2021 Vol. 38, No. 5
2021, 38(5): 883-895.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210118
Abstract:
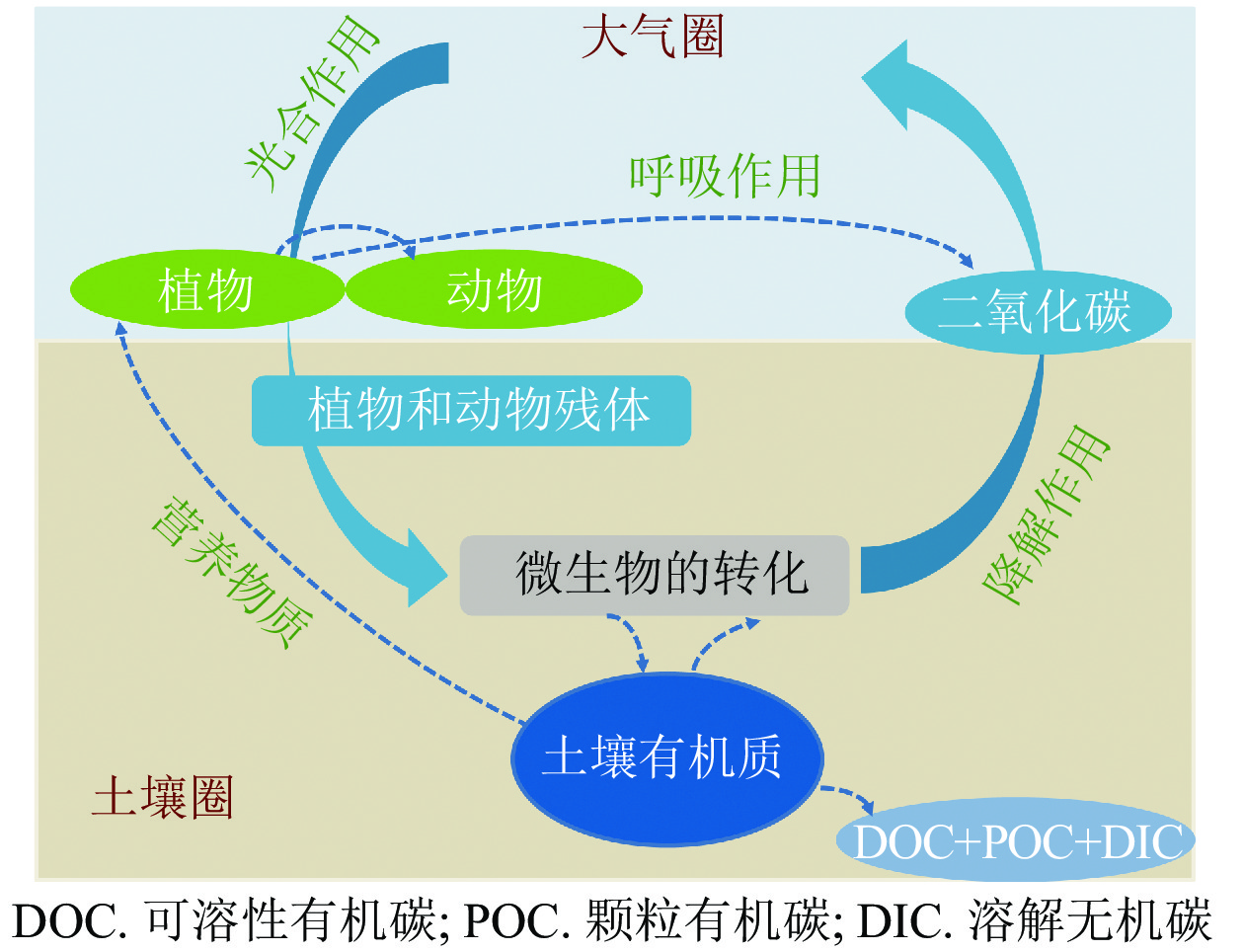
As one of the key processes controlling global carbon storage, carbon cycle in coastal wetland is a process significantly affected by nitrogen input due to the inshore water eutrophication. Given the fact that nitrogen input affects the carbon cycle of coastal wetland in a rather complex way, carbon cycle model has been selected as an effective method to clarify the process with the ultimate purpose to evaluate the carbon storage function of coastal wetland under the global climate change. With an review conducted of the migration and transformation of carbon components in coastal wetlands at different interfaces of atmosphere, vegetation, water and soil and a summary made of the regulations of the response of carbon cycle on nitrogen, it was found that carbon storage and flux is affected by multiple factors. Also, on this basis, carbon cycle models with carbon, nitrogen and water related modules were introduced along with the efforts made to promote their adaptability to wetlands and their application on wetlands, which shall provide reference for the employment of the model in the description of the carbon exchange in coastal wetland under the influence of nitrogen input. Finally, it was concluded that, to further develop the model, closer attention should be focused on the tidal process with nitrogen input and the promotion of model simulation accuracy. [Ch, 1 fig. 1 tab. 126 ref.]
As one of the key processes controlling global carbon storage, carbon cycle in coastal wetland is a process significantly affected by nitrogen input due to the inshore water eutrophication. Given the fact that nitrogen input affects the carbon cycle of coastal wetland in a rather complex way, carbon cycle model has been selected as an effective method to clarify the process with the ultimate purpose to evaluate the carbon storage function of coastal wetland under the global climate change. With an review conducted of the migration and transformation of carbon components in coastal wetlands at different interfaces of atmosphere, vegetation, water and soil and a summary made of the regulations of the response of carbon cycle on nitrogen, it was found that carbon storage and flux is affected by multiple factors. Also, on this basis, carbon cycle models with carbon, nitrogen and water related modules were introduced along with the efforts made to promote their adaptability to wetlands and their application on wetlands, which shall provide reference for the employment of the model in the description of the carbon exchange in coastal wetland under the influence of nitrogen input. Finally, it was concluded that, to further develop the model, closer attention should be focused on the tidal process with nitrogen input and the promotion of model simulation accuracy. [Ch, 1 fig. 1 tab. 126 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 896-905.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200624
Abstract:
Objective Soil moisture variations can affect microbial-mediated N transformation. The purpose of this study is to determine the gross transformation rate of soil N, and explore the dynamic change of N in soil and the response mechanism of N transformation to soil water change. Method By using 15N paired labeling technique and a numerical optimization model, the gross conversation rates of the main N transformation processes including organic N mineralization, \begin{document}${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}${\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
Result The responses of different types of soil N transformation to moisture change varied substantially. With the increase of soil moisture (from 20% to 100% water holding capacity), the gross mineralization rate of labile organic N (\begin{document}$M_{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{lab}}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$M_{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{rec}}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$M_{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{lab}}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$M_{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{rec}}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$O_{{\rm{NH}}_{4}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$O_{{\rm{N}}_{{\rm{rec}}}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$O_{{\rm{N}}_{{\rm{rec}}}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$O_{{\rm{NH}}_{4}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$O_{{\rm{NH}}_{4}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$O_{{\rm{N}}_{{\rm{rec}}}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}${\rm{NH}}_4^{+} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$I_{{\rm{NH}}_{4}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$ {\rm{NO}}_3^{-} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$C_{{\rm{NO}}_{3}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$I_{{\rm{NH}}_{4}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
\begin{document}$C_{{\rm{NO}}_{3}} $\end{document} ![]()
![]()
Conclusion Different types of inorganic nitrogen production and consumption have different responses to water change in red soil. The availability of nitrogen in red soil could be improved by increasing soil water content appropriately. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 48 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 906-915.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210458
Abstract:
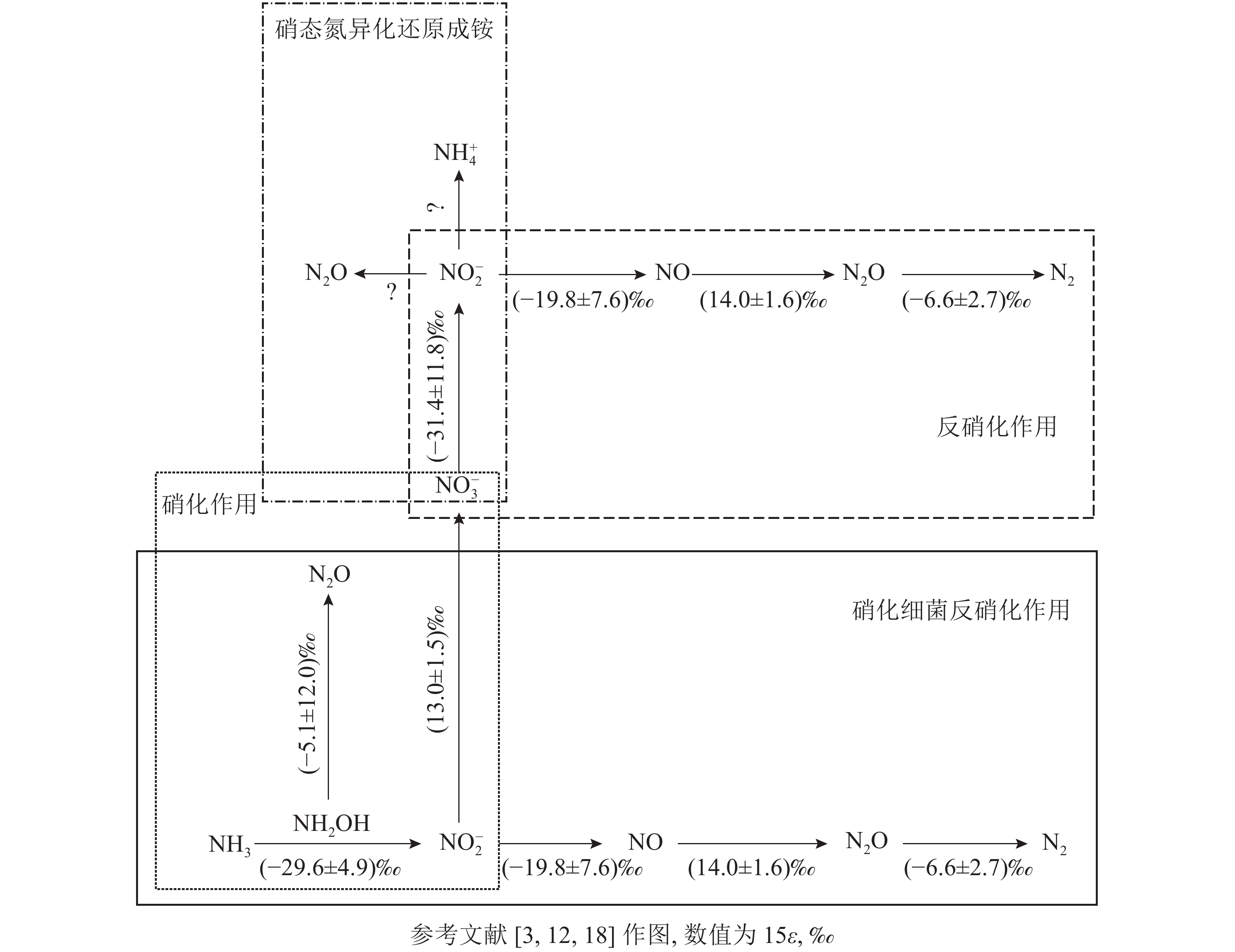
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is one of the potent greenhouse gases and also plays an important role in ozone layer decomposition. N2O production and emission processes in soil are complexed. Therefore, accurate source partitioning will help to constrain emission budgets. The application of stable isotope natural abundance technique have stimulated significant progress in N2O source partitioning and promoted identification in various N2O microbial production processes, which make use of various N2O isotope signatures δ15Nbulk(the average of15N), δ18O(the average of 18O) and δ15Nsp(site preference of 15N in different positions of N2O molecule). However, some factors also add uncertainties to N2O source partitioning, such as the range of isotope signatures, changes of isotope composition, and various fractionation factors associated with N2O reduction. It is also noteworthy that microbial processes and related isotopic effects are critical. In this review, the isotopic effects during N2O production and reduction and related factors are summarized; advances in approaches for N2O source-partitioning are concluded, including isotope natural abundance and isotopomer methods. The review focused on the progress of isotopic signatures δ15Nbulk, δ18O and δ15Nsp value in constraing N2O sources. In the future, the measurement of isotope fractionation, a combination of isotope signatures and advanced methodologies are advised for better studying N2O sources and pathways. [Ch, 2 fig. 80 ref.]
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is one of the potent greenhouse gases and also plays an important role in ozone layer decomposition. N2O production and emission processes in soil are complexed. Therefore, accurate source partitioning will help to constrain emission budgets. The application of stable isotope natural abundance technique have stimulated significant progress in N2O source partitioning and promoted identification in various N2O microbial production processes, which make use of various N2O isotope signatures δ15Nbulk(the average of15N), δ18O(the average of 18O) and δ15Nsp(site preference of 15N in different positions of N2O molecule). However, some factors also add uncertainties to N2O source partitioning, such as the range of isotope signatures, changes of isotope composition, and various fractionation factors associated with N2O reduction. It is also noteworthy that microbial processes and related isotopic effects are critical. In this review, the isotopic effects during N2O production and reduction and related factors are summarized; advances in approaches for N2O source-partitioning are concluded, including isotope natural abundance and isotopomer methods. The review focused on the progress of isotopic signatures δ15Nbulk, δ18O and δ15Nsp value in constraing N2O sources. In the future, the measurement of isotope fractionation, a combination of isotope signatures and advanced methodologies are advised for better studying N2O sources and pathways. [Ch, 2 fig. 80 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 916-925.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210293
Abstract:
Global climate change accelerates plant growth and biomass accumulation, and nitrogen has become one of main limiting factors for primary productivity in forest ecosystems. The microbial process mediated by root exudates in rhizosphere is of great significance in driving soil nutrient cycle and increasing nitrogen availability. This study reviewed the effects and mechanisms of simulated root exudates input on soil nitrogen mineralization, nitrification, and denitrification. It was found that organic acids, sugars, and amino acids in root exudates accelerated the decomposition of organic matter and nitrogen mineralization, which partly alleviated the demand of plants for nitrogen. Root exudates inputs with different carbon content and C/N ratio drove rhizosphere microorganisms to exercise different nutrient utilization strategies. Through biological and abiotic effects, root exudates mineralized nitrogen in organic matter and supplied it to plants for absorption and utilization. Biological nitrification inhibitors in root exudates inhibited soil nitrification and reduced nitrogen leaching. Root exudates also promoted soil denitrification by controlling the denitrifying bacterial community in the rhizosphere. In conclusion, plants can improve underground carbon distribution and affect nitrogen transformation in rhizosphere soil by increasing the input of root exudates, which is vital for maintaining nitrogen cycle and alleviating nutrient limitation. [Ch, 2 tab. 70 ref.]
Global climate change accelerates plant growth and biomass accumulation, and nitrogen has become one of main limiting factors for primary productivity in forest ecosystems. The microbial process mediated by root exudates in rhizosphere is of great significance in driving soil nutrient cycle and increasing nitrogen availability. This study reviewed the effects and mechanisms of simulated root exudates input on soil nitrogen mineralization, nitrification, and denitrification. It was found that organic acids, sugars, and amino acids in root exudates accelerated the decomposition of organic matter and nitrogen mineralization, which partly alleviated the demand of plants for nitrogen. Root exudates inputs with different carbon content and C/N ratio drove rhizosphere microorganisms to exercise different nutrient utilization strategies. Through biological and abiotic effects, root exudates mineralized nitrogen in organic matter and supplied it to plants for absorption and utilization. Biological nitrification inhibitors in root exudates inhibited soil nitrification and reduced nitrogen leaching. Root exudates also promoted soil denitrification by controlling the denitrifying bacterial community in the rhizosphere. In conclusion, plants can improve underground carbon distribution and affect nitrogen transformation in rhizosphere soil by increasing the input of root exudates, which is vital for maintaining nitrogen cycle and alleviating nutrient limitation. [Ch, 2 tab. 70 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 926-936.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200549
Abstract:
The sustainability and uncertainty of global climate warming have a profound impact on the sustainable development of human society. The continuous increase of atmospheric N2O concentration is one of the major contributions to the global climate warming. Soil is an important site of nitrogen transformation and a biochemical reaction reservoir of the nitrogen cycle, and also an important source of N2O emissions. Therefore, changes in soil N2O emission rate will significantly affect atmospheric N2O concentration. Biochar refers to the aromatic chemicals prepared by pyrolysis of biomass under the condition of complete or partial hypoxia. Biochar has the characteristics of porosity, strong adsorption, chemical stability, high pH and large cation exchange capacity. After it is applied to soils, biochar will directly or indirectly affect the transformation process of soil nitrogen and significantly affect the soil N2O emissions. This article reviewed the research progress of biochar effects on nitrogen transformation and N2O emission in the soil ecosystem, elaborated the effects of biochar input on the dynamic changes of soil inorganic nitrogen, nitrification, denitrification and N2O emission. Futher, in terms of biochar’s absorption and reduction of nitrogen leaching, effects on soil physicochemical properties, abundance and diversity of soil ammonia oxidizing bacterial, along with functional genes of denitrifying bacteria, the machamnisms influencing the processes above-mentioned are specifically elucidated in details. The future research of biochar in increasing soil sinks, reducing emissions and mitigating the greenhouse effect, as well as the related technology promotion, have been prospected. [Ch, 109 ref.]
The sustainability and uncertainty of global climate warming have a profound impact on the sustainable development of human society. The continuous increase of atmospheric N2O concentration is one of the major contributions to the global climate warming. Soil is an important site of nitrogen transformation and a biochemical reaction reservoir of the nitrogen cycle, and also an important source of N2O emissions. Therefore, changes in soil N2O emission rate will significantly affect atmospheric N2O concentration. Biochar refers to the aromatic chemicals prepared by pyrolysis of biomass under the condition of complete or partial hypoxia. Biochar has the characteristics of porosity, strong adsorption, chemical stability, high pH and large cation exchange capacity. After it is applied to soils, biochar will directly or indirectly affect the transformation process of soil nitrogen and significantly affect the soil N2O emissions. This article reviewed the research progress of biochar effects on nitrogen transformation and N2O emission in the soil ecosystem, elaborated the effects of biochar input on the dynamic changes of soil inorganic nitrogen, nitrification, denitrification and N2O emission. Futher, in terms of biochar’s absorption and reduction of nitrogen leaching, effects on soil physicochemical properties, abundance and diversity of soil ammonia oxidizing bacterial, along with functional genes of denitrifying bacteria, the machamnisms influencing the processes above-mentioned are specifically elucidated in details. The future research of biochar in increasing soil sinks, reducing emissions and mitigating the greenhouse effect, as well as the related technology promotion, have been prospected. [Ch, 109 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 937-944.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210411
Abstract:
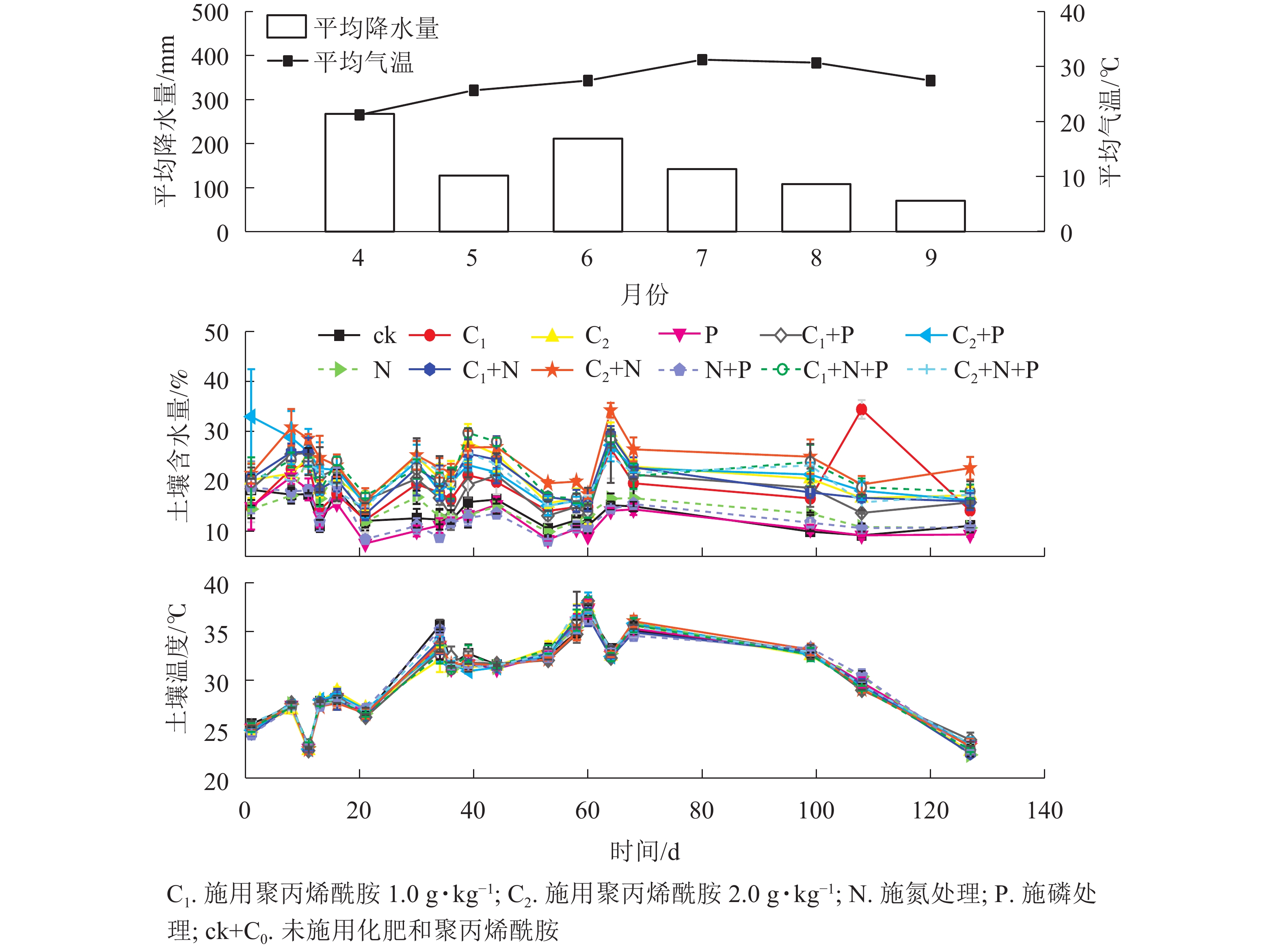
Objective The application of chemical fertilizer accelerates soil nitrous oxide (N2O) emission and intensifies global climate change. Soil moisture content is a key factor affecting soil N2O emission in arid and uneven rainfall distribution areas, so the application of water retaining agent (such as polyacrylamide) affects soil N2O emission. The purpose of this study is to explore the effect of polyacrylamid on soil N2O emission under the application of N and P fertilizer. Method Taking Camellia oleifera forest soil as the research object, different treatments were set, including different fertilizer additions (N, P, N+P, ck), different polyacrylamide dosage (C0: 0 g·kg−1, C1: 1.0 g·kg−1, C2: 2.0 g·kg−1) and their interaction. The soil N2O emission during the growth of C. oleifera seedlings was determined by static chamber gas chromatography. Result (1) The application of polyacrylamide significantly increased the soil moisture content of C. oleifera (P<0.05), which increased with the increase of the application amount. Compared with C0, the soil moisture content of C1 and C2 increased by 47.1% and 57.4% respectively, but the application of polyacrylamide did not promote soil N2O emission (F=2.75, P>0.05). (2) The application of P fertilizer significantly increased the cumulative soil N2O emission (P<0.05), which increased by 13.3% compared with ck. (3) Compared with the soil supplemented only with polyacrylamide, the N2O emission fluxes of soil treated with 1.0 g·kg−1 polyacrylamide and N, P, N+P fertilizer increased significantly by 56.0%, 61.7%, and 40.7%, respectively (P<0.05). The N2O emission fluxes of soil treated with 2.0 g·kg−1 polyacrylamide and P, N+P fertilizer increased significantly by 38.7% and 58.1%, respectively. Conclusion The application of polyacrylamide in C.oleifera soil can effectively improve soil water holding capacity, but will not promote soil N2O emission, which is conducive to the development of efficient water-saving forestry and the mitigation of global climate change. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 35 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 945-952.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210403
Abstract:
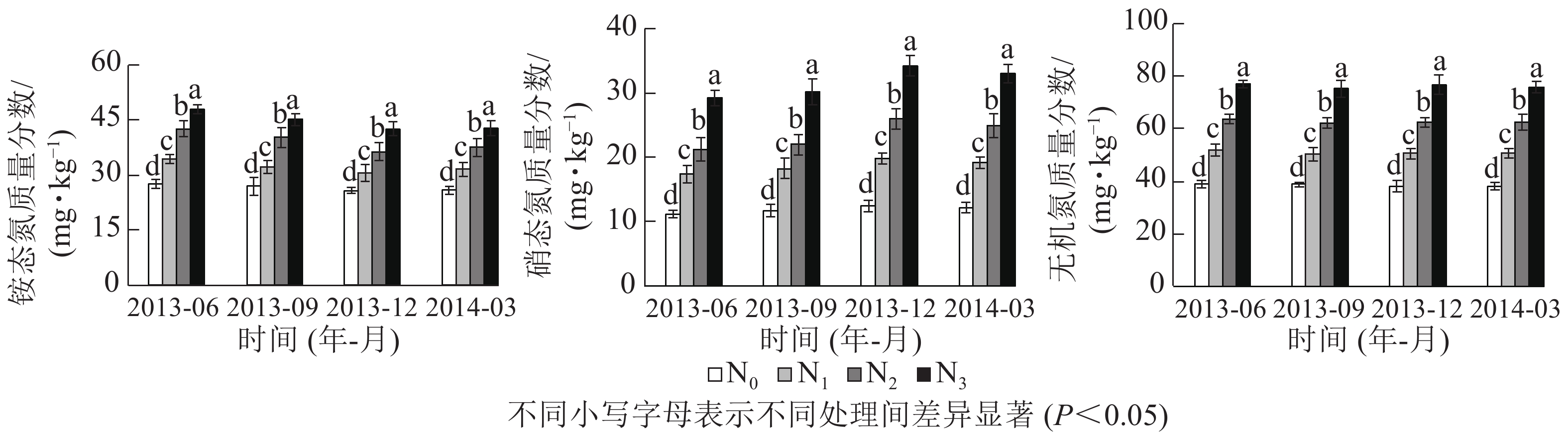
Objective With an experiment conducted Guanzhuang National Forestry Farm, Sha County, Sanming City of Fujian Province, this study is aimed to investigate the effects of long-term nitrogen (N) deposition and seasonal change on inorganic N and N transformation rates in the Method Besides a long-term (10-year-long) N addition experiment with four gradients (control: N0, low: N1, medium: N2, high: N3), the cultivation experiment in situ was conducted to determinate the N mineralization, nitrification and leaching rates in response to N addition. Result (1) N addition significantly increased the mass fractions of ammonium N (NH4 +-N), nitrate N (NO3 −-N) and total inorganic N, showing the trend of N3, N2, N1 and N0, and the ammonium N was higher than nitrate N. (2) N transformation rates increased with the N addition gradients, while high N addition significantly promoted the N transformation rates. (3) Seasonal changes significantly affected N transformation rates, and the N mineralization, nitrification and leaching rates were higher in summer and lower in winter. Conclusion N addition significantly increased soil inorganic N and N transformation rates whereas soil pH, C/N ratio and temperature may be the factors of N addition driving soil inorganic N and N transformation rates in the C. lanceolata plantation
2021, 38(5): 953-962.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210531
Abstract:
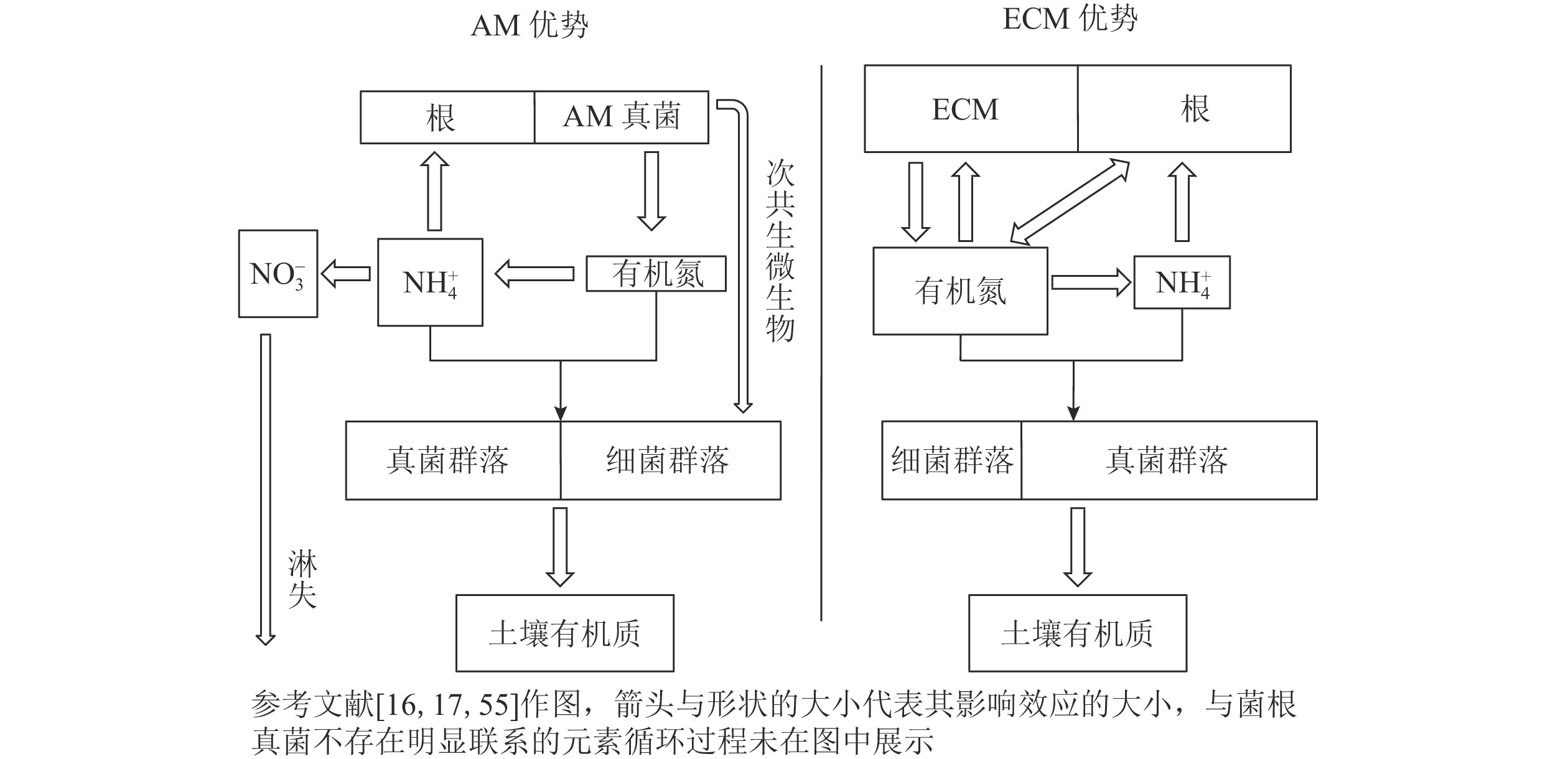
Mycorrhiza is a bridge between plants and soil in terrestrial ecosystems, and acts on soil carbon cycling by affecting litter decomposition, soil aggregation, and root exudates. Different types of mycorrhiza have different physiological functions, among which ectomycorrhiza (ECM) and arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) are the most widely distributed mycorrhizal types. Previous studies showed that different mycorrhizal types affected soil organic carbon input through the distribution of host photosynthetic products. The stability of soil organic carbon was affected by the differences of metabolites and winding action, and the soil organic carbon mineralization was affected by regulating the litter decomposition characteristics and interrelationship between mycorrhizae and microbe. In order to understand how ECM and AM affect soil carbon cycling and its key regulatory factors, this study reviewed the effects of different types of mycorrhiza on soil carbon cycling from four aspects and discussed the influence mechanisms: differences in the distribution process of photosynthetic products such as providing carbon and litter quantity to mycorrhizae, carbon sink functions of different mycorrhizal types and the impacts on soil aggregation, differences in soil organic carbon mineralization such as litter decomposition, priming effect and soil respiration in different dominant mycorrhizal ecosystems, and different accumulation capacity for soil carbon and corresponding microbial communities in different dominant mycorrhizal ecosystems. Finally, the future research direction is proposed, aiming to provide theoretical basis for how to enhance the carbon sink functions of ecosystems by relying on mycorrhiza in the context of “carbon neutrality”. [Ch, 2 fig. 94 ref.]
Mycorrhiza is a bridge between plants and soil in terrestrial ecosystems, and acts on soil carbon cycling by affecting litter decomposition, soil aggregation, and root exudates. Different types of mycorrhiza have different physiological functions, among which ectomycorrhiza (ECM) and arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) are the most widely distributed mycorrhizal types. Previous studies showed that different mycorrhizal types affected soil organic carbon input through the distribution of host photosynthetic products. The stability of soil organic carbon was affected by the differences of metabolites and winding action, and the soil organic carbon mineralization was affected by regulating the litter decomposition characteristics and interrelationship between mycorrhizae and microbe. In order to understand how ECM and AM affect soil carbon cycling and its key regulatory factors, this study reviewed the effects of different types of mycorrhiza on soil carbon cycling from four aspects and discussed the influence mechanisms: differences in the distribution process of photosynthetic products such as providing carbon and litter quantity to mycorrhizae, carbon sink functions of different mycorrhizal types and the impacts on soil aggregation, differences in soil organic carbon mineralization such as litter decomposition, priming effect and soil respiration in different dominant mycorrhizal ecosystems, and different accumulation capacity for soil carbon and corresponding microbial communities in different dominant mycorrhizal ecosystems. Finally, the future research direction is proposed, aiming to provide theoretical basis for how to enhance the carbon sink functions of ecosystems by relying on mycorrhiza in the context of “carbon neutrality”. [Ch, 2 fig. 94 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 963-972.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200502
Abstract:
The fast development of the industry has been accompanied with a significant increase of the global atmospheric CO2, which will affect the transformation and renewal of soil organic carbon (SOC), and then its stability. Therefore, an exploration of the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on SOC stability is not only an important attempt to evaluate the feedback effect of terrestrial ecosystem on climate change, but also of great significance to the effective storage of element C in soil and the sustainability of soil fertility. With an overview of previous researches, this study is aimed at a summary of the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on SOC stability and its stability indexes (biological index, chemical index, other index, etc.), the interaction between exogenous N and elevated atmospheric CO2 on SOC stability as well as the variation trend of SOC stability over time. The results showed that elevated atmospheric CO2 resulted in an increase in the proportion of labile organic carbon (readily oxidized carbon, particulate organic carbon, dissolved organic carbon, etc.), and a decrease in SOC stability, especially in nitrogen limitation environment. It was also found, with a summary of the research findings in recent decades, that there was a gradual decrease in the SOC stability reduction rate with the increase of high CO2 treatment time, indicating that the soil itself is equipped with the capacity to adapt and recover on its own. In conclusion, given the the feedback effect of SOC stability variation on plant physiology and growth, future researches on the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on SOC stability should be focused on promoting the sustainability of soil fertility in farmland ecosystem and increasing crop production and productivity. [Ch, 1 fig. 74 ref.]
The fast development of the industry has been accompanied with a significant increase of the global atmospheric CO2, which will affect the transformation and renewal of soil organic carbon (SOC), and then its stability. Therefore, an exploration of the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on SOC stability is not only an important attempt to evaluate the feedback effect of terrestrial ecosystem on climate change, but also of great significance to the effective storage of element C in soil and the sustainability of soil fertility. With an overview of previous researches, this study is aimed at a summary of the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on SOC stability and its stability indexes (biological index, chemical index, other index, etc.), the interaction between exogenous N and elevated atmospheric CO2 on SOC stability as well as the variation trend of SOC stability over time. The results showed that elevated atmospheric CO2 resulted in an increase in the proportion of labile organic carbon (readily oxidized carbon, particulate organic carbon, dissolved organic carbon, etc.), and a decrease in SOC stability, especially in nitrogen limitation environment. It was also found, with a summary of the research findings in recent decades, that there was a gradual decrease in the SOC stability reduction rate with the increase of high CO2 treatment time, indicating that the soil itself is equipped with the capacity to adapt and recover on its own. In conclusion, given the the feedback effect of SOC stability variation on plant physiology and growth, future researches on the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on SOC stability should be focused on promoting the sustainability of soil fertility in farmland ecosystem and increasing crop production and productivity. [Ch, 1 fig. 74 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 973-984.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200598
Abstract:
As an important part of soil carbon pool, the stability, growth or attenuation of soil organic carbon are closely related to the change of atmospheric CO2 concentration. Soil microorganisms, an indispensable part of forest ecosystem, participate in the decomposition of organic matter and the transformation of soil matter and play an important role in maintaining soil quality. The relationship between soil organic carbon and microbial characteristics is extremely close. In recent years, the research on soil in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation in China has mainly focused on litter decomposition, soil nutrient turnover, soil microbial characteristics and so on. With the wide application of high-throughput sequencing technology, the research on soil organic carbon and microbial characteristics of C. lanceolata plantation has made a lot of important progress. In this study, the research progress on pool characteristics, activity, and stability of soil organic carbon as well as community structure and diversity of soil microorganisms and their influencing factors in C. lanceolata plantation were reviewed, and the future research direction of soil organic carbon and soil microorganism in C. lanceolata plantation was put forward. [Ch, 79 ref.]
As an important part of soil carbon pool, the stability, growth or attenuation of soil organic carbon are closely related to the change of atmospheric CO2 concentration. Soil microorganisms, an indispensable part of forest ecosystem, participate in the decomposition of organic matter and the transformation of soil matter and play an important role in maintaining soil quality. The relationship between soil organic carbon and microbial characteristics is extremely close. In recent years, the research on soil in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation in China has mainly focused on litter decomposition, soil nutrient turnover, soil microbial characteristics and so on. With the wide application of high-throughput sequencing technology, the research on soil organic carbon and microbial characteristics of C. lanceolata plantation has made a lot of important progress. In this study, the research progress on pool characteristics, activity, and stability of soil organic carbon as well as community structure and diversity of soil microorganisms and their influencing factors in C. lanceolata plantation were reviewed, and the future research direction of soil organic carbon and soil microorganism in C. lanceolata plantation was put forward. [Ch, 79 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 985-999.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210133
Abstract:
Soil organic matter (SOM), an important component of ecosystems, plays an important role in the biogeochemical cycling of soil nutrients. However, it is difficult to analyze SOM chemistry due to its complexity and diversity resulting from microbial and physicochemical transformations of organic residues from plants, microorganisms and animals. Pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS) is a fast and reproducible technique to obtain qualitative and quantitative analysis of SOM chemistry, in which has been commonly used in recent years. This paper summarized the components and sources of SOM, accordingly, reviewed the literature which study on chemical composition of SOM with Py-GC/MS technology. The basic theoretical studies of SOM chemistry with Py-GC/MS technology mainly focus on: the chemical composition of SOM and precursor substances from which it is derived, the analysis of specific SOM chemical components, SOM responses to climate change and land use change, and the effects of SOM chemistry on soil processes and functions. The application of Py-GC/MS technology on SOM chemistry included: evaluating the stability of SOM, investigating the cycling of soil nutrition and the succession process of ecosystem. This study showed that: (1) There are some differences in SOM chemical composition among different ecosystems, because the accumulation of compounds from different plants and the mechanisms related to the chemical composition of initial litter can directly influenced the chemical composition of SOM; (2) The SOM chemical composition is closely related to the external environmental conditions and is the result of the comprehensive influence of several factors. For instance, climate is the most important factor that influenced the content and dynamic of SOM by affecting the distribution of vegetation, photosynthetic production and soil microbial activity. Besides, nitrogen deposition, land use change, wildfire and tillage pattern also can influence the contents and qualities of SOM. Overall, it is important to investigate the SOM-related ecological process and the mechanism of SOM response to climate change and human activities, from the perspective of the essence of SOM (chemical composition and structure) based on Py-GC/MS technology. [Ch, 1 fig. 107 ref.]
Soil organic matter (SOM), an important component of ecosystems, plays an important role in the biogeochemical cycling of soil nutrients. However, it is difficult to analyze SOM chemistry due to its complexity and diversity resulting from microbial and physicochemical transformations of organic residues from plants, microorganisms and animals. Pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS) is a fast and reproducible technique to obtain qualitative and quantitative analysis of SOM chemistry, in which has been commonly used in recent years. This paper summarized the components and sources of SOM, accordingly, reviewed the literature which study on chemical composition of SOM with Py-GC/MS technology. The basic theoretical studies of SOM chemistry with Py-GC/MS technology mainly focus on: the chemical composition of SOM and precursor substances from which it is derived, the analysis of specific SOM chemical components, SOM responses to climate change and land use change, and the effects of SOM chemistry on soil processes and functions. The application of Py-GC/MS technology on SOM chemistry included: evaluating the stability of SOM, investigating the cycling of soil nutrition and the succession process of ecosystem. This study showed that: (1) There are some differences in SOM chemical composition among different ecosystems, because the accumulation of compounds from different plants and the mechanisms related to the chemical composition of initial litter can directly influenced the chemical composition of SOM; (2) The SOM chemical composition is closely related to the external environmental conditions and is the result of the comprehensive influence of several factors. For instance, climate is the most important factor that influenced the content and dynamic of SOM by affecting the distribution of vegetation, photosynthetic production and soil microbial activity. Besides, nitrogen deposition, land use change, wildfire and tillage pattern also can influence the contents and qualities of SOM. Overall, it is important to investigate the SOM-related ecological process and the mechanism of SOM response to climate change and human activities, from the perspective of the essence of SOM (chemical composition and structure) based on Py-GC/MS technology. [Ch, 1 fig. 107 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 1000-1011.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210365
Abstract:
Logging, as one of the routine forest management activities, is an important human interference measure affecting forest soil respiration, an important source of atmospheric CO2. Therefore, research on the effects of logging on forest soil respiration has important scientific significance and application value for better understanding forest carbon cycle and coping with global climate change. This paper, with logging divided into two types: clear cutting and partial cutting (further classified as selective cutting, gradual cutting, thinning and regeneration cutting, etc.), is aimed to conduct a review of research advances on the effects of clear cutting and partial cutting on soil respiration, a discussion of the main mechanisms of clear cutting and partial cutting on soil respiration as well as a summary of the effects of current cutting on forest soil respiration and its components and soil temperature sensitivity (Q10) with future research prospects put forward. Results showed that the researches on soil respiration are mainly focused on the following aspects: (1) the direction and extent of the effect of clear cutting or cutting intensity on soil respiration; (2) the dynamic characteristics of soil respiration with time and environmental factors such as soil temperature after clear cutting or partial cutting; (3) effects of clear cutting or partial cutting on soil respiration components; (4) the effect of clear cutting or partial cutting on Q10 and (5) the effect mechanism of clear cutting or partial cutting on soil respiration. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) the effect of cutting varies with different cutting intensity, cutting measures, treatment of cutting residues, climate types, forest types and vegetation restoration time; (2) the results showed that the soil autotrophic respiration usually decreased and heterotrophic respiration usually increased after logging, and the total soil respiration showed that autotrophic respiration and heterotrophic respiration offset each other, and this effect would decrease with the increase of vegetation restoration. It is proposed that further efforts should be focused on the impact of different intensity of harvesting, different vegetation restoration stages, other forest management measures and rising atmospheric CO2 concentration on regional soil respiration and components, so as to better understand the impact mechanism of harvesting on forest ecosystem carbon cycle. [Ch, 2 tab. 89 ref.]
Logging, as one of the routine forest management activities, is an important human interference measure affecting forest soil respiration, an important source of atmospheric CO2. Therefore, research on the effects of logging on forest soil respiration has important scientific significance and application value for better understanding forest carbon cycle and coping with global climate change. This paper, with logging divided into two types: clear cutting and partial cutting (further classified as selective cutting, gradual cutting, thinning and regeneration cutting, etc.), is aimed to conduct a review of research advances on the effects of clear cutting and partial cutting on soil respiration, a discussion of the main mechanisms of clear cutting and partial cutting on soil respiration as well as a summary of the effects of current cutting on forest soil respiration and its components and soil temperature sensitivity (Q10) with future research prospects put forward. Results showed that the researches on soil respiration are mainly focused on the following aspects: (1) the direction and extent of the effect of clear cutting or cutting intensity on soil respiration; (2) the dynamic characteristics of soil respiration with time and environmental factors such as soil temperature after clear cutting or partial cutting; (3) effects of clear cutting or partial cutting on soil respiration components; (4) the effect of clear cutting or partial cutting on Q10 and (5) the effect mechanism of clear cutting or partial cutting on soil respiration. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) the effect of cutting varies with different cutting intensity, cutting measures, treatment of cutting residues, climate types, forest types and vegetation restoration time; (2) the results showed that the soil autotrophic respiration usually decreased and heterotrophic respiration usually increased after logging, and the total soil respiration showed that autotrophic respiration and heterotrophic respiration offset each other, and this effect would decrease with the increase of vegetation restoration. It is proposed that further efforts should be focused on the impact of different intensity of harvesting, different vegetation restoration stages, other forest management measures and rising atmospheric CO2 concentration on regional soil respiration and components, so as to better understand the impact mechanism of harvesting on forest ecosystem carbon cycle. [Ch, 2 tab. 89 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 1012-1022.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210186
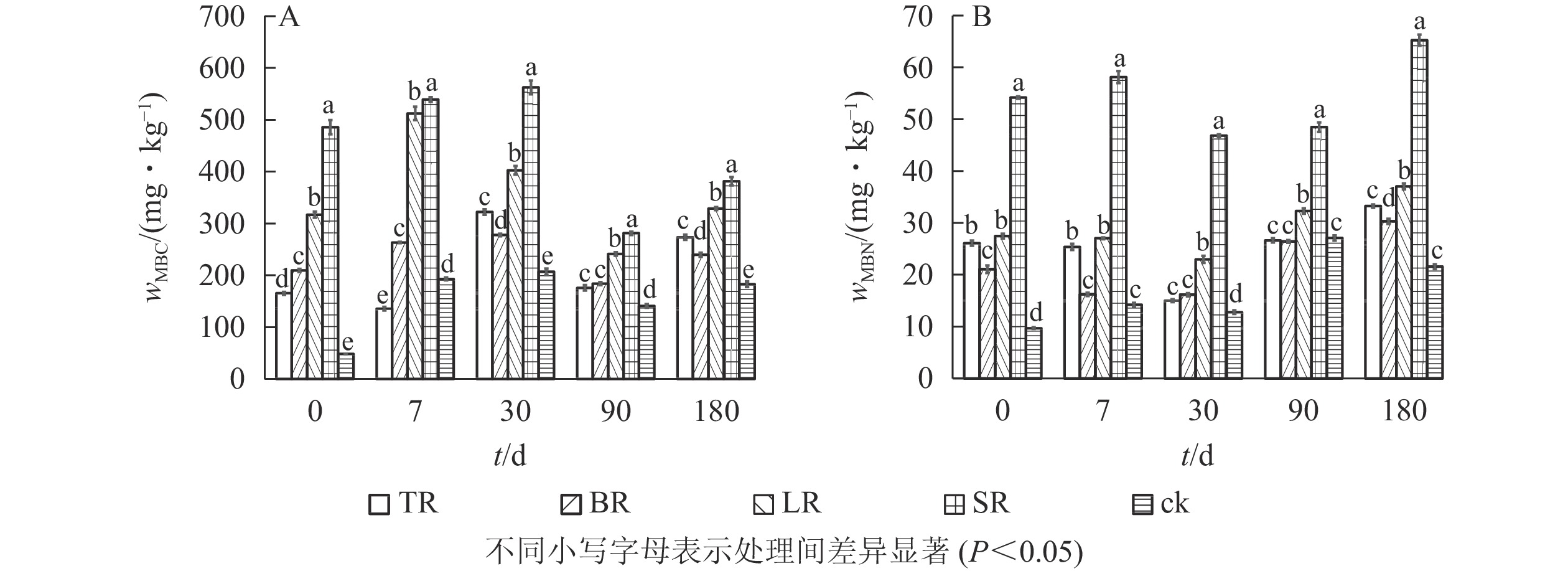
Abstract:
Objective Impacts of the addition of poplar harvesting residues on soil nutrients and CO2 emission were investigated in controlled conditions to provide a reference for its potential utilization. Method The indoor incubation experiment was carried out by selecting logging residues of twigs, barks, and leaves from a poplar plantation and the rice straw as research materials. Based on the litter amount in the unit area of the poplar plantation, the fresh soil equivalent to 100 g of dry soil weight and biomass materials equivalent to 2% of dry soil weight were mixed evenly. Then the mixed soils were loaded into a homemade polyethylene plastic box, and incubated in a constant temperature incubator at 25℃ for 180 days in darkness. During the culture period, the soil moisture content was controlled to 60% of the field moisture capacity. Dynamic variations in microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and nitrogen (MBN), inorganic nitrogen (NH4 +-N and NO3 −-N), available phosphorus (AP) and available potassium (AK) as well as CO2 in the soil were measured. Result (1) The addition of all four residue biomass significantly affected microbial biomass and nutrient availability in the soil (P<0.05). Compared with the control, the soil MBC contents treated by the residue biomass of poplar twigs, barks, leaves and straw increased by 50%, 31%, 80% and 109% respectively, while the soil MBN contents increased by 54%, 40%, 72% and 203%, respectively. The contents of NH4 +-N in the soil treated with bark and twigs residues were higher than those in the control and rice straw treatments, whereas the NO3 −-N content in the soil was in the order of control>rice straw>leaf residue>bark residue>twig residue treatments. The highest AP content was observed in the soil treated with twigs, while the AK content in the soil treated with rice straw was higher than that treated with other biomass residues. (2) After adding biomass residues into the soil, the daily release rate of CO2 from the soil showed a tendency with being relatively fast in the initial period, gradually slowing down in the middle stage, and tending to be stable in the later stage of the incubation. After 180 days of indoor incubation, the cumulative CO2 emission from the soil treated with rice straw was significantly higher than that of the other treatments (P<0.05), followed by the soil treated with poplar leaves. (3) Correlation analysis showed that microbial biomass, nutrient contents and CO2 daily release rate in the soil were obviously correlated to the properties of biomass residues. Of them, a significantly positive correlation of soil microbial biomass to the contents of total nitrogen, total phosphorus and total potassium but a significantly negative correlation to the total carbon content and C/N ratio in the biomass residues were detected (P<0.05). Meanwhile, the CO2 daily emission rate was positively correlated to the contents of MBC, MBN, NH4 +-N, AP and AK in the soil (P<0.05), whereas a significantly negative correlation of the CO2 daily emission rate to the contents of NO3 −-N was observed (P<0.01). Conclusion From the views of soil nutrients and environmental effects, application of poplar harvesting residues not only can increase the contents of soil available nutrients, but also relatively reduce carbon emissions compared with the rice straw. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 47 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 1023-1032.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210390
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to explore the vertical and temporal variation characteristics of soil organic carbon(SOC) content and storage in Pinus tabulaeformis forest, so as to provide a theoretical basis for soil carbon storage prediction and carbon sink management in P. tabulaeformis forest. Method Based on the literature data from 1980 to 2017, the characteristics of spatial and temporal variation for SOC content and storage in P. tabulaeformis forest under brown soil and cinnamon soil types were discussed using the methods of one-way ANOVA, multiple comparison, correlation analysis and path analysis, and the driving factors were analyzed combined with China’s forest management measures and growth characteristics of P. tabulaeformis in different periods. Result The change of SOC content and storage in P. tabulaeformis forest decreased significantly with the increase of soil depth (P<0.05), and 0−20 cm soil layer was the main contribution layer of carbon pool, accounting for 45%−50% of SOC storage in 0−60 cm soil layer. In the past 40 years, the content and storage of SOC showed the temporal variation characteristics of first decreasing and then increasing, among which 2000−2009 was the lowest, and then increased significantly, reaching the highest storage point of 247.02 Tg in 2017. Conclusion Soil bulk density, soil total nitrogen and stand canopy density are the main factors affecting the change of SOC content, and the profound effects of forest management and protection measures on the three factors are the important reasons for the significant temporal changes of SOC content and storage in P. tabulaeformis forest. [Ch, 3 fig. 5 tab. 49 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 1033-1039.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210500
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the change characteristics of soil organic carbon mass fraction and storage at 0−40 cm under different vegetation restoration measures in the environment of photovoltaic power station, so as to provide theoretical basis for the optimal allocation of ecological management mode of photovoltaic power station in arid area. Method Three artificial vegetation plots(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus, Medicago sativa) in the photovoltaic power station were selected as the research objects, and the natural vegetation plots undisturbed by power station construction were used as the control. Result After replanting, the soil organic carbon mass fraction and storage of P. sylvestris var. mongolica, A. membranaceus var. mongholicus and M. sativa were still significantly lower than those of the control (P<0.05). However, compared with the other two plots, the soil organic carbon mass fraction of P. sylvestris var. mongolica sample plot increased significantly by 4.99 and 6.80 g·kg−1, while the organic carbon storage increased significantly by 14.52 and 19.37 t·hm−2 (P<0.05). The mass fraction and storage of soil organic carbon in the study area decreased significantly with the increase of soil depth (P<0.05). Vegetation type, soil depth and their interaction significantly affected the organic carbon mass fraction in the study area. In addition, soil pH and electrical conductivity were also important indicators affecting the mass fraction and storage of organic carbon. Conclusion With the advancement of environmental governance in the power station, compared with herbages, P. sylvestris var. mongolicacan can be artificially planted in the photovoltaic power station to improve soil carbon sequestration and minimize human interference in the later stage, which is of great significance to improve regional ecological benefits. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 39 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 1040-1049.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200729
Abstract:
Large amounts of microplastics have been accumulated in soils and their degradation is relatively slow. The residual time of microplastics in soils could be extended to decades or even over a hundred years. Therefore, the ecological effects of long-term residual of the microplastics in soils has been of concerned widely in recent years. Published papers related to the microplastics and their effects in soils were collected and introduced in order to make a full review in the field. The research advances were presented based on the different ecological receptors, which included change of soil physical environment due to the accumulation of microplastics, ingestion of microplastics by invertebrates from soils and their effects on the enteric microorganism, response of soil microbial community and soil enzyme to microplastics pollution, plant uptake of microplastics and their effects. The studies of effects on soil physical environment in the present of microplastics mainly focus on soil density, soil aggregate composition and water hold capacity. Such effects were supposed to have further impacts on soil enzyme activity, microbial community composition and even plant growth based on current limited studies. Many other studies at present were also concentrated on the migration of microplastics induced by soil invertebrates e.g. earthworm, springtail. Meanwhile, microplastics in the soil might be ingested by soil invertebrates and subsequently caused some negative effects and influence on the gut microorganism community of the soil invertebrates. There were also some studies focusing on the microplastics accumulation through food chain regarding the effects of microplastics on soil animals. For example, microplastics might be accumulated in chicken through the predation of earthworm by chicken. After the introduction of current studies, several research proposal were put forward based on the complication of microplastic’s properties and the shortage of current researches. These proposal contained four aspects: (1) development of standard protocols for the study of ecotoxicology of soil microplastics pollution, (2) studying the interaction mechanism between microplastics and microorganisms, plants and invertebrates, (3) revealing microbiological mechanisms that regulation of the transformation of materials and microplastics in soils, (4) exploring plastishere in soils of different ecosystems. All these researches are expected to be supportive to assessment of the ecological effects of soil microplastics pollution. [Ch, 80 ref.]
Large amounts of microplastics have been accumulated in soils and their degradation is relatively slow. The residual time of microplastics in soils could be extended to decades or even over a hundred years. Therefore, the ecological effects of long-term residual of the microplastics in soils has been of concerned widely in recent years. Published papers related to the microplastics and their effects in soils were collected and introduced in order to make a full review in the field. The research advances were presented based on the different ecological receptors, which included change of soil physical environment due to the accumulation of microplastics, ingestion of microplastics by invertebrates from soils and their effects on the enteric microorganism, response of soil microbial community and soil enzyme to microplastics pollution, plant uptake of microplastics and their effects. The studies of effects on soil physical environment in the present of microplastics mainly focus on soil density, soil aggregate composition and water hold capacity. Such effects were supposed to have further impacts on soil enzyme activity, microbial community composition and even plant growth based on current limited studies. Many other studies at present were also concentrated on the migration of microplastics induced by soil invertebrates e.g. earthworm, springtail. Meanwhile, microplastics in the soil might be ingested by soil invertebrates and subsequently caused some negative effects and influence on the gut microorganism community of the soil invertebrates. There were also some studies focusing on the microplastics accumulation through food chain regarding the effects of microplastics on soil animals. For example, microplastics might be accumulated in chicken through the predation of earthworm by chicken. After the introduction of current studies, several research proposal were put forward based on the complication of microplastic’s properties and the shortage of current researches. These proposal contained four aspects: (1) development of standard protocols for the study of ecotoxicology of soil microplastics pollution, (2) studying the interaction mechanism between microplastics and microorganisms, plants and invertebrates, (3) revealing microbiological mechanisms that regulation of the transformation of materials and microplastics in soils, (4) exploring plastishere in soils of different ecosystems. All these researches are expected to be supportive to assessment of the ecological effects of soil microplastics pollution. [Ch, 80 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 1050-1057.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200761
Abstract:
Objective This objective is to investigate the contents and stoichiometric characteristics of soil organic C, total N and total P in Torreya grandis stands of different ages, so as to provide basic data for the management and protection of T. grandis. Method T. grandis of four different ages (0−100, 100−300, 300−500 and >500 a) were selected from Zhuji National Forest Park of T. grandis‘Merrilli’ in Zhejiang Province. Soil samples were collected from different soil layers (0−20, 20−40, 40−60 cm) to analyze the content and stoichiometric characteristics of soil C, N, and P in T. grandis stands of different ages. Result (1) The contents of soil organic C and total N at four ages were 10.90−24.22 and 1.22−2.22 g·kg−1 respectively, which increased first and then decreased with forest age, but without significant differences. The contents of soil total P ranged from 0.24 to 0.80 g·kg−1, which decreased first and then increased with forest age, but the differences were not significant(P>0.05). (2) The average values of soil C∶N and N∶P at four ages were 8.59−10.89 and 3.06−6.16 respectively, which increased first and then decreased with forest age, but the differences were not significant(P>0.05). The soil C∶P ratio was 31.54−63.72 at different forest ages, which showed a trend of decreasing first and then increasing with age, and the C∶P ratio of some forest ages had significant differences(P<0.05). (3) There was a significant positive correlation between soil C, N, and P contents at different forest ages, and extremely significant positive correlation between C and N (P<0.01). There was a significant negative correlation between P and C∶P ratio, P and N∶P ratio, and an extremely significant positive correlation between C∶P ratio and N∶P ratio(P<0.01). Conclusion The growth of T. grandis is mainly limited by soil P. Therefore, reasonable addition of P fertilization can be considered to improve soil fertility and nutrient cycling between plant and soil. [Ch, 4 tab. 34 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 1058-1065.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210211
Abstract:
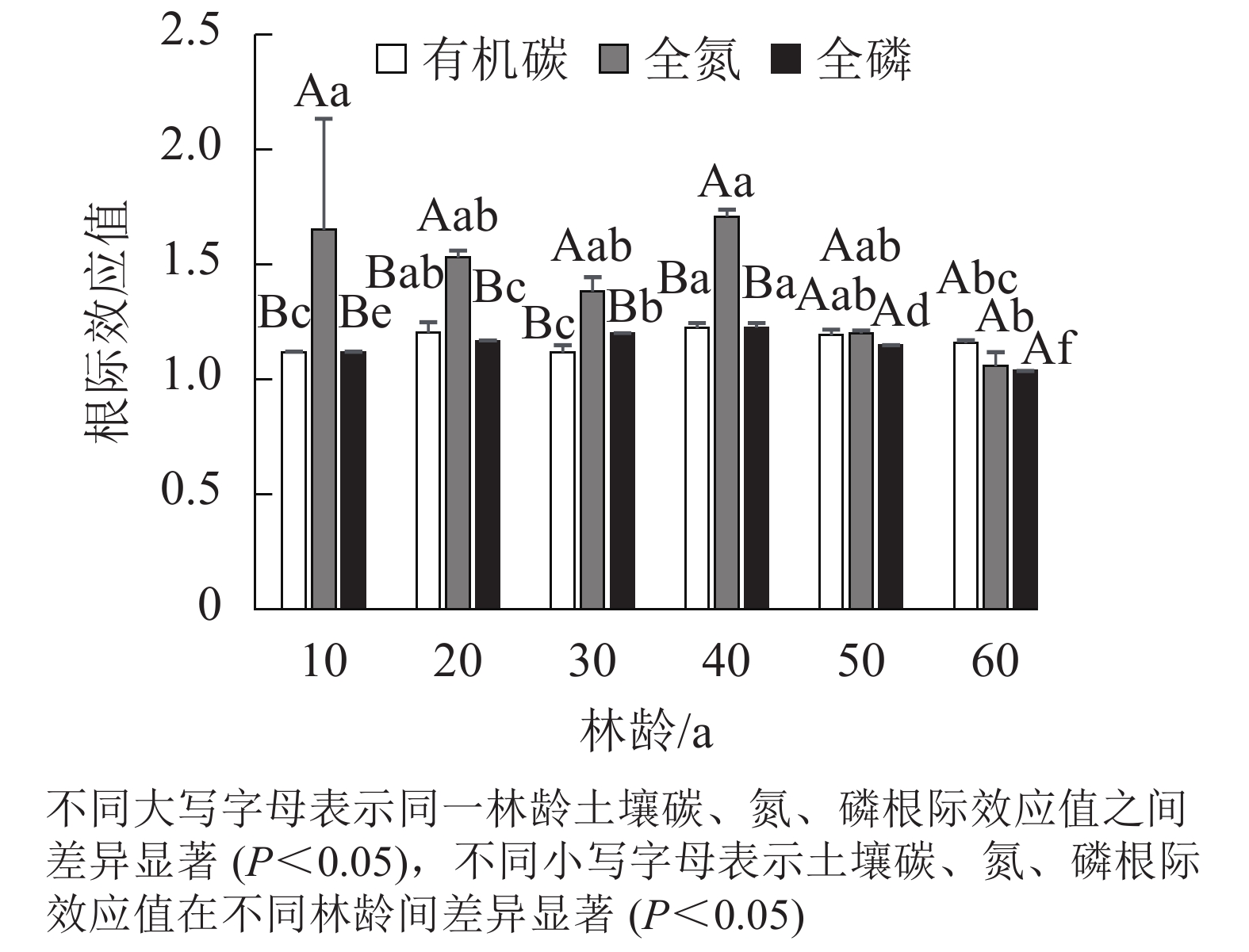
Objective The purpose is to explore the relationship between C, N, and P contents in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations at different ages in sandy land of northwest Liaoning Province, so as to provide theoretical basis for cultivation and management of P. sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in this area. Method Using space-temporal exchange method, six P. sylvestris var. mongolica plantations (10, 20, 30, 40, 50 and 60 a) were selected in Zhanggutai area to analyze the differences and influencing factors of C, N, P contents and stoichiometric ratio between rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil of different stand ages. Result The soil of P. sylvestris var. mongolica plantation in the sandy land of northwest Liaoning was poor, and the contents of C, N, and P in rhizosphere soil were higher than those in non-rhizosphere soil. The root system had a significant effect on nutrient enrichment and balance maintenance. Stand age, rhizosphere, and their interaction had significant effects on soil C, N, P contents and their ecological stoichiometry. Soil C∶N of the P. sylvestris var. mongolica plantation was mainly affected by total N, soil C∶P was mainly affected by soil organic carbon, and soil N∶P was more affected by total N than total P. The soil C∶N ratio of P. sylvestris var. mongolica plantation at all ages was much higher than that of the national average level, which was manifested as N limitation, especially in the 60 a over mature forest. The limitation of N and P in rhizosphere soil of P. sylvestris var. mongolica plantation was synergistic to some extent. Conclusion The growth of P. sylvestris var. mongolica at all ages is restricted by N, and non-rhizosphere soil is more deficient in N compared with rhizosphere soil. In forest management, the difference between rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil should be fully considered. It is suggested that N fertilizer and N-fixing plants should be applied and introduced to P. sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in sandy land of northwest Liaoning to relieve N limitation, and P fertilizer should be added to the root system. [Ch, 1 fig. 5 tab. 28 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 1066-1075.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210501
Abstract:
Chinese hickory (Carya cathayensis) is a unique woody nut and oil tree species in China. Chinese hickory industry brings high income for local farmers in its main production region. Soil fertility such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in soils determines the healthy growth of Chinese hickory. Therefore, research related to soil fertility are attracting more attention in China. The soil fertility of Chinese hickory plantation was mainly influenced by elevation, parent materials and antropogenic management, among which the intensive management plays an important role in soil fertility variation. Intensive management could lead to the heavy decrease of soil fertility such as soil acidification, the decrease of soil organic carbon and available nutrient contents. The removement of understory resulted in the severe soil erosion as well as obvious nutrient loss. The composition of soil microbial community changed and its diversity declined. What’s more, due to the deterioration of soil quality, the yield and quality of hickory nut dropped. The application of organic materials and sod cultivation increased soil pH, as well as the contents of soil organic carbon and available nutrients, and further effectively improved soil fertility. Current researches mainly focus on the spatio-temporal changes of soil fertility. Reasonable fertilizer application and the effect of net harvesting of hickory nut on soil fertility need further study. The formation mechanism along with the control techniques of soil erosion in Chinese hickory plantation also need deeply explored, which can provide basic information and technique support. [Ch, 71 ref.]
Chinese hickory (Carya cathayensis) is a unique woody nut and oil tree species in China. Chinese hickory industry brings high income for local farmers in its main production region. Soil fertility such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in soils determines the healthy growth of Chinese hickory. Therefore, research related to soil fertility are attracting more attention in China. The soil fertility of Chinese hickory plantation was mainly influenced by elevation, parent materials and antropogenic management, among which the intensive management plays an important role in soil fertility variation. Intensive management could lead to the heavy decrease of soil fertility such as soil acidification, the decrease of soil organic carbon and available nutrient contents. The removement of understory resulted in the severe soil erosion as well as obvious nutrient loss. The composition of soil microbial community changed and its diversity declined. What’s more, due to the deterioration of soil quality, the yield and quality of hickory nut dropped. The application of organic materials and sod cultivation increased soil pH, as well as the contents of soil organic carbon and available nutrients, and further effectively improved soil fertility. Current researches mainly focus on the spatio-temporal changes of soil fertility. Reasonable fertilizer application and the effect of net harvesting of hickory nut on soil fertility need further study. The formation mechanism along with the control techniques of soil erosion in Chinese hickory plantation also need deeply explored, which can provide basic information and technique support. [Ch, 71 ref.]
2021, 38(5): 1076-1081.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200753
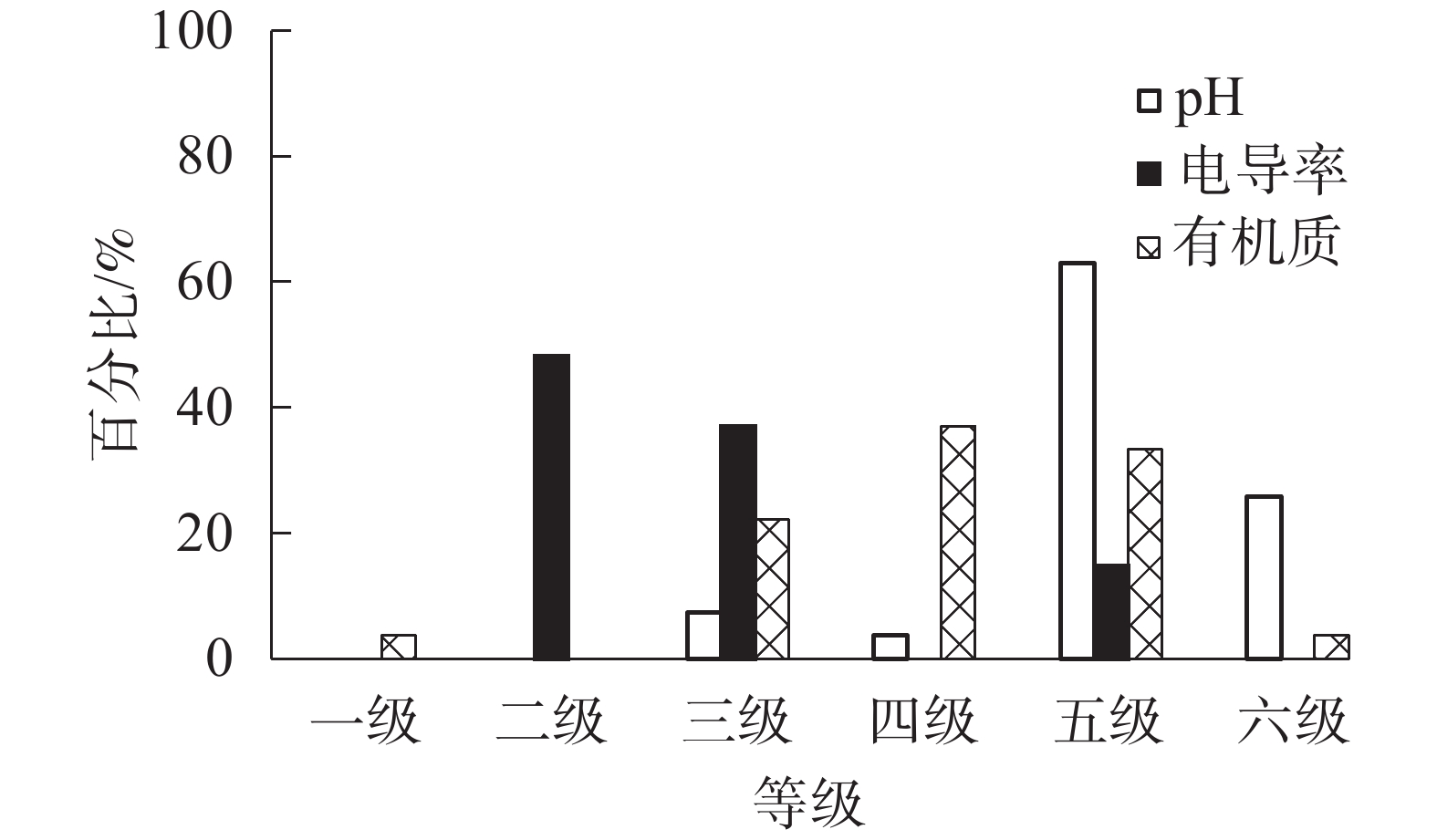
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to analyze soil fertility index and soil fertility quality in typical relocation sites in Shanghai, and to explore the soil fertility quality characteristics of the relocated land in villages and industrial enterprises in the city, so as to provide basis for the use of the relocated soil in landscaping. Method The 20 typical relocation sites of urban villages and 16 relocation sites of industrial enterprises in Shanghai were selected, and 7 soil fertility indexes including pH, electrical conductivity(EC), organic matter, hydrolytic nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium and bulk density were selected as fertility evaluation indexes. The modified Nemoro method was used to comprehensively evaluate the quality of soil fertility in the relocation sites. Result The soil in the relocation site was alkaline, with suitable EC, relatively low contents of organic matter and hydrolytic nitrogen, rich contents of available phosphorus and available potassium, and high soil bulk density. The average comprehensive index of soil fertility in Shanghai was only 0.86. The comprehensive index of soil fertility in the relocation sites of urban villages was significantly higher than that in the relocation sites of industrial enterprises (P<0.05). Conclusion The soil fertility in the relocation sites of Shanghai is relatively poor, 59.3% of which belong to “poor” grade and 40.7% belong to “general” grade. The soil fertility of urban villages is better than that of industrial enterprises. Before the relocated land is used for urban landscaping, soil fertility quality should be improved by technical means to meet the requirements of planting. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 23 ref.]