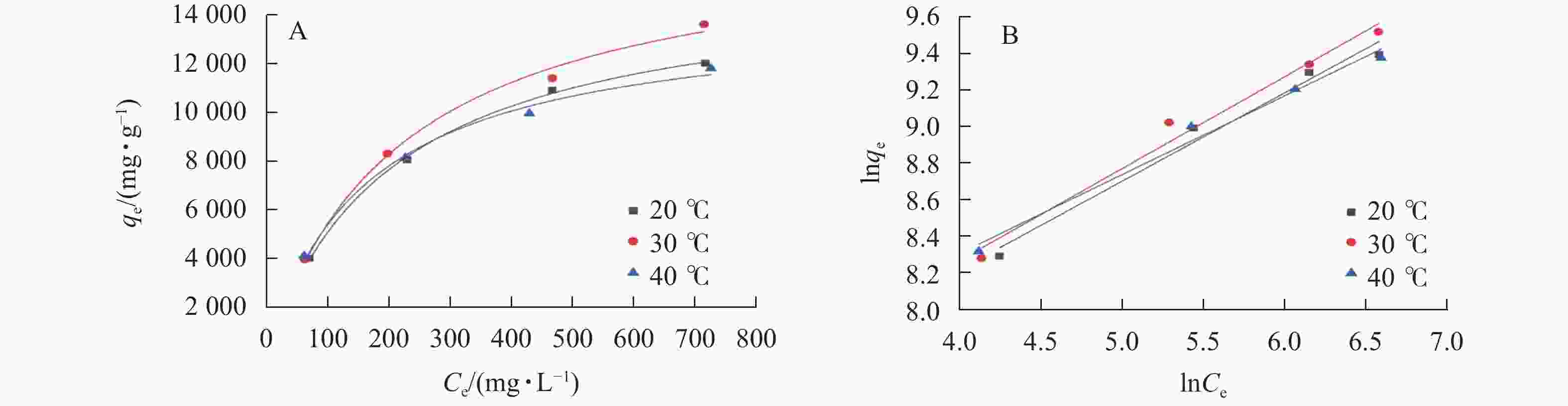
图 6 SPC600吸附大豆油的Langmuir (A)和Freundlich (B)等温线拟合曲线
Figure 6. Langmuir (A) and Freundlich (B) isotherm curves of SPC600 adsorption of soybean oil
表 3 不同温度下SPC600吸附等温方程及拟合参数
Table 3. Adsorption isotherm equations and correlation coefficients for SPC600 at different temperatures
温度/℃ Langmuir模型 Freundlich模型 qm/(mg·g−1) kL R2 n kF R2 20 15 495.40 0.004 9 0.998 4 3.46 5.48 0.984 9 30 17 374.08 0.004 5 0.991 5 3.38 5.46 0.986 6 40 14 085.93 0.006 2 0.989 6 3.93 5.82 0.990 7 -
酸碱度往往影响菌的生长活性,如溶液的电离程度[13]和细胞膜的运输[38],且对微生物的化学形态和固定化载体的表面活性位点[39]有明显影响。由图7A可知:固定化微生物对大豆油的降解率随pH的上升先增加后减小,在pH为7时降解率高达73.30%。当模拟废水为酸性时,其中的H+会争夺吸附材料上的吸附位点[13],从而间接影响固定化微生物对大豆油的降解能力。当模拟废水为碱性时,降解率下降,可能原因是SPC600的官能团发生去质子化,在表面形成带负电荷的活性点位,静电作用影响了固定化微生物的生长和降解能力[40]。
-
由图7B可知:模拟废水温度在20~30 ℃时,固定化微生物对大豆油的降解率先大幅上升,至30 ℃时最高(73.30%),之后迅速下降。这说明模拟废水的温度对SPC600固定化微生物的降解作用影响较大。出现该现象的原因可能是模拟废水的温度影响微生物的新陈代谢能力,从而降低微生物降解模拟废水中大豆油的能力。当温度较高(≥35 ℃)时,模拟废水中的溶解氧降低,从而降低了微生物的活性和氧化作用[38];当温度较低(≤25 ℃)时,降低了微生物的生物活性,进而降低微生物的降解率。因此,废水温度对固定化微生物影响较大,适宜的温度(近室温)才能发挥最大作用。
-
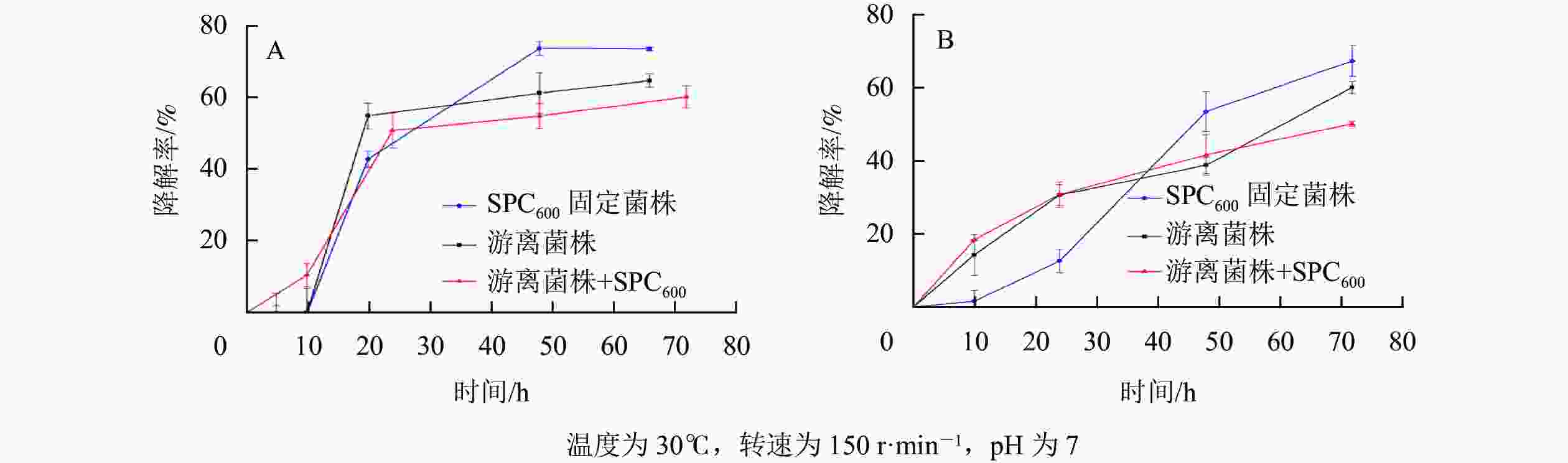
由图8可知:随着降解时间的延长,SPC600固定化菌株、游离菌株和游离菌株+SPC600对模拟废水、实际餐饮废水油脂的降解率均先呈现上升趋势:模拟废水开始降解速率较快(图8A),而实际餐饮废水开始降解速率缓慢(图8B),之后降解速率逐渐趋于平缓。这可能与降解过程中产生的有毒代谢物质积累过多和废水中营养物质消耗有关[41]。值得注意的是,在降解初期(<2 d),游离菌株和游离菌株+SPC600的降解速率均高于SPC600固定化菌株,之后(>2 d) SPC600固定化菌株降解速率迅速上升远高于游离菌株和游离菌株+SPC600;游离菌株和游离菌株+SPC600的油脂降解变化规律基本一致,且游离菌株+SPC600的降解率反而低于单一的游离菌株。出现该现象的可能原因是在投入废水初期,游离菌株分散,初期接触油脂的速度很快,而固定化菌株因菌体被固定,在初期处于未激活状态,使在较短时间内游离菌株的油脂降解率高于固定化菌株;后期菌株逐渐活化,固定化菌株与废水环境直接接触,利用废水中油脂作为碳源开始生长繁殖,降解率逐渐升高[42]。对于游离菌株与SPC600直接混合,由于SPC600在短时间内将大部分油脂吸附(图5),而不能与游离在废水中的菌株充分接触,随着时间推移只有部分游离菌株与SPC600结合(图1),开始降解吸附到SPC600上的油脂,因此,其降解率不及单一游离菌株。经计算对比,2 d后,对于模拟废水,固定化菌株对油脂的降解率达73.9%,比游离菌株平均高10.7%,比游离菌株+SPC600的高16.1%;对于实际废水,固定化菌株对油脂的降解率达67.6%,比游离菌株平均高11.0%,比游离菌株+SPC600的高14.4%。海绵热解炭固定化为降解菌株提供了良好的“居所”,减少外界环境因素对菌株的影响,延长微生物降解作用时间,进而提高油脂降解率。
-
SPC600具有丰富的“网络”结构和断裂分支,且表面含有大量的羟基、羰基等含氧官能团,有利于提高其吸附能力和微生物固定能力。在30 ℃和pH为7条件下,对大豆油的降解率达82.81%,此时吸附容量高达8 093.1 mg·g−1。SPC600对大豆油的吸附在240 min达到平衡,吸附过程遵循准二级吸附动力学方程,以化学吸附为主,且吸附过程属于放热反应。在适宜的条件下(30 ℃和pH 7),降解初期(<2 d),游离菌株、游离菌株+SPC600降解效率高于SPC600固定化菌株,但之后(>2 d) SPC600固定化菌株降解效率优于游离菌株、游离菌株+SPC600,且平均高出10%以上。
综上所述,海绵热解炭固定化为降解菌株提供了良好的“居所”,减少了外界环境因素对菌株的影响,延长微生物降解作用时间,进而提高油脂降解率,实现“以废治废”,在餐饮废水油脂的治理中具有较好的应用前景。
Adsorption-degradation of oil in catering wastewater by the microorganism immobilized on sponge pyrolytic carbon
-
摘要:
目的 随着餐饮行业的迅速发展,餐饮废水油脂对环境的危害日益严重,因此对餐饮废水油脂的治理刻不容缓。 方法 以废弃海绵为原料,经热解炭化制得吸附性能良好的海绵热解炭(SPCx,x为热解温度),利用冷场发射扫描电子显微镜、傅里叶变换红外光谱和X射线光电子能谱对其形貌、结构等理化性质进行表征。利用SPCx吸附废水中大豆油,研究了热解温度、废水pH和温度等对吸附性能的影响;分析了SPC600吸附剂的吸附动力学和吸附等温线,采用Langmuir和Freundlich模型对数据进行分析。基于此,探究了SPC600固定化微生物对模拟废水和实际废水中油脂的吸附-降解规律。 结果 海绵热解炭(SPC600)具有丰富的“网络”结构和断裂分支,且表面含有大量的羟基、羰基和醚键等含氧官能团,进而提高了其对油脂吸附和微生物固定能力。优化的SPC600,在pH 7和吸附温度30 ℃时,吸附容量高达8 093.1 mg·g−1。吸附过程符合准二级动力学方程,且是以化学吸附为主的放热过程。将筛选的降解油脂菌株与SPC600制成固定化微生物吸附剂,对实际油脂废水的降解率可达67.6%,比游离菌株和游离菌株+SPC600分别平均高11.0%和14.4%。 结论 采用海绵热解炭固定化微生物技术,在稳定降解菌株的同时提高了油脂降解率,实现“以废治废”,避免二次污染,具有较好的应用前景。图8表3参42 Abstract:Objective The objective of this study is to explore the effective treatment of catering wastewater, which has become increasingly harmful to the environment with the rapid development of catering industry. Method Sponge pyrolytic carbon (SPCx) with good adsorption performance was prepared from waste sponge by pyrolysis and carbonization. The physical and chemical properties such as the morphology and structure of the materials were characterized by cold field emission scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Through the adsorption of soybean oil in wastewater by SPCx, the effects of pyrolysis temperature, wastewater pH and temperature on the adsorption performance were studied. The adsorption kinetics and adsorption isotherm of SPC600 adsorbent were analyzed, and the Langmuir and Freundlich models were used to analyze the data. Based on this, the oil adsorption-degradation law of SPC600 immobilized microorganisms in simulated wastewater and actual wastewater was explored. Result Sponge pyrolytic carbon (SPC600) had abundant “network” structure and fracture branches, and contained a large number of hydroxyl, carbonyl, ether bonds, and other oxygen-containing functional groups on its surface, which improved its ability to adsorb oil and immobilize microoganism. The optimized SPC600 had an adsorption capacity of 8 093.1 mg·g−1 at pH 7 and adsorption temperature of 30 ℃. The adsorption process of oil conformed to the pseudo-second-order kinetic equation, and was an exothermic process dominated by chemical adsorption. The screened oil-degrading strains and SPC600 were made into immobilized microbial adsorbents, and the degradation rate of actual oil wastewater reached 67.6%, which was 11.0% and 14.4% higher than that of free strain and free strain+SPC600 respectively. Conclusion The sponge pyrolytic carbon immobilized microbial technology can stabilize the degrading strain and improve the oil degradation rate, so as to achieve the effect of “treating waste with waste” and avoid secondary pollution, which has a good application prospect. [Ch, 8 fig. 3 tab. 42 ref.] -
表 1 SPC600的吸附动力学方程式及拟合参数
Table 1. Adsorption kinetics equations and correlation coefficients for SPC600
准一级动力方程 准二级动力方程 k1 qe1/(mg·g−1) R2 k2 qe2/(mg·g−1) R2 0.112 1 7 785.6 0.869 6 0.002 6 8 027.1 0.981 1 表 2 不同吸附材料对油脂的吸附容量对比
Table 2. Comparison of oil adsorption capacity of different adsorption materials
序号 吸附材料 吸附容量/
(mg·g−1)参考
文献序号 吸附材料 吸附容量/
(mg·g−1)参考
文献序号 吸附材料 吸附容量/
(mg·g−1)参考
文献1 壳聚糖 99.9 [30] 5 甘蔗渣 6 650.0 [33] 9 松木屑生物炭 1 960.0 [36] 2 不可溶膳食纤维 1 270.0 [31] 6 萝藦种毛纤维 81 520.0 [34] 10 水稻生物炭 10 880.0 [37] 3 新鲜粽叶 1 766.4 [32] 7 辣木种子活性炭 111.1 [35] 11 磁性活性炭 1 900.0 4 改性花生壳 166.7 [28] 8 豆荚活性炭 104.2 [35] 12 海绵热解炭 8 093.1 本研究 说明:松木屑生物炭和磁性活性炭吸附石油;水稻生物炭吸附石蜡油;其余均吸附植物油脂 表 3 不同温度下SPC600吸附等温方程及拟合参数
Table 3. Adsorption isotherm equations and correlation coefficients for SPC600 at different temperatures
温度/℃ Langmuir模型 Freundlich模型 qm/(mg·g−1) kL R2 n kF R2 20 15 495.40 0.004 9 0.998 4 3.46 5.48 0.984 9 30 17 374.08 0.004 5 0.991 5 3.38 5.46 0.986 6 40 14 085.93 0.006 2 0.989 6 3.93 5.82 0.990 7 -
[1] 于志强. 餐饮业含油废水污染现状及防治对策[J]. 中国环保产业, 2015(7): 47 − 49. YU Zhiqiang. Pollution status and prevention countermeasures of oily waste water in catering trade [J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2015(7): 47 − 49. [2] 俞骞, 刘勇. 餐饮废水处理方法的研究进展[J]. 工程建设与设计, 2017(11): 114 − 116. YU Qian, LIU Yong. Research progress of treatment methods for restaurant wastewater [J]. Construction &Design For Project, 2017(11): 114 − 116. [3] YU Li, HAN Mei, HE Fang. A review of treating oily wastewater[J/OL]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 10(2): S1913-S1922[2022-04-05]. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.020. [4] 周俊, 焦赟仪, 陈翔宇, 等. 餐饮废水处理方法的研究现状与展望[J]. 湖南城市学院学报(自然科学版), 2016, 25(6): 73 − 75, 78. ZHOU Jun, JIAO Yunyi, CHEN Xiangyu, et al. Introduction and prospect of treatment technique for restaurant wastewater [J]. Journal of Hunan City University (Natural Science), 2016, 25(6): 73 − 75, 78. [5] 史航, 李兵, 郭建忠. 功能化枝状复合吸附材料的制备及吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的性能[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(2): 396 − 404. SHI Hang, LI Bing, GUO Jianzhong. Preparation of functional dendritic composite adsorbents and their adsorption properties for Cr(Ⅵ) [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2022, 39(2): 396 − 404. [6] 杨瑞, 张翻. 含油废水处理技术进展[J]. 当代化工, 2018, 47(8): 1695 − 1701. YANG Rui, ZHANG Fan. Development of oily wastewater treatment technology [J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(8): 1695 − 1701. [7] SONGSAENG S, THAMYONGKIT P, POOMPRADUB S. Natural rubber/reduced-graphene oxide composite materials: Morphological and oil adsorption properties for treatment of oil spills [J]. Journal of Advanced Research, 2019, 20: 79 − 89. [8] 肖继波, 赵委托, 褚淑祎, 等. 薯类淀粉废水处理技术及资源化利用研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2013, 30(2): 292 − 298. XIAO Jibo, ZHAO Weituo, CHU Shuyi, et al. Research progress on treatment technology and resource utilization of potato starch wastewater [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2013, 30(2): 292 − 298. [9] 范金石, 王超, 郝延颖, 等. 表面活性剂废水处理技术浅述[J]. 日用化学工业, 2020, 50(6): 413 − 418. FAN Jinshi, WANG Chao, HAO Yanying, et al. Brief overview of wastewater treatment technologies used for removal of surfactants [J]. China Surfactant Detergent &Cosmetics, 2020, 50(6): 413 − 418. [10] 王亚军, 蔡文娟, 耿冲冲, 等. 1株油脂降解菌的筛选及其降解条件优化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(5): 1031 − 1038. WANG Yajun, CAI Wenjuan, GENG Chongchong, et al. Screening of a oil-degrading strain and optimization of its degradation conditions [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2020, 29(5): 1031 − 1038. [11] 包木太, 巩元娇. 微生物固定法降解含油污水的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2009, 28(3): 511 − 517. BAO Mutai, GONG Yuanjiao. Treatment of oil-containing wastewater by immobilized microorganism [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2009, 28(3): 511 − 517. [12] 陈爽, 王良恺, 文涛, 等. 新型粉煤灰陶粒固定化有效微生物群落对模拟水产养殖废水净化效果[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(4): 761 − 768. CHEN Shuang, WANG Liangkai, WEN Tao, et al. Purification effect of immobilized effective microorganism community of fly ash ceramsite on aquaculture wastewater [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2020, 37(4): 761 − 768. [13] 张太平, 肖嘉慧, 胡凤洁. 生物炭固定化微生物技术在去除水中污染物的应用研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1084 − 1093. ZHANG Taiping, XIAO Jiahui, HU Fengjie. Research progress in the removal of contaminants from water by immobilized microorganisms combined with biochar [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(5): 1084 − 1093. [14] 杨振生, 张阳阳, 李春利, 等. 疏水聚氨酯海绵吸油材料研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019, 47(8): 34 − 38. YANG Zhensheng, ZHANG Yangyang, LI Chunli, et al. Progress of hydrophobic polyurethane sponge used as oil sorbent material [J]. New Chemical Materials, 2019, 47(8): 34 − 38. [15] 周志国, 陈文亮, 滕东晓, 等. 不同改性剂对聚氨酯海绵亲油疏水改性研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019, 47(12): 210 − 214. ZHOU Zhiguo, CHEN Wenliang, TENG Dongxiao, et al. Analysis of different hydrophobic modification methods for polyurethane sponge [J]. New Chemical Materials, 2019, 47(12): 210 − 214. [16] 胡蝶, 李文奇, 张利萍, 等. 废报纸生物质炭的制备及对铜离子的吸附性能[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37(2): 325 − 334. HU Die, LI Wenqi, ZHANG Liping, et al. Biochar derived from waste newspapers for removing copper ions from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2020, 37(2): 325 − 334. [17] 杨智博, 李晓红, 张丹丹, 等. 高效油脂降解混合菌株筛选及降解条件的优化[J]. 水处理技术, 2021, 47(7): 36 − 41. YANG Zhibo, LI Xiaohong, ZHANG Dandan, et al. Screening of high-efficiency oil-degrading mixed strains and optimzation of degradation conditions [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2021, 47(7): 36 − 41. [18] 刘兴赋, 程盛勇, 陈慧, 等. 大孔树脂对蜘蛛香总酚酸的吸附热力学和动力学研究[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2020, 36(5): 443 − 450. LIU Xingfu, CHENG Shengyong, CHEN Hui, et al. Study on thermodynamics and dynamics of adsorption of AB-8 resin to total phenolic from Valerianae jatamansi rhizoma et radix [J]. Ion Exchange and Adsorption, 2020, 36(5): 443 − 450. [19] 黄茜, 蒋梦莹, 王丽晓, 等. 竹炭固定化微生物对水中壬基酚的降解效率[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(5): 1677 − 1685. HUANG Qian, JIANG Mengying, WANG Lixiao, et al. Degradation of nonylphenol in water by microorganisms immobilized on bamboo charcoal [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(5): 1677 − 1685. [20] FRANKEL M L, BHUIYAN T I, VEKSHA A, et al. Removal and biodegradation of naphthenic acids by biochar and attached environmental biofilms in the presence of co-contaminating metals [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 216: 352 − 361. [21] LI Kexin, DING Dong, FANG Dezhen, et al. Hydrothermal deposition of titanate on biomass carbonaceous aerogel to prepare novel biomass adsorbents for Rb+ and Cs+ [J]. Colloids and Surface A, 2020, 590: 1 − 11. [22] 胡楠. 改性丝瓜络纤维素对污染物的吸附性能研究[D]. 郑州: 河南师范大学, 2013. HU Nan. Adsorption Properties of Modified Luffa Celluloses for Pollutants[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Normal University, 2013. [23] 郑华楠, 宋晴, 朱义, 等. 芦苇生物炭复合载体固定化微生物去除水中氨氮[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(2): 310 − 318. ZHENG Huanan, SONG Qing, ZHU Yi, et al. Removing ammonia nitrogen from wastewater by immobilized microorganism with reed biochar composite carrier [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2019, 13(2): 310 − 318. [24] YOUSAF A B, IMRAN M, ZEB A, et al. Synergistic effect of graphene and multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite supported Pd nanocubes on enhancing catalytic activity for electro-oxidation of formic acid [J]. Catalysis Science and Technology, 2016, 6(13): 4794 − 4801. [25] 王娟, 施辰阳, 谢超亚, 等. 生物炭水凝胶固定微生物处理含酚废水[J]. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 44(1): 44 − 50. WANG Juan, SHI Chenyang, XIE Chaoya, et al. Study on the treatment of phenolic wastewater by carbonaceous hydrogels immobilized microorganisms [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2021, 44(1): 44 − 50. [26] NAYAK A, BHUSHAN B, GUPTA V, et al. Chemically activated carbon from lignocellulosic wastes for heavy metal wastewater remediation: effect of activation conditions [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 493: 228 − 240. [27] 杜勇. 生物炭固定化微生物去除水中苯酚的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2012. DU Yong. Study of Biochar Immobilized Bacteria and its Phenol Removal[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012. [28] 卢静静, 张银, 侯艺艺, 等. 改性花生壳在油脂脱酸中的应用及其吸附平衡研究[J]. 食品科技, 2018, 43(4): 53 − 64. LU Jingjing, ZHANG Yin, HOU Yiyi, et al. Application and adsorption equilibrium of modified peanut shells in adsorption of free fatty acids from oil [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2018, 43(4): 53 − 64. [29] HO Y S. Second-order kinetic model for the sorption of cadmium onto tree fern: a comparison of linear and non-linear methods [J]. Water Research, 2006, 40: 119 − 125. [30] SRINIVASAN A, VIRARAGHAVAN T. Oil removal from water using biomaterials [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(17): 6594 − 6600. [31] 刘秉书, 吴淑华, 孙谕莹, 等. 挤压豌豆纤维粉制备的不可溶膳食纤维油脂吸附能力研究[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2020, 41(9): 50 − 55. LIU Bingshu, WU Shuhua, SUN Yuying, et al. Study on theadsorption capacity of insoluble dietary fiber oil prepared from extruded pea fiber powder [J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(9): 50 − 55. [32] 李静, 蔡征昊, 周仕林, 等. 不同粽叶对油脂的吸附性能研究[J]. 实验室科学, 2016, 19(6): 8 − 14. LI Jing, CAI Zhenghao, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Study on the oil adsorption properties of different indocalamus leaves [J]. Laboratory Science, 2016, 19(6): 8 − 14. [33] BONI H T, de OLIVEIRA D, ULSON de SOUZA A A, et al. Bioadsorption by sugarcane bagasse for the reduction in oil and grease content in aqueous effluent [J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 13(4): 1169 − 1176. [34] WANG Zhonqian, WANG Dengfeng, LI Zuguang, et al. Metaplexis japonica seed hair fiber: a hydrophobic natural fiber with robust oil-water separation properties [J]. Cellulose, 2020, 27(5): 2427 − 2435. [35] SANTOS T M, de JESUS F A, da SILVA G F, et al. Synthesis of activated carbon from oleifera moringa for removal of oils and greases from the produced water [J]. Environmental Nanotechnology,Monitoring and Management, 2020, 14: 1 − 11. [36] 孟蒙蒙, 夏文香, 许如康, 等. 盐酸改性松木屑生物炭吸附海洋溢油的模拟研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2022, 41(3): 474 − 481. MENG Mengmeng, XIA Wenxiang, XU Rukang, et al. Study on adsorption of marine oil spill by hydrochloric acid modified pine sawdust biochar [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2022, 41(3): 474 − 481. [37] HUANG Xiaoye, JIANG Ying, YU Ruobing. Popped rice biochar and superhydrophobic SiO2/popped rice biochar for oil adsorption [J]. Silicon, 2020, 13: 1 − 9. [38] LIN Chen, GAN Li, CHEN Zuliang. Biodegradation of naphthalene by strain Bacillus fusiformis (BFN) [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 182: 771 − 777. [39] TENG Zedong, SHAO Wen, ZHANG Keyao, et al. Enhanced passivation of lead with immobilized phosphate solubilizing bacteria beads loaded with biochar/ nanoscale zero valent iron composite [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 1 − 26. [40] 董程. 磁性辣木籽壳生物炭的制备及其吸附性能研究[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2021. DONG Cheng. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Magnetic Moringa oleifera Seed Shell Biochar[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2021. [41] 李琋, 王雅璇, 罗廷, 等. 利用生物炭负载微生物修复石油烃-镉复合污染土壤[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(2): 677 − 687. LI Xi, WANG Yaxuan, LUO Ting, et al. Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-cadmium co-contaminated soil by biochar loaded microorganisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(2): 677 − 687. [42] 吴梦莉, 李洁, 智燕彩, 等. 微生物固定化生物炭对水体铵态氮去除效果的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(5): 1071 − 1078. WU Mengli, LI Jie, ZHI Yancai, et al. Synthesis of microbial immobilized biochar for the removal of ammonia nitrogen from aqueous solutions [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(5): 1071 − 1078. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220338






 下载:
下载: