2014 Vol. 31, No. 3
2014, 31(3): 329-335.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.001
Abstract:
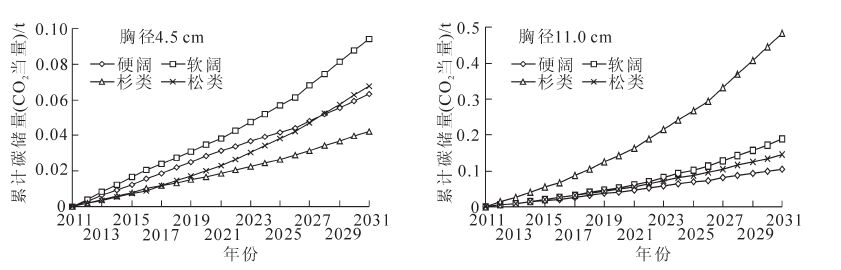
In the context of global climate change, forest carbon sequestration has become one of important measures of international mitigation of climate warming. With the development of carbon sequestration afforestation,forest carbon sequestration measurement has drawn more and more international attention. According to the Guidelines for Carbon Accounting and Monitoring in the Afforestation Projects ,carbon sequestration afforestation and carbon sequestration measures were carried out in the highway interchange hub area in Jiaxing City,Zhejiang Province,and the accounting period would last from 2011 to 2031. The result indicated that the project was a carbon source in 2011,the cumulative amount of net carbon sequestration being -81.59 t(CO2 equivalent,i.e.,CO2e). It became a carbon sequestration from 2012 and the cumulative amount of net carbon sequestration was 1 747.84 t(CO2e). The cumulative amount of net carbon sequestration would reach 11 396.84 t(CO2e) in 2017. By 2031,the cumulative amount of net carbon sequestration would reach 45 886.07 t(CO2e),the average annual net carbon sequestration would be 2 294.30 t(CO2e),and the oxygen emission would be 2 031.00 t. It would have huge carbon sequestration potentials and significant ecological benefits.
In the context of global climate change, forest carbon sequestration has become one of important measures of international mitigation of climate warming. With the development of carbon sequestration afforestation,forest carbon sequestration measurement has drawn more and more international attention. According to the Guidelines for Carbon Accounting and Monitoring in the Afforestation Projects ,carbon sequestration afforestation and carbon sequestration measures were carried out in the highway interchange hub area in Jiaxing City,Zhejiang Province,and the accounting period would last from 2011 to 2031. The result indicated that the project was a carbon source in 2011,the cumulative amount of net carbon sequestration being -81.59 t(CO2 equivalent,i.e.,CO2e). It became a carbon sequestration from 2012 and the cumulative amount of net carbon sequestration was 1 747.84 t(CO2e). The cumulative amount of net carbon sequestration would reach 11 396.84 t(CO2e) in 2017. By 2031,the cumulative amount of net carbon sequestration would reach 45 886.07 t(CO2e),the average annual net carbon sequestration would be 2 294.30 t(CO2e),and the oxygen emission would be 2 031.00 t. It would have huge carbon sequestration potentials and significant ecological benefits.
2014, 31(3): 336-342.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.002
Abstract:
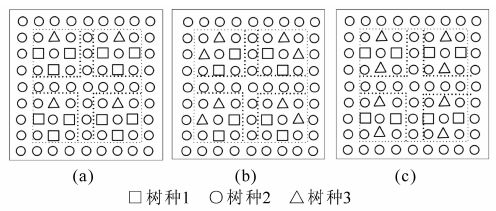
Mingling is an important spatial structure to describe the degree of segregation in mixed forests. Due to ignore the spatial distribution of trees around the object tree,traditional mingling, species diversity mingling and the tree species segregation index may have an equal mingling in mixed forests with different mixed degree. Complete mingling has not accurately described a fully mixed forest when there are few adjacent trees in a unit. Thus,mingling research for an entire mixed forest as well as a mingling index for comparison of different mixed forests was problematic. To surmount these obstacles,an improved mingling index was proposed based on two factors:1)species spatial structure characteristics together with species diversity,and 2)the influence of tree species types and distribution differences within a unit. Comparative analyses of different mingling indices were carried out based on typical mixed forests in theory and different mixed degree's field data in Mount Tianmu. The results show:1)the improving mingling has different mingling for the mixed degree of different forest;and 2)it can describe forest mingling of mixed forests which have low mixed degree more accurately. So it is an available mixed forests spatial structure index.
Mingling is an important spatial structure to describe the degree of segregation in mixed forests. Due to ignore the spatial distribution of trees around the object tree,traditional mingling, species diversity mingling and the tree species segregation index may have an equal mingling in mixed forests with different mixed degree. Complete mingling has not accurately described a fully mixed forest when there are few adjacent trees in a unit. Thus,mingling research for an entire mixed forest as well as a mingling index for comparison of different mixed forests was problematic. To surmount these obstacles,an improved mingling index was proposed based on two factors:1)species spatial structure characteristics together with species diversity,and 2)the influence of tree species types and distribution differences within a unit. Comparative analyses of different mingling indices were carried out based on typical mixed forests in theory and different mixed degree's field data in Mount Tianmu. The results show:1)the improving mingling has different mingling for the mixed degree of different forest;and 2)it can describe forest mingling of mixed forests which have low mixed degree more accurately. So it is an available mixed forests spatial structure index.
2014, 31(3): 343-351.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.003
Abstract:
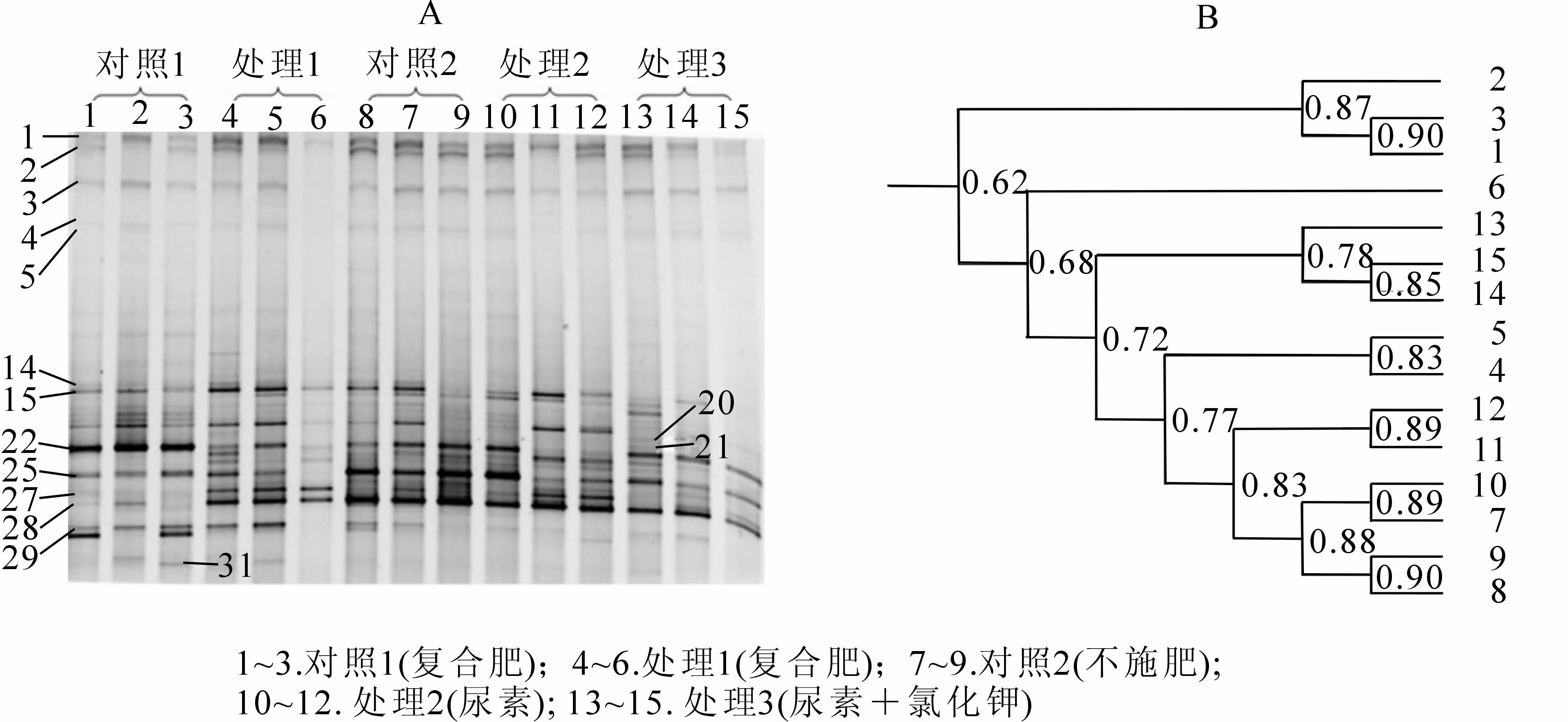
For intensive management of Phyllostachys violascens stands, heavy winter mulching, to increase soil temperature, and winter fertilization are widely used techniques which affect the activity of soil ammonia oxidizing organisms. To understand the effects of mulch and fertilization on ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB)and ammonia oxidizing archaea(AOA)communities, two experiments were conducted:1)with a constant N fertilizer rate of 360 kg·hm-2 applied as m(N):m(P2O5):m(K2O)=16:16:16 and treatments(Tr) with mulch (Tr1)and no mulch(ck1);and 2) with mulch in each treatment and ck,three fertilizer combinations at a constant N rate of 360 kg·hm-2[Tr1(as above)——applied as a compound fertilizer,Treatment 2(Tr2)——applied N as urea,Treatment 3(Tr3)——applied fertilizer as urea and potassium chloride(KCl),and ck2——no fertilizer applied]. The community structure and functional gene abundance of soil AOB and AOA were measured using polymerase chain reaction——denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis(PCR-DGGE) and real-time——polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with the Shannon diversity index being used for analysis. Results showed a majority of common AOB and AOA species represented by bands on DEEG profile were produced from the all treatments. The AOB community structure with no mulch(ck1) was different from the other treatments which received mulch in the winter season, and Tr3 was different from the other mulched treatments. The Shannon diversity index for AOB species with Tr1 was significantly higher(P<0.05)than Tr3. The higher (P<0.05)amoA abundance for both AOB and AOA was observed in Tr3. Results from the combination of PCR-DGGE and RT-PCR for both AOA and AOB, showed Tr3 best in species diversity and gene abundance of ammonia oxidizing organisms;whereas,Tr2 was worst. Thus,to sustain the activity of ammonia oxidizing organisms and to improve N recycling,urea in combination with KCl should be applied.
For intensive management of Phyllostachys violascens stands, heavy winter mulching, to increase soil temperature, and winter fertilization are widely used techniques which affect the activity of soil ammonia oxidizing organisms. To understand the effects of mulch and fertilization on ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB)and ammonia oxidizing archaea(AOA)communities, two experiments were conducted:1)with a constant N fertilizer rate of 360 kg·hm-2 applied as m(N):m(P2O5):m(K2O)=16:16:16 and treatments(Tr) with mulch (Tr1)and no mulch(ck1);and 2) with mulch in each treatment and ck,three fertilizer combinations at a constant N rate of 360 kg·hm-2[Tr1(as above)——applied as a compound fertilizer,Treatment 2(Tr2)——applied N as urea,Treatment 3(Tr3)——applied fertilizer as urea and potassium chloride(KCl),and ck2——no fertilizer applied]. The community structure and functional gene abundance of soil AOB and AOA were measured using polymerase chain reaction——denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis(PCR-DGGE) and real-time——polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with the Shannon diversity index being used for analysis. Results showed a majority of common AOB and AOA species represented by bands on DEEG profile were produced from the all treatments. The AOB community structure with no mulch(ck1) was different from the other treatments which received mulch in the winter season, and Tr3 was different from the other mulched treatments. The Shannon diversity index for AOB species with Tr1 was significantly higher(P<0.05)than Tr3. The higher (P<0.05)amoA abundance for both AOB and AOA was observed in Tr3. Results from the combination of PCR-DGGE and RT-PCR for both AOA and AOB, showed Tr3 best in species diversity and gene abundance of ammonia oxidizing organisms;whereas,Tr2 was worst. Thus,to sustain the activity of ammonia oxidizing organisms and to improve N recycling,urea in combination with KCl should be applied.
2014, 31(3): 352-357.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.004
Abstract:
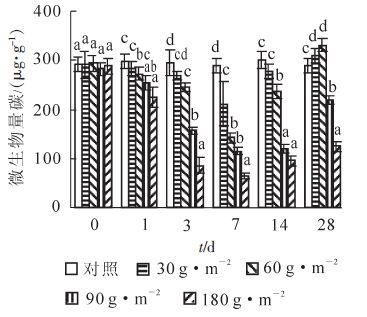
To study the effect of CaCN2 on soil microbial biomass carbon, the ratio of fungal to bacterial biomass,and soil enzyme activities,and to determine the optimum rate of calcium cyanamide(CaCN2)use in Phyllostachys violascens stands with intensive management,an experiment with a randomized complete block design was established. Soil CaCN2 treatments were 0(control),30,60,90,and 180 g·m-2,each with three replicates. Soil samples were taken 1,3,7,14,and 28 d after CaCN2 application. One-way ANOVA with Duncan's multiple range test was used to compare the difference between samples, and statistical significance was determined at the 5% level(P<0.05). Results indicated that the 90 and 180 g·m-2 CaCN2 treatments had significantly lower(P<0.05) soil microbial biomass. Other treatments were inhibited in the short term, but recovered gradually. Compared with bacteria, fungi were more sensitive to CaCN2 with the ratio of fungal to bacterial biomass decreasing significantly(P<0.05)as the CaCN2 rates increased. As with soil microbial biomass,CaCN2 also inhibited soil enzyme activities. Compared to the control, 28 d after application of CaCN2,soil dehydrogenase,urease,and invertase activities in each treatment were significantly higher(P<0.05);however, phosphatase activity showed no significant differences. Since low dose of CaCN2(30 g·m-2)had only a short-term effect on soil microbial properties and a high dose(180 g·m-2)had a strong influence,application of 60-90 g·m-2(CaCN2) should be recommended in bamboo stands.
To study the effect of CaCN2 on soil microbial biomass carbon, the ratio of fungal to bacterial biomass,and soil enzyme activities,and to determine the optimum rate of calcium cyanamide(CaCN2)use in Phyllostachys violascens stands with intensive management,an experiment with a randomized complete block design was established. Soil CaCN2 treatments were 0(control),30,60,90,and 180 g·m-2,each with three replicates. Soil samples were taken 1,3,7,14,and 28 d after CaCN2 application. One-way ANOVA with Duncan's multiple range test was used to compare the difference between samples, and statistical significance was determined at the 5% level(P<0.05). Results indicated that the 90 and 180 g·m-2 CaCN2 treatments had significantly lower(P<0.05) soil microbial biomass. Other treatments were inhibited in the short term, but recovered gradually. Compared with bacteria, fungi were more sensitive to CaCN2 with the ratio of fungal to bacterial biomass decreasing significantly(P<0.05)as the CaCN2 rates increased. As with soil microbial biomass,CaCN2 also inhibited soil enzyme activities. Compared to the control, 28 d after application of CaCN2,soil dehydrogenase,urease,and invertase activities in each treatment were significantly higher(P<0.05);however, phosphatase activity showed no significant differences. Since low dose of CaCN2(30 g·m-2)had only a short-term effect on soil microbial properties and a high dose(180 g·m-2)had a strong influence,application of 60-90 g·m-2(CaCN2) should be recommended in bamboo stands.
2014, 31(3): 358-365.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.005
Abstract:
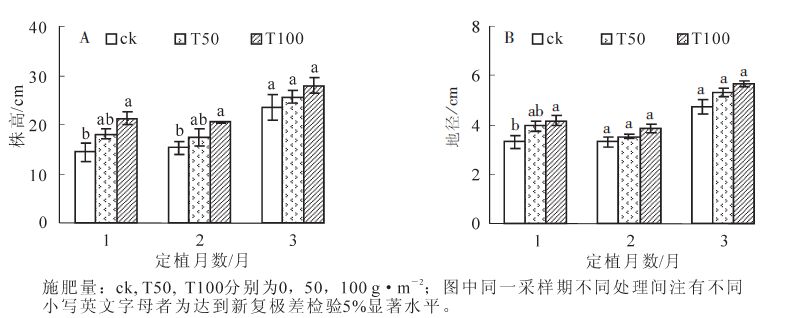
A field experiment was conducted on nursery land of Zhoushan Forestry Academy in 2012 to compare three fertilizer treatments:no fertilizer (ck),a normal rate with 50 g·m-2 of 15-15-15 compound fertilizer (T50), and twice the normal rate(T100),on growth, nutrient uptake and utilization of Cinnamomum japonicum var. chenii seedlings. Results showed that sapling growth of root and stem biomass as well as height and ground diameter significantly increased with increasing rate of fertilizer(P<0.05). Increasing the rate of fertilizer also significantly increased(P<0.05)nutrient concentrations in leaves and nutrient uptake by the plants. By contrast, both nutrient use efficiency and fertilization efficiency decreased significantly (P<0.05) with increasing fertilizer rate,being the same order in T50 and T100:N >P >K. By the end of the experiment,soil available nutrient levels of T50 remained similar to the initial ones;whereas,T100 caused K increased,and ck caused K depleted. For the survival rate, T50 resulted optimal nutrient status in the plants, which was best for transplanting, but T100 induced luxury nutrient supply. Therefore, the optimum fertilizer rate for C. japonicum var. chenii was 50-100 g·m-2.
A field experiment was conducted on nursery land of Zhoushan Forestry Academy in 2012 to compare three fertilizer treatments:no fertilizer (ck),a normal rate with 50 g·m-2 of 15-15-15 compound fertilizer (T50), and twice the normal rate(T100),on growth, nutrient uptake and utilization of Cinnamomum japonicum var. chenii seedlings. Results showed that sapling growth of root and stem biomass as well as height and ground diameter significantly increased with increasing rate of fertilizer(P<0.05). Increasing the rate of fertilizer also significantly increased(P<0.05)nutrient concentrations in leaves and nutrient uptake by the plants. By contrast, both nutrient use efficiency and fertilization efficiency decreased significantly (P<0.05) with increasing fertilizer rate,being the same order in T50 and T100:N >P >K. By the end of the experiment,soil available nutrient levels of T50 remained similar to the initial ones;whereas,T100 caused K increased,and ck caused K depleted. For the survival rate, T50 resulted optimal nutrient status in the plants, which was best for transplanting, but T100 induced luxury nutrient supply. Therefore, the optimum fertilizer rate for C. japonicum var. chenii was 50-100 g·m-2.
2014, 31(3): 366-372.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.006
Abstract:
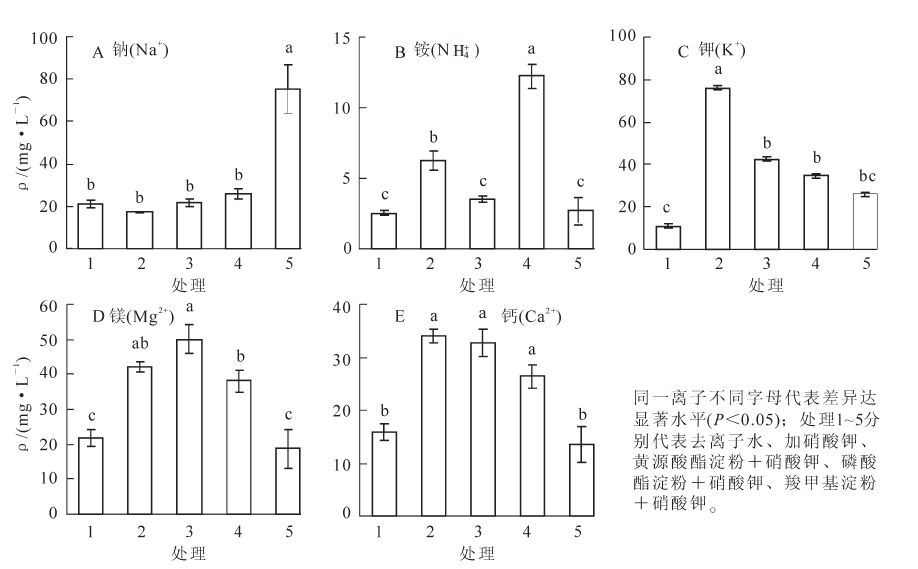
Nutrient loss reduction is the most effective and economical method to control non-point source pollution. To find modified starches with favorable absorption of nutrient ions from the soil,two absorbing experiments for a negative charge,anionic starch were conducted. In the first experiment,potassium nitrate solutions were supplied as the nutrient solution and the adsorption effect of three starches:carboxymethyl,phosphate ester,and xanthate,were evaluated. In the second experiment a solution of ammonium chloride was used as the nutrient solution and because of a high sodium ion content in the carboxymethyl starch,the xanthate anion starch was used as the adsorption material for simulation tests such as fertilization,natural drying,and leaching to determine the starch's adsorption effect. Results showed that the tested anionic starches adsorbed nutrient ions well with carboxymethyl> phosphate ester> xanthate. The first experiment showed that when potassium nitrate was supplied as the nutrient solution,the xanthate anion starch had strong adsorption effects with sodium,potassium,calcium,and magnesium;however,in the second experiment when ammonium chloride was used as the nutrient solution there was favorable adsorption with sodium,potassium,and ammonium ions but not calcium and magnesium ions. Thus,although the kinds of nutrient solutions used to test the starches affected adsorption,a high degree of substitution was possible with xanthate starch being an ideal adsorbent without potential risk,and the phosphate ester starch could be an ideal adsorbent in semiarid regions without risk of ammonium ions leaching.
Nutrient loss reduction is the most effective and economical method to control non-point source pollution. To find modified starches with favorable absorption of nutrient ions from the soil,two absorbing experiments for a negative charge,anionic starch were conducted. In the first experiment,potassium nitrate solutions were supplied as the nutrient solution and the adsorption effect of three starches:carboxymethyl,phosphate ester,and xanthate,were evaluated. In the second experiment a solution of ammonium chloride was used as the nutrient solution and because of a high sodium ion content in the carboxymethyl starch,the xanthate anion starch was used as the adsorption material for simulation tests such as fertilization,natural drying,and leaching to determine the starch's adsorption effect. Results showed that the tested anionic starches adsorbed nutrient ions well with carboxymethyl> phosphate ester> xanthate. The first experiment showed that when potassium nitrate was supplied as the nutrient solution,the xanthate anion starch had strong adsorption effects with sodium,potassium,calcium,and magnesium;however,in the second experiment when ammonium chloride was used as the nutrient solution there was favorable adsorption with sodium,potassium,and ammonium ions but not calcium and magnesium ions. Thus,although the kinds of nutrient solutions used to test the starches affected adsorption,a high degree of substitution was possible with xanthate starch being an ideal adsorbent without potential risk,and the phosphate ester starch could be an ideal adsorbent in semiarid regions without risk of ammonium ions leaching.
2014, 31(3): 373-379.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.007
Abstract:
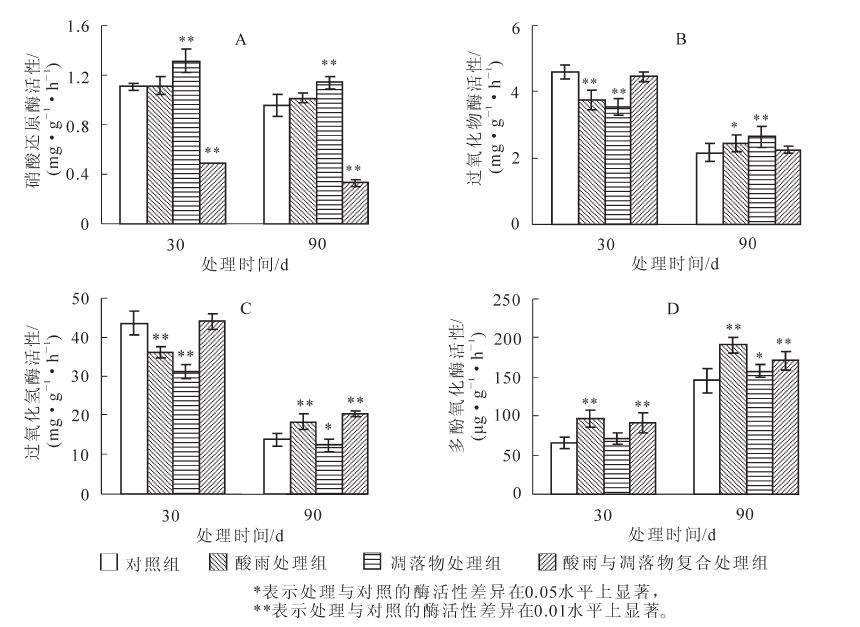
To determine the effects of acid rain and litter on enzyme activities of Cryptomeria forestry soils on Mount Tianmu,rhizosphere soil from Cryptomeria fortunei seedlings was treated with Tr1:simulated acid rain(pH 4.0),Tr2:litter(500 g·m-2),and Tr3:Tr1 and Tr2 combined,to determine soil oxidoreductase and hydrolase activities in rhizosphere soil after short-term(30 d) and a long-term(90 d) processing. Results showed that for soil nitrate reductase activity,Tr1 had no significant effect,but Tr2 significantly increased(P<0.01)and Tr3 significantly reduced(P<0.01)activity. All three treatments significantly improved soil polyphenol oxidase activity(P<0.05). For soil peroxidase activity,Tr3 had no significant effect,but Tr1 and Tr2 were inhibited after 30 d and promoted after 90 d(P<0.05). For soil catalase enzyme activity,Tr2 inhibited and Tr3 promoted activity(P<0.01). Soil urease activity after 30 d was highly significant(P<0.01) for all three treatments. Soil acid phosphatase activity significantly decreased(P<0.05) with Tr1 as well as with Tr2 and Tr3 over 90 d(P<0.05). Soil protease activity was inhibited with Tr3 for 90 d(P<0.05) and with Tr1 and Tr2(P<0.05). Tr1 after 90 d inhibited(P<0.05) soil invertase activity, but after 30 d Tr2 and Tr3 had a catalytic role on soil invertase activity(P<0.05). Thus,long term coexistence of acid rain and woodland litter were able to mitigate,except for protease,the adverse effects of each other on soil enzyme activities,and contributed to improved soil conditions.
To determine the effects of acid rain and litter on enzyme activities of Cryptomeria forestry soils on Mount Tianmu,rhizosphere soil from Cryptomeria fortunei seedlings was treated with Tr1:simulated acid rain(pH 4.0),Tr2:litter(500 g·m-2),and Tr3:Tr1 and Tr2 combined,to determine soil oxidoreductase and hydrolase activities in rhizosphere soil after short-term(30 d) and a long-term(90 d) processing. Results showed that for soil nitrate reductase activity,Tr1 had no significant effect,but Tr2 significantly increased(P<0.01)and Tr3 significantly reduced(P<0.01)activity. All three treatments significantly improved soil polyphenol oxidase activity(P<0.05). For soil peroxidase activity,Tr3 had no significant effect,but Tr1 and Tr2 were inhibited after 30 d and promoted after 90 d(P<0.05). For soil catalase enzyme activity,Tr2 inhibited and Tr3 promoted activity(P<0.01). Soil urease activity after 30 d was highly significant(P<0.01) for all three treatments. Soil acid phosphatase activity significantly decreased(P<0.05) with Tr1 as well as with Tr2 and Tr3 over 90 d(P<0.05). Soil protease activity was inhibited with Tr3 for 90 d(P<0.05) and with Tr1 and Tr2(P<0.05). Tr1 after 90 d inhibited(P<0.05) soil invertase activity, but after 30 d Tr2 and Tr3 had a catalytic role on soil invertase activity(P<0.05). Thus,long term coexistence of acid rain and woodland litter were able to mitigate,except for protease,the adverse effects of each other on soil enzyme activities,and contributed to improved soil conditions.
2014, 31(3): 380-385.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.008
Abstract:
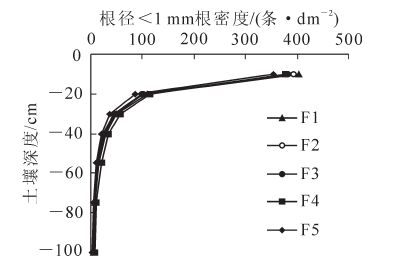
In recent years,widespread death has occurred at the largest Asian artificial Sea Buckthorn(Hippophae rhamnoides)forest in Jianping,Liaoning. To evaluate the effects of Sea Buckthorn degradation on soil loss,the death rates of Sea Buckthorn were determined using standard plot methods with five treatments and three replications. Moreover,soil root density and soil anti-scouring capability were measured on site with soil profile methods and soil anti-scouring instruments,respectively. Results showed that soil root density for a root diameter less than 1 mm decreased at P<0.05 with an increase of soil depth within the 0-30 cm limit with 72%-80% in 0-20 cm. With a rise in the Sea Buckthorn death rate,the root density decreased significantly at P<0.05,and with an increase of soil depth, the soil anti-scouring capability decreased significantly at P<0.05. The relationship between soil anti-scouring capability and root density were fitted to power functions y=xb. The decrease of root density and soil anti-scouring capability meant damage of soil texture. Conversely,this will accelerate death rate of Sea Buckthorn,and vicious cycle format. Thus, effective measures,such as replanting shrubs,should be taken to reduce the harmful ecological effects of Sea Buckthorn degradation.
In recent years,widespread death has occurred at the largest Asian artificial Sea Buckthorn(Hippophae rhamnoides)forest in Jianping,Liaoning. To evaluate the effects of Sea Buckthorn degradation on soil loss,the death rates of Sea Buckthorn were determined using standard plot methods with five treatments and three replications. Moreover,soil root density and soil anti-scouring capability were measured on site with soil profile methods and soil anti-scouring instruments,respectively. Results showed that soil root density for a root diameter less than 1 mm decreased at P<0.05 with an increase of soil depth within the 0-30 cm limit with 72%-80% in 0-20 cm. With a rise in the Sea Buckthorn death rate,the root density decreased significantly at P<0.05,and with an increase of soil depth, the soil anti-scouring capability decreased significantly at P<0.05. The relationship between soil anti-scouring capability and root density were fitted to power functions y=xb. The decrease of root density and soil anti-scouring capability meant damage of soil texture. Conversely,this will accelerate death rate of Sea Buckthorn,and vicious cycle format. Thus, effective measures,such as replanting shrubs,should be taken to reduce the harmful ecological effects of Sea Buckthorn degradation.
2014, 31(3): 386-393.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.009
Abstract:
To use the land rationally and to meet the requirement of monitoring land-use conditions in the mountain city of Lin'an,Zhejiang Province,the spectral angle mapping(SAM) method was used. Endmembers of the same type were selected to reduce endmember variation and to obtain classification for the years 1994,2002,and 2010 with Thematic Mapper(TM)/Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus(ETM+) images. Then the land-use structure for Lin'an City was produced to show urban land-use changes. Results showed that the SAM method was applicable for classification of a mountain city,and the accuracy of the three images was greater than 92% with Kappa>0.70. The primary land-use structure for Lin'an City was woodland with urban land increasing as arable land declined. The images showed that Lin'an City has entered a period of rapid urbanization,so an increase in land conflicts may be encountered.
To use the land rationally and to meet the requirement of monitoring land-use conditions in the mountain city of Lin'an,Zhejiang Province,the spectral angle mapping(SAM) method was used. Endmembers of the same type were selected to reduce endmember variation and to obtain classification for the years 1994,2002,and 2010 with Thematic Mapper(TM)/Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus(ETM+) images. Then the land-use structure for Lin'an City was produced to show urban land-use changes. Results showed that the SAM method was applicable for classification of a mountain city,and the accuracy of the three images was greater than 92% with Kappa>0.70. The primary land-use structure for Lin'an City was woodland with urban land increasing as arable land declined. The images showed that Lin'an City has entered a period of rapid urbanization,so an increase in land conflicts may be encountered.
2014, 31(3): 394-398.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.010
Abstract:
The purpose of this study is to measure the stress wave propagation time and improve the accuracy of identifying the internal decay of wood. An algorithm of stress wave propagation time estimation combining high order cumulants with wavelet transformation was presented. The proposed algorithm removed the noise of stress wave signal with filtering algorithm, then input the filtered signal to the generalized cross-correlation time delay model, and calculated the estimation of the stress wave propagation time. The results of simulation and experiments showed that the accuracy of the measured stress wave propagation time was improved by 81.5 per cent. Further more, under low, medium and high signal to noise ratios (SNR), the experimental results demonstrated the anti-interference ability of the new algorithm.
The purpose of this study is to measure the stress wave propagation time and improve the accuracy of identifying the internal decay of wood. An algorithm of stress wave propagation time estimation combining high order cumulants with wavelet transformation was presented. The proposed algorithm removed the noise of stress wave signal with filtering algorithm, then input the filtered signal to the generalized cross-correlation time delay model, and calculated the estimation of the stress wave propagation time. The results of simulation and experiments showed that the accuracy of the measured stress wave propagation time was improved by 81.5 per cent. Further more, under low, medium and high signal to noise ratios (SNR), the experimental results demonstrated the anti-interference ability of the new algorithm.
2014, 31(3): 399-403.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.011
Abstract:
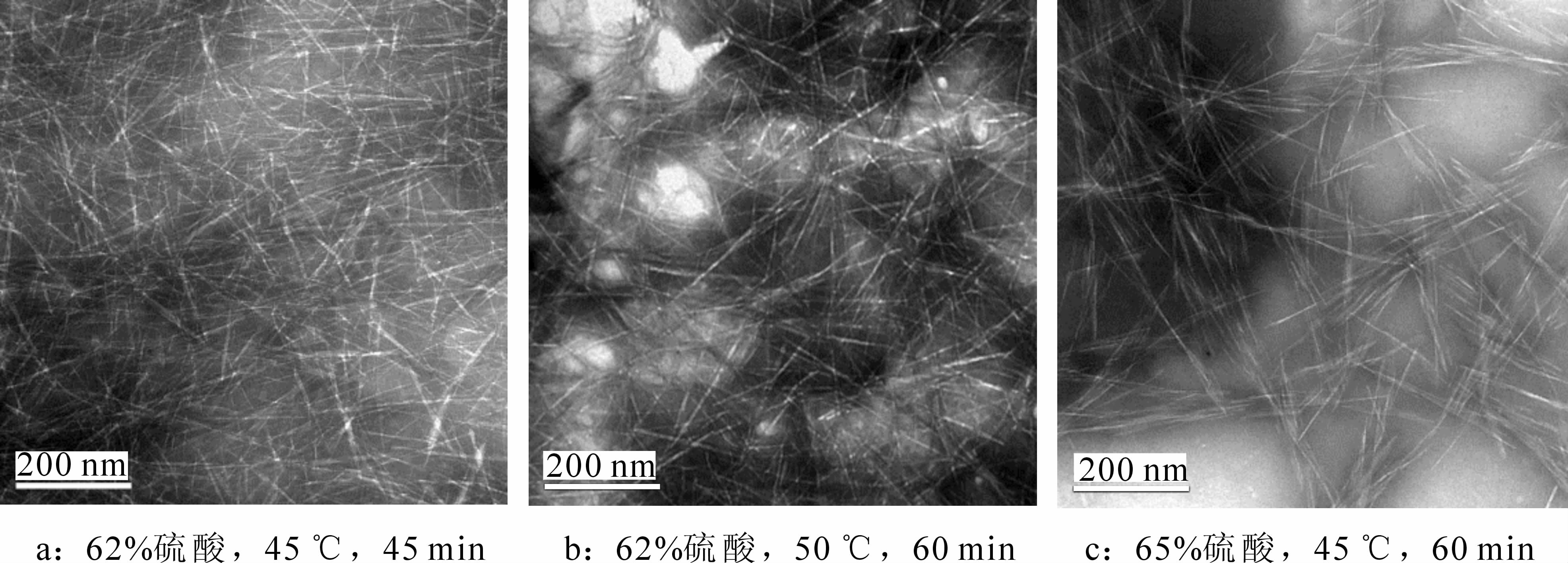
To make better use of the Miscanthus floridulus stalk,sulfuric acid hydrolysis was used to prepare an M. floridulus cellulose nano-crystal(CNC). The influence of sulfuric acid mass fraction,acid hydrolysis time,and temperature on CNC yield,suspension stability,and particle size were analyzed through orthogonal experiments to determine the optimal reaction condition. CNC morphology and its suspension stability were studied using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Results showed M. floridulus CNC had a rod-like structure 100-200 nm in length and 5-15 nm in diameter with yield ranging from 25%-50%. Zeta potential results revealed that M. floridulus CNC suspensions were stable,and the hydrodynamic diameter of CNC measured with DLS was slightly shorter than that measured by TEM images. The orthogonal analysis for CNC yield showed that the order of the effect from the three factors was sulfuric acid mass fraction (P=0.03)> acid hydrolysis time (P=0.06)> temperature (P=0.35);for CNC particle size,the order of the effect from the three factors was sulfuric acid mass fraction (P=0.03)> acid hydrolysis temperature (P=0.22)> time (P=0.38). In summary,the optimal reaction condition for preparing M. floridulus CNC was sulfuric acid mass fraction (62%),hydrolysis time (45 min) and temperature (45℃).
To make better use of the Miscanthus floridulus stalk,sulfuric acid hydrolysis was used to prepare an M. floridulus cellulose nano-crystal(CNC). The influence of sulfuric acid mass fraction,acid hydrolysis time,and temperature on CNC yield,suspension stability,and particle size were analyzed through orthogonal experiments to determine the optimal reaction condition. CNC morphology and its suspension stability were studied using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Results showed M. floridulus CNC had a rod-like structure 100-200 nm in length and 5-15 nm in diameter with yield ranging from 25%-50%. Zeta potential results revealed that M. floridulus CNC suspensions were stable,and the hydrodynamic diameter of CNC measured with DLS was slightly shorter than that measured by TEM images. The orthogonal analysis for CNC yield showed that the order of the effect from the three factors was sulfuric acid mass fraction (P=0.03)> acid hydrolysis time (P=0.06)> temperature (P=0.35);for CNC particle size,the order of the effect from the three factors was sulfuric acid mass fraction (P=0.03)> acid hydrolysis temperature (P=0.22)> time (P=0.38). In summary,the optimal reaction condition for preparing M. floridulus CNC was sulfuric acid mass fraction (62%),hydrolysis time (45 min) and temperature (45℃).
2014, 31(3): 404-409.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.012
Abstract:
To study the effects on the early flowering capacity of the FLOWERING LOCUS T(FT) gene in transgenic poplar driven by a Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S (CaMV35S) promoter, provide basic data for effective application of FT gene on forest trees, an FT gene vector driven by a CaMV35S promoter was constructed using Gateway technology, and then genetic transformation of hybrid poplar was performed with this vector. The early flowering capability of transgenic poplar induced by 35S::FT was discussed both from flower development and floral organ variation viewpoints. Results showed that transformation of the meristem attributive and initial floral structure of 35S::FT transgenic poplar happened in the tube culture stage. If the flowering plants were not sub-cultured in vitro or timely transplanted into soil to culture in a greenhouse, the initial floral structure withered or ceased development. Within 3-5 weeks of greenhouse culture the initial floral structure continued to develop and finished floral organ differentiation and development. The floral organ was incomplete typically with pistil/stamen and flower disc structures but no mature bract structures; stamens also failed to mature. Flowers induced by 35S::FT were single flowers rather than catkins as with wild-types. Most flowers were unisexual, but bisexual flowers appeared on male transgenic plants. Flowering frequency of transgenic plants declined sharply with the increase of subculture time, but the proportion of bisexual flowers on male transgenic plants rose. 35S promoter is not suitable in genetic transformation for the purpose of getting normal floral organ.
To study the effects on the early flowering capacity of the FLOWERING LOCUS T(FT) gene in transgenic poplar driven by a Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S (CaMV35S) promoter, provide basic data for effective application of FT gene on forest trees, an FT gene vector driven by a CaMV35S promoter was constructed using Gateway technology, and then genetic transformation of hybrid poplar was performed with this vector. The early flowering capability of transgenic poplar induced by 35S::FT was discussed both from flower development and floral organ variation viewpoints. Results showed that transformation of the meristem attributive and initial floral structure of 35S::FT transgenic poplar happened in the tube culture stage. If the flowering plants were not sub-cultured in vitro or timely transplanted into soil to culture in a greenhouse, the initial floral structure withered or ceased development. Within 3-5 weeks of greenhouse culture the initial floral structure continued to develop and finished floral organ differentiation and development. The floral organ was incomplete typically with pistil/stamen and flower disc structures but no mature bract structures; stamens also failed to mature. Flowers induced by 35S::FT were single flowers rather than catkins as with wild-types. Most flowers were unisexual, but bisexual flowers appeared on male transgenic plants. Flowering frequency of transgenic plants declined sharply with the increase of subculture time, but the proportion of bisexual flowers on male transgenic plants rose. 35S promoter is not suitable in genetic transformation for the purpose of getting normal floral organ.
2014, 31(3): 410-416.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.013
Abstract:
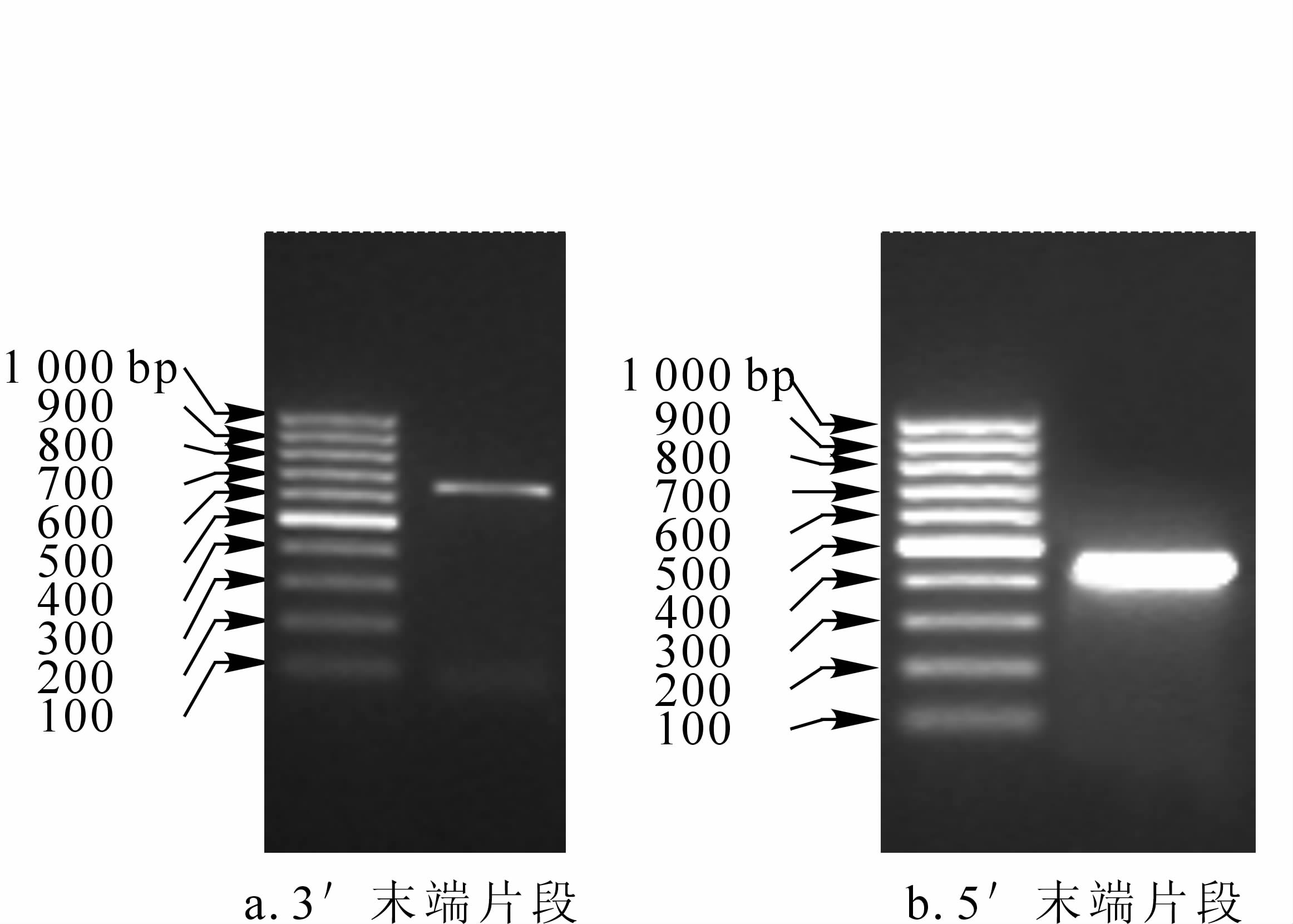
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase (MDS) gene had been regarded as a key regulating plot in plant 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway.To dissect the MDS gene sequence information and predict the gene function of Eucommia ulmoides,the homologous MDS gene cDNA was isolated from leaves by the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) techniques, and the sequence analysis was also conducted by series of bioinformatic methods.Results showed that and the full-length cDNA of EuMDS was 976 bp, including a 5'non-coding region of 119 bp and a 3'non-coding region of 146 bp with 236 amino acids encoded.The transit peptide sequence (A1-A56) and multiple conserved functional sites (A84, A87, A89, A121, A213, A217, A221, A223, and A228) of plant MDS enzyme were found in the deduced coding sequence of EuMDS.The secondary structure of the EuMDS protein was predicted with proportions of α-helix to 40.3%, β-sheet to 13.6%, and loop/coil to 46.2%.The calculated protein tertiary structure of EuMDS was exhibited as a molecular cavity formed by three subunits.Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the evolutionary relationship of EuMDS protein was closest to the Humulus lupulus MDS protein.It was suggested that the cloned EuMDS exert an important function in Eucommia ulmoides terpene biosysthesis.
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase (MDS) gene had been regarded as a key regulating plot in plant 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway.To dissect the MDS gene sequence information and predict the gene function of Eucommia ulmoides,the homologous MDS gene cDNA was isolated from leaves by the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) techniques, and the sequence analysis was also conducted by series of bioinformatic methods.Results showed that and the full-length cDNA of EuMDS was 976 bp, including a 5'non-coding region of 119 bp and a 3'non-coding region of 146 bp with 236 amino acids encoded.The transit peptide sequence (A1-A56) and multiple conserved functional sites (A84, A87, A89, A121, A213, A217, A221, A223, and A228) of plant MDS enzyme were found in the deduced coding sequence of EuMDS.The secondary structure of the EuMDS protein was predicted with proportions of α-helix to 40.3%, β-sheet to 13.6%, and loop/coil to 46.2%.The calculated protein tertiary structure of EuMDS was exhibited as a molecular cavity formed by three subunits.Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the evolutionary relationship of EuMDS protein was closest to the Humulus lupulus MDS protein.It was suggested that the cloned EuMDS exert an important function in Eucommia ulmoides terpene biosysthesis.
2014, 31(3): 424-430.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.015
Abstract:
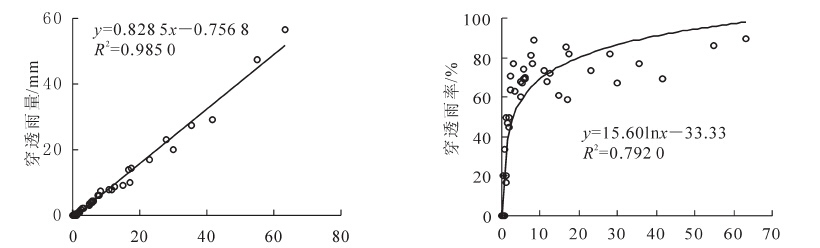
Water transport through the canopy layer, important in forest hydrology and soil and water conservation, was studied to determine characteristics of rainfall redistribution and the eco-hydrological functions of forests.Using the fixed point observation method, rainfall, throughfall, and stemflow of Cunninghamia lanceolata in the Yangtze River Delta were studied during the high flow season.A water balance method was adopted to calculate canopy interception, and a regression analysis was employed to select the main factors affecting rainfall redistribution and to establish the relationship among throughfall, stemflow, canopy interception, rainfall, and rainfall intensity.Results indicated a cumulative rainfall of 470.7 mm with most rainfall events from April to September 2012 featuring light rain with low intensity.Cumulative throughfall was 344.1 mm; total stemflow was 10.3 mm; and total canopy interception was 116.3 mm.The fitted regression equation showed that the minimum rainfall necessary for throughfall was 0.9 mm, and the minimum rainfall needed to start stemflow was 4.1 mm.
Water transport through the canopy layer, important in forest hydrology and soil and water conservation, was studied to determine characteristics of rainfall redistribution and the eco-hydrological functions of forests.Using the fixed point observation method, rainfall, throughfall, and stemflow of Cunninghamia lanceolata in the Yangtze River Delta were studied during the high flow season.A water balance method was adopted to calculate canopy interception, and a regression analysis was employed to select the main factors affecting rainfall redistribution and to establish the relationship among throughfall, stemflow, canopy interception, rainfall, and rainfall intensity.Results indicated a cumulative rainfall of 470.7 mm with most rainfall events from April to September 2012 featuring light rain with low intensity.Cumulative throughfall was 344.1 mm; total stemflow was 10.3 mm; and total canopy interception was 116.3 mm.The fitted regression equation showed that the minimum rainfall necessary for throughfall was 0.9 mm, and the minimum rainfall needed to start stemflow was 4.1 mm.
2014, 31(3): 437-441.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.017
Abstract:
We studied the attractiveness of Melia azedarach to Anoplophora chinensis by both bioassay in the laboratory and field trapping.The results indicated that Melia azedarach had strong attractiveness to Anoplophora chinensis.The increase in the number of Melia azedarach would result in increased attractiveness.The trapping rate of 100 Melia azedarach trees was 79.25 per cent while that of 50 Melia azedarach trees was only 28.57 per cent.In the same environment, the average feeding area of Melia azedarach branch was 6.19 cm2, larger than that of Koelreuteria integrifoliola and Casuarina equisetifolia.The research findings would provide new theoretical foundation and technique for the control and prevention of Anoplophora chinensis.
We studied the attractiveness of Melia azedarach to Anoplophora chinensis by both bioassay in the laboratory and field trapping.The results indicated that Melia azedarach had strong attractiveness to Anoplophora chinensis.The increase in the number of Melia azedarach would result in increased attractiveness.The trapping rate of 100 Melia azedarach trees was 79.25 per cent while that of 50 Melia azedarach trees was only 28.57 per cent.In the same environment, the average feeding area of Melia azedarach branch was 6.19 cm2, larger than that of Koelreuteria integrifoliola and Casuarina equisetifolia.The research findings would provide new theoretical foundation and technique for the control and prevention of Anoplophora chinensis.
2014, 31(3): 442-449.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.018
Abstract:
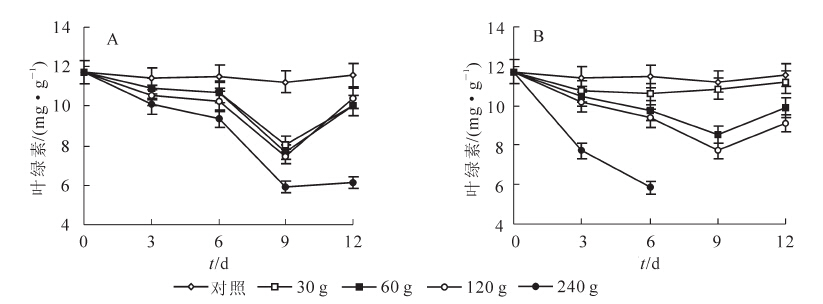
To control Alternanthera philoxeroides via allelopathy, the powder from Melia azedarach and Oenanthe javanica was applied directly to A.philoxeroides.A complete randomized design with M.azedarach treatments of 30 g, 60 g, 120 g and 240 g and O.javanica treatments of 30 g, 60 g, 120 g and 240 g with 3 replications were employed.Results showed that after 9 d, 240 g of O.javanica powder killed A.philoxeroides.After 12 d with the 240 g treatment of M.azedarach powder there were highly significant reductions (P<0.01) in the chlorophyll content (47.1%), net photosynthetic rate (Pn)(71.2%), stomatal conductance (Cond)(73.5%), and transpiration rate (Tr)(68.3%) in A.philoxeroides, and a highly significant increase (P<0.01) for intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci)(39.6%).Also, after 12 d with the 120 g treatment of O.javanica powder, there were highly significant reductions (P<0.01) in the chlorophyll content (21.3%), Pn (22.2%), Cond (54.2%), and Tr (46.4%) in A.philoxeroides, and a highly significant increase (P<0.01) for Ci(38.4%).When M.azedarach and O.javanica powders were used to treat A.philoxeroides, the superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) activity as well as the malonaldehyde (MDA)content first increased and then decreased with prolonged treatment time.However, the soluble protein content gradually decreased.Overall, plant growth and root sucker production of A.philoxeroides were greatly inhibited with M.azedarach and O.javanica powder, and the inhibition gradually increased with an increase of powder indicating that they could be used for the allelopathic control.
To control Alternanthera philoxeroides via allelopathy, the powder from Melia azedarach and Oenanthe javanica was applied directly to A.philoxeroides.A complete randomized design with M.azedarach treatments of 30 g, 60 g, 120 g and 240 g and O.javanica treatments of 30 g, 60 g, 120 g and 240 g with 3 replications were employed.Results showed that after 9 d, 240 g of O.javanica powder killed A.philoxeroides.After 12 d with the 240 g treatment of M.azedarach powder there were highly significant reductions (P<0.01) in the chlorophyll content (47.1%), net photosynthetic rate (Pn)(71.2%), stomatal conductance (Cond)(73.5%), and transpiration rate (Tr)(68.3%) in A.philoxeroides, and a highly significant increase (P<0.01) for intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci)(39.6%).Also, after 12 d with the 120 g treatment of O.javanica powder, there were highly significant reductions (P<0.01) in the chlorophyll content (21.3%), Pn (22.2%), Cond (54.2%), and Tr (46.4%) in A.philoxeroides, and a highly significant increase (P<0.01) for Ci(38.4%).When M.azedarach and O.javanica powders were used to treat A.philoxeroides, the superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) activity as well as the malonaldehyde (MDA)content first increased and then decreased with prolonged treatment time.However, the soluble protein content gradually decreased.Overall, plant growth and root sucker production of A.philoxeroides were greatly inhibited with M.azedarach and O.javanica powder, and the inhibition gradually increased with an increase of powder indicating that they could be used for the allelopathic control.
2014, 31(3): 450-456.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.019
Abstract:
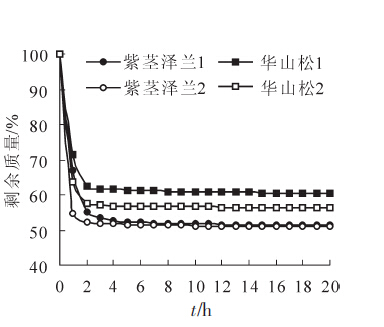
To understand the combustion characteristics of Eupatorium adenophorum, combustion experiments of fresh old leaves and new leaves of Eupatorium adenophorum and its contrast species were conducted under 100 per cent of oxygen concentration and by vertical burning test respectively during the rigid forest fire protection period to find out the burning rate and damage degree of the different leaves under experimental conditions.The ignition time and temperature of fresh branches of Eupatorium adenophorum and Alnus nepalensis were measured by igniting experiments.Burning rate of dry stems of Eupatorium adenophorum and dry branches of Pinus armandii were tested through combustion experiments under 50 per cent of oxygen concentration and drying test under 105℃ constant temperature, and the curves of moisture loss of the dry stems and branches were drawn.The results indicated that combustion features of fresh old leaves of Eupatorium adenophorum were similar to those of Hedera nepalensis var.sinensis, Mucuna sempervirens and Ligustrum lucidum.But the damage degree of the fresh old leaves of Eupatorium adenophorum was less than that of Cyclobalanopsis glaucoides and Machilus yunnanensis.In the vertical burning test, the burning rate of Eupatorium adenophorum was the highest and its damage degree was medium among the 6 new leaves.The fresh stem of Eupatorium adenophorum was more retardant than the fresh branches of Alnus nepalensis in terms of similar quality or dimensions.The burning rate of dry stems of Eupatorium adenophorum was greater than that of dry branches of Pinus armandii in the case of similar diameter.The moisture loss rate of dry stems of Eupatorium adenophorum was higher than that of dry branches of Pinus armandii.
To understand the combustion characteristics of Eupatorium adenophorum, combustion experiments of fresh old leaves and new leaves of Eupatorium adenophorum and its contrast species were conducted under 100 per cent of oxygen concentration and by vertical burning test respectively during the rigid forest fire protection period to find out the burning rate and damage degree of the different leaves under experimental conditions.The ignition time and temperature of fresh branches of Eupatorium adenophorum and Alnus nepalensis were measured by igniting experiments.Burning rate of dry stems of Eupatorium adenophorum and dry branches of Pinus armandii were tested through combustion experiments under 50 per cent of oxygen concentration and drying test under 105℃ constant temperature, and the curves of moisture loss of the dry stems and branches were drawn.The results indicated that combustion features of fresh old leaves of Eupatorium adenophorum were similar to those of Hedera nepalensis var.sinensis, Mucuna sempervirens and Ligustrum lucidum.But the damage degree of the fresh old leaves of Eupatorium adenophorum was less than that of Cyclobalanopsis glaucoides and Machilus yunnanensis.In the vertical burning test, the burning rate of Eupatorium adenophorum was the highest and its damage degree was medium among the 6 new leaves.The fresh stem of Eupatorium adenophorum was more retardant than the fresh branches of Alnus nepalensis in terms of similar quality or dimensions.The burning rate of dry stems of Eupatorium adenophorum was greater than that of dry branches of Pinus armandii in the case of similar diameter.The moisture loss rate of dry stems of Eupatorium adenophorum was higher than that of dry branches of Pinus armandii.
2014, 31(3): 457-464.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.020
Abstract:
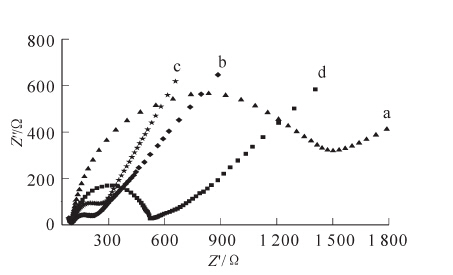
Dialdehyde cellulose(DAC), an immobilized enzyme matrix material,was used to prepare an immobilized acetylcholinesterase according to immobilized enzyme chemical linking technology.The immobilized acetylcholinesterase was then used to prepare a new multilayer chitosan/immobilized acetylcholinesterase/functionalized carbon nanotube/glassy carbon electrode (Chi/DAC-AChE/F-CNTs/GCE) biosensor.AC impedance (ACI), cyclic voltammetry(CV), and differential pulse voltammetry(DPV) were utilized to characterize the detection performance of pesticides acting on the biosensor.Results showed that the new Chi/DAC-AChE/F-CNTs/GCE biosensor was successfully prepared and had a good response to carbaryl (CAB).This new sensor provided a quick and easy detection method with a wide range and a high sensitivity having a minimum detection limit of 3.5 μg·L-1 with good reproducibility and stability.These results could provide a new analytical method for the detection of carbamate pesticides.
Dialdehyde cellulose(DAC), an immobilized enzyme matrix material,was used to prepare an immobilized acetylcholinesterase according to immobilized enzyme chemical linking technology.The immobilized acetylcholinesterase was then used to prepare a new multilayer chitosan/immobilized acetylcholinesterase/functionalized carbon nanotube/glassy carbon electrode (Chi/DAC-AChE/F-CNTs/GCE) biosensor.AC impedance (ACI), cyclic voltammetry(CV), and differential pulse voltammetry(DPV) were utilized to characterize the detection performance of pesticides acting on the biosensor.Results showed that the new Chi/DAC-AChE/F-CNTs/GCE biosensor was successfully prepared and had a good response to carbaryl (CAB).This new sensor provided a quick and easy detection method with a wide range and a high sensitivity having a minimum detection limit of 3.5 μg·L-1 with good reproducibility and stability.These results could provide a new analytical method for the detection of carbamate pesticides.
2014, 31(3): 465-472.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.021
Abstract:
To obtain the optimal medium for growth of Cordyceps militaris DY-1, statistical designs were utilized on the fermentation medium.The dry weight of mycelium was measured analytically.First, the carbon source, nitrogen source, and inorganic salts were screened one factor at a time, and the carbon:nitrogen ratio was optimized through orthogonal testing.Then, the Plackett-Burman design was used to screen the critical factors of mycelium production.Last, a central composite design and response surface methodology were utilized to determine the optimal concentrations of the critical factors.After, the optimal medium was used in inoculation experiments to verify the predicted values.Results demonstrated that the optimal media was composed of the following factors:maltose, 16.40 g·L-1; yeast extract powder, 5.00 g·L-1; KNO3, 1.00 g·L-1; MgSO4, 0.20 g·L-1; KH2PO4, 1.80 g·L-1; and FeSO4, 0.02 g·L-1.The practical corresponding response of 32.11 g·L-1 was closer to the predicted response of 32.22 g·L-1.Using the optimum medium, the dry weight of the mycelium active substances was effectively enhanced 4.12 times compared with the initial level.The present study laid the foundation for the further research and application of Cordyceps militaris DY-1.
To obtain the optimal medium for growth of Cordyceps militaris DY-1, statistical designs were utilized on the fermentation medium.The dry weight of mycelium was measured analytically.First, the carbon source, nitrogen source, and inorganic salts were screened one factor at a time, and the carbon:nitrogen ratio was optimized through orthogonal testing.Then, the Plackett-Burman design was used to screen the critical factors of mycelium production.Last, a central composite design and response surface methodology were utilized to determine the optimal concentrations of the critical factors.After, the optimal medium was used in inoculation experiments to verify the predicted values.Results demonstrated that the optimal media was composed of the following factors:maltose, 16.40 g·L-1; yeast extract powder, 5.00 g·L-1; KNO3, 1.00 g·L-1; MgSO4, 0.20 g·L-1; KH2PO4, 1.80 g·L-1; and FeSO4, 0.02 g·L-1.The practical corresponding response of 32.11 g·L-1 was closer to the predicted response of 32.22 g·L-1.Using the optimum medium, the dry weight of the mycelium active substances was effectively enhanced 4.12 times compared with the initial level.The present study laid the foundation for the further research and application of Cordyceps militaris DY-1.
2014, 31(3): 473-480.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.022
Abstract:
The purpose of this paper is to provide a theoretical reference for management countermeasures of bamboo adaptability considering a background of environmental change, especially climate change.During growth various environmental stresses affect bamboo which in turn responds with a physical answer and adaptation.In the long-term evolutionary process, bamboo has formed corresponding protection mechanisms and ecological adaptation strategies; however, physiological plasticity is the most direct response to environmental impacts from stress including temperature, moisture, soil salinity, nutrients, atmospheric pollution, and heavy metals.The effects of environmental stress on physiological plasticity of bamboo are reviewed from active oxygen metabolism, membrane lipid peroxidation and the antioxidant enzyme system, osmotic regulation system, and photosynthetic physiology to name a few.The key research direction of bamboo in physiological adaptability and response mechanism, sifting of stress resistance, distribution and carbon balance with environmental stress is also presented.
The purpose of this paper is to provide a theoretical reference for management countermeasures of bamboo adaptability considering a background of environmental change, especially climate change.During growth various environmental stresses affect bamboo which in turn responds with a physical answer and adaptation.In the long-term evolutionary process, bamboo has formed corresponding protection mechanisms and ecological adaptation strategies; however, physiological plasticity is the most direct response to environmental impacts from stress including temperature, moisture, soil salinity, nutrients, atmospheric pollution, and heavy metals.The effects of environmental stress on physiological plasticity of bamboo are reviewed from active oxygen metabolism, membrane lipid peroxidation and the antioxidant enzyme system, osmotic regulation system, and photosynthetic physiology to name a few.The key research direction of bamboo in physiological adaptability and response mechanism, sifting of stress resistance, distribution and carbon balance with environmental stress is also presented.
2014, 31(3): 481-487.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.023
Abstract:
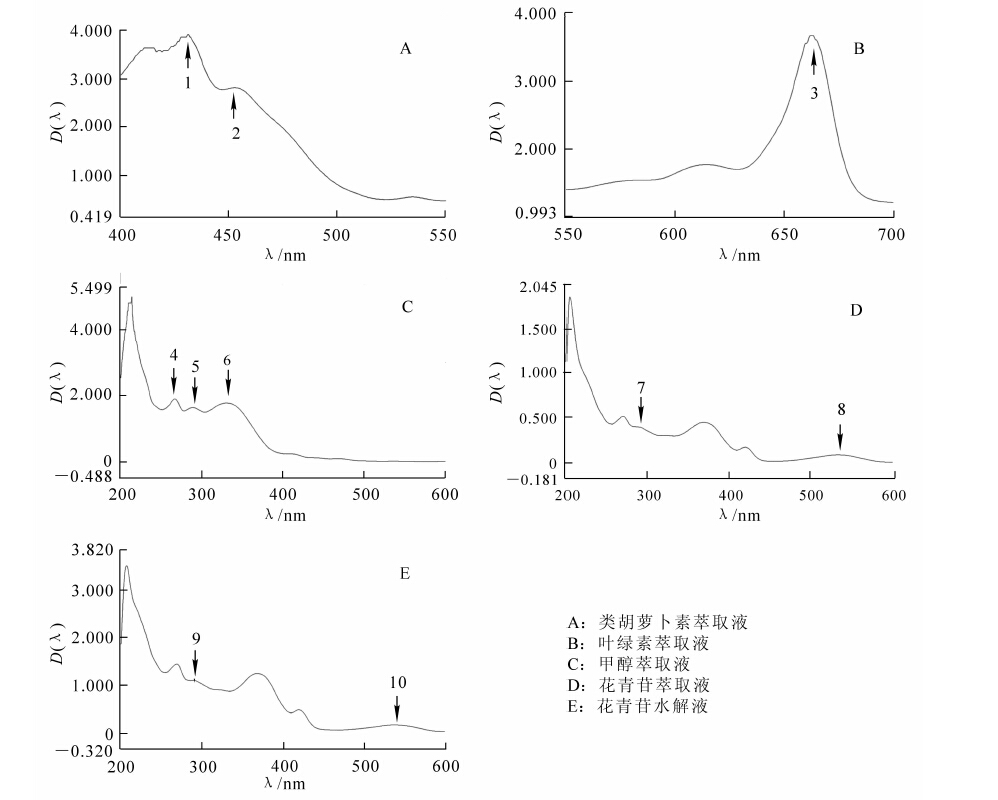
Prunus cerasifera, the most common foliage tree on the landscape, have purple leaves throughout their growing season.To provide a theoretical basis for cultivar improvement and to determine their role in breeding, pigments of P.cerasifera leaves were qualitatively identified using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), thin layer chromatography, and UV photo-spectrometer; and then quantitatively analyzed with HPLC-Diode array detector (DAD).Results demonstrated that the main chromogenic pigments in P.cerasifera leaves were carotenoids, chlorophyll(mainly chlorophyll a), cyanidin, petunidin, cyanidin-galactoside, pelargonidin, and other monomeric phenols (quercetin, rutin, and dihydromyricetin).Accumulation of cyanidin-galactoside and cyanidin caused the red coloration; and chlorophyll, carotenoids, quercetin, and rutin played an important role as co-pigments.Pigments and the coloring mechanism of leaves could provide a theoretical basis for cultivar improvement and could play an important role in P.cerasifera breeding.
Prunus cerasifera, the most common foliage tree on the landscape, have purple leaves throughout their growing season.To provide a theoretical basis for cultivar improvement and to determine their role in breeding, pigments of P.cerasifera leaves were qualitatively identified using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), thin layer chromatography, and UV photo-spectrometer; and then quantitatively analyzed with HPLC-Diode array detector (DAD).Results demonstrated that the main chromogenic pigments in P.cerasifera leaves were carotenoids, chlorophyll(mainly chlorophyll a), cyanidin, petunidin, cyanidin-galactoside, pelargonidin, and other monomeric phenols (quercetin, rutin, and dihydromyricetin).Accumulation of cyanidin-galactoside and cyanidin caused the red coloration; and chlorophyll, carotenoids, quercetin, and rutin played an important role as co-pigments.Pigments and the coloring mechanism of leaves could provide a theoretical basis for cultivar improvement and could play an important role in P.cerasifera breeding.
2014, 31(3): 488-493.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.024
Abstract:
To better understand the pipe model theory and hydraulic architecture characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings in different growth stages (early, fast, and last), the improved flushing method was used to measure the hydraulic architecture parameters of two-year-old R.pseudoacacia seedlings with an adequate water supply for three growth stages (early, fast, and last) and there are 20 repeats in every growth stages.Significance tests were done between hydraulic architecture parameters and stem segment diameter and different growth stages by ANOVA.Then the pipe theory was discussed based on hydraulic architecture theory.Results showed that with sufficient water, the hydraulic conductivity (Kh), stem area specific hydraulic conductivity (Ks), leaf specific conductivity (Kl), and Huber value (Hv) of R.pseudoacacia seedlings increased (P<0.05) as the stem segment diameter enlarged.For the three seedling growth stages, Kh, Ks, and Kl were significantly different (P<0.05) with early growth stage> fast growth stage> last growth stage.Hv was greatest (P>0.05) in the early growth stage with no significant differences in fast and last growth stages.Thus, (1) with sufficient water, water transportation efficiency of thicker stems is greater than the thinner stems; (2) hydraulic architecture characteristics of seedlings were different (P<0.05) in three growth stages; and (3) the pipe model theory was not perfect, especially for understanding the inner water transportation processes of a tree and their control mechanism.
To better understand the pipe model theory and hydraulic architecture characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings in different growth stages (early, fast, and last), the improved flushing method was used to measure the hydraulic architecture parameters of two-year-old R.pseudoacacia seedlings with an adequate water supply for three growth stages (early, fast, and last) and there are 20 repeats in every growth stages.Significance tests were done between hydraulic architecture parameters and stem segment diameter and different growth stages by ANOVA.Then the pipe theory was discussed based on hydraulic architecture theory.Results showed that with sufficient water, the hydraulic conductivity (Kh), stem area specific hydraulic conductivity (Ks), leaf specific conductivity (Kl), and Huber value (Hv) of R.pseudoacacia seedlings increased (P<0.05) as the stem segment diameter enlarged.For the three seedling growth stages, Kh, Ks, and Kl were significantly different (P<0.05) with early growth stage> fast growth stage> last growth stage.Hv was greatest (P>0.05) in the early growth stage with no significant differences in fast and last growth stages.Thus, (1) with sufficient water, water transportation efficiency of thicker stems is greater than the thinner stems; (2) hydraulic architecture characteristics of seedlings were different (P<0.05) in three growth stages; and (3) the pipe model theory was not perfect, especially for understanding the inner water transportation processes of a tree and their control mechanism.
2014, 31(3): 417-423.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2014.03.014
Abstract:
A comparative study of the in-situ and ex-situ habitat characteristics of two endangered species including Cinnamomum japonicum var.chenii and Neolitsea sericea was conducted in the Zhoushan archipelago.The results indicated that the two species both grew in the subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests.The natural habitat of Cinnamomum japonicum var.chenii was characterized by acid and thick soil with rich organic matter; and that of Neolitsea sericea was characterized by acid and thin soil with rich soil fertility.Community structure of ex-situ conservation area was a typical evergreen and deciduous broadleaved mixed forest.The soil in the ex-situ conservation was acid and contained moderate organic matters.A comparative analysis of climate, community and soil characteristics was conducted between the natural and ex-situ habitats.The results indicated that their natural climatic conditions, community characteristics, and soil physical and chemical properties were very similar.Based on our research findings and the principle of maintaining the population diversity as much as possible, we conducted an ex-situ conservation of five populations of Cinnamomum japonicum var.chenii and five populations of Neolitsea sericea.These two species already bloomed and borne fruits in the ex-situ conservation area.
A comparative study of the in-situ and ex-situ habitat characteristics of two endangered species including Cinnamomum japonicum var.chenii and Neolitsea sericea was conducted in the Zhoushan archipelago.The results indicated that the two species both grew in the subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests.The natural habitat of Cinnamomum japonicum var.chenii was characterized by acid and thick soil with rich organic matter; and that of Neolitsea sericea was characterized by acid and thin soil with rich soil fertility.Community structure of ex-situ conservation area was a typical evergreen and deciduous broadleaved mixed forest.The soil in the ex-situ conservation was acid and contained moderate organic matters.A comparative analysis of climate, community and soil characteristics was conducted between the natural and ex-situ habitats.The results indicated that their natural climatic conditions, community characteristics, and soil physical and chemical properties were very similar.Based on our research findings and the principle of maintaining the population diversity as much as possible, we conducted an ex-situ conservation of five populations of Cinnamomum japonicum var.chenii and five populations of Neolitsea sericea.These two species already bloomed and borne fruits in the ex-situ conservation area.