2025 Vol. 42, No. 4
2025, 42(4): 657-666.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250338
Abstract:
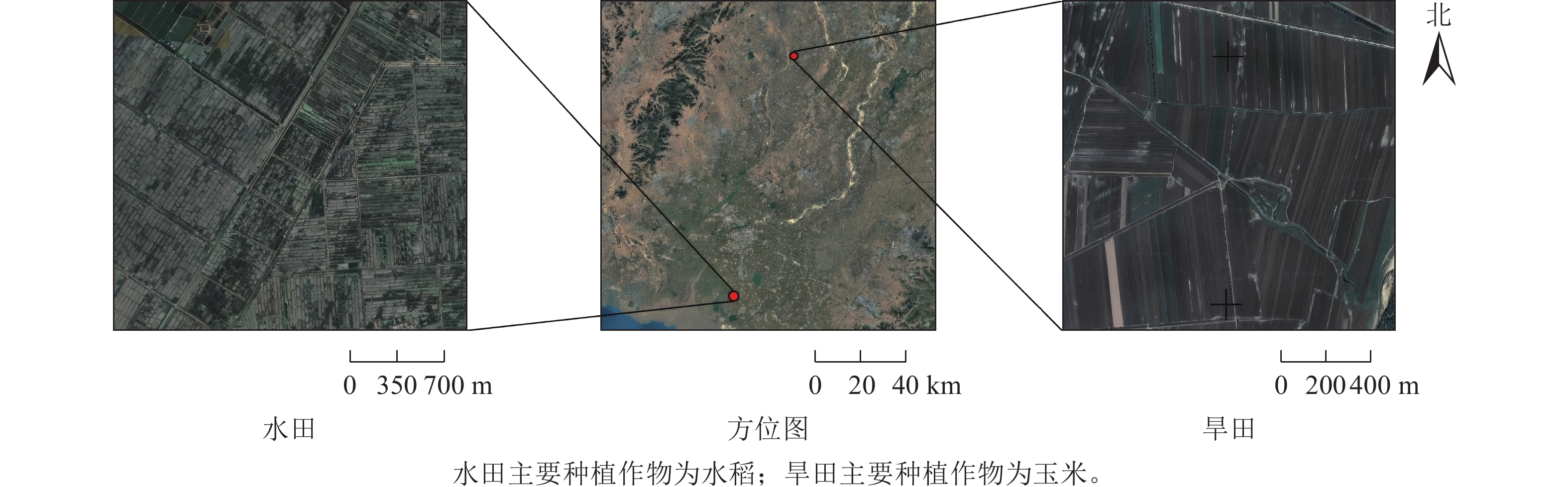
Objective Satellite remote sensing has merged as the primary approach for monitoring crop phenology. This method has many advantages, including large monitoring area and convenient data acquisition. However, high-resolution remote sensing satellites, which are essential for accurate observation, have a long revisit period. Inevitably multiple dates are affected by unfavorable conditions such as atmospheric and cloud fog. As result, the data for high-resolution time-series crop phenology detection becomes sparse, failing to provide sufficient images during the rapidly changing crop growth period. A new method is proposed to enhance the accuracy of time series monitoring and achieve precse phenology detection. Method Paddy fields and dry fields were selected as research plots. First, a time-series remote sensing data filling method wes explored by combining with generative image processing technology. Then a lightweight super-resolution reconstruction generative adversarial networks (GAN) was proposed for image reconstruction. Finally, the reconstructed data were utilized to conduct intensive time series monitoring and phenological extraction of crop growing season. Result (1) In terms of image super-resolution reconstruction, the proposed method achieved values of 0.834 and 28.69 in structural similarity (SSIM) and peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), respectively. It can reconstruct heterologous remote sensing data more effectively than mainstream methods. (2) After time series reconstruction, the revisit period of remote sensing images in 2 experimental areas decreased from 6.40 d and 6.63 d to 5.70 d and 5.88 d respectively, and the spatial resolution increased to 10 m. (3) Regarding phenological extraction, the extraction results of 4 smoothing methods differed from those of original data extraction, and were superior to the interpolation-based methods commonly used for time series imputation. Conclusion The proposed method can effectively fill the time-series of satellite images, enhance the continuity of observation data, and enable accurate high spatiotemporal-resolution monitoring of crop phenology. [Ch, 9 fig. 3 tab. 27 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 667-676.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250325
Abstract:
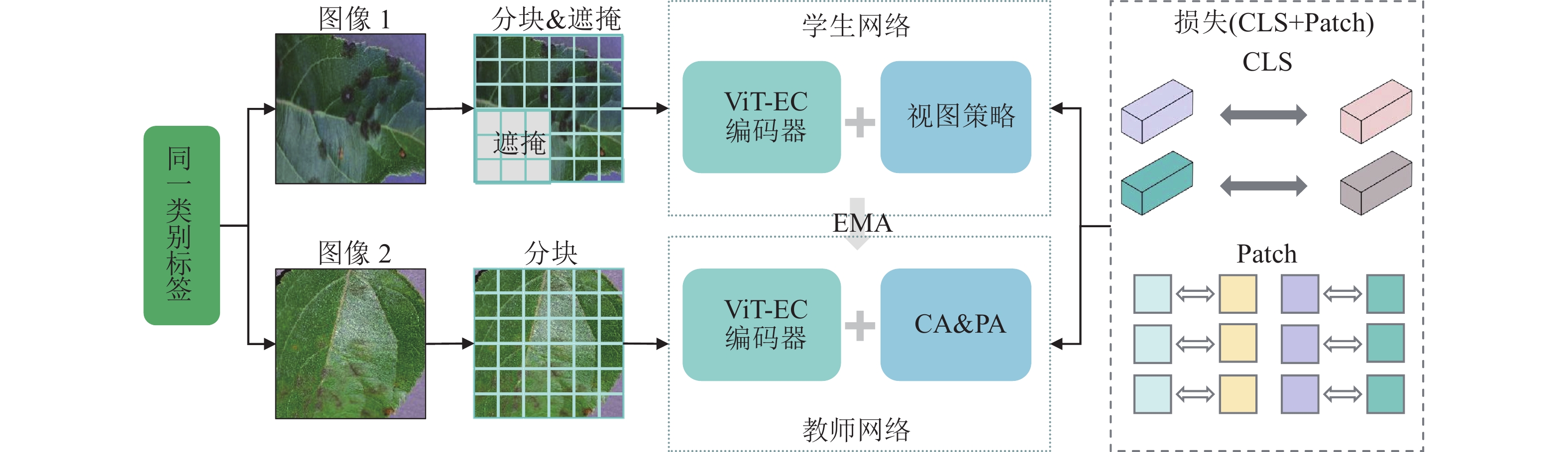
Objective This study aims to address the strong dependence of plant disease recognition on large-scale annotated data and its poor adaptability to novel diseases, and enhance the performance of few-shot learning methods under complex environments, so as to provide a theoretical basis for few-shot plant disease recognition. Method A novel recognition framework, enhanced context-aware knowledge distillation (ECKD), was proposed by integrating a few-shot transformer with supervised masked knowledge distillation. The framework adopts a collaborative architecture composed of teacher and student networks, and introduces strategies such as global feature alignment, local feature alignment, and supervised masked image modeling views. To enhance feature extraction and semantic understanding, a new encoder ViT-EC was developed using a channel attention residual module and a context-aware module. The model was evaluated using prototype-based classifiers on the PlantVillage dataset under 5-way 1-shot and 5-way 5-shot tasks. Result The prototype classifier based on the ECKD framework achieved average accuracies of 74.98% and 88.28% in the 5-way 1-shot and 5-way 5-shot tasks, respectively, significantly outperforming several existing methods. Ablation studies confirmed the positive contributions of the attention residual module, context-aware module, and the supervised masked image modeling strategy in enhancing global semantic understanding and local feature reconstruction, especially under incomplete data conditions. Conclusion The ECKD framework effectively alleviates the challenges of few-shot learning in plant disease recognition by integrating multi-view augmentation strategies and a knowledge distillation mechanism. It significantly improves recognition accuracy and model stability, offering an efficient and practical solution for intelligent agricultural perception systems with promising applicability. [Ch, 8 fig. 4 tab. 29 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 677-683.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240664
Abstract:
Objective Forest environments are often characterized by rich textures and uneven lighting conditions, which poses challenges for traditional oriented FAST and rotated BRIEF (ORB) image feature extraction methods in extracting key features such as tree trunks and branches. This study aims to solve the problem of ORB feature extraction in complex forest environments through research and improvement of existing algorithms. Method The global and local Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) image enhancement technique was introduced to improve the effect of forest land feature extraction. Meanwhile, the application of Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) in texture analysis was explored to investigate its impact on feature point selection, so that the extraction of feature points could be more focused on the features of tree trunks and branches. By integrating these methods, efforts were made to enhance the response value and the number of feature points, thereby improving the overall performance of feature extraction. Result After image enhancement, the median response value of feature points increased from 98 to 113, and the mean value increased from 99.27 to 112.05. After GLCM texture analysis, the number of feature points on tree trunks and branches increased by approximately 5.78% and 5.08% respectively, while the proportion of feature points on grassland decreased to about 4.88%, demonstrating a significant improvement. Conclusion The proposed method demonstrates good adaptability in complex forest environments, which not only improves the accuracy of feature extraction but also lays a foundation for subsequent forest image analysis. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 28 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 684-693.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250324
Abstract:
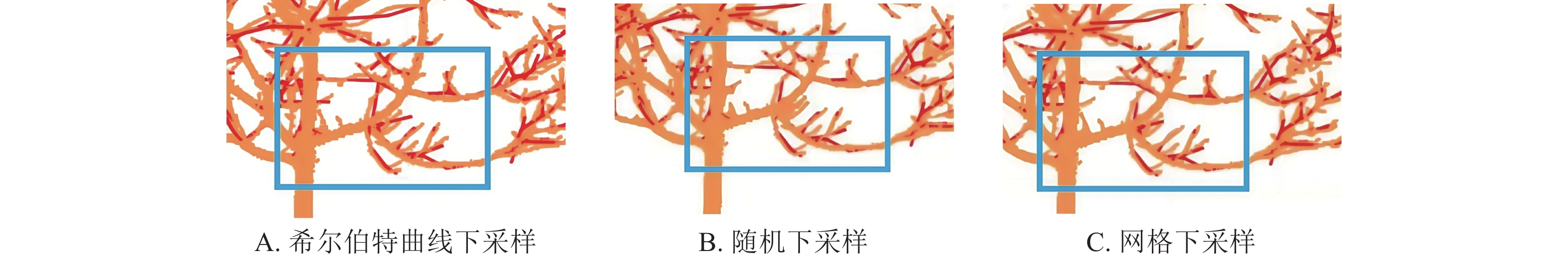
Objective This study aims to propose an approach for tree skeleton extraction based on terrestrial LiDAR point clouds, so as to achieve high-precision and high-fidelity 3D tree reconstruction. Method For the segmented point cloud of a single tree, Hilbert curve was used for downsampling and denoising to improve computational efficiency and remove noise. After branch and leaf separation and obtaining the complete branch point cloud, a semantic Laplacian contraction algorithm was applied to extract the initial skeleton of the tree. Finally, the tree skeleton was optimized using branch smoothing technology to obtain a high fidelity and topologically correct tree skeleton structure. Result Compared with traditional methods, the proposed approach extracted an average of 12.3% more skeleton nodes and an average improvement of 42.0% in point cloud interval accuracy, reaching 0.011−0.021 m. This method has significant advantages in topological integrity and detail preservation, while the continuity and natural morphology of the skeleton are further enhanced in combination with the branch smoothing optimization technique. Conclusion This method can effectively overcome the limitations of conventional skeleton extraction algorithms, significantly improve robustness and accuracy, and provide high-fidelity tree skeleton data support for applications such as plant phenotyping and tree growth assessment. [Ch, 7 fig. 4 tab. 28 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 694-702.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250177
Abstract:
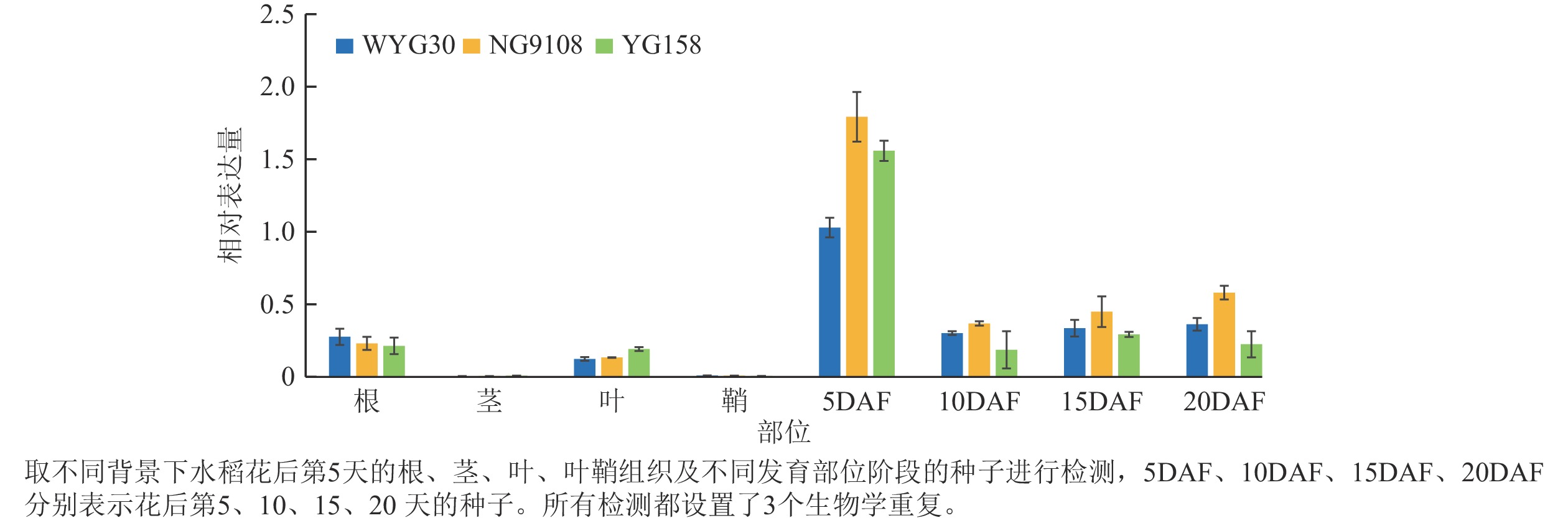
Objective Quality improvement of rice (Oryza sativa) has become a core topic in modern breeding research in China. Understanding the regulatory roles of relevant genes in rice protein, starch and eating and cooking quality is crucial for the genetic improvement of rice quality. Method The CRISPR/Cas9 technology was utilized to knockout the OsAAP13 gene (LOC_Os04g39489), which has high expression levels in the endosperm of three japonica rice cultivars ‘Wuyungeng 30’, ‘Nangeng 9108’ and ‘Yanggeng 158’, constructing the corresponding mutants. Agronomic traits, protein and starch content, as well as eating quality, were comprehensively evaluated, and gene function was validated across multiple genetic backgrounds. Result OsAAP13 exhibited peak expression in grains at 5 days after flowering. Measurements of agronomic traits and rice physicochemical properties revealed that the knockout of OsAAP13 did not affect major agronomic traits of rice, but significantly reduced total protein content (7.8%−15.8%) and certain protein fractions (globulin 5.5%−21.1% and glutelin 9.0%−15.8%). Total starch content increased in the mutants (2.1%−8.7%), while amylose content decreased (4.0%−6.9%). Eating quality assessments of the mutant rice showed a significant improvement in palatability (2.9%−11.6%). Conclusion Knocking out OsAAP13 can effectively improve multiple physicochemical traits and eating quality of rice while maintaining excellent agronomic traits, providing important theoretical support for future rice quality improvements. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 31 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 703-713.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240570
Abstract:
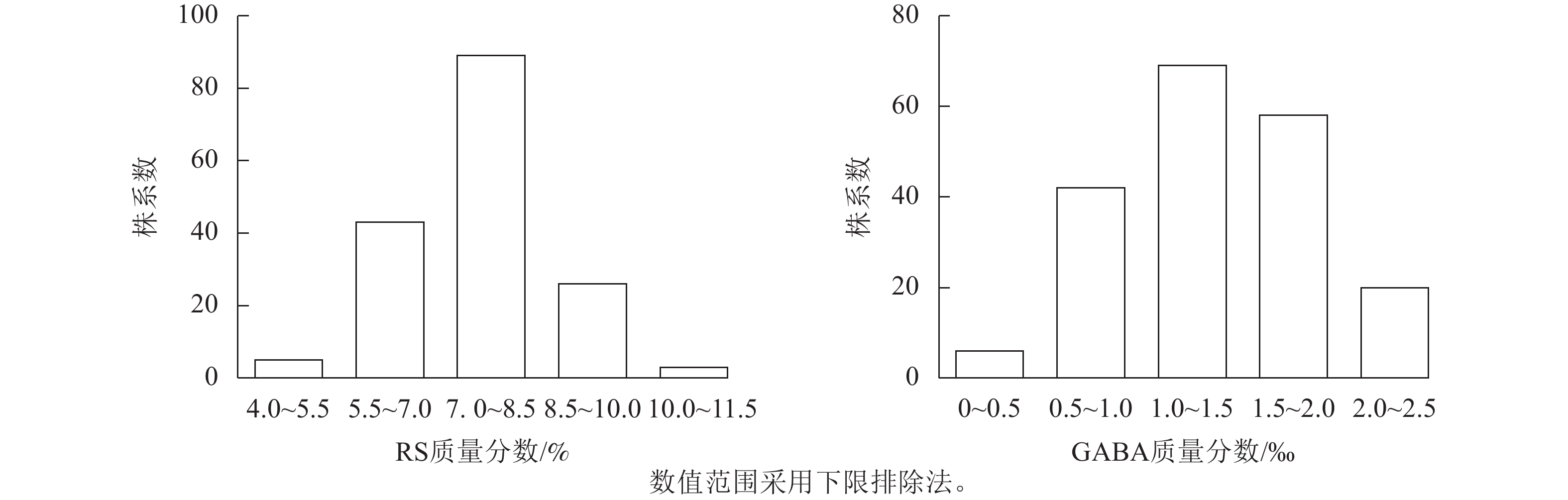
Objective Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum), as a high-quality minor grain crop, contains a variety of functional components, such as resistant starch (RS) and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping of functional components in Tartary buckwheat grains is of great significance for molecular genetic improvement of Tartary buckwheat. Method The recombinant inbred lines population constructed by using ‘Xiaomijiao’ and ‘Jinqiaomai No. 2’ as parents (XJ-RILs) was used as the test material. The contents of RS and GABA of the XJ-RILs population and its parents were determined. Based on the genetic map, QTLs controlling RS and GABA were located, and candidate genes within the QTL intervals were identified and analyzed. Result The XJ-RILs population exhibited significant transgressive segregation and a skewed normal distribution for RS and GABA contents, ranging from 4.51% to 10.52% and 0.37‰ to 2.50‰, respectively. Based on their contents, the population was classified into five categories (C1 to C5), among which the C1 category had high levels of both RS and GABA, and three superior lines with high RS and three with high GABA were selected. QTL mapping for RS and GABA in the XJ-RILs population detected a total of two QTLs controlling RS and one controlling GABA, with phenotypic contribution rates of 7.59%, 6.34%, and 5.05%, respectively. A total of 108 candidate genes for RS were identified within the QTL regions, and their expression patterns were classified into six categories (R1 to R6). Among them, 30 genes in R4, R5, and R6 showed higher expression levels in seeds. Similarly, 64 candidate genes for GABA were identified and their expression patterns were classified into six categories (G1 to G6), with 21 genes in G4, G5, and G6 exhibiting higher expression in seeds. Among the candidate genes for RS and GABA, 16 and 6 genes, respectively, harbored SNP/Indel variations. Conclusion Three elite lines with high RS and three with high GABA were selected. Two QTL loci controlling RS and one QTL locus controlling GABA were identified. Within these loci intervals, 108 and 64 genes were screened respectively, with 30 RS-related and 21 GABA-related candidate genes preliminarily identified . [Ch, 4 fig. 6 tab. 40 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 714-724.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240508
Abstract:
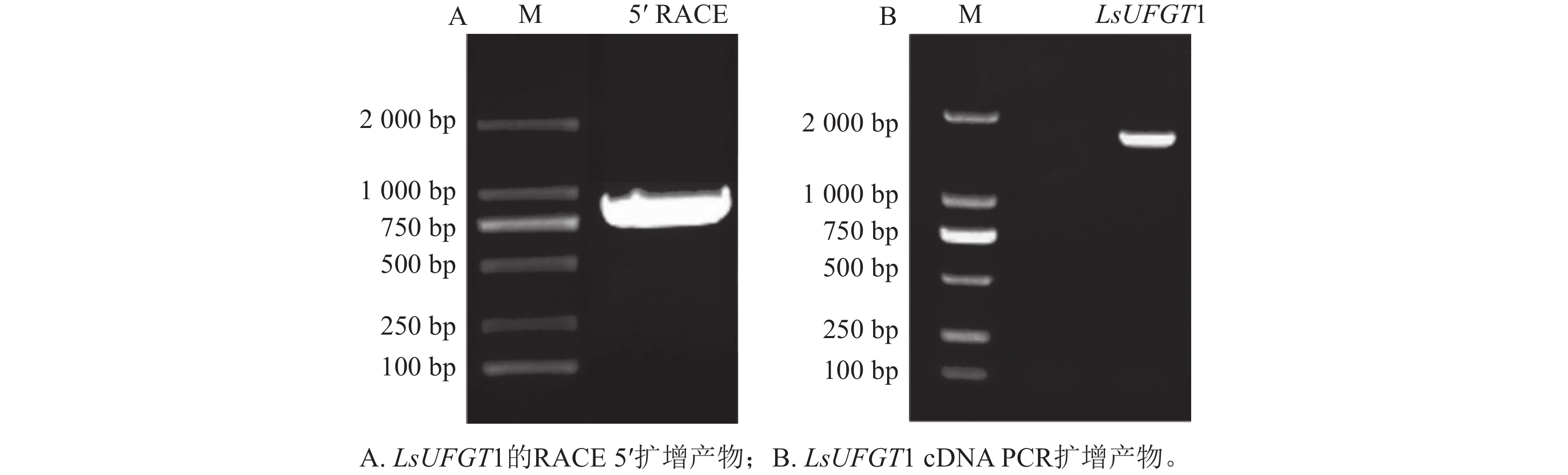
Objective Anthocyanins are important components that determine flower color in plants. Flavonoid-3-O-glycosyltransferase (UFGT) plays a role in the downstream of anthocyanins biosynthesis, which converts unstable pigments into stable anthocyanins. This study analyzed the function of LsUFGT1 gene in Lycoris sprengeri, which would provide a theoretical basis for further studying the flower coloration mechanism in L. sprengeri. Method Several molecular biology techniques such as gene cloning, reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), genome walking, histological staining, and dual luciferase reporter assay, were used to study the functions of LsUFGT1 and its promoter. Result (1) The cDNA sequence of LsUFGT1 was obtained with a length of 1 632 bp, with an open reading frame of 1 398 bp, encoding 465 amino acids; the homology between LsUFGT1 and NtUFGT1 in Narcissus ntazettatorium was up to 60.57%. (2) The expression of LsUFGT1 was consistent with the trend of total anthocyanin contents, and was the most highest at blooming period, whereas the difference in expression between the pink and blue petal parts was not significant. (3) The LsUFGT1 promoter with 1 184 bp length was cloned, which contained cis-acting elements such as MYB binding site, response to light, hormone and adverse stress. β-glucosidase (GUS) histological staining in Arabidopsis thaliana showed that the LsUFGT1 promoter had promoter activity. (4) Dual luciferase reporter assays revealed that LsMYB4 and LsMYB5 were able to significantly inhibit the activity of the LsUFGT1 promoter (P<0.05). Conclusion LsMYB4 and LsMYB5 modulated anthocyanin accumulation by directly binding to the LsUFGT1 promoter in L. sprengeri. [Ch, 9 fig. 2 tab. 38 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 725-735.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240587
Abstract:
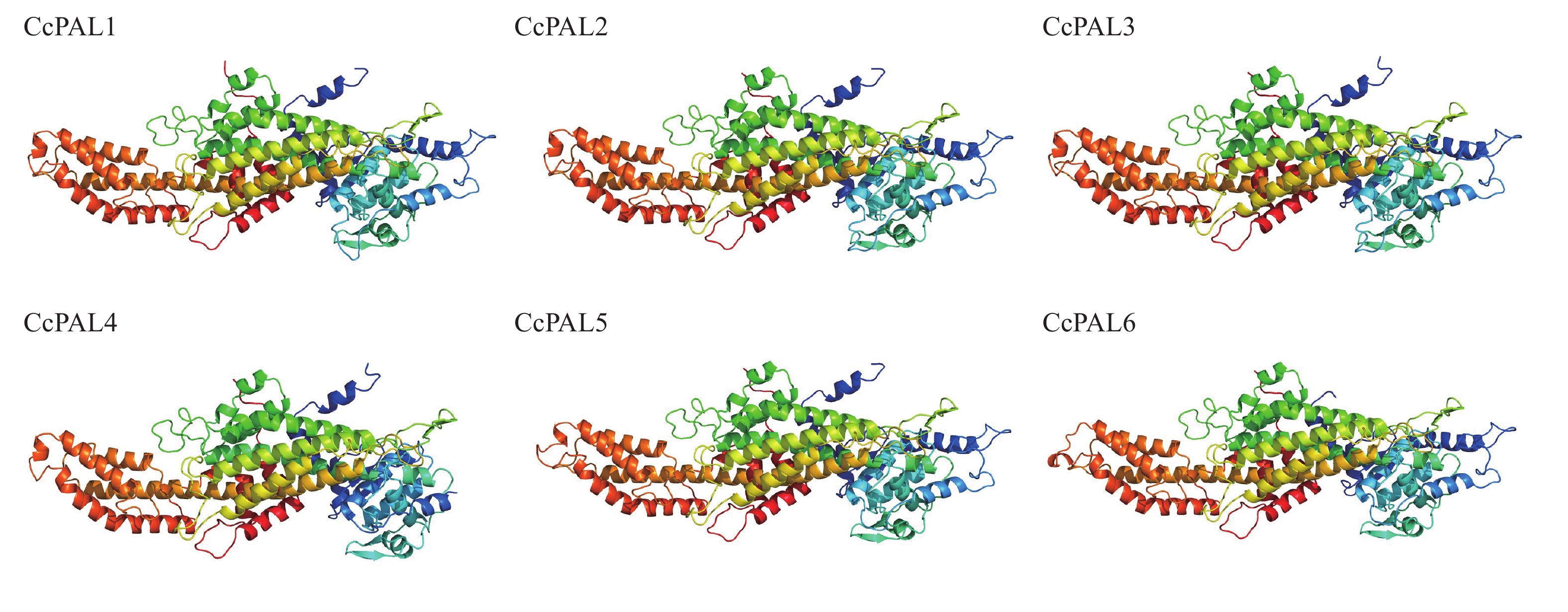
Objective Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), the initial enzyme in the biosynthesis of phenolic substances, is of crucial significance in plant growth, development, and environmental adaptation. The present study aims to identify the members of the PAL gene family in Carya cathayensis (CcPALs) and analyze their expression patterns during callus proliferation and browning. This analysis may provide a theoretical basis for the manipulation of CcPALs to inhibit browning and promote regeneration. Method Based on the whole-genome data of C. cathayensis, PAL family members containing conserved PAL motifs were screened. The physicochemical properties and gene-structure characteristics of CcPAL proteins were predicted and analyzed. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using PAL sequences from multiple species. Additionally, the expression changes of CcPALs in callus after subculture were examined through transcriptomic analysis. Result There were six PALs in C. cathayensis in total. The amino-acid lengths ranged from 657 to 760. These proteins were all acidic, stable, and hydrophilic, mainly localized in the nucleus and endoplasmic reticulum. The secondary structure of the protein was dominated by α-helix and random coil. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that CcPAL1−CcPAL4 cluster in the dicotyledonous plant branch, while CcPAL5 and CcPAL6 cluster in the gymnosperm branch. Expression analysis showed that the CcPALs displayed different expression patterns after callus subculture. Conclusion CcPALs exhibit high conservation. However, CcPAL5 and CcPAL6 were more closely related to gymnosperm PALs, potentially indicating significant functional differences from CcPAL1−CcPAL4 in secondary metabolism. During the callus proliferation and browning process, the expression patterns of CcPALs in different branches vary. This variation may potentially regulate the metabolic flux of phenolic substances and thus influence the regeneration process of C. cathayensis. [Ch, 7 fig. 4 tab. 37 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 736-744.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240594
Abstract:
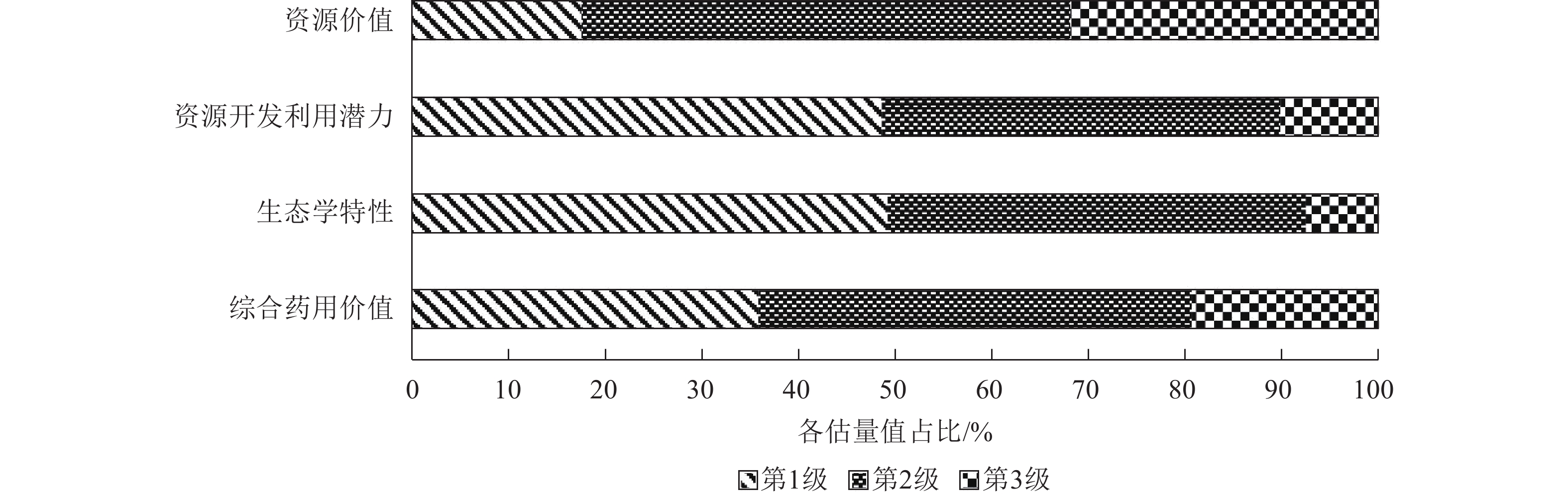
Objective Based on a survey of traditional Chinese medicinal resources on Nanji Islands, this study aims to understand the overall situation of wild medicinal plant resources in this area and provide scientific basis for the development and utilization of wild medicinal plant resources. Method A transect survey approach was employed to investigate medicinal plant resources on Nanji Islands. Based on the survey results, the Delphi method was applied to determine the indicator layer and scheme layer of the analytic hierarchy process (AHP). A medicinal value evaluation model was constructed for fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Finally, a comprehensive ranking of the development potential of wild medicinal plants on Nanji Islands was conducted based on the evaluation results. Result The comprehensive evaluation model of wild medicinal plants analyzed and evaluated 9 indicators including medicinal efficacy (C1), medicinal parts (C2), medicinal categories (C3), utilization degree (C4), community status (C5), frequency (C6), life type (C7), water ecological type (C8), and ecological habits (C9) from 3 dimensions: resource value, resource development and utilization potential, and ecological characteristics. 382 wild medicinal plant species belonging to 275 genera in 89 families were classified into 3 levels, among which 137 species were classified as 1st level wild medicinal plants with a comprehensive medicinal value assessment metric (hA) greater than 4.04. There were 171 species of 2nd level wild medicinal plants (3.08<hA≤4.04). There were 74 species of 3rd level medicinal plants (hA≤3.08). Conclusion Medicinal plant resources on Nanji Islands are abundant. Priority can be given to the development and utilization of medicinal herbs such as Aster turbinatus, Chrysanthemum indicum, and Ixeridium dentatum, while the germplasm resources of Aristolochia debilis, Herminium lanceum, and Platycarya strobilacea should be protected. [Ch, 1 fig. 3 tab. 32 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 745-753.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250253
Abstract:
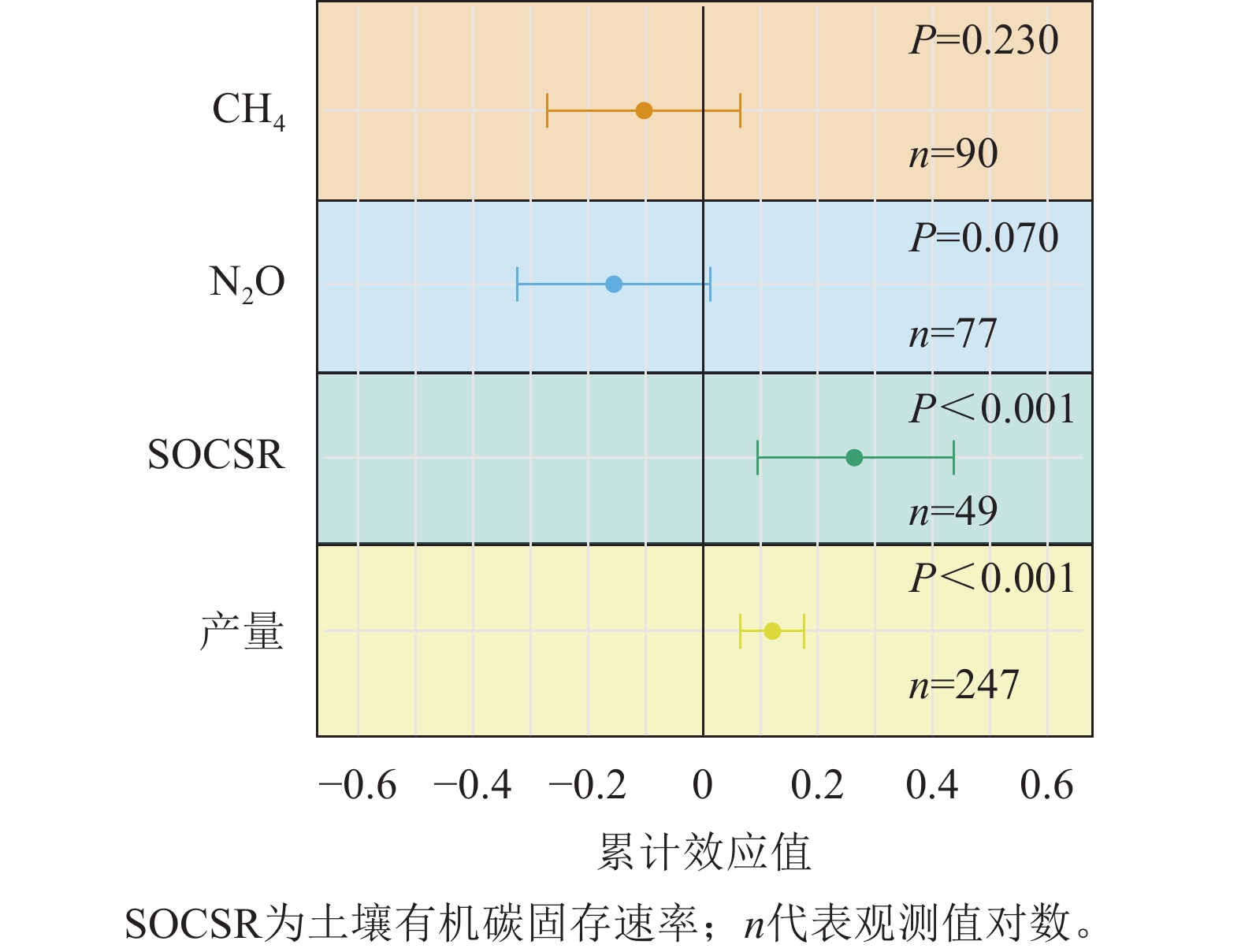
Objective Biochar is considered a feasible measure for maintaining production and reducing emissions due to its carbon sequestration and soil improvement functions. Research on the environmental and economic benefits of biochar, providing scientific basis for achieving green transformation of agriculture, promoting sustainable development of farmland, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Method Integrating multi-source data from China’s rice paddy system, constructing a mixed-effects model, and combining meta-analysis to evaluate the impact of biochar on greenhouse gas emissions, crop yield, and carbon sequestration capacity. Subgroup analysis was also conducted to demonstrate the influence of other variables on the biochar effect. And based on the net environmental and economic benefits (NEEB), the environmental benefits of biochar input were systematically quantified by incorporating crop yield benefits, environmental benefits, agricultural costs, and environmental losses. Result Biochar increased crop yield by 12.8% and soil carbon sequestration by 30.5%, enhancing NEEB. CH4/N2O emissions showed no significant changes. Effects varied with biochar type and fertilization practices. Conclusion Biochar application enhances soil carbon sequestration and NEEB, supporting sustainable rice cultivation. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 28 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 754-764.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240596
Abstract:
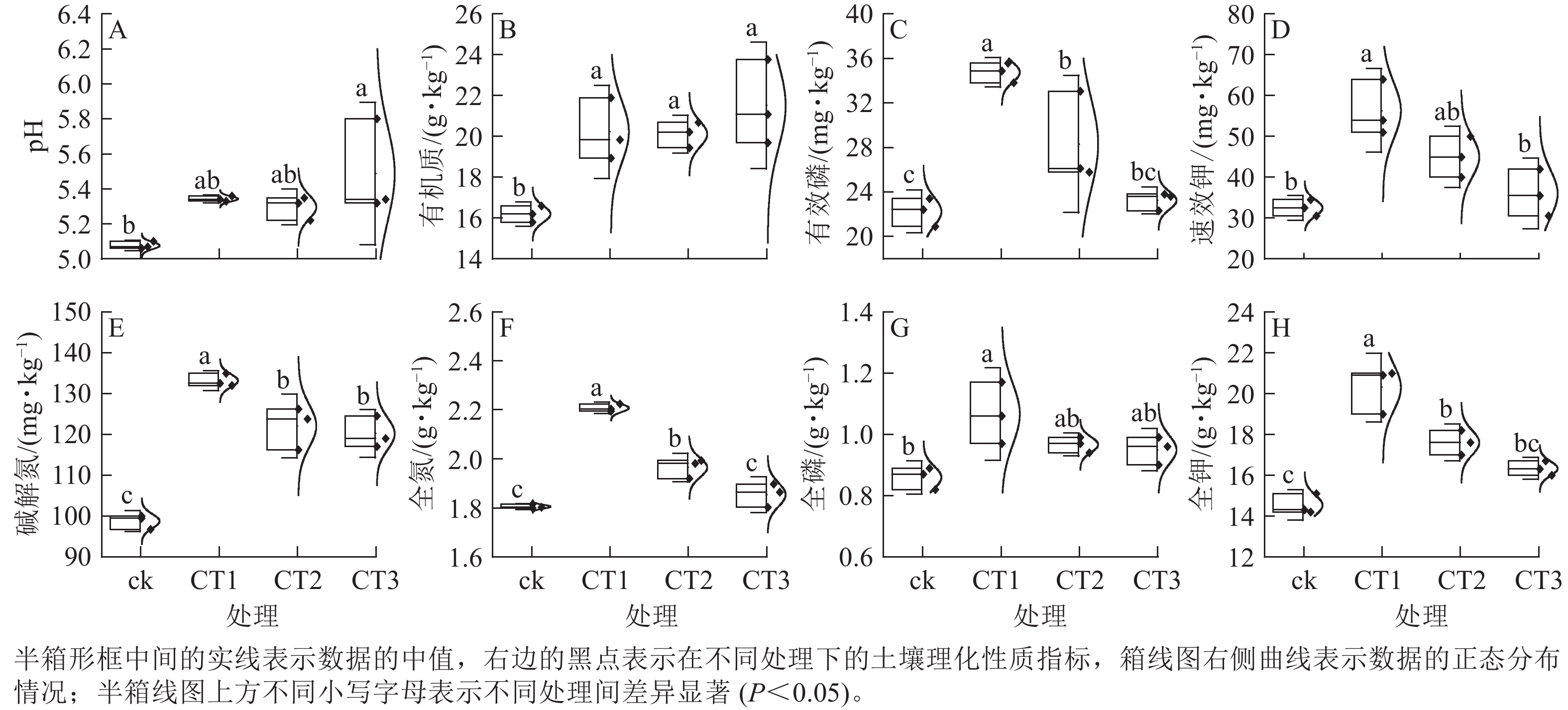
Objective Based on comprehensive index of soil fertility quality(IFI), this study aims to evaluate the effects of grass cultivation and biochar addition on soil fertility in pear orchards, and to reveal the soil fertilization effects of biochar application and grass cultivation as well. Method A field experiment was conducted in a pear orchard in Longyou County, Quzhou City of Zhejiang Province in 2023. 4 treatments were set up: inter-row sowing of Trifolium repens, inter-row sowing of Astragalus sinicus, biochar application, and conventional tillage (control). Each treatment was repeated 3 times. During the maturity period of pear trees (Pyrus spp.), surface soil samples (0−20 cm) and fruit samples under different treatments were collected and analyzed. Radar charts were used to analyze the limiting factors of soil fertility level in pear orchards, and IFI was used to assess the effects of different grass cultivation and biochar additions on soil fertilization in pear orchard. Result (1) Soil pH, total nitrogen, soluble organic carbon and microbial nitrogen showed weak variability, while the other indicators were moderately variable, among which the coefficients of variation of soil available phosphorus and soluble organic nitrogen were relatively large, indicating that soil available phosphorus and soluble organic nitrogen were sensitive to different grass treatments. (2) Radar plots of the affiliation values showed that soil pH, alkaline available nitrogen and available potassium were the main factors restricting soil fertility level in pear orchards. (3) IFI calculated by the weighted model showed that compared with the control, IFI under the treatment of T. repens was the highest, followed by biochar and A. sinicus treatments. (4) The biochar treatment had a significant effect on improving fruit quality (P<0.05). (5) Correlation analysis showed that soil microbial biomass carbon and titratable acid mass fraction were significantly (P<0.05) or extremely significantly positively correlated (P<0.01) with the weight of a single pear fruit, and they were the key factor affecting pear yield per plant. Conclusion IFI calculated based on the weighted model can characterize soil fertility quality. Based on this index, T. repens treatment was the most effective in improving soil fertility, followed by biochar and A. sinicus treatments, and the biochar treatment has a better effect on improving fruit quality. [Ch, 5 fig. 3 tab. 40 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 765-773.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240662
Abstract:
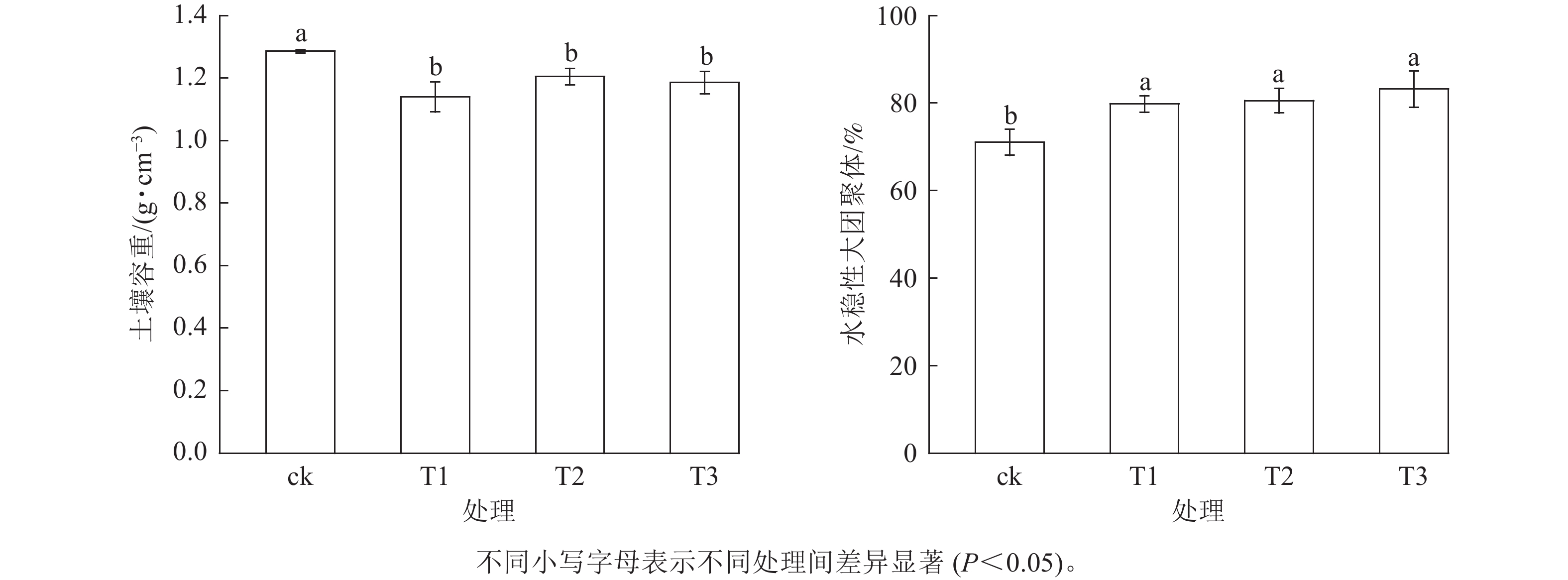
Objective The objective is to analyze the impact of the rice-frog integrated farming model on soil aggregate structure, soil nutrients, and rice (Oryza sativa) yield, and provide a theoretical basis for constructing rice-frog integrated farming model. Method Field experiments were conducted in Lin’an District, Hangzhou City of Zhejiang Province from April to September in 2023 to analyze the differences in soil aggregate structure, soil nutrients, and rice yield under different frog density treatments: low density (T1, 0.9×104 individuals·hm−2); medium density (T2, 1.2×104 individuals·hm−2); high density (T3, 1.8×104 individuals·hm−2); and control treatment (ck), rice monoculture. Result Compared with ck, rice-frog integrated treatments significantly (P<0.05) reduced soil bulk density and increased the content of soil water-stable macroaggregates which increased with frog density, but had no significant effect on total nitrogen content. Soil ammonium nitrogen content decreased with increasing frog density, while soil nitrate nitrogen content significantly increased. T1 treatment significantly reduced soil total phosphorus and available phosphorus contents, but with the increase of frog density, both soil total phosphorus and available phosphorus contents increased. Medium and high density treatments significantly decreased soil available potassium content. Rice-frog integrated farming model significantly reduced soil organic matter content, especially in T2 and T3 treatments where the decrease was greater. The number of effective panicles, seed setting rate, and rice yield were all significantly lower than those of ck, and the yield decreased by 15.49% in T3 treatment. However, in terms of comprehensive benefits, the comprehensive cultivation model of rice and frog was significantly higher than ck, and the comprehensive benefits increased with increasing frog density. Conclusion The rice-frog integrated farming model under high-density treatment has the most significant improvement in soil aggregate structure, and soil nutrients can still maintain at a certain level. The decrease in rice yield is relatively small, and the comprehensive benefits are the most significant. It is recommended as a suitable model for rice-frog integrated cultivation. It is suggested to increase the application rates of nitrogen, potassium and organic fertilizers during non-farming period to maintain nutrient balance, stabilize the number of rice panicles, and promote high yield. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 37 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 774-783.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240667
Abstract:
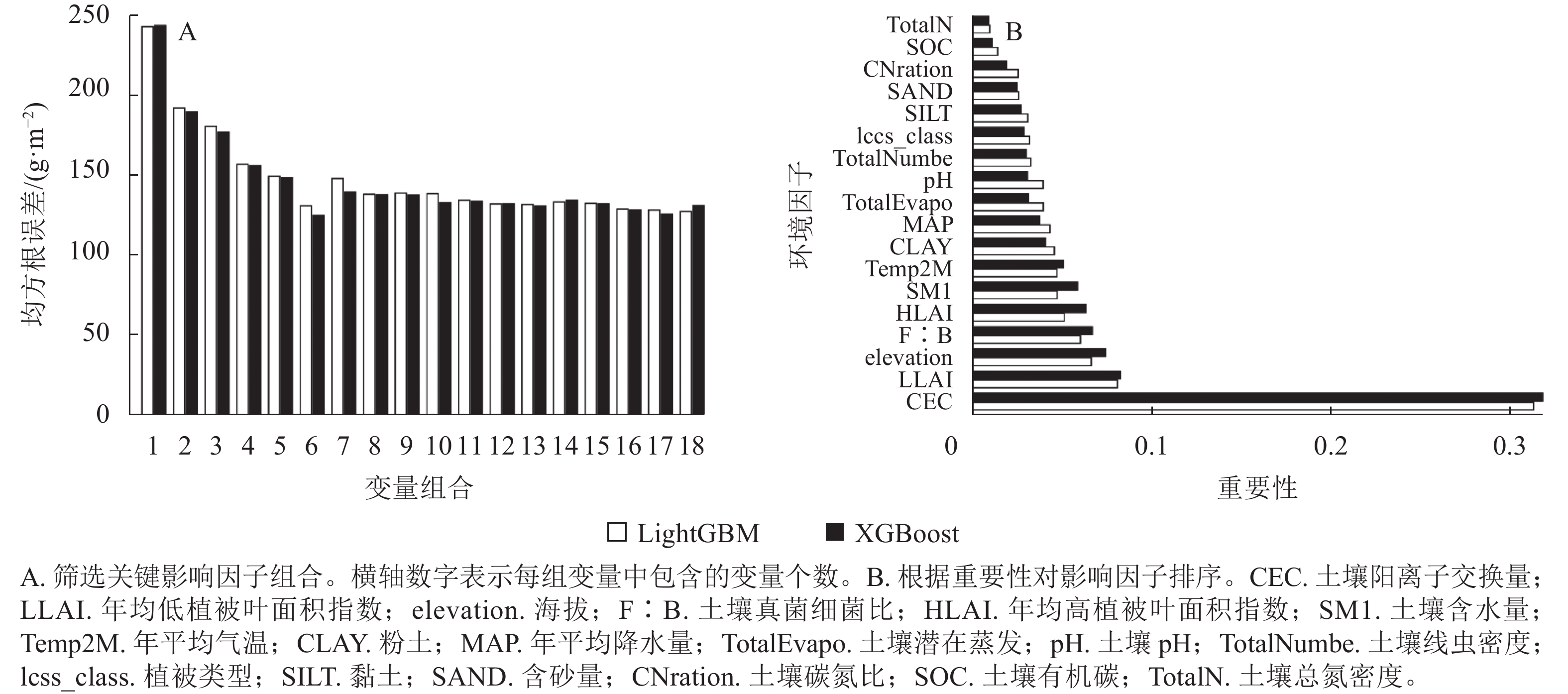
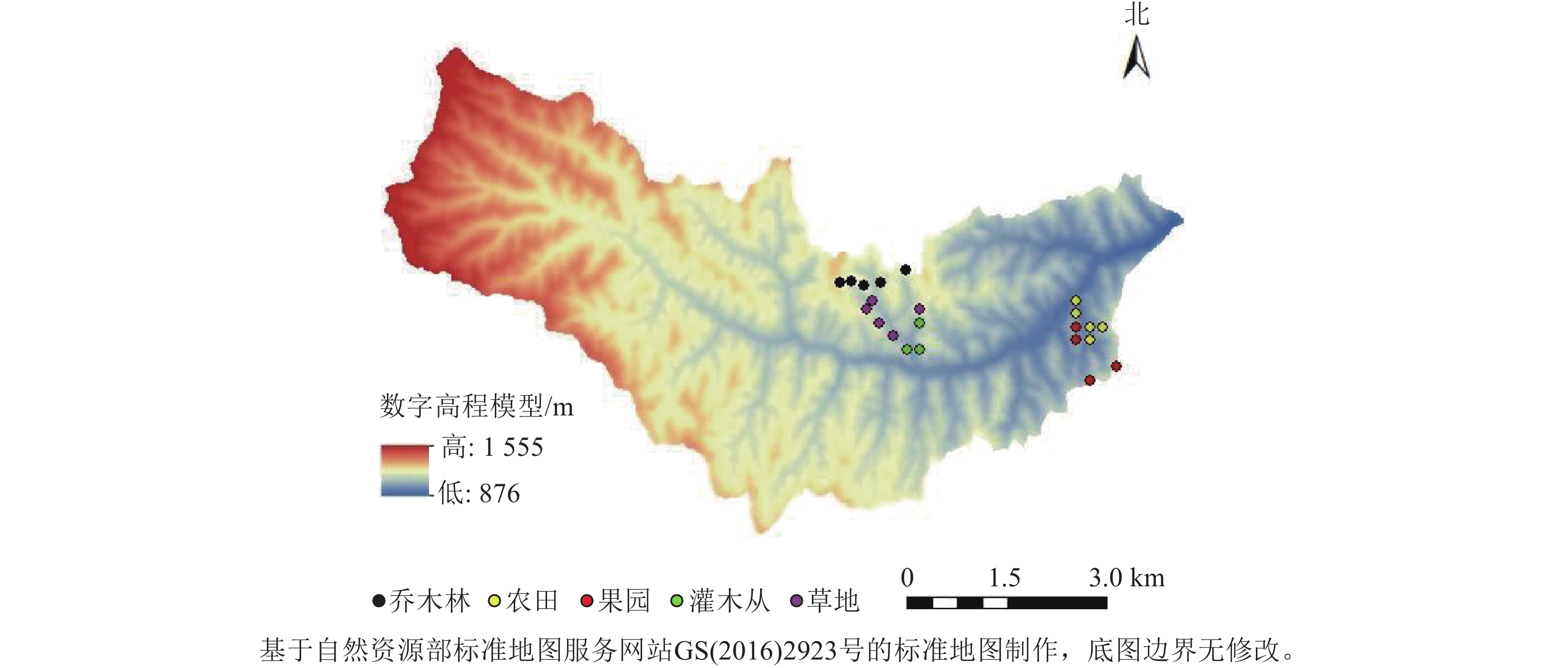
Objective XGBoost and LightGBM models exhibit differentiated advantages within the gradient boosting decision tree framework. This study aims to systematically compare the performance differences between the two in estimating soil heterotrophic respiration (Rh), which will help to explore the potential of gradient boosting machines in ecosystem carbon flux prediction and promote the optimization of such models in large-scale carbon cycle simulations. Method A database of soil Rh and environmental factors in China’s terrestrial ecosystems was constructed based on the Global Soil Respiration Database (SRDB). XGBoost and LightGBM models were used to estimate and compare soil Rh from 2000 to 2023. The spatial pattern and main influencing factors of soil Rh in China’s terrestrial ecosystems were further investigated. Result (1) Both models demonstrated high predictive accuracy (R2 = 0.91 for the test set). XGBoost model showed strong fitting ability on the training set, while LightGBM model performed better in controlling the error on the test set. (2) The annual average values of soil Rh estimated by XGBoost and LightGBM models from 2000 to 2023 were 299.57 and 294.60 g·m−2·a−1, respectively, with interannual variations of 19.51 and 32.43 g·m−2·a−1, respectively. (3) The spatial distribution of soil Rh was high in the south and low in the north, mainly influenced by soil properties and leaf area index. This spatial heterogeneity reflected different responses of soil Rh to environmental changes. Conclusion The gradient boosting machine model demonstrates good adaptability in the modeling and prediction of large-scale soil Rh. It can effectively capture the spatiotemporal variations of soil Rh and demonstrate strong predictive ability. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 33 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 784-792.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240622
Abstract:
Objective Vegetation restoration is a primary measure for ecological construction of the Loess Plateau, and water is a major limiting factor for vegetation recovery in this region. This study aims to conduct research on water dynamics of different land use types, provide a basis for vegetation restoration in comprehensive watershed management, and optimize land use and water resource management strategies. Method During the growing season of 2023 (May to September), 5 typical land use types in Caijiachuan watershed of Jixian County, Shanxi Province, located in gully regions of the Loess Plateau, were systematically monitored for soil moisture at different depths (0−10, 10−20, 20−40, 40−60, 60−80, 80−100, 100−120, 120−140, 140−160, 160−180 cm), including woodland (Robinia pseudoacacia), shrubland (Rosa xanthina), grassland (Artemisia gmelinii), orchard (Malus Pumila), and farmland (Zea mays). Based on field measurement data, the impact of different land use types and soil depths on soil moisture were analyzed. The vertical layers of soil moisture for different land use types were divided by the optimal segmentation method. Result The variation trends of soil moisture and rainfall were consistent in different land use types during the growing season. There were significant differences in soil moisture at different depths among various land use types (P<0.05). The soil moisture content of different land use types from high to low was as follows: farmland (21.06%), shrubland (17.88%), grassland (15.17%), orchard (15.02%), and woodland (13.29%). The vertical variation of soil moisture exhibited a certain degree of hierarchy. The vertical layers of soil moisture in each land use type were divided into strong variation layer, moderate variation layer, and weak variation layer. The vertical layers of grassland and woodland were consistent, with a strong variation layer of 0−10 cm, a moderate variation layer of 10−100 cm, and a weak variation layer of 100−180 cm. The strong and moderate variation layers of shrubland ranged from 0 to 140 cm, with a depth range greater than that of other land use types. The strong and moderate variation layers in the orchard were between 0−80 cm, with a depth range lower than that of other land use types. Farmland showed distinct vertical stratification, with the strongest variation in the deep layer (100−180 cm), a moderate variation from 0 to 20 cm layer, and a weak variation from 20 to 100 cm layer. Conclusion Soil moisture dynamics are affected by rainfall, land use types and engineering measures. When carrying out vegetation restoration, special attention should be paid to the dynamic changes in soil moisture of different land use types. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 37 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 793-801.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240535
Abstract:
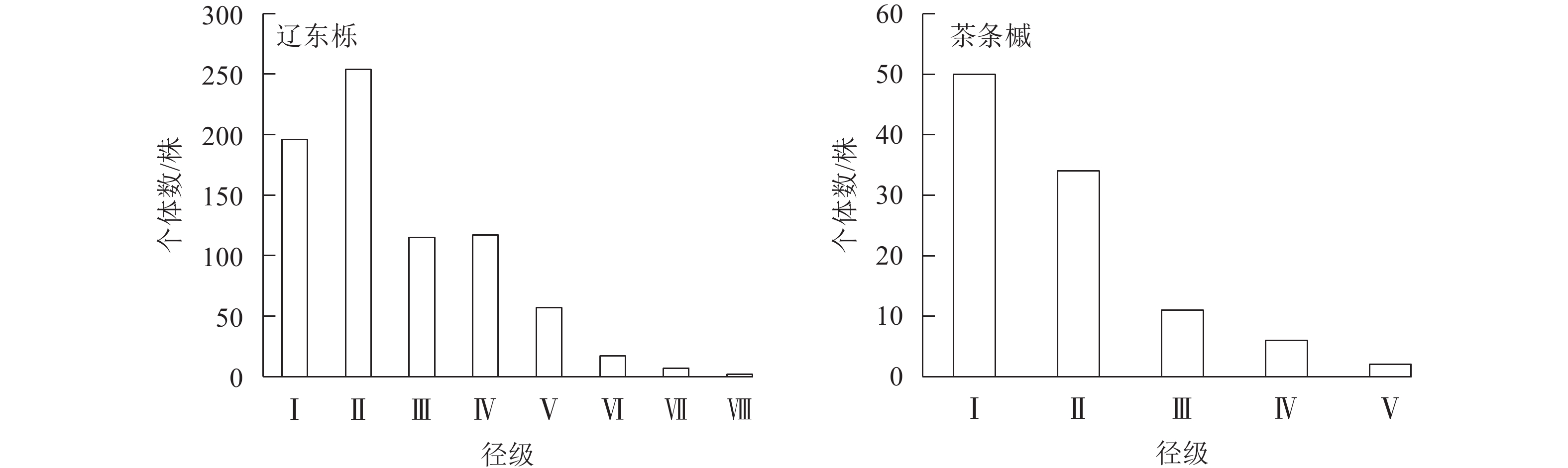
Objective This study aims to explore the spatial distribution pattern of tree species in Quercus mongolica natural forest, a major forest type in Shanxi Province, and understand its growth and development status, so as to provide reference for the rational management of the forest and conversion of Q. mongolica plantation. Method The research object was a 0.96 hm2 plot of Q. mongolica natural forest investigated in 2021 in Chengzhuanggou Forest Farm on the west side of Lüliang Mountain. The diameter class structure was used instead of the age structure. The spatial distribution pattern and spatial correlation of individuals with different diameter levels in the dominant population were analyzed by point pattern analysis. Result Q. mongolica and Acer ginnala were dominant species, and their diameter structure was an inverted “J ” type, indicating a growth type with stable population structure and good regeneration. The population of Q. mongolica showed a cluster distribution within the research scale, while that of A. ginnala exhibited a pattern of small-scale cluster distribution and large-scale random distribution. The small diameter individuals of the two dominant populations were mainly clustered in small scale, while the large diameter individuals were randomly distributed. The intraspecies association of Q. mongolica was positive only among middle and small size trees, and the smaller the diameter difference, the greater the degree and spatial scale range of positive association. The population of A. ginnala showed positive correlation only between small-scale GradeⅠand GradeⅡindividuals. With the increase of the scale, the overall correlation between the dominant populations changed from no correlation to negative correlation and then to no correlation. The spatial correlation between populations of different diameter classes only appeared among trees of medium and small diameter classes, and the correlation was negative. Conclusion Q. mongolica natural forest in the study area is at the early stage of succession, with a stable dominant population structure and good renewal status. To accelerate the succession process, artificial intervention should appropriately supplemented to promote the development of forest stands towards top-level communities. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 31 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 802-812.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240554
Abstract:
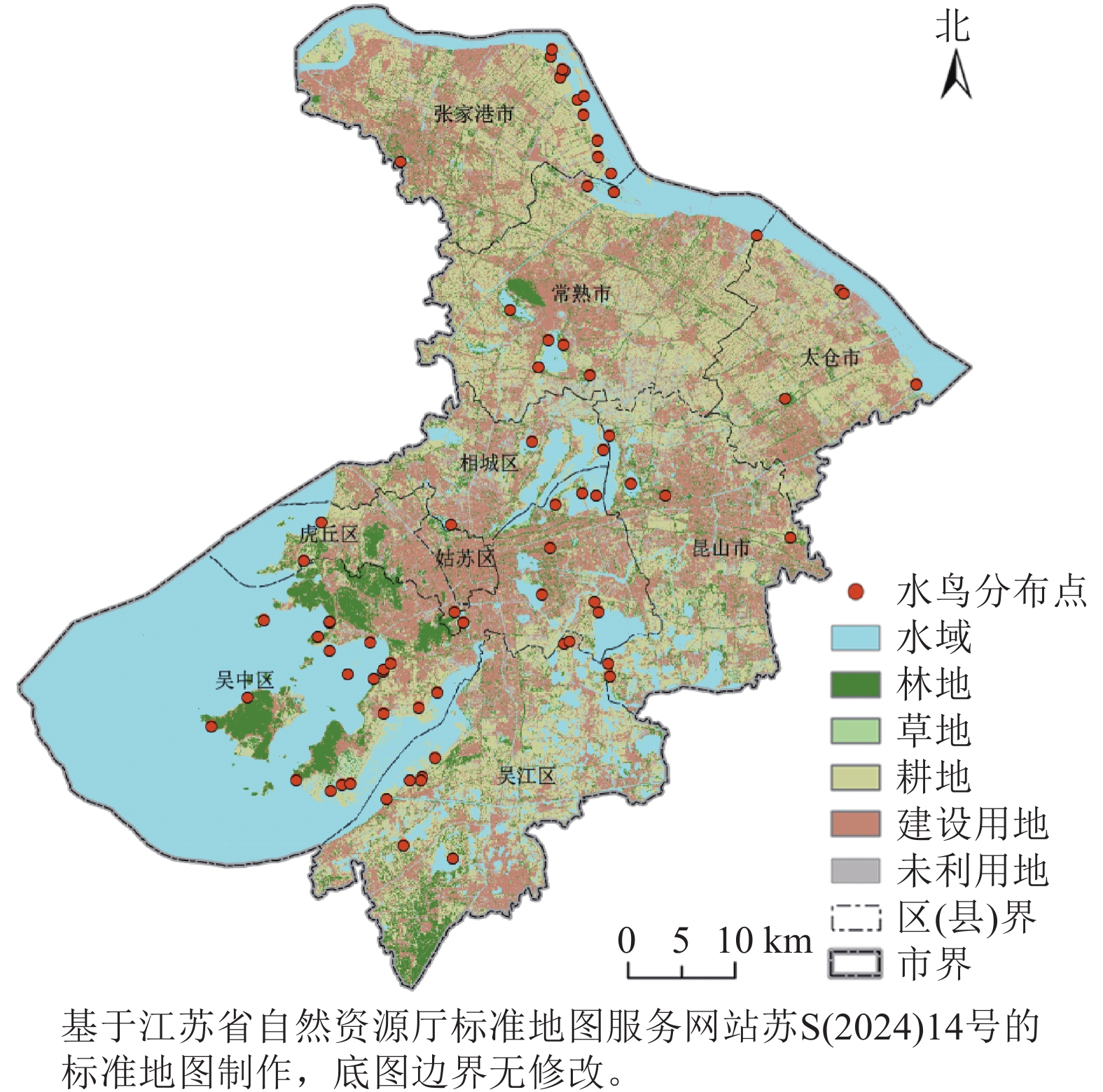
Objective Threatened waterbirds are key indicator species of wetland habitat quality. Constructing a habitat network of threatened waterbirds is conducive to protecting regional waterbird diversity and enhancing the function of wetland ecosystem. Method Taking Suzhou municipal area as the study area, the distribution points and related environmental variable data of threatened waterbirds in 2022 were selected, and habitat suitability of threatened waterbirds was evaluated by MaxEnt model. On this basis, combined with the patch importance index, habitat source areas were identified and corridors were determined by using circuit theory, and habitat pinch points and barrier points were identified to construct a habitat network of threatened waterbirds in Suzhou. Result (1) The habitat suitability of threatened waterbirds in Suzhou in 2022 was good, and the highly suitable habitats were significantly fragmented. (2) There were 31 habitat source areas, with a total area of 196.55 km², and their spatial distribution presented a cluster feature, gathering along the Yangtze River, Yangcheng Lake, Cheng Lake and Taihu Lake, respectively. (3) There were 62 habitat corridors with a total length of 705.55 km, including 9 high-resistance corridors and 53 low-resistance corridors. The appropriate width of the corridors was 600 m. (4) 50 habitat pinch points and 28 habitat barrier points were found to have significant impacts on the migration and dispersal of threatened waterbirds in the region. Conclusion During the study period, the habitat suitability of threatened waterbirds in Suzhou is good. The quantitative construction method of habitat network is explored, and suggestions for the optimization of habitat network are put forward. This study provides scientific reference for regional biodiversity conservation and response to regional habitat changes. [Ch, 6 fig. 5 tab. 38 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 813-824.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240590
Abstract:
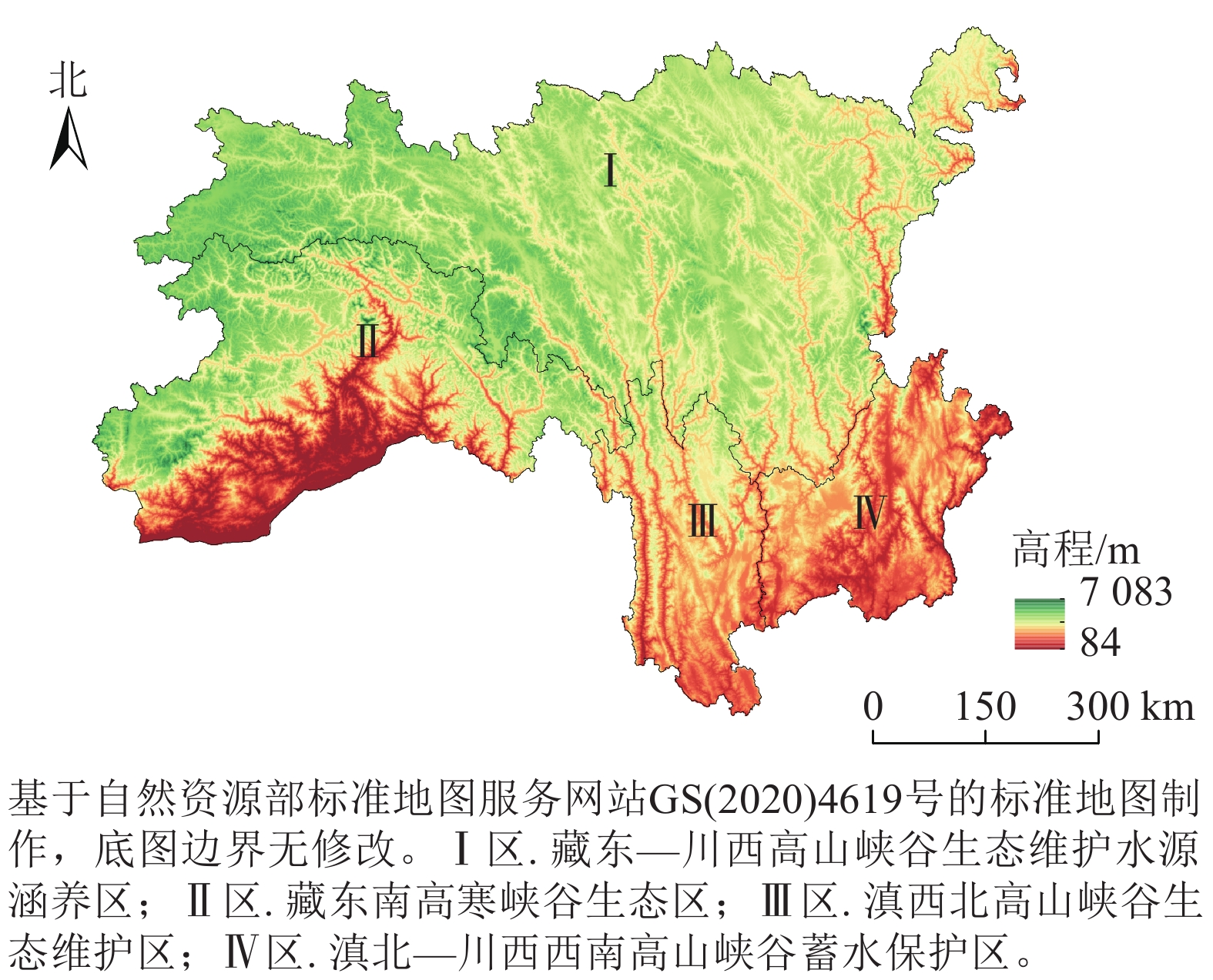
Objective As an important ecological barrier area in China, the southwest alpine canyon region requires analysis of land use change and ecosystem services under different scenarios. This study aims to provide a theoretical basis for ecological environment protection and future development. Method Based on the China Land Cover Dataset (CLCD), this paper analyzed the patterns of land use change in the region, and used the InVEST model to evaluate the spatial-temporal evolution rules of 4 types of ecosystem services (water yield, carbon storage, habitat quality, soil conservation) in southwest alpine canyon region from 2002 to 2022. The PLUS model was used to simulate the spatial distribution pattern of land use in 2032, 2042 and 2052 under different scenarios. And integrating the InVEST and PLUS model to evaluate the evaluated law of 4 types of ecosystem services in southwest alpine canyon region under different scenarios. Result (1) From 2002 to 2022, the land use types in the southwest alpine canyon region were mainly forest and grassland, each accounting for more than 44% of the total area. During the period, the transfer of land use was concentrated in forest, cropland and grassland. (2) From 2002 to 2022, the average water yield in southwestern alpine canyon region decreased, the average carbon storage increased, the average habitat quality improved, the average soil conservation decreased. (3) From 2032 to 2052, under the natural development scenario, the average values of 4 types of ecosystem service functions all increased; under the cultivated land protection scenario, the average values of 4 types of ecosystem service functions all decreased; under the economic priority scenario, the average values of water yield and soil conservation amount decreased, while the average values of carbon storage and habitat quality increased. Conclusion The terrain in southwest alpine canyon region was complex. There was a relatively large area of forest land and grassland in the region, and the overall situation of carbon storage and habitat quality was relatively good. However, a large amount of snow-covered areas and unused land also led to a decrease in both water yield and soil conservation amount. [Ch, 9 fig. 39 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 825-834.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240614
Abstract:
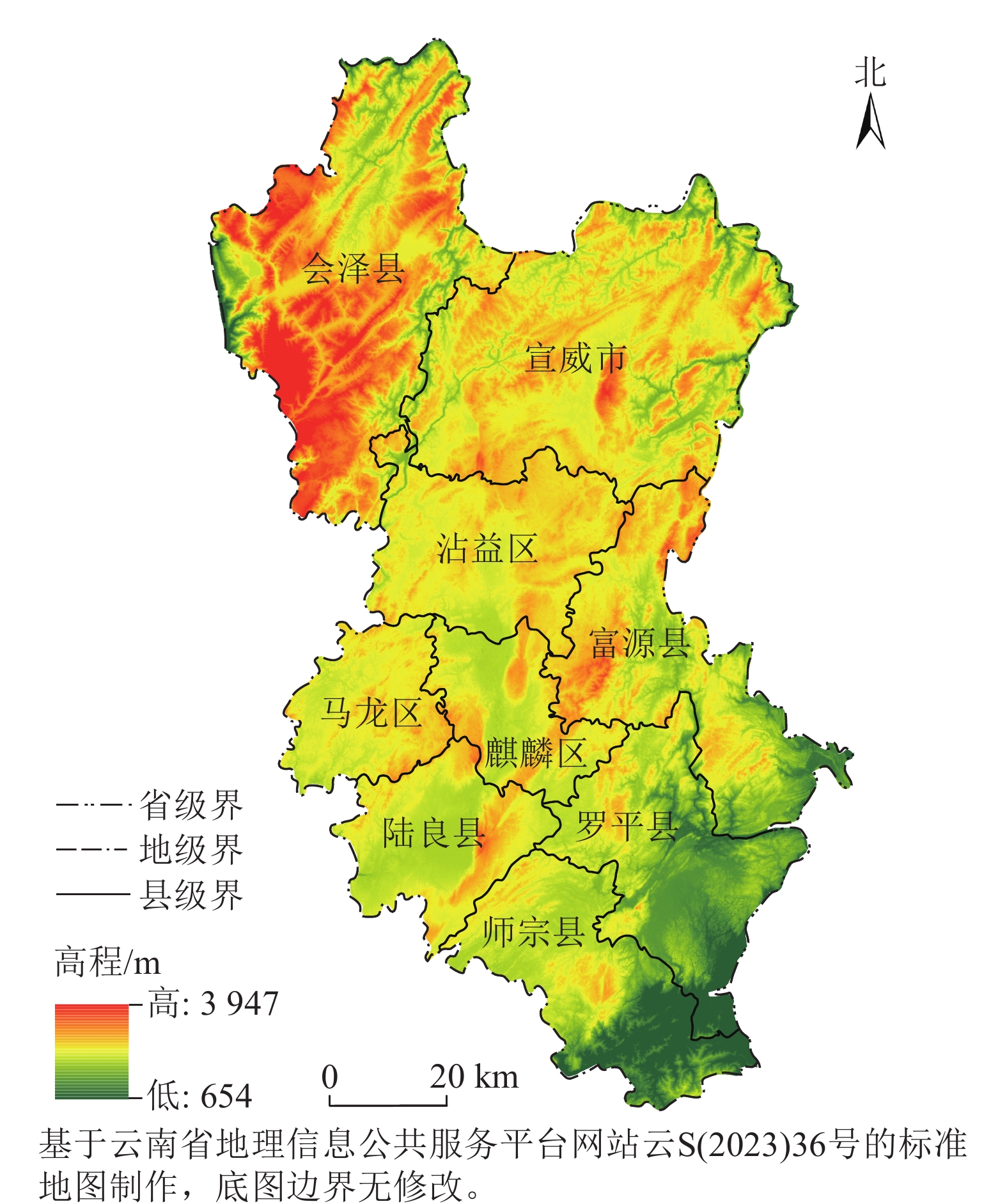
Objective The study is to analyze and simulate land use and habitat quality in Qujing City, so as to provide scientific basis for the spatial allocation of regional land resources and ecological construction. Method Based on the land use data of 1980, 2000 and 2020, the land use changes from 1980 to 2020 in Qujing City were analyzed. And PLUS-InVEST model, combined with the transfer matrix, multi-scenario simulation and habitat quality evaluation methods, were comprehensively used to analyze the spatio-temporal dynamic changes of land use and habitat quality in 2040, and summarize the driving mechanism. Result Grassland and forestland in mountainous, cultivated land and construction land in dam together constituted the land types in Qujing City. Among them, grassland and forest land were the main types, accounting for more than 72%. From 2000 to 2040, habitat quality showed a downward trend overall, but the area of high-grade habitats was increasing. Habitat quality was closely related to the spatial distribution of land use, and showed a “mountain-dam” and “lock-in” effect, which was high in the north and low in the south. The northern part of Qujing City was the hot spot concentration area of habitat quality, and the southern part was the cold spot concentration area. Ecological protection scenario was more suitable than the others for regional development needs, the contribution of watersheds to habitat quality was small but extremely important for Qujing City. Conclusion In the future, the restoration of degraded areas of forest and grassland in mountainous areas should be strengthened to alleviate ecological degradation. Strengthening the protection and construction of ecological land in the dam area is a important way to improve the level of habitat quality. Moderately increasing the area of water land is the best way to slow down the decline of regional habitat quality. [Ch, 4 fig. 6 tab. 33 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 835-843.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240406
Abstract:
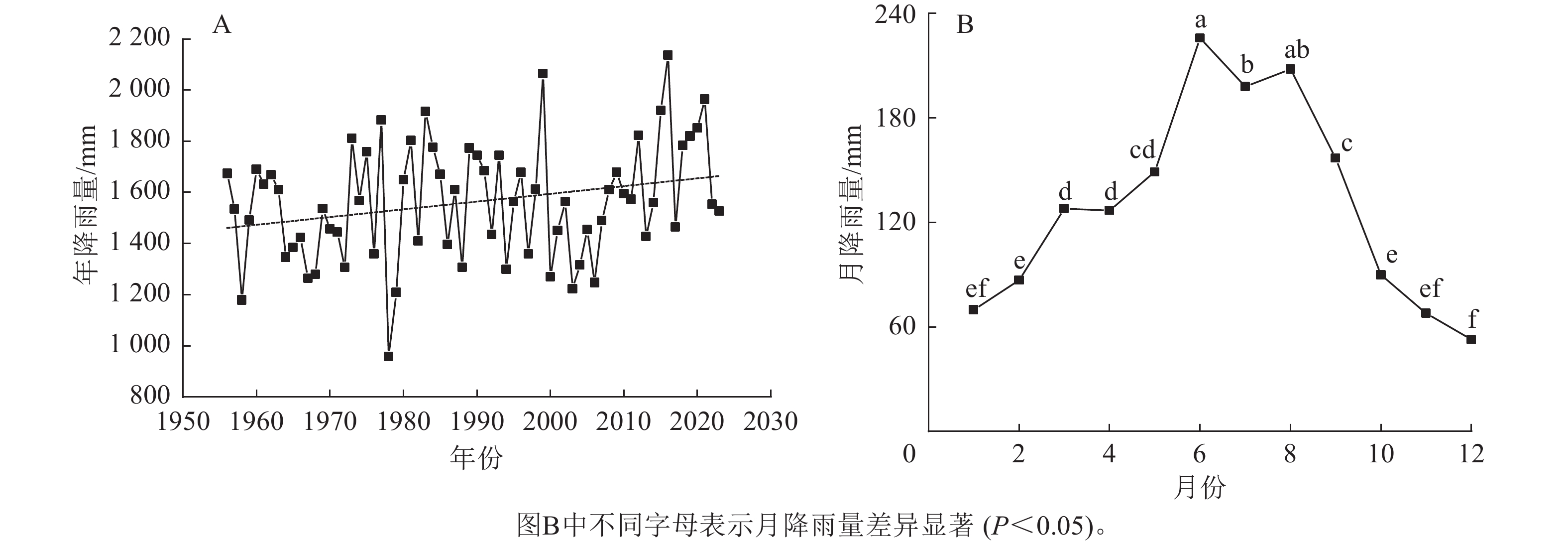
Objective Nitrogen pollution in water is still the primary threat to the current water environment in watershed. The Taihu Lake Basin is an important water source area for the economically developed coastal areas in eastern China, but its water quality is currently in a mildly polluted state, and thus, the study of nitrogen characteristics in Taihu Lake Basin provides the reference for improving the water environment of the basin. Method This paper took the Xitiaoxi Watershed, an important water source area in the upper reaches of Lake Taihu, as the research area. Based on the rainfall observation data of Anji County Hydrological Station from 1956 to 2023 and the water quality monitoring data from 2016 to 2023, the difference of rainfall in different time dimensions was analyzed, the dynamic distribution characteristics of water nitrogen in the study area were investigated, and the characteristics of water nitrogen change with time in the reservoir-type water source in Xitiaoxi Watershed were defined. Result Rainfall in the study area showed an upward trend, and the rainy season was from March to September each year, with accounting for 60.04% of the annual rainfall. From the time dimension, due to the dilution effect of heavy rainfall in rainy season on water body, the water nitrogen concentration of reservoir-type water source in rainy season was generally lower than that in non-rainy season. In particular, the water nitrogen concentration of Laoshikan Reservoir in rainy season in 2023 was only 0.02 mg·L−1, which had reached the Class Ⅰ water standard. From the spatial dimension, the water nitrogen concentration in the southwest of the watershed was lower, while the nitrogen concentration in the middle and lower reaches where human activities were more frequent was higher. As for the overall water quality of the watershed, the maximum nitrogen concentration of Xitiaoxi Watershed in 2016 was 9.09 mg·L−1, and the average was 3.19 mg·L−1, indicating that the basin belonged to inferior Class Ⅴ water. In 2023, the average nitrogen concentration in Xitiaoxi Watershed was 1.32 mg·L−1, which met the requirements of Class Ⅳ water. Conclusion From 2016 to 2023, the water quality of the watershed as a whole improved. Rainfall was a key factor affecting nitrogen quality concentration in water bodies, on the annual scale, water nitrogen concentration was negatively correlated with rainfall, while on the seasonal scale, water nitrogen concentration was positively correlated with rainfall. [Ch, 4 fig. 29 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 844-852.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240589
Abstract:
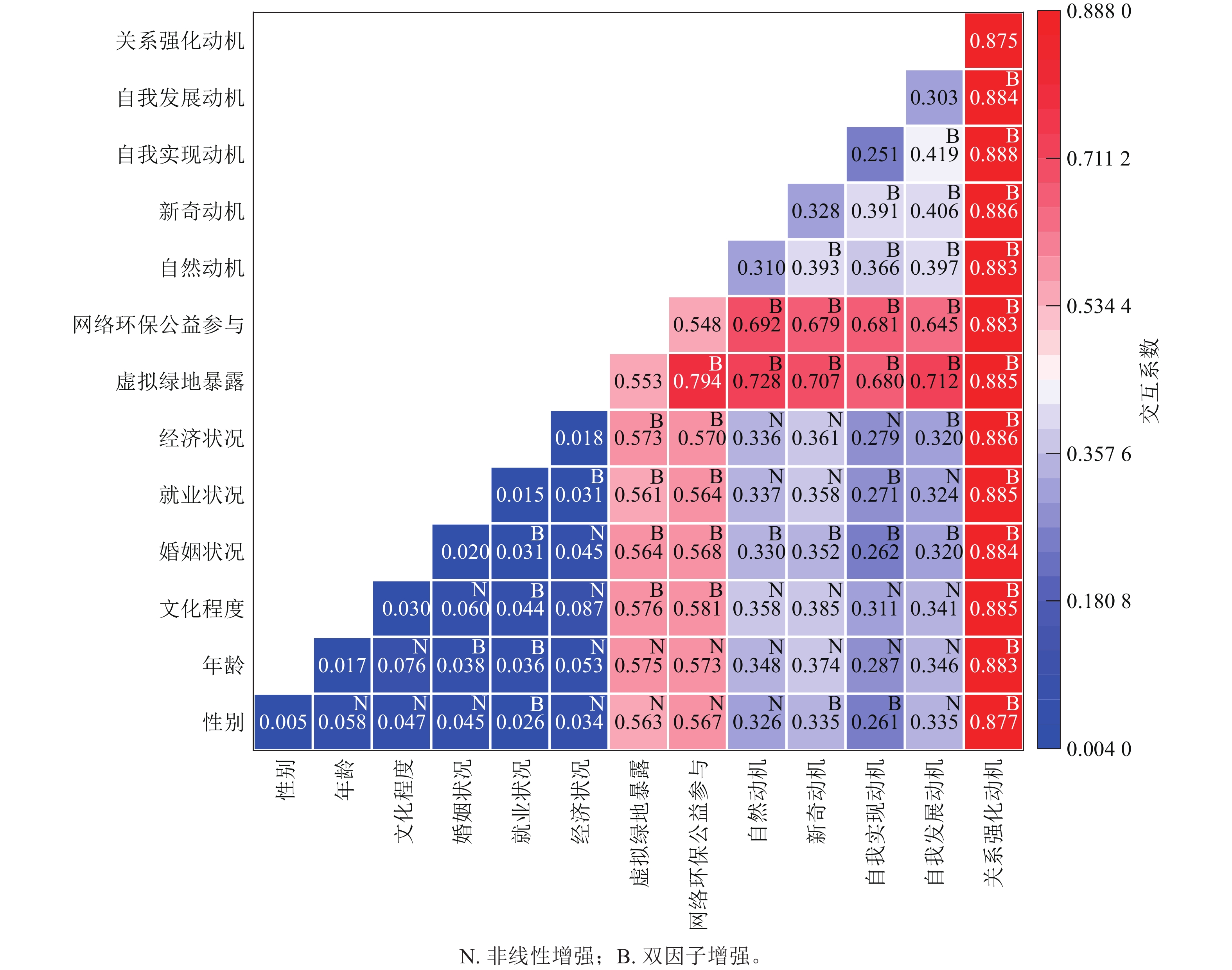
Objective This study aims to explore the driving mechanism of health benefit perception among recreational users in suburban forest parks and provide scientific support for optimizing park construction and management. Method Taking Liangxi National Forest Park in Huzhou City in Zhejiang Province as a case study, a “motivation-attribute-benefit” analytical framework was constructed by integrating questionnaire survey and geographical detector technology to analyze the nonlinear effects of motivational factors and individual attributes on health benefits. Result (1) Motivational factors exhibited significantly higher explanatory power on perceived health benefits than individual attributes, and the effect of relationship strengthening motivation was the strongest, followed by virtual green space exposure and online environmental public welfare engagement. (2) There existed a nonlinear correlation between motivation and health benefit, an inverted “U” shaped curve between novelty motivation and self-actualization motivation, and a linear relationship between natural motivation and relationship strengthening motivation. (3) Although gender and age among individual attributes had weak independent effects, they interacted with motivation and generated nonlinear enhancement effects. Conclusion The perception of health benefit in suburban forest parks is driven by a multidimensional motivational system characterized by threshold effects and spatial heterogeneity. Virtual environmental exposure amplifies therapeutic effects through cognitive transfer mechanism, and the coupling of online and offline behaviors is a key path to improve the efficiency of intensive recourse utilization. [Ch, 1 fig. 4 tab. 32 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 853-863.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240639
Abstract:
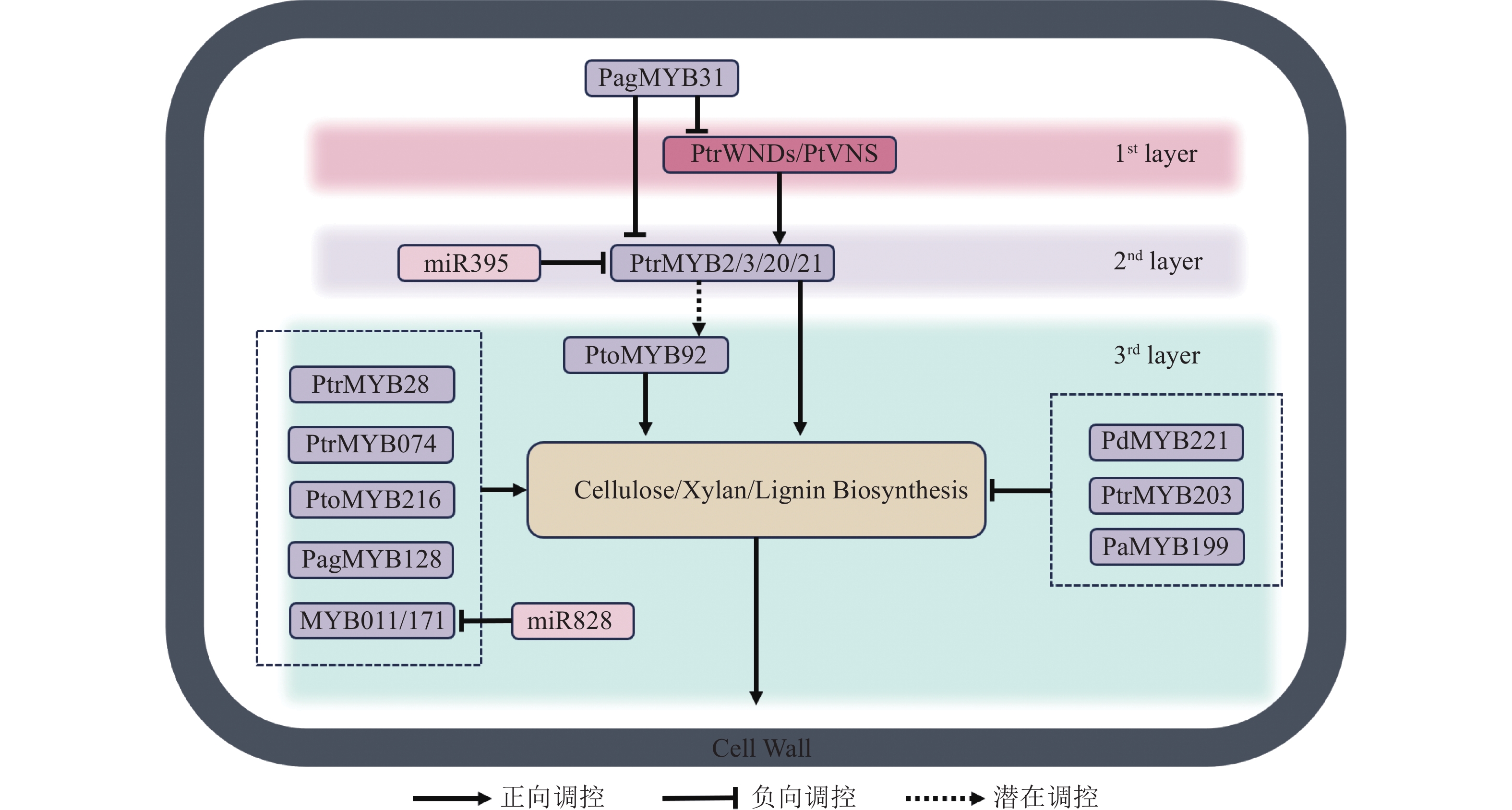
The secondary cell wall of plants is crucial for maintaining structural integrity, providing mechanical support, and facilitating the transport of water and minerals. With advancements in molecular biology and bioinformatics, the molecular regulatory mechanisms underlying secondary cell wall formation have been gradually elucidated. The research has indicated that transcription factors (such as NAC and MYB) and microRNA constitute a multi-layered regulatory network, which plays vital roles in secondary cell wall formation. NAC and MYB transcription factors are directly involved in the biosynthesis of secondary walls by activating genes related to lignin, cellulose, and xylan synthesis. At the same time, microRNA achieve fine-tuned regulation of secondary cell wall development by targeting these transcription factors and their downstream genes. This review focuses on summarizing the recent research progress in secondary cell wall formation, especially the interplay and regulatory mechanisms of transcription factors and microRNA in this process. Moreover, it also discusses the current research challenges and future directions in this field. The systematic organization of these findings will enhance the understanding of the molecular basis of plant xylem development, providing theoretical support for wood improvement and bioenergy development. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 87 ref.]
The secondary cell wall of plants is crucial for maintaining structural integrity, providing mechanical support, and facilitating the transport of water and minerals. With advancements in molecular biology and bioinformatics, the molecular regulatory mechanisms underlying secondary cell wall formation have been gradually elucidated. The research has indicated that transcription factors (such as NAC and MYB) and microRNA constitute a multi-layered regulatory network, which plays vital roles in secondary cell wall formation. NAC and MYB transcription factors are directly involved in the biosynthesis of secondary walls by activating genes related to lignin, cellulose, and xylan synthesis. At the same time, microRNA achieve fine-tuned regulation of secondary cell wall development by targeting these transcription factors and their downstream genes. This review focuses on summarizing the recent research progress in secondary cell wall formation, especially the interplay and regulatory mechanisms of transcription factors and microRNA in this process. Moreover, it also discusses the current research challenges and future directions in this field. The systematic organization of these findings will enhance the understanding of the molecular basis of plant xylem development, providing theoretical support for wood improvement and bioenergy development. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 87 ref.]
2025, 42(4): 864-874.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240642
Abstract:
Generalized Polygonum plants include annual and perennial herbs, which are widely distributed in the north temperate zone and are found in both the southern and northern regions of China. These plants hold significant medicinal, ecological, and economic value. In recent years, with increasing attention to the development of natural pharmaceuticals and ecological resources, generized Polygonum species have become a prominent focus in plant resource research due to their abundant reserves, diverse chemical constituents, and extensive bioactivities. This review systematically summarizes the taxonomy, representative species, diverse secondary metabolites, and pharmacological activities of generized Polygonum plants. Twelve representative species are highlighted, including Polygonum divaricatum, P. multiflorum, Reynoutria japonica, P. aviculare, P. amplexicaule, and Atraphaxis frutescens. Current research on general Polygonum species primarily focuses on the following areas: (1) extraction and structural characterization of phytochemicals, leading to the identification of numerous bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, anthraquinones, terpenoids, and glycosides; (2) experimental validation and mechanistic studies of pharmacological effects, demonstrating potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, hypoglycemic, and neuroprotective activities; (3) modern investigations into traditional medicinal uses and clinical applications, such as the anti-aging potential of P. multiflorum and the therapeutic application of resveratrol from R. japonica; and (4) ecological functions and resource utilization, with certain species exhibiting remarkable ecological adaptation and potential in phytoremediation. In conclusion, Polygonum species have present broad potential for both fundamental research and applied development. Future studies should dedicate targeted screening and mechanistic elucidation of bioactive compounds, integration of molecular biology and omics technologies to uncover functional genes and biosynthetic pathways, and exploration of their applications in ecological remediation, sustainable agriculture, and functional foods. [Ch, 80 ref.]
Generalized Polygonum plants include annual and perennial herbs, which are widely distributed in the north temperate zone and are found in both the southern and northern regions of China. These plants hold significant medicinal, ecological, and economic value. In recent years, with increasing attention to the development of natural pharmaceuticals and ecological resources, generized Polygonum species have become a prominent focus in plant resource research due to their abundant reserves, diverse chemical constituents, and extensive bioactivities. This review systematically summarizes the taxonomy, representative species, diverse secondary metabolites, and pharmacological activities of generized Polygonum plants. Twelve representative species are highlighted, including Polygonum divaricatum, P. multiflorum, Reynoutria japonica, P. aviculare, P. amplexicaule, and Atraphaxis frutescens. Current research on general Polygonum species primarily focuses on the following areas: (1) extraction and structural characterization of phytochemicals, leading to the identification of numerous bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, anthraquinones, terpenoids, and glycosides; (2) experimental validation and mechanistic studies of pharmacological effects, demonstrating potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, hypoglycemic, and neuroprotective activities; (3) modern investigations into traditional medicinal uses and clinical applications, such as the anti-aging potential of P. multiflorum and the therapeutic application of resveratrol from R. japonica; and (4) ecological functions and resource utilization, with certain species exhibiting remarkable ecological adaptation and potential in phytoremediation. In conclusion, Polygonum species have present broad potential for both fundamental research and applied development. Future studies should dedicate targeted screening and mechanistic elucidation of bioactive compounds, integration of molecular biology and omics technologies to uncover functional genes and biosynthetic pathways, and exploration of their applications in ecological remediation, sustainable agriculture, and functional foods. [Ch, 80 ref.]