2025 Vol. 42, No. 3
column
2025, 42(3): 433-443.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240461
Abstract:
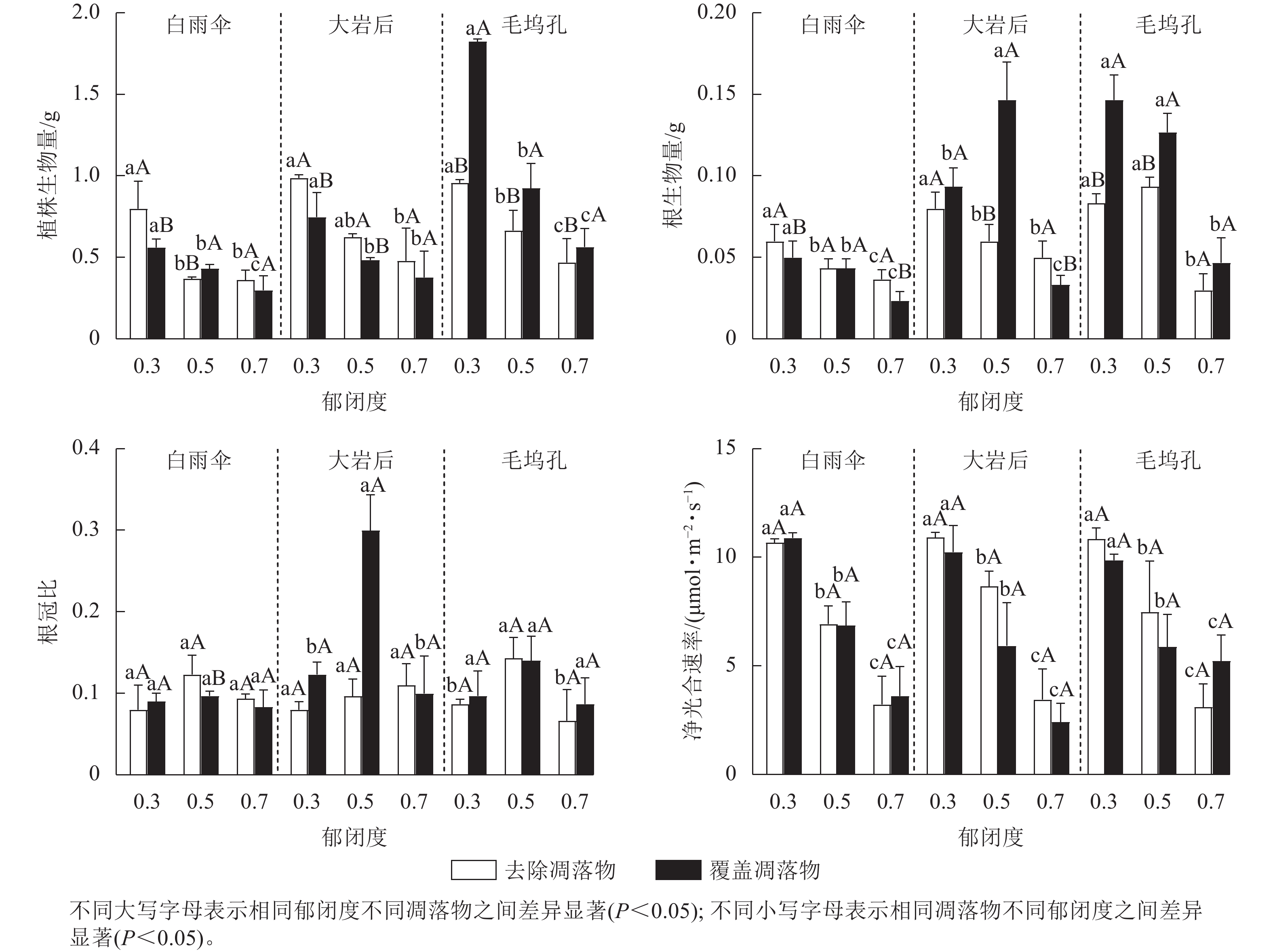
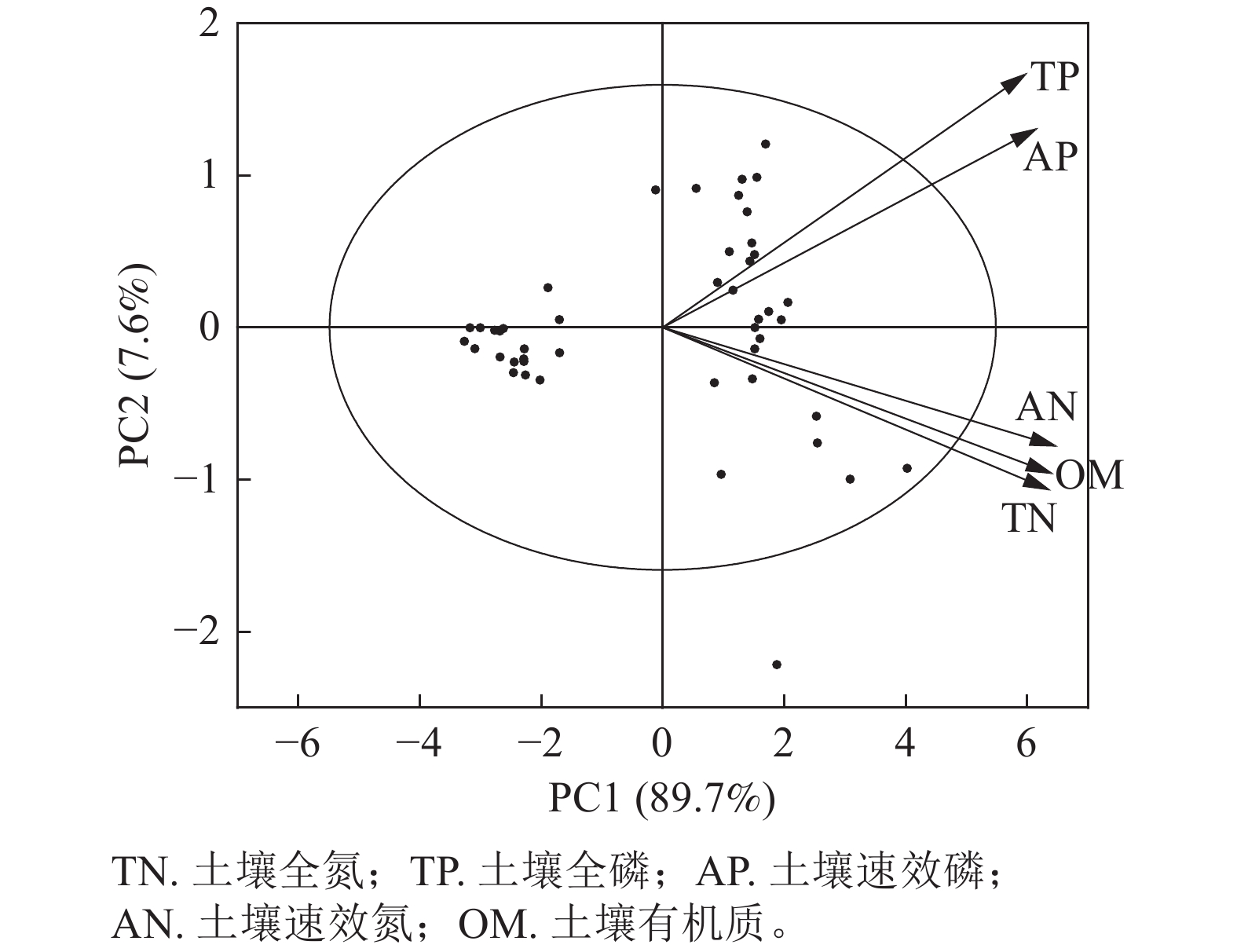
Objective This study, with an investigation into the response of yield and active component accumulation of medicinal plants to the regulation of forest canopy density and litter treatment, is aimed to provide theoretical basis for the regulation of light intensity and nutrient content of medicinal plants in simulated cultivation. Method Corydalis yanhusuo, a medicinal plant under Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) forest plantation, was first selected as the research object before two-factorial split plot design was employed to explore the impact of three canopy density treatments (high, medium and low) and two litter treatments (removal and mulching) on the yield and active accumulation component of Corydalis yanhusuo. Result The yield of tuber and tetrahydropalmatine content of C. yanhusuo were significantly affected by canopy density, litter and their interaction with the yield decreasing when the litter was removed and the tetrahydropalmatine content increasing with the increase of canopy density. The yield and tetrahydropalmatine content of the three treatments did not show a consistent pattern with the increase of canopy density when litter was covered. According to the radar map, the best planting scheme was to remove litter at low canopy density. Plant biomass, soil organic carbon and soluble nitrogen contents were the important factors affecting tuber yield, while net photosynthetic rate, soil available phosphorus and organic carbon contents were the important factors affecting tetrahydropalmatine content. Conclusion The litter removal treatment with low canopy density can significantly increase the tuber yield of C. yanhusuo and maintain the tetrahydropalmatine content. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 35 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 444-456.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240473
Abstract:
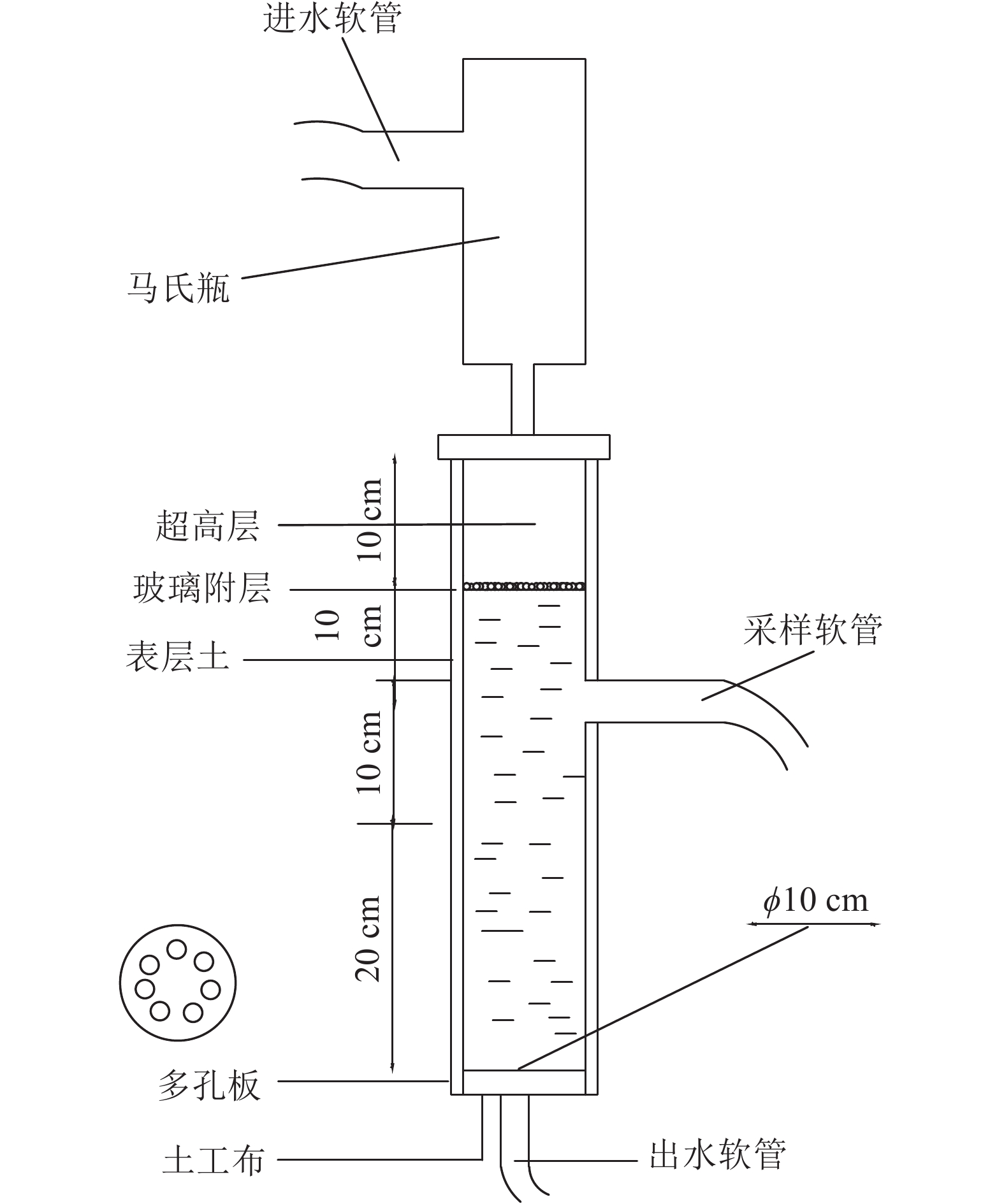
Objective This study aims to investigate the variations of soil nutrients during leaching processes under different vegetation restoration modes in degraded red soil regions and to enrich the understanding of water-soil-nutrient loss patterns and their influencing mechanism. Method 4 different vegetation restoration modes, named Pinus massoniana pure forest (PM), P. elliottii pure forest (PE), mixed P. massoniana and Schima superba forest (RMS), and mixed P. elliottii and S. superba forest (RES), were taken as the objects of the study. The characteristics of the soil runoff, sediment production, sediment particle changes and nutrient loss during the process of leaching were investigated in four leaching intensities, namely, 60, 90, 120, and 150 mm·h−1 in the red soil vegetation restoration area of Taihe County, Jiangxi Province. Result (1) With the increase of leaching intensity, the flow rate and sediment yield of red soil also increased, and the composition and stability characteristics of sediment particles changed significantly. Mean weight diameter (DMW) and >0.250 mm sediment particles (R0.25) increased significantly (P<0.05). PM with low understory vegetation cover had low agglomerate stability under leaching erosion, and soil aggregates in RMS with high vegetation cover had high stability. (2) At a leaching intensity of 150 mm·h−1, the nutrient loss in red soil was significantly higher than that in 60 mm·h−1, but there was no significant difference in nutrient loss in 90 and 120 mm·h−1. Sediment was the main medium for nutrient migration and loss in this study. (3) Nutrient loss in red soil was positively correlated with leaching intensity, runoff yield rate, sediment yield, and R0.25, while negatively correlated with sediment ≤0.053 mm particles. (4) Random forest analysis showed that leaching intensity and runoff rate were the main factors affecting nutrient loss, with contribution rates of 16.33% and 20.91%, respectively. Conclusion With the increase of leaching intensity, the runoff and sediment yield significantly increase, and the composition and stability of sediment particles change. Moreover, leaching intensity and runoff rate are the main factors affecting nutrient loss. In the ecological construction of the subtropical degraded red soil zone in China, emphasis should be placed on enhancing the richness of understory vegetation in the vegetation restoration area in order to improve the structure of the forest stand and consolidate the results of management. [Ch, 7 fig. 2 tab. 44 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 457-467.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240582
Abstract:
Objective Based on hydrological process simulation analysis, this study aims to explore the optimal configuration of water conservation forests in the upper reaches of Baiyangdian mountainous area and improve the quality of water conservation forests. Method Taking 2016 as an example, SWAT (Soil and Water Assessment Tool) model was used to verify the applicability of the localization process in Angezhuang watershed in the upper reaches of Baiyangdian. A total of 63 site types were classified according to the site conditions of Angezhuang watershed, and site quality grades were evaluated. The spatial configurations of water conservation forests were carried out according to the site conditions. Then SWAT model was used to simulate the runoff under different spatial configurations of water conservation forests. Result The simulation results showed that under the scenario dominated by mixed and coniferous forests, the runoff of the watershed reduced by 15.79% during the wet season compared with the measured value, and increased by 15.83% during the dry season. In terms of spatial configuration, broad-leaved forests were mainly distributed on gentle slopes and slopes, with sunny slopes as the best. The mixed forests were mainly distributed on slopes and steep slopes. Coniferous forests were mainly distributed on steep slopes, with shade slopes as the best. Shrubs were mainly distributed on slopes and steep slopes, especially in areas with thin soil layers. Conclusion Under the spatial configuration dominated by mixed and coniferous forests, water conservation forests have the best function in accommodating water sources. [Ch, 4 fig. 5 tab. 31 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 468-476.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240381
Abstract:
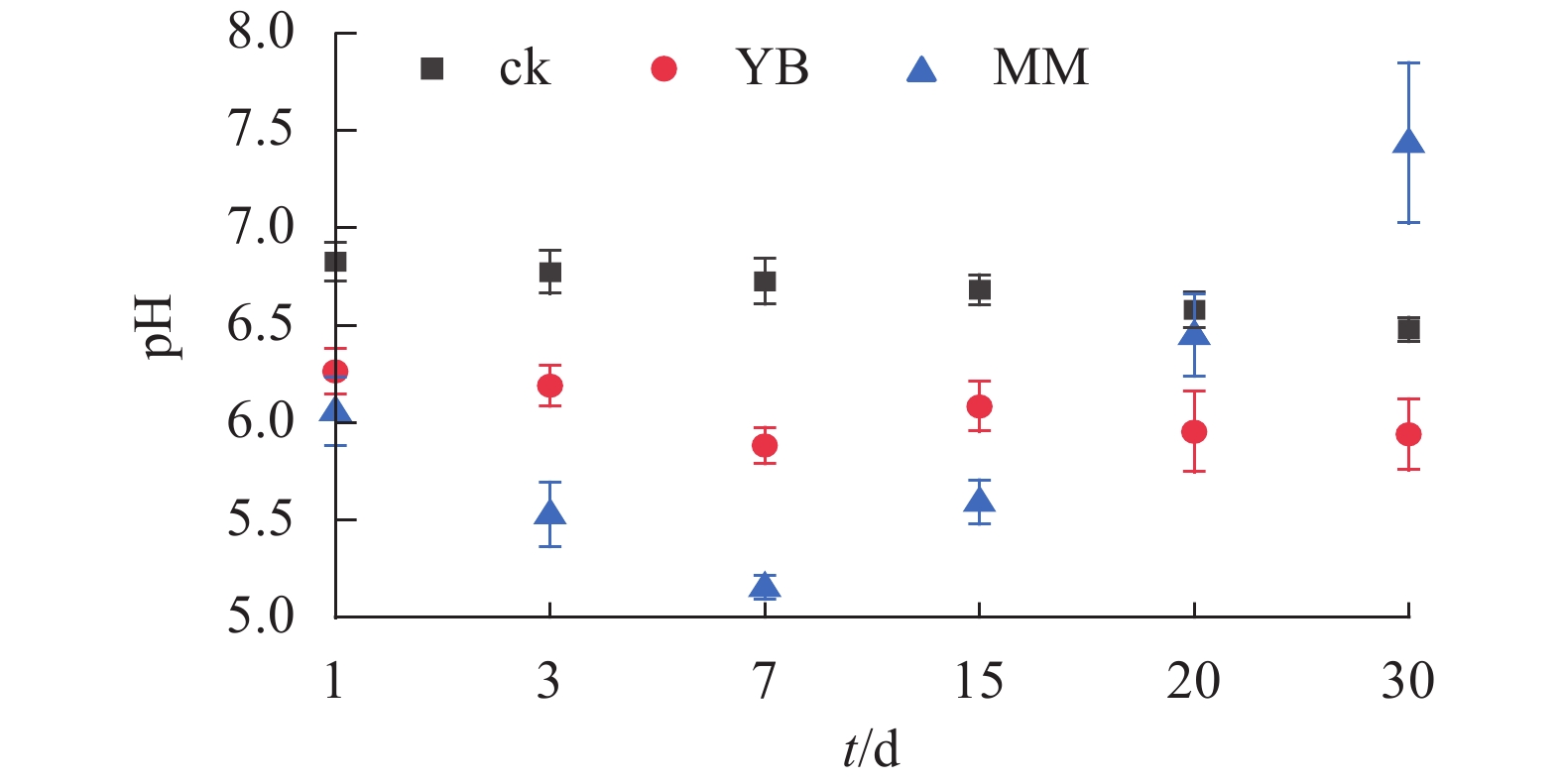
Objective Analyze the effects of different microorganisms on the weathering and elemental release of basalt, to explore the role of microorganisms in the weathering process of basalt, and to provide a theoretical basis for microorganisms promoting basalt weathering. Method Different microbial strains (Bacillus mucilaginosus and Trichoderma asperellum) were selected to carry out simulation experiments on biological weathering of basalt. By means of elemental geochemical methods (elemental dissolution amount and rate) and mineral analytical methods (material composition), the effects of microorganisms on the release amount, release rate, and release capacity of Si, Ca, Al, Fe, and Mg elements from basalt were investigated, and preliminarily explored the release mechanisms. Result Microorganisms contributed to the weathering of basalt and the dissolution of elements, compared to the control group, the pH of the fungal and bacterial system solutions decreased by 1.46 and 0.88 units, respectively. Compared to the control group, the release amounts of Si, Ca, Al, Fe and Mg elements in basalt was significantly increased by 10.2, 2.6, 8.2, 92.9 and 9.9 times under the action of fungi, and it was significantly increased by 2.7, 1.2, 1.7, 19.7 and 3.2 times under bacterial action. The order of element release from basalt under the action of fungi and bacteria was same (Ca>Mg>Fe>Si>Al). Microorganisms create an acidic environment mainly by secreting organic acids or by complexing to promote the weathering of basalt and increase the rate of elemental dissolution. Conclusion Microorganisms can effectively increase the release and rate of elements during the weathering process of basalt, there are also differences among different strains. The release and rate of elements during the weathering process of basalt under the treatment of T. asperellum are higher than those under the treatment of B. mucilaginosus, indicating that fungi have a more significant role in accelerating the weathering process of basalt. [Ch, 6 fig. 41 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 477-485.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240426
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to screen a high-yielding indoleacetic acid strain from earthworm compost, and optimize its fermentation parameters to increase indoleacetic acid yield, so as to provide reference for enriching indoleacetic acid producing resource pool and preparing high-quality bacterial fertilizers. Method Salkowski colorimetric method combined with high-performance liquid chromatography was used to screen high-yielding strains of indoleacetic acid, and the target strains were identified through 16S rRNA sequence analysis. The metabolites of the target strains were analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, and the synthesis pathway of indoleacetic acid was explored based on metabolomics analysis. Single factor experiments were performed to optimize the fermentation parameters of the target strains for producing indoleacetic acid. The effect of the target strains on promoting seed germination was evaluated through seed germination experiments. Result A new strain with high indoleacetic acid yield of 39.99 mg·L−1 was isolated from earthworm compost. It was identified as Bacillus sp. by 16S rRNA sequencing analysis and named GA2022. The optimum fermentation parameters for producing indoleacetic acid from strain GA2022 were incubation time 36 h, inoculum amount 2% (v/v), NaCl concentration 20.0 g·L−1, initial pH 8, L-tryptophan concentration 3.0 g·L−1, and incubation temperature 40 ℃. Under these optimal conditions, the indoleacetic acid yield of strain GA2022 could reach 204.25 mg·L−1, which was 410.75% higher than that before optimization. The results of mass spectrometry showed that this strain might possess 3 indoleacetic acid synthesis pathways, namely indole-3-acetamide pathway, indole-3-pyruvate pathway, and indole-3-ethanol pathway. The strain could promote the seed germination of Brassica rapa var. chinensis. Conclusion A high-yielding indoleacetic acid strain GA2022 is obtained from earthworm compost. The simultaneous coexistence of 3 indoleacetic acid synthesis pathways endows it with high indoleacetic acid production capacity and saline-alkali tolerance. [Ch, 7 fig. 1 tab. 31 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 486-494.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240483
Abstract:
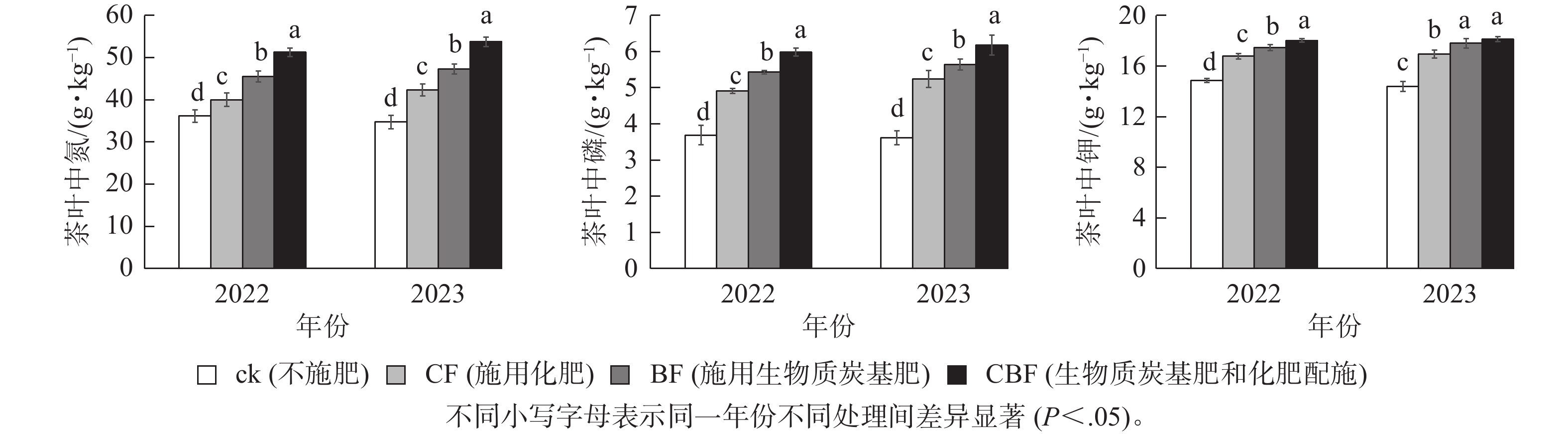
Objective To clarifying the impacts of biochar-based fertilizers on soil nutrients, tea yield and quality in tea gardens is conducive to enhancing the production efficiency of tea gardens and promoting the transition of agricultural production towards low-carbon, recycling-oriented practices. Method Focusing on tea gardens, this study conducted two years field experiments with four treatments: no fertilization (ck), chemical fertilizer application (CF), biochar-based fertilizer application (BF), and a 1∶1 combination of biochar-based fertilizer and chemical fertilizer (CBF). The study investigated the effects of these treatments on soil nutrients and tea plant growth. Result (1) Compared with ck, CF, BF, and CBF treatments significantly increased soil pH, total nitrogen, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, available phosphorus, and readily available potassium contents, and significantly increased the absorption of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium by tea plants (P<0.05), with CBF treatment showing better effects than CF and BF treatments. (2) Compared to CF treatment, the tea yield in BF and CBF treatments increased by 23.13%−24.54% and 53.27%−53.75%, respectively, and the pairwise differences among different fertilization treatments reached a significant level (P<0.05). The type of fertilization significantly affects the contents of water extract, caffeine, tea polyphenols and free amino acids in tea leaves (P<0.05), with the trend being CBF>BF>CF>ck, while the polyphenol/amino acids showed opposite changes. (3) Grey relational analysis showed that soil pH, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen, and available phosphorus are key factors influencing tea yield, while soil pH and the concentrations of potassium and nitrogen in tea leaves have a greater impact on tea quality. Conclusion The application of biochar-based fertilizers combined with chemical fertilizers can improve soil nutrient conditions in tea gardens, increase tea yield, and enhance tea quality. This method is as an effective measure to promote green and sustainable agricultural development. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 37 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 495-502.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240482
Abstract:
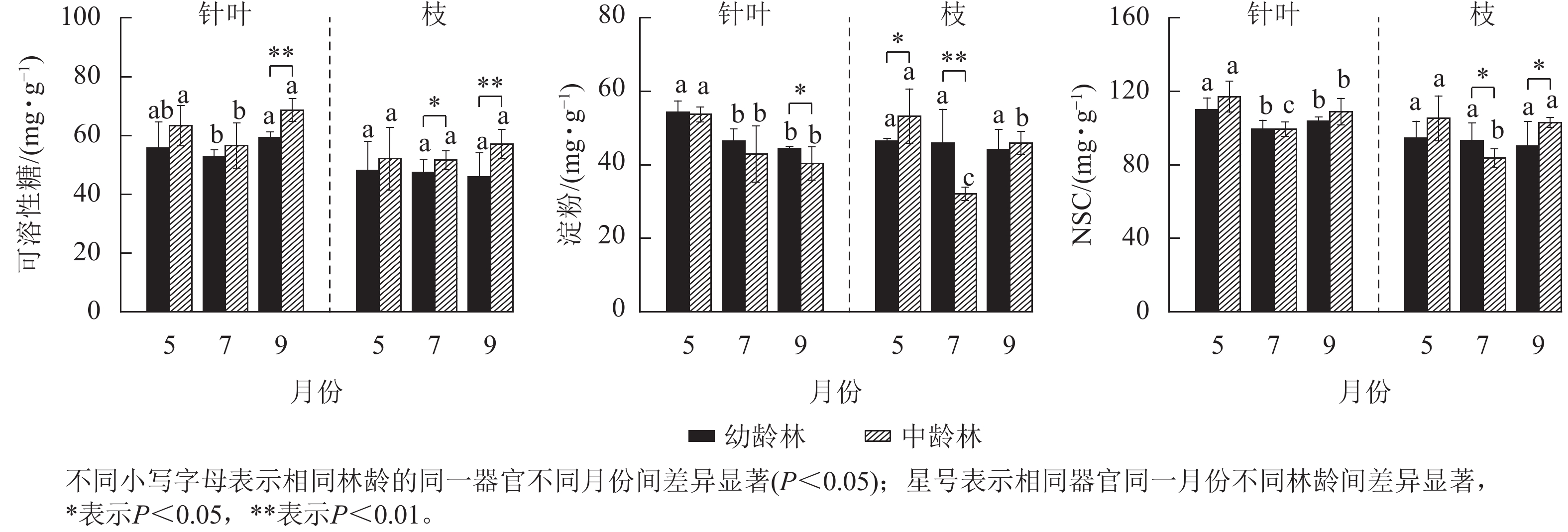
Objective The study on the changes of ecological stoichiometric characteristics of non-structural carbohydrate, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in the growing season of middle-aged and young Pinus koraiensis plantations can further understand of the nutrient utilization strategies of conifer species at different ages during the growing season. Method The changes in non-structural carbohydrate (NSC), soluble sugar, starch, carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) stoichiometry in the needles and branches of young (15-year-old) and middle-aged (50-year-old) P. koraiensis were studied. Result (1) In the growing season, the contents of soluble sugar, NSC, P and C/N in the needles of middle-aged and young forests first decreased and then increased, while the contents of C and N, C/P and N/P showed the opposite trend; the seasonal changes in the branches of middle-aged and young P. koraiensis were different. (2) The contents of soluble sugar, NSC, N and N/P in the needles were greater than those in the branches, while C/N was smaller than that in the branches. (3) The soluble sugar content in middle-aged forests was higher than that in young forests, the starch, N and N/P in the needles were lower than those in young forests, the contents of NSC and C/N were slightly higher than those in young forests. (4) The correlations of NSC and C, N and P contents between the branches and needles of middle-aged and young forests were different. Conclusion The contents of NSC and its components, C, N and P contents have seasonal fluctuations, and the nutrient utilization of middle-aged and young P. koraiensis is different. In the Caohekou area of Benxi City, Liaoning Province, middle-aged and young P. koraiensis show N limitation, and could be supplemented with nitrogen fertilizer in early spring. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 31 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 503-512.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240623
Abstract:
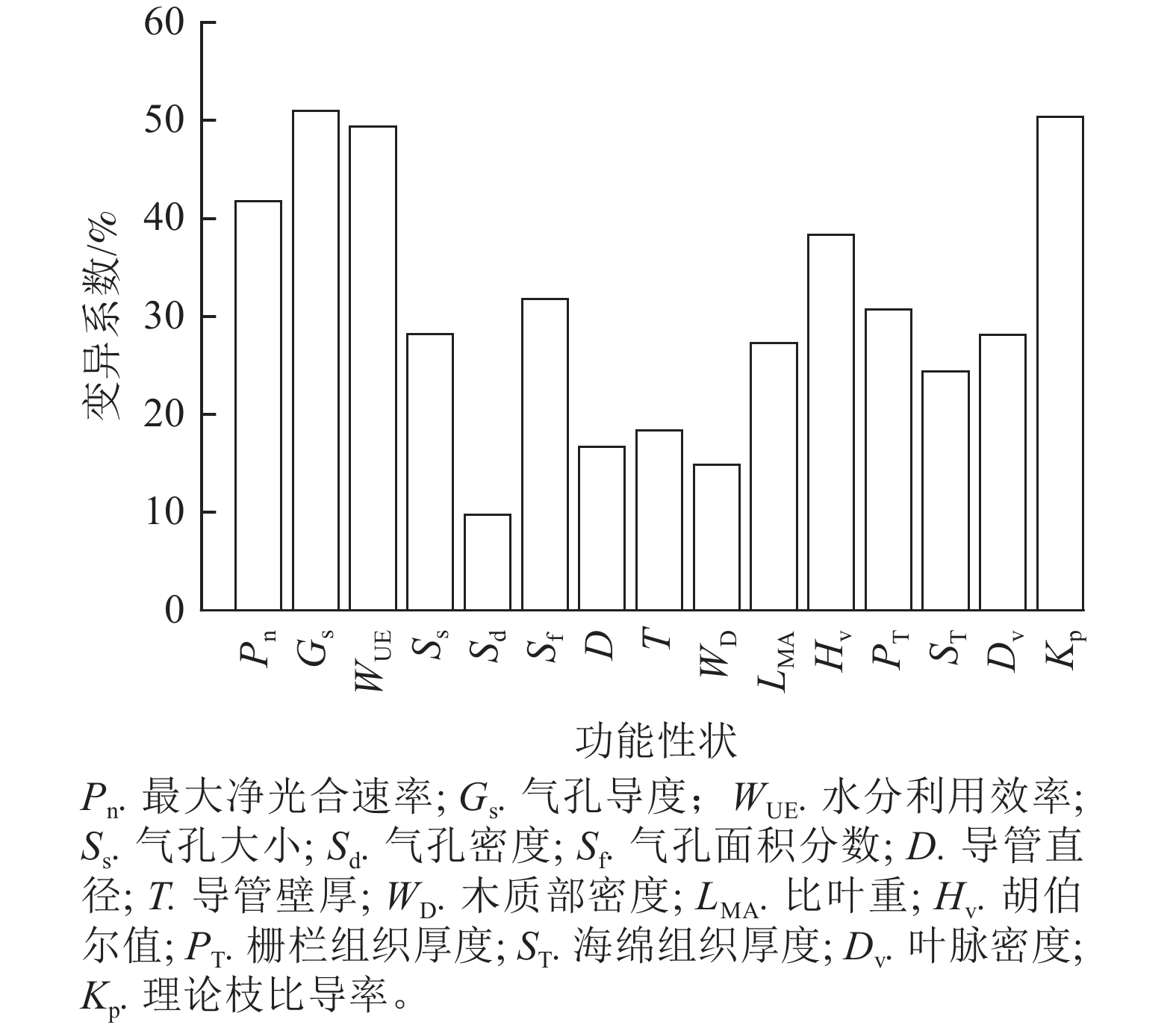
Objective Global warming and the polarization of precipitation patterns have led to large-scale forest mortality in certain regions. Investigating the variation patterns and interrelationships of plant functional traits along precipitation gradients reflects plants’ adaptation strategies to climate change, which is crucial for predicting the impacts of future climate change on plant communities. Method Robinia pseudoacacia, a common species of precipitation gradient, was selected as the research object. One-way ANOVA was used to quantify the variation of functional traits (including 15 traits such as leaf photosynthesis, stomata, branch anatomy, leaf morphology, leaf anatomy, and water supply) along the precipitation gradient. The coupling relationship of the above traits was explored by path analysis, and the adaptation strategy of R. pseudoacacia was clarified. Finally, hierarchical partitioning analysis was used to reveal the main climatic factors driving the variation of R. pseudoacacia traits. Result (1) With the decrease of precipitation, the stomatal size first increased and then decreased, and the vessel diameter, the theoretical branch specific conductivity, and the stomatal density showed an upward trend. (2) There were strong causal relationships among the photosynthesis, stomata and water supply traits of R. pseudoacacia leaves, in which the changes of stomatal conductance were attributed to stomatal size and leaf vein density, and the changes of the maximum net photosynthetic rate were attributed to stomatal conductance. (3) The mean annual precipitation (MAP), aridity index (AI), and mean annual temperature (MAT) all had an impact on the variation of functional traits. AI explained higher than the MAP and MAT for the variation of stomatal conductance, specific leaf mass, Huber value, stomatal density, spongy tissue thickness, and theoretical branch-specific conductivity. The explanatory power of the above climatic factors for the variation of branch anatomical traits and water supply traits (except Huber value) was 60%−90%. Conclusion R. pseudoacacia adapts to drought through coordinated adjustments in water supply, stomatal traits, and photosynthetic performance, with aridity index being the dominant climatic driver of functional trait variations. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 40 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 513-523.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240415
Abstract:
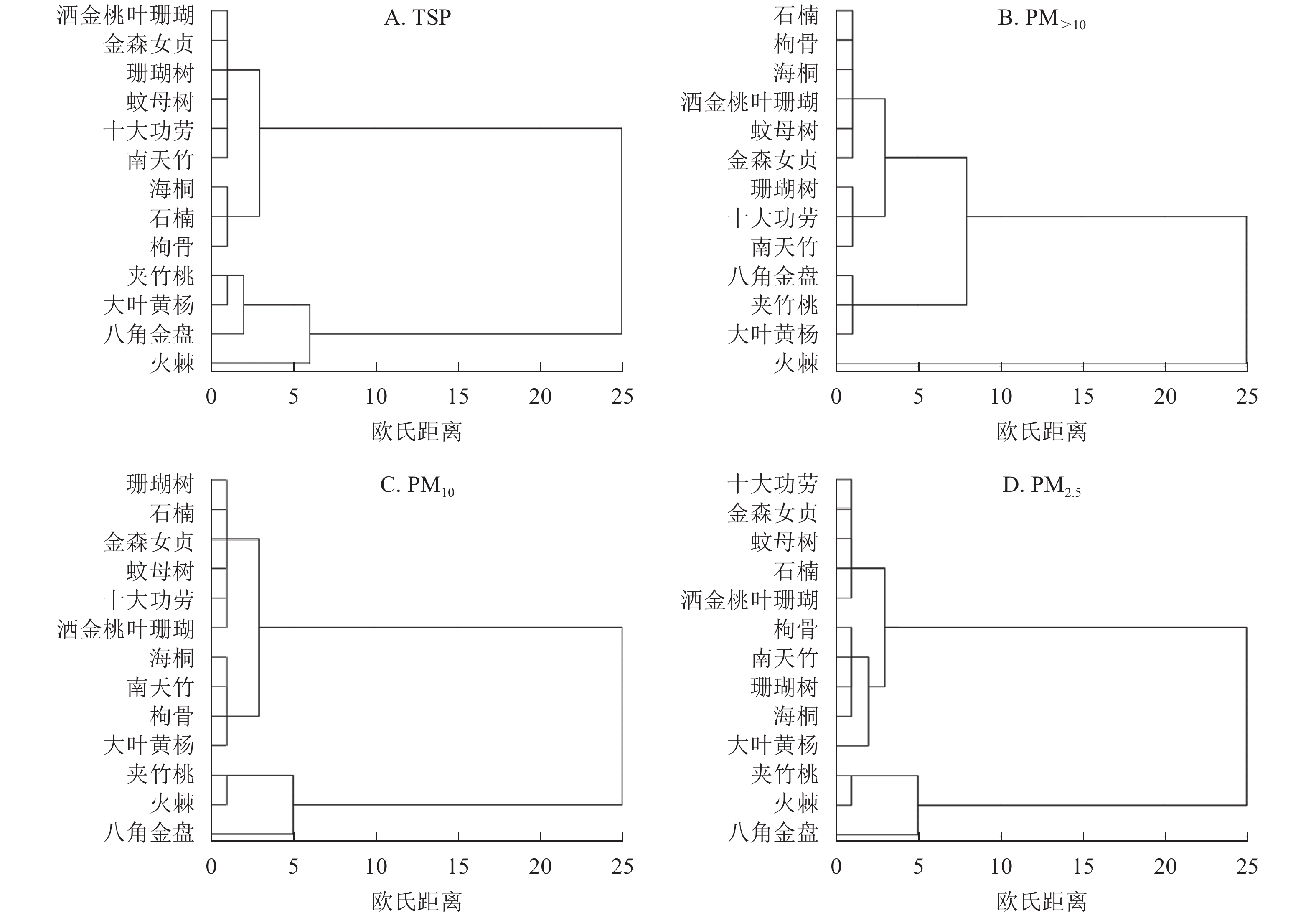
Objective The objective is to investigate the effects of leaf surface microstructure of garden plants on particle retention capacity, and provide theoretical basis for the selection of urbangarden tree species. Method The 13 evergreen shrubs, including Pyracantha fortuneana, Fatsia japonica and Nerium oleander were studied in Zhengzhou City, Henan Province. The retention of particles of different sizes [total suspended particulate matter (TSP), large particulate matter (PM>10), inhalable particulate matter (PM10) and fine particulate matter (PM2.5)] per unit leaf area was measured by graded membrane filtration method. The microstructure of leaf surface was observed by scanning electron microscopy and ultra depth microscope, and the relationship between particle retention capacity and leaf surface microstructure features was analyzed. Result (1) There were significant differences in the retention capacity of 13 evergreen shrubs with different particle sizes (P<0.05), and the strongest comprehensive dust-retention ability was found in P. fortuneana, F. japonica, and N. oleander, with a dust retention capacity per unit area of 2.59, 2.23 and 1.97 g·m−2, respectively, 3.58−4.70 times that of Mahonia fortunei and Nandina domestica, which had a weak dust retention capacity. (2) Particles tended to be distributed near the midrib and leaf tip. Observation of leaf surface microstructure revealed that there were various structures such as grooves, fuzz, and protrusions on the upper surface. Most of the stomata were located on the lower surface of the leaf. These structures synergistically affected the retention of particles in plants, and concurrently enhanced the roughness of leaf surfaces. The surface roughness in N. oleander leaves was the highest (4.53 μm), with regular semi-circular protrusions on the upper surface and large concave stomata on the lower surface, surrounded by hairy tissue to attach dust particles. (3) Correlation analysis indicated that leaf area, roughness, stomatal length were significantly positively correlated with the content of TSP, PM10 and PM2.5 retention per unit leaf area (P<0.05 or P<0.01), and stomatal width and stomatal area were significantly positively correlated with PM10 and PM2.5 retention (P<0.05). Conclusion P. fortuneana, F. japonica, and N. oleander are recommended as excellent garden dust-retaining species in controlling air pollution in Zhengzhou City. [Ch, 5 fig. 3 tab. 35 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 524-532.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240507
Abstract:
Objective This study aimed to elucidate the impacts of species diversity, structural diversity, and soil nutrients on tree biomass in forest stands, thereby providing a scientific basis for sustainable forest management and enhanced carbon sequestration capacity. Method The study focuses on Quercus mongolica forest in the mountainous region of eastern Liaoning Province. A Linear Regression Model was employed to analyze the effects of species diversity, structural diversity, and soil nutrients on tree biomass of forest stands. Based on this analysis, the most representative measures of species and structural diversity were identified. Subsequently, a structural equation model was constructed to quantitatively evaluate the direct and indirect effects on tree biomass. Result (1) Both species diversity and structural diversity significantly influenced tree biomass of forest stands. Species richness (r=−0.503, P<0.01) and Shannon index (r=−0.417, P<0.01) within species diversity were significantly negatively correlated with tree biomass of forest stands, while the Shannon index of diameter at breast height within structural diversity was significantly positively correlated with tree biomass of forest stands (r=0.405, P<0.01). (2) The optimal structural equation model indicated significant direct effects of species diversity and structural diversity on tree biomass of forest stands, with path coefficients of −0.394 (P<0.01) and 0.280 (P<0.05) respectively. Although soil nutrients did not have a significant direct impact on tree biomass, they influenced it indirectly through their effects on structural diversity and stand density, with path coefficients of −0.470 (P<0.01) and −0.655 (P<0.01) respectively. Conclusion These findings emphasize the primary role of species and structural diversity as direct drivers of tree biomass in Q. mongolica forest, while soil nutrients indirectly contribute to tree biomass by shaping forest stand structure. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 46 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 533-543.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240458
Abstract:
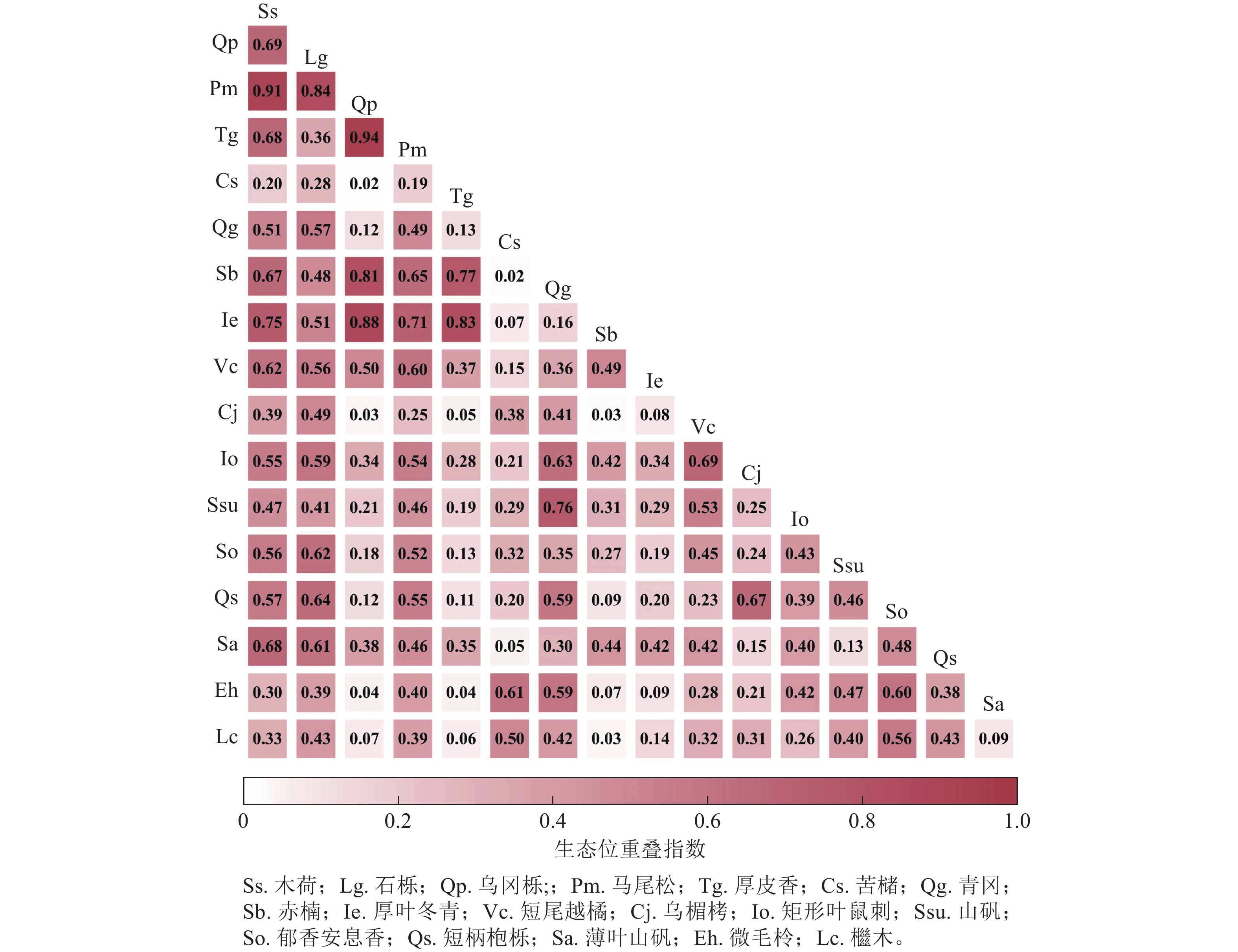
Objective The study is to explore the niche and interspecific association of dominant species of woody plants in the evergreen broad-leaved forest in Bailushan scenic area, Zhejiang Province and understand their relationship and succession characteristics, so as to provide reference for ecological restoration and biodiversity conservation of subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests. Method Taking the dominant species of woody plants in the evergreen broad-leaved forest in the study area as the research object, a long-term fixed plot with an area of 1 hm2 was established. Ecological niche analysis, variance ratio method (RV), χ2 test, Pearson correlation coefficient, and Spearman rank correlation coefficient were used to analyze the niche and interspecific relationship of dominant woody plant species with importance values greater than 1.00%. Result (1) Schima superba, Lithocarpus glaber, Quercu sphillyreoides, and Pinus massoniana were the constructive species of the community. Among them, S. superba had the highest importance value (VI=27.37%), Levins niche width (BL=20.95), and Shannon niche width (BS=3.11), while the other three species had importance values greater than 10%. The average BL and BS were 16.63 and 2.87, respectively. (2) The mean niche overlap index (Oik) of dominant species was 0.39. Most species were relatively independent in resource utilization and interspecific competition was weak. S. superba, L. glaber, Q. sphillyreoides, and P. massoniana had high niche overlap (mean Oik=0.73), indicating a high degree of similarity in resource utilization. The niche overlap index of Castanopsis sclerophylla with these four species was relatively low (mean Oik=0.17), indicating the weakest competition. (3) The overall association of dominant species in the community showed a significant positive correlation (P<0.05). According to χ2 test, among the 153 pairs out of 18 dominant woody plant species, only 12 pairs showed significant associations (P<0.05), while 91.00% pairs were not significantly correlated. Similar results were observed in Pearson correlation and Spearman rank correlation tests, and 71.25% and 71.90% of species pairs were not significantly correlated. The positive and negative association ratio was greater than 1, indicating that species tended to distribute independently. Conclusion The community is in the middle to late stage of succession and has a relatively stable ecological state. In the management of evergreen broad-leaved forests in the early or middle stage of succession in central Zhejiang, it is recommended to moderately retain P. massoniana when regulating high-density stands and appropriately plant Q. sphillyreoides in forest gaps and edges to promote positive succession and enhance the stability of forest ecosystems. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 36 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 544-553.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240486
Abstract:
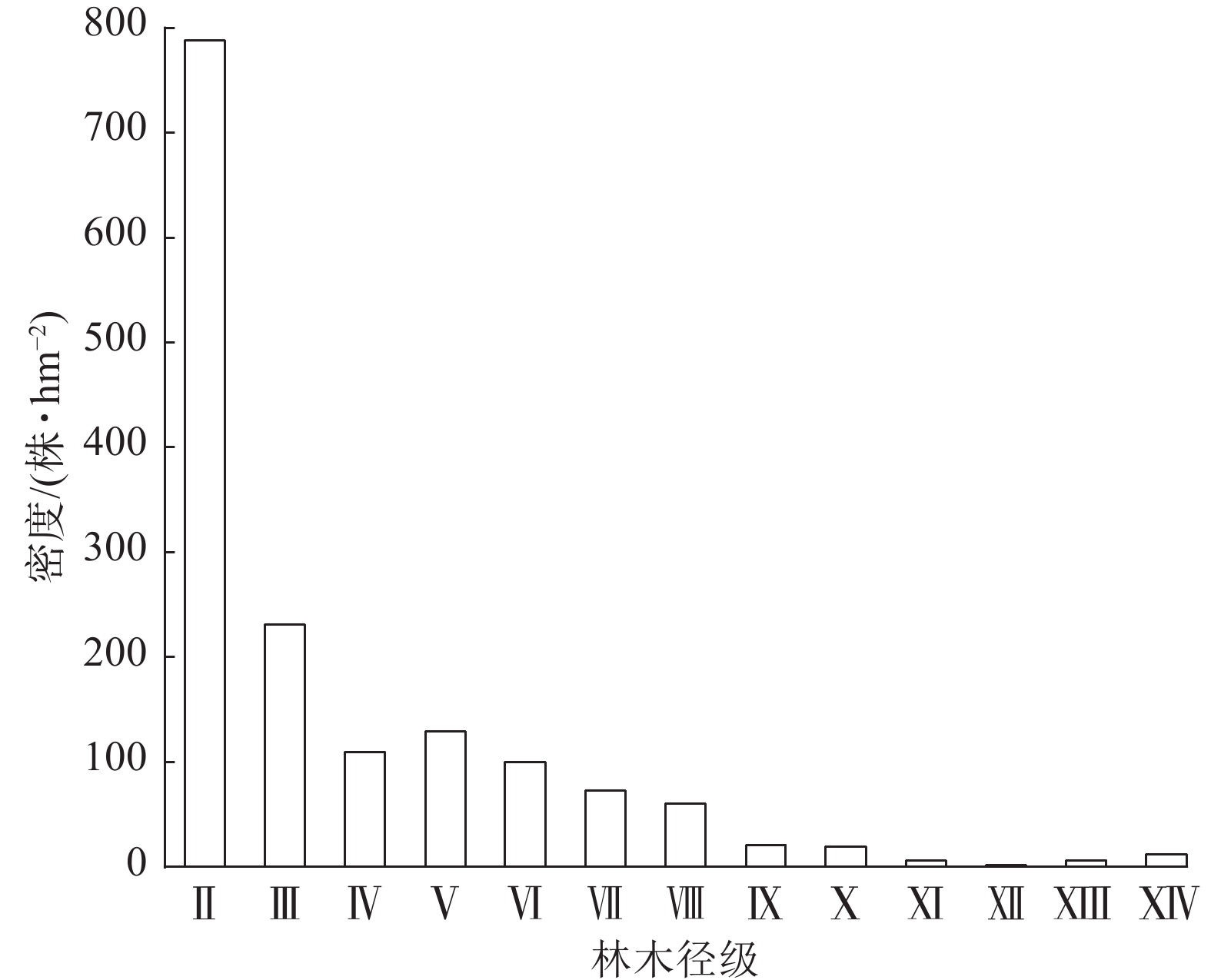
Objective This study aims to explore the spatial distribution pattern and correlation of the major tree species in deciduous broad-leaved forests in the transition zone from northern margin of subtropical zone to warm temperate zone in China. Method Taking the deciduous broad-leaved forest of Tianma National Nature Reserve as research object, the adjacent grid method was used to divide the forest into nine 24 m × 24 m sample plots. The names and spatial coordinates of tree species with diameter at breast height (DBH) ≥ 2.5 cm in the sample plots were recorded. The major tree species were determined based on their important values. The spatial distribution pattern and correlation of major tree species were analyzed by using spatial point pattern O-ring function, complete spatial stochastic zero model, and heterogeneous Poisson zero model. Result There were 27 species belonging to 20 genera and 17 families in Mazongling area of Tianma National Nature Reserve, with Quercus serrata and Castanea seguinii as dominant species, and Platycarya strobilacea as subdominant species. The diameter structure of trees showed an inverted “J”-type distribution. The spatial pattern results showed that the dominant tree species were initially clustered in 0−30 m scale, and gradually tended to be irregular and random with the increase of the scale. The spatial correlation analysis revealed that there was no significant correlation among the three dominant tree species (i.e., Q. glandulifera var. brevipetiolata, C. seguinii, and P. strobilacea). However, there was some correlation among the three dominant species and their companion tree species at a certain scale. Conclusion The community type is typical heterogeneous forests of Quercus spp. and P. strobilacea deciduous broad-leaved forests. Q. serrata forest regeneration was better and had an increasing trend, while the regeneration of C. seguinii and P. strobilacea forests was poor and the growth trend was not obvious. With the succession of the community, the light-loving and slightly shade-tolerant species will gradually replace the light-loving species. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 35 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 554-563.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240471
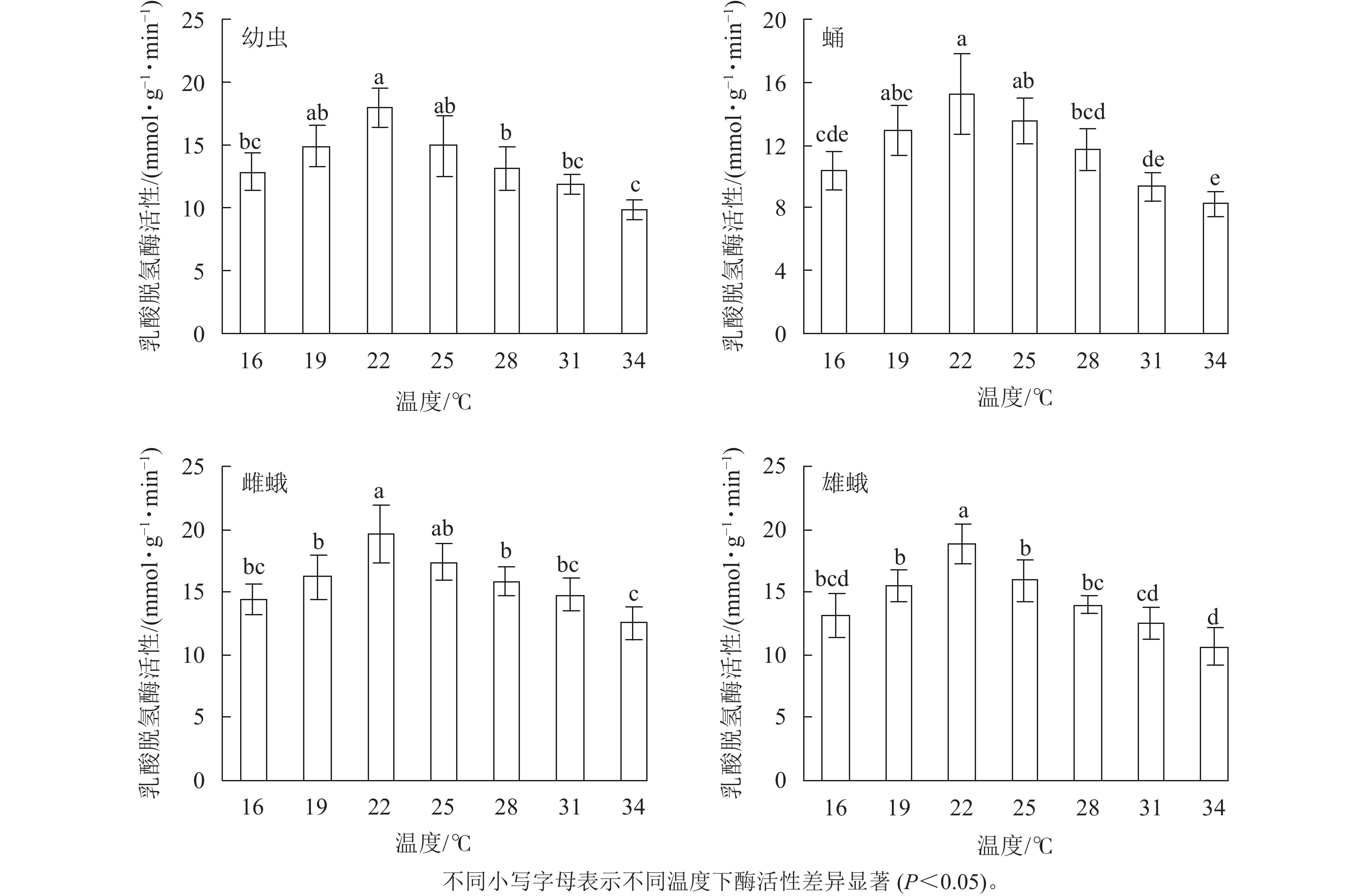
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to investigate the effect of temperature on enzyme activity in Heterolocha jinyinhuaphaga. Method The experimental insects were collected from Sanjie Town, Chuzhou City in Anhui Province and reared in a laboratory. The photoperiod was 14 h of daylight and 10 h of darkness, and the relative humidity was 70%. The activity of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), peroxidase (POD), carboxylesterase (CarE) and acid phosphate (ACP) was measured in larvae, pupae, female and male moths of H. jinyinhuaphaga at different temperatures (16, 19, 22, 25, 28, 31, and 34 ℃). Result There were differences in the activity of 4 enzymes in larvae, pupae, female and male moths of H. jinyinhuaphaga at different temperatures. At 16−34 ℃, the activity of the 4 enzymes increased first, and then decreased with increasing temperature. LDH activity in larvae, pupae, female, and male moths was the highest at 22 ℃ (17.93, 15.25, 19.63, and 18.81 mmol·g−1·min−1, respectively), POD activity was the highest at 25 ℃ (34.63, 31.83, 37.19, and 36.87 mmol·g−1·min−1, respectively), CarE activity was the highest at 28 ℃ (26.78, 23.36, 29.44, and 28.32 mmol·g−1·min−1, respectively), ACP activity was the highest at 25 ℃ (13.82, 11.37, 15.43, and 14.38 mmol·g−1·min−1, respectively). According to the established regression model, the optimal temperatures for the highest LDH activity in larvae, pupae, female, and male moths were found to be 21.45, 21.44, 22.32 and 21.56 ℃, respectively, the optimal temperatures for the highest POD activity were 26.16, 25.94, 25.67 and 25.54 ℃, respectively, the optimal temperatures for the highest CarE activity were 29.20, 29.65, 28.93 and 28.92 ℃, respectively, the optimal temperatures for the highest ACP activity were 25.05, 26.39, 24.86 and 25.24 ℃, respectively. Two-way ANOVA showed that the interaction between temperature and insect stage had no significant effect on the activity of 4 enzymes. Conclusion Temperature can affect the activity of LDH, POD, CarE and ACP in larvae, pupae, female and male moths of H. jinyinhuaphaga. [Ch, 4 fig. 26 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 564-571.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240552
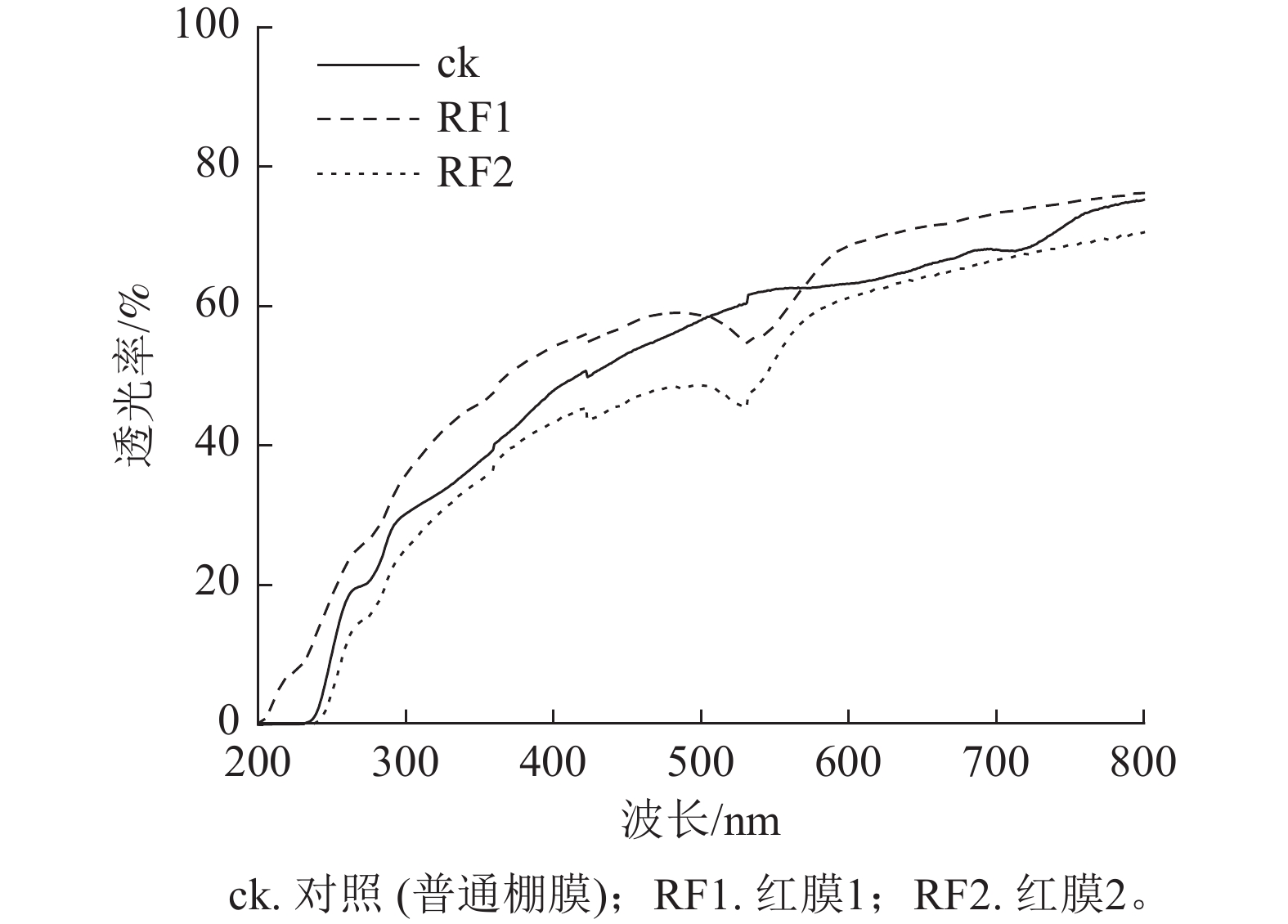
Abstract:
Objective The aim of this study is to uncover the promoting effects of 2 red films (RF1 and RF2) on photosynthetic abilities and fruit qualities in fruit vegetables, and then promote fruit vegetable production by using suitable red film. Method This study investigated the effects of greenhouses that were separately covered with RF1 and RF2 on the chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and the content of sugars, soluble solids, soluble proteins and total phenolics in fruits in 3 vegetables, including cucumber, squash and pepper. Result Compared with the control (common greenhouse film), RF1 significantly improved the maximum photochemical quantum yield (φPo), electron transfer efficiency caused by the captured excitons (Ψo) and quantum yield of electron transfer (φEo) in squash and pepper, but declined their maximum quantum yield of non-photochemical deexcitation (φDo) (P<0.05). RF2 significantly improved the φPo and Ψo in cucumber, as well as φPo, Ψo and φEo in pepper, but declined the φDo in the 2 vegetables (P<0.05). For sugar content, RF2 significantly (P<0.05) promoted the accumulation of sucrose, fructose, reducing sugar and total sugar in cucumber and squash fruits, as well as sucrose accumulation in pepper fruits (P<0.05). Under the two red films, the soluble solid content in cucumber and squash fruits was increased remarkably (P<0.05), and the soluble protein content in cucumber and pepper fruits was increased remarkably (P<0.05). Meanwhile, the 2 red films can improve the total phenolic content in squash fruits, and RF2 improved the total phenolic content in pepper fruits. Conclusion The 2 red films showed different effects on the improvement of photosynthetic abilities and fruit qualities in cucumber, squash and pepper, and RF2 was preferable for increasing the sugar content in the three vegetable fruits and total phenolic content in pepper fruits. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 36 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 572-580.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240480
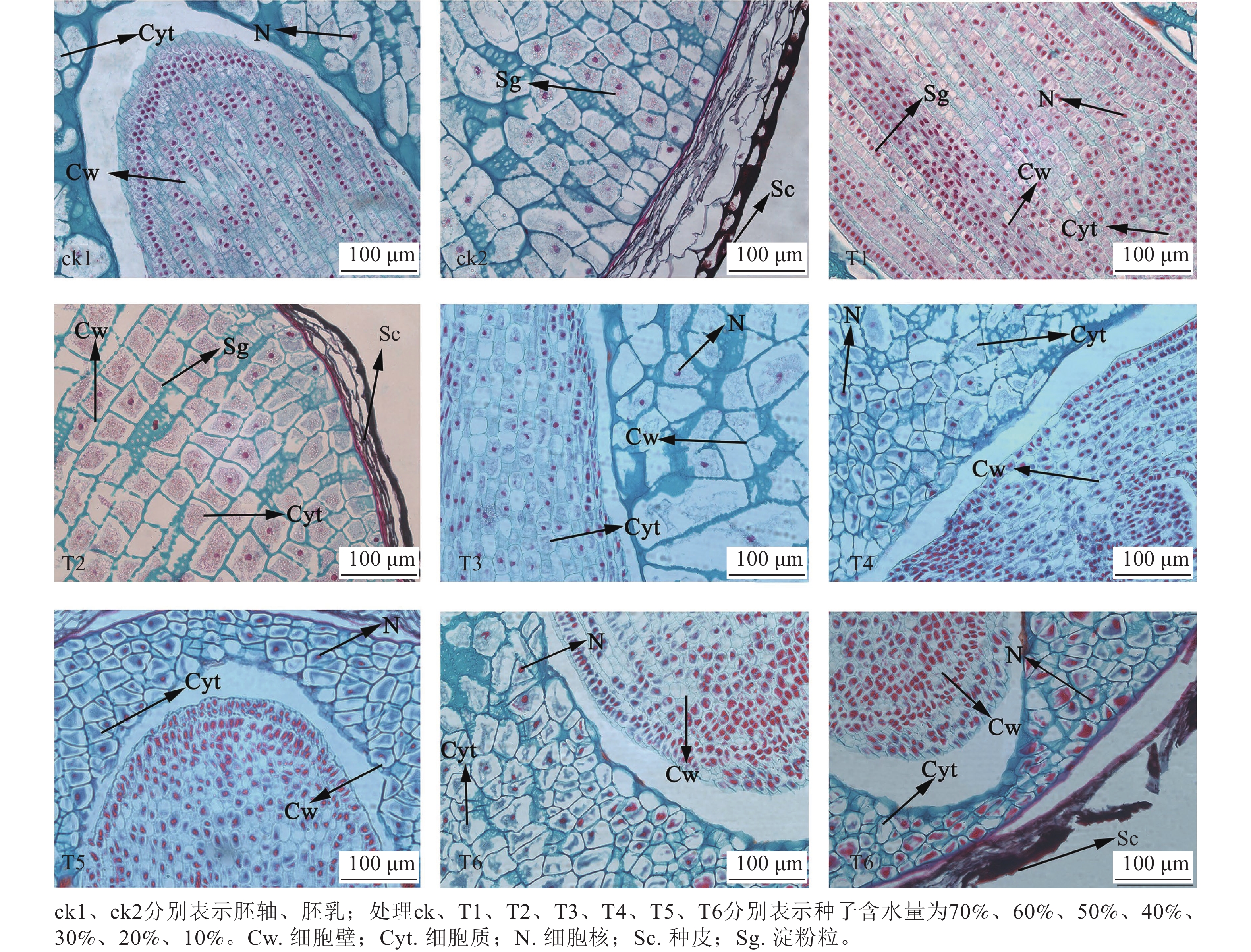
Abstract:
Objective This study is to investigate the changes in cell morphology and physiological indicators during the dehydration of Lycoris radiata seeds, and determine their critical and semi-lethal moisture contents, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the long-term seed preservation of Lycoris species. Method Fresh mature seeds of L. radiata (with a moisture content of 70%) were used as materials. The silica gel dehydration method was used to sequentially reduce the moisture content of the seeds to 60%, 50%, 40%, 30%, 20%, and 10%. The samples were taken to measure the relative conductivity, vitality, germination rate, mass molar concentration of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anions, as well as the activities of catalase, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase. Result (1) The average moisture content of freshly harvested mature seeds was as high as 70%, but they would quickly lose moisture at natural room temperature (25 ℃) (dropping to 10% in just 44 hours), with critical and semi lethal moisture contents of 40% and 10%, respectively. (2) When the seeds of L. radiata fell off, the embryonic development was basically mature. (3) During the process of seed dehydration, its external morphology gradually wrinkled and shriveled. When the dehydration was severe, plasmolysis occurred in seed cells, and the starch granules inside the cells gradually changed from granular to flake. At the same time, there would also be a significant amount of cellular degradation. (4) As the seed moisture content decreased, its vitality and catalase activity also significantly decreased (P<0.05), and there was a highly significant positive correlation between the two (P<0.01). In addition, the relative conductivity, superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase activities all significantly increased, while the germination rate showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. Conclusion The seeds of L. radiata are extremely sensitive to dehydration. Mild dehydration (moisture content between 30% and 40%) is beneficial for seed germination, whereas excessive dehydration can quickly lead to the loss of seed viability. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 30 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 581-591.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240428
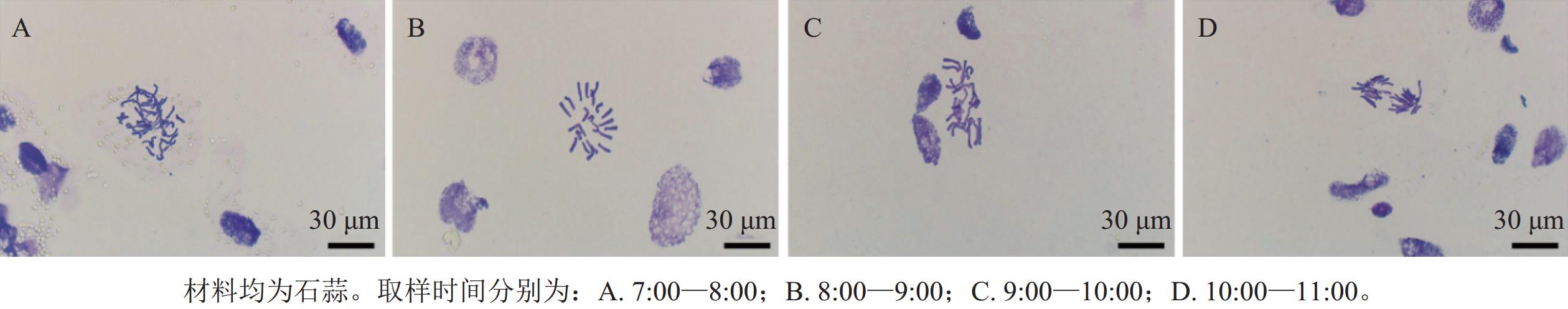
Abstract:
Objective The chromosomal karyotype characteristics of interspecific hybrids and chromosomal allocation of their parents in genus Lycoris are analyzed, which will further provide a basis for hybrid breeding in Lycoris. Method Conventional chromosome preparation and fluorescence in situ hybridization were used to analyze chromosome numbers and karyotypes of interspecific hybrids and parents in the genus Lycoris. Result (1) The optimum chromosome section system: from 8:00 to 9:00 AM, the root tips of Lycoris plants were pretreated with 0.002 mol·L−1 8-hydroxyquinoline for 2.5 h, fixed with Carnoy’s fixative, and then digested with a mixture of 5.0% cellulase and 0.3% pectinase at 37 ℃ for 1.5 h. The chromosome slides were prepared using the flame-drying method. (2) Chromosome karyotype analysis revealed 2 types of karyotype formulas for the hybrids between L. radiata and L. sprengeri, which were 2n=22=22A and 2n=22=2sm+20A. The karyotype formula for the hybrids with L. longituba as the parent was 2n=2x=18=4m+14A. The chromosome karyotype was primarily composed of 4A and 3B, which was intermediate between the parent species L. radiata, L. sprengeri, and L. longituba. (3) Fluorescence in situ hybridization revealed that there were 2 and 3 45S rDNA hybridization signals on the chromosomes of L. radiata and L. sprengeri, respectively. The 45S rDNA signals were found on chromosome 3 in both species. The numbers of 45S rDNA signals varied in the tested hybrids whose most signals located at the chromosome ends. Conclusion The karyotyping and fluorescence in situ hybridization system of Lycoris have been optimized and applied to the identification of hybrids in Lycoris and the distribution of parental chromosomes. These results will provide a theoretical basis for the creation of new germplasm resources and the breeding of new varieties of Lycoris genus. [Ch, 11 fig. 4 tab. 24 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 592-600.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240584
Abstract:
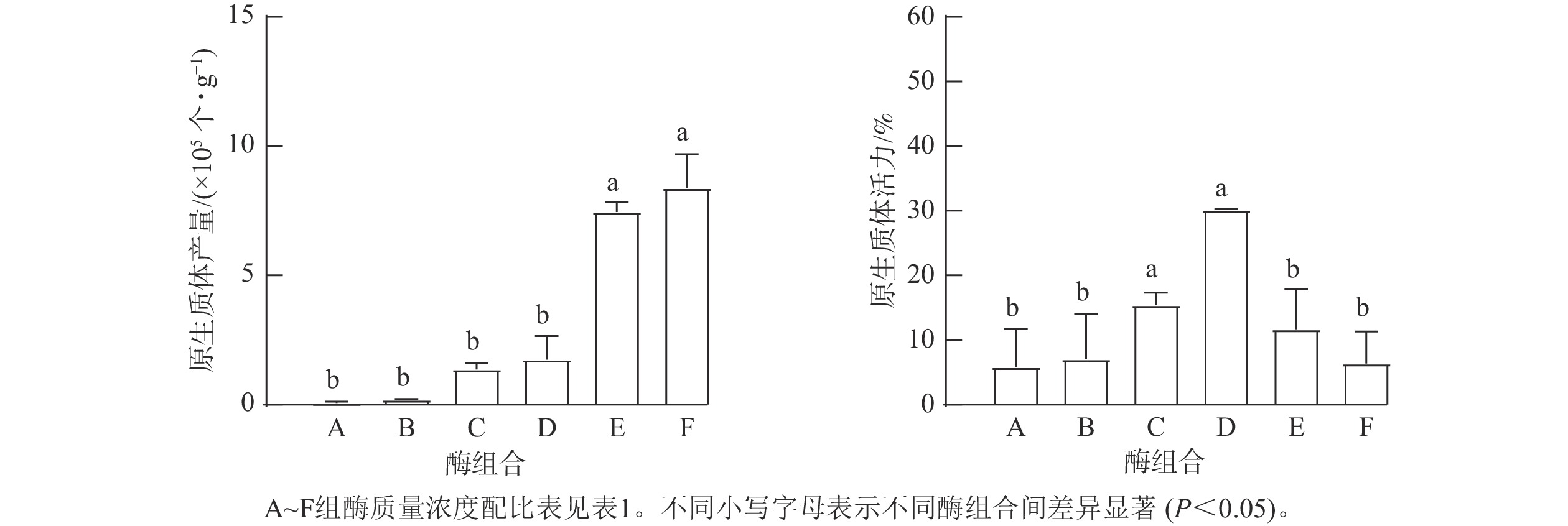
Objective This study aims to establish an efficient and stable technology for the isolation and transient transformation of mesophyll cell protoplasts from Phoebe bournei, which is a rare species in China. Method The young leaves of P. bournei were used as test materials, and 3 conditions were examined individually to clarify the effectient isolation conditions for protoplasts from P. bournei: different enzyme solution combinations, leaf expansion stages and osmotic pressure. Furthermore, the PEG-mediated transformation method was used to compare the 3 conditions﹣PEG concentration, plasmid concentration, and transformation temperature to screen the efficient transient transformation conditions of protoplasts from P. bournei leaves. Result The young leaves of P. bournei were selected at 7 days of leaf development and immersed in 0.4 mol·L−1 mannitol for 20 minutes, followed by treatment with the enzymatic solution from group 2, which comprised 15 mg·L−1 cellulase R-10, 10 mg·L−1 cellulase RS, 10 mg·L−1 lyase R-10, 4 mg·L−1 pectinase Y-23 and 10 mg·L−1 hemicellulase. The enzymatic digestion was conducted for 3 hours at room temperature under low light conditions to achieve the best effect of protoplast isolation from P. bournei leaves, yielding 7.7×106 cells·g−1 FW with a viability of up to 72%. The transient transformation of protoplasts was mediated using the PEG method, where in a plasmid concentration of 2 μg·μL−1 was combined with freshly isolated P. bournei leaf protoplasts. An equal volume of a 50% PEG 4000 solution was then added to this mixture, which was incubated at 42 ℃ for 15 minutes. Plasmids containing green fluorescent proteins, specifically pAN580-GFP and PbTPSa25-GFP, were successfully transformed into P. bournei protoplasts, resulting in a transformation efficiency of 61%. Additionally, confocal microscopy revealed that the PbTPSa25 protein was localized in the cytoplasm. Conclusion This study successfully isolated protoplasts from young leaves of P. bournei by optimizing various conditions, including enzyme formulation and osmotic pressure. and effectively transferred an exogenous plasmid vector into P. bournei protoplasts using a PEG-mediated method, thereby establishing a system for the instantaneous transformation of protoplasts. This protocol provides a robust experimental platform and technological support for in-depth research on gene function and genetic improvement in P. bournei. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 35 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 601-610.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240484
Abstract:
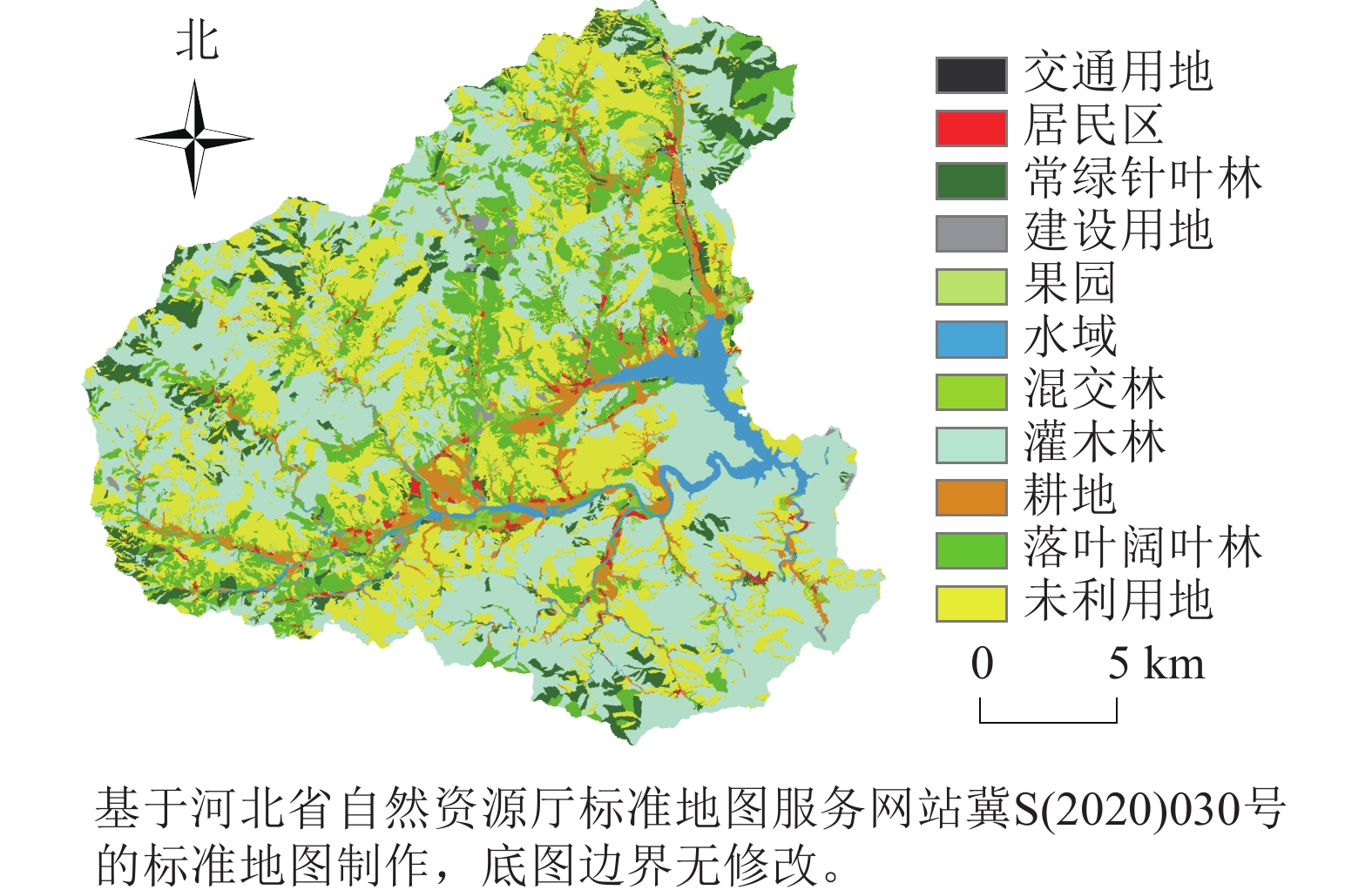
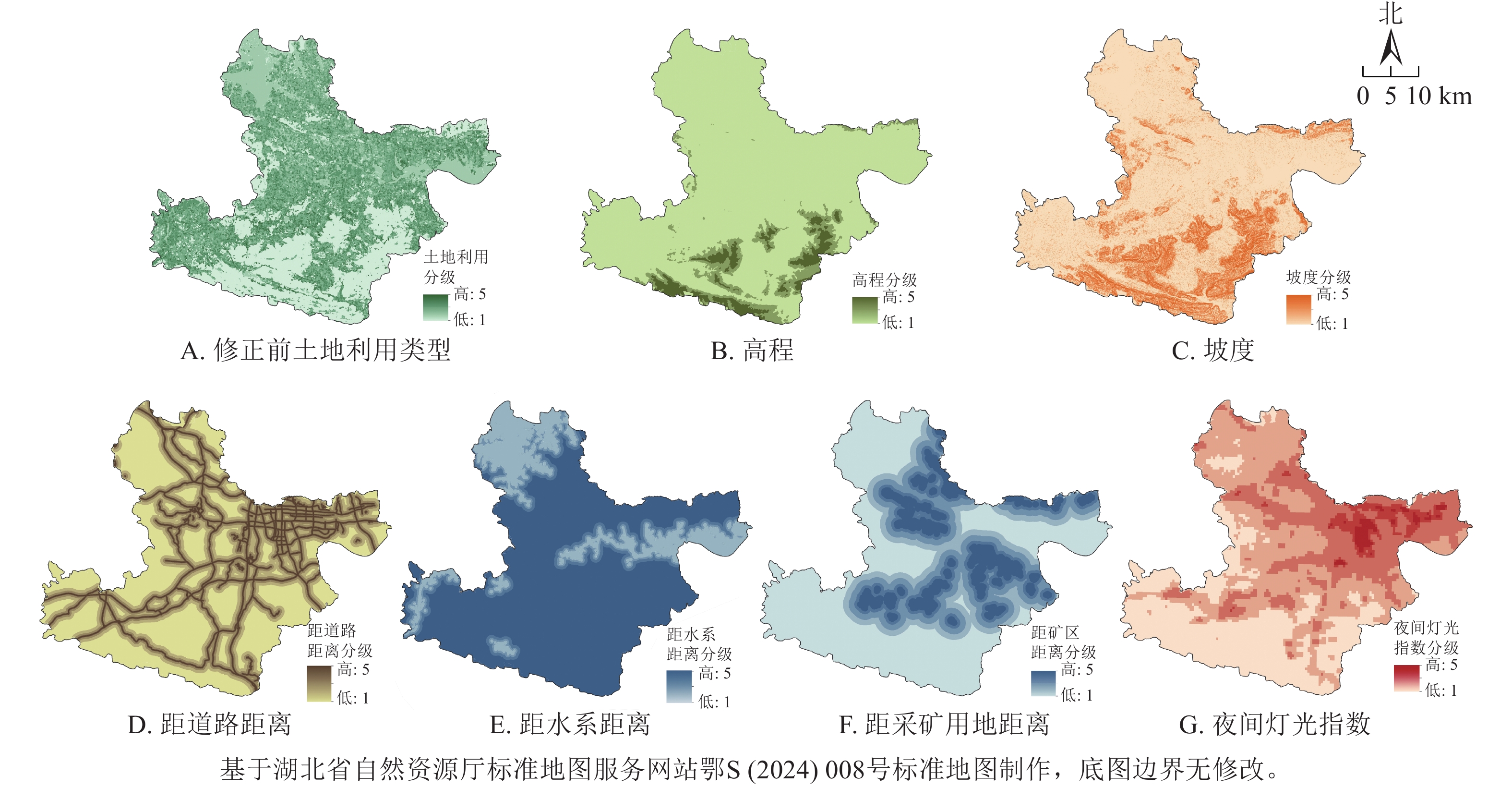
Objective Daye mining area in Hubei Province is a significant production base for copper and iron ore in China. While exploiting resources to promote regional economic development, it also poses significant challenges to local ecological balance. This study aims to construct a scientific and reasonable ecological network from a macro perspective, and identify key areas for protection and restoration, which is crucial for maintaining the ecological equilibrium in the region. Method Taking Daye mining area as the research object, remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) was adopted to identify ecological source areas and correct ecological resistance surface. Then, circuit theory was used to identify ecological corridors, ecological pinch points, and ecological obstacle points, and to construct the ecological network pattern of Daye mining area. Result The ecological network pattern of Daye mining area consisted of 11 ecological source areas, 18 ecological corridors, 17 ecological pinch points, and 32 ecological obstacle points. The ecological source areas were primarily distributed in the southern, western, and eastern parts of the city, covering a total area of 442.24 km². The total length of the ecological corridor was 104.55 km, of which the central and southern regions were characterized by high-grade resistance corridors, the northeast was mostly medium-grade resistance corridors, and the west was mostly low-grade resistance corridors. Ecological pinch points were mainly concentrated on the low-resistance corridors in the west, while ecological barrier points were mostly distributed on high resistance corridors in the central and southern regions. Based on the above elements, an ecological network pattern of “south mountain, north lake, multi-corridor, and multi-point” was constructed. Conclusion RSEI can effectively identify ecological source areas with high ecological value and connectivity. Based on the revised ecological resistance surface, it is possible to accurately identify the ecological corridor with the minimum resistance value, which significantly enhances the rationality of the entire ecological network structure. [Ch, 6 fig. 4 tab. 30 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 611-621.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240488
Abstract:
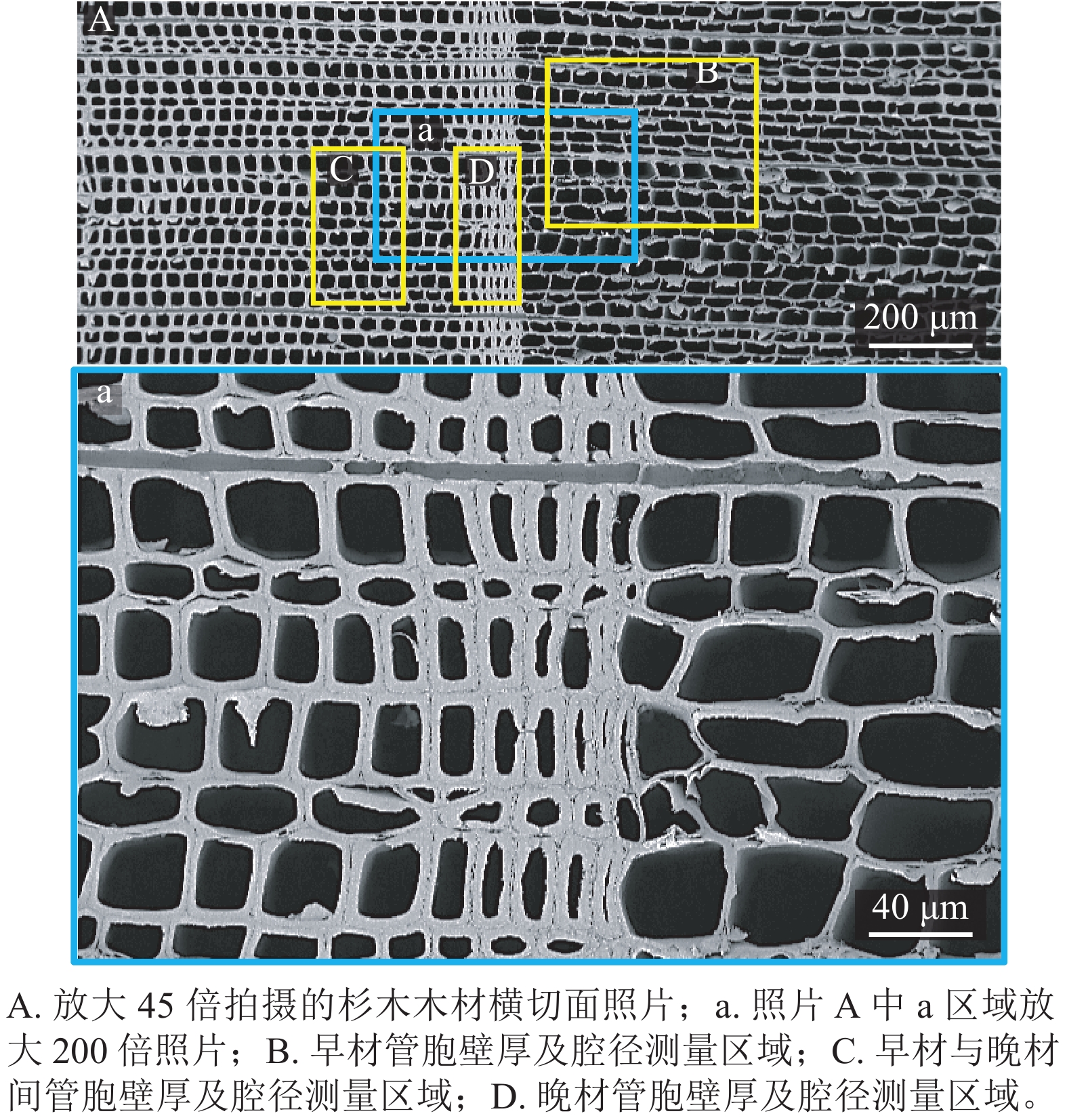
Objective The compressive strength of wood perpendicular to grain is an important factor for selecting materials used in wood building and flooring. The study aims to investigate the compressive strength perpendicular to grain of sandwich-compressed Cunninghamia lanceolata wood, in order to provide reference for its high value-added utilization in wood products such as flooring and furniture. Method Taking C. lanceolata wood as the research object, a sandwich compression method under hydrothermal control was used to process sandwich-compressed wood with different compression layer locations and thicknesses. The changes in wood structure and tracheid structure caused by sandwich compression were studied, and the impact of density distribution of sandwich-compressed C. lanceolata wood on the compressive strength perpendicular to grain under tangential and radial loading was analyzed. Result Scanning electron microscopy observation and measurement results showed that the average radial lumen diameter of the earlywood was 45.7 μm, while that of latewood was only 4.6 μm, and the wall thickness of early wood tracheid was only half of that of latewood. The average ratio of the double wall thickness to the lumen diameter of tracheid in the tangential and radial directions of earlywood was 0.14, while that of latewood was 3.08. After sandwich compression, the cell wall of earlywood in the compressed layer was greatly deformed until the cell lumen almost disappeared, while the cell morphology in the latewood area remained almost unchanged. The earlywood density in the compressed layer significantly increased from below 0.200 g·cm−3 to above 0.500 g·cm−3, but in most cases, the density of the compressed earlywood was still lower than the latewood density of natural C. lanceolata. The density distribution of compressed layer exhibited several density peaks of latewood. The compressive strength perpendicular to grain of the control samples and sandwich-compressed samples under tangential loading was more than 2 times of that under radial loading. There was a significant linear correlation (P<0.01) between the compressive strength perpendicular to grain under radial and tangential loading and the mean and minimum density of compressed wood. The relationship between compressive strength perpendicular to grain and density under radial loading is more closely related than that under tangential loading. Conclusion The earlywood density in the compressed layer significantly increases. A slight increase in earlywood density can significantly improve the compressive strength perpendicular to grain of compressed wood. [Ch, 9 fig. 1 tab. 28 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 622-630.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240536
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the optimal cutting parameters for cutting force and extraction quality when extracting bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) vascular bundle fibers by milling, and provide theoretical reference for efficient acquisition of high-quality natural vascular bundle fibers with uniform thickness and good consistency in length and size. Method Cutting speed (Vc), feed per tooth (fz), and cutting depth (Ap) were taken as variables, unidirectional milling and orthogonal cutting experiments were conducted on bamboo boards using a double-edged straight groove hard alloy woodworking carving knife. The influence of cutting parameters on cutting force was verified by range analysis and variance analysis. The experimental data were analyzed by multivariate nonlinear regression method to establish an empirical formula for cutting force. Based on transient cutting geometric model and single-factor experiments, the effects of cutting speed, cutting depth, and feed per tooth on the quality of vascular bundle fiber extraction were investigated. Result During the cutting process, only X-Y-directional cutting forces were generated on the workpiece, while the Z-directional cutting force continuously fluctuated near zero value. Cutting depth had an extremely significant impact on cutting force. Within the X-Y plane, cutting force mainly acted along parallel the feed direction of the tool, and feed per tooth had a more significant influence on cutting force than cutting speed. The vertical tool feed direction was mainly affected by extrusion force, and cutting speed had a more significant effect on cutting force than feed per tooth. The coefficient of determination (R2) of nonlinear regression equation for cutting force along the tool feed direction was 0.956, which could accurately predict the magnitude of cutting force. The determination coefficient of the nonlinear regression equation for cutting force in the vertical tool feed direction was 0.697, but the error between its predicted and theoretical value was within ±5 N, reflecting the overall trend of cutting force in this direction. The error between the average fiber length obtained by milling and the target length was within ±0.1 mm. Within the range of cutting parameters, when cutting parameters were Vc=188.5 m·min−1, Ap=12 mm, and fz=0.2 mm, vascular bundle fibers with larger diameters and higher aspect ratio were obtained. Conclusion Cutting depth is the most important factor affecting the magnitude of cutting force. In the parallel tool feed direction, feed per tooth has a greater impact on cutting force than cutting speed. In the vertical tool feed direction, cutting speed has a greater impact on cutting force than feed per tooth. The nonlinear regression model of cutting force can accurately calculate cutting force in various directions and the overall trend of change. The milling method can accurately control the target length of vascular bundle fibers. Higher cutting speed, greater cutting depth, and smaller feed per tooth can help obtain vascular bundle fibers with larger aspect ratio and diameters. [Ch, 9 fig. 5 tab. 26 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 631-644.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250239
Abstract:
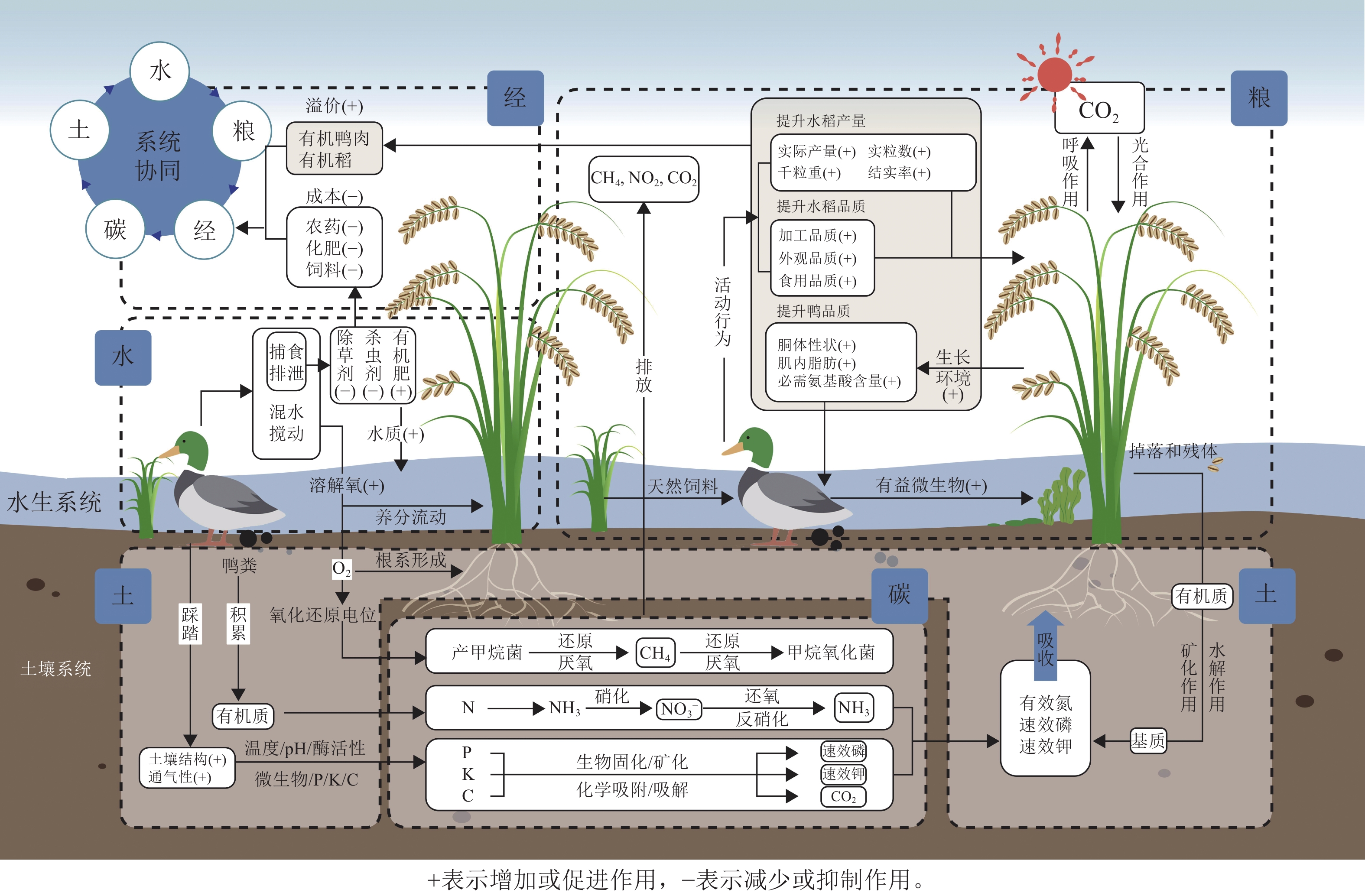
Rice-duck co-culture is a creative agricultural technology model that essentially responds to the ecological technology of the traditional rice cultivation system. By reviewing the development of rice-duck co-culture in China, this study aims to construct a collaborative framework of “water-soil-grain-economy-carbon” system, clarify its mechanism, and analyze its ecological effects and impact mechanism from the perspectives of water regulation, soil conservation, stable production, income increase and carbon sequestration. The research revealed: (1) The co-culture of rice and duck in China experienced 4 phases: concept implantation and technology germination, technology introduction and industry shaping, standardization and promotion, and technological upgrade and creative development. It was deeply integrated into creative agricultural technology and drove its iterative upgrading, providing an innovative paradigm for sustainable agricultural development. (2) The co-culture of rice and duck significantly optimized the physical and chemical properties of water bodies, while promoting soil structure amelioration, enriching soil colonies and water body biodiversity, and achieving ecological regulation and collaborative improvement of water and soil environments. (3) The co-culture of rice and duck effectively promoted the improvement of rice yield and quality, as well as the flavor of duck meat. While reducing production costs, it also increased the comprehensive income of planting and breeding, providing a practical path for the realization of the value of creative agricultural technology models. (4) The rice-duck co-culture system significantly suppressed CH4 emissions and slightly affected the release of other greenhouse gases, resulting in an overall decrease in the global warming potential of the system, which helped to mitigate the negative effects of agricultural production on climate change. Therefore, in the future, several key scientific issues still need to be addressed in terms of industrial development and ecological sustainability in order to enhance the adaptability and sustainability of rice-duck intercropping. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 84 ref.]
Rice-duck co-culture is a creative agricultural technology model that essentially responds to the ecological technology of the traditional rice cultivation system. By reviewing the development of rice-duck co-culture in China, this study aims to construct a collaborative framework of “water-soil-grain-economy-carbon” system, clarify its mechanism, and analyze its ecological effects and impact mechanism from the perspectives of water regulation, soil conservation, stable production, income increase and carbon sequestration. The research revealed: (1) The co-culture of rice and duck in China experienced 4 phases: concept implantation and technology germination, technology introduction and industry shaping, standardization and promotion, and technological upgrade and creative development. It was deeply integrated into creative agricultural technology and drove its iterative upgrading, providing an innovative paradigm for sustainable agricultural development. (2) The co-culture of rice and duck significantly optimized the physical and chemical properties of water bodies, while promoting soil structure amelioration, enriching soil colonies and water body biodiversity, and achieving ecological regulation and collaborative improvement of water and soil environments. (3) The co-culture of rice and duck effectively promoted the improvement of rice yield and quality, as well as the flavor of duck meat. While reducing production costs, it also increased the comprehensive income of planting and breeding, providing a practical path for the realization of the value of creative agricultural technology models. (4) The rice-duck co-culture system significantly suppressed CH4 emissions and slightly affected the release of other greenhouse gases, resulting in an overall decrease in the global warming potential of the system, which helped to mitigate the negative effects of agricultural production on climate change. Therefore, in the future, several key scientific issues still need to be addressed in terms of industrial development and ecological sustainability in order to enhance the adaptability and sustainability of rice-duck intercropping. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 84 ref.]
2025, 42(3): 645-656.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240564
Abstract:
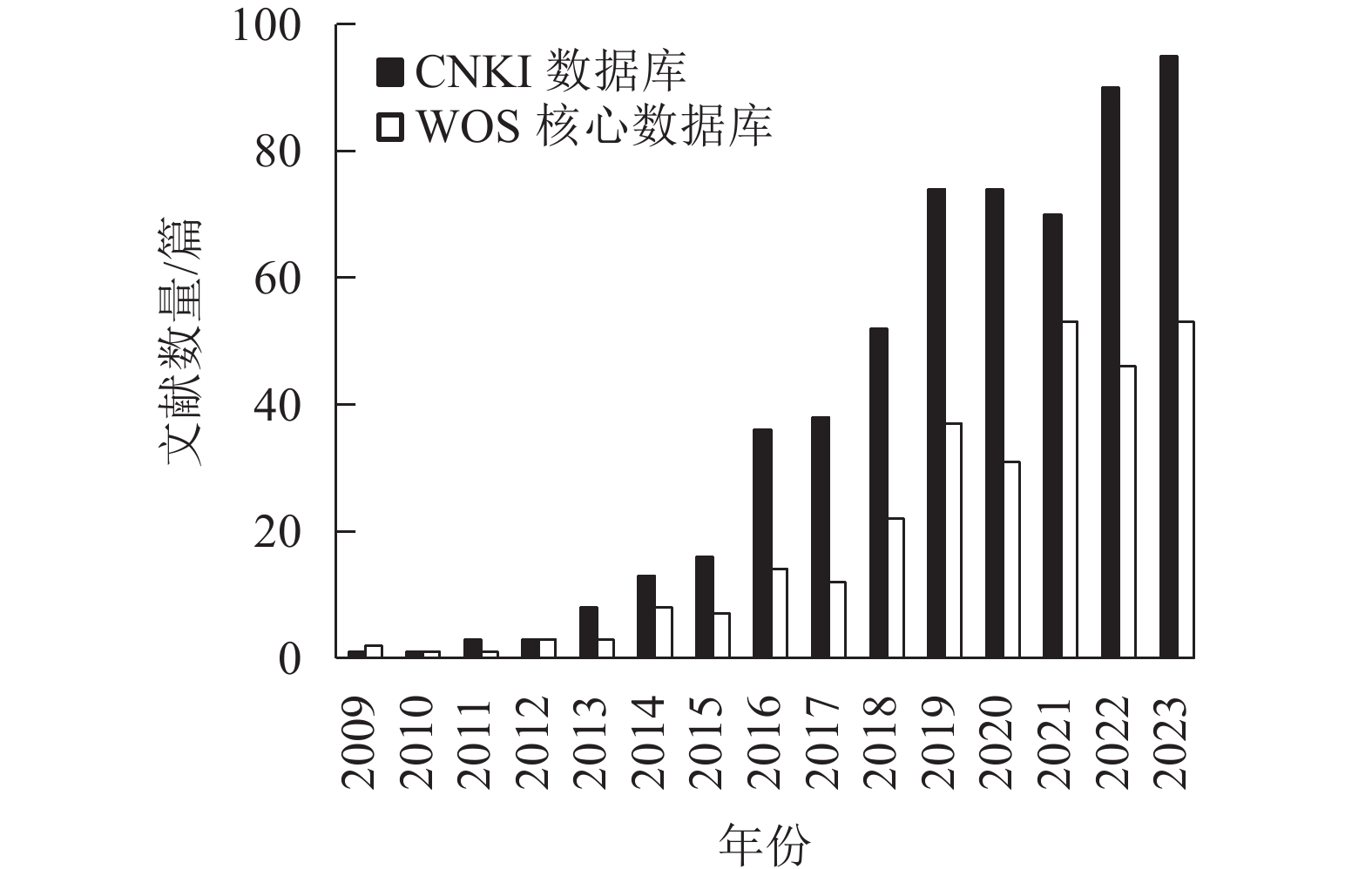
Soil carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) stoichiometric characteristics are indicators to characterize the composition of soil organic matter and nutrient availability, which play a key role in understanding the carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycle in soil and the balance of ecosystem. However, the current research on the specific effects of each driving factor on soil stoichiometric characteristics needs to be further strengthened. By analyzing the annual publications and research hotspots in the field of soil ecological stoichiometry home and abroad from 2009 to 2023, we discussed the changes of soil ecological stoichiometric characteristics in 4 parts: biological factors (plant, soil microorganism and soil animal), natural environmental factors (geological hazard, topography and soil parent material), global climate change factors (climate warming, extreme weather, nitrogen deposition, acid rain) and human activity (land use pattern). The driving factors of the change of soil ecological stoichiometric ratios were discussed, and the law and internal mechanism of the change of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometric ratios were expounded. The results showed that plant, soil microorganism, soil animal and their interactions jointly drive soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycle. Soil animals affect microbial community structure through feeding and thus influence soil carbon turnover. The complexity of microbial community regulates soil C-N-P coupling. Geological disasters disturb the balance of soil stoichiometry through nutrient loss and decreased microbial activity. Topography, climate warming and extreme climate indirectly affect soil stoichiometry by changing water and heat conditions, whereas the mineral composition and structure of parent material directly regulate soil C∶N∶P. Nitrogen deposition and acid rain affect plant growth and soil microbial activity through soil acidification and nutrient loss and thus change soil C-N-P stoichiometry. Land use patterns directly or indirectly affect soil stoichiometry through agricultural management and vegetation cover. Environmental factors affect soil C-N-P stoichiometry through biotic factors, directly or indirectly, but with uncertain direction and degree. Further study should pay attention to the synergistic effect of multiple factors and multi-path regulation mechanism so as to provide a reference for soil nutrient management and ecosystem stability in the context of global change. [Ch, 3 fig. 70 ref.]
Soil carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) stoichiometric characteristics are indicators to characterize the composition of soil organic matter and nutrient availability, which play a key role in understanding the carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycle in soil and the balance of ecosystem. However, the current research on the specific effects of each driving factor on soil stoichiometric characteristics needs to be further strengthened. By analyzing the annual publications and research hotspots in the field of soil ecological stoichiometry home and abroad from 2009 to 2023, we discussed the changes of soil ecological stoichiometric characteristics in 4 parts: biological factors (plant, soil microorganism and soil animal), natural environmental factors (geological hazard, topography and soil parent material), global climate change factors (climate warming, extreme weather, nitrogen deposition, acid rain) and human activity (land use pattern). The driving factors of the change of soil ecological stoichiometric ratios were discussed, and the law and internal mechanism of the change of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometric ratios were expounded. The results showed that plant, soil microorganism, soil animal and their interactions jointly drive soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycle. Soil animals affect microbial community structure through feeding and thus influence soil carbon turnover. The complexity of microbial community regulates soil C-N-P coupling. Geological disasters disturb the balance of soil stoichiometry through nutrient loss and decreased microbial activity. Topography, climate warming and extreme climate indirectly affect soil stoichiometry by changing water and heat conditions, whereas the mineral composition and structure of parent material directly regulate soil C∶N∶P. Nitrogen deposition and acid rain affect plant growth and soil microbial activity through soil acidification and nutrient loss and thus change soil C-N-P stoichiometry. Land use patterns directly or indirectly affect soil stoichiometry through agricultural management and vegetation cover. Environmental factors affect soil C-N-P stoichiometry through biotic factors, directly or indirectly, but with uncertain direction and degree. Further study should pay attention to the synergistic effect of multiple factors and multi-path regulation mechanism so as to provide a reference for soil nutrient management and ecosystem stability in the context of global change. [Ch, 3 fig. 70 ref.]