-
云杉花墨天牛Monochamus saltuarius属鞘翅目Coleoptera天牛科Cerambycidae沟胫天牛亚科Lamiinae墨天牛属Monochamus,褐梗天牛Arhopalus rusticus属鞘翅目天牛科椎天牛亚科Spondyliites梗天牛属Arhopalus,是危害树木的2种重要蛀干害虫。云杉花墨天牛与褐梗天牛危害寄主的习性,主要是幼虫钻蛀:成虫产卵于树皮间隙或啃食树皮后产卵于韧皮部内,卵孵化后幼虫钻蛀进入树皮内,在韧皮部蛀食形成不规则的虫道,而后钻蛀进入木质部并在此越冬。幼虫在木质部虫道上下左右蛀食,虫道不断扩大,对树体造成极大伤害。2018年云杉花墨天牛首次被中国确认为东北地区松材线虫病的媒介昆虫,同时,红松Pinus koraiensis也被确认为松材线虫的自然感病寄主;褐梗天牛也存在携带松材线虫的可能[1−2]。松材线虫病是毁灭性的森林病害[3],对松属Pinus植物危害极大,被称为松树的癌症。
生态位模型是利用物种已知的分布数据和相关环境变量,根据一定的算法运算(如利用物种分布点相关联的环境参数)来构建模型,判断物种的生态需求,并将运算结果投射至不同的时间和空间中以预测物种的实际分布和潜在分布[4]。生态位宽度和生态位重叠指数是研究生态位的2个最重要的指数[5−6],可反映种群对资源的利用能力及所处群落的稳定性。利用生态位研究害虫的种内和种间分布已被广泛应用于害虫的生物学特性和防治技术研究。高娜等[7]研究发现:在黑松P. thunbergii枯立木上松墨天牛M. alternatus在树干2 m以下分布最多;松墨天牛与褐梗天牛资源的相似性较高,褐梗天牛的幼虫在黑松林中主要分布在1~2 m高度处。宋冀营等[8]研究发现:松墨天牛捕食性天敌莱氏猛叩甲Tetrigus lewisi和松墨天牛的伴随度较高。孟维洋等[9]调查发现:在斑克松P. banksiana上云杉花墨天牛幼虫主要分布在10~180 cm高度上,其中20~60 cm高度受害最重。
目前,有关天牛的生态位研究多集中于幼虫的营养生态位,作为东北地区松材线虫病的新媒介昆虫——云杉花墨天牛,国内对于其幼虫分布及生态位的研究较少。在对辽宁省抚顺市苍石林场的林间调查时发现:同一红松林内同时诱到大量云杉花墨天牛与褐梗天牛,两者的寄主都包括红松,并且已对红松资源造成巨大危害。因此,本研究旨在探讨云杉花墨天牛和褐梗天牛幼虫在红松受害木上的垂直空间分布,用生态位方法分析云杉花墨天牛和褐梗天牛的种间关系,计算两者的生态位宽度和生态位重叠指数,明确两者在红松林内的垂直空间生态位与分布格局,进而推测现实分布与潜在分布,以期为探索松材线虫病的蔓延扩散规律提供参考。
-
研究区位于辽宁省抚顺市国有清原满族自治县苍石林场(42°10′22″N,124°92′81″E)。该地属中温带大陆性季风气候,年平均气温为5.3 ℃,7月平均气温为22.9 ℃,年平均降水量为806.5 mm。试验林地内建群树种为红松,林内还有零星云杉Picea asperata、落叶松Larix gmelinii分布,林龄为17~20 a。
-
2022年7月中旬在试验地随机选取10株被天牛危害的红松(胸径为14.0~17.0 cm,树高为4.1~5.2 m)。树干上可观察到天牛的侵入孔,但无羽化孔。从树干基部伐倒,并将伐桩连同根部刨出。将树干由下至上,分割成木段,按生长顺序编号,运回实验室。
以40 cm为取样单位,并按序编号。解剖观察树体内云杉花墨天牛和褐梗天牛幼虫的数量及分布位置:剥开韧皮部,辨认韧皮部幼虫种类并计数;清理韧皮部的粪便和残渣,记录树干木质部上的侵入孔;将木段纵劈,清理出天牛幼虫,辨认并计数。将收集的云杉花墨天牛和褐梗天牛幼虫,浸入体积分数为75%乙醇中5~10 min,取出后在体视镜下观察并拍照,记录其形态特征。
-
以红松的树干作为天牛幼虫的栖息资源,以松树的垂直高度作为资源序列,每40 cm为1个资源等级。①生态位宽度是指物种利用或趋于利用所有可利用资源状态而减少种内个体相遇的程度[13]。可衡量物种资源利用情况,其值大小反映物种在群落中的竞争地位,生态位宽度大的物种能利用更多的资源。采用LEVINS[14]提出方法计算生态位宽度,取值范围为0~1。②生态位重叠指数是2个物种在同一资源位上的相遇频率[15],反映了不同物种在资源利用上的相似程度或差异性,生态位重叠指数越高,表示物种间的竞争关系越激烈。生态位重叠指数采用PIANKA [16] 的方法计算,此方法也可作为种间竞争系数的测度方法[17],取值范围为0~1。
-
采用SPSS 25.0和Excel分析处理数据。采用单因素方差分析法(one-way ANOVA)分析天牛幼虫在红松树干上的垂直空间分布差异显著性,采用邓肯法(α=0.05)进行多重比较,使用Origin绘图。
-
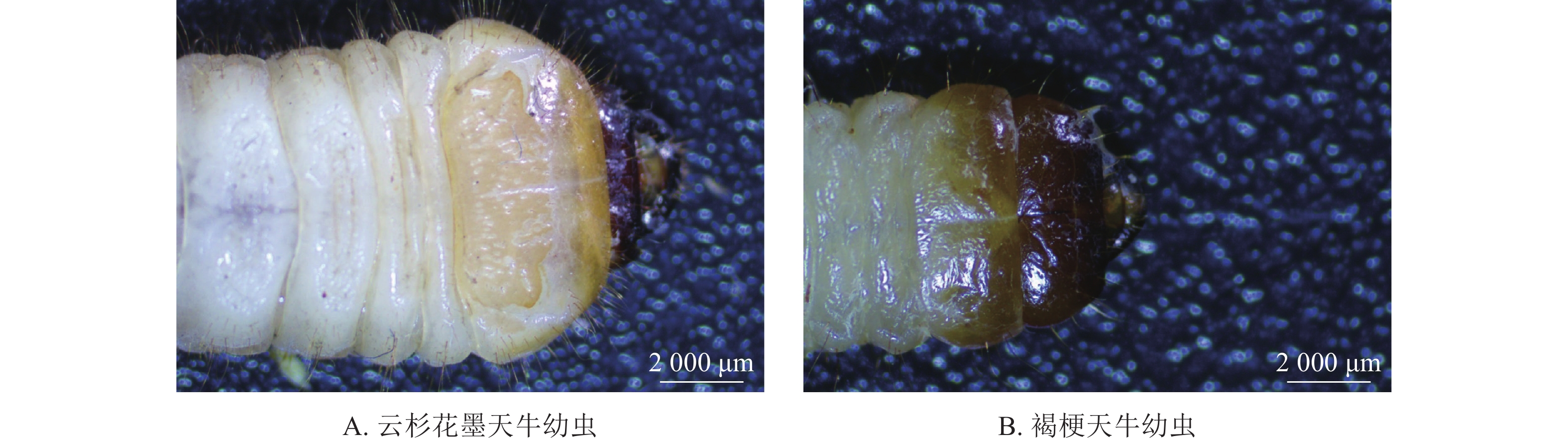
观察发现:云杉花墨天牛与褐梗天牛幼虫的头部和前胸背板具有不同的典型特征(图1)。云杉花墨天牛幼虫形态特征:成熟幼虫整体呈乳白至淡黄色,体长17~24 mm;头部长椭圆形,长大于宽,通常缢缩入前胸背板;前胸背板前缘具密毛,中后方具“凸”形褐色斑纹,盾片前侧角边缘暗褐色,盾片上面具陷斑,不具后背板褶。褐梗天牛幼虫形态特征:成熟幼虫乳白色,体长18~23 mm;头部横阔,呈横向近四边形,宽大于长,后缘中部内凹,两侧中后方较宽,前方狭,通常不缢缩入前胸背板;前胸背板中前方具稀疏毛,左前侧和右前侧呈暗褐色,中后方具“山”形淡黄色斑纹,上具细颗粒状突起,不具后背板褶。
-
调查结果显示:云杉花墨天牛幼虫在红松上的分布为(87.20±8.45) 头·株−1,褐梗天牛幼虫在红松上的分布为(24.40±2.37) 头·株−1。红松受害木上云杉花墨天牛幼虫呈正偏态分布,地下部分未发现幼虫,地上80~120 cm处分布最多,为(16.40±2.38) 头·株−1,占整株云杉花墨天牛幼虫数量的20.30%,显著高于80 cm以下及120 cm以上高度的幼虫数量(P<0.05);40~160 cm处数量占整株云杉花墨天牛幼虫数量的49.60%,为(41.60±6.53) 头·株−1;树干4 m以上幼虫相对较少,占整株云杉花墨天牛幼虫数量的0.92% (图2)。
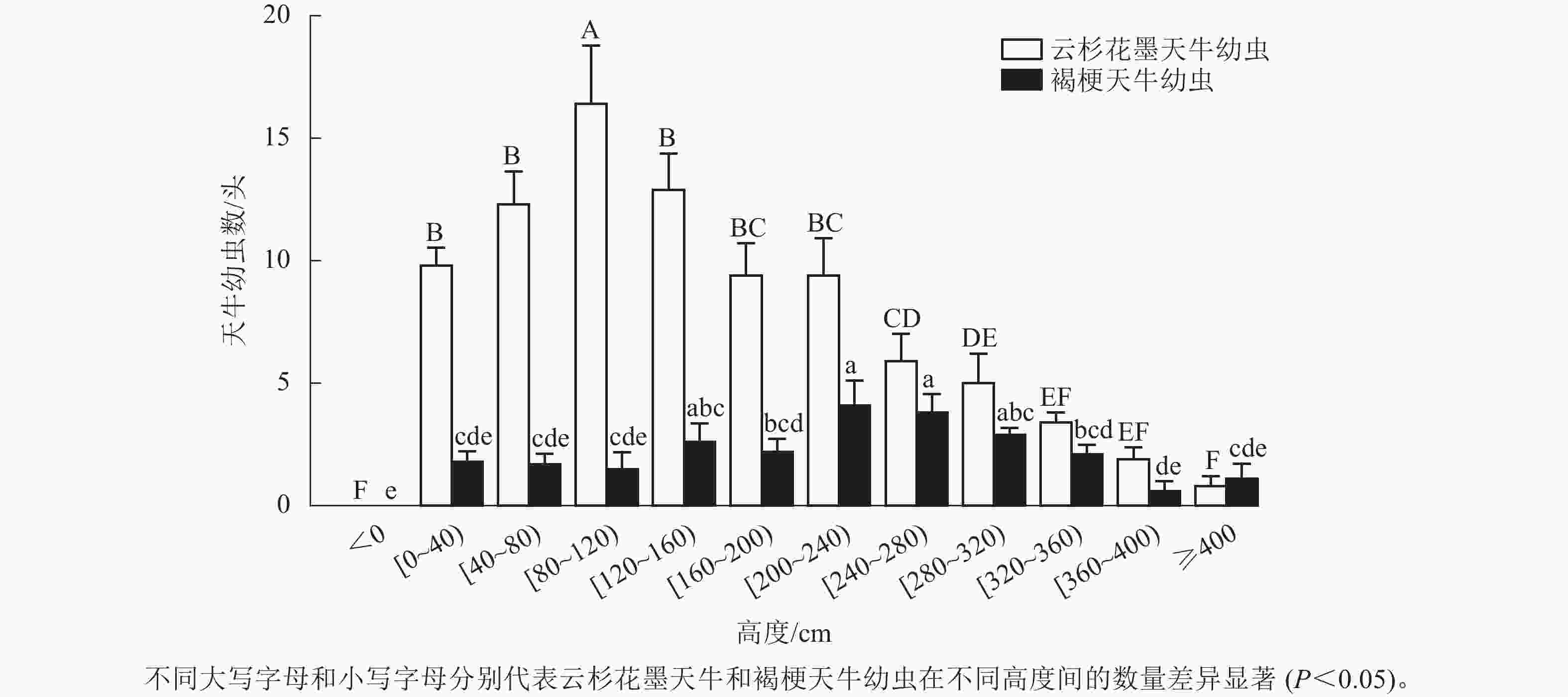
图 2 云杉花墨天牛与褐梗天牛幼虫在红松受害木上的垂直分布
Figure 2. Vertical distribution of M. saltuarius and A. rusticus larvae on dead standing trees of P. koraiensis
红松受害木地上部分整株均有褐梗天牛幼虫分布,地下部分未发现幼虫。200~280 cm高度处的褐梗天牛幼虫数量最多,为(7.90±1.77) 头·株−1,占总体幼虫数量的33.63%,且显著高于120 cm以下、160~200 cm及320 cm以上的幼虫数(P<0.05,图2)。
-
以红松的树干作为天牛幼虫的栖息资源,以松树的垂直高度作为资源序列,对云杉花墨天牛幼虫和褐梗天牛幼虫进行生态位分析。结果表明:云杉花墨天牛幼虫和褐梗天牛幼虫生态位宽度分别为0.694 4和0.757 6,说明这2种天牛在红松受害木上的垂直空间分布都较为均匀,且褐梗天牛比云杉花墨天牛分布广泛。
云杉花墨天牛幼虫与褐梗天牛幼虫在红松受害木上垂直空间的生态位重叠值为0.804 6,说明两者的生态位在红松受害木垂直空间上高度重叠,对垂直空间资源共享程度较高。
-
了解物种空间生态位与分布格局可为种群动态消长、预测物种实际分布和潜在分布提供重要参考依据。本研究结果表明:在寄主红松上,云杉花墨天牛幼虫的数量远超褐梗天牛幼虫的数量。该结果与袁源等[18]在辽宁省抚顺市松材线虫入侵松林内对天牛种类及数量的调查结果类似。这说明在当地红松中,云杉花墨天牛相对褐梗天牛处于优势地位。
本研究发现:云杉花墨天牛幼虫在红松上的生态位宽度达0.694 4,在树干垂直空间上较广泛分布,80~120 cm高度处幼虫数量最多,且在树干上有着在一定高度以上随高度增加数量逐渐减少的趋势,垂直高度上呈正偏态分布。这与时勇等[12]的研究结果类似。云杉花墨天牛幼虫主要分布在树干的中下部,这与松墨天牛[19]、锈色粒肩天牛Apriona swainsoni [20]等种类的天牛幼虫在寄主树干上的分布规律相同。褐梗天牛幼虫在红松上的生态位宽度达0.757 6,树干垂直空间分布较云杉花墨天牛幼虫广,在垂直空间上分布较为均匀,200~280 cm高度处幼虫数量最多。赵建文等[21]研究表明:死亡1 或2 a的黑松枯立木上褐梗天牛幼虫多存在于0~1 m处,而在衰弱树上褐梗天牛幼虫在3~4 m高度处数量最多。天牛虫害发生与多种因素有关,寄主植物、植物生理状态、林龄、地点的不同及林缘小气候条件都可能使天牛产卵高度受到影响。
在4 m以上高度,云杉花墨天牛和褐梗天牛幼虫数量都很少。推测随着树木高度增加,树干直径减小,可供成虫产卵的树体表面积及体积也随之减小,成虫产卵量降低,且捕食昆虫的鸟类会在较高处活动,可能影响天牛成虫活动,从而造成在高处产卵量降低。本研究发现:在红松树干0~40 cm高度处均有云杉花墨天牛幼虫与褐梗天牛幼虫分布,在地下部分均未发现这2种天牛幼虫,故在红松林间防控时,应尽量降低伐桩高度,但是否对疫木伐桩进行伐除或者覆膜处理,还需进一步研究。
生态位宽度可反映物种对特定小生境的占据程度,但不能反映数量的多少,结合研究对象的平均虫口密度,更能反映出其对同一资源的利用程度。褐梗天牛幼虫生态位宽度略高于云杉花墨天牛幼虫,分布更为均匀,但平均每株树内云杉花墨天牛幼虫数量更多,可见云杉花墨天牛对红松的资源利用程度更高。两者的生态位重叠值超过0.8,说明两者在红松垂直空间上有较高重叠,对空间资源的共享程度较高,其生态特性相似度比较高,一定程度上反映了两者存在较大竞争关系。云杉花墨天牛与褐梗天牛在红松林内的竞争激烈程度,还与其资源丰富度以及种群密度有关。李㛃等[15]认为:资源量与供求比以及资源满足生物需要的程度对研究生态位重叠与竞争的关系是非常重要的,生态位有较大重叠的不同物种,随着种群密度的增加,可利用的资源越匮乏,竞争越激烈。研究发现:用人工饲料喂养地中海实蝇Ceratitis capitata与橘小实蝇Bactrocera dorsalis,只有在种群密度很高的情况下,它们物种间才表现出激烈竞争[22]。刘慧等[23]对橘小实蝇和番石榴实蝇B. orrecta幼虫之间的竞争机制研究表明:它们的幼虫生态位重叠指数高,且寄主选择高度一致,随着种群密度的增加,种间竞争加剧,对番石榴实蝇的存活率有较大消极影响。
天牛与其他钻蛀性昆虫之间也存在竞争关系。宋冀营等[24]研究发现:马尾松P. massoniana中松墨天牛与马尾松角胫象Shirahoshizo patruelis、横坑切梢小蠹Blastophagus minor、黑翅土白蚁Odontotermes formosanus等3种昆虫都有较高的生态位相似性,利用共同的空间和营养资源,相互竞争,达到暂时共存。严晓素等[25]对染病黑松上的钻蛀性昆虫的物种组成及生态位进行研究发现:松墨天牛与马尾松角胫象、横坑切梢小蠹、纵坑切梢小蠹Tomicus Piniperda的生态位重叠指数均较高。本次研究中,在红松受害木树干80 cm以下的树干中,还发现存在大量松六齿小蠹Ips acuminatus、松瘤象甲Sipalus gigas幼虫等害虫,猜测可能与云杉花墨天牛、褐梗天牛幼虫争夺生存资源,但其他蛀干害虫对云杉花墨天牛和褐梗天牛幼虫在红松上的生态位分布影响还不清楚,有待进一步调查。
Niche distribution of Monochamus saltuarius and Arhopalus rusticus on host Pinus koraiensis
-
摘要:
目的 从垂直空间角度,明确云杉花墨天牛Monochamus saltuarius和褐梗天牛Arhopalus rusticus在红松Pinus koraiensis上的空间分布,探索这2种天牛的种间关系,为其防治措施提供理论基础。 方法 在辽宁抚顺的红松P. koraiensis林中同时监测到云杉花墨天牛与褐梗天牛成虫,且在同一株红松上能发现这2种天牛幼虫。以红松作为天牛幼虫的栖息资源,以红松的垂直高度作为资源序列,选取受天牛危害的红松立木,以40 cm为单位,研究云杉花墨天牛与褐梗天牛幼虫的形态学特征、在红松受害木上的分布位置、生态位宽度及生态位重叠度。 结果 云杉花墨天牛幼虫在红松上的分布为(87.20±8.45)头·株−1,褐梗天牛幼虫在红松上的分布为(24.40±2.37)头·株−1。云杉花墨天牛幼虫在红松上呈正偏态分布,地上80~120 cm处分布最多,为(16.40±2.38)头·株−1,显著高于80 cm以下及120 cm以上高度的幼虫数量(P<0.05);褐梗天牛幼虫在红松受害木地上部分均匀分布,200~280 cm高度处数量最多,占总体幼虫数量的33.63%,显著高于120 cm以下、160~200 cm及320 cm以上的幼虫数(P<0.05);在红松受害木地下部分均未发现这2种害虫的幼虫。云杉花墨天牛幼虫和褐梗天牛幼虫的生态位宽度有一定差异,分别为0.694 4和0.757 6,生态位重叠指数为0.804 6。 结论 云杉花墨天牛幼虫主要分布在红松树干中下部,褐梗天牛幼虫在红松树干各高度上均匀分布,两者在红松上生态位重叠较高,生态特性相似程度较高,一定程度上表明两者在红松林内有较高竞争关系。图2参25 Abstract:Objective This study aims to clarify the spatial distribution of Monochamus saltuarius and Arhopalus rusticus on Pinus koraiensis from the perspective of vertical space, and explore the interspecific relationship between these two species, so as to provide theoretical basis for their control measures. Method Adults of M. saltuarius and A. rusticus were simultaneously detected in P. koraiensis forest in Fushun, Liaoning Province, and both species of beetle larvae were found on the same P. koraiensis tree. Taking P. koraiensis as the habitat resource of longhorn beetle larvae and the vertical height of P. koraiensis as the resource sequence, P. koraiensis affected by longhorn beetles was selected using 40 cm as a unit to study the morphological characteristics, distribution location, niche width and niche overlap of M. saltuarius and A. rusticus larvae. Result The distribution of M. saltuarius larvae on P. koraiensis was (87.20±8.45) heads per plant, and that of A. rusticus larvae was (24.40±2.37) heads per plant. The distribution of M. saltuarius larvae was positively skewed on P. koraiensis, with the largest distribution of (16.40±2.38) heads per plant at 80 − 120 cm above ground, significantly higher than the number below 80 cm and above 120 cm (P<0.05). A. rusticus larvae were evenly distributed in the aboveground parts of the affected trees, with the most abundant at a height of 200 − 280 cm, accounting for 33.63% of the total number of larvae, significantly higher than the number below 120 cm, 160 − 200 cm and above 320 cm (P<0.05). No larvae of these two pests were found in the underground parts of damaged P. koraiensis. There was a certain difference in niche width between M. saltuarius and A. rusticus larvae, with values of 0.694 4 and 0.757 6, respectively, and a niche overlap value of 0.804 6. Conclusion M. saltuarius larvae are mainly distributed in the middle and lower parts of the trunk of P. koraiensis, while A. rusticus larvae are evenly distributed at various heights of the trunk. The ecological niche overlap between the two is relatively high on P. koraiensis, and the degree of similarity in ecological characteristics is relatively high, indicating a high competitive relationship between the two in P. koraiensis forest to a certain extent. [Ch, 2 fig. 25 ref.] -
Key words:
- Monochamus saltuarius /
- Arhopalus rusticus /
- Pinus koraiensis /
- host /
- ecological niche
-
[1] ŽUNIČN-KOSI A, STRITIH-PELJHAN N, ZOU Yunfan, et al. A male-produced aggregation-sex pheromone of the beetle Arhopalus rusticus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae, Spondylinae) may be useful in managing this invasive species [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 15 − 17. [2] WANG Yang, CHEN Fengmao, WANG Lichao, et al. Investigation of beetle species that carry the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner and Buhrer) Nickle, in China [J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2020, 32(4): 1745 − 1751. [3] 叶建仁. 松材线虫病在中国的流行现状、防治技术与对策分析[J]. 林业科学, 2019, 55(9): 1 − 10. YE Jianren. Epidemic status of pine wilt disease in China and its prevention and control techniques and counter measures [J]. Scientia Slivae Sinicae, 2019, 55(9): 1 − 10. [4] 朱耿平, 刘国卿, 卜文俊, 等. 生态位模型的基本原理及其在生物多样性保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(1): 90 − 98. ZHU Gengping, LIU Guoqing, BU Wenjun, et al. Ecological niche modeling and its applications in biodiversity conservation [J]. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(1): 90 − 98. [5] 刘思泽, 尹海锋, 沈逸, 等. 间伐强度对马尾松人工林间伐初期林下植被群落物种组成和多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(9): 2866 − 2874. LIU Size, YIN Haifeng, SHEN Yi, et al. Effects of thinning intensity on species composition and diversity of undergrowth vegetation community in Pinus massoniana plantation at initial stage of thinning [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(9): 2866 − 2874. [6] 张德魁, 王继和, 马全林, 等. 古浪县北部荒漠植被主要植物种的生态位特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2007, 26(4): 471 − 475. ZHANG Dekui, WANG Jihe, MA Quanlin, et al. Niche characteristics of main plant species in desert areas of north Gulang County, Gansu Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2007, 26(4): 471 − 475. [7] 高娜, 姚洪锡, 姜雪峰, 等. 松材线虫染病黑松上松褐天牛与褐梗天牛生态位的研究[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2013, 32(5): 4 − 7. GAO Na, YAO Hongxi, ZHANG Xuefeng, et al. Niche of Monochamus alternatus and Arhopalus rusticus in Pinus thunbergii infected with Bursaphelenchus xylophilus [J]. Forest Pest and Disease, 2013, 32(5): 4 − 7. [8] 宋冀营, 骆有庆, 严晓素, 等. 松褐天牛的捕食性天敌莱氏猛叩甲的生态位[J]. 昆虫知识, 2007, 44(5): 707 − 710. SONG Jiying, LUO Youqing, YAN Xiaosu, et al. The niche of Tetrigus lewisi, a predaceous natural enemy of Monochamus alternatus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 2007, 44(5): 707 − 710. [9] 孟维洋, 王凯军, 铁利伟, 等. 云杉花墨天牛虫害发生与环境条件关系的研究初报[J]. 吉林林业科技, 1997(4): 10 − 12. MENG Weiyang, WANG Kaijun, TIE Liwei, et al. A preliminary report on the relationship between occurrence of Monochamus saltuarius and environmental conditions [J]. Jilin Forest Science and Technology, 1997(4): 10 − 12. [10] 华立中. 天牛幼虫的外部形态及亚科检索图[J]. 昆虫知识, 1992, 29(2): 109 − 112. HUA Lizhong. External morphology and subfamily search map of longhorn beetle larvae [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 1992, 29(2): 109 − 112. [11] 钱庭玉. 为害松树的天牛幼虫[J]. 植物检疫, 1990, 4(4): 268 − 272. QIAN Tingyu. The longicorn larvae that damage pine trees [J]. Plant Quarantine, 1990, 4(4): 268 − 272. [12] 时勇, 范立淳, 张彦龙, 等. 云杉花墨天牛幼虫在红松树干上的分布规律[J]. 林业科学, 2022, 58(7): 128 − 133. SHI Yong, FAN Lichun, ZHANG Yanlong, et al. Distribution rule of Monochamus saltuarius larvae in the trunk of Pinus koraiensis [J]. Scientia Slivae Sinicae, 2022, 58(7): 128 − 133. [13] HURLBERT S H. The measurement of niche overlap and some relatives [J]. Ecology, 1978, 59: 67 − 77. [14] LEVINS R. Evolution in Changing Environments [M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1968: 120. [15] 李㛃, 朱金兆, 朱清科. 生态位理论及其测度研究进展[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2003, 25(1): 100 − 107. LI Jie, ZHU Jinzhao, ZHU Qingke. A review on niche theory and niche metrics [J]. Journal of Beijing Forest University, 2003, 25(1): 100 − 107. [16] PIANKA E R. The Structure of lizard communities [J]. Annual Review of Ecology &Systematics, 1973, 4: 53 − 74. [17] 陈潜, 许志春, 张连生, 等. 褐梗天牛幼虫和成虫空间分布的地统计学研究[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(3): 975 − 983. CHEN Qian, XU Zhichun, ZHANG Liansheng, et al. Geostatistical analysis of the spatial distribution of Arhopalus rusticus larvae and adults [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(3): 975 − 983. [18] 袁源, 任利利, 余润, 等. 辽宁抚顺松材线虫入侵松林内天牛种类调查[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2022, 59(2): 446 − 456. YUAN Yuan, REN Lili, YU Run, et al. Investigation of cerambycid beetle species in pine forests invaded by pine wood nematode in Fushun, Liaoning province [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2022, 59(2): 446 − 456. [19] 高娜. 松褐天牛寄主选择特性及幼虫生态位的研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2013. GAO Na. Study on Host Choice and Niche of Monochamus alternatus Larvae [D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2013. [20] 王晓红, 杨忠岐, 张彦龙, 等. 锈色粒肩天牛幼虫在国槐树干上的分布及虫口预测模型[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2015, 34(1): 20 − 22. WANG Xiaohong, YANG Zhongqi, ZHANG Yanlong, et al. Distribution of Apriona swainsoni larva on the trunk of Sophora japonica and the establishment of its population prediction model [J]. Forest Pest and Disease, 2015, 34(1): 20 − 22. [21] 赵建文, 高锋, 董飘, 等. 松材线虫病疫木伐桩剥皮处理对褐梗天牛发生的影响[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(3): 464 − 468. ZHAO Jianwen, GAO Feng, DONG Piao, et al. Effect of peeling treatment to diseased stumps of pine wood nematode on the occurrence of Arhopalus rusticus [J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 53(3): 464 − 468. [22] KEISER I, KOBAYASHI R M, MIYASHITA D H, et al. Suppression of mediterranean fruit flies by oriental fruit flies in mixed infestations in guava [J]. Journal of Economic Entomology, 1974, 67(3): 355 − 360. [23] 刘慧, 龚碧涯, 向敏, 等. 橘小实蝇和番石榴实蝇幼虫之间的竞争机制[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2023, 45(1): 239 − 245. LIU Hui, GONG Biya, XIANG Min, et al. Mechanism of interspecific competition between Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) and Bactrocera correcta (Bezzi) during larval stage [J]. Journal of Environmental Entomoligy, 2023, 45(1): 239 − 245. [24] 宋冀营, 骆有庆, 石娟, 等. 松材线虫染病松树上钻蛀性昆虫生态位的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2005, 27(6): 108 − 111. SONG Jiying, LUO Youqing, SHI Juan, et al. Niche characteristics of boring insects within Pinus massoniana infected by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus [J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2005, 27(6): 108 − 111. [25] 严晓素, 武海卫, 李天君, 等. 松材线虫染病黑松上钻蛀性昆虫生态位的研究[J]. 中国森林病虫, 2007, 26(5): 8 − 11. YAN Xiaosu, WU Haiwei, LI Tianju, et al. Niches of borers in Pinus thunbergii infected by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus [J]. Forest Pest and Disease, 2007, 26(5): 8 − 11. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20230167






 下载:
下载: