-
上饶早梨Pyrus pyrifolia是江西省上饶县花厅、田墩、五府山等11个乡镇的国家地理标志农产品,被认为是药食兼优的夏令佳品[1-2],栽培历史长,以‘黄皮消’‘Huangpixiao’和‘六月雪’‘Liuyuexue’2个品种品质最为优良[3]。对上饶早梨脱毒快繁[4-5]和品种鉴定[6-7]的研究表明:来源上饶县花厅镇的上饶早梨道地性农家种‘六月雪’和‘黄皮消’经简单重复序列标记(SSR)和扩增片段长度多态性(AFLP)分子标记的聚类分析聚为1类,但生物学性状、农艺性状和果实品质均有一定差异[8]。因此,找出两者基因差异对地方品种的育种选种工作十分重要。自2000年模式植物拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana的基因组被完全解析后,已有越来越多的种质被全基因组测序[9];研究认为,野生种、农家种、栽培种的全基因组重测序是筛选重要性状关键基因的一个重要内容[10]。梨基因组测序的完成[11-13]和高通量测速技术的快速发展,使梨种质资源的全基因组变异分析成为可能,而全基因组单核苷酸多肽位点(SNP)和插入缺失位点(INDEL)相关标记的开发,对作物分子辅助育种和基因组学研究具有重要的作用。周贺等[14]对褐色砂梨‘黄花’Pyrus pyrifolia ‘Huanghua’色泽形成期的果皮转录组数据进行SNP分子标记开发,共筛选到1 178个可能与果皮色泽形成相关的SNP标记。李节法[15]以6年生砂梨品种‘翠冠’P. pyrifolia ‘Cuiguan’的果实膨大早期、中期和成熟期样品进行比较转录组学分析,鉴定到4 121个选择性剪切位点,30 560个SNP位点和7 443个SSR标记位点。WU等[16]、MONTANARI等[17]和TERAKAMI等[18]也通过SNP标记构建了梨遗传图谱。但梨的INDEL标记研究较少。本研究以上饶县花厅镇上饶早梨道地性农家种‘六月雪’和‘黄皮消’为材料,通过全基因组重测序,深度挖掘其基因组SNP,INDEL和结构变异位点(SV)等位点,为上饶早梨优质品种相关标记的开发、优异基因的挖掘提供参考。
-
上饶县花厅镇上饶早梨道地性农家品种‘六月雪’和‘黄皮消’试管苗由上饶师范学院生命科学学院植物组织培养室提供。
-
参照十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)提取法提取样品DNA。
-
以吸光度比值D(260)/D(280)和Qubit 2.0(Life technologies, USA),Bioanalyzer 2100(Agilent,Germany)软件分析完成总DNA样品的质量控制。称取1 μg基因组总DNA片段化处理至300~400 bp,进行末端修复、末端加‘A’处理、接头(Adapters)连接反应,连接至Illumina公司测序平台的测序接头后进行聚合酶链式反应(PCR)扩增。连接产物用质量分数2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳,选择400~500 bp的片段,随后用连接介导PCR(LM-PCR)进行扩增获得DNA文库。按照Illumina公司HiSeq 2500测序系统(Hiseq 2500)的操作说明对形成的DNA文库进行双端125 bp的高通量测序。
-
鉴于Illlumina Hiseq 2500错误率对结果的影响,对原始数据进行质量控制(QC)。参考数据库为西洋梨基因组Pyrus communis Genome v1.0数据库。分别对每个样本使用bowtie 2软件进行测序短序列匹配(reads mapping),并用UnifiedGenotyper软件进行SNP和INDEL的提取[19-21]。采用ANNOVAR软件对获得的SNP和INDEL进行功能注释[22]。SNP常见变异分析(common variation, CV)及差异INDEL分析首先获取2个样品相同位置的SNP/INDEL,再根据非同义SNP(nonsynonymous SNP,nsSNP)/INDEL获取相关基因[23]。将差异SNP和INDEL分别与转录组数据进行关联分析,分别考察差异SNP和INDEL相关的表达数据[24]。候选基因的富集分析递交至AgriGO软件用于富集基因本体术语(gene ontology terms)[25]。拷贝数变异位点(CNV)分析采用VarScan软件进行[26]。
-
以HiSeq 2500测序系统提供的起初测序数据为原始数据,即各样本测序得到的短序列(reads)数及碱基总数,共得到275 092 822个短序列和34 661 695 572个碱基,其中‘六月雪’中含短序列140 696 312个,碱基17 727 735 312个,‘黄皮消’中短序列134 396 510个,碱基16 933 960 260个。为剔除Illlumina Hiseq 2500错误率对结果的影响,需对原始数据进行质量控制,包括去除低质量序列,去除接头,以进行后续工作。质量控制后得到232 434 654个短序列和29 286 766 152个碱基,总有效数据比例为84.5%;其中‘六月雪’含短序列119 056 332个,碱基150 010 978 322个,有效数据比例为84.6%;‘黄皮消’含短序列113 378 320个,碱基14 285 668 320个,有效数据比例为84.4%。
-
经过测序将短序列匹配至参考基因组。‘六月雪’组中总匹配的短序列数为68 859 074个,占所有短序列数的57.8%,含唯一匹配的短序列数为31 889 494个,占总匹配数的26.8%;覆盖全基因的深度为24.35,覆盖全基因组的百分比为93.0%;当覆盖深度≥3时,覆盖全基因组的百分比为89.4%。‘黄皮消’组总匹配的短序列数为66 580 757个,占所有短序列数的58.7%,含唯一匹配的短序列数为32 165 247个,占总匹配数的28.4%;覆盖全基因的深度为23.89,覆盖全基因组的百分比为93.0%,覆盖深度≥3时,覆盖全基因组的百分比为89.5%。
-
‘六月雪’中共得到SNP 6 171 357个,在编码区的无义突变有335 659个,有义突变有281 871个;因SNP突变获得终止子6 001个,丢失终止子1 226个;在基因5'非翻译区(5'UTR内的SNP总数、在3'UTR内的SNP总数及位于5'UTR和3'UTR间的SNP总数均为0;在不同可变剪切的基因组区域内找到SNP 3 383个,内含子区域内找到1 298 966个,启动子区域内找到1 301 726个,基因间区域内找到2 942 525个。
‘黄皮消’中共得到SNP 6 140 603个,在编码区的无义突变有332 280个,有义突变有278 064个;因SNP突变获得终止子6 034个,丢失终止子1 210个;在基因5'非翻译区(5'UTR)内的SNP总数、在3'UTR内的SNP总数及位于5'UTR和3'UTR间的SNP总数均为0,在不同可变剪切的基因组区域内找到SNP 3 274个,内含子区域找到1 285 052个,启动子区域内找到1 291 598个,基因间区域内找到2 943 091个。
-
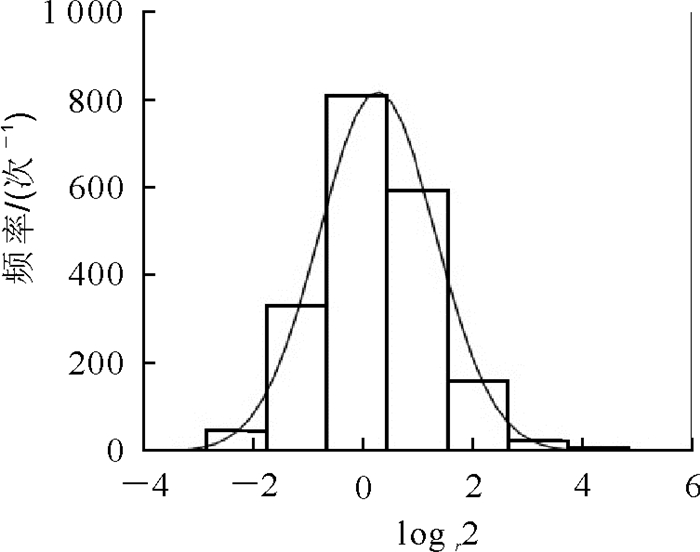
对获得的335 659个(‘六月雪’)和332 280个(‘黄皮消’)nsSNP进行常见变异分析发现,2个品种共有2 282个nsSNP关联了2 067个基因,nsSNP对基因的平均关联频率超过了1。其中,烟草花叶病毒耐药蛋白N(PCP017781),假定的抗病RPP13样蛋白1(PCP007357),可能的抗病RPP8样蛋白2(PCP030706),可能的LRR类受体丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶At3g47570(PCP021305),未注释蛋白1(PCP008176),烟草花叶病毒耐药蛋白N(PCP007457),烟草花叶病毒耐药蛋白N(PCP018815),未注释蛋白2(PCP021753),含重复锚蛋白的蛋白质At5g02620(PCP022078),烟草花叶病毒耐药蛋白N(PCP030478),抗病蛋白RGA2(PCP014224),可能的LRR类受体丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶At1g53420(PCP031574),假定的抗病蛋白RGA3(PCP023580)等蛋白编码的基因则关联了10个以上nsSNP。为进一步研究候选基因的选择压力,对得到的2 067个基因的nsSNP与同义SNP的比值(nsSNP/synonymous SNP,r)进行考察,发现r的对数呈现正态分布(图 1),其值约为2,说明进化有一定的正向选择压力。
-
由于生物学定义混乱的原因,不同的生物学数据库可能会使用不同的术语。为了解决这个问题,基因本体联合会(Gene Onotology Consortium)建立了“基因本体论”(gene ontolog,GO)数据库,目的是通过利用统一化的、结构化的语言建立一个适用于不同物种的、对基因和蛋白质功能进行定义和描述,并且能够随着研究的不断深入而更新的语言词汇标准。GO数据库包含基因参与的生物过程、所处细胞位置及具有的分子功能3个方面信息,其注释信息可对基因功能进行预测。GO显著性富集分析以基因本体术语(GO term)为单位,确定差异表达基因行使的主要生物学功能。分析全局GO功能与候选基因所处的功能发现,刺激、结合反应等功能的基因相对于背景基因(1 306条)富集(图 2)。通过差异基因富集得到的GO terms(图 3及表 1)可知,全部25 698条信息中,ADP结合、蛋白酪氨酸激酶活性、腺苷核糖核酸结合、嘌呤核苷结合、核苷结合、腺苷核苷酸结合、防御反应、蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性、转移酶活性、转运含磷基团、嘌呤核糖裂解键、核糖核酸结合、嘌呤核苷酸结合、蛋白激酶活性、RNA导向的DNA聚合酶活性、磷酸转移酶活性、醇基作为受体、DNA聚合酶活性、RNA依赖性DNA复制、翻译后蛋白质修饰、脯氨酸氨基酸、磷酸化、蛋白质改性过程等GO terms具有显著性意义。
表 1 nsSNP关联的候选基因及其功能的GO富集分析
Table 1. GO terms enriched by candidate gene (nsSNP)
GO数据库中唯一的标记信息 GO term类型 GO功能的描述信息 输入的具有GO term注释的候选基因数 该GO term中基因总数 富集分析统计学显著水平 错误发现率 GO:0043531 分子功能F ADP结合 60 415 9.20 E-13 9.60 E-10 GO:0004713 分子功能F 蛋白酪氨酸激酶活性 145 1 649 1.10 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0032559 分子功能F 腺苷核糖核酸结合 297 3 947 9.30 E-10 2.50 E-07 GO:0001883 分子功能F 嘌呤核苷结合 310 4 170 1.50 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0001882 分子功能F 核苷结合 313 4 181 6.50 E-10 2.50 E-07 GO:0030554 分子功能F 腺苷核苷酸结合 310 4 170 1.50 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0006952 生物学功能P 防御响应 52 402 1.50 E-09 2.10 E-06 GO:0004674 分子功能F 蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性 118 1 331 1.90 E-08 2.80 E-06 GO:0016772 分子功能F 转移含磷基团的转移酶活性 213 2 779 2.90 E-08 3.80 E-06 GO:0032555 分子功能F 嘌呤核糖核酸结合 309 4 320 4.50 E-08 4.70 E-06 GO:0032553 分子功能F 核糖核酸结合 309 4 320 4.50 E-08 4.70 E-06 GO:0017076 分子功能F 嘌呤核苷酸结合 323 4 552 5.10 E-08 4.90 E-06 GO:0004672 分子功能F 蛋白激酶活性 153 1 995 1.50 E-06 1.30 E-04 GO:0003964 分子功能F RNA导向的DNA聚合酶活性 19 106 1.70 E-06 1.40 E-04 GO:0016773 分子功能F 以醇基为受体的磷酸转移酶活性 168 2 246 2.20 E-06 1.50 E-04 GO:0034061 分子功能F DNA聚合酶活性 22 138 2.20 E-06 1.50 E-04 GO:0006278 生物学功能P 依赖RNA的DNA复制 19 106 1.70 E-06 6.40 E-04 GO:0043687 生物学功能P 蛋白质翻译后修饰 170 2 265 1.60 E-06 6.40 E-04 GO:0006468 生物学功能P 蛋白氨基酸磷酸化 153 1 979 9.80 E-07 6.40 E-04 GO:0006464 生物学功能P 蛋白质修饰过程 178 2 429 3.80 E-06 1.10 E-03 GO:0016301 分子功能F 激酶活性 164 2 277 2.00 E-05 1.30 E-03 GO:0005524 分子功能F ATP结合 240 3 538 2.40 E-05 1.50 E-03 GO:0016779 分子功能F 核苷酸转移酶活性 36 335 2.70 E-05 1.60 E-03 GO:0005515 分子功能F 蛋白质结合 395 6 182 3.30 E-05 1.80 E-03 GO:0043412 生物学功能P 高分子修饰 180 2 513 1.20 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0006950 生物学功能P 胁迫响应 76 882 1.10 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0016310 生物学功能P 磷酸化 158 2 160 1.20 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0030246 分子功能F 碳水化合物结合 36 353 8.00 E-05 4.20 E-03 GO:0000166 分子功能F 核苷酸结合 362 5 741 1.40 E-04 6.90 E-03 GO:0016740 分子功能F 转移酶活性 303 4 740 1.70 E-04 8.00 E-03 GO:0006796 生物学功能P 磷酸盐代谢过程 163 2 319 6.60 E-05 9.60 E-03 GO:0006793 生物学功能P 磷代谢过程 163 2 319 6.60 E-05 9.60 E-03 GO:0051704 生物学功能P 多生物过程 18 129 1.10 E-04 1.40 E-02 GO:0050896 生物学功能P 刺激响应 87 1 124 1.30 E-04 1.60 E-02 GO:0009875 生物学功能P 花粉-雌蕊相互作用 16 122 5.00 E-04 4.60 E-02 GO:0008037 生物学功能P 细胞识别 16 122 5.00 E-04 4.60 E-02 GO:0048544 生物学功能P 花粉识别 16 122 5.00 E-04 4.60 E-02 GO:0009856 生物学功能P 授粉 16 122 5.00 E-04 4.60 E-02 -
‘六月雪’样本共得到INDEL 800 388个,编码区内移码插入总数为6 092个,移码缺失总数8 884个;编码区内因INDEL突变获得终止子426个,丢失终止子107个;在基因5'UTR内的INDEL总数为31个,在基因3'UTR内的INDEL总数和位于5'UTR和3'UTR间的INDEL总数均为0,在不同可变剪切的基因组区域内找到INDEL 786个,内含子区域内找到201 635个,启动子区域内找到198 924个,基因间区域内找到383 503个。
‘黄皮消’样本共得到INDEL 799 603个,编码区内移码插入总数为6 021个,移码缺失总数8 708个;编码区内因INDEL突变获得终止子440个,丢失终止子105个;基因5'UTR内找到INDEL 26个,基因3'UTR内、不同基因的5'UTR和3'UTR间则未找到;在不同可变剪切的基因组区域内找到INDEL 758个,内含子区域内找到199 949个,启动子区域内找到198 089个,基因间区域内找到385 507个。
-
2个样本共获得INDEL15 509和15 274个。对这些INDEL的差异分析发现,共有5 115个INDEL关联到了3 682个基因,其中24个终止子丢失(stop-loss)INDEL关联了24个基因,165个终止子获得(stop-gain)INDEL关联了160个基因,1 901个移码插入(frame-shift insertion)INDEL关联了1 629个基因,3 025个移码缺失(frame-shift deletion)INDEL关联了2 453个基因。分析发现1 276个基因内的INDEL数量超过1个;假定的抗病RPP13样蛋白1(PCP007357),烟草花叶病毒耐药蛋白N(PPCP015254),未注释蛋白1(PCP015680),烟草花叶病毒耐药蛋白N(PCP030478),假定的酰胺酶C869.01(PCP023678),ATP依赖的RNA解旋酶DHX36(PCP003694),甘露糖寡糖α-1, 2-甘露糖苷酶MNS1(PCP005093),未注释蛋白2(PCP017985),富有丝氨酸/精氨酸的分裂因子SC35(PCP000011),来自转座子逆转录病毒相关的Pol聚蛋白TNT 1-94(PCP032808),未注释蛋白3(PCP031973)等蛋白编码的基因均具有7个以上INDEL。
-
分析全局GO功能发现,INDEL关联的候选基因中,刺激响应、结合、催化活性等功能相对于背景基因(1 306条)来说更加富集;INDEL关联的差异基因的富集分析(图 5及表 2)结果与nsSNP关联的候选基因的GO富集分析一致,全部25 698条信息中。
表 2 INDEL关联的候选基因及其功能的GO富集分析
Table 2. GO terms enriched by candidate gene (INDEL)
GO数据库中唯一的标记信息 GO term类型 GO功能的描述信息 输入的具有GO term注释的候选基因数 该GO term中基因总数 富集分析统计学显著水平 错误发现率 GO:0043531 分子功能F ADP结合 60 415 9.20 E-13 9.60 E-10 GO:0004713 分子功能F 蛋白酪氨酸激酶活性 145 1 649 1.10 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0032559 分子功能F 腺苷核糖核酸结合 297 3 947 9.30 E-10 2.50 E-07 GO:0001883 分子功能F 嘌呤核苷结合 310 4 170 1.50 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0001882 分子功能F 核苷结合 313 4 181 6.50 E-10 2.50 E-07 GO:0030554 分子功能F 腺苷核苷酸结合 310 4 170 1.50 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0006952 生物学功能P 防御响应 52 402 1.50 E-09 2.10 E-06 GO:0004674 分子功能F 蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性 118 1 331 1.90 E-08 2.80 E-06 GO:0016772 分子功能F 转移含磷基团的转移酶活性 213 2 779 2.90 E-08 3.80 E-06 GO:0032555 分子功能F 嘌呤核糖核酸结合 309 4 320 4.50 E-08 4.70 E-06 GO:0032553 分子功能F 核糖核酸结合 309 4 320 4.50 E-08 4.70 E-06 GO:0017076 分子功能F 嘌呤核苷酸结合 323 4 552 5.10 E-08 4.90 E-06 GO:0004672 分子功能F 蛋白激酶活性 153 1 995 1.50 E-06 1.30 E-04 GO:0003964 分子功能F RNA导向的DNA聚合酶活性 19 106 1.70 E-06 1.40 E-04 GO:0016773 分子功能F 以醇基为受体的磷酸转移酶活性 168 2 246 2.20 E-06 1.50 E-04 GO:0034061 分子功能F DNA聚合酶活性 22 138 2.20 E-06 1.50 E-04 GO:0006278 生物学功能P 依赖RNA的DNA复制 19 106 1.70 E-06 6.40 E-04 GO:0043687 生物学功能P 蛋白质翻译后修饰 170 2 265 1.60 E-06 6.40 E-04 GO:0006468 生物学功能P 蛋白氨基酸磷酸化 153 1 979 9.80 E-07 6.40 E-04 GO:0006464 生物学功能P 蛋白氨基酸磷酸化 178 2 429 3.80 E-06 1.10 E-03 GO:0016301 分子功能F 激酶活性 164 2 277 2.00 E-05 1.30 E-03 GO:0005524 分子功能F ATP结合 240 3 538 2.40 E-05 1.50 E-03 GO:0016779 分子功能F 核苷酸转移酶活性 36 335 2.70 E-05 1.60 E-03 GO:0005515 分子功能F 蛋白质结合 395 6 182 3.30 E-05 1.80 E-03 GO:0043412 生物学功能P 高分子修饰 180 2 513 1.20 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0006950 生物学功能P 胁迫响应 76 882 1.10 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0016310 生物学功能P 磷酸化 158 2 160 1.20 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0030246 分子功能F 碳水化合物结合 36 353 8.00 E-05 4.20 E-03 GO:0000166 分子功能F 核苷酸结合 362 5 741 1.40 E-04 6.90 E-03 GO:0016740 分子功能F 转移酶活性 303 4 740 1.70 E-04 8.00 E-03 GO:0006796 生物学功能P 磷酸盐代谢过程 163 2 319 6.60 E-05 9.60 E-03 GO:0006793 生物学功能P 磷代谢过程 163 2 319 6.60 E-05 9.60 E-03 GO:0051704 生物学功能P 多生物过程 18 129 1.10 E-04 1.40 E-02 GO:0050896 生物学功能P 刺激响应 87 1 124 1.30 E-04 1.60 E-02 GO:0009875 生物学功能P 花粉-雌蕊相互作用 16 122 5.00 E-03 4.60 E-02 GO:0008037 生物学功能P 细胞识别 16 122 5.00 E-03 4.60 E-02 GO:0048544 生物学功能P 花粉识别 16 122 5.00 E-03 4.60 E-02 GO:0009856 生物学功能P 授粉 16 122 5.00 E-03 4.60 E-02 -
用VarScan软件对拷贝数变异(CNV)分析,共获得CNV 37 039个,其中缺失CNV(deletion CNV)20 629个,中性CNV(neutral CNV)7 577个,扩增CNV(amplification CNV)8 833个。
-
近年来,迅猛发展的基因组测序技术已被广泛应用于植物基因组重测序等研究[27]。SNP是基因组DNA序列上广泛存在的最基本的变异形式[28],植物基因组上平均每数百bp就存在一个SNP[29]。将SNP和传统分子标记相结合用于分子辅助育种,通过全基因组重测序(WGR)得到测序数据,与参考基因组进行序列比对,可分析SNP遗传变异信息,开发出数量较为丰富的分子标记,实现遗传资源的高效利用[30]。
全基因组重测序为从基因组水平开发SNP标记提供了新的技术条件,将SNP识别、验证和基因型分析与传统分子标记相结合,能快速挖掘到候选基因和获得导致表型的SNP位点[9]。中国6个玉米Zea mays优良自交系的非重复区大约存在1 272 134个SNP和30 178个INDEL,其中68 966个SNP和571个INDEL位于功能基因内[31]。对梁Setaria italica ‘SLX’品种的全基因组重测序发现,‘SLX’基因组存在762 082个SNP,26 802个INDEL,10 109个SV[32];对包括野生种、培育种及改良品种在内的360份番茄Lycopersicon esculentum进行全基因组重测序,发现番茄的驯化和改良是2个相对独立的过程,影响果实颜色的主效基因是SlMYB12[33]。对302株大豆Glycine max进行全基因组重测序,检测到了162个受选择的拷贝数变异(CNV),并发现植株进化、发育性状与受选择区域相关[34]。大豆品种‘齐黄34’‘Qihuang34’经全基因组重测序检测到1 519 494个SNP,357 549个INDEL,4 506个SV,17 748个基因变异,其中转录、复制、重组、修复、信号传导机制等6个功能类序列存在较多的变异基因[35]。梨的全基因组重测序少见报道[11-13],大多是通过转录组分析来发掘SNP位点并进行功能注释。编码区内的SNP一般可分为同义SNP(synonymous SNP)和非同义SNP(non-synonymous SNP),其中同义SNP所致的编码序列的改变不会引起氨基酸序列变化,而非同义SNP会使氨基酸序列发生改变,最终影响蛋白质序列[36],因此认为非同义SNP是导致生物性状改变的直接原因,开发并研究这类SNP标记往往具有更为重要的生物学意义。本研究中,‘六月雪’和‘黄皮消’样本中总SNP数量分别为6 171 357和6 140 603个,编码区内无义突变内总数(nsSNP)分别为335 659和332 280个;对nsSNP的CV分析发现共有2 282个nsSNP关联了2 067个基因。2个样本的总INDEL数量分别为800 388和799 603个,位于编码区内的分别有15 509和15 274个;共5 115个差异INDEL关联到了3 682个基因,令烟草花叶病毒耐药蛋白N和抗病蛋白等关键基因发生变异。差异nsSNP基因和差异INDEL富集得到的GO terms一致。针对这些突变位点进行SNP和INDEL相关标记的开发、优异基因的挖掘将为分子标记辅助育种提供重要的标记资源,对上饶早梨‘六月雪’和‘黄皮消’育种研究具有重要的指导意义。
Whole genome re-sequencing analysis of two cultivars ('Liuyuexue' and 'Huangpixiao') of Pyrus pyrifolia in Shangrao
-
摘要: 以上饶早梨Pyrus pyrifolia 2个品种‘六月雪’‘Liuyuexue’和‘黄皮消’‘Huangpixiao’试管苗为材料,进行全基因组重测序分析。结果表明:2个样本的总单核苷酸多态位点(SNP)数量分别为6 171 357和6 140 603个,编码区内无义突变位点(nsSNP)分别为335 659和332 280个。对nsSNP的常见变异(common variant,CV)分析发现,共有2 282个nsSNP关联了2 067个基因。2个样本的总插入缺失位点(INDEL)分别为800 388和799 603个,其中15 509和15 274个位于编码区,共5 115个差异INDEL关联到了3 682个基因,烟草花叶病毒(tobacco mosaic virus)耐药蛋白N,抗病蛋白等关键基因发生变异。差异nsSNP和差异INDEL富集得到的基因本体术语(GO terms)一致。本实验结果可为上饶早梨2个品种‘六月雪’和‘黄皮消’SNP和INDEL相关标记的开发、优异基因的挖掘提供参考。Abstract: A whole genome re-sequencing analysis was carried out with plantlets for two cultivars ('Liuyuexue' and 'Huangpixiao') of early pear (Pyrus pyrifolia) in Shangrao using a common variant analysis for nsSNPs (nonsynonymous mutations single-nucleotide polymorphism). Results showed a total number of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in the two samples of 6 171 357 for 'Liuyuexue' and 6 140 603 for 'Huangpixiao', and a total number of nsSNP within the coding region of 335 659 for 'Liuyuexue' and 332 280 for 'Huangpixiao'. Using the common variant analysis for nsSNPs, 2 282 nsSNPs were found associated with 2 067 genes. The total indel numbers of the two samples were 800 388 for 'Liuyuexue' and 799 603 for 'Huangpixiao'. In the coding area, 15 509 indels for 'Liuyuexue' and 15 274 indels for 'Huangpixiao' were obtained, and 5 115 differential indels were associated with 3 682 genes. Key genes of the tobacco mosaic virus resistant protein N and the disease resistant protein as well as others were mutated. Enriched gene ontology (GO) terms of differential nsSNPs and differential indels were consistent. Results of this study could provide important references for the development of SNP and indel related markers and the extraction of excellent genes for the two cultivars ('Liuyuexue' and 'Huangpixiao') of early pear in Shangrao.
-
表 1 nsSNP关联的候选基因及其功能的GO富集分析
Table 1. GO terms enriched by candidate gene (nsSNP)
GO数据库中唯一的标记信息 GO term类型 GO功能的描述信息 输入的具有GO term注释的候选基因数 该GO term中基因总数 富集分析统计学显著水平 错误发现率 GO:0043531 分子功能F ADP结合 60 415 9.20 E-13 9.60 E-10 GO:0004713 分子功能F 蛋白酪氨酸激酶活性 145 1 649 1.10 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0032559 分子功能F 腺苷核糖核酸结合 297 3 947 9.30 E-10 2.50 E-07 GO:0001883 分子功能F 嘌呤核苷结合 310 4 170 1.50 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0001882 分子功能F 核苷结合 313 4 181 6.50 E-10 2.50 E-07 GO:0030554 分子功能F 腺苷核苷酸结合 310 4 170 1.50 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0006952 生物学功能P 防御响应 52 402 1.50 E-09 2.10 E-06 GO:0004674 分子功能F 蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性 118 1 331 1.90 E-08 2.80 E-06 GO:0016772 分子功能F 转移含磷基团的转移酶活性 213 2 779 2.90 E-08 3.80 E-06 GO:0032555 分子功能F 嘌呤核糖核酸结合 309 4 320 4.50 E-08 4.70 E-06 GO:0032553 分子功能F 核糖核酸结合 309 4 320 4.50 E-08 4.70 E-06 GO:0017076 分子功能F 嘌呤核苷酸结合 323 4 552 5.10 E-08 4.90 E-06 GO:0004672 分子功能F 蛋白激酶活性 153 1 995 1.50 E-06 1.30 E-04 GO:0003964 分子功能F RNA导向的DNA聚合酶活性 19 106 1.70 E-06 1.40 E-04 GO:0016773 分子功能F 以醇基为受体的磷酸转移酶活性 168 2 246 2.20 E-06 1.50 E-04 GO:0034061 分子功能F DNA聚合酶活性 22 138 2.20 E-06 1.50 E-04 GO:0006278 生物学功能P 依赖RNA的DNA复制 19 106 1.70 E-06 6.40 E-04 GO:0043687 生物学功能P 蛋白质翻译后修饰 170 2 265 1.60 E-06 6.40 E-04 GO:0006468 生物学功能P 蛋白氨基酸磷酸化 153 1 979 9.80 E-07 6.40 E-04 GO:0006464 生物学功能P 蛋白质修饰过程 178 2 429 3.80 E-06 1.10 E-03 GO:0016301 分子功能F 激酶活性 164 2 277 2.00 E-05 1.30 E-03 GO:0005524 分子功能F ATP结合 240 3 538 2.40 E-05 1.50 E-03 GO:0016779 分子功能F 核苷酸转移酶活性 36 335 2.70 E-05 1.60 E-03 GO:0005515 分子功能F 蛋白质结合 395 6 182 3.30 E-05 1.80 E-03 GO:0043412 生物学功能P 高分子修饰 180 2 513 1.20 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0006950 生物学功能P 胁迫响应 76 882 1.10 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0016310 生物学功能P 磷酸化 158 2 160 1.20 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0030246 分子功能F 碳水化合物结合 36 353 8.00 E-05 4.20 E-03 GO:0000166 分子功能F 核苷酸结合 362 5 741 1.40 E-04 6.90 E-03 GO:0016740 分子功能F 转移酶活性 303 4 740 1.70 E-04 8.00 E-03 GO:0006796 生物学功能P 磷酸盐代谢过程 163 2 319 6.60 E-05 9.60 E-03 GO:0006793 生物学功能P 磷代谢过程 163 2 319 6.60 E-05 9.60 E-03 GO:0051704 生物学功能P 多生物过程 18 129 1.10 E-04 1.40 E-02 GO:0050896 生物学功能P 刺激响应 87 1 124 1.30 E-04 1.60 E-02 GO:0009875 生物学功能P 花粉-雌蕊相互作用 16 122 5.00 E-04 4.60 E-02 GO:0008037 生物学功能P 细胞识别 16 122 5.00 E-04 4.60 E-02 GO:0048544 生物学功能P 花粉识别 16 122 5.00 E-04 4.60 E-02 GO:0009856 生物学功能P 授粉 16 122 5.00 E-04 4.60 E-02 表 2 INDEL关联的候选基因及其功能的GO富集分析
Table 2. GO terms enriched by candidate gene (INDEL)
GO数据库中唯一的标记信息 GO term类型 GO功能的描述信息 输入的具有GO term注释的候选基因数 该GO term中基因总数 富集分析统计学显著水平 错误发现率 GO:0043531 分子功能F ADP结合 60 415 9.20 E-13 9.60 E-10 GO:0004713 分子功能F 蛋白酪氨酸激酶活性 145 1 649 1.10 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0032559 分子功能F 腺苷核糖核酸结合 297 3 947 9.30 E-10 2.50 E-07 GO:0001883 分子功能F 嘌呤核苷结合 310 4 170 1.50 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0001882 分子功能F 核苷结合 313 4 181 6.50 E-10 2.50 E-07 GO:0030554 分子功能F 腺苷核苷酸结合 310 4 170 1.50 E-09 2.50 E-07 GO:0006952 生物学功能P 防御响应 52 402 1.50 E-09 2.10 E-06 GO:0004674 分子功能F 蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性 118 1 331 1.90 E-08 2.80 E-06 GO:0016772 分子功能F 转移含磷基团的转移酶活性 213 2 779 2.90 E-08 3.80 E-06 GO:0032555 分子功能F 嘌呤核糖核酸结合 309 4 320 4.50 E-08 4.70 E-06 GO:0032553 分子功能F 核糖核酸结合 309 4 320 4.50 E-08 4.70 E-06 GO:0017076 分子功能F 嘌呤核苷酸结合 323 4 552 5.10 E-08 4.90 E-06 GO:0004672 分子功能F 蛋白激酶活性 153 1 995 1.50 E-06 1.30 E-04 GO:0003964 分子功能F RNA导向的DNA聚合酶活性 19 106 1.70 E-06 1.40 E-04 GO:0016773 分子功能F 以醇基为受体的磷酸转移酶活性 168 2 246 2.20 E-06 1.50 E-04 GO:0034061 分子功能F DNA聚合酶活性 22 138 2.20 E-06 1.50 E-04 GO:0006278 生物学功能P 依赖RNA的DNA复制 19 106 1.70 E-06 6.40 E-04 GO:0043687 生物学功能P 蛋白质翻译后修饰 170 2 265 1.60 E-06 6.40 E-04 GO:0006468 生物学功能P 蛋白氨基酸磷酸化 153 1 979 9.80 E-07 6.40 E-04 GO:0006464 生物学功能P 蛋白氨基酸磷酸化 178 2 429 3.80 E-06 1.10 E-03 GO:0016301 分子功能F 激酶活性 164 2 277 2.00 E-05 1.30 E-03 GO:0005524 分子功能F ATP结合 240 3 538 2.40 E-05 1.50 E-03 GO:0016779 分子功能F 核苷酸转移酶活性 36 335 2.70 E-05 1.60 E-03 GO:0005515 分子功能F 蛋白质结合 395 6 182 3.30 E-05 1.80 E-03 GO:0043412 生物学功能P 高分子修饰 180 2 513 1.20 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0006950 生物学功能P 胁迫响应 76 882 1.10 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0016310 生物学功能P 磷酸化 158 2 160 1.20 E-05 2.30 E-03 GO:0030246 分子功能F 碳水化合物结合 36 353 8.00 E-05 4.20 E-03 GO:0000166 分子功能F 核苷酸结合 362 5 741 1.40 E-04 6.90 E-03 GO:0016740 分子功能F 转移酶活性 303 4 740 1.70 E-04 8.00 E-03 GO:0006796 生物学功能P 磷酸盐代谢过程 163 2 319 6.60 E-05 9.60 E-03 GO:0006793 生物学功能P 磷代谢过程 163 2 319 6.60 E-05 9.60 E-03 GO:0051704 生物学功能P 多生物过程 18 129 1.10 E-04 1.40 E-02 GO:0050896 生物学功能P 刺激响应 87 1 124 1.30 E-04 1.60 E-02 GO:0009875 生物学功能P 花粉-雌蕊相互作用 16 122 5.00 E-03 4.60 E-02 GO:0008037 生物学功能P 细胞识别 16 122 5.00 E-03 4.60 E-02 GO:0048544 生物学功能P 花粉识别 16 122 5.00 E-03 4.60 E-02 GO:0009856 生物学功能P 授粉 16 122 5.00 E-03 4.60 E-02 -
[1] 徐芬芬, 叶利民, 樊生树, 等. N, O-羧甲基壳聚糖在上饶早梨保鲜上的应用研究[J].北方园艺, 2015(21):137-139. XU Fenfen, YE Limin, FAN Shengshu, et al. Study on the application of N, O-carboxymethyl chitosan in the Shangrao early pear storage[J]. Northern Hortic, 2015(21):137-139. [2] 徐芬芬, 樊生树, 叶利民.采收期和贮藏温度对上饶早梨保鲜效果的影响[J].保鲜与加工, 2016, 16(3):11-15. XU Fenfen, FAN Shengshu, YE Limin. Effects of harvest time and storage temperature on the fresh-keeping effect of Shangrao early pears[J]. Storage Process, 2016, 16(3):11-15. [3] 洪森荣, 张铭心, 董雅凤, 等.上饶早梨嫩梢热处理嫁接苗脱毒效果分析[J].分子植物育种, 2017, 15(8):3388-3392. HONG Senrong, ZHANG Mingxin, DONG Yafeng, et al. Virus-free effect analysis of grafted seedlings using heat-treated young shoots of early pear in Shangrao[J]. Mol Plant Breed, 2017, 15(8):3388-3392. [4] 尹明华, 周宇瑶, 杨星鹏, 等.上饶早梨主栽品种病毒种类分析及其茎尖脱毒技术效率比较[J].浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(1):89-100. YIN Minghua, ZHOU Yuyao, YANG Xingpeng, et al. Analysis of virus species in main cultivars of early pear in Shangrao and the efficiency of their shoot tip virus-free techniques[J]. Acta Agric Zhejiang, 2017, 29(1):89-100. [5] 夏华炎, 徐路, 肖虹, 等.上饶早梨主栽品种离体快繁体系的建立[J].南方农业学报, 2016, 47(9):1547-1552. XIA Huayan, XU Lu, XIAO Hong, et al. Establishment of in vitro propagation system of main cultivars of Shangrao early pear[J]. J Southern Agric, 2016, 47(9):1547-1552. [6] 尹明华, 周宇瑶, 苏爱芳, 等.上饶早梨道地性农家种遗传多样性与亲缘关系的荧光AFLP分子标记分析[J].基因学与应用生物学, 2016, 35(11):3178-3188. YIN Minghua, ZHOU Yuyao, SU Aifang, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity and genetic relationships of local genuine landraces of early pear in Shangrao by fluorescence AFLP molecular markers[J]. Genomics Appl Biol, 2016, 35(11):3178-3188. [7] 尹明华, 何林森, 朱奇志, 等.上饶早梨品种鉴定及再生苗遗传稳定性SSR检测[J].分子植物育种, 2016, 14(11):3120-3129. YIN Minghua, HE Linsen, ZHU Qizhi, et al. Identification of early pear main cultivars in Shangrao and genetic stability SSR analysis of their regenerated plants[J]. Mol Plant Breed, 2016, 14(11):3120-3129. [8] 洪森荣, 周宇瑶, 黄慧.上饶早梨离体保存库再生苗遗传稳定性的同工酶分析[J].基因组学与应用生物学, 2016, 35(12):3552-3561. HONG Senrong, ZHOU Yuyao, HUANG Hui. Isoenzyme analysis of genetic stability of the plantlets regenerated from conservation bank in vitro of early pear in Shangrao[J]. Genomics Appl Biol, 2016, 35(12):3552-3561. [9] 袁金红, 李俊华, 黄小城, 等.基于全基因组重测序的SNP分析在作物基因定位中的研究进展[J].植物生理学报, 2015, 51(9):1400-1404. YUAN Jinhong, LI Junhua, HUANG Xiaocheng, et al. Advance of SNP analysis based on whole genome resequencing in crop gene mapping[J]. Plant Physiol J, 2015, 51(9):1400-1404. [10] QI Jianjian, LIU Xin, SHEN Di, et al. A genomic variation map provides insights into the genetic basis of cucumber domestication and diversity[J]. Nat Genet, 2013, 45(12):1510-1515. [11] WU Jun, WANG Zhiwen, SHI Zebin, et al. The genome of pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.)[J]. Genome Res, 2012, 23(2):396-408. [12] 莫文娟, 袁德义, 段经华, 等.新高系梨9个品种SSR标记分析[J].浙江林学院学报, 2009, 26(5):639-645. MO Wenjuan, YUAN Deyi, DUAN Jinghua, et al. Simple sequence repeat analysis on pear cultivars in Niitaka line[J]. J Zhejiang For Coll, 2009, 26(5):639-645. [13] YAMAMOTO T, TERAKAMI S. Genomics of pear and other Rosaceae fruit trees[J]. Breed Sci, 2016, 66(1):148-159. [14] 周贺, 李浩男, 蔡斌华, 等.砂梨果皮转录组SNP位点发掘及其功能注释分析[J].青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 31(2):105-111. ZHOU He, LI Haonan, CAI Bihua, et al. SNP mining and functional annotation in transcriptome of sand pear[J]. J Qingdao Agric Univ Nat Sci, 2014, 31(2):105-111. [15] 李节法.赤霉素促进梨果实库强的转录组学和蛋白质组学研究[D].上海: 上海交通大学, 2015. LI Jiefa. Transcriptome and Proteomics Study of Gibberellin Promoting Pear Fruit Storehouse Strength[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2015. [16] WU Jun, LI Leiting, LI Meng, et al. High-density genetic linkage map construction and identification of fruit-related QTLs in pear using SNP and SSR markers[J]. J Exp Bot, 2014, 65(20):5771-5781. [17] MONTANARI S, SAEED M, KNÄBEL M, et al. Identification of Pyrus single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and evaluation for genetic mapping in European pear and interspecific Pyrus hybrids[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10):e77022. doi:10.1371/journal.pone. 0077022. [18] TERAKAMI S, NISHITANI C, YAMAMOTO T. Development of SNP markers for marker-assisted selection in pear[J]. Acta Hortic, 2013, 976(976):463-469. [19] ROBINSON M D, Mc CARTHY D J, SMYTH G K. EdgeR:a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(1):139-140. [20] LANGMEAD B, SALZBERG S L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2[J]. Nat Method, 2013, 9(4):357-359. [21] DePRISTO M A, BANKS E, POPLIN R, et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data[J]. Nat Genet, 2011, 43(5):491-498. [22] WANG Kai, LI Mingyao, HAKONARSON H. ANNOVAR:functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data[J]. Nucleic Acid Res, 2010, 38(16):e164. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq603. [23] SILVA J, SCHEFFLER B, SANABRIA Y, et al. Identification of candidate genes in rice for resistance to sheath blight disease by whole genome sequencing[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2012, 124(1):63-74. [24] DU Zhou, ZHOU Xin, LING Yi, et al. Agrigo:a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community[J]. Nucl Acid Res, 2010, 38(Web Server issue):W64-W70. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq310. [25] KOBOLDT D C, ZHANG Qunyuan, LARSON D E, et al. VarScan 2:somatic mutation and copy number alteration discovery in cancer by exome sequencing[J]. Genome Res, 2012, 22(3):568-576. [26] OLSHEN A B, VENKATRAMAN E S, LUCITO R, et al. Circular binary segmentation for the analysis of array-based DNA copy number data[J]. Biostatistics, 2004, 5(4):557-572. [27] SU Zhenqiang, NING Baitang, FANG Hong, et al. Next-generation sequencing and its applications in molecular diagnostics[J]. Exp Rev Mol Diagn, 2011, 11(3):333-343. [28] SCHMID K J, SÖRENSEN T R, STRACKE R, et al. Large-scale identification and analysis of genome-wide single-nucleotide polymorphisms for mapping in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Genome Res, 2003, 13(6A):1250-1257. [29] HUANG Xuehui, WEI Xinghua, SANG Tao, et al. Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces[J]. Nat Genet, 2010, 42(11):961-967. [30] CABEZAS J A, IBÁÑEZ J, LIJAVETZKY D, et al. A 48 SNP set for grapevine cultivar identification[J]. BMC Plant Biol, 2011, 11(1):153. [31] LAI Jinsheng, LI Ruiqiang, XU Xun, et al. Genome-wide patterns of genetic variation among elite maize inbred lines[J]. Nat Genet, 2010, 42(11):1027-1030. [32] BAI Hui, CAO Yinghao, QUAN Jianzhang, et al. Identifying the genome-wide sequence variations and developing new molecular markers for genetics research by re-sequencing a landrace cultivar of foxtail millet[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9):e73514. [33] LIN Tao, ZHU Guangtao, ZHANG Junhong, et al. Genomic analyses provide insights into the history of tomato breeding[J]. Nat Genet, 2014, 46(11):1220-1226. [34] ZHOU Zhengkui, JIANG Yu, WANG Zheng, et al. Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2015, 33(4):408-414. [35] 张彦威, 李伟, 张礼凤, 等.基于重测序的大豆新品种齐黄34的全基因组变异挖掘[J].中国油料作物学报, 2016, 38(2):150-158. ZHANG Yanwei, LI Wei, ZHANG Lifeng, et al. Genome-wide variations of soybean cultivar Qihuang 34 by whole genome re-sequencing[J]. Chin J Oil Crop Sci, 2016, 38(2):150-158. [36] 田义轲, 王彩虹, 白牡丹, 等.基于梨贝壳杉烯氧化酶基因PpKO序列的功能性SNP标记[J].园艺学报, 2012, 39(10):1876-1884. TIAN Yike, WANG Caihong, BAI Mudan, et al. Development of functional SNP markers anchored PpKO gene in pear[J]. Acta Hortic Sin, 2012, 39(10):1876-1884. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2019.02.003







 下载:
下载: