Current Issue
column
2026, 43(1): 1-10.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240586
Abstract:
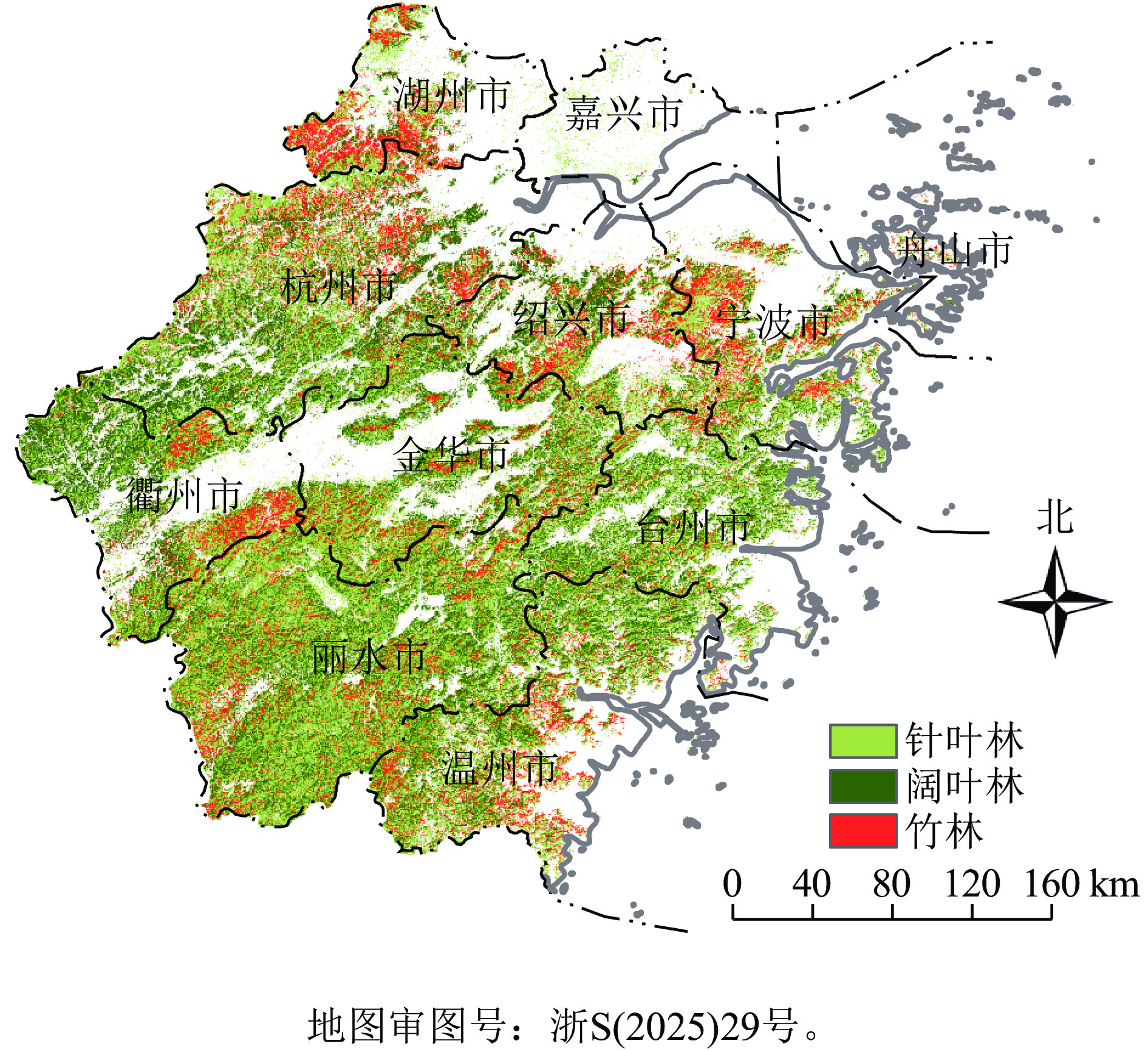
Objective This study aims to simulate and analyze the spatiotemporal characteristics of forest net primary productivity (NPP) in Zhejiang Province, reveal the impact of seasonal drought on the spatiotemporal evolution of NPP, and provide a scientific basis for forest response and adaptation to climate change. Method The spatiotemporal characteristics of seasonal drought in Zhejiang Province from 1990 to 2015 were analyzed using the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. The spatiotemporal pattern of forest NPP in Zhejiang Province was simulated based on the boreal ecosystem prodctivity simulator (BEPS) model, and the impact of seasonal drought on forest NPP was further investigated. Result (1) The drought was of generally moderate intensity, with summer being the most severe season for drought, accounting for 42.20% of the area with severe or above drought, followed by winter. In addition, except for spring, there was a trend of aridification in the other three seasons. (2) The average forest NPP from 1990 to 2015 was 371.53 g·m−2·a−1, with the highest value in spring (95.22 g·m−2·month−1). (3) The impact of drought on forest NPP was the greatest in summer and autumn, with deviations of −4.88% and −4.62%, respectively, and relatively smaller in spring and winter, with deviations of −3.31% and −3.56%, respectively. The cities (counties) that had the greatest impact on NPP in 4 seasons were Songyang (−12.49%), Longquan (−12.79%), Ningbo (−17.90%), and Jiande (−11.77%). Conclusion This study reveals significant seasonal and spatial changes in forest NPP in Zhejiang Province from 1990 to 2015. The spatiotemporal impact of seasonal drought on NPP cannot be ignored. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 26 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 11-23.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250170
Abstract:
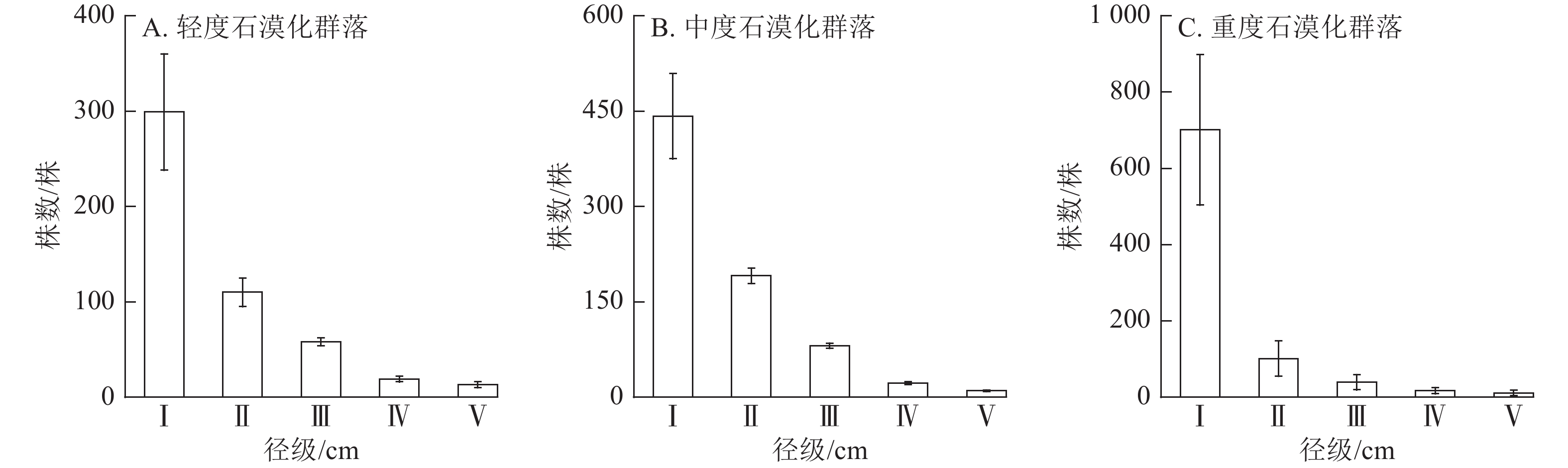
Objective This study aims to explore the relationship between community characteristics and carbon storage in rocky desertification areas of Northern Guangdong, and to reveal the key community characteristic indicators that affect carbon storage. Method Forest communities with mild, moderate, and severe levels of rocky desertification in Northern Guangdong were selected as the research objects. Three 30 m×40 m forest plots were selected by typical sampling, and one-way analysis of variance, Pearson correlation analysis, and random forest model were used to analyze the characteristics of forest communities, carbon storage and their relationship in rocky desertification areas in Northern Guangdong. Result (1) The dominant tree species of the forest community in rocky desertification areas were Castanopsis jucunda, Pinus massoniana, Quercus acutissima, etc., and the species diversity of moderate rocky desertification communities was the highest. (2) The diameter structure of the forest communities at three desertification levels all showed an inverted “J” shape. Among them, diameter Class Ⅰ was dominant (mild desertification accounting for 53.8%, moderate 67.8%, and severe 77.4%). The vertical structure was mainly composed of Classes Ⅰ−Ⅱ, and the community structure tended to simplify with increasing desertification intensity. The average stand density in descending order was severe, moderate, and mild desertification communities. (3) Carbon storage of the three forest communities, ranking from large to small, was as follows: moderate rocky desertification communities, mild rocky desertification communities, and severe rocky desertification communities, with no significant differences in carbon storage among communities. The carbon storage of dead wood and litter was the least among carbon storage components. (4) There was no significant correlation between species diversity and carbon storage characteristics. DBH and tree height were significantly positively correlated with carbon storage characteristics (P<0.05). There was no significant correlation between forest density and carbon storage characteristics. Bedrock exposure degree was significantly negatively correlated with soil carbon storage (P<0.01), but not significantly correlated with total carbon storage. The relative importance of species dominance index, DBH, and tree height to carbon storage was 21.23%, 19.95%, and 19.55%, respectively. Conclusion The species diversity of forest communities in rocky desertification areas of Northern Guangdong is the highest in the moderate rocky desertification community, with overall smaller species diameter classes and unclear vertical structural stratification. The carbon storage of dominant species is the main component of the community carbon storage, and the influence of community structure on carbon storage is dominant. [Ch, 6 fig. 5 tab. 40 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 24-32.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250130
Abstract:
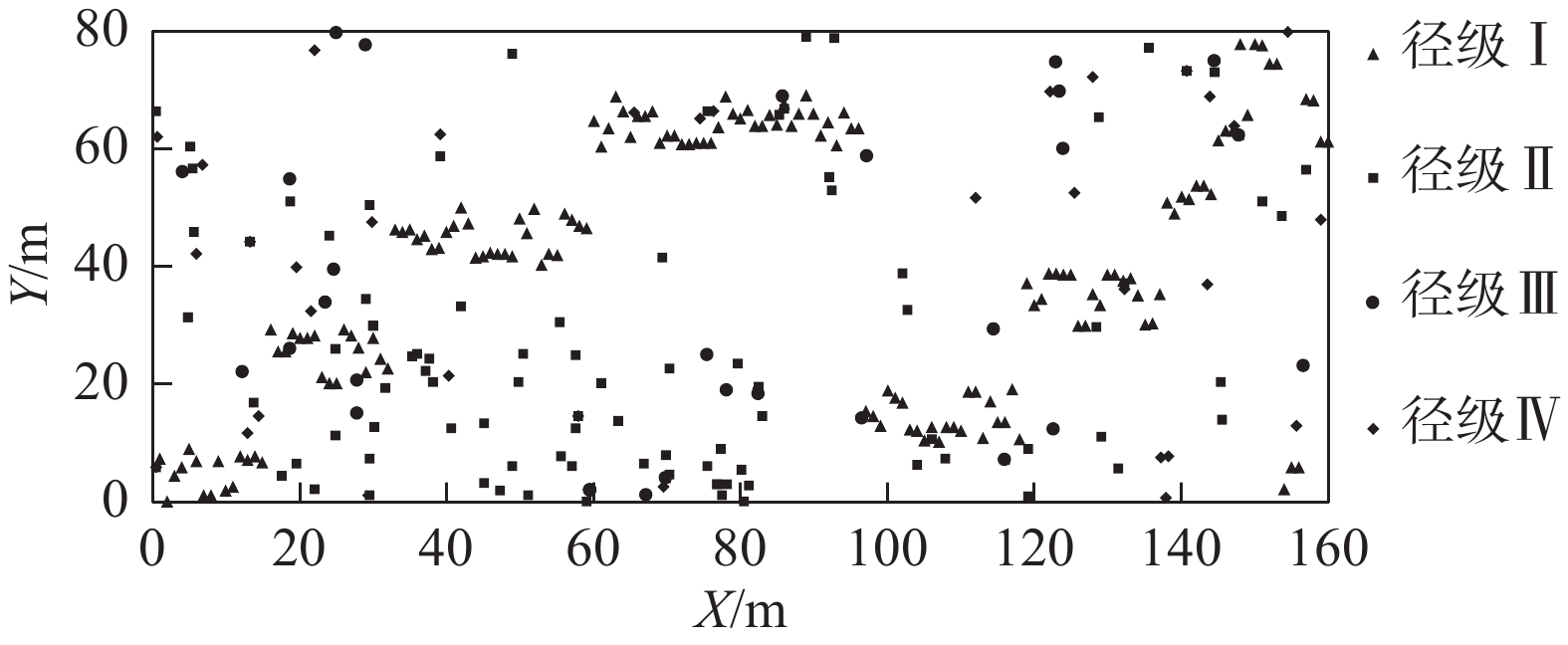
Objective The objective is to investigate the spatial pattern and influencing mechanism of Mallotus philippensis population in karst forests, which will help to deepen our understanding of the development rules and potential ecological processes of the population and provide reference for the conservation of karst forests and restoration of degraded forests. Method Based on a fixed plot of 1.28 hm² in Maolan evergreen deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest and using the data of M. philippensis population and environmental factors investigated in 2023, point pattern analysis and Pearson correlation analysis were adopted to explore the diameter class structure, spatial distribution pattern of the population and its correlation with environmental factors. Result (1) The number of trees in different diameter grades of M. philippensis population varied, and the overall distribution showed a growth pattern. The number in diameter grade Ⅰ was the largest, while that in diameter grade Ⅲwas the smallest. (2) With the increase of diameter grade, the spatial distribution pattern of M. philippensis population transformed from clustered distribution to random distribution from diameter grade Ⅰ to diameter grade Ⅳ. (3) Overall, there was a positive spatial correlation between each pair of the four diameter grades on a small scale (mostly 0−2 m). At the remaining scales, there was no spatial correlation among the diameter classes. (4) The overall distribution of M. philippensis was significantly positively correlated with soil moisture content, soil available potassium and soil total phosphorus (P<0.05). Among the soil topographic factors, altitude and slope significantly affected the spatial distribution of M. philippensis population in diameter grade Ⅱ (P<0.01). Conclusion M. philippensis population in Maolan karst forest shows a growth pattern. As the diameter grade increases, its spatial pattern shifts from clustered distribution to random distribution, affected by environmental heterogeneity (soil & topography), intraspecific competition, etc. [Ch, 3 fig. 2 tab. 36 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 33-44.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250155
Abstract:
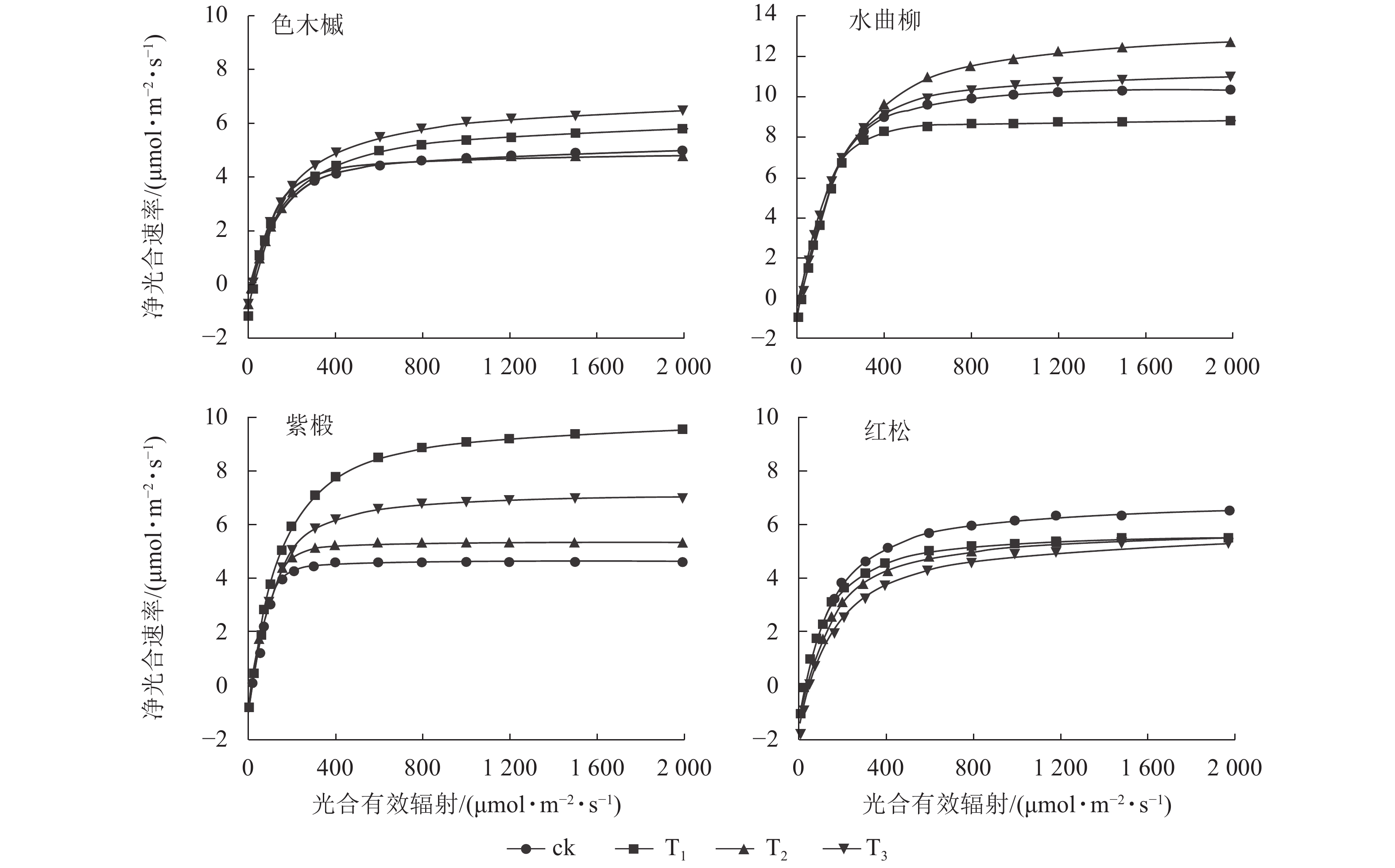
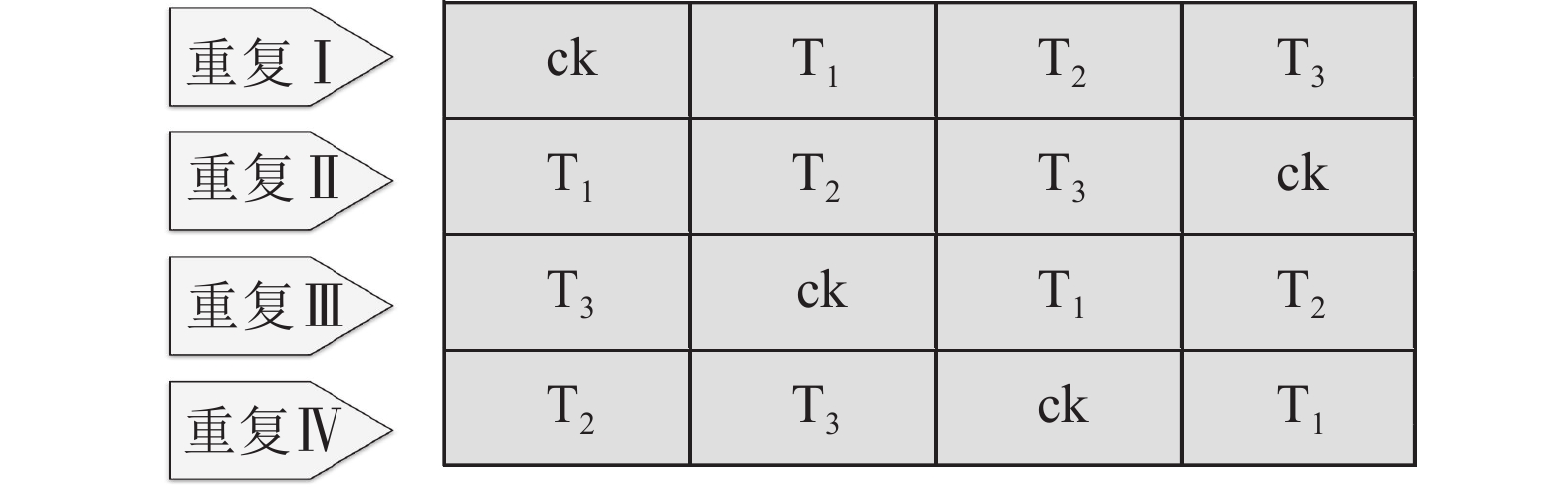
Objective Logging is a critical disturbance factor in forest ecosystems. This study aims to investigate the effects of logging intensity on leaf functional traits in a coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest, so as to provide scientific basis for post-logging species recovery. Method The 4 main tree species (Acer mono, Fraxinus mandshurica, Tilia amurensis, and Pinus koraiensis) in the conifer-broadleaf mixed forest of Jiaohe, Jilin Province were selected as the research subjects. The 4 different treatments were set up: control (ck, logging intensity was 0), light logging (T1, 17.24%), moderate logging (T2, 34.74%), and heavy logging (T3, 51.85%). Samples were collected and data on photosynthetic characteristics and leaf structural traits were analyzed. One-way ANOVA and least significant difference (LSD) tests were employed to compare inter-group differences. Result Different logging intensities significantly affected the photosynthetic characteristics and leaf structural traits of A. mono, F. mandshurica, T. amurensis, and P. koraiensis, whose maximum net photosynthetic rate was the highest under logging intensities of T3, T2, T1, and ck, and the lowest under logging intensities of T2, T1, ck and T3. Through the analysis of leaf structural traits, it was found that the leaf mass per area of A. mono, F. mandshurica, and T. amurensis was the highest under T1, while the leaf dry matter content of A. mono and F. mandshurica was the highest under T3. The leaf tissue density of F. mandshurica and T. amurensis was the highest under T1, while that of A. mono was the highest under T2. The relative content of chlorophyll in the leaves of each tree species showed no significant differences among the species. Conclusion Logging affects the photosynthetic characteristics and leaf structural traits of various tree species. Broadleaved species such as A. mono, F. mandshurica, and T. amurensis have the strongest carbon assimilation ability under T3, T2, and T1 intensities, and logging can improve their leaf structural parameters. The photosynthetic capacity of P. koraiensis decreases with increasing logging intensity, while leaf structural traits do not change with logging intensity. Low-intensity logging can promote photosynthetic capacity and efficiency of resource allocation of broadleaved species, while high-intensity logging can lead to the maladaptation of P. koraiensis. [Ch, 1 fig. 4 tab. 48 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 45-53.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250297
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to clarify the impacts of different pruning intensities on the growth and stem form of Erythrophleum fordii, so as to provide a theoretical basis for its pruning and cultivation. Method Taking a 4-year-old pure forest of E. fordii as the research object, four treatments were set up: no pruning (control, ck), low-intensity pruning (removing branches below 1/3 of tree height, T1), medium-intensity pruning (removing branches below 1/2 of tree height, T2), and high-intensity pruning (removing branches below 2/3 of tree height, T3). Each treatment consisted of 9 rows and 72 trees per plot, with four replicates. Tree height, diameter at breast height (DBH), crown width, and under-branch height were measured for four consecutive years. ANOVA and multiple comparisons were employed to analyze the effects of different pruning treatments and years on growth (height, DBH, volume), crown dynamics (crown width), and stem form (height to diameter ratio, breast height form factor, under-branch height, crown height, and crown height rate. Result T1 significantly promoted DBH and volume of the tree (P<0.05), with effects concentrated in the first year after pruning. T3 significantly inhibited tree height and volume growth in the first and third years after treatment, with the inhibitory effect on tree height reaching a significant level (P<0.05). The regulation of crown width by pruning exhibited stage-specific characteristics, with crown width increasing instead of decreasing in the first year after pruning, negative growth occurring in the second year and weakening with increasing pruning intensity, and no significant difference in pruning intensity in the fourth year. Pruning significantly (P<0.05) increased under-branch height but reduced crown height, crown height rate, breast height form factor, and height to diameter ratio, indicating that early pruning might reduce the bole fullness while optimizing the stem form. Conclusion The responses of growth to pruning showed significant annual fluctuations, with impacts mainly concentrated in the first year after pruning, and gradually weakening thereafter. After the fourth year, there is no significant effect. Considering both growth and stem form indicators, T1 achieves the optimal balance between DBH, volume, and under-branch height, and is the optimal strategy for cultivating large-diameter timber. [Ch, 2 fig. 7 tab. 25 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 54-65.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250163
Abstract:
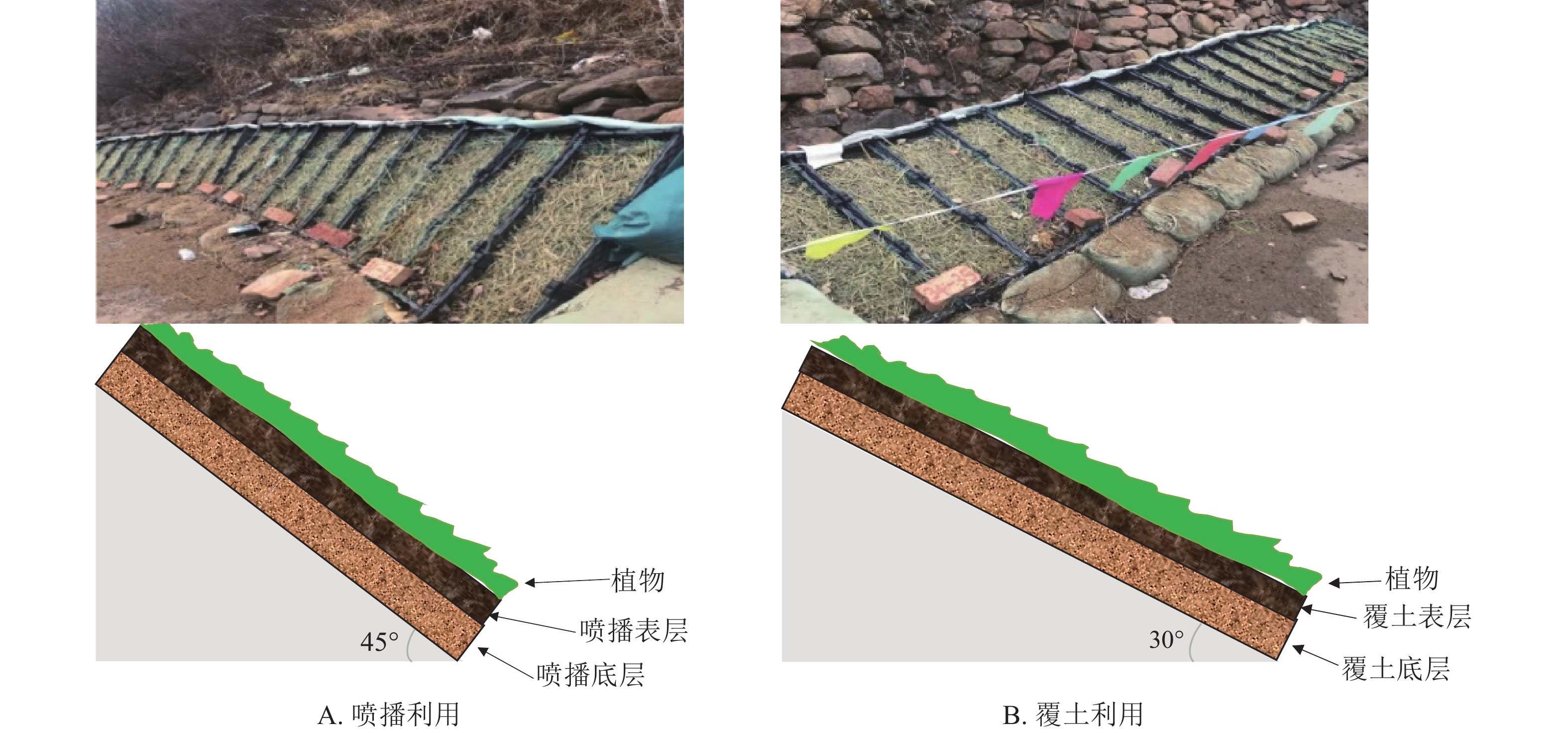
Objective The objective is to study the vegetation restoration effects under 2 different topsoil utilization modes, and further clarify the topsoil utilization mode and configuration that requires less topsoil but achieves better vegetation restoration effects. Method Taking the core area of Dahaituo National Nature Reserve in Chicheng County, Hebei Province as the research area, 11 groups of spray seeding experiments and 7 groups of soil covering experiments were set up using planting troughs to study the indicators such as plant germination quantity, germination trend, survival rate, plant community characteristics, and plant community diversity. The entropy weight-TOPSIS method was employed to comprehensively analyze the vegetation restoration effects under the two topsoil utilization modes. Result (1) The overall vegetation restoration effect of soil covering was better than that of spray seeding, and the community composition was mainly herbaceous plants. Soil covering generally performed better in terms of plant germination quantity, species diversity, coverage and biodiversity index. (2) Soil covering mode (5 cm topsoil+8 cm bottom soil, and 4 cm topsoil+8 cm bottom soil) and seed spraying mode (5 cm test topsoil+8 cm test bottom soil, and 4 cm test topsoil+8 cm test bottom soil) can achieve good vegetation restoration effects and establish suitable native vegetation. (3) The entropy weight-TOPSIS method evaluation showed that the optimal vegetation restoration effects were achieved with the following soil treatments: surface layer 5 cm+ bottom layer 8 cm under soil covering utilization mode, and surface layer 5 cm+ bottom layer 8 cm under seed spraying utilization mode. Conclusion In order to achieve good vegetation restoration effect and reduce the amount of topsoil, it is recommended to cover the soil with 5 cm topsoil+8 cm bottom soil and spray seeding with 5 cm test topsoil+8 cm test bottom soil. [Ch, 5 fig. 6 tab. 31 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 66-75.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250198
Abstract:
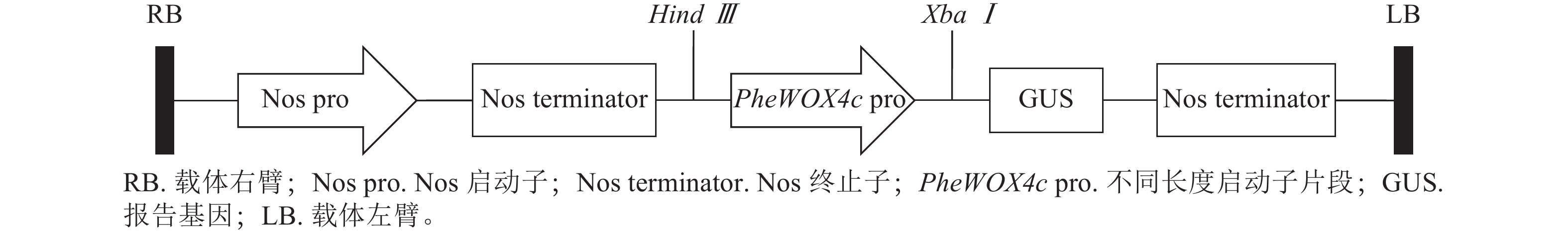
Objective The WOX4 gene, a key member of the WOX gene family, is involved in the regulation of plant growth and development. This study aims to investigate the biological function and expression regulation mechanism of PheWOX4c promoter in Phyllostachys edulis, and provide a reference for the regulation mechanism of the growth and development process of Ph. edulis. Method Based on the distribution of cis-acting elements identified by Plant CARE, plant expression vectors with different lengths of the 5′-end deletion promoter were constructed with the reporter gene GUS. Different environmental factors were selected for the treatment of transiently transformed leaves of Nicotiana tabacum. The full-length promoter and each length promoter fragment activities of PheWOX4c gene were analyzed by GUS staining, as well as the response pattern of promoters with different environmental factors. Result PheWOX4c gene promoter had multiple hormonal response elements such as salicylic acid (SA), abscisic acid (ABA), auxin (IAA), and methyl jasmonate (MeJA), as well as cis-acting elements involved in abiotic stresses such as low temperature and drought. GUS staining revealed that the promoter activity of PheWOX4c gene was inhibited by SA, ABA, IAA and low temperature treatment. This indicated the presence of a response element negatively regulating SA and also a response element negatively regulating ABA between −507 and −137 bp of promoter sequence, whereas a response element positively regulating ABA was found between −137 and 0 bp. MeJA response enhancer elements were found between −2 045 and −1 745 and between −137 and 0 bp, and low temperature negative regulatory elements were found between −1 140 and −507 bp. Conclusion PheWOX4c gene promoter contains multiple hormonal response elements and abiotic stress response elements. Different regulatory elements respond differently to different hormones, indicating that PheWOX4c gene is regulated by multiple transcription factors, with a very complex upstream regulatory network. [Ch, 7 fig. 2 tab. 38 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 76-85.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250366
Abstract:
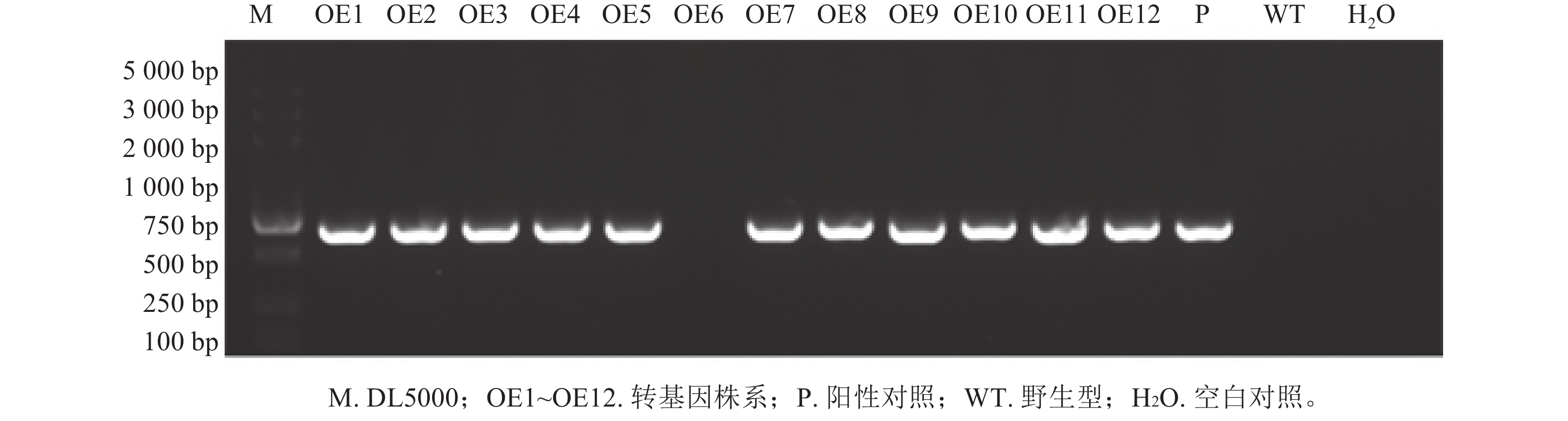
Objective This study aims to reveal the molecular mechanism of plant architecture in Prunus mume and clarify the role of AP2/ERF transcription factor family in branching regulation, so as to provide theoretical basis and candidate genes for the improvement of plant architecture in P. mume. Method PmERF011 gene sequence was obtained via gene cloning technology, and bioinformatics methods were employed to analyze its phylogenetic relationship and promoter cis-acting elements. The spatiotemporal expression patterns of PmERF011 in different tissues (roots, stems, and leaves) of P. mume were detected by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). An overexpression vector was constructed and transformed into Arabidopsis thaliana, followed by phenotypic observation and statistical analysis to verify its transgenic function. Result PmERF011 belonged to the AP2/ERF transcription factor family, which was highly homologous to related species in Rosaceae family (P. persica and P. armeniaca), but significantly different from A. thaliana and Oryza sativa. The analysis of promoter cis-acting elements revealed that it contained methyl jasmonate and auxin response elements. The results of tissue-specific assay showed that PmERF011 had the highest expression level in roots and stem xylems, but lower expression level in leaves. The results of transgenic A. thaliana showed that overexpression of PmERF011 significantly increased the number of lateral branches in A. thaliana (P<0.05). Conclusion PmERF011 has the function of promoting branch growth, which is a candidate gene for the improvement of plant architecture in P. mume and other Prunus species. [Ch, 7 fig. 2 tab. 46 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 86-95.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250246
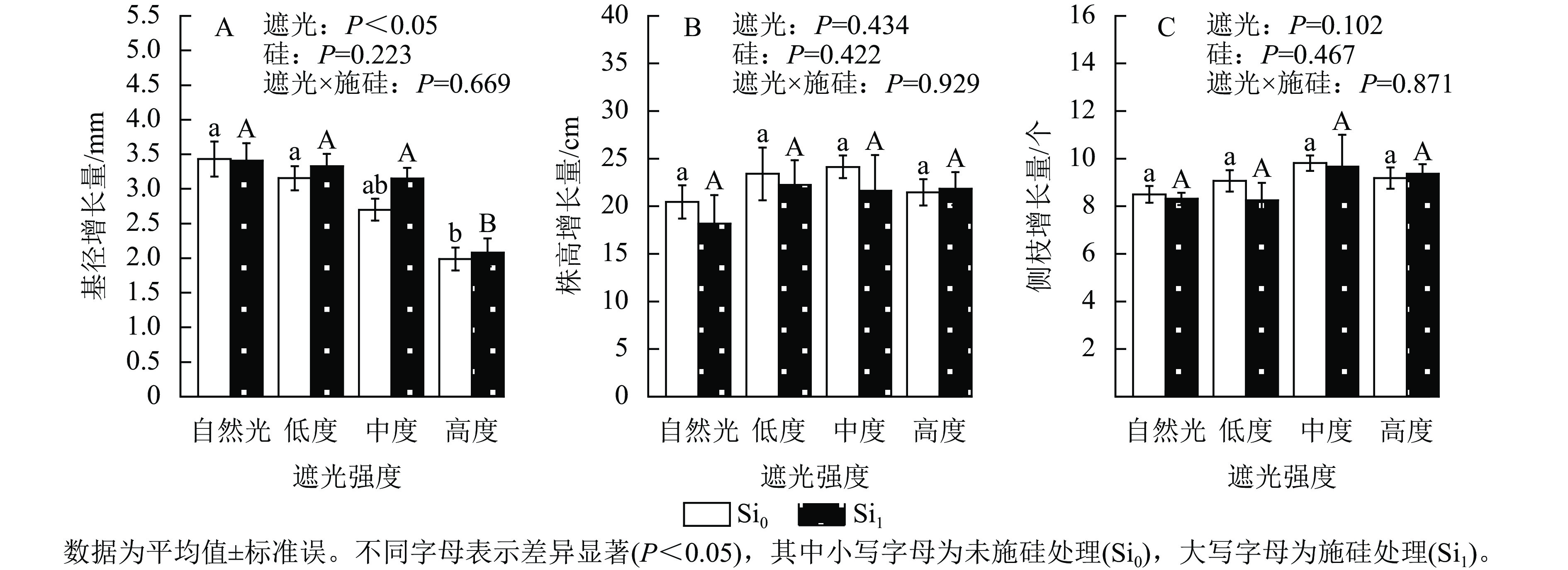
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the adaptation mechanism of Platycladus orientalis seedlings to weak light environment and clarify the alleviation effect of exogenous silicon on shading stress. Method Three-year-old P. orientalis seedlings were used as materials, covered with black nylon mesh, and subjected to four shading gradients: natural light, low shading, moderate shading, and high shading. Combined with 0 (Si0) and 2 mmol·L−1 (Si1) sodium silicate exogenous silicate treatment levels, a total of eight treatments were randomly set up. Physiological indicators such as growth, photosynthetic pigments, osmotic regulation, and antioxidant physiology of seedlings under different treatments were measured, and low-light adaptation characteristics of seedlings and the regulatory effect of silicon were analyzed Result (1) Shading treatment significantly inhibited the growth of ground diameter of P. orientalis by 5.18%−40.51% (Ρ<0.05). The silicon treatment promoted the growth of ground diameter, and the thickening rate reached 4.72%−16.67%. The shading environment promoted plant height growth, but under natural light and low to moderate shading conditions, silicon application treatment inhibited plant height growth, indicating that silicon application within a certain range of light intensity exerted a dual regulatory effect of “ground diameter thickening-apical inhibition”. (2) As the light intensity decreased, the contents of chlorophyll a and b increased, while chlorophyll a/b showed a downward trend, which was beneficial to improving the capture efficiency of the photosynthetic system at week light intensity. (3) Light shading induced dynamic responses of osmotic regulatory substances. Soluble sugars and proline first increased then declined, while soluble proteins exhibited the inverse trend, which activated the antioxidant protection system such as elevating peroxidase (POD) and catalase (CAT) activities and reducing malondialdehyde (MDA) (Ρ<0.01) content. Exogenous silicon enhanced osmotic regulation and antioxidant capacity, soluble sugars (SS) and proteins (SP) contents and POD activity, while reducing the mass molar concentration of MDA. Conclusion P. orientalis seedlings enhance their light capture capacity by increasing chlorophyll synthesis and activating antioxidant enzymes to improve their shade tolerance. Exogenous silicon can optimize morphogenesis to varying degrees, and enhance the osmotic regulation and antioxidant properties, thereby improving the ability of the seedlings to resist weak light stress. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 39 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 96-104.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250192
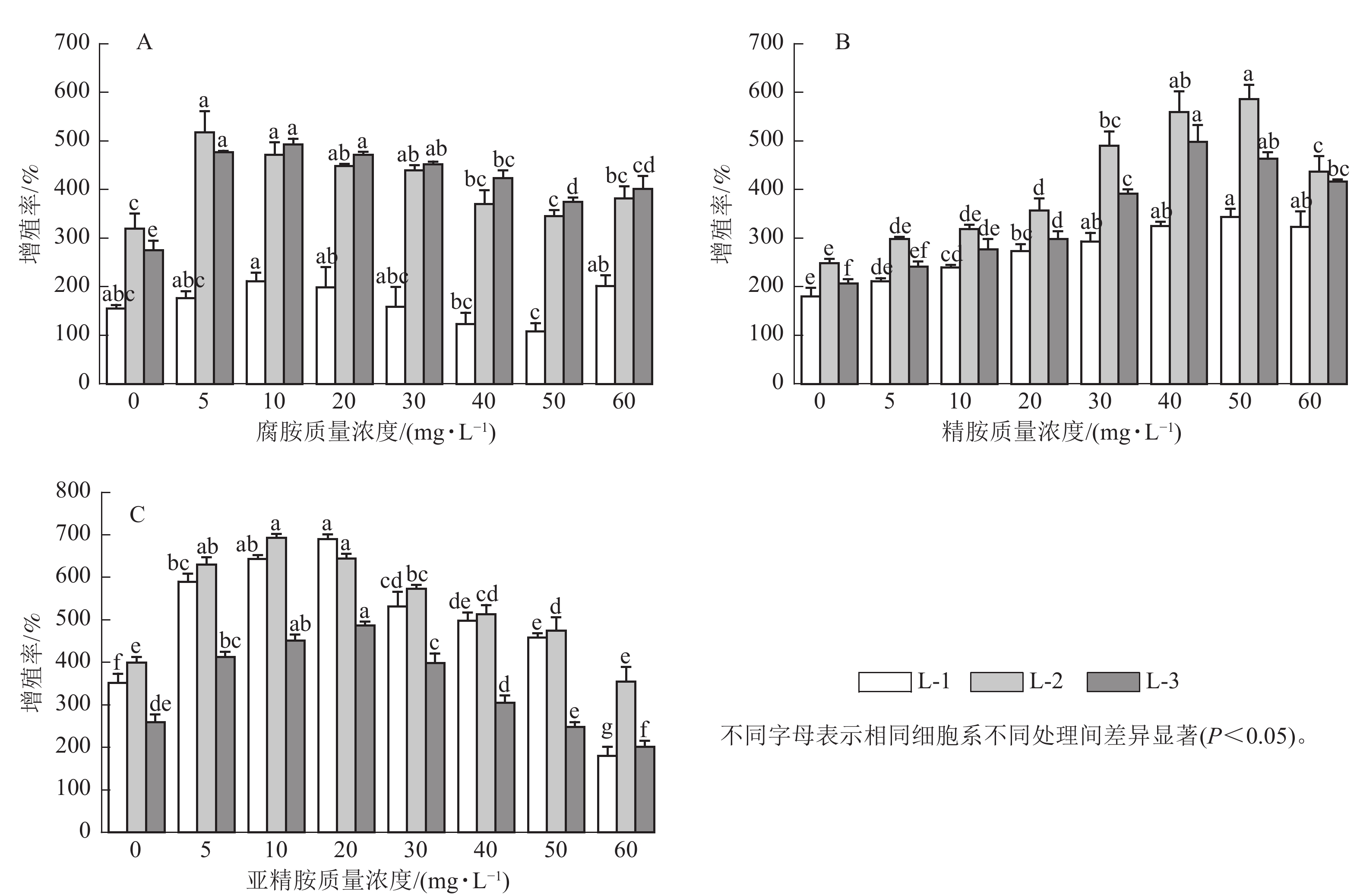
Abstract:
Objective To elucidate the physiological and biochemical effects of adding exogenous polyamines (PAs) on the embryogenic calli of Pinus koraiensis, which can enhance the proliferation ability of P. koraiensis embryogenic calli. Method By adding putrescine (Put), spermine (Spm) and spermidine (Spd) with different concentrations to the proliferation medium, the proliferation rate of embryonic calli were checked. The levels of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), and indoleacetic acid (IAA), abscisic acid (ABA), ethylene (ETH) were analyzed. Furthermore, the dynamic changes of Put, Spm and Spd levels response to exogenous PAs were also determined. Result Exogenous PAs had a positive effect on the proliferation of embryogenic calli, with 5−30 mg·L−1 Put, 40−50 mg·L−1 Spm, and 10−20 mg·L−1 Spd exhibiting the most significant promoting effects. In the cultivation of three cell lines, 5−30 mg·L−1 Put increased proliferation by 2.22%−79.27%; 40−50 mg·L−1 Spm enhanced proliferation by 80.56%−141.12%; and 10−20 mg·L−1 Spd boosted proliferation by 61.25%−96.21%. Additionally, exogenous addition of PAs significantly reduced intracellular H2O2 content and antioxidant enzyme activities (P<0.05) while increasing endogenous PAs and hormone levels within the cells. Specifically, exogenous supplementation of 50 mg·L−1 Spm could notably elevate the levels of endogenous PAs and hormones (P<0.05). Exogenous addition of 10 mg·L−1 Put significantly increased intracellular ethylene and Spm contents (P<0.05), whereas exogenous supplementation of 20 mg·L−1 Spd effectively promoted the increase in IAA, Put, and Spm contents. Conclusion The addition of exogenous PAs at appropriate concentrations can elevate endogenous PAs levels, hormone content, and antioxidant capacity, thereby facilitating the proliferation of embryogenic calli in P. koraiensis. [Ch, 4 fig. 35 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 105-115.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250193
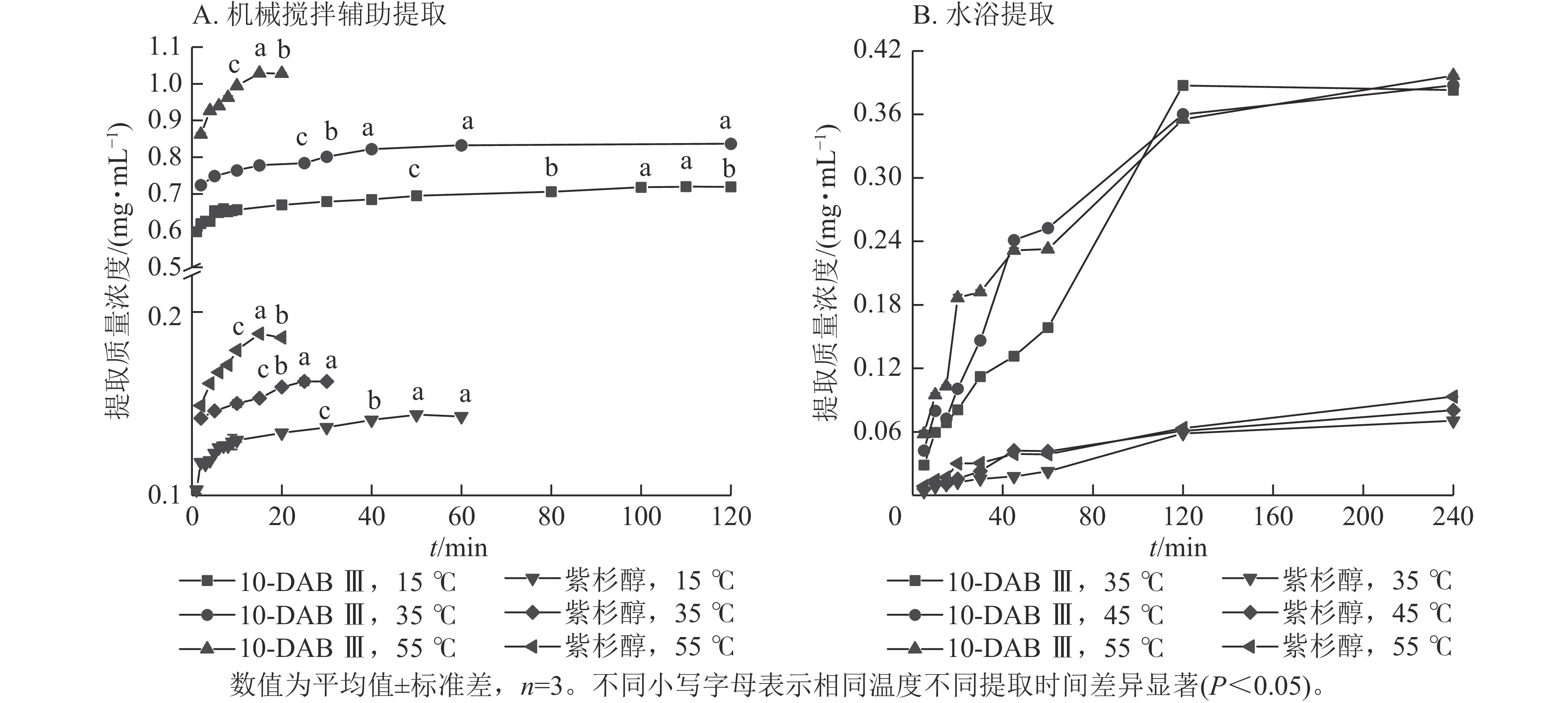
Abstract:
Objective The objective of this study is to investigate the kinetics, thermodynamics, and mass transfer mechanism of extracting 10 deacetylbaccatin Ⅲ (10-DAB Ⅲ) and taxol from the branches and leaves of Taxus yunnanensis by mechanical stirring assistance and water bath heating. Method The first-order and second-order extraction kinetics models were fitted, and the empirical diffusion model was used to estimate temperature-dependent variation laws of the diffusion coefficient (De), mass transfer coefficient (KT) and Biot number (Biot) of 10-DAB Ⅲ and taxol in T. yunnanensis, so as to explain the mass transfer behavior during the extraction process. Result (1) The activation energy for the activation of 10-DAB Ⅲ and taxol by mechanical stirring-assisted extraction was 40.745 and 18.762 kJ·mol−1 respectively, higher than those obtained by water bath extraction (36.428 and 16.668 kJ·mol−1 respectively). The extraction rates of both mechanical stirring-assisted and water bath heating extraction methods increased with the rise of extraction temperature. Among the 2 extraction methods, 10-DAB Ⅲ and taxol had the highest extraction rates at an extraction temperature of 328 K. The mechanical stirring-assisted extraction rates of the 2 components were 84.40% and 93.88%, respectively, while the water bath heating extraction rates were 71.62% and 93.35% respectively. (2) The results of thermodynamic study on the extraction process indicated that the enthalpy change (\begin{document}$ \Delta H $\end{document} \begin{document}$ \Delta S $\end{document} \begin{document}$ \Delta G $\end{document} Conclusion The second-order extraction kinetics model better aligns with method of extracting 10-DAB Ⅲ and taxol from T. yunnanensis by mechanical stirring assistance, while the first-order model is suitable for the slow extraction of 10-DAB Ⅲ and taxol by water bath. Both the logarithm (lnk) of the solute extraction rate (k) and the logarithm (lnKe) of the equilibrium rate constant (Ke) exhibit a linear relationship with the reciprocal of the extraction temperature. The extraction process of 10-DAB Ⅲ and taxol from T. yunnanensis belongs to internal diffusion. [Ch, 6 fig. 3 tab. 32 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 116-124.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250218
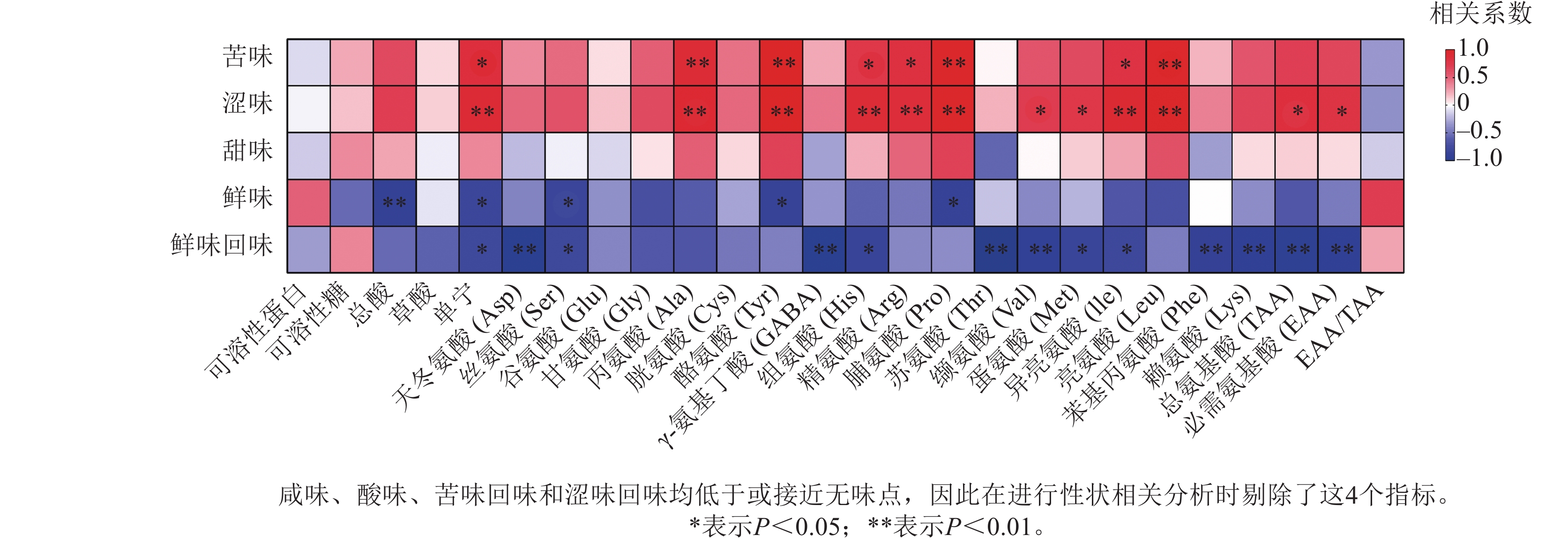
Abstract:
Objective Chimonobambusa hejiangensis is an excellent bamboo species for bamboo shoots. Studying the differences in quality and flavor of bamboo shoots among different cultivars can provide significant references for targeted breeding of superior cultivars. Method The 3 Ch. hejiangensis cultivars were selected as research objects, with Phyllostachys edulis, Ph. violascens, and Bambusa multiplex as controls. Nutritional components, amino acids, and taste indicators were measured according to national standards. Quality and taste evaluations were conducted through difference analysis and correlation analysis. Result Ch. hejiangensis shoots exhibited higher soluble protein content and EAA/TAA ratio compared to control bamboo shoots, while total acid, tannin, total amino acids, and bitter amino acid contents were lower. Significant differences existed among the 3 cultivars: Ch. hejiangensis ‘Mantianxing’ showed the lowest total acid (0.85 g·kg−1) and tannin (364.67 mg·kg−1), lower than Ch. hejiangensis ‘Qiaobaixue’ and Ch. hejiangensis ‘Dawujin’. Ch. hejiangensis ‘Qiaobaixue’ had the highest total amino acids (2 288.4 mg·kg−1) and essential amino acids (785.8 mg·kg−1), while Ch. hejiangensis ‘Mantianxing’ achieved the highest EAA/TAA ratio (0.36). Ch. hejiangensis ‘Qiaobaixue’ had the highest proportion of bitter amino acids (26.67%), whereas Ch. hejiangensis ‘Mantianxing’ showed the highest proportions of umami (14.25%), sweet (25.66%), and aromatic amino acids (11.08%). In taste evaluation, Ch. hejiangensis ‘Qiaobaixue’ exhibited the strongest bitterness and astringency with the weakest umami, while Ch. hejiangensis ‘Mantianxing’ had minimal astringency and the strongest umami with umami aftertaste. Correlation analysis revealed that tyrosine were most positively correlated with astringency(r=0.964) and bitterness(r=0.955) and moderately correlated with tannin. Conclusion Ch. hejiangensis shoots possess superior nutritional quality. Ch. hejiangensis ‘Qiaobaixue’ excels in nutrient and amino acid content, its strong bitterness limits palatability. Ch. hejiangensis ‘Mantianxing’, with enhanced umami, reduced bitterness, minimal astringency, and optimal amino acid composition, demonstrates superior taste and nutritional value, making it the most suitable cultivar for shoot-oriented breeding. [Ch, 1 fig. 4 tab. 25 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 125-132.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250273
Abstract:
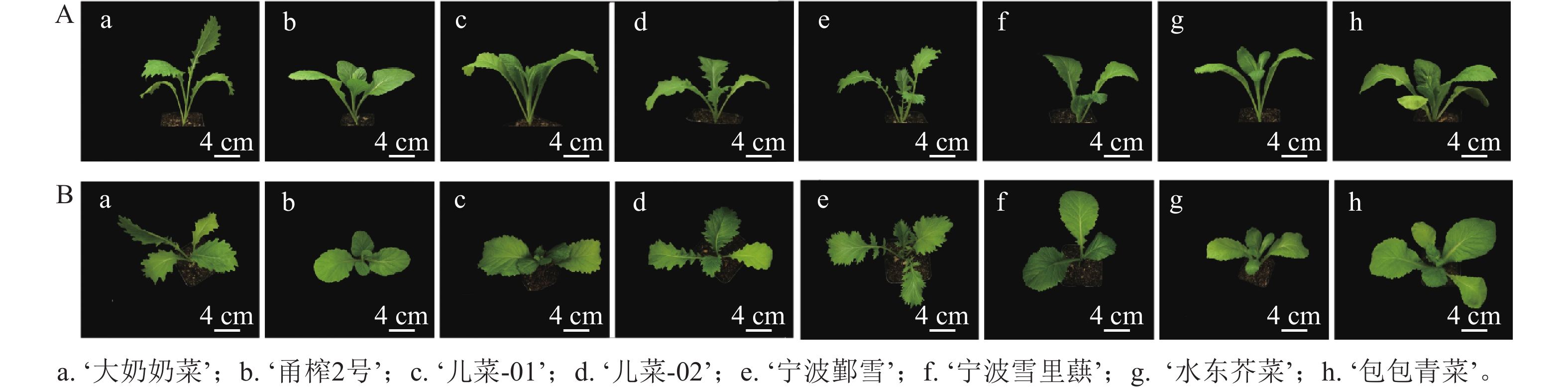
Objective To systematically analyze the glucosinolate (GSL) content in the leaves of different mustard (Brassica juncea) cultivars, with the aim of investigating the effects of GSL content and composition on plant disease resistance. Method 4 stem mustard cultivars (B. juncea var. tumida), namely ‘Danainaicai’‘Ercai-01’‘Ercai-02’‘Yongzha No.2’, and 4 leaf mustard cultivars (B. juncea var. rugosa), namely ‘Ningboyinxue’‘Ningboxuelihong’‘Shuidongjiecai’‘Baobaoqingcai’, were selected as experimental materials to determine the GSL content in their leaves. Disease resistance was assessed by measuring plaque areas through live inoculation with Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Result Significant differences were observed in the total GSL content among the leaves of different mustard cultivars. The total GSL content ranged from 1.851 to 4.844 µmol·g−1, while the aliphatic GSL (AGSL) content varied between 1.766 and 4.831 µmol·g−1. Both the total GSL and AGSL contents were highest in ‘Yongzha No. 2’ and lowest in ‘Ercai-02’. Indole GSL (IGSL) content ranged from 0.006 to 0.035 µmol·g−1, with the highest level in ‘Ercai-02’ and the lowest in ‘Danainaicai’. The GSL content of each component in ‘Shuidongjiecai’ fell into the intermediate range. Sinigrin (SIN) accounted for more than 95% of the total GSL content across all cultivars. At 12 hours post-inoculation, the plaque area of ‘Ercai-01’ was the largest. At 24 hours, the plaque area of ‘Baobaoqingcai’ was the largest, whereas ‘Yongzha No. 2’ exhibited the smallest plaque area at both time points. At 36 hours, ‘Ningboxuelihong’ had the largest plaque area, while ‘Danainaicai’ showed the smallest plaque area (P<0.05). Conclusion The resistance of mustard cultivars to pathogenic bacteria was closely associate with the total amount, component content, and proportion of GSL. Stem mustard cultivars generally exhibited higher GSL content compared to leaf mustard cultivars. Among the test cultivars, ‘Yongzha No. 2’ demonstrated the strongest resistance to the nuclear plate fungus, followed by ‘Shuidongjiecai’. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 29 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 133-141.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250112
Abstract:
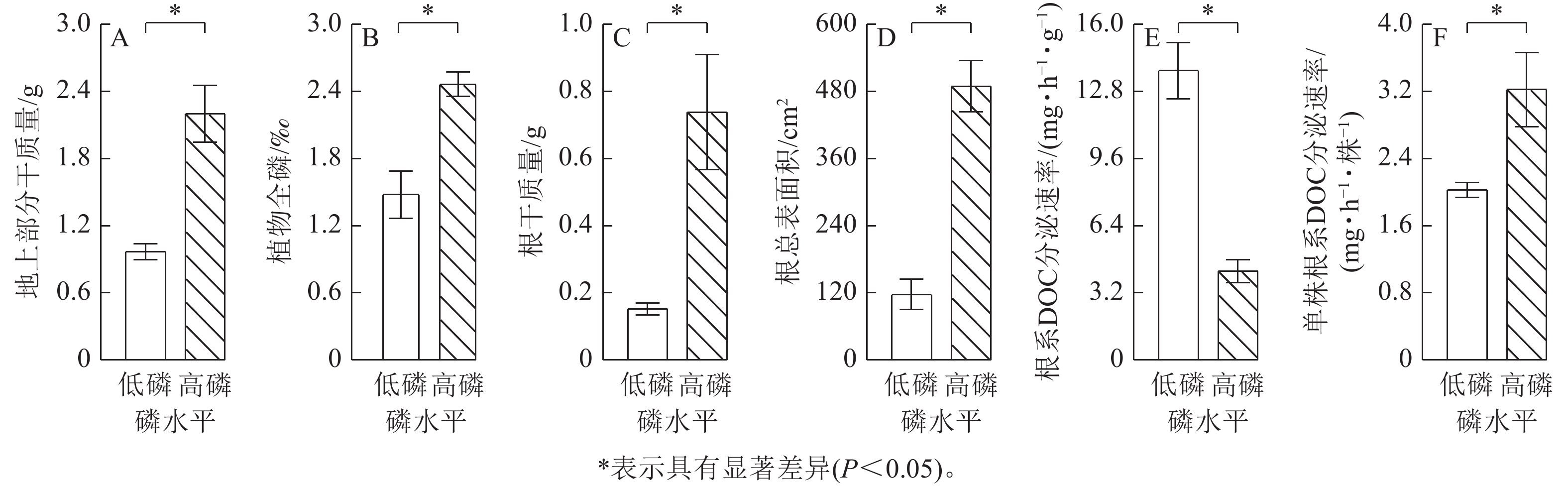
Objective This study aims to investigate the effects of soil available phosphorus content on the growth of Zea mays, the allocation of photosynthetic products to the belowground parts, and the structure of rhizosphere microbial communities. It also explores the responses of maize to low-phosphorus stress and the impacts of these responses on the carbon dynamics in the rhizosphere soil. Method Root-box cultivation methods were employed to grow maize under high and low phosphorus conditions. Relevant indicators related to soil, roots, root exudates, plant samples, and microbial community structure were measured and analyzed. Result Under high phosphorus condition, the phosphorus content in maize leaves increased, which promoted the growth of both the aboveground and underground parts of maize. High phosphorus condition also increased the secretion of total root exudate dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and enhanced the activities of chitinase, glucosidase, cellulase, and acid phosphatase in the rhizosphere. Additionally, it significantly increased the relative abundance of Acidobacteriota, Actinobacteriota, and Gemmatimonadota in the rhizosphere (P<0.05). Under low phosphorus condition, the infection rate of arbuscular mycorrhizal and the content of easily extracted glomalin-related soil protein (EE-GRSP) were significantly higher than that under high phosphorus condition (P<0.05). Conclusion Under low phosphorus condition, the mycorrhizal infection rate and the secretion efficiency of root exudates in maize were increased, and this promoted the growth of R-strategy microorganisms and the content of glomalin-related soil protein (GRSP) in the rhizosphere. Under high phosphorus condition, the rhizosphere of maize has higher activities of chitinase, glucosidase, cellulase, and acid phosphatase. These enzyme activities are positively correlated with the relative abundance of K-strategy microorganisms. [Ch, 5 fig. 32 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 142-152.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250128
Abstract:
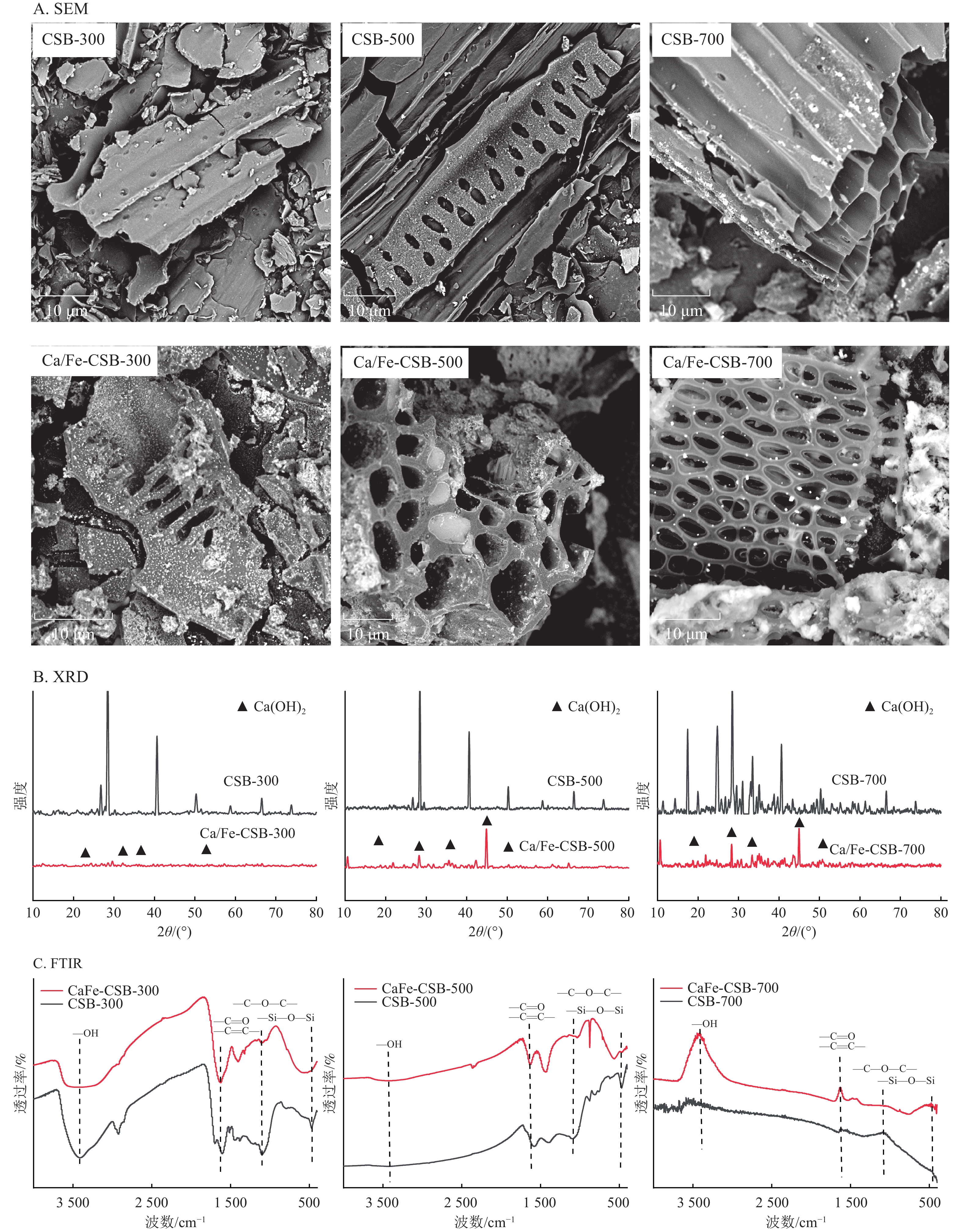
Objective This study investigates the influence of pyrolysis temperature and calcium-iron (Ca/Fe) modification on the pore structure of biochar and its phosphate adsorption performance, aiming to provide reference for the application of modified biochar in the field of water treatment. Method Biochars and Ca/Fe-modified biochars were synthesised at 300, 500, and 700 ℃, and characterised using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) to investigate their microstructure and surface chemistry. Batch adsorption experiments were conducted to evaluate the effects of pyrolysis temperature, dosage, solution pH, and co-existing ions on phosphate removal. Furthermore, adsorption mechanisms were elucidated using isotherm and kinetic models. Result With increasing pyrolysis temperature, the pore structure of biochar developed progressively. Notably, Ca/Fe-modified biochar produced at 700 ℃ exhibited a highly ordered porous architecture and enlarged specific surface area, achieving a maximum phosphate adsorption capacity of 890.836 mg·g−1 and a removal efficiency of 90.32%. Adsorption isotherms fitted the Sips model, while kinetic data followed the pseudo-second-order model, indicating chemisorption as the dominant mechanism. XRD analysis confirmed the formation of Ca(OH)2 at high temperature, which contributed to enhanced phosphate fixation. Adsorption performance was influenced by pH, dosage, and co-existing ions; alkaline conditions and optimised dosage improved phosphate removal, whereas competing anions such as \begin{document}${\mathrm{NO}}_3^- $\end{document} \begin{document}$ {\mathrm{SO}}_4^{2 - } $\end{document} Conclusion Tuning pyrolysis temperature and Ca/Fe modification significantly enhances the pore architecture and adsorption performance of biochar, offering an efficient material for phosphate removal from aqueous environments. [Ch, 5 fig. 4 tab. 32 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 153-165.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250126
Abstract:
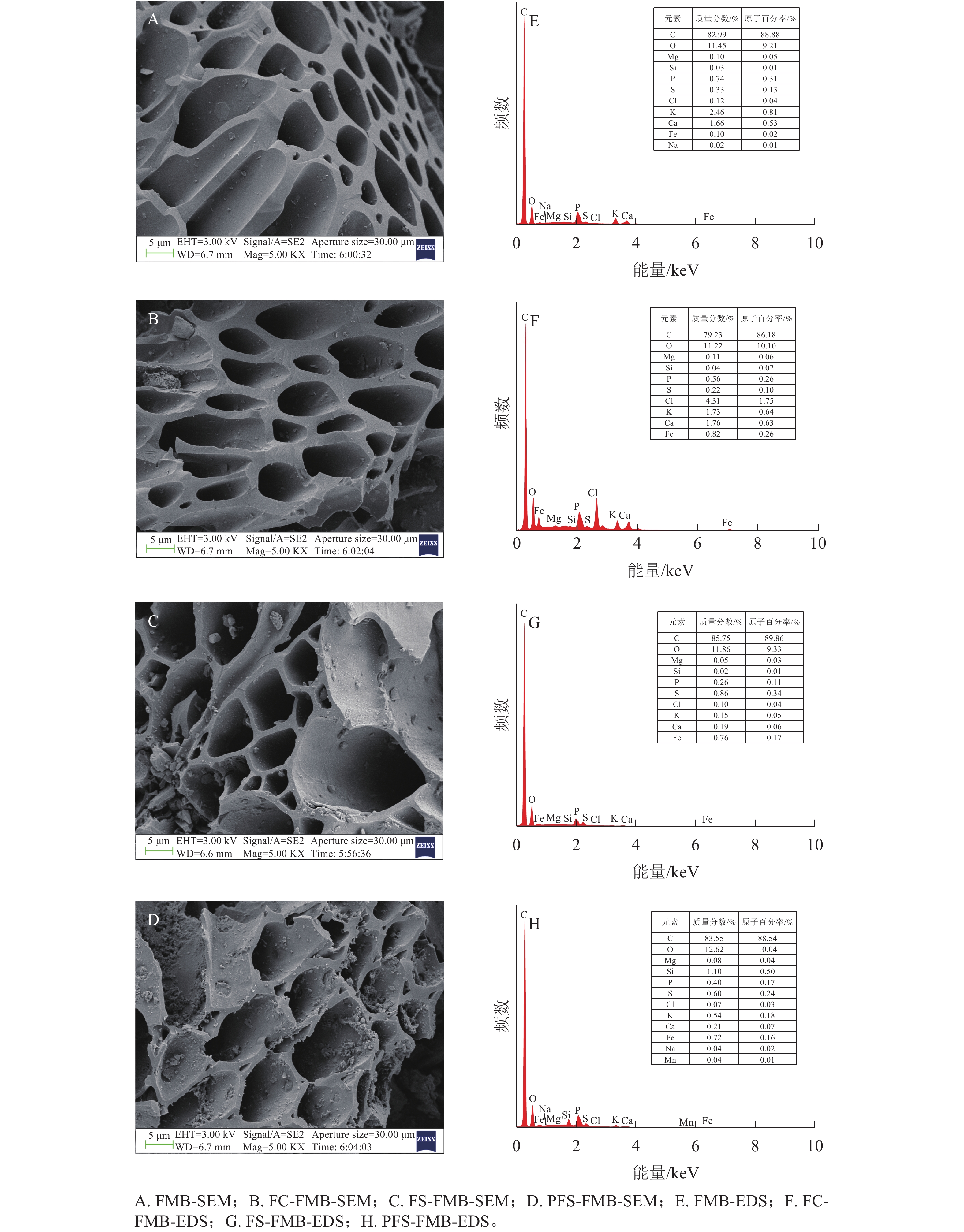
Objective The study aims to explore the potential and mechanisms of iron-based modification in enhancing the adsorption and immobilization capacity of biochar for As(Ⅲ), and construct an effective carbon sequestration and arsenic control system. Method The common garden waste Ficus microcarpa stems and leaves was used as the raw material for making biochar. Batch adsorption experiments were conducted in combination with various analytical techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The structural properties of the raw biochar (FMB), ferric chloride-modified biochar (FC-FMB), ferric sulfate-modified biochar (FS-FMB), and polymerized ferric sulfate-modified biochar (PFS-FMB) were systematically investigated, along with their adsorption performance and mechanisms for As(Ⅲ) in aqueous solutions. Result Iron-based modification effectively increased the specific surface area of biochar by 3.36 to 4.22 times. Moreover, the modified biochar surfaces were enriched with more functional groups, and iron oxides were successfully loaded onto the biochar surface. At the pH value of 5, PFS-FMB achieved the highest removal rate of As(Ⅲ), reaching 91.16%, which was significantly higher than that of other biochar types. Adsorption kinetics analysis showed that the adsorption process of As(Ⅲ) followed the Elovich kinetic model, while the adsorption isotherms fitted well with the Langmuir isotherm model. The maximum adsorption capacities of 4 kinds of biochars for As(Ⅲ) from high to low were PFS-FMB (13.53 mg·g−1), FS-FMB (6.36 mg·g−1), FC-FMB (3.11 mg·g−1), FMB (1.29 mg·g−1). The adsorption of As(Ⅲ) by iron-based modified biochar was mainly chemical adsorption, which achieved through surface complexation. The adsorption mechanism involved the coordination between arsenite anions and iron oxides, as well as the complexation of surface hydroxyl functional groups. Conclusion Iron-based modified biochar is an efficient arsenic adsorbent, among which PFS-FMB demonstrated the best adsorption performance. [Ch, 9 fig. 3 tab. 50 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 166-174.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250158
Abstract:
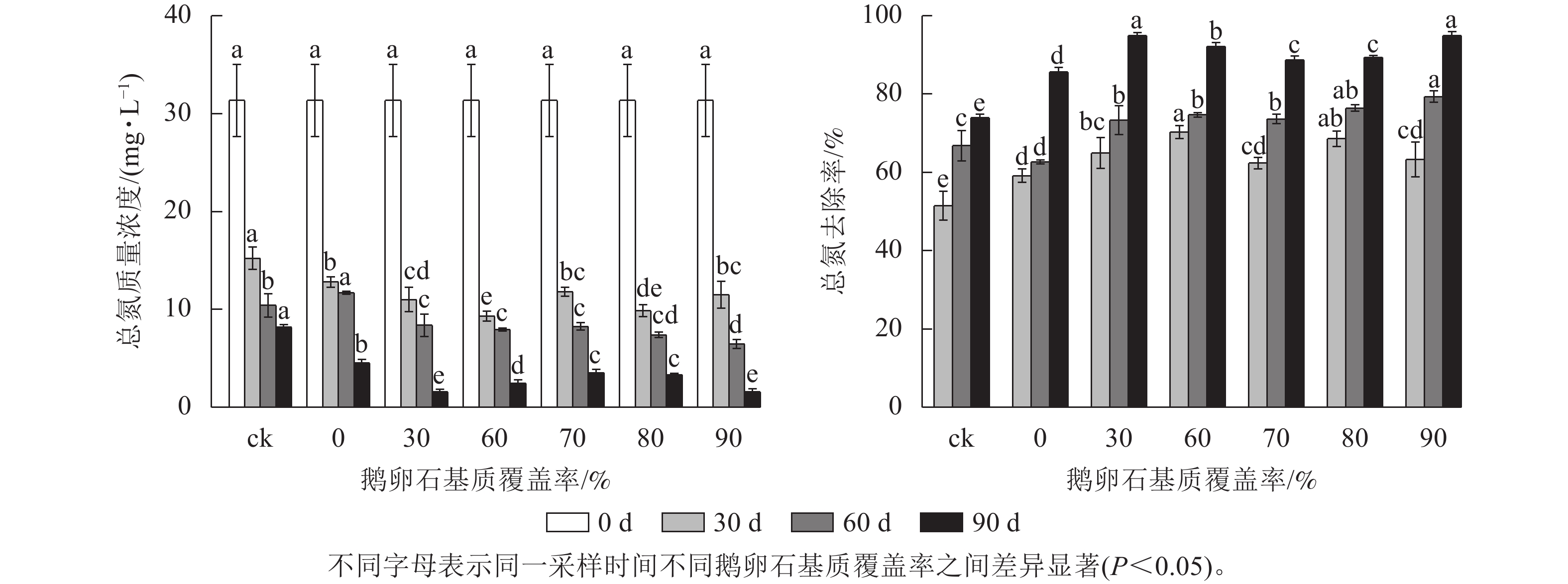
Objective By covering the substrate sediment of Vallisneria natans with cobblestone substrate at different coverage rates, discussion on the ability and effect of V. natans in purifying water pollution in different growth environments, providing data support for water ecological restoration and application. Method From May to October 2024, using sandy loam soil as the substrate for planting V. natans and pebbles as the covering substrate, artificial planting experiments were conducted to study the purification effect of V. natans on total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and arsenic (As) in water at cobblestone coverage rates of 0, 30%, 60%, 70%, 80%, and 90%, respectively. Result Under different coverage rates of cobblestone substrate, the purification of TN, TP and As in water by V. natans was different. With the increase of coverage rate, the overall removal rate of pollutants in water increased first, then decreased, and then increased. V. natans itself was the main way to purify water quality, followed by pollutant precipitation and the adsorption of substrate sediment and cobblestones. The TN removal rate was highest when the cobblestones coverage rate was 30%, decreasing from the initial 31.33 mg·L−1 to 1.59 mg·L−1, with a removal rate of 94.93%. The TP removal rate was highest when the cobblestones coverage was 30%, decreasing from the initial 1.56 mg·L−1 to 0.04 mg·L−1, with a removal rate of 97.43%. The removal rate of As was highest when the cobblestones coverage was 30%, decreasing from the initial 967.33 μg·L−1 to 4.00 μg·L−1, with a removal rate of 99.59%. Analysis of variance showed that there were significant differences (P<0.05) in the removal efficiency of TN, TP and As in water with different cobblestones coverage rates. Conclusion The coverage rate of cobblestones have an impact on the purification of water quality by V. natans. When the coverage rate was 30%, V. natans has the best removal effect on TN, TP, and As in the water. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 37 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 175-185.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250182
Abstract:
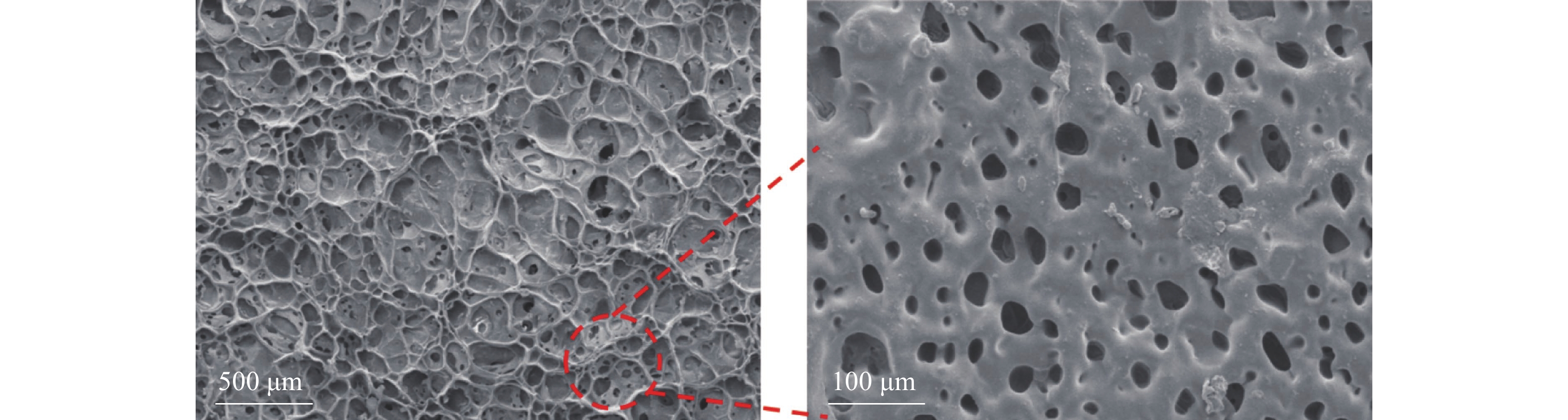
Objective To address the challenges of difficult degradation of azo anionic dyes in environmental wastewater treatment and the poor environmental adaptability of traditional adsorbents, this study aimed to develop a novel composite hydrogel based on agricultural and forestry biomass (lignin) for efficient dye adsorption, thereby providing a new strategy for the preparation of green materials of water treatment. Method A novel lignin-based composite hydrogel (HPAAM-VIM-LS) was synthesized via free radical copolymerization. Its microstructure and chemical composition were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and tensile/compression tests were performed to evaluate thermal stability and mechanical properties. Adsorption experiments investigated its adsorption performance and reusability for the anionic dye Congo red (CR). The adsorption mechanism was elucidated by analyzing adsorption kinetics and isotherm models in conjunction with structural characterization. Result HPAAM-VIM-LS exhibited a three-dimensional porous network structure. Its surface, rich in hydroxyl, carboxyl, and imidazolium cationic groups, provided abundant active sites. The thermal decomposition temperature exceeded 189.9 ℃. The material demonstrated a tensile strain of 746%, an elastic modulus of 15.15 MPa, and high adsorption efficiency across pH 5.0−8.0 and temperatures of 25−55 ℃. Under optimal conditions (pH 6.0, 35 ℃), a CR removal rate of 96.4% and a maximum adsorption capacity of 490.58 mg·g−1 were achieved. Structural analysis revealed that the adsorption mechanism was synergistically driven by electrostatic attraction, hydrogen bonding, π—π stacking, pore filling, and coordination. The adsorption process followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and was jointly controlled by external/intraparticle diffusion and chemisorption. HPAAM-VIM-LS maintained a CR removal rate more than 85% after 7 adsorption-desorption cycles. Conclusion This study successfully prepared an environmentally friendly lignin-based composite hydrogel, HPAAM-VIM-LS, combining high adsorption capacity, broad environmental adaptability, and excellent mechanical properties. It provides an efficient and sustainable solution for the resource utilization of lignin and the treatment of dye-containing wastewater. [Ch, 11 fig. 3 tab. 29 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 186-196.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250202
Abstract:
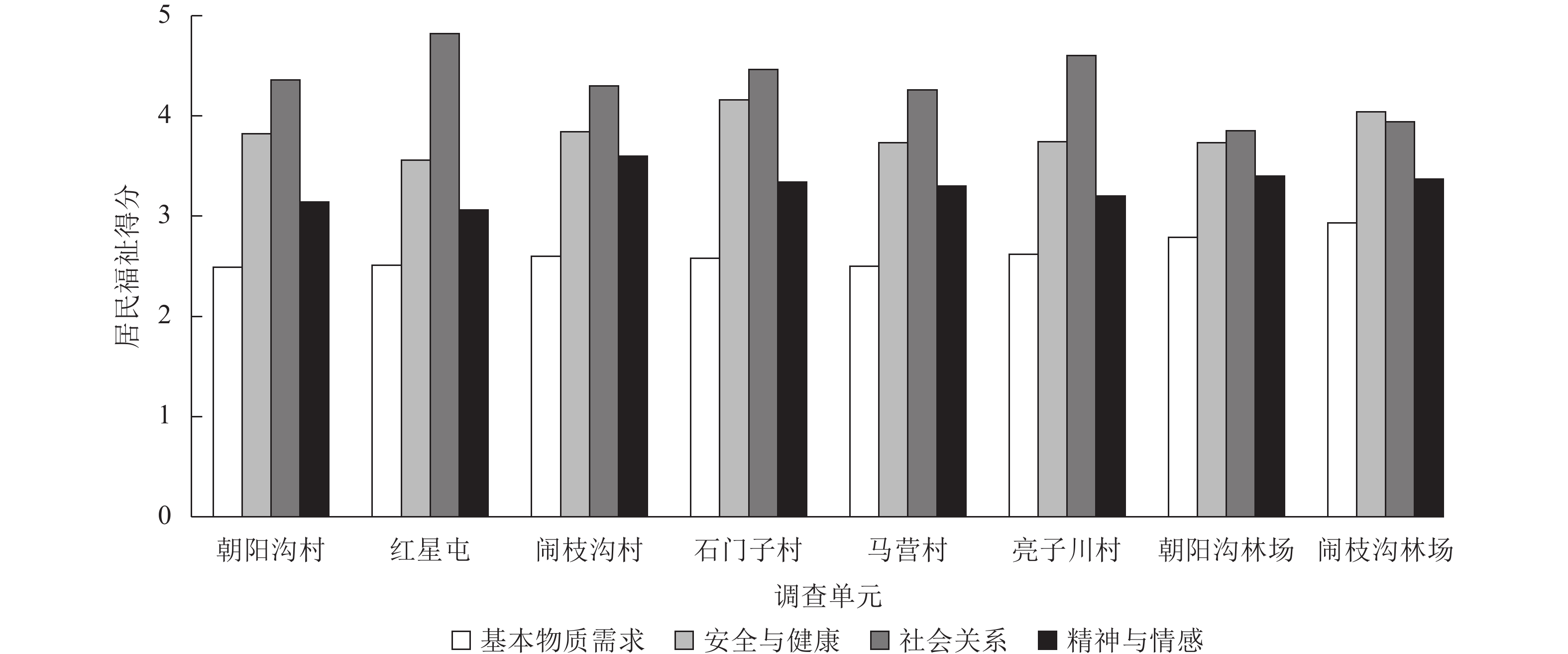
Objective The aim is to explore the relationship between ecosystem services and the well-being of local people, which is of great significance for promoting sustainable development in national parks. Method Taking Dongning area of Northeast Tiger and Leopard National Park as a case study, an analytical framework of ecosystem services and the well-being of local residents was constructed from the perspective of residents’ perception, and the coupling coordination degree model was used to analyze the relationship between the two. Result (1) Both the social relationship (P=0.000) and basic material needs (P=0.000) of farmers were significantly lower than those of forest workers. The social relationship (P=0.043) and basic material needs (P=0.001) in core areas were significantly lower than those in general areas. (2) The perception of cultural services (P=0.000) and support services (P=0.025) in core areas was significantly lower than that in general areas. Compared with forest workers, farmers had significantly weaker perception of cultural services (P = 0.000) and supporting services (P = 0.004), but significantly stronger perception of supply services (P = 0.006). (3) The coupling coordination between ecosystem services and residents’ well-being was poor, with 75% of the study area in a moderate imbalance or transitional state. The overall dimensional differences showed an unbalanced feature of “services leading, well-being lagging”, with particularly weak coordination between cultural services and basic material needs, safety and health, social relations and spiritual well-being. Conclusion Group difference and regional balance should be considered in the formulation of national park policy, so as to enhance the sustainable development of ecosystem services and the well-being of local residents. [Ch, 5 fig. 7 tab. 31 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 197-207.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250146
Abstract:
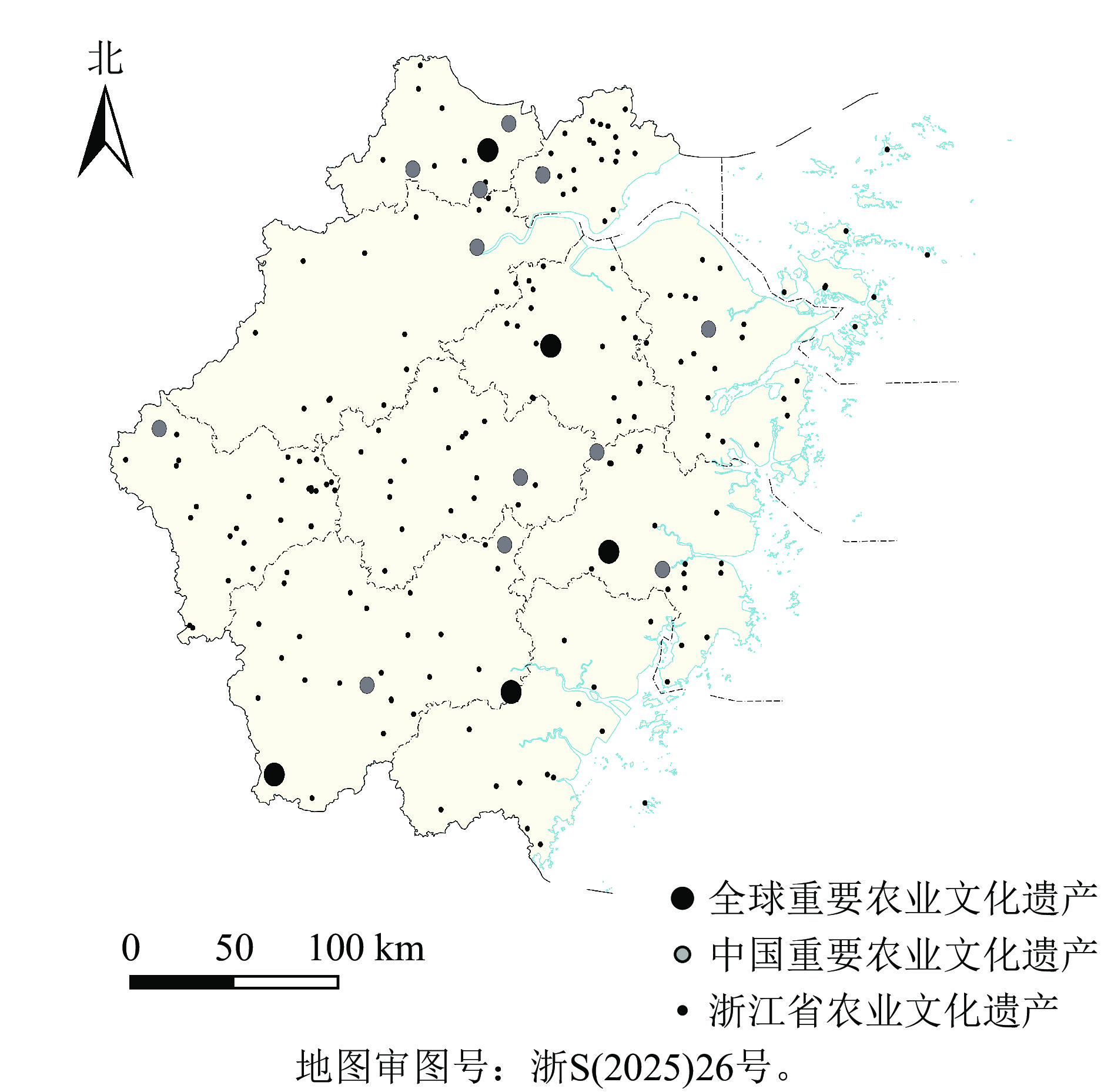
Objective As a province in China to initiate the identification and protection of agricultural heritage, Zhejiang Province leads the country in the number of important agricultural heritage sites both in China and worldwide. The aim of this study is to investigate the spatial distribution pattern and influencing factors of agricultural heritage in Zhejiang, which provides valuable insights for the conservation and sustainable utilization of agricultural heritage across China. Method Based on 205 agricultural heritage sites recognized by Department of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of Zhejiang Province in 2024, the spatial pattern, morphology, and concentration degree were analyzed by using ArcGIS 10.2. Combined with the topography of Zhejiang Province, agricultural heritage sites were classified spatially, and influencing factors were examined. Result The spatial distribution of agricultural heritage in Zhejiang was characterized by an overall dispersed pattern and small-scale multi-point aggregation. The concentration of agricultural heritage was relatively high at the city level, mainly concentrated in Lishui and Quzhou. At the county level, Longyou County exhibited the highest concentration. Zhejiang’s agricultural heritage zones were spatially divided into high mountain agricultural heritage zone in hilly areas of west Zhejiang, plain and basin agricultural heritage zone in Jinqu Basin of central Zhejiang, water town agricultural heritage zone in plains of north Zhejiang, composite agricultural heritage zone in hilly areas of east Zhejiang, and marine and fishery agricultural heritage zone in southeast coastal plains and islands. Conclusion The spatial distribution pattern of agricultural heritage in Zhejiang is mainly influenced by a combination of natural factors, including elevation, climate, and hydrological systems, as well as socio-economic factors such as economic development level, population, urbanization rate, and historical culture. [Ch, 6 fig. 37 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 208-218.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250164
Abstract:
Plant belowground foraging traits are crucial for plant nutrient acquisition and environmental adaptation. Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) availability, as key driving factors, have a profound impact on plant belowground nutrient acquisition strategies. First, it introduces the classification of plant belowground foraging traits. This include absorptive root traits (morphology, architecture, and proliferation), mycorrhizal traits (mycorrhizal fungal colonization rate and hyphal density), and exudation traits (root carbon exudation rate and root enzyme activity). Subsequently, it illustrates the effects of N and P addition on these foraging traits. Regarding absorptively root traits, studies have shown that the effects of N and P addition vary depending on tree species and nutrient conditions. Plants optimize resource acquisition by altering their morphology, architecture, and proliferation characteristics. For mycorrhizal traits, mycorrhizal fungi regulate belowground resource acquisition through differentiated strategies (For example, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi rely on hyphal extension for inorganic nutrient uptake, while ectomycorrhizal fungi secrete enzymes to decompose organic matter), however, N and P addition generally suppress mycorrhizal colonization rates. As for exudation traits, root acid phosphatase and nitrate reductase, which are key indicators reflecting plant P and N acquisition and metabolism, were significantly regulated by N and P addition. Next, it also explores the coordination mechanisms among belowground foraging traits. This includes synergies and trade-offs among traits, as well as cost-benefit optimization in resource allocation. Finally, addressing current research gaps, future research directions are proposed, focusing on N-P interactions, the synergistic response mechanisms among root secretory traits, absorptive roots, and mycorrhizal traits, in situ observations of mature plants in the field, and foraging strategies of different mycorrhizal types of tree species. These directions aim to deepen our understanding of plant belowground nutrient acquisition strategies and their adaptation mechanisms to environmental changes, providing a scientific basis for the management of forest ecosystems. [Ch, 2 tab. 95 ref.]
Plant belowground foraging traits are crucial for plant nutrient acquisition and environmental adaptation. Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) availability, as key driving factors, have a profound impact on plant belowground nutrient acquisition strategies. First, it introduces the classification of plant belowground foraging traits. This include absorptive root traits (morphology, architecture, and proliferation), mycorrhizal traits (mycorrhizal fungal colonization rate and hyphal density), and exudation traits (root carbon exudation rate and root enzyme activity). Subsequently, it illustrates the effects of N and P addition on these foraging traits. Regarding absorptively root traits, studies have shown that the effects of N and P addition vary depending on tree species and nutrient conditions. Plants optimize resource acquisition by altering their morphology, architecture, and proliferation characteristics. For mycorrhizal traits, mycorrhizal fungi regulate belowground resource acquisition through differentiated strategies (For example, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi rely on hyphal extension for inorganic nutrient uptake, while ectomycorrhizal fungi secrete enzymes to decompose organic matter), however, N and P addition generally suppress mycorrhizal colonization rates. As for exudation traits, root acid phosphatase and nitrate reductase, which are key indicators reflecting plant P and N acquisition and metabolism, were significantly regulated by N and P addition. Next, it also explores the coordination mechanisms among belowground foraging traits. This includes synergies and trade-offs among traits, as well as cost-benefit optimization in resource allocation. Finally, addressing current research gaps, future research directions are proposed, focusing on N-P interactions, the synergistic response mechanisms among root secretory traits, absorptive roots, and mycorrhizal traits, in situ observations of mature plants in the field, and foraging strategies of different mycorrhizal types of tree species. These directions aim to deepen our understanding of plant belowground nutrient acquisition strategies and their adaptation mechanisms to environmental changes, providing a scientific basis for the management of forest ecosystems. [Ch, 2 tab. 95 ref.]
2026, 43(1): 219-228.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250219
Abstract:
The slope where forest fire occurs is typically covered with the ash layer of the fire, which is a critical factor altering post-fire hydrological and erosional processes on hill slopes. Due to the multiple opposing effects of forest fire ash coverage on slope hydrological and erosional processes, the superimposed effects may lead to highly variable and context-dependent results. By reviewing relevant research literature, the impact mechanism and role of forest fire ash on slope hydrological and erosional processes are summarized. The fire ash layer covers the soil surface, forming a dual system of fire ash and soil. The “ash blanket” effect or sealing effect of forest fire ash can increase or decrease slope permeability and water holding capacity. The erodibility or crust formation sealing can either reduce or increase the slope’s resistance to erosion. The erosion and migration of forest fire ash layer on the slope may form fire ash patches or mud, which reduces or increases the surface runoff erosion capacity. Fire ash particles and their aqueous solutions infiltrating into soil can alter soil physicochemical properties through multiple pathways: potentially diminishing infiltration capacity via pore clogging, enhancing erosion resistance through promoting formation of soil aggregates, and exerting long-term impacts by either facilitating or inhibiting ecological recovery via fertilization effects or biological toxicity. Identification of dominant impact mechanism of forest fire ash on slope hydrological and erosional processes under specific wildfire, precipitation, and soil conditions is crucial to improving the simulation ability of post fire hydrological erosion and the accuracy of risk prediction. [Ch, 73 ref.]
The slope where forest fire occurs is typically covered with the ash layer of the fire, which is a critical factor altering post-fire hydrological and erosional processes on hill slopes. Due to the multiple opposing effects of forest fire ash coverage on slope hydrological and erosional processes, the superimposed effects may lead to highly variable and context-dependent results. By reviewing relevant research literature, the impact mechanism and role of forest fire ash on slope hydrological and erosional processes are summarized. The fire ash layer covers the soil surface, forming a dual system of fire ash and soil. The “ash blanket” effect or sealing effect of forest fire ash can increase or decrease slope permeability and water holding capacity. The erodibility or crust formation sealing can either reduce or increase the slope’s resistance to erosion. The erosion and migration of forest fire ash layer on the slope may form fire ash patches or mud, which reduces or increases the surface runoff erosion capacity. Fire ash particles and their aqueous solutions infiltrating into soil can alter soil physicochemical properties through multiple pathways: potentially diminishing infiltration capacity via pore clogging, enhancing erosion resistance through promoting formation of soil aggregates, and exerting long-term impacts by either facilitating or inhibiting ecological recovery via fertilization effects or biological toxicity. Identification of dominant impact mechanism of forest fire ash on slope hydrological and erosional processes under specific wildfire, precipitation, and soil conditions is crucial to improving the simulation ability of post fire hydrological erosion and the accuracy of risk prediction. [Ch, 73 ref.]