-
水土流失是中国重要的环境问题,以坡面径流小区为研究单元探讨不同措施下的水土流失规律已成为水土保持工作者的重要研究手段之一[1]。降雨是导致水土流失的直接动力因子。根据时程变化特征的多样性,可将降雨分为不同雨型,径流过程因雨型的不同存在极大变异[2]。研究雨型对径流过程的影响对进一步明确产流产沙规律具有重要意义。基于自然降雨过程的复杂性,国内外学者针对降雨时段特征开展了很多研究,并根据研究结果提出了诸多雨型划分方法。目前,关于雨型分类的研究可归纳为以下4个方向:①以气象标准划分雨型[3-6],研究坡面径流及侵蚀规律。这种划分方法仅以24 h降雨量为分类依据。②以模拟降雨及人工设计降雨过程为主的雨型设计,如Huff雨型及芝加哥雨型等,但这些模型是以美国降雨数据为依据建立的。EWEA等[2]研究表明:此类雨型存在极大的地区不兼容性。此外,国内外一些学者还根据人工模拟降雨设计了总降雨量相同的4类雨型[7-12],分别为均匀型、递增型、递减型及中峰型。该类设计雨型一定程度上实现了雨强在不同降雨时段的非均匀性分布,但因模拟降雨器无法及时调整瞬时雨强的变化,导致模拟降雨和实际降雨过程仍存在较大差异。③以降雨数量特征[13-20]为分类标准的雨型划分,常见的多以降雨量(P)、降雨历时(t)、最大30 min雨强(I30)等为分类指标。该类雨型基于对产流产沙结果影响较大的数量特征指标进行聚类分析,对降雨数量特征的描述较为充分,但未考虑不同峰值雨强出现时序对径流及侵蚀的影响。④以雨峰出现时序为划分标准进行分类[21-22]。如邬铃莉等[23]根据I30的出现时间将不同的降雨划分为均值型、递增型、递减型和中峰型,并探讨了不同雨型下的土壤侵蚀规律。杨云斌等[24]以量纲-累计降雨过程曲线法将自然降雨划分为前期型降雨、中期型降雨、后期型降雨及均匀性降雨。该类雨型侧重于讨论雨峰位置对产流产沙过程的影响,较少考虑降雨数量特征的影响。
综上可知,在雨型划分方面,已有的划分方法标准不一,未充分体现自然降雨的雨型特征,且研究重点不一致,较少有研究对径流过程特征进行分析。本研究以P、t及I30为分类指标进行聚类分析,在根据降雨数量特征进行雨型划分的基础上,进一步探讨雨峰位置对径流过程的影响,使雨型划分更加系统,雨型特征的表征更加完整,不同雨型下的径流过程特征也更加明确,可为提高坡面尺度径流过程研究精度提供参考。
-
研究区位于北京市密云区密云水库上游以东黄各庄村,40°28′48″~40°28′518″N,116°59′33″~117°03′25″E,海拔为145~900 m。气候属暖温带半湿润大陆性季风气候,年平均气温为10.5 ℃,年平均降水量为669.0 mm,年降水变幅大,而且降水年内分配极不均匀,全年降水量80%~85%集中在 7—10月。土壤类型主要是山地酸性盐类淋溶褐土。研究区内植被以荆条Vitex negulido var. heterophylla群系为主,伴生灌木有酸枣Ziziphus jujuba var. spinosa、薄皮木Leptodermis oblonga、蚂蚱腿子Myripnois dioica、多花胡枝子Lespedeza floribunda等,草本植物以丛生隐子草Cleistogenes caespitosa、白颖薹草Carex duriuscula subsp. rigescens、旱生卷柏Selaginella stauntoniana、中华卷柏Selaginella sinensis为主。
-
2019年6月—2020年10月在研究区选择3种典型的样地,样地大小为20 m×5 m,水平投影面积为100 m2。在样地附近布设翻斗式雨量筒[FDY(B)-0.2]记录降雨过程,在径流小区集流井内成对悬挂压力式水位计(U20-001-04,精度±0.3 cm)记录水位变化,其中一个悬空作为气压计,同时通过降雨后实际测量的水位对水位计数据进行校准。样地基本信息见表1。
表 1 样地基本情况表
Table 1. Basic situation of the plots
小区名称 植被盖度/
%小区规格
(m×m)坡度/
(°)整地措施 水平条山杏小区 84.49 20×5 23 大水平条 穴状侧柏小区 100.00 20×5 20 穴状 鱼鳞坑蒙古栎小区 88.32 20×5 25 鱼鳞坑 说明:山杏Armeniaca sibirica、侧柏Platycladus orientalis、 蒙古栎Quercus mongolica -
首先将全部自然降雨数据划分为独立的场次降雨。以降雨时间为120 min,降水量≤2 mm为场次界定指标[25]。每个场次降雨数据以5 min为单位统计累计降雨量,绘制降雨过程,并分别计算相应的降雨特征指标:降雨量(P)、降雨历时(t)、最大30 min雨强(I30)。
-
受压力式水位计读取精度的影响,成对校准数据最大可产生6 mm的偏差。该偏差属于仪器系统误差,不可消除。同时,因仪器间误差的影响,读取的水位和实际水位之间有一定的差距。数据处理前先根据未产流前压力数据计算水位计和气压计之间的压力差平均值,消除压力差后再换算成径流深。同时,由于压力式水位计传感器位置的影响,需在读数后加上14 mm的起测水位。计算公式如下。
$$ H=\frac{\left[({P}_{1}+\Delta P) \mu +{H}_{\text{0}}\right] {S}_{1}}{{S}_{2}} 。$$ 其中:H为径流深(mm);P1为水位计读数(kPa);ΔP为水位计和气压计之前的压力差(kPa);μ为单位换算系数,值为101.97;H0为起测水位,值为14 mm;S1为集流井池底面积(mm2);S2为小区面积(mm2)。
-
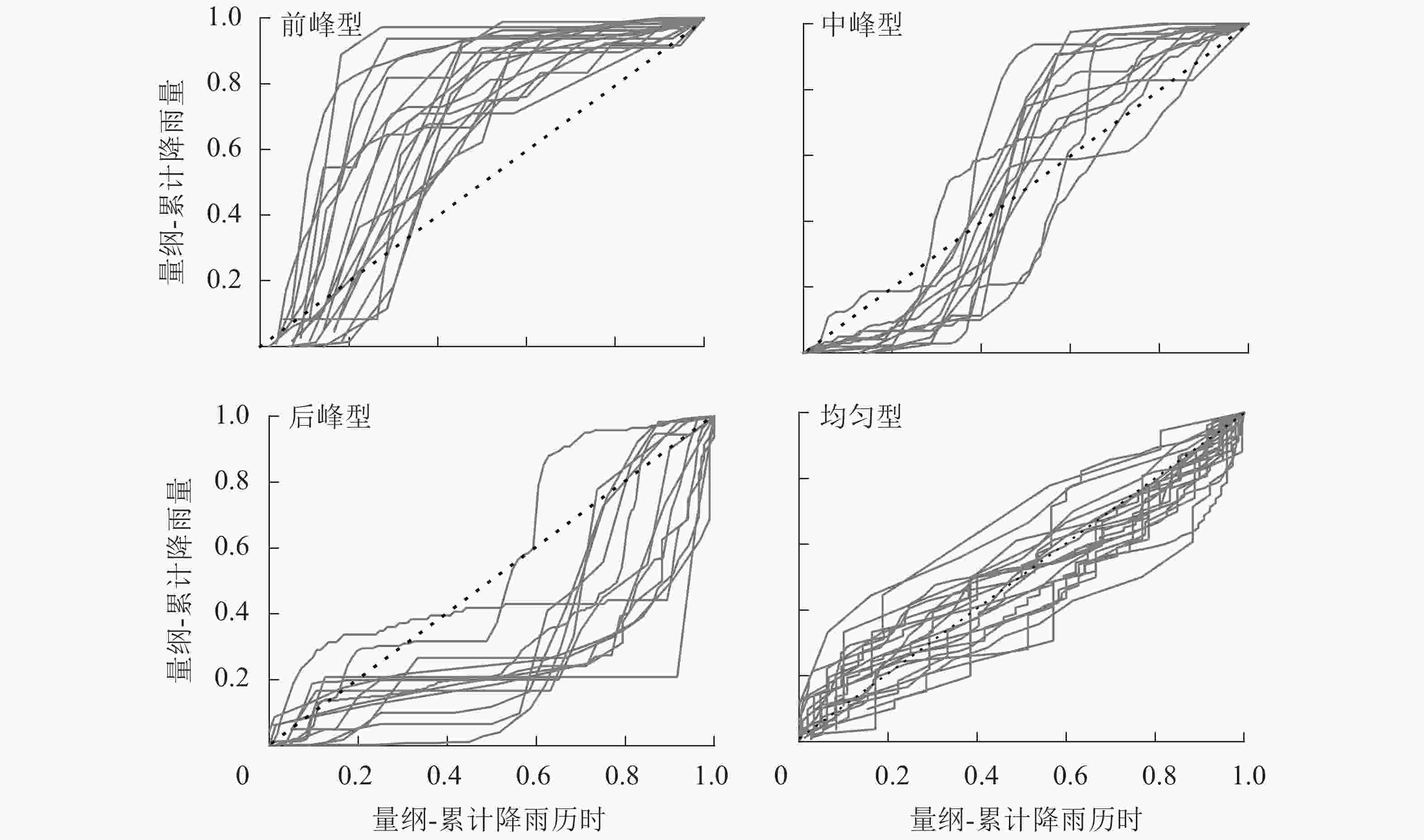
将降雨量小于2 mm(认为是对径流无效的降雨)的先剔除[25],根据降雨主要数量特征指标P、t和I30为划分依据,采用K均值聚类分析方法进行一级雨型分类,并采用判别分析对聚类结果进行检验。然后根据降雨在降雨时段集中出现的时间,采用量纲-曲线法[22]进行过程雨型二级分类。具体做法如下:①将获得的降雨过程数据中的瞬时降雨量及持续时间分别除以场次总降雨量及总历时,使其无量纲;②将无量纲的降雨量及历时分别累加至1;③以无量纲累计降雨量为纵坐标,累计历时为横坐标绘制量纲-累计降雨历时曲线;④最后将累计历时均分为3个时间段,根据40%降雨量集中出现的时段划分出4种过程雨型,分别为前峰型(40%降雨量集中在第1个时间段)、中峰型(40%降雨量集中在第2个时间段)、后峰型(40%降雨量集中在第3个时间段)和均匀型(降雨量均匀分布在3个时间段)。
-
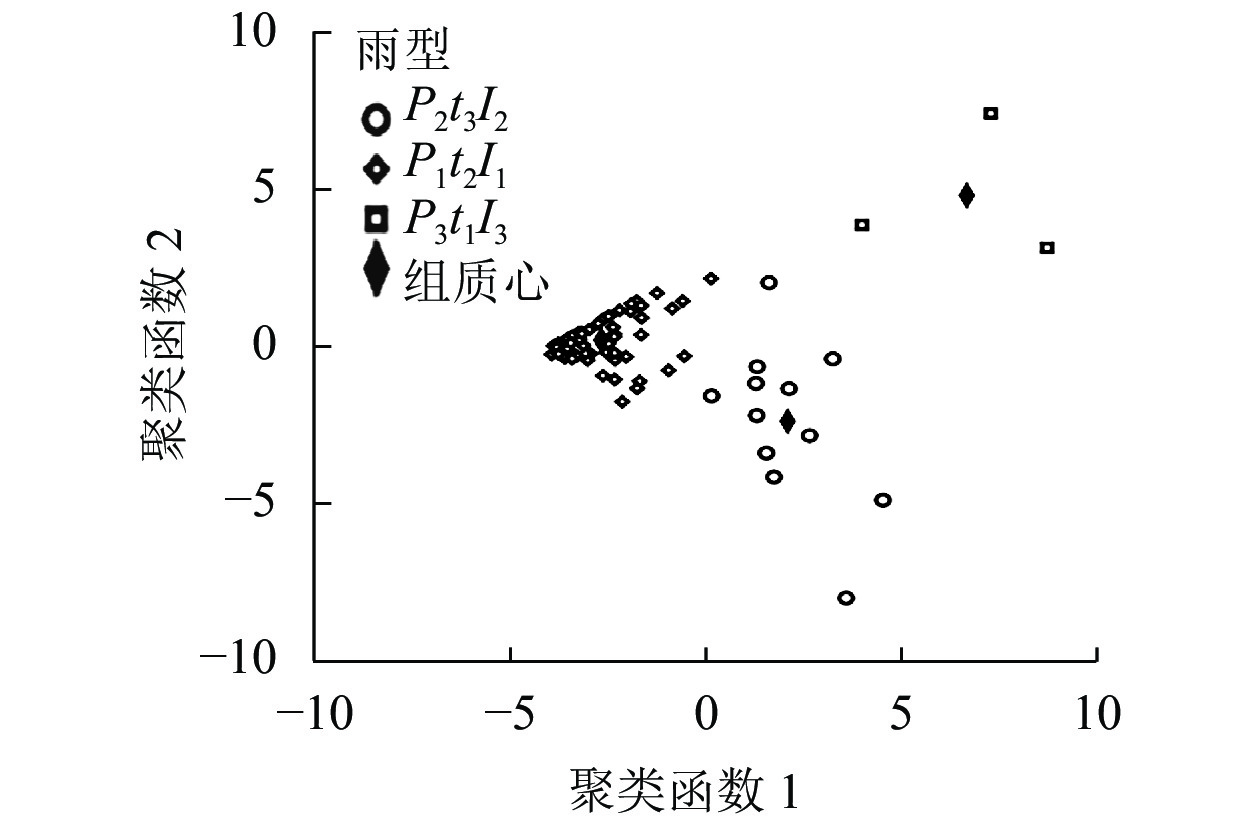
根据聚类分析结果,研究区共分出P2t3I2(中雨量、长历时、中雨强),P1t2I1(小雨量、中历时、小雨强)和P3t1I3(大雨量、短历时、大雨强)等3类雨型。由表2可以看出:研究区研究期间主要降雨类型为P1t2I1雨型,频次占比为81.01%,为小雨量(1.80~23.80 mm)、中历时(0.17~9.03 h)、小雨强(1.60~38.80 mm·h−1)降雨;其次为P2t3I2雨型,特征为中雨量(27.20~68.20 mm)、长历时(1.01~15.25 h)、中雨强(16.40~52.00 mm·h−1),占比为15.19%;P3t1I3雨型在研究期间仅发生过3次,占比最小,该雨型特征为大雨量(41.20~74.80 mm)、短历时(0.68~2.33 h)、大雨强(69.20~106.00 mm·h−1)。从累计降雨量上来看,P2t3I2雨型和P1t2I1雨型对总降雨量的贡献相近,分别占研究期间总降雨量的43.13%和42.90%,P3t1I3雨型对总降雨量的贡献最小,占比仅为13.97%。
表 2 不同雨型的降雨特征
Table 2. Rainfall characteristics of different rain types
雨型 项目 特征变量 频次 比例/% P/mm t/h I30/(mm·h−1) P2t3I2 (中雨量、长历时、中雨强) 累计值 523.40 88.09 345.20 12 15.19 均值 43.62 7.34 28.76 范围 27.20~68.20 1.01~15.25 16.40~52.00 P1t2I1 (小雨量、中历时、小雨强) 累计值 520.60 147.54 686.80 64 81.01 均值 8.13 2.31 10.74 范围 1.80~23.80 0.17~9.03 1.60~38.80 P3t1I3 (大雨量、短历时、大雨强) 累计值 169.60 5.34 275.20 3 3.80 均值 56.53 1.78 91.74 范围 41.20~74.80 0.68~2.33 69.20~106.00 从图1可以看出:3类雨型聚类函数的散点分别聚集在3个相对集中的区域,聚类函数均通过显著性检验(P<0.01),说明聚类效果较好。3种雨型中,其中P3t1I3雨型有着较为明显的特征,各聚类函数的散点均匀地集中在质心周围。P2t3I2雨型和P1t2I1雨型有部分边界相接,说明这2种雨型差异相对中等,存在部分相似雨情,但整体来看,2种雨型还是存在明显的差异。
-
从图2可以看出:前峰型降雨-量纲累计降雨过程曲线呈上凸型,曲线前半段斜率较大,后半段比较平缓,曲线大致位于y=x线上方,即降雨主要集中在降雨前期。中峰型降雨其量纲-累计降雨过程曲线近S型,曲线前半段和后半段均比较平缓,中段曲线陡然上升,曲线前半段位于y=x曲线下方,呈下凹型,经中段集中上升后,后半段位于y=x曲线上方,呈上凸型。后峰型降雨量纲-累计降雨过程曲线呈下凹型,曲线前半段比较平缓,后半段斜率较大,整体曲线基本位于y=x曲线下方,降雨主要集中降雨后期。均匀型降雨其量纲-累计降雨过程曲线基本沿y=x曲线呈稳定上升,整个曲线斜率相差不大,即降雨基本均匀分布在每个降雨时段。
从表3可以看出:4种过程雨型发生频次从大到小排序为均匀型(28次)、前峰型(21次)、后峰型(17次)、中峰型(13次),其中峰值型降雨(前峰型、中峰型、后峰型)发生总场次是均匀型降雨的1.82倍。P2t3I2雨型条件下,4种过程雨型发生频次比较均匀,为2~4次。P1t2I1雨型条件下,4种过程雨型发生的频次从大到小依次为均匀型(24次)、前峰型(17次)、后峰型(13次)、中峰型(10次),分别占到P1t2I1雨型降雨总场次的37.50%、26.56%、20.31%及15.63%。P3t1I3雨型条件下,前峰型降雨发生了2次,后峰型1次。通常在自然条件下,P3t1I3雨型中不存在均匀型降雨过程。根据最小显著性差异法(LSD)多重比较的结果可以看出:P2t3I2雨型条件下,4种过程雨型特征指标差异不显著;P1t2I1雨型条件下,各过程雨型特征指标差异显著(P<0.05);P1t2I1雨型条件下,前峰型、后峰型降雨在降雨量上分别与中峰型、均匀型降雨差异显著(P<0.05),前峰型、后峰型降雨小于中峰型、均匀型降雨;在降雨历时上,前峰型、中峰型和后峰型分别与均匀型降雨差异显著(P<0.05),其降雨历时均小于均匀型;从最大30 min雨强来看,前峰型、中峰型和后峰型显著大于均匀型降雨。
表 3 降雨过程雨型特征指标统计
Table 3. Rainfall pattern characteristic index statistics of rainfall process
雨型 过程雨型 P/mm t/h I30/(mm·h−1) 频次 P2t3I2 前峰型 41.50 a 2.75 a 20.90 a 2 中峰型 40.60 a 8.79 a 11.80 a 3 后峰型 42.27 a 8.81 a 12.73 a 3 均匀型 47.95 a 7.45 a 14.30 a 4 P1t2I1 前峰型 6.66 b 0.87 b 5.89 b 17 中峰型 10.82 c 1.75 b 7.92 b 10 后峰型 11.57 c 2.16 b 7.86 b 13 均匀型 6.20 b 3.63 c 2.58 c 24 P3t1I3 前峰型 47.40 1.51 43.80 2 中峰型 - - - - 后峰型 74.80 2.33 50.00 1 均匀型 - - - - 说明:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);−表示 无此类数据 -
根据雨型划分结果,分别统计了不同雨型下的场均径流特征值(表4)。从表4可以看出:3种雨型下的径流深从大到小依次为P3t1I3雨型(0.673 0 mm)、P2t3I2雨型(0.446 0 mm)、P1t2I1雨型(0.222 0 mm);从径流系数来看,从大到小依次为P3t1I3雨型(0.016 0)、P1t2I1雨型(0.014 0)、P2t3I2雨型(0.012 0);从径流深峰值来看,从大到小依次为P3t1I3雨型(0.0372 mm·min−1)、P2t3I2雨型(0.0222 mm·min−1)、P1t2I1雨型(0.0166 mm·min−1);从径流贡献率来看,从大到小依次为P2t3I2雨型(49.98%)、P1t2I1雨型(31.16%)、P3t1I3雨型(18.85%)。
表 4 不同雨型下场均径流特征
Table 4. Characteristics of average runoff in different rainfall types
雨型 径流深/
mm径流系数 径流深峰值/
(mm·min−1)径流贡献率/% P2t3I2 0.446 0 0.012 0 0.022 2 49.98 P1t2I1 0.222 0 0.014 0 0.016 6 31.16 P3t1I3 0.673 0 0.016 0 0.037 2 18.85 综合以上结果可以发现:P3t1I3雨型条件下,场均径流深、径流系数及径流深峰值均最大,初始产流时间最短,说明P3t1I3雨型是3种雨型中最容易发生激烈产流的雨型,其产流迅速且产流量最大。对比P2t3I2、P1t2I1雨型径流深、径流深峰值及径流系数的关系可以得到,P2t3I2雨型条件下虽然可以产生较大的径流量,但其径流系数小于P1t2I1雨型,主要原因是P2t3I2雨型为中雨量长历时降雨,从而导致降水有较多的时间参与入渗,降雨损失比较高且降雨总量较大,导致P2t3I2雨型其径流转化效率低于P1t2I1雨型。P1t2I1雨型虽为研究区发生频次最高的雨型,但该种雨型下径流量最小。对比3种雨型下径流总量占比可以发现:P2t3I2雨型为研究区产流的主要雨型,其径流总量占比接近研究期间总径流量的50%,P1t2I1雨型虽然发生频次最高,但其总径流量小于P2t3I2雨型,P3t1I3雨型具有最大的频次径流量,但发生频次最低,对总径流量的贡献最小。
-
表5可以看出:不同过程雨型下的径流特征值差异明显。从径流深和径流系数来看,从大到小均表现为前峰型、后峰型、中峰型、均匀型。从径流深来看,前峰型降雨分别为中峰型、后峰型及均匀型的2.13、1.35及3.51倍。从径流系数来看,前峰型降雨分别为中峰型、后峰型及均匀型的1.46、1.27及2.42倍。径流深峰值从大到小依次为前峰型、后峰型、中峰型。径流贡献率从大到小依次为前峰型(39.20%)、后峰型(38.67%)、中峰型(18.39%)、均匀型(3.74%)。
表 5 不同过程雨型对径流特征的影响
Table 5. Influence of rainfall patterns in different processes on runoff characteristics
过程雨型 径流深/
mm径流系数 径流深峰值/
(mm·min−1)径流贡献率/% 前峰型 0.484 0 0.016 5 0.0292 39.20 中峰型 0.227 0 0.011 3 0.0132 18.39 后峰型 0.358 0 0.012 9 0.0201 38.67 均匀型 0.138 0 0.006 8 - 3.74 说明:均匀型降雨通常产流较少或不产流,径流量数据为 人工测量,无产流过程。-表示均匀型降雨过程下 产流过程不存在明显的径流深峰值 综合以上结果分析,4种过程雨型对总径流量的贡献率体现为峰值型降雨远大于均匀型降雨,其中前峰型和后峰型降雨其径流贡献率相差不大,均匀型最小。4种过程雨型在场均径流深和径流系数从大到小均体现为前峰型、后峰型、中峰型、均匀型。
-
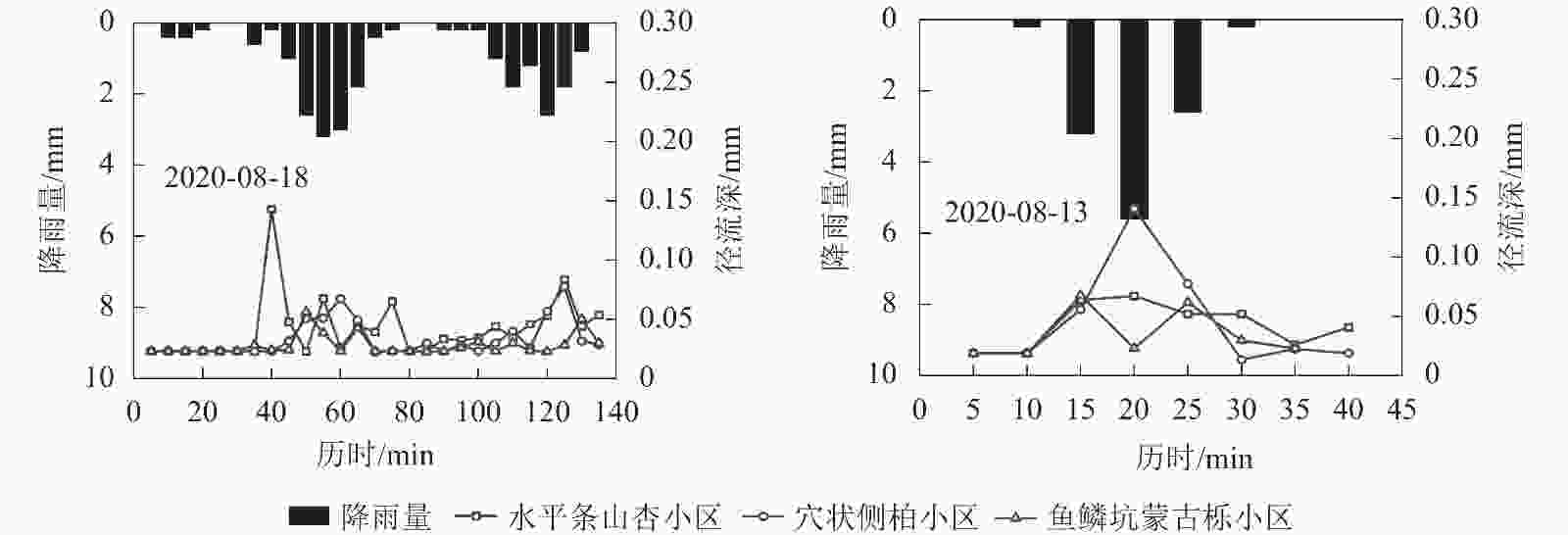
对比2场雨强相近,降雨量不同的典型降雨条件下,3个样地径流过程特征,分析降雨量对径流过程特征的影响。由图3可见:2020年8月18日P为23.8 mm,t为2.23 h,I30为24.00 mm·h−1;2020年8月13日P为11.8 mm,t为0.50 h,I30为23.60 mm·h−1。2场降雨过程雨峰均在降雨中期出现。
对比2场降雨各小区之间的径流特征关系可以发现:2020年8月18日降雨条件下各小区径流深均大于2020年8月13日降雨,后者是前者的近2倍,说明降雨量对径流深的影响较大。降雨量越大,径流深越大。除水平条山杏样地外,2场降雨条件下各小区在径流系数、径流深峰值上均表现为2020年8月13日略大于2020年8月18日。从产流时间及洪峰滞后时间来看,2020年8月18日降雨条件下的值大于2020年8月13日降雨,即2020年8月13日降雨条件下更早产流且径流转化效率更高,这可能与2场降雨历时及雨峰分布情况不同有关。说明降雨量对径流系数、径流深峰值及产流时间等的影响并不明显。不同样地之间,穴状侧柏样地和鱼鳞坑蒙古栎样地径流深及径流系数随降雨量增加变化幅度较小,能够有效减少径流,水平条山杏样地随降雨量增加其径流深及径流系数增加较大。
-
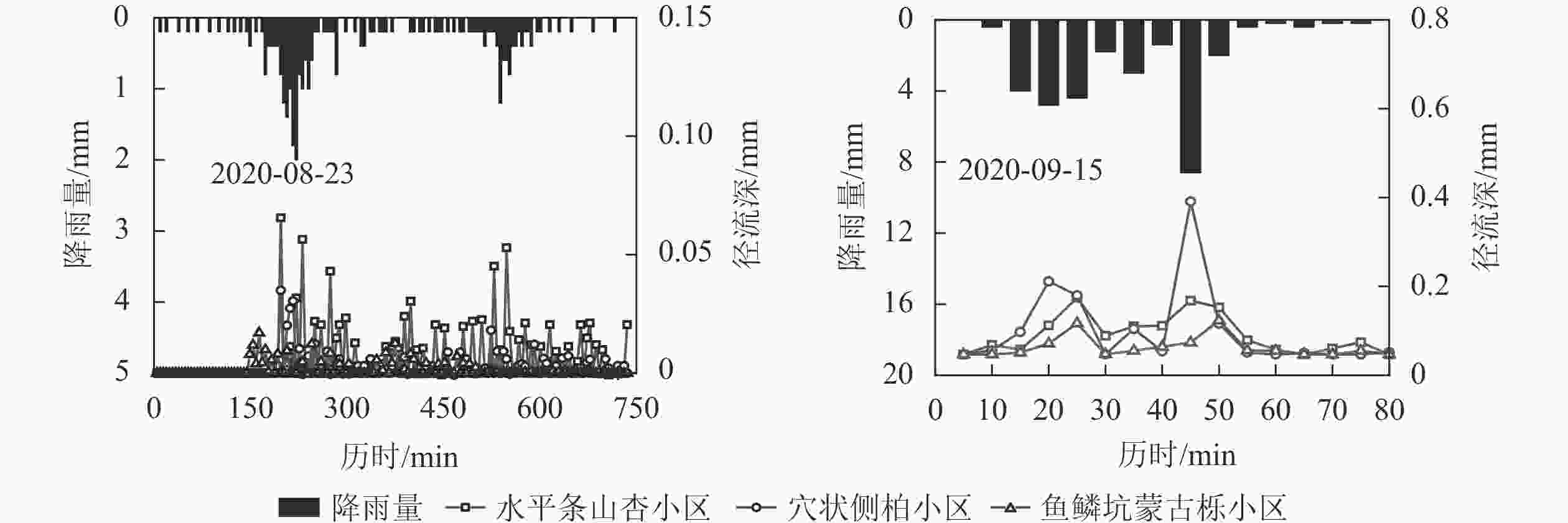
对比2场降雨量接近,雨强不同的典型降雨条件下的各小区的径流过程特征值,分析雨强对径流过程的影响。由图4可见:2020年8月23日P为33.6 mm,t为12.75 h,I30为16.56 mm·h−1,降雨过程存在2次雨峰,较大的雨峰出现在降雨前期;2020年9月15日P为31.8 mm,t为1.33 h,I30为48.00 mm·h−1,雨峰主要集中在降雨前期。
对比以上2场降雨条件下各样地径流特征值可以发现:2020年9月15日降雨条件下,各小区径流深、径流系数及径流深峰值均大于2020年8月23日降雨条件。2020年9月15日降雨条件下,各小区径流深、径流系数及径流深峰值分别为2020年8月23日降雨条件下的1.36~4.37、1.44~4.61及2.06~10.46倍,说明雨强对径流深、径流系数及径流深峰值影响均比较明显,且对径流深峰值的影响大于径流深。从初始产流时间及洪峰滞后时间看,2020年9月15日降雨条件下各小区差异较小,即大雨强条件下,植物措施减流效益不明显,各样地产流时间基本同步。这与张杰豪等[26]认为小雨强下植被措施的保水效果优于大雨强下的保水效果的研究地结论一致。不同样地之间,随雨强增大,径流深、径流系数及径流深峰值增加幅度均较大,尤其以穴状侧柏样地最为明显,说明大雨强条件下穴状侧柏样地减流效果最差。
-
径流过程对降雨雨型特征的敏感性很高[2],建立雨型与径流侵蚀的关系是提高水力侵蚀研究精度的有效途径。本研究以P、t、I30为依据,采用K-均值聚类方法进行雨型一级划分,在此基础上用量纲-曲线法进一步划分了过程雨型,并探讨了不同雨型下的径流特征。本研究采用的雨型划分方法综合考虑了降雨主要数量特征及雨峰位置的影响,为雨型划分提供了新的思路。从研究结果来看,以P3t1I3雨型为大雨量、短历时、大雨强降雨是最容易产流的雨型,同时也是易导致各种山洪灾害的主要雨型,这与前人的研究一致[13-20]。3种雨型下各样地的径流过程差异明显,且随着雨强和降雨量的增大,各样地之间的差异减小,这主要是因为P与I30越大,径流过程受前期含水量、植被措施等的影响就越小[27]。不同过程雨型对径流特征的影响也比较大,总体体现为峰值型降雨径流量大于均值型,这主要是因为峰值型降雨过程增加了径流的紊动,同时雨峰集中时段的降雨相比于均匀型降雨具备更大的降雨动能,其产流能力更强。雨峰集中在降雨前期,前期较大的雨强易迅速击打地表导致林地土壤更容易形成短期的土壤板结,减少了入渗,增加了径流。当阵雨雨期集中在后期时,林地拦蓄作用明显,随着后期雨峰到来及林地拦蓄逐渐饱和开始出现地表径流。而均匀型降雨过程中,不会出现极端雨强,整体雨强较小,雨滴动能较弱,林地拦蓄系统有较多的时间发挥作用,从而导致大部分降水被林冠拦截及补给入渗,产流量极少或不产流[23]。此外,在降雨特征与径流关系上,本研究发现降雨量对径流深的影响较大。这与前人的结论一致[24]。I30对径流深、径流深峰值及径流系数影响均比较明显,且对径流深峰值的影响程度大于径流深,这主要是因为I30决定的产流方式是蓄满产流或超渗产流[17],径流深峰值越大,说明径流过程更加激烈。这符合超渗产流的特点。
-
根据P、t、I30可将研究区降雨划分为3型:P2t3I2雨型(中雨量、长历时、中雨强),P1t2I1雨型(小雨量、中历时、小雨强),P3t1I3雨型(大雨量、短历时、大雨强),其中P1t2I1雨型在研究区发生频次最高,P2t3I2雨型和P1t2I1雨型在降雨总量上占比基本一致,P3t1I3雨型发生频率最低。4种过程雨型的发生频次从大到小依次为均匀型(28次)、前峰型(21次)、后峰型(17次)、中峰型(13次)。
不同雨型下的径流特征差异明显。从单次降雨看,P3t1I3雨型在研究区产流能力最强,P2t3I2雨型次之,P1t2I1雨型最小。从对径流总量的贡献来看,P2t3I2雨型是研究区的主要产流雨型,其产流量占到研究区产流总量的49.98%,P3t1I3雨型最小。
不同过程雨型对径流特征影响较大。从径流总量及场次径流深来看,均表现为峰值型降雨大于均匀型降雨,各峰值的径流总量及场次径流深从大到小依次表现为前峰型、后峰型、中峰型,即降雨量集中在降雨前期最容易产流。降雨量对径流深的影响最大,I30对径流深、径流系数及径流深峰值的影响均比较大,且对径流深峰值的影响要大于对径流深的影响。
Effects of different rainfall patterns on slope runoff characteristics in the upper reaches of Miyun Reservoir
-
摘要:
目的 探讨不同自然降雨雨型对径流过程的影响。 方法 根据降雨数量特征及雨峰集中时间对密云水库上游地区自然降雨进行二级分类,分别探究不同雨型及过程雨型下的径流特征。 结果 ①根据降雨量(P)、降雨历时(t)、最大30 min雨强(I30)可将研究区降雨划分为3类:P2t3I2雨型(中雨量、长历时、中雨强)、P1t2I1雨型(小雨量、中历时、小雨强)、P3t1I3雨型(大雨量、短历时、大雨强),其中,P1t2I1雨型在研究区发生频次最高,占比81.01%。4种过程雨型的发生频次从大到小依次为均匀型、前峰型、后峰型、中峰型。②不同雨型下的径流特征差异明显,从单次降雨看,P3t1I3雨型单次产流能力最强, P2t3I2雨型在研究区的径流贡献率最大。③不同过程雨型对径流特征影响较大,降雨量集中在降雨前期最容易产流。④降雨量对径流深的影响最大,I30对径流深、径流系数及径流深峰值的影响均比较大,且对径流深峰值的影响要大于对径流深的影响。 结论 坡面径流特征对降雨雨型及过程雨型敏感性很高,采用合理的雨型划分方法研究雨型—径流关系可提高水力侵蚀研究精度。图4表5参27 Abstract:Objective The objective is to explore the effects of different natural rainfall patterns on runoff process. Method According to the quantitative characteristics of rainfall and the concentration period of rainfall peaks, the natural rainfall in the upper reaches of Miyun Reservoir was classified into two levels, and the runoff characteristics under different rain patterns and process rain patterns were investigated. Result (1) According to P (precipitation ), t (rainfall duration) and I30 (maximum 30 min rainfall intensity), the rainfall in the study area could be divided into three patterns: P2t3I2 rain (medium rainfall, long duration and medium rainfall intensity), P1t2I1 rain (light rainfall, medium duration and light rainfall intensity) and P3t1I3 rain (heavy rainfall, short duration and heavy rain intensity). P1t2I1 rain pattern had the highest frequency in the study area. The occurrence frequency of the four process rain patterns ranging from large to small was uniform, pre-peak, post-peak, and mid-peak. (2) The runoff characteristics under different rainfall patterns were significantly different. In terms of single rainfall, P3t1I3 had the largest single runoff production capacity, while P2t3I2 had the largest contribution rate to runoff. (3) Rainfall patterns of different processes had significant effects on runoff characteristics, and the rainfall concentrated in the early rainfall period was most likely to produce runoff. (4) Rainfall had the greatest impact on runoff depth. I30 had a great impact on runoff depth, runoff coefficient and runoff depth peak, and the impact on runoff depth peak was greater than that on runoff depth. Conclusion The characteristics of slope runoff are highly sensitive to rainfall patterns and process rainfall patterns. Using reasonable rainfall pattern division method to study the relationship between rainfall patterns and runoff can improve the accuracy of hydraulic erosion research. [Ch, 4 fig. 5 tab. 27 ref.] -
Key words:
- rain pattern division /
- runoff process /
- cluster analysis /
- rainfall characteristics
-
表 1 样地基本情况表
Table 1. Basic situation of the plots
小区名称 植被盖度/
%小区规格
(m×m)坡度/
(°)整地措施 水平条山杏小区 84.49 20×5 23 大水平条 穴状侧柏小区 100.00 20×5 20 穴状 鱼鳞坑蒙古栎小区 88.32 20×5 25 鱼鳞坑 说明:山杏Armeniaca sibirica、侧柏Platycladus orientalis、 蒙古栎Quercus mongolica 表 2 不同雨型的降雨特征
Table 2. Rainfall characteristics of different rain types
雨型 项目 特征变量 频次 比例/% P/mm t/h I30/(mm·h−1) P2t3I2 (中雨量、长历时、中雨强) 累计值 523.40 88.09 345.20 12 15.19 均值 43.62 7.34 28.76 范围 27.20~68.20 1.01~15.25 16.40~52.00 P1t2I1 (小雨量、中历时、小雨强) 累计值 520.60 147.54 686.80 64 81.01 均值 8.13 2.31 10.74 范围 1.80~23.80 0.17~9.03 1.60~38.80 P3t1I3 (大雨量、短历时、大雨强) 累计值 169.60 5.34 275.20 3 3.80 均值 56.53 1.78 91.74 范围 41.20~74.80 0.68~2.33 69.20~106.00 表 3 降雨过程雨型特征指标统计
Table 3. Rainfall pattern characteristic index statistics of rainfall process
雨型 过程雨型 P/mm t/h I30/(mm·h−1) 频次 P2t3I2 前峰型 41.50 a 2.75 a 20.90 a 2 中峰型 40.60 a 8.79 a 11.80 a 3 后峰型 42.27 a 8.81 a 12.73 a 3 均匀型 47.95 a 7.45 a 14.30 a 4 P1t2I1 前峰型 6.66 b 0.87 b 5.89 b 17 中峰型 10.82 c 1.75 b 7.92 b 10 后峰型 11.57 c 2.16 b 7.86 b 13 均匀型 6.20 b 3.63 c 2.58 c 24 P3t1I3 前峰型 47.40 1.51 43.80 2 中峰型 - - - - 后峰型 74.80 2.33 50.00 1 均匀型 - - - - 说明:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);−表示 无此类数据 表 4 不同雨型下场均径流特征
Table 4. Characteristics of average runoff in different rainfall types
雨型 径流深/
mm径流系数 径流深峰值/
(mm·min−1)径流贡献率/% P2t3I2 0.446 0 0.012 0 0.022 2 49.98 P1t2I1 0.222 0 0.014 0 0.016 6 31.16 P3t1I3 0.673 0 0.016 0 0.037 2 18.85 表 5 不同过程雨型对径流特征的影响
Table 5. Influence of rainfall patterns in different processes on runoff characteristics
过程雨型 径流深/
mm径流系数 径流深峰值/
(mm·min−1)径流贡献率/% 前峰型 0.484 0 0.016 5 0.0292 39.20 中峰型 0.227 0 0.011 3 0.0132 18.39 后峰型 0.358 0 0.012 9 0.0201 38.67 均匀型 0.138 0 0.006 8 - 3.74 说明:均匀型降雨通常产流较少或不产流,径流量数据为 人工测量,无产流过程。-表示均匀型降雨过程下 产流过程不存在明显的径流深峰值 -
[1] 史志华, 刘前进, 张含玉, 等. 近10年土壤侵蚀与水土保持研究进展与展望[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(5): 1117 − 1127. SHI Zhihua, LIU Qianjin, ZHANG Hanyu, et al. Study on soil erosion and conservation in the past 10 years: progress and prospects [J]. Acta Pedol Sin, 2020, 57(5): 1117 − 1127. [2] EWEA H, ELFEKI A M, BAHRAWI J, et al. Sensitivity analysis of runoff hydrographs due to temporal rainfall patterns in Makkah Al-Mukkramah region, Saudi Arabia[J/OL]. Arabian J Geosci, 2016, 9(5): 424[2021-06-10]. doi:10.1007/s12517-016-2443-5. [3] 张杰, 谢颂华, 莫明浩, 等. 不同自然降雨雨型下红壤坡地地表径流和壤中流输出特征[J]. 水电能源科学, 2017, 35(7): 18 − 21. ZHANG Jie, XIE Songhua, MO Minghao, et al. Characteristics of surface runoff and interflow output on red-soil slope under different rainfall patterns of natural rainfall conditions [J]. Water Resour Power, 2017, 35(7): 18 − 21. [4] 周大淜. 川中紫色土丘陵区侵蚀性降雨及侵蚀特征研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2010. ZHOU Dapeng. Study on Characteristics of Erosive Rainfall and Erosion of Hilly Region of Purple Soil in Central Sichuan Province [D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2010. [5] 潘欣, 王玉杰, 张会兰, 等. 官厅水库上游典型植物措施特性及在侵蚀性降雨下的水沙效应分析[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(7): 76 − 84. PAN Xin, WANG Yujie, ZHANG Huilan, et al. Runoff and sediment effects in erosive rainfall of typical plant conservation practice in the upper reach of Guanting Reservoir, Beijing [J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2015, 37(7): 76 − 84. [6] 王改玲, 王青杵, 石生新. 晋北黄土区降雨特征及其对坡地土壤侵蚀的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(1): 1 − 5. WANG Gailing, WANG Qingchu, SHI Shengxin. Rainfall characters and its effect on loess slopeland erosion in Northern Shanxi Province [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2013, 27(1): 1 − 5. [7] ALAVINIA M, SALEH F N, ASADI H. Effects of rainfall patterns on runoff and rainfall-induced erosion [J]. Int J Sediment Res, 2018, 34(3): 270 − 278. [8] NG C W W, WANG B, TUNG Y K. Three-dimensional numerical investigations of groundwater responses in an unsaturated slope subjected to various rainfall patterns [J]. Can Geotech J, 2001, 38(5): 1049 − 1062. [9] RAN Qihua, WANG Feng, GAO Jihui. Modelling effects of rainfall patterns on runoff generation and soil erosion processes on slopes[J/OL]. Water, 2019, 11(11): 2221[2021-06-10]. doi: 10.3390/w11112221. [10] 安娟, 于妍, 吴元芝. 降雨类型对褐土横垄坡面土壤侵蚀过程的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(24): 150 − 156. AN Juan, YU Yan, WU Yuanzhi. Effects of rainfall patterns on hillslope soil erosion process of cinnamon soil in contour ridge system [J]. Trans Chin So Agric Eng, 2017, 33(24): 150 − 156. [11] 郑粉莉, 边锋, 卢嘉, 等. 雨型对东北典型黑土区顺坡垄作坡面土壤侵蚀的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(2): 90 − 97. ZHENG Fenli, BIAN Feng, LU Jia, et al. Effects of rainfall patterns on hillslope erosion with longitudinal ridge in typical black soil region of Northeast China [J]. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach, 2016, 47(2): 90 − 97. [12] 黎俊佑, 马岚, 刘京晶, 等. 雨型对华北土石山区坡面土壤侵蚀的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(4): 1 − 6. LI Junyou, MA Lan, LIU Jingjing, et al. Effects of rainfall patterns on slope soil erosion in the rocky mountain area of North China [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2020, 34(4): 1 − 6. [13] DUAN Jian, YANG Jie, TANG Chongjun, et al. Effects of rainfall patterns and land cover on the subsurface flow generation of sloping ferralsols in southern China[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(8): e0182706[2021-06-10]. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182706. [14] 朱楠, 张会兰, 马超, 等. 北京延庆县雨型和坡面措施对水沙及污染物的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(12): 3509 − 3517. ZHU Nan, ZHANG Huilan, MA Chao, et al. Runoff/sediment yield and pollutant characteristics under varying rainfall types and slope measures in Yanqing County in Beijing [J]. Chin J Ecol, 2015, 34(12): 3509 − 3517. [15] 王帅兵, 宋娅丽, 王克勤, 等. 不同雨型下反坡台阶减少红壤坡耕地氮磷流失的效果[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(13): 160 − 169. WANG Shuaibing, SONG Yali, WANG Keqin, et al. Effects of reverse-slope terrace on nitrogen and phosphorus loss in sloping farmland of red loam under different rainfall pattens [J]. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng, 2018, 34(13): 160 − 169. [16] 马星, 郑江坤, 王文武, 等. 不同雨型下紫色土区坡耕地产流产沙特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(2): 17 − 21. MA Xing, ZHENG Jiangkun, WANG Wenwu, et al. Characteristics of the runoff and sediment yield of sloping farmland in the purple soil area under different rainfall patterns [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2017, 31(2): 17 − 21. [17] 高磊, 饶良懿, 崔飞波, 等. 太行山土石山区侵蚀性降雨对典型植物措施产流产沙的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(1): 5 − 11. GAO Lei, RAO Liangyi, CUI Feibo, et al. Effect of erosive rainfall on runoff and sediment yield of typical plant measures in rocky mountain areas of Taihang [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2017, 31(1): 5 − 11. [18] 谭顺菊, 高华端, 代裕. 羊鸡冲小流域主要雨型对砂页岩坡耕地土壤侵蚀的影响[J]. 中国水土保持, 2016(4): 44 − 47, 77. TAN Shunju, GAO Huaduan, DAI Yu. Influence of main rainfall patterns of Yangjichong small watershed to soil erosion of arenaceous shale sloping farmland [J]. Soil Water Conserv China, 2016(4): 44 − 47, 77. [19] 黄凯, 李瑞, 李勇, 等. 贵州省黔南区不同侵蚀性雨型条件下生物措施对坡面产流产沙的响应[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(6): 14 − 21. HUANG Kai, LI Rui, LI Yong, et al. Response of runoff and sediment yield to biological measures on slopes under different erosive rain patterns in southern Guizhou [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2020, 34(6): 14 − 21. [20] 杜波, 唐丽霞, 潘佑静, 等. 贵州喀斯特地区侵蚀性次降雨产流产沙特征研究[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2016, 36(5): 111 − 117. DU Bo, TANG Lixia, PAN Youjing, et al. Study on the characteristics of single erosive rainfall and runoff and sediment yield in karst area of Guizhou [J]. J Southwest For Univ, 2016, 36(5): 111 − 117. [21] WANG Wenting, YIN Suiqing, XIE Yun, et al. Effects of four storm patterns on soil loss from five soils under natural rainfall [J]. Catena, 2016, 141: 56 − 65. [22] A Yinglan, WANG Guoqiang, SUN Wenchao, et al. Stratification response of soil water content during rainfall events under different rainfall patterns [J]. Hydrol Proc, 2018, 32(20): 1 − 12. [23] 邬铃莉, 王云琦, 王晨沣, 等. 降雨类型对北方土石山区坡面土壤侵蚀的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(24): 157 − 164. WU Lingli, WANG Yunqi, WANG Chenfeng, et al. Effect of rainfall patterms on hillslope soil erosion in rocky mountain area of north China [J]. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng, 2017, 33(24): 157 − 164. [24] 杨云斌, 张建军, 李梁, 等. 晋西黄土区降雨过程对小流域产流的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(3): 105 − 114. YANG Yunbin, ZHANG Jianjun, LI Liang, et al. Effects of rainfall process on runoff in small watersheds in the Loess Plateau of western Shanxi Province, Northern China [J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2019, 41(3): 105 − 114. [25] 马京津, 宋丽莉, 张晓婧. 对2种不同取样方法Pilgrim&Cordery设计雨型的比较研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2016, 35(3): 220 − 226. MA Jingjin, SONG Lili, ZHANG Xiaojing. The comparison of two different sampling schemes on design storm pattern by the Pilgrim&Cordery [J]. Torrential Rain Disasters, 2016, 35(3): 220 − 226. [26] 张杰豪, 梁心蓝, 黄洪粮, 等. 不同耕作措施对花生结荚期产流产沙过程的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(1): 71 − 78. ZHANG Jiehao, LIANG Xinlan, HUANG Hongliang, et al. Effects of different tillage practices on the yield of runoff and sediment in peanut podding stage [J]. J Soil Water Conserv, 2021, 35(1): 71 − 78. [27] 韩勇. 侵蚀性降雨雨型对黄土区浅沟坡面侵蚀特征的影响[D]. 北京: 中国科学院, 2016. HAN Yong. Effects of Rainfall Regime on Soil and Water Loss at Loessial Hillslope with Ephemeral Gully[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016. -

-
链接本文:
https://zlxb.zafu.edu.cn/article/doi/10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210429







 下载:
下载: