2025 Vol. 42, No. 5
2025, 42(5): 944-955.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250474
Abstract:
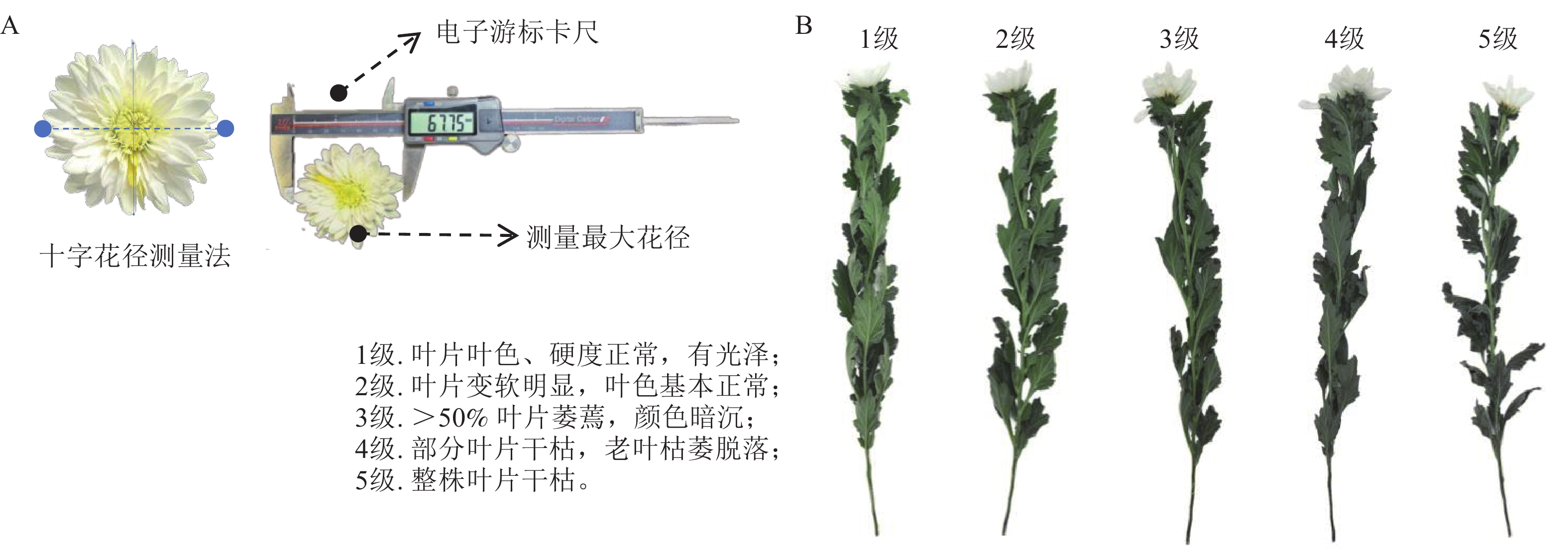
Objective Enhancing storage tolerance and extending vase life constitutes the core objective of postharvest preservation research for cut flowers. This study aims to systematically evaluate and screen cut chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × morifolium) cultivars with superior storage tolerance and vase performance, thereby laying a robust material foundation for postharvest quality improvement and breeding of new cut chrysanthemum cultivars. Method A total of 275 cut chrysanthemum germplasm resources were used as research materials. Postharvest preservation-related indicators during the dry storage period and vase period were determined. The storage tolerance and vase performance of cut chrysanthemums were analyzed and evaluated by using difference analysis, variation analysis, correlation analysis, cluster analysis and principal component analysis. Result There were significant differences in postharvest storage tolerance and vase ornamental performance among different cut chrysanthemum cultivars. ‘Nannong Hongyi’ ‘Qinhuai Ruixue’ and ‘Pip’ had excellent storage tolerance, long vase life and outstanding comprehensive traits, which were suitable for promotion and application as main cultivars with good storage and transportation resistance and long ornamental period. ‘Nannong Lifengche’ and ‘Nannong Binyun’ had prominent storage tolerance, which were suitable for long-distance transportation and long-term storage, and could be used as excellent parents for breeding export-oriented cut chrysanthemum cultivars. ‘Nannong Hongdiandian’ and ‘Rongshan’ had a long vase ornamental period; although their storage tolerance was relatively poor, they were very suitable for localized high-quality production and could be used as key parents for breeding high-end gift flower cultivars. Conclusion On the basis of the storage tolerance, vase life data, and associated statistical analyses of 275 cut chrysanthemum germplasm resources, a total of 7 elite germplasms with strong storage tolerance and prolonged vase life were identified. In practical breeding applications, parental materials can be selected in line with distinct breeding objectives to facilitate targeted variety development. [Ch, 4 fig. 7 tab. 47 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 956-966.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250486
Abstract:
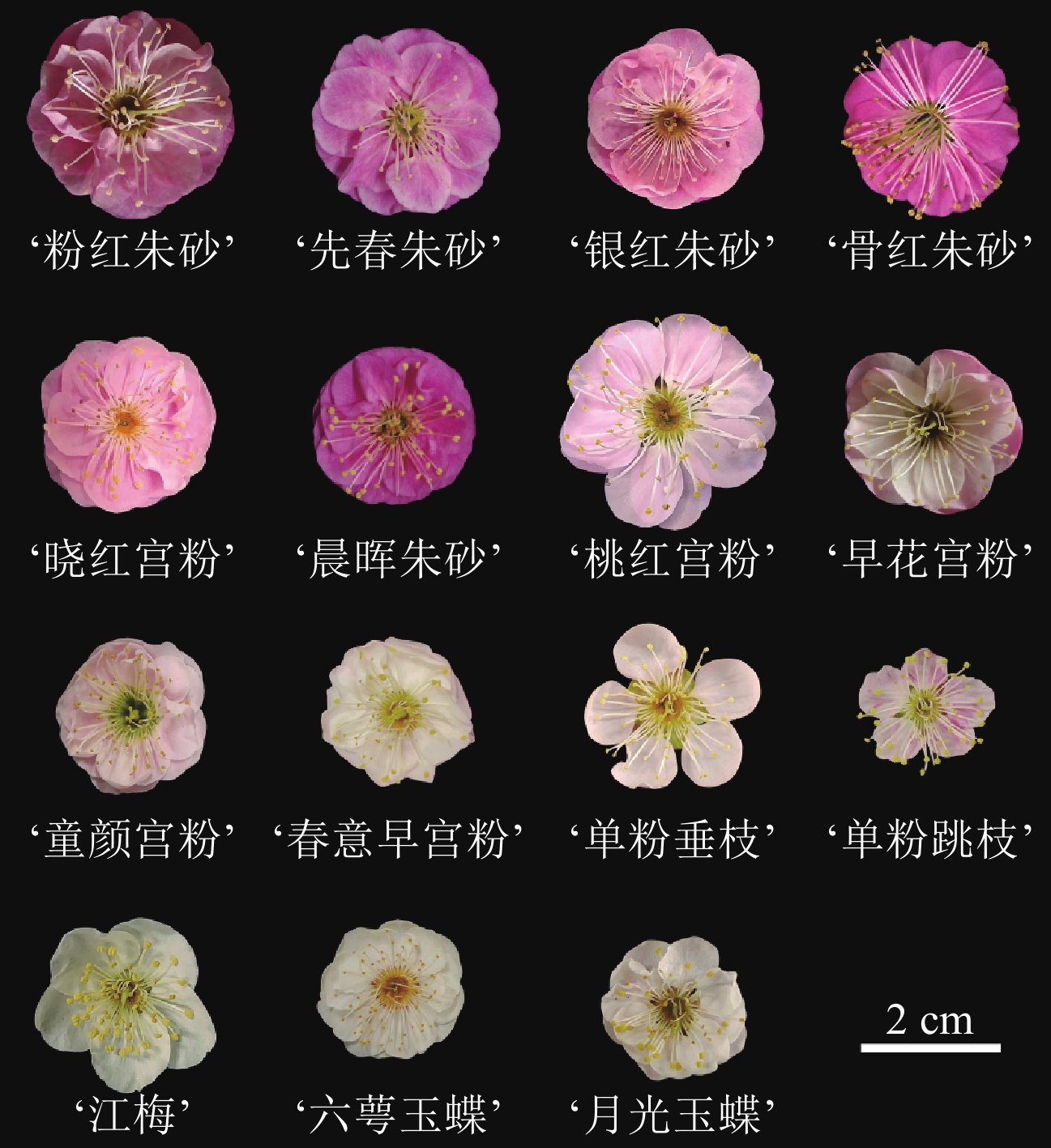
Objective This study investigates the pigment composition of different cultivar groups of Prunus mume and its impact on flower color variation, thereby providing a foundation for targeted breeding strategies focused on floral coloration. Method Fifteen different flower color cultivars of P. mume were selected. The flower color phenotypes of the petals were determined using the Royal Horticultural Society Color Chart of the United Kingdom. The ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) technique was employed to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze the flavonoid compounds in the petals of P. mume. The correlations between the flower color phenotypes and pigment components were analyzed through cluster analysis, correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and multiple linear regression. Result As results, cluster analysis categorized the flower color phenotypes of the 15 P. mume cultivars into four groups: white, light pink, pink, and purplish-red. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of flavonoids revealed that purplish-red, pink, and light pink cultivars contained anthocyanins, primarily cyanidin and peonidin glycosides, with cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside being the most abundant. In contrast, white cultivars lacked anthocyanins but exhibited substantial accumulation of other flavonoids, such as isoquercitrin. Principal component analysis indicated that anthocyanins (PC1 contribution rate: 40.64%) were the core pigments responsible for red hues in P. mume. Notably, red-green chromaticity (a*) showed a significant positive correlation with peonidin-3-O-rutinoside (P<0.05), while higher total anthocyanin content correlated with lower lightness (L*), resulting in darker flower coloration. Other flavonoids (PC2 contribution rate: 19.87%) played a secondary regulatory role. The multiple regression model confirmed the dominance of anthocyanins in color determination: total anthocyanins negatively correlated with L* (P<0.01), peonidin-3-O-rutinoside was a key contributor to a*, and peonidin-3-O-glucoside showed a negative correlation with yellow-blue chromaticity (b*, P<0.05). Conclusion The differentiation of P. mume flower colors is governed by a metabolic network characterized by “anthocyanin-driven pigmentation and flavonoid co-regulation”. Cyanidin and peonidin glycosides are core components for formation of red hue, while other flavonoids likely play secondary roles in pigment stability or environmental adaptation. [Ch, 8 fig. 2 tab. 34 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 967-974.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250493
Abstract:
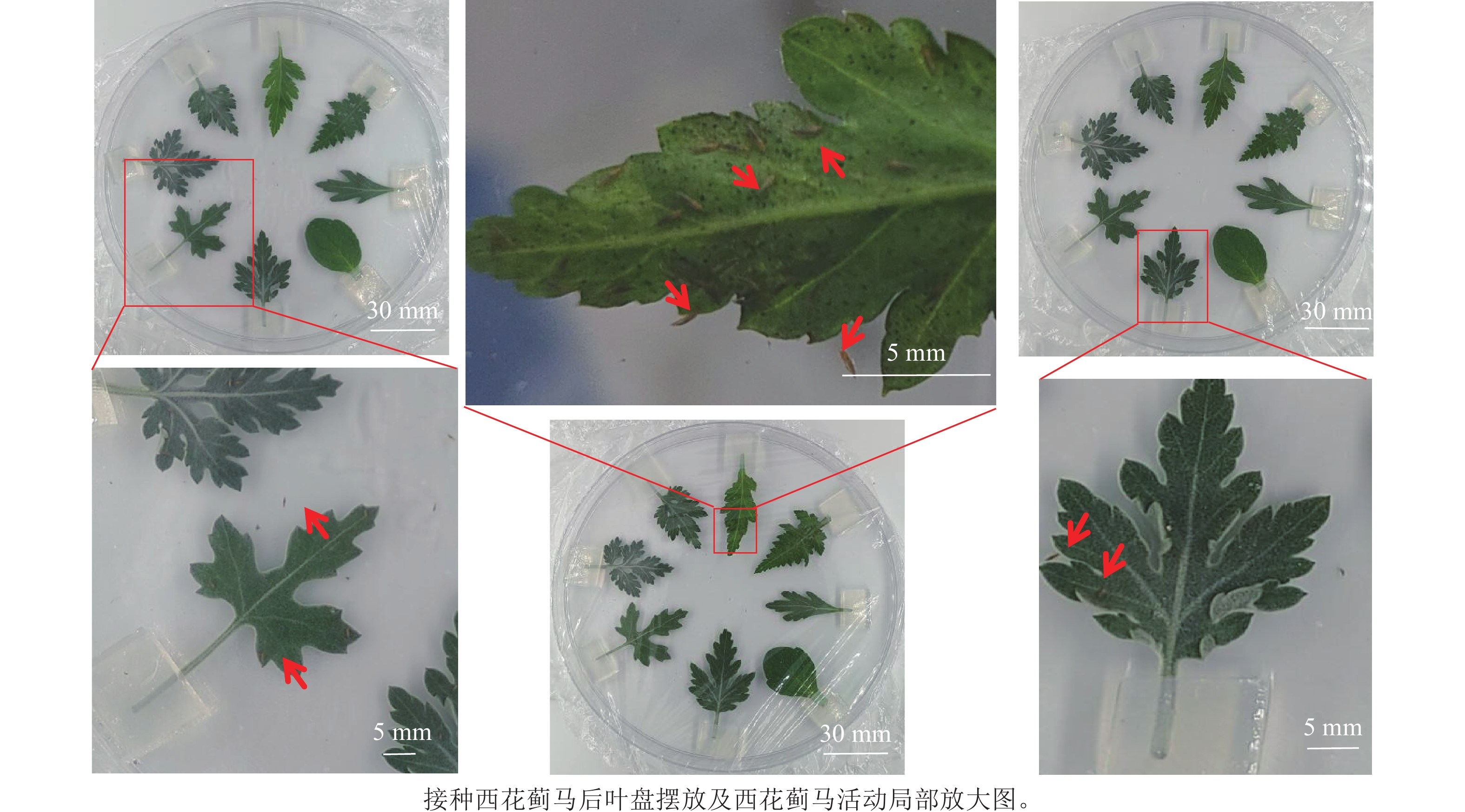
Objective The objective is to systematically evaluate the resistance characteristics of 31 wild germplasm resources from Chrysanthemum and its related genera such as Crossostephium to Frankliniella occidentalis through an in vitro inoculation experimental system. Method The detached leaf selection method was employed to quantitatively measure the avoidance behavior of adult thrips within 24 hours, as well as to determine the density of secretory glandular trichomes and T-shaped glandular trichomes on leaves. Result The population size of F. occidentalis after inoculation was classified into five resistance grades (highly resistant, moderately resistant, lowly resistant, susceptible, and highly susceptible) through quantitative grading, among which four species, namely Aster spathulifolius, Crossostephium chinense, Chrysanthemum zawadskii and Chrysanthemum makinoi, showed significant resistance, while Chrysanthemum nankingense and Ajania × marginatum showed high sensitivity. Pearson correlation analysis revealed there was a significant negative correlation between the density of secretory glandular trichomes on the adaxial leaf surface and the population size of F. occidentalis(P<0.05), indicating that this type of glandular trichome might exert a repellent effect by secreting terpenoid secondary metabolites. Conclusion The intrinsic relationship between leaf morphological resistance traits and F. occidentalis behavior have been clarified, providing a phenotypic basis for investigating the molecular mechanism of chrysanthemum resistance to F. occidentalis. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 28 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 975-983.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250464
Abstract:
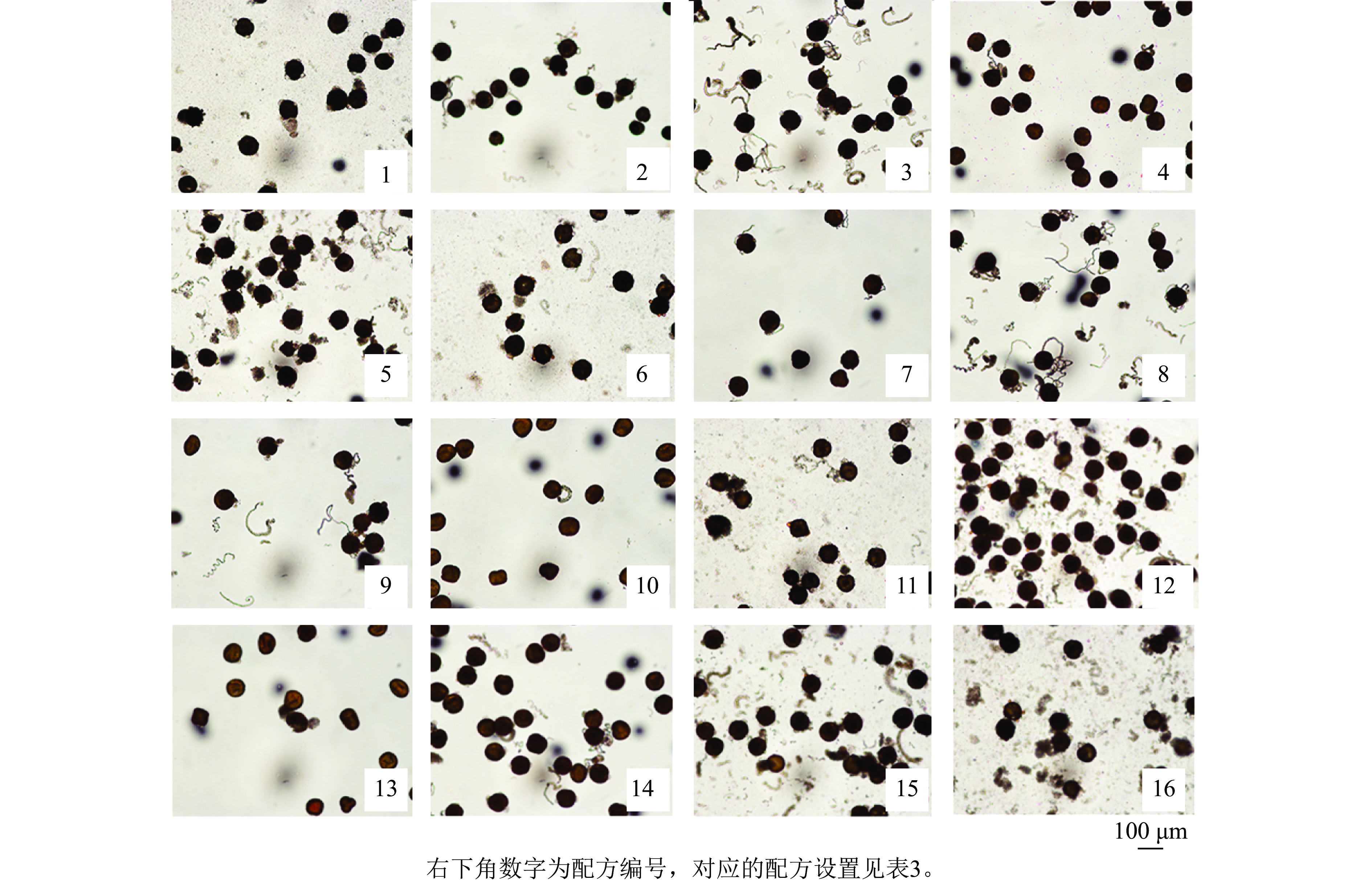
Objective This study aims to investigate the pollen viability and stigma receptivity of Pelargonium spp. and provide a basis for hybrid breeding of Pelargonium. Method Taking the cloning cultivar ‘Savannah Hot Pink’ as the representative material, the effects of 4 components, including sucrose, boric acid, polyethylene glycol 4000 (PEG 4000), and calcium chloride on the in vitro pollen germination viability were evaluated through an orthogonal design experiment. The optimum medium for geranium in vitro pollen germination viability was identified, and a method for determining the in vitro pollen germination viability of geranium based on this medium was established. The pollen viability of 9 different geranium cultivars, including ‘Savannah TexMex Merlot Sizzle’ and ‘Big EEZE Pink Splash’, were determined by the optimum medium. Additionally, benzidine-hydrogen peroxide method was used to observe the changes in stigma receptivity of ‘Savannah Hot Pink’. Result The results showed that the order of influence of each component on the pollen germination of ‘Savannah Hot Pink’ from highest to lowest was: PEG 4000, boric acid, calcium chloride, sucrose. The optimum medium was 50 g·L−1 sucrose + 250 mg·L−1 boric acid + 200 g·L−1 PEG 4000 + 5 mg·L−1 calcium chloride. Under this formulation, the average pollen germination rate was the highest, reaching 68.89%. Based on the optimum medium, the pollen viability was obviously different among 9 different geranium cultivars, with the pollen germination rate ranging from 25.56% to 76.67%. During the full flowering period in spring, as the flowers developed, the geranium stigmas in the flattened state exhibited the strongest receptivity, which was the optimum developmental stage for pollination. The stigma receptivity in this state was the strongest at around 10:00 on sunny days, indicating the best time for pollination. Conclusion Based on the optimization of the optimum medium for in vitro pollen germination, this study established a method for assessing the pollen viability, obtaining pollen germination rate ranging from 25.56% to 76.67% for different varieties, and identified the optimum developmental stage and timing for stigma pollination, which helps improve the efficiency of geranium hybrid breeding. [Ch, 2 fig. 7 tab. 34 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 984-993.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250429
Abstract:
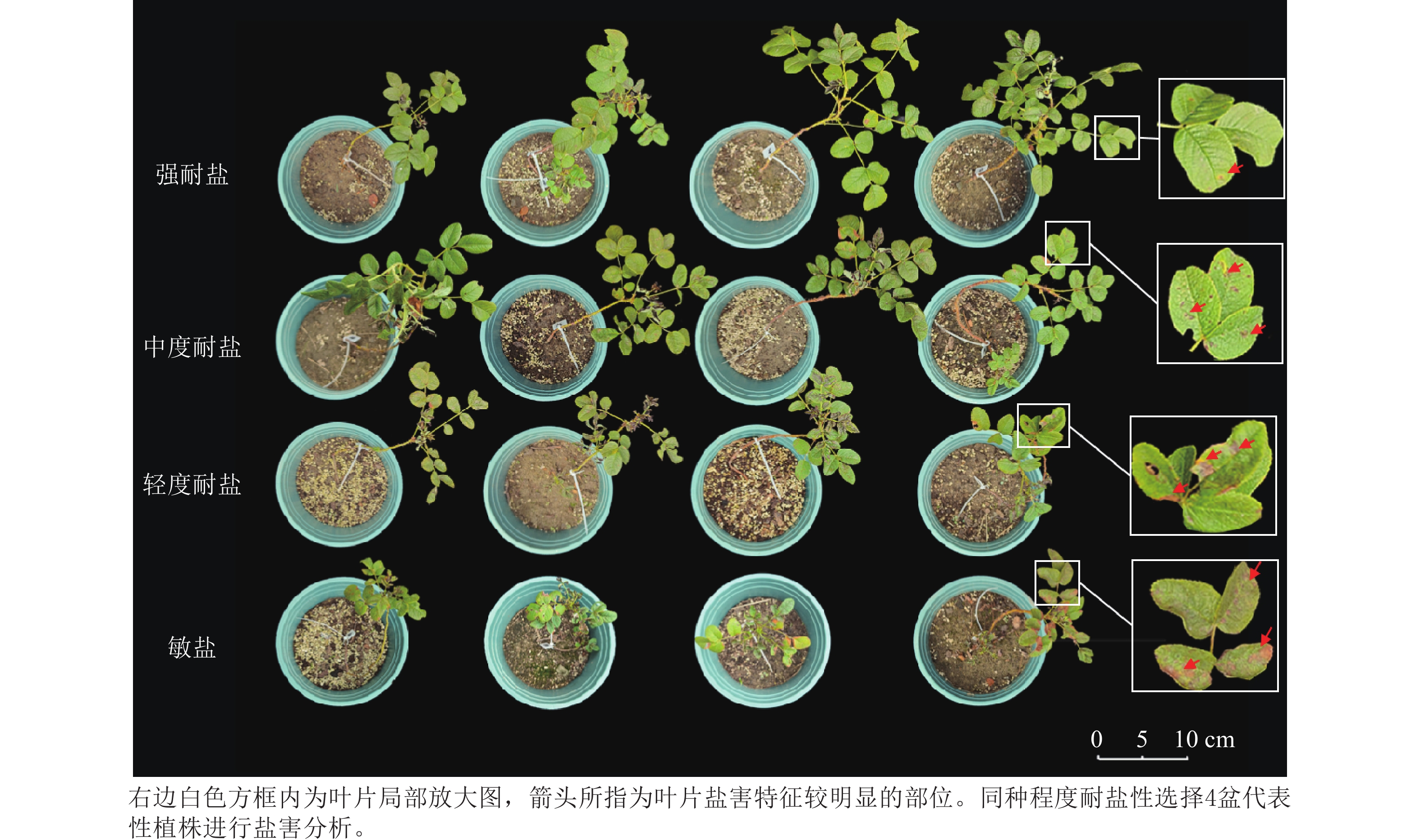
Objective This study aims to provide a parental selection strategy for salt-tolerant breeding of Rosa rugosa, with the goal of enhancing breeding efficiency. Method F1 generation seedlings were first obtained by crossing wild R. rugosa with R. rugosa ‘Alba Plena’. The salt tolerance of these seedlings was then evaluated under salt stress conditions. Resequencing and high-resolution melting (HRM) genotyping were employed to screen and validate single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) associated with salt tolerance. Result Among the 83 F1 seedlings, more than 50% exhibited moderate or higher salt tolerance, with 12 individuals showing strong salt tolerance. Resequencing and SNP analysis of all hybrid progenies detected a total of 11 412 504 SNP loci, among which cytosine (C)>thymine (T) and guanine (G)>adenine (A) were the most frequent mutation types. The largest proportion of SNP (approximately 34.46%) were located in intergenic regions. Furthermore, 5 well-genotyped SNP loci and their corresponding primers were screened. Among them, type Ⅰ of SNP63 could effectively eliminate salt-sensitive individuals, demonstrating its potential for marker-assisted selection in breeding for salt tolerance in R. rugosa. Conclusion The 12 salt-tolerant R. rugosa F1 generation exhibiting stronger salt tolerance than their parent lines were obtained, and a significantly salt tolerance-associated SNP marker (SNP63) was preliminarily identified, which will significantly enhance breeding efficiency. [Ch, 5 fig. 5 tab. 25 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 994-1002.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250441
Abstract:
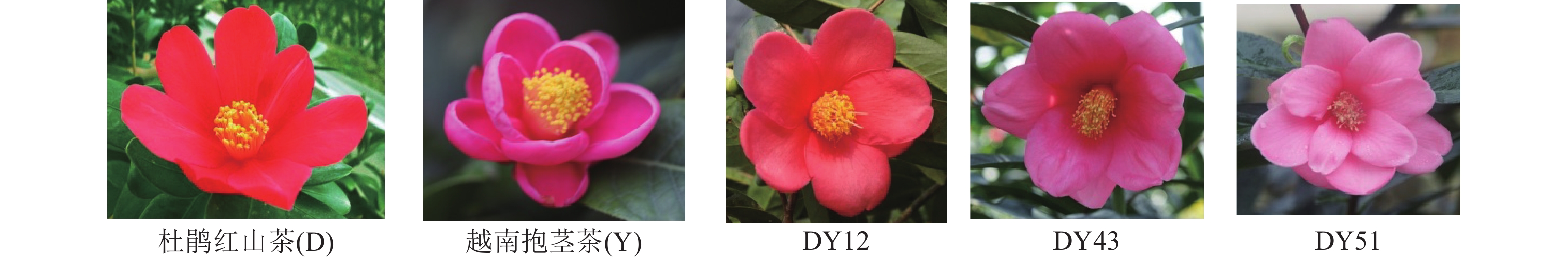
Objective The object of this study is to determine anthocyanin components in petals from Camellia azalea, C. amplexicaulis and their hybrids. The material basis of their color formation is clarified and the variability characteristics of main anthocyanin components and contents are revealed, which will provide a basis for the germplasm innovation and their efficient utilization. Method Flower colors of C. azalea, C. amplexicaulis and their hybrids were measured by CIE L*a*b* scale. Anthocyanin components and contents of C. azalea, C. amplexicaulis and their hybrids were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detection (HPLC-DAD) and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS). The relationship between the variation of flower colors and anthocyanin components was explored by multiple liner regression analyses. Result 16 anthocyanin components were detected in C. azalea, C. amplexicaulis and 18 hybrids. The total anthocyanin in hybrids was between the parents. The variation of Cy3GaEpC、Cy3GEpCX and Cy3GEpC in hybrids was large, and most of their contents were higher than that of parents, and the rest components were basically between parents. Conclusion Anthocyanins with galactoside in hybrids entirely came from C. azalea, and anthocyanins with 2-O-xylosyl mainly came from C. azalea. Anthocyanins with glucoside and without 2-O-xylosyl came from C. azalea and C. amplexicaulis. Cy3GaEpCX and Cy3Ga were the main anthocyanins affecting the hybrids flower color, and had significant correlation with color variation. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 37 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 1003-1013.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250468
Abstract:
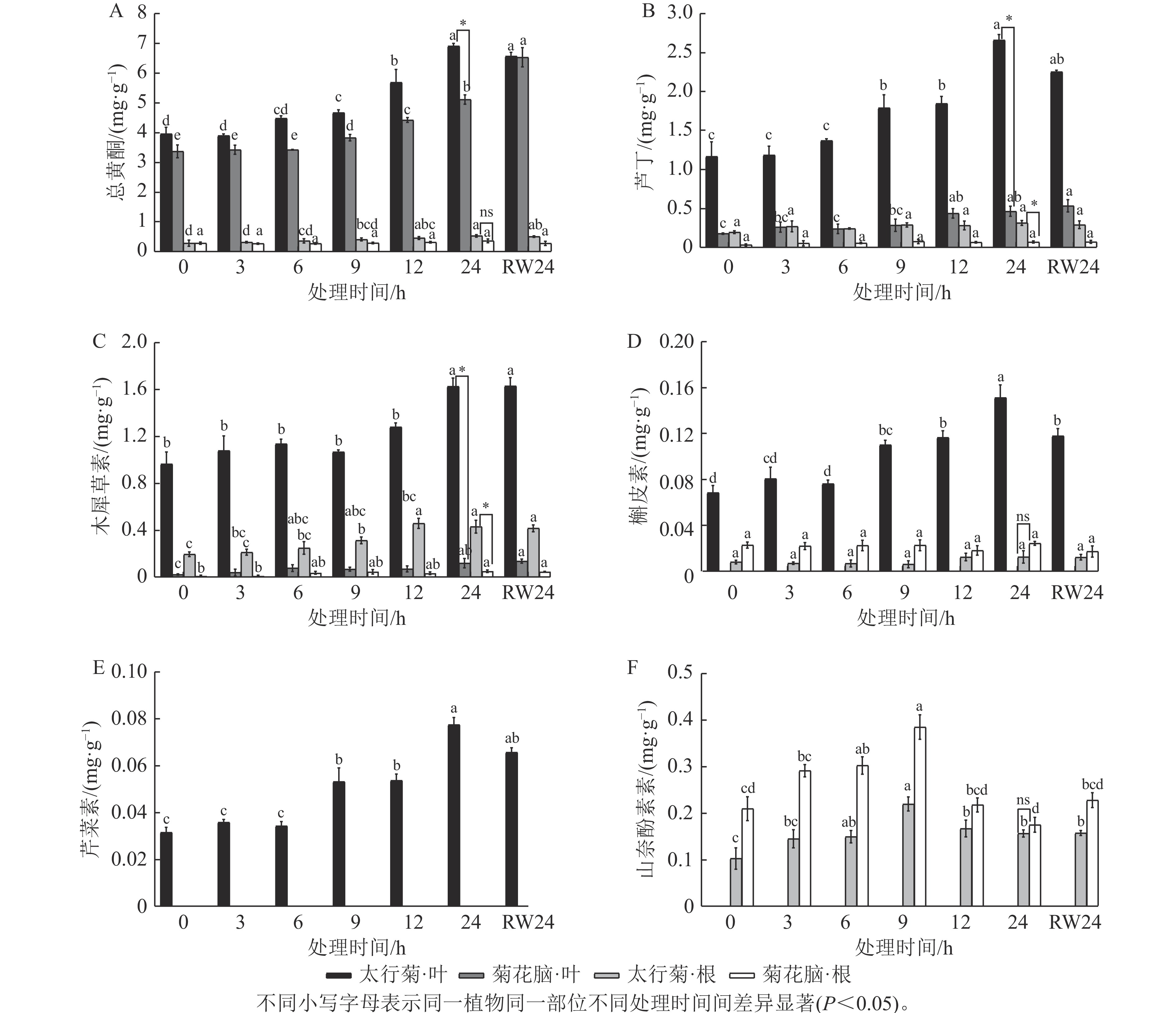
Objective This study aims to investigate the role of flavonoids in the drought stress response of Opisthopappus taihangensis and to provide valuable gene resources for the breeding of drought-tolerant chrysanthemums. Method Drought-tolerant O. taihangensis and drought-sensitive Chrysanthemum nankingense were used as experimental materials. Under simulated drought and rehydration conditions, the total flavonoid content and the levels of 5 flavonoids in O. taihangensis were measured. Meanwhile, the key candidate gene OtMYB12, potentially involved in flavonoid biosynthesis, was identified, and its expression dynamics and subcellular localization were analyzed. Result (1) Under drought stress, flavonoid content in O. taihangensis leaves and roots progressively increased with stress duration, peaking at 24 h, and decreased significantly after rehydration, and remained consistently higher than those in the corresponding organs of C. nankingense. (2) Among 5 flavonoids, rutin accumulated most abundantly in leaves and roots. All compounds showed progressive accumulation under drought stress and decreased after rehydration. (3) OtMYB12 remained a single-copy gene during evolution, localized in the nucleus, and its expression dynamics were highly correlated with accumulation patterns of flavonoid and its structural gene. Conclusion Flavonoids participate in the drought stress response of O. taihangensis, and OtMYB12 likely plays a key role in this process by regulating flavonoid biosynthesis. [Ch, 4 fig. 2 tab. 56 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 1014-1024.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250457
Abstract:
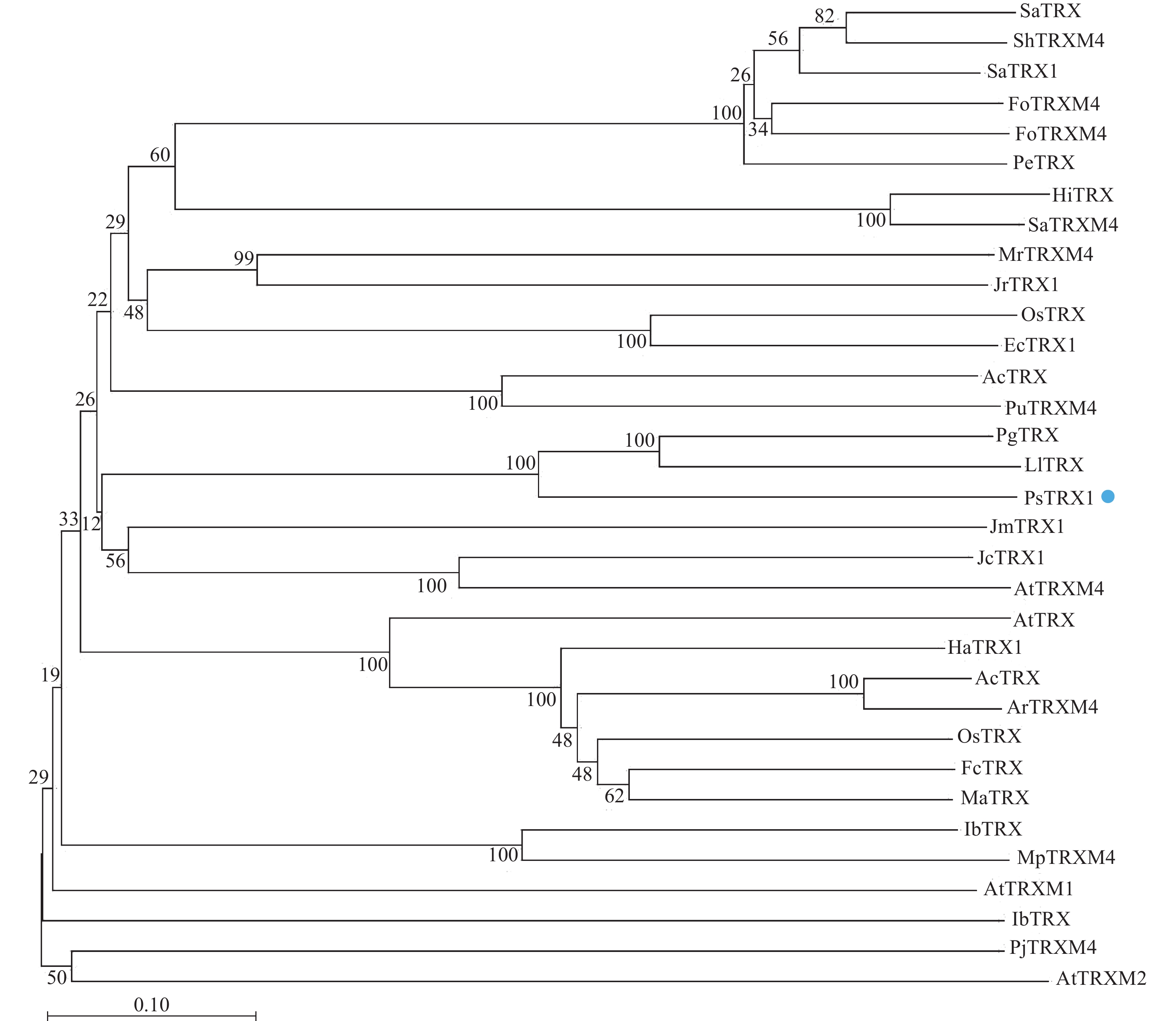
Objective This study aims to investigate the expression patterns of the PsTRX1 gene in various tissues of Paeonia suffruticosa (peony) under heat stress and its function in response to high temperature stress. Method (1) Multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis of the PsTRX1 gene in P. suffruticosa were conducted. (2) Subcellular localization of the PsTRX1 gene was experimentally determined. (3) RT-qPCR was performed on P. suffruticosa treated with high temperature to quantify the expression dynamics of PsTRX1 under heat stress. (4) Heterologous overexpression of PsTRX1 in Arabidopsis thaliana was carried out, and high temperature treatment was applied to both overexpressed and wild-type (WT) plants. Through phenotypic analysis and physiological index measurement, the role of PsTRX1 in response to high-temperature stress was clarified. Result (1) The phylogenetic tree revealed that the PsTRX1 protein of P. suffruticosa belonged to the thioredoxin family. Multiple sequence alignment results showed that the PsTRX1 protein sequence contained one conserved thioredoxin domain and one WCGPC motif. (2) Subcellular localization results demonstrated that the PsTRX1 protein was localized in the chloroplasts. (3) RT-qPCR analysis indicated that under high-temperature stress, the PsTRX1 gene rapidly responded to the heat stress in stems, leaves, and petioles, indicating that the expression of the PsTRX1 gene was induced by the heat treatment. (4) Under high temperature stress, compared with WT plants, the overexpressed PsTRX1 gene lines exhibited better growth conditions, higher chlorophyll content, lower contents of malondialdehyde (MDA) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), significantly enhanced activities of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, POD). The decrease in chlorophyll fluorescence value was also significantly reduced. Conclusion The PsTRX1 gene positively regulates heat tolerance of plants. [Ch, 8 fig. 2 tab. 35 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 1025-1036.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250469
Abstract:
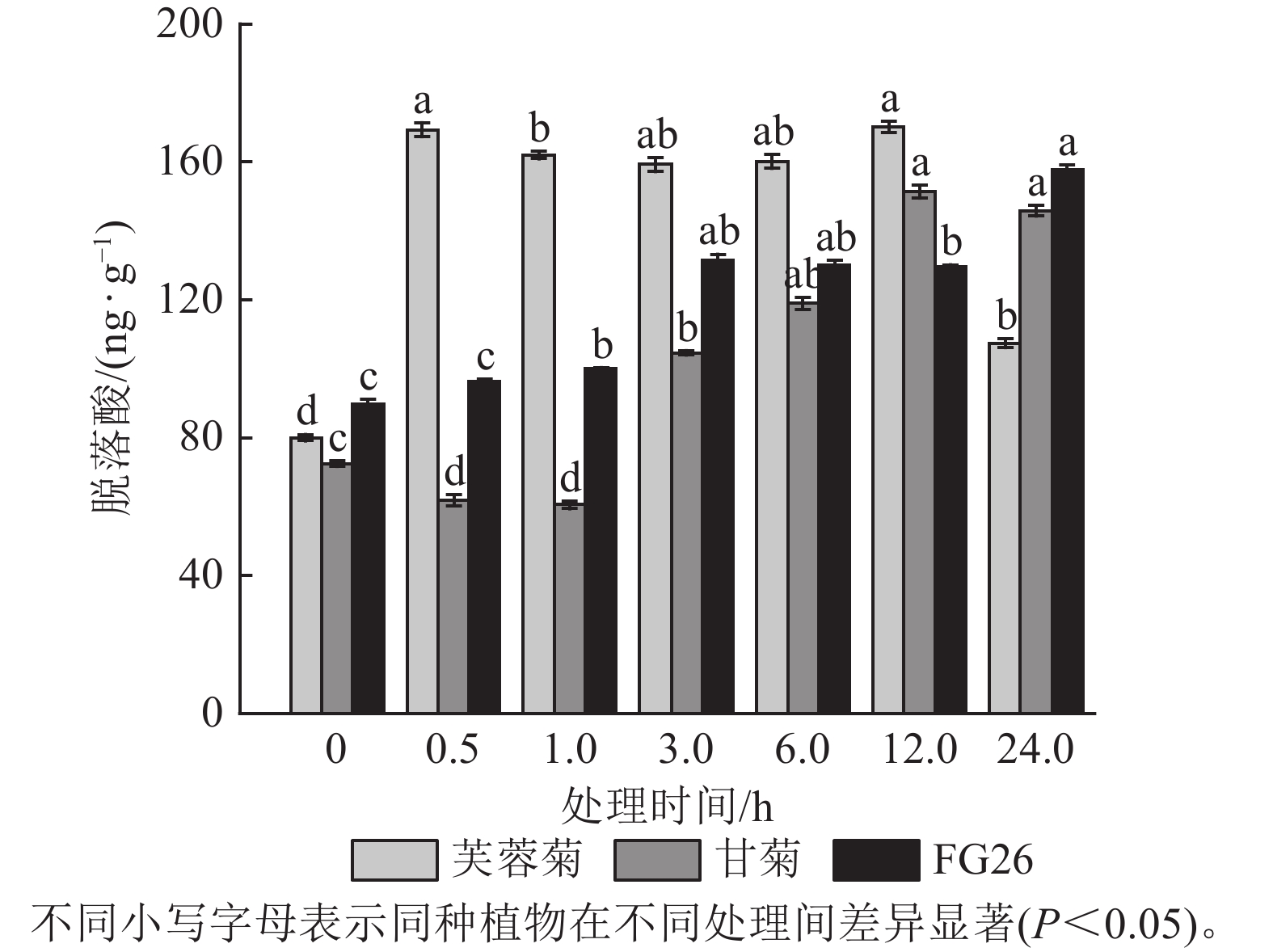
Objective This study aims to investigate the role of abscisic acid (ABA) in the salt tolerance of Crossostephium chinense and its hybrid progeny under salt stress, so as to provide a basis for breeding and innovation of salt-tolerant chrysanthemum germplasm. Method Salt-tolerant C. chinense, salt-sensitive Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium, and their relatively salt-tolerant hybrid progeny FG26 were used as materials. The dynamic changes of endogenous ABA under 700 mmol·L−1 NaCl treatment were analyzed. With 0 mmol·L−1 sodium chloride treatment and application of clear water as the control group (ck), the changes in physiological indicators under three different treatments, namely 300 mmol·L−1 NaCl stress (T1), T1 combined with 200 μmol·L−1 exogenous ABA (T2), and T1 combined with 1 mmol·L−1 ABA synthesis inhibitor Na2WO4 (T3) were examined to reveal the physiological differences among the three materials with varying salt tolerance and to clarify the differential regulatory mechanisms of ABA in their responses to salt stress. The expression patterns and evolutionary history of key genes in the ABA signaling pathway were explored by transcriptomic and phylogenetic analysis. Result (1)Under 700 mmol·L−1 NaCl treatment, the endogenous ABA mass fraction in the plants increased significantly (P<0.05). The response speed and peak value of C. chinense were higher than those of FG26 and C. lavandulifolium. (2) Compared to T1, the endogenous abscisic acid mass fractions in the three plants after T2 treatment increased by 2.03, 2.14, and 2.99 times, respectively, all showing an upward trend. Meanwhile, the proline mass fraction in C. chinense increased by 44.42% compared to T1, while that in C. lavandulifolium and FG26 decreased by 71.74% and 22.27%, respectively. Compared to T1, the superoxide dismutase activity and mass molar concentration of malondialdehyde in C. chinense and FG26 showed no significant changes, while in C. lavandulifolium, the superoxide dismutase activity decreased by 11.45%, and the mass molar concentration of malondialdehyde decreased significantly by 37.63% (P<0.05). (3) After salt stress, the expression of PP2C family genes HAB1, HAI1, and AHG1-1 in the ABA signaling pathway was specifically up-regulated only in C. chinense and FG26, while no significant change was observed in C. lavandulifolium. Conclusion Endogenous ABA plays an important regulatory role in salt stress response, and exogenous application of ABA can specifically regulate physiological metabolism in different plants to enhance stress resistance. The strong salt tolerance of C. chinense may be attributed to its efficient ABA response, osmotic adjustment, and stable antioxidant and membrane protection system. Salt tolerance related traits and key genes such as HAB1, HAI1, and AHG1-1 can be partially inherited by the progeny FG26 through hybridization. It has been confirmed that C. chinense possesses great potential as a new salt-tolerant variety for breeding. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 68 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 1037-1047.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250463
Abstract:
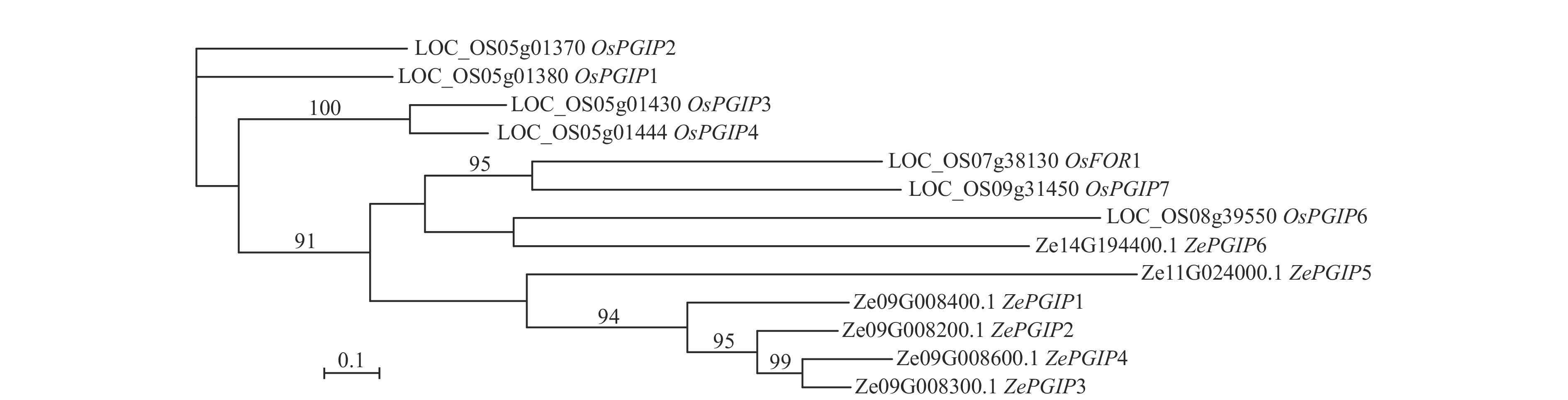
Objective This objective is to reveal the structural characteristics of the PGIP gene family in colored Zantedeschia elliottiana (calla lily) and their differential expression under Pectobacterium carotovorum (soft rot bacteria) infection, so as to provide a theoretical basis for functional studies of ZePGIP genes as well as the elucidation of the resistance mechanism to P. carotovorum in Z. elliottiana. Method Bioinformatics methods were employed to identify and analyze the members of the PGIP gene family across the entire genome of Z. elliottiana. The expression patterns of ZePGIP genes under infection by P. carotovorum were detected by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). Result A total of 6 ZePGIP genes, namely ZePGIP1, ZePGIP2, ZePGIP3, ZePGIP4, ZePGIP5, and ZePGIP6, were identified in the genome of the colored Z. elliottiana. Phylogenetic and conserved domain analysis revealed that these genes contained conserved motifs within the same subfamily. Among them, MEME-1 and MEME-2 exhibited high sequence similarity, and MEME-1, MEME-2, MEME-6 could be detected in all members, demonstrating a high degree of conservation. Promoter cis-element analysis showed that ZePGIP promoters contained response elements associated with abscisic acid, auxin, methyl jasmonate, light, low temperature, gibberellin, stress, and salicylic acid. Gene collinearity analysis indicated that ZePGIP2 and ZePGIP5 were paralogous genes. Gene collinearity analysis across species in the Araceae family identified two pairs of orthologous genes between Z. elliottiana and Pinellia pedatisecta, Pistia stratiotes, Colocasia esculenta, and Amorphophallus konjac. The inoculation and correlation analysis of P. carotovorum indicated that ZePGIP genes displayed differential responses to P. carotovorum infection, among which ZePGIP2 and ZePGIP6 were inhibited in the early stage of infection but significantly induced in the later stage. Conclusion The PGIP gene family mainly exists in the form of tandem repeats in colored Z. elliottiana and exhibits a highly conserved structure. ZePGIP2 and ZePGIP6 show significant responses to P. carotovorum infection, suggesting that they may play a crucial role in resisting P. carotovorum. [Ch, 8 fig. 37 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 1048-1058.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250283
Abstract:
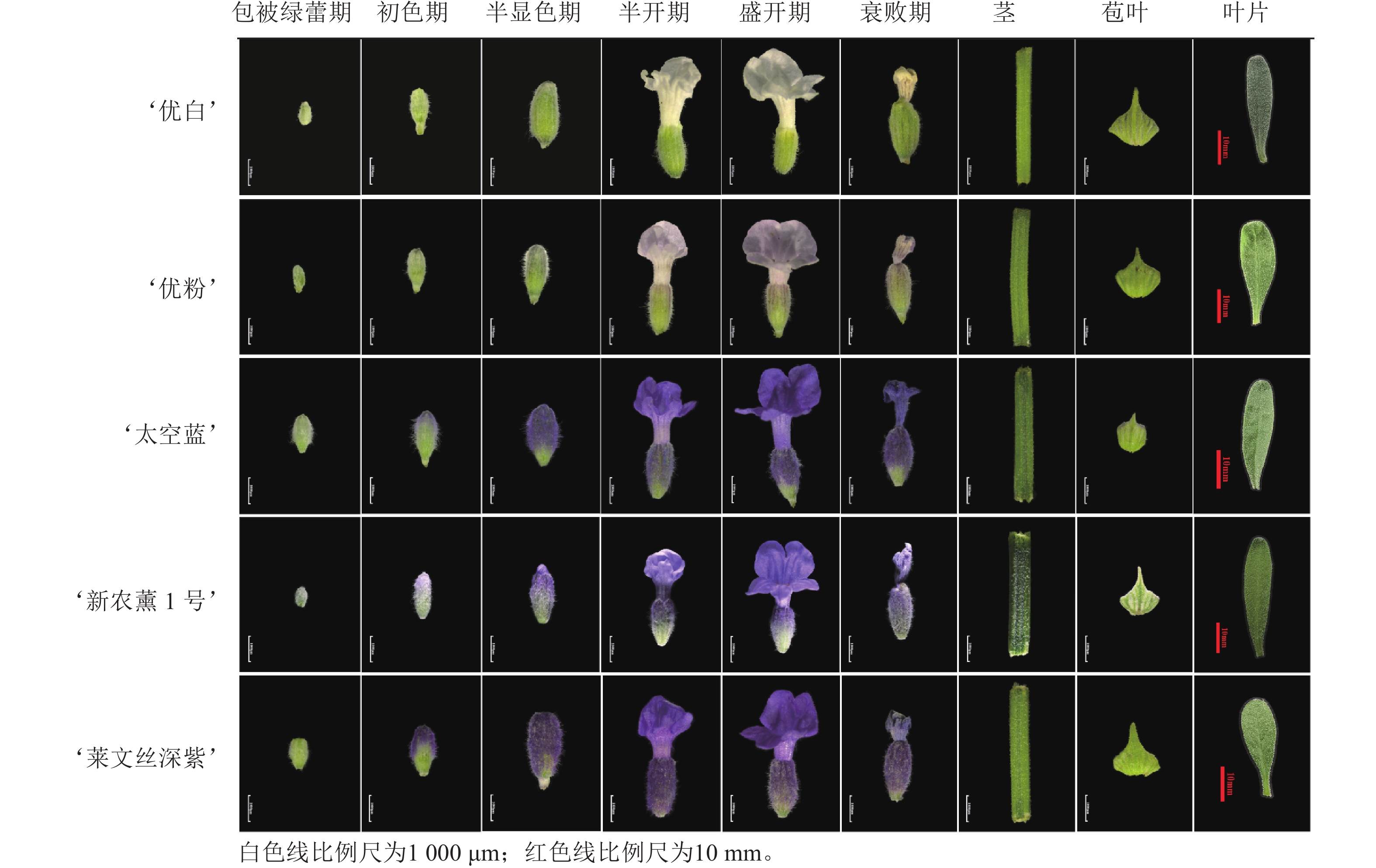
Objective Chalcone synthase (CHS) is a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of anthocyanins in plants. This study aims to investigate the relationship between the LaCHS gene and anthocyanin metabolism in Lavandula angustifolia and analyze its biological functions, so as to provide insights for clarifying its mechanism of floral color regulation. Method The LaCHS gene was cloned using young leaves of L. angustifolia ‘Levens Deep Purple’ as experimental material. Bioinformatics analysis was employed to study the physicochemical properties and phylogenetic relationships of the LaCHS protein. The expression levels of the LaCHS gene in various organs of L. angustifolia cultivars, including ‘Superior White’ ‘Premium Pink’ ‘Space Blue’ ‘Xinnongxun No.1’ and ‘Levens Deep Purple’, were analyzed using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), and differences in relative anthocyanin content among these cultivars were quantitatively assessed. The function of the LaCHS gene in ‘Levens Deep Purple’ was validated through heterologous overexpression in Nicotiana benthamiana and virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS). Result A 1 173 bp cDNA sequence of the LaCHS gene was obtained, encoding 390 amino acids. The secondary structure of the LaCHS protein was primarily composed of α-helices and random coils, belonging to the PLN03173 superfamily. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the LaCHS protein had a relatively close genetic relationship with CHS proteins of species such as holy basil (Ocimum tenuiflorum) and perilla (Perilla frutescens). RT-qPCR analysis revealed that the LaCHS gene exhibited distinct tissue-specific expression, mainly expressed in floral organs. Across the different developmental stages of the flower organs of 5 L. angustifolia cultivars, the expression level of the LaCHS gene was the highest during the full-bloom or withering stage, while the relative content of anthocyanin reached the peak in the withering stage. Among the vegetative organs, the tissues with the highest gene expression levels were bracts or stems, while the bracts had the highest relative anthocyanin content. The expression trend of LaCHS was basically consistent with accumulation dynamics of anthocyanins. The expression level of the LaCHS gene in N. benthamiana with heterologous overexpression was significantly upregulated, accompanied by synchronous upregulation of key structural genes (NbF3′H and NbDFR) in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway, along with an increase in relative anthocyanin content. The expression level of the LaCHS gene in the gene-silenced L. angustifolia strain was significantly reduced, and the relative content of anthocyanins also decreased simultaneously. Conclusion The LaCHS gene has a positive regulatory effect on the biosynthesis of L. angustifolia anthocyanins, and affects anthocyanin accumulation. [Ch, 8 fig. 2 tab. 35 ref.]
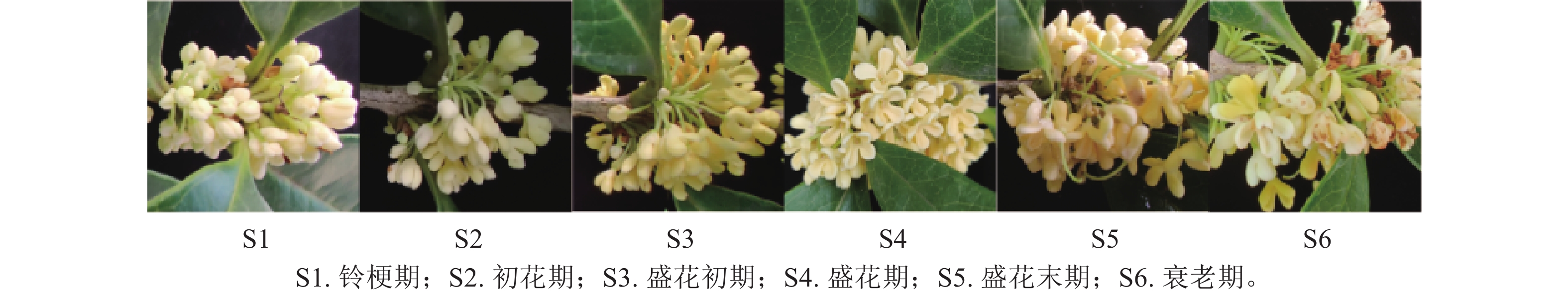
2025, 42(5): 1059-1067.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250446
Abstract:
Objective The short flowering period and the easy senescence and browning of petals restrict the development and utilization of the economic value of Osmanthus fragrans. Exploring the regulatory function of OfSAUR21 gene on senescence can provide a theoretical basis for the study of the molecular mechanism of petal senescence regulation in O. fragrans. Method Using O. fragrans ‘Liuye Jingui’ as the material, the OfSAUR21 gene was cloned. Bioinformatics analysis was conducted to explore the physicochemical properties and phylogenetic relationships of the OfSAUR21 protein. Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) was used to analyze the expression pattern of the OfSAUR21 gene at different flowering stages, and preliminary identification of gene function was performed through transient transformation of O. fragrans petals. Result A cDNA sequence of the OfSAUR21 gene with a length of 294 bp was cloned, which could encode 97 amino acids. It had no signal peptide or transmembrane domain, and its subcellular localization was predicted to be in chloroplasts, containing a conserved domain of the Auxin_inducible superfamily. Homology alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis revealed that this gene had the closest genetic relationship with wild olive (Olea europaea var. sylvestris). The results of RT-qPCR analysis showed that the expression of this gene was the highest in the petal senescence stage. The OfSAUR21 gene was introduced into O. fragrans petals through transient transformation. Confirmation by RT-qPCR and ethylene analysis showed that the browning rate of O. fragrans petals with the successfully introduced target gene increased, and the ethylene release amount also increased. Conclusion OfSAUR21 contains a complete conserved domain of the auxin-inducible superfamily, is a member of the early auxin-responsive gene family, exhibits the highest expression level at the late full-bloom stage, and positively regulates ethylene production and senescence in O. fragrans. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 36 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 1068-1077.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250430
Abstract:
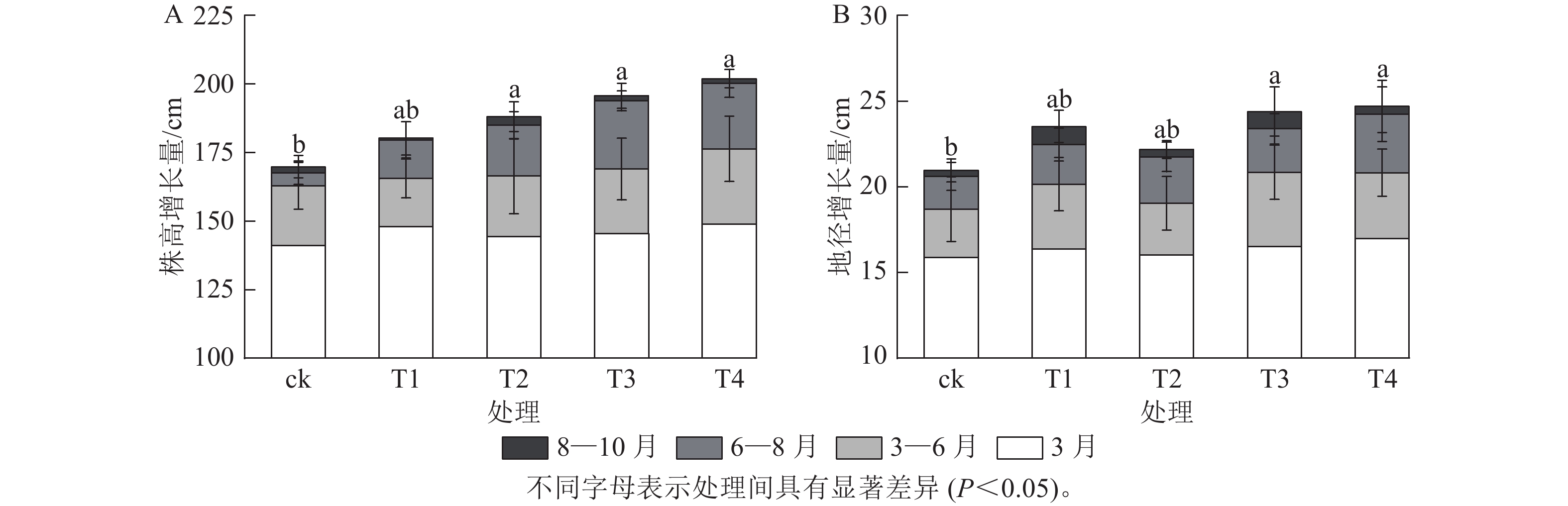
Objective In the low-altitude regions of Southwest China, high autumn temperatures affect the leaf coloration of Acer rubrum (red maple). Based on the retarding effect of nitrogen on plant senescence, this study investigates the impact of nitrogen application on the growth and leaf coloration of A. rubrum. Method Using the cultivar A. rubrum ‘Red Crown’ as the test subject, urea was applied at different gradient treatments: ck (0 g·plant−1), T1 (50 g·plant−1), T2 (100 g·plant−1), T3 (150 g·plant−1), and T4 (200 g·plant−1). Growth indicators, leaf morphological traits, leaf color parameters, soluble sugar (SS) content, leaf color Lab values, and chroma (C*) were measured. The leaf color transition period was divided into 6 stages (Ⅰ−Ⅵ), and the optimal viewing period was recorded. Result The cumulative plant height growth (H) and ground diameter growth (GD) in T3 and T4 were significantly greater than those in ck (P<0.05). The leaf area (LA) of T4 in July, September, and October was significantly higher than that of ck (P<0.05). In the early color transition stage (Ⅰ), the total chlorophyll (Chl) and carotenoid (Car) content in T4 were significantly higher than those in ck (P<0.05). During the color transition period (Ⅱ−Ⅵ), the maximum soluble sugar (SS) and anthocyanin (Ant) content in T4 were significantly higher than those in ck (P<0.05). Chl and Car in ck began to decline rapidly in stage Ⅱ, whereas those in T4 remained high in stages Ⅱ and Ⅲ and only started to decrease in stage Ⅳ. Significant differences were observed in the upward trends of Ant and SS among the treatment groups: SS, Ant, and the red-green chromaticity (a*) in ck increased significantly from stage Ⅱ, peaking in stage Ⅳ, whereas those in T4 only rose significantly in stage Ⅳ−20 days later than ck. By stage Ⅵ, Ant and a* in T4 reached their maximum values. Dynamic monitoring of the relative chlorophyll content (SPAD) showed that ck had the lowest SPAD, with the earliest decline and leaf color transition. In contrast, T4 exhibited the highest SPAD, with the latest leaf color transition. The leaf color transition in T4 was delayed by 20 days compared to ck, and the optimal viewing period was extended by 13 days. Correlation analysis indicated that H was positively correlated with GD and LA, while LA was positively correlated with Chl and Car but negatively correlated with a* and L* (P<0.1). Anthocyanin content was significantly positively correlated with a but negatively correlated with chlorophyll a (Chl a), chlorophyll b (Chl b), and Car (P<0.05). Conclusion Under the high autumn temperatures in low-altitude regions of Southwest China, nitrogen application significantly promotes the growth of A. rubrum, increases chlorophyll content, delays leaf senescence, and postpones leaf color transition. When urea is applied at 150−200 g·plant−1, leaf senescence is delayed, and exposure to low temperatures enhances anthocyanin synthesis, significantly improving leaf color quality and extending the optimal viewing period of A. rubrum. [Ch, 7 fig. 2 tab. 41 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 1078-1089.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250401
Abstract:
Objective The shade tolerance of colorful-leaf plants directly influences their ornamental value and application potential in indoor low-light environments. Establishing a scientific and efficient shade tolerance evaluation system and identifying key indicators are of great significance for the rapid identification and widespread application of shade-tolerant germplasm. Method This study utilized 11 popular and highly ornamental colorful-leaf plants, including 2 Alocasia cultivars, 3 Caladium cultivars, and 6 Begonia cultivars. 4 shading gradients 0(ck), 50%, 75%, and 90%, were established to evaluate plant morphology, chlorophyll content, and leaf color parameters. Principal component analysis and membership function method were employed to comprehensively assess shade tolerance, while stepwise regression analysis was applied to develop predictive models under different shading conditions and identify key indicators for shade tolerance evaluation. Result Under shading stress, most tested plants adapted to the low-light environment by increasing plant height, petiole length, leaf length, leaf L* value (lightness), and chlorophyll b content. Comprehensive shade tolerance evaluation indicated that C. ‘Yanzhihong’ and C. ‘Fense Hesheng’ exhibited the strongest shade tolerance, while B. ‘Shanhu’ and B. ‘Dongyun’ showed the weakest. Stepwise regression analysis revealed that key identification indicators varied under different shading intensities: at 50% shading, the main indicators were plant height and leaf L* value; at 75% shading, they were plant height, leaf L* value, total chlorophyll content, and leaf length; and at 90% shading, the key indicators were chlorophyll a, crown width, and chlorophyll b. Conclusion This study established a comprehensive evaluation system for shade tolerance in colorful-leaf plants and identified shade-intensity-specific key indicators, which can provide a theoretical foundation and methodological reference for both shade tolerance assessment and indoor horticultural applications of these plants. [Ch, 4 tab. 39 ref.]
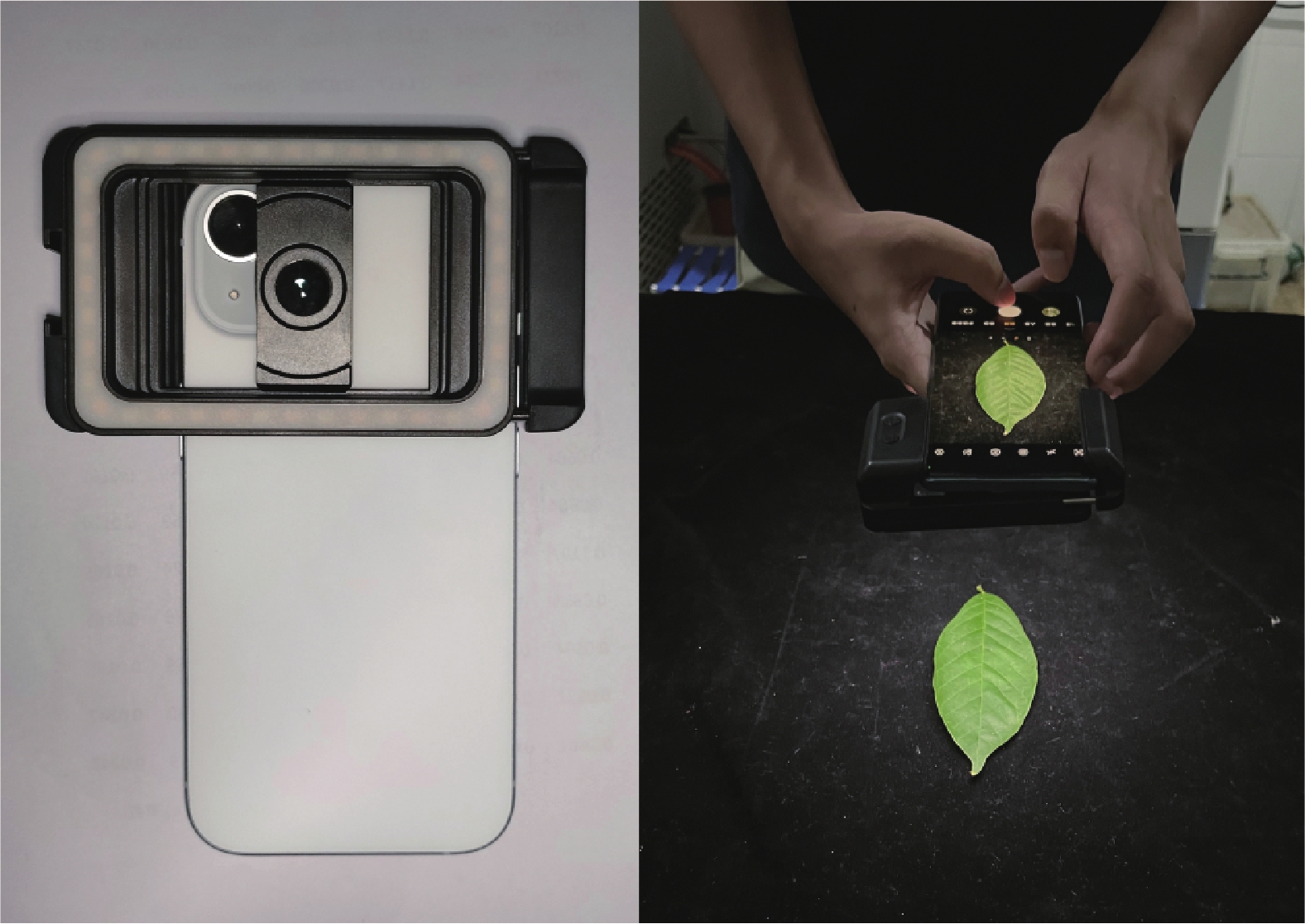
2025, 42(5): 1090-1101.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250460
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to develop a method for predicting chlorophyll and nitrogen in leaves of Yulania denudata and Y. biondii based on smartphone RGB images. Method Mature leaf of Y. denudata and Y. biondii were used as the research objects. Leaf images were collected using 2 smartphone models, namely iPhone13 and Honor 70Pro+. The color feature parameters of the leaves were extracted via Python and the OpenCV library. Combined with the leaf chlorophyll and nitrogen measured by a chlorophyll meter, prediction models were constructed based on three algorithms: Linear Regression, Artificial Neural Network, and Support Vector Regression. Result Among the constructed models, the Linear Regression model achieved the best performance in predicting chlorophyll (R2=0.740) and nitrogen (R2=0.741) of Y. denudata leaves imaged by the Honor 70Pro+. The Artificial Neural Network model exhibited the optimal performance in predicting chlorophyll (R2=0.728) of Y. biondii leaves captured by the iPhone13 and nitrogen (R2=0.735) of Y. denudata leaves imaged by the Honor 70Pro+. For the Support Vector Regression model, it showed the best predictive ability for both chlorophyll (R2=0.748) and nitrogen (R2=0.742) of Y. biondii leaves captured by the Honor 70Pro+. Conclusion The prediction method of chlorophyll and nitrogen based on smartphone RGB images shows good feasibility in the leaves of Yulania plants, and the prediction performance of all models reaches a relatively high level. Interspecific differences among Yulania species result in variations in the fitting performance of the prediction models. [Ch, 10 fig. 1 tab. 28 ref.]
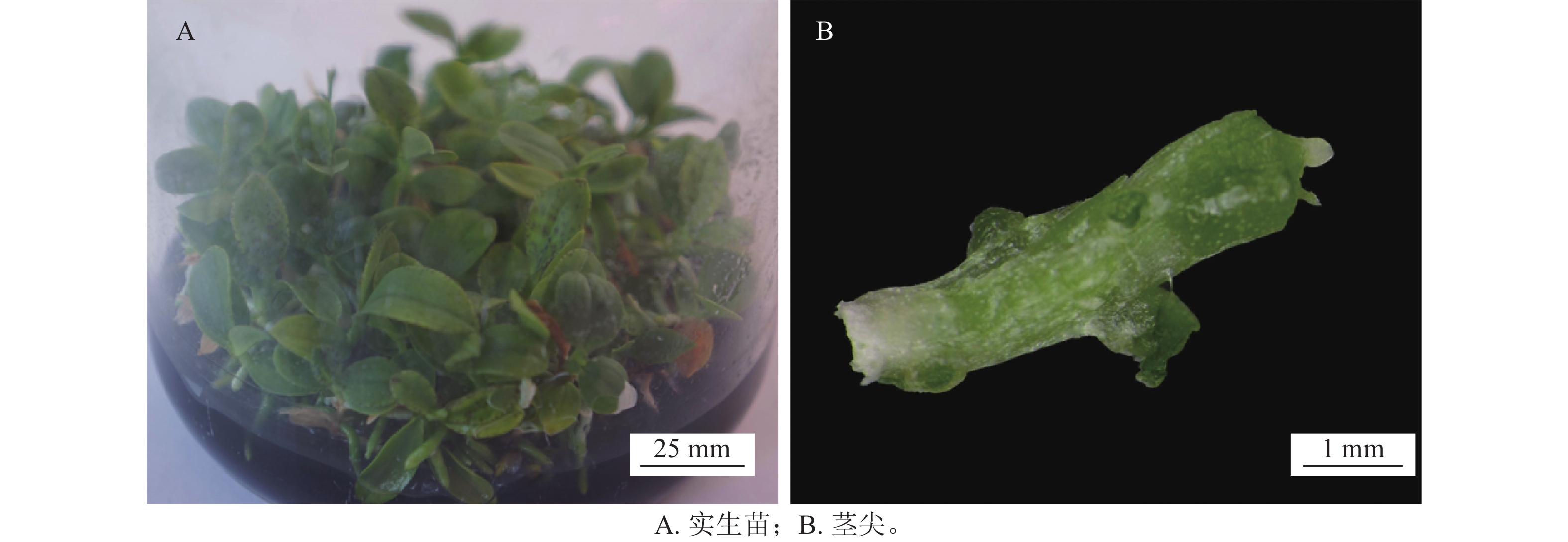
2025, 42(5): 1102-1109.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250172
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the optimal conditions for cryopreservation of Phalaenopsis zhejiangensis shoot tips and establish an applicable droplet vitrification preservation system for long-term and stable conservation of its germplasm resources. Method P. zhejiangnsis seedlings were used as experimental materials, and droplet vitrification cryopreservation method was used to preserve P. zhejiangensis shoot tips. By a single factor test method, pre-cultured sucrose concentrations, loading time, and different vitrification solution (PVS2) treatment time were set in the cryopreservation preservation program to optimize the preservation conditions. Paraffin sections were used to observe the damage to the shoot tip tissue structure during ultra-low temperature preservation. Result The highest survival rate of 70.0% was achieved when the shoot tips of P. zhejiangensis were stored in a 0.5 mol·L−1 sucrose pre-culture medium at 4℃ in the dark for 2 days, treated with loading solution for 20 minutes and vitrification solution for 120 minutes, then placed into small droplets of tin foil, frozen in liquid nitrogen for 1 hour, and treated with unloading solution for 20 minutes. After regeneration culture, the regeneration rate was 43.33%. Histological observation of paraffin sections revealed that the damage to cell structure and function caused by liquid nitrogen freezing and unloading was relatively significant. Therefore, optimizing the pre-culture and loading treatment of the shoot tips of P. zhejiangensis prior to cryopreservation was of great significance for reducing cellular damage and maintaining cell integrity. Conclusion The established droplet vitrification cryopreservation system offers an efficient and simple method for long-term conservation of P. zhejiangensis germplasm resources. [Ch, 4 fig. 34 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 875-887.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250385
Abstract:
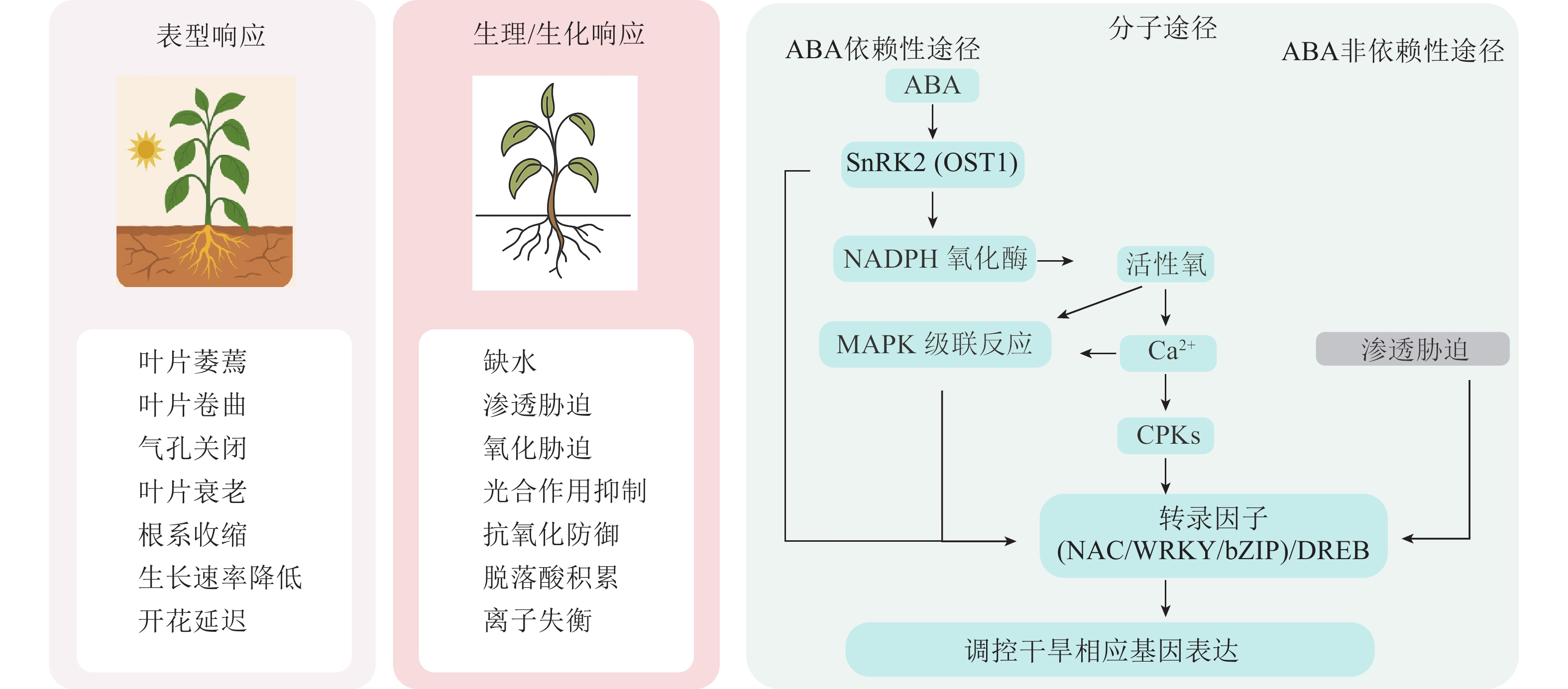
Drought stress, one of the main abiotic stresses, is a primary limiting factor for plant growth, development, yield, and quality, posing a significant threat to the sustainable development of global agriculture. Drought resistance, a complex quantitative trait controlled by multiple genes, involves multi-level regulatory mechanisms, making it challenging for traditional research methods to systematically elucidate its molecular basis. In recent years, the rapid development of multi-omics approaches has provided support for systematically revealing the mechanisms of plant responses to drought stress. This review summarizes the advancements of technologies such as genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, as well as their applications in drought resistance research in horticultural plants. This review highlights the research progress of multi-omics joint analysis in key areas such as the mining of drought-resistance genes, the analysis of signaling pathway, and the development of drought resistance molecular markers. Furthermore, this review summarizes the challenges and limitations of multi-omics approaches in plant drought resistance applications. It prospects the application of new technologies like spatial omics, single-cell omics, and AI-driven multi-omics data mining in plant drought resistance research, aiming to provide theoretical support for drought resistance mechanism research and stress-resistant breeding. [Ch, 1 fig. 1 tab. 95 ref.]
Drought stress, one of the main abiotic stresses, is a primary limiting factor for plant growth, development, yield, and quality, posing a significant threat to the sustainable development of global agriculture. Drought resistance, a complex quantitative trait controlled by multiple genes, involves multi-level regulatory mechanisms, making it challenging for traditional research methods to systematically elucidate its molecular basis. In recent years, the rapid development of multi-omics approaches has provided support for systematically revealing the mechanisms of plant responses to drought stress. This review summarizes the advancements of technologies such as genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, as well as their applications in drought resistance research in horticultural plants. This review highlights the research progress of multi-omics joint analysis in key areas such as the mining of drought-resistance genes, the analysis of signaling pathway, and the development of drought resistance molecular markers. Furthermore, this review summarizes the challenges and limitations of multi-omics approaches in plant drought resistance applications. It prospects the application of new technologies like spatial omics, single-cell omics, and AI-driven multi-omics data mining in plant drought resistance research, aiming to provide theoretical support for drought resistance mechanism research and stress-resistant breeding. [Ch, 1 fig. 1 tab. 95 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 888-897.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250432
Abstract:
Plant genetic transformation technology is a key means in modern plant gene function research and molecular breeding. However, the use of traditional methods for genetic transformation is highly dependent on plant tissue culture, and there are obvious genotype limitations and other problems. Agrobacterium-mediated non-tissue culture genetic transformation technology has emerged as a new form, which is gradually applied in a variety of plants due to its simple operation and no need to undergo dedifferentiation and regeneration. This paper systematically sorts out the basic principles of Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation and various methods of non-tissue culture transformation, including seed-mediated method, flower organ transformation method, living injection delivery method, cutting-impregnation-budding method, virus delivery method, electroporation method, etc. Other non-tissue culture genetic transformation methods independent of Agrobacterium were also summarized, including nanoparticle-assisted delivery, developmental regulator-assisted transformation, pollen tube-mediated transformation, and viral vector-mediated transformation. By comparing application examples, transformation efficiencies, advantages and disadvantages, and suitable plant species across different methods, it clearly demonstrates the potential of non-tissue-culture transformation systems in enhancing genetic transformation efficiency, broadening the range of applicable species, and lowering the technical barriers required for transformation. The purpose is to provide corresponding theoretical reference and technical support for the establishment of efficient, stable and universal plant non-tissue culture genetic transformation. [Ch, 2 tab. 71 ref.]
Plant genetic transformation technology is a key means in modern plant gene function research and molecular breeding. However, the use of traditional methods for genetic transformation is highly dependent on plant tissue culture, and there are obvious genotype limitations and other problems. Agrobacterium-mediated non-tissue culture genetic transformation technology has emerged as a new form, which is gradually applied in a variety of plants due to its simple operation and no need to undergo dedifferentiation and regeneration. This paper systematically sorts out the basic principles of Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation and various methods of non-tissue culture transformation, including seed-mediated method, flower organ transformation method, living injection delivery method, cutting-impregnation-budding method, virus delivery method, electroporation method, etc. Other non-tissue culture genetic transformation methods independent of Agrobacterium were also summarized, including nanoparticle-assisted delivery, developmental regulator-assisted transformation, pollen tube-mediated transformation, and viral vector-mediated transformation. By comparing application examples, transformation efficiencies, advantages and disadvantages, and suitable plant species across different methods, it clearly demonstrates the potential of non-tissue-culture transformation systems in enhancing genetic transformation efficiency, broadening the range of applicable species, and lowering the technical barriers required for transformation. The purpose is to provide corresponding theoretical reference and technical support for the establishment of efficient, stable and universal plant non-tissue culture genetic transformation. [Ch, 2 tab. 71 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 898-910.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250476
Abstract:
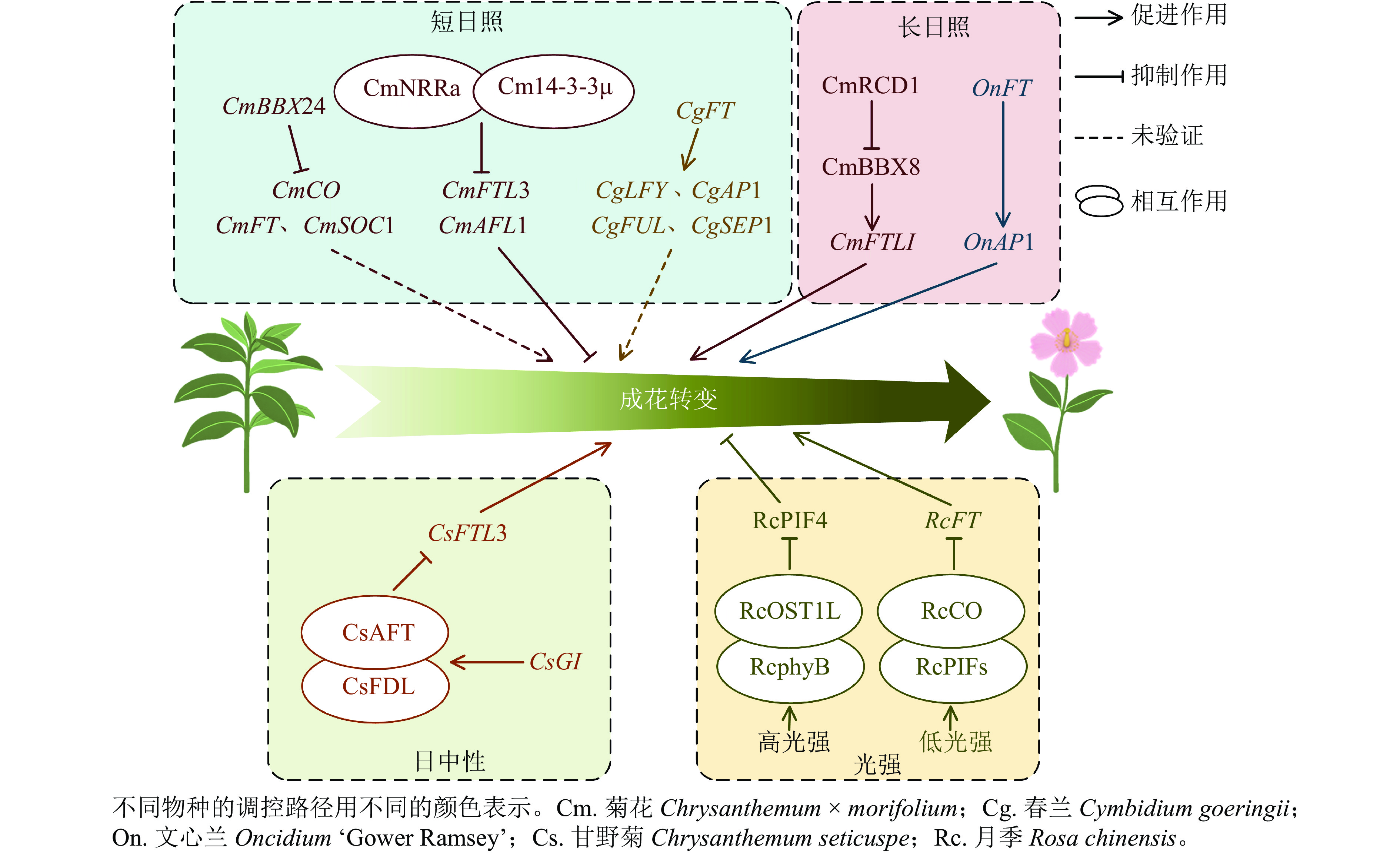
As a crucial ornamental and economic trait of ornamental plants, flowering time directly affects their commercial value and market supply capacity. Achieving precise regulation of flowering time and year-round production has become an urgent demand for industrial development. Therefore, exploring how to achieve precise flowering period regulation based on the floral induction process of ornamental plants and its relationship with environmental factors holds significant importance for meeting market demands. With the continuous in-depth research on the flowering mechanism and the advancement of cultivation techniques, remarkable progress has been made in the regulation of the flowering period of ornamental plants. This paper summarized the morphological formation and developmental patterns of flower bud differentiation in ornamental plants, and systematically reviewed the latest research progress on 6 floral induction molecular pathways (photoperiod, gibberellin, ambient temperature, vernalization, autonomous, and age), and major flowering time regulation technologies (light, temperature, plant growth regulator, and cultivation method) in ornamental plants. Based on the main problems existing in the research, the key research directions for the future were proposed, to provide theoretical support and practical reference for the precise flowering period regulation and commercial production of ornamental plants. [Ch, 2 fig. 1 tab. 105 ref.]
As a crucial ornamental and economic trait of ornamental plants, flowering time directly affects their commercial value and market supply capacity. Achieving precise regulation of flowering time and year-round production has become an urgent demand for industrial development. Therefore, exploring how to achieve precise flowering period regulation based on the floral induction process of ornamental plants and its relationship with environmental factors holds significant importance for meeting market demands. With the continuous in-depth research on the flowering mechanism and the advancement of cultivation techniques, remarkable progress has been made in the regulation of the flowering period of ornamental plants. This paper summarized the morphological formation and developmental patterns of flower bud differentiation in ornamental plants, and systematically reviewed the latest research progress on 6 floral induction molecular pathways (photoperiod, gibberellin, ambient temperature, vernalization, autonomous, and age), and major flowering time regulation technologies (light, temperature, plant growth regulator, and cultivation method) in ornamental plants. Based on the main problems existing in the research, the key research directions for the future were proposed, to provide theoretical support and practical reference for the precise flowering period regulation and commercial production of ornamental plants. [Ch, 2 fig. 1 tab. 105 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 911-921.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250472
Abstract:
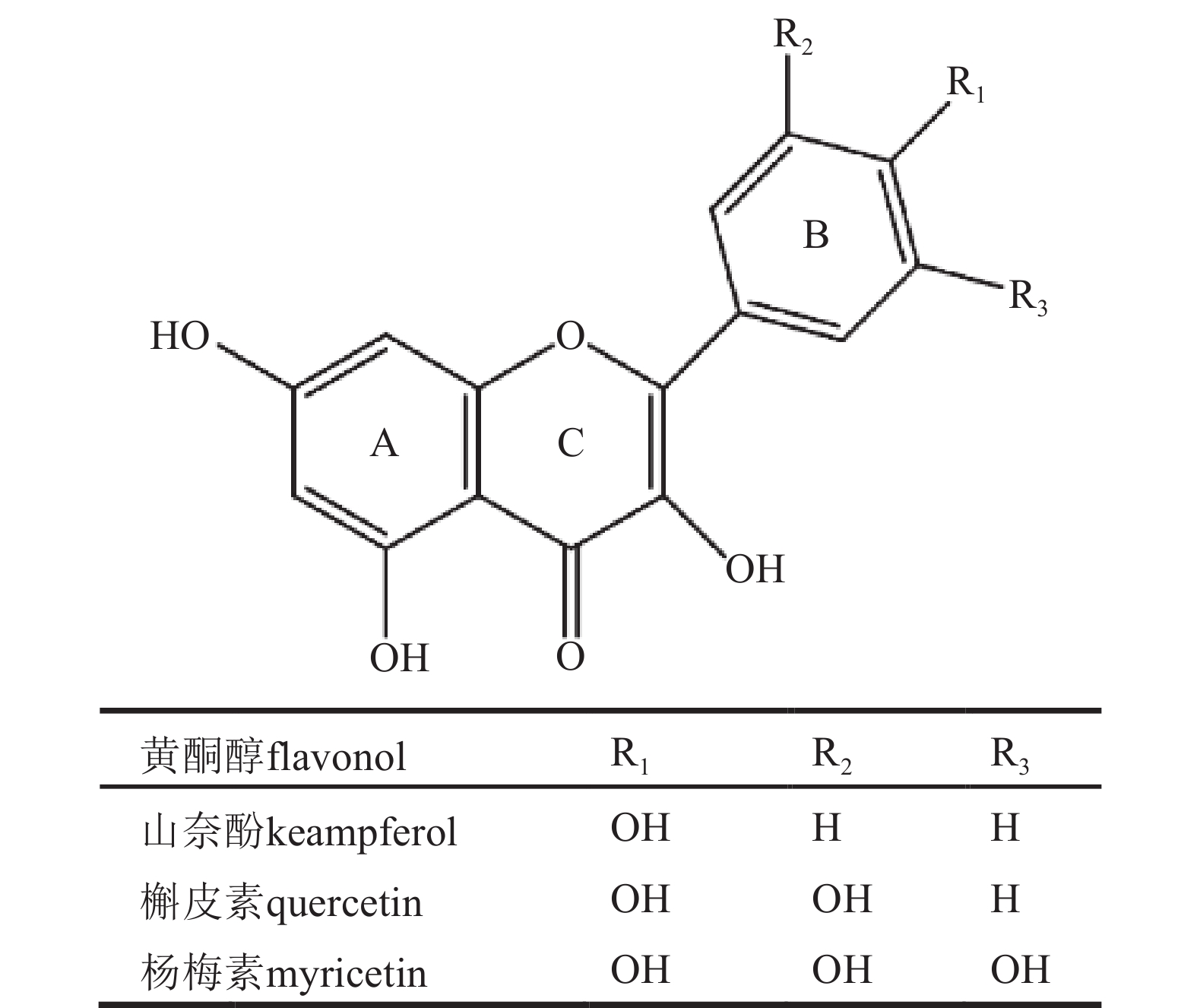
Flavonols are the most widely distributed and abundant flavonoids in the plant kingdom. They play crucial roles in plant growth and development, stress resistance, and adaptation to environmental challenges, while also possessing potent antioxidant properties that are of significant importance to human health. Given the multiple values of flavonols, elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of their biosynthetic pathways has become a research hotspot. As one of the largest families of transcription factors in plants, MYB transcription factors play a central regulatory role in the biosynthesis of flavonols. MYB can directly regulate downstream target genes, collaborate with bHLH and WD40 proteins to form MBW complexes for coordinated regulation, and integrate environmental signals such as light, temperature, and drought to achieve precise control of flavonol synthesis. This paper reviewed the physiological functions and biosynthetic pathways of flavonols, with a particular focus on the structural characteristics of MYB transcription factors and their molecular mechanisms in regulating flavonol synthesis, summarized key MYB transcription factor members involved in flavonol regulation across different species and their functions, while addressing the limitations of current research and outlining future directions, aiming to provide a theoretical basis for improving the nutritional value of crops and breeding new cultivars of flowers with novel colors. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 78 ref.]
Flavonols are the most widely distributed and abundant flavonoids in the plant kingdom. They play crucial roles in plant growth and development, stress resistance, and adaptation to environmental challenges, while also possessing potent antioxidant properties that are of significant importance to human health. Given the multiple values of flavonols, elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of their biosynthetic pathways has become a research hotspot. As one of the largest families of transcription factors in plants, MYB transcription factors play a central regulatory role in the biosynthesis of flavonols. MYB can directly regulate downstream target genes, collaborate with bHLH and WD40 proteins to form MBW complexes for coordinated regulation, and integrate environmental signals such as light, temperature, and drought to achieve precise control of flavonol synthesis. This paper reviewed the physiological functions and biosynthetic pathways of flavonols, with a particular focus on the structural characteristics of MYB transcription factors and their molecular mechanisms in regulating flavonol synthesis, summarized key MYB transcription factor members involved in flavonol regulation across different species and their functions, while addressing the limitations of current research and outlining future directions, aiming to provide a theoretical basis for improving the nutritional value of crops and breeding new cultivars of flowers with novel colors. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 78 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 922-933.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20240567
Abstract:
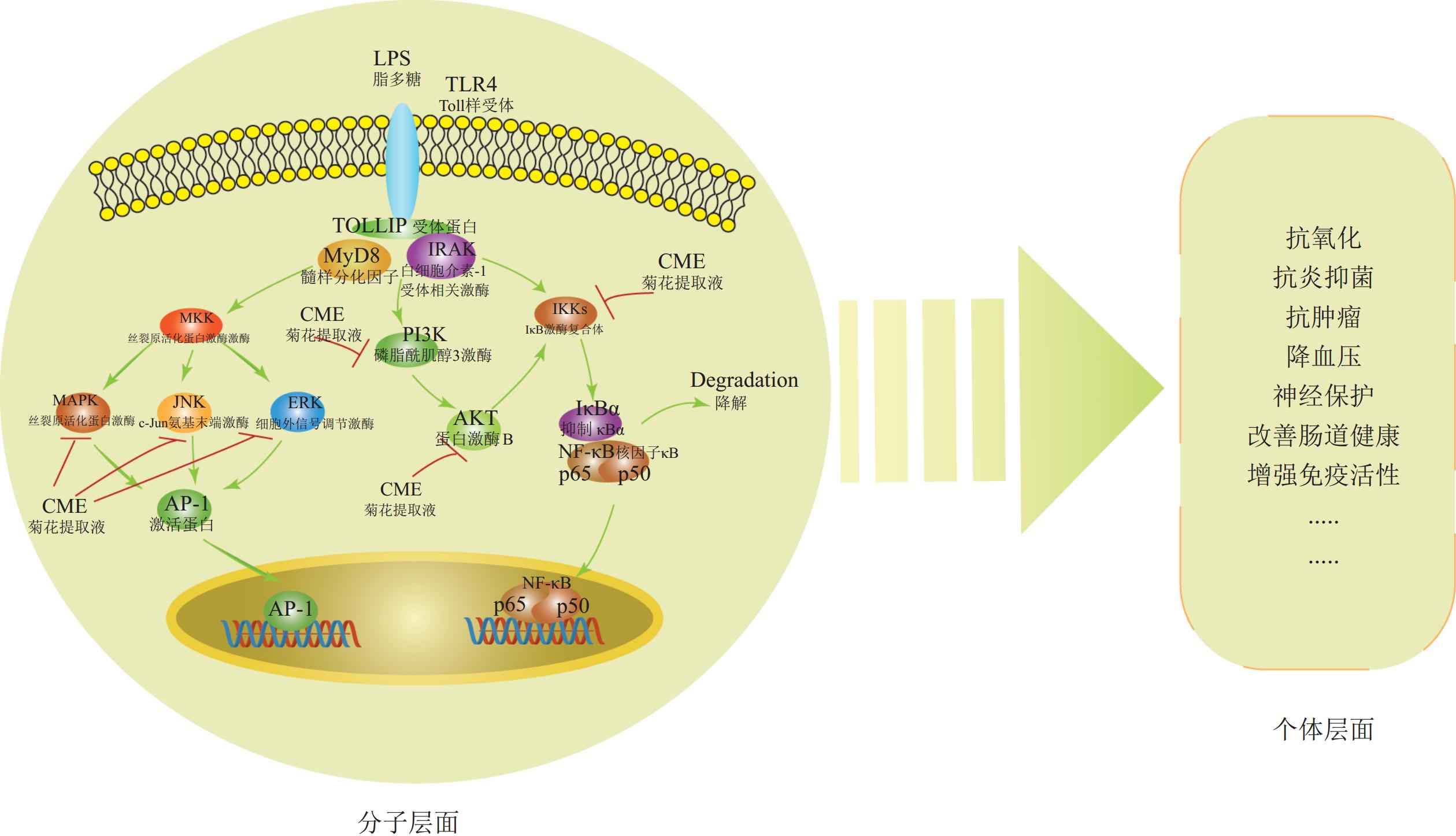
Chrysanthemum × morifolium, a plant with a long history of ornamental, edible, and medicinal uses, contains bioactive compounds with multiple functions, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumor properties. This article reviews the types and mechanisms of action of bioactive compounds in C. × morifolium, summarizes their biosynthetic pathways, and elucidates the regulatory mechanisms governing their synthesis. Chalcone synthase (CHS), chalcone isomerase (CHI), flavanone 3-hydroxylase (F3H), flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase (F3'H), flavone synthase (FNS), flavonol synthase (FLS), 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL), and UDP-glycosyltransferase (UGT) have been identified as key players in the synthesis of bioactive compounds. The biosynthesis is hierarchically regulated: transcription factor families such as MYB, bHLH, and AP2/ERF, modulate structural gene expression by binding to specific promoter elements. Additionally, miRNAs affect the synthesis of these compounds by targeting crucial structural genes and transcription factors. Although many researches have been conducted on flavonoid structure and biosynthesis in C. × morifolium, studies on the synthesis mechanism of chlorogenic acid, an important pharmacological component, remain limited and require further exploration. Clarifying the global regulatory network of bioactive compound biosynthesis and the molecular crosstalk between secondary metabolic pathways will be crucial for developing sustainable and efficient synthesis strategies for C. × morifolium active compounds, thereby advancing the development of the C. × morifolium industry. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 81 ref.]
Chrysanthemum × morifolium, a plant with a long history of ornamental, edible, and medicinal uses, contains bioactive compounds with multiple functions, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumor properties. This article reviews the types and mechanisms of action of bioactive compounds in C. × morifolium, summarizes their biosynthetic pathways, and elucidates the regulatory mechanisms governing their synthesis. Chalcone synthase (CHS), chalcone isomerase (CHI), flavanone 3-hydroxylase (F3H), flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase (F3'H), flavone synthase (FNS), flavonol synthase (FLS), 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL), and UDP-glycosyltransferase (UGT) have been identified as key players in the synthesis of bioactive compounds. The biosynthesis is hierarchically regulated: transcription factor families such as MYB, bHLH, and AP2/ERF, modulate structural gene expression by binding to specific promoter elements. Additionally, miRNAs affect the synthesis of these compounds by targeting crucial structural genes and transcription factors. Although many researches have been conducted on flavonoid structure and biosynthesis in C. × morifolium, studies on the synthesis mechanism of chlorogenic acid, an important pharmacological component, remain limited and require further exploration. Clarifying the global regulatory network of bioactive compound biosynthesis and the molecular crosstalk between secondary metabolic pathways will be crucial for developing sustainable and efficient synthesis strategies for C. × morifolium active compounds, thereby advancing the development of the C. × morifolium industry. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 81 ref.]
2025, 42(5): 934-943.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20250422
Abstract:
The highly heterozygous genetic background of Lilium spp. (lily) leads to complex trait segregation and difficulties in fixing superior genotypes. Coupled with the long growth cycle and widespread interspecific and intergeneric incompatibility barriers in distant hybridization, the efficiency of traditional hybridization breeding methods in the genetic improvement of lilies is severely limited. Research on the isolation and culture of lily protoplasts can provide technical support for somatic hybridization breeding, bypassing the barriers of sexual reproduction and creating interspecific and even intergeneric somatic hybrids, thus opening up new approaches for the utilization of distant genetic resources. This review summarizes the research progress on the isolation and culture of lily protoplasts over the past few decades, mainly focusing on the following aspects: (1) Factors affecting the isolation and purification of lily protoplasts, including tissue sources for protoplast isolation, pretreatment of isolation materials, enzymatic digestion conditions of protoplasts, osmotic pressure and pH of the digestion solution, and purification methods of protoplasts; (2) Factors influencing the cultivation of lily protoplasts, including composition of the protoplast culture medium, methods of protoplast culture, and density of protoplast culture; (3) Domestic and international cases of lily protoplast regeneration and analysis. Currently, the establishment of isolation and purification systems for lily protoplasts is relatively mature, but there are limited cases of complete plant regeneration from protoplast culture, and there are still significant bottlenecks in the establishment of regeneration systems. Future research should focus on systematically optimizing lily protoplast culture conditions, including the type of culture medium, carbon source types, and combinations and ratios of plant growth regulators. On the basis of establishing a stable and efficient regeneration system, the excellent traits of distant species can be introduced into cultivated varieties through protoplast fusion technology. At the same time, the mechanisms of regeneration and stable inheritance should be analyzed and applied to somatic hybridization, gene editing, and other breeding technologies. [Ch, 1 tab. 59 ref.]
The highly heterozygous genetic background of Lilium spp. (lily) leads to complex trait segregation and difficulties in fixing superior genotypes. Coupled with the long growth cycle and widespread interspecific and intergeneric incompatibility barriers in distant hybridization, the efficiency of traditional hybridization breeding methods in the genetic improvement of lilies is severely limited. Research on the isolation and culture of lily protoplasts can provide technical support for somatic hybridization breeding, bypassing the barriers of sexual reproduction and creating interspecific and even intergeneric somatic hybrids, thus opening up new approaches for the utilization of distant genetic resources. This review summarizes the research progress on the isolation and culture of lily protoplasts over the past few decades, mainly focusing on the following aspects: (1) Factors affecting the isolation and purification of lily protoplasts, including tissue sources for protoplast isolation, pretreatment of isolation materials, enzymatic digestion conditions of protoplasts, osmotic pressure and pH of the digestion solution, and purification methods of protoplasts; (2) Factors influencing the cultivation of lily protoplasts, including composition of the protoplast culture medium, methods of protoplast culture, and density of protoplast culture; (3) Domestic and international cases of lily protoplast regeneration and analysis. Currently, the establishment of isolation and purification systems for lily protoplasts is relatively mature, but there are limited cases of complete plant regeneration from protoplast culture, and there are still significant bottlenecks in the establishment of regeneration systems. Future research should focus on systematically optimizing lily protoplast culture conditions, including the type of culture medium, carbon source types, and combinations and ratios of plant growth regulators. On the basis of establishing a stable and efficient regeneration system, the excellent traits of distant species can be introduced into cultivated varieties through protoplast fusion technology. At the same time, the mechanisms of regeneration and stable inheritance should be analyzed and applied to somatic hybridization, gene editing, and other breeding technologies. [Ch, 1 tab. 59 ref.]