2021 Vol. 38, No. 6
2021, 38(6): 1083-1090.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200696
Abstract:
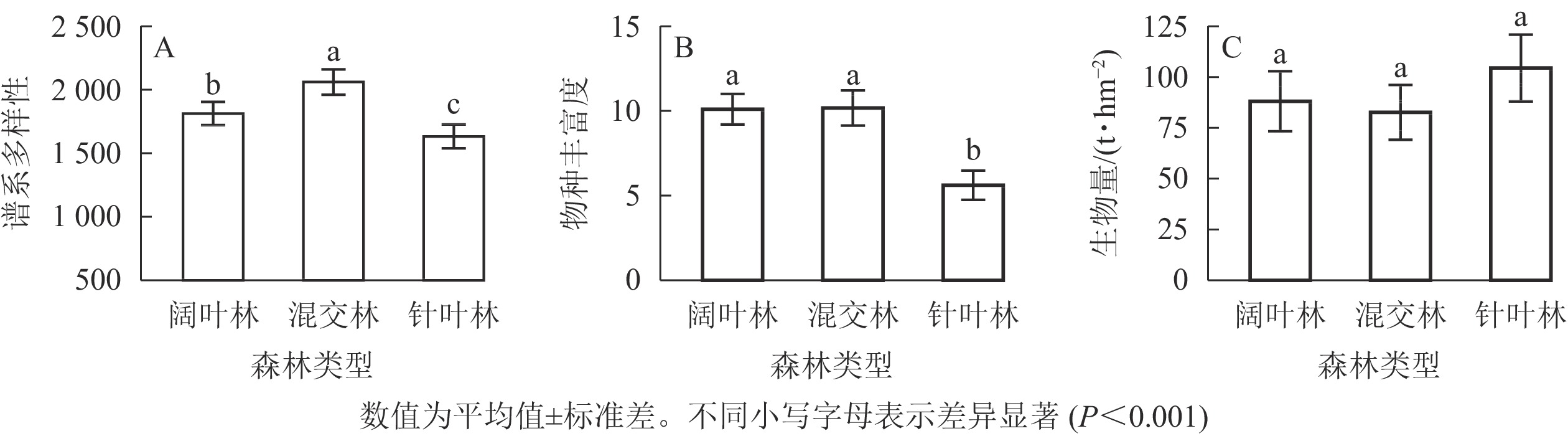
Objective This research aims to explore the impact of biodiversity and site factors on biomass of public welfare forest in Zhejiang Province, and to study the stability of its community structure. Method Based on the survey data of public welfare forest from three counties in Zhejiang, the effects of ten soil and terrain factors (soil hygroscopic water, soil pH, soil organic matter, soil available nitrogen, soil available phosphorus, soil available potassium, altitude, slope, aspect and soil thickness) and biodiversity (species richness and phylogenetic diversity) on the biomass of three forest types (coniferous forest, coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest, and broad-leaved forests) were explored. Result Compared with species richness, phylogenetic diversity was better to distinguish forest types, in which broad-leaved forest and mixed forest had higher biodiversity, and coniferous forest had higher biomass. When only considering the effects of individual factors, phylogenetic diversity (P=0.041) and species richness (P< 0.001) were significantly and positively correlated with biomass in broad-leaved forests. When considering the effects of environmental factors, species richness, phylogenetic diversity, soil available nitrogen, soil thickness and soil hygroscopic water had significant effects (P<0.05) on biomass of broad-leaved forests, while soil thickness and soil pH had significant effects (P< 0.05) on biomass of coniferous forests. Phylogenetic diversity was negatively correlated with biomass due to the joint effect of environmental factors. Conclusion Environmental factors and biodiversity jointly affect the biomass of public welfare forest in Zhejiang Province. In the future management of public welfare forest, measures should be taken to increase soil fertility of coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest, and improve the species structure of broad-leaved forest, so as to better maintain and enhance the ecosystem function of public welfare forest. [Ch, 2 fig. 2 tab. 44 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1091-1099.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200707
Abstract:
Objective Quercus wutaishanica is the main tree species in Liupan Mountains. This study aims to analyze the spatial distribution pattern and correlation of Q. wutaishanica population in Liupan Mountains, so as to understand the growth and development status and population development process of Q. wutaishanica community in this area. Method Based on 12 pure forest plots of Q. wutaishanica in Liupan Mountains, the population structure and dynamics of Q. wutaishanica were studied by static life table, diameter class structure, survival coefficient, mortality rate, disappearance rate and survival analysis. Point pattern was used to analyze the spatial pattern and spatial correlation of Q. wutaishanica population in Liupan Mountain area. Result (1) The distribution of diameter class structure of Q. wutaishanica in the sample plots was close to the inverted J type, with good renewal status and stable structure. (2) The survival curve of Q. wutaishanica population was close to the deevey-Ⅱcurve. (3) The population of Q. wutaishanica was stable in the early and middle stages and declined in the late stage. (4) The young and middle age individuals of Q. wutaishanica showed aggregation distribution in small scale, which changed from aggregation distribution to random distribution with the increase of scale. Individuals of near maturity tended to distribute evenly on small scale and randomly on large scale. Conclusion The tree population of Q. wutaishanica in Liupan Mountains is relatively stable and in good regeneration condition. The young and middle age individuals of Q. wutaishanica show aggregation distribution in small scale, and the correlation between middle age and near mature individuals is not obvious in large scale, independent of each other. In order to keep the structure of Q. wutaishanica forest stable, human regulation should be strengthened to ensure the stable environmental conditions for population regeneration of Q. wutaishanica forest. [Ch, 8 fig. 2 tab. 24 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1100-1108.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200599
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation of the precise spatial distribution of suitability of Pinus tabulaeformis, a main afforestation tree species in the upper reaches of Baiyangdian Daqing River Basin, is aimed to enhance its guiding role in the construction of water conservation forest and improve the forest water conservation capacity in the basin. Method Based on the principles of plant ecology and plant geography, with 190 sample siets data obtained from field survey, and the 24 geographical environment variables (elevation, slope, slope, meteorology, rock type, soil type, etc.) examined, an analysis was conducted of the meteorological factors using multiple linear regression Kriging interpolation (MLRK). Result The model of the suitability prediction of P. tabulaeformis reached a very accurate level (ROC=0.869). The accumulated temperature, the annual maximum daily precipitation, elevation and the standard deviation of annual temperature were the main geographical environment variables of the suitability of the P. tabulaeformis. The high suitable area of P. tabulaeformis enjoyed better spatial distribution of suitability in areas like Lingqiu County, Laiyuan County, Laishui County, Yi County, Fangshan District among other counties and districts. Conclusion The suitable conditions of P. tabulaeformis in Baiyangdian Daqing River Basin are as follows: the accumulated temperature staying at 2 800−3 800 ℃, the altitude remaining 500−1 200 m, the average annual maximum daily precipitation being 70−110 mm whereas the average annual standard deviation of temperature kept at 0.31−0.42 ℃. And it can be seen that with such conditions P. tabulaeformis forest can grow well and develop better. [Ch, 8 fig. 2 tab. 30 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1109-1116.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200751
Abstract:
Objective With an investigation of different radiation use efficiency models estimating the gross primary production (GPP) of evergreen needle-leaved forest (ENF) under the influence of drought, this paper is aimed to provide basis for accurately simulating GPP of ENF in Northern Hemisphere. Method MODIS data and flux site observation data at 8-day scale were used to simulate the GPP of ENF. Firstly, Pearson correlation coefficient and random forest factor evaluation method were used to analyze the correlation and importance of each driving factor of GPP while precipitation and potential evapotranspiration (PET) were used to calculate the dry-wet index to classify the dry-wet type of each site. Secondly, the VPMsw model was constructed by deleting the moisture parameter in the vegetation photosynthesis model (VPM). Finally, the accuracy of GPP estimated from VPM model and VPMsw model were quantitatively compared under different dry and wet types at each site. Result (1) GPP had strong correlation with temperature and PET, but weak correlation with Land Surface Water Index (LSWI). (2) compared with the VPM model, the accuracy of VPMsw model in fitting GPP was improved in arid and semi-arid sites, and the root mean square error (RMSE) decreased by 6.5% and 23.4%, respectively. the accuracy of GPP estimates in semi-arid sites was significantly improved by the VPMsw model. Conclusion VPMsw model was more accurate in simulating GPP in arid and semi-arid areas because LSWI could not well reflect the water content of the ENF in arid and semi-arid areas under the influence of drought. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 25 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1117-1126.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200792
Abstract:
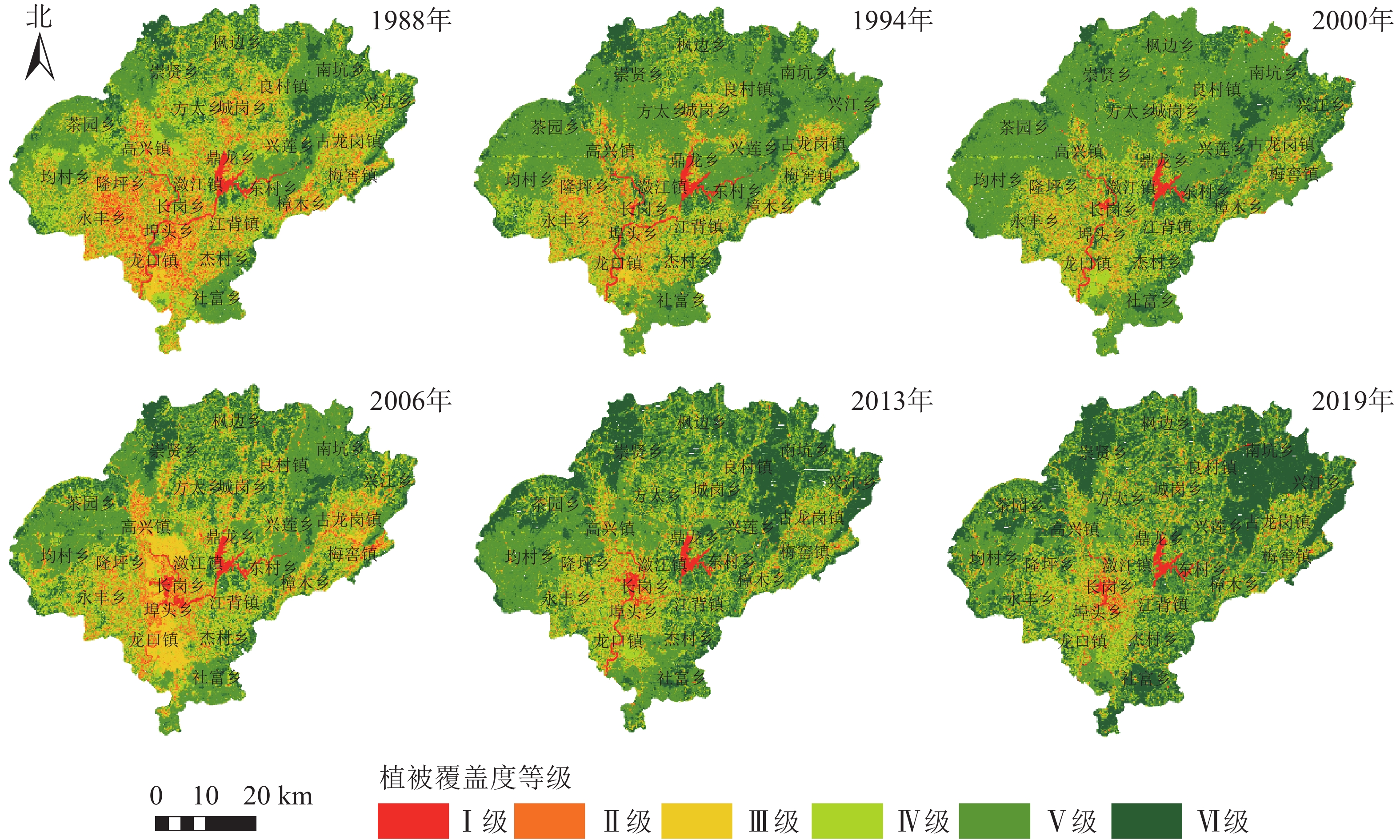
Objective With an analysis of the change characteristics of vegetation coverage and its spatial patterns, this study is aimed to provide reference for ecological environment construction and land use. Method Taking Xingguo County in Jiangxi Province as the study area, with the six phases of Landsat TM/OLI remote sensing data employed, under the guidance of the pixel dichotomy model of normalized difference vegetation index and the principle of landscape ecology, an investigation has been conducted of the characteristics of vegetation coverage and spatial pattern evolution in different periods from 1988 to 2019. Result (1) The annual vegetation coverage of Xingguo County has witness an increase from 63.89% in 1988 to 79.16% in 2019 with the growth area accounting for 72.18% of the total area (mainly due to the the increase of woodland and agricultural land) whereas the decline area accounting for 11.30% (mainly due to the increase of construction land) and the vegetation coverage at all levels was mainly featured with the evolution towards a higher-level coverage. (2) The vegetation coverage was featured with a smaller distribution in the center and south of the county and a larger distribution in the east, west and north of the county, which was generally consistent with the altitude and over the 31 years, the areas with a significant increase in vegetation coverage were mainly towns in the southern area including Longkou Township, Jiecun Township and Shefu Township while the areas with a significant decline were mainly towns in the center such as Lianjiang Township and Changgang Township. (3) From 1988 to 2019, the vegetation coverage witnessed a changing trend featured with fragmentation, heterogeneity, decreased diversity, uneven spatial distribution as well as enhanced aggregation and in terms of the spatial pattern under different coverage levels, the heterogeneity of patches covered by extremely low, low, medium and high vegetation decreased, and the shape of patches is featured as increasingly simpler; at the same time, the high and extremely high vegetation coverage was dominant, with its shape becoming irregular whereas the extremely high vegetation coverage was mainly distributed in a concentrated contiguous form. Conclusion The vegetation coverage and its spatial pattern of Xingguo County generally develop in a benign direction, which is conducive to the sustainable development of the region. Also, land use types, altitude, human activities and other factors have an important impact on the vegetation spatial pattern. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 35 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1127-1135.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200816
Abstract:
Objective As an ecological network covering the city, green infrastructure (GI) network plays an important role in mitigating the heat island effect. The purpose of this study is to explore the construction method and reasonable planning and layout of GI, as well as effective measures to improve the urban thermal environment. Method The main urban area of Nanjing City in Jiangsu Province was taken as the research object. Based on the morphological spatial pattern analysis (MSPA), the “source” patches with high connectivity and significant cooling effect were selected. The landscape pattern index reflecting the landscape pattern and the surface cooling rate reflecting the surface coverage characteristics were superposed to construct the resistance surface. Then, the minimum cost path method was used to generate corridors. Result (1) 507 core patches with high cooling rate were identified, and 25 patches were selected as “source” patches based on landscape connectivity analysis. (2) 20 corridors were identified by the minimum cost path method. Together with the “source” patches, the urban GI network was constructed to mitigate the heat island effect. (3) The network was optimized based on Green Space System Planning of Nanjing, and the overall spatial structure of “three rings, six belts and multiple lines” was proposed. Conclusion The comprehensive application of various methods makes it more reasonable to construct a GI network to mitigate the heat island effect, and provides a new research approach for building a GI network and improving urban living environment. [Ch, 5 fig. 6 tab. 27 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1136-1143.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200808
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to investigate the effects of different irrigation methods on the growth and spatial distribution of fine roots of Populus, so as to provide theoretical and technical basis for the cultivation of plantation by drip irrigation. Method The 5-year old ‘107’ Populus × euramericana ‘Neva’ was selected as the research object, and standard trees were selected from the plantations cultivated by drip irrigation and furrow irrigation. Root drills were used to sample trees at 20, 50, 100 and 150 cm from tree trunks in the directions of inter plant, diagonal and inter row. The differences of fine root biomass density, fine root length density and fine root specific root length were compared. Result In inter plant direction, the difference of fine root biomass density between drip irrigation and furrow irrigation increased with the increase of horizontal distance, and the difference was significant (P<0.05). With the increase of horizontal distance, the differences between diagonal and inter row directions decrease. Under drip irrigation, the fine root biomass density was the highest at 50 cm away from the trunk in the direction of inter plant, and the highest at 20 cm away from the trunk in the direction of diagonal and inter row. Under drip irrigation, the difference of fine root length density with furrow irrigation increased with the increase of the horizontal distance(P<0.05), while the difference of diagonal and row direction decreased with the increase of the horizontal distance. Under drip irrigation, the root length density of fine roots was the largest at 50 cm from the trunk in the direction of inter plant, and the largest at 20 cm away from the trunk in the direction of diagonal and inter row. Under drip and furrow irrigation, the fine root biomass of 0−40 cm soil layers accounted for 81% and 73% of that in 0−60 cm soil layers, respectively, while the fine root length accounted for 85% and 80%. The specific root length under drip irrigation and furrow irrigation increased with the increase of horizontal distance, and the difference of specific root length under furrow irrigation was greater than that under drip irrigation. The difference of specific root length in different directions was the largest at 20 cm away from the trunk and the smallest at 50 cm away from the trunk. Conclusion Drip irrigation can promote the growth and turnover of fine roots, affect their spatial distribution, and improve forest productivity. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 28 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1144-1152.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200803
Abstract:
Objective The objective of this study is to analyze the genetic variation and correlation of seedling growth and leaf traits of Populus deltoides hybrid, so as to provide materials for breeding new poplar varieties. Method The hybrid experiment was carried out with different varieties of P. deltoides as parents, and the seedling growth and leaf traits of nine hybrid combinations were measured. The genetic variation and genetic interaction of growth traits and leaf traits were studied through analysis of variance, estimation of genetic parameters, genetic correlation analysis and path analysis. On this basis, the joint selection of fine hybrid combinations of P. deltoides was carried out. Result There were significant (P< 0.05) or extremely significant (P< 0.01) differences in seedling height, ground diameter, volume and leaf traits among hybrid combinations. The family heritability of the three growth traits (seedling height, ground diameter, volume) and the five leaf traits (leaf length, leaf width, petiole length, leaf perimeter and leaf area) were all above 0.8, which were controlled by intensity heredity. The genetic variation coefficient ranged from 8.6% (leaf length) to 31.13% (volume), which was beneficial to the selection of superior hybrid combinations. The correlation analysis showed that there was a extremely significant positive genetic correlation (P<0.01) between leaf traits (leaf length, leaf width, petiole length, leaf perimeter, leaf area) and seedling height, ground diameter and volume. The analysis of correlation genetic progress indicated that, except for leaf shape index, lateral vein angle and leaf width base distance, the genetic correlation progress and indirect selection efficiency of other leaf traits to the three growth traits were higher. The path analysis showed that seedling height and ground diameter had greater direct genetic control on volume, while leaf length, leaf width, petiole length, leaf area and leaf perimeter had greater indirect genetic control on volume through seedling height and ground diameter. Combined selection of growth and leaf traits of nine hybrid combinations of P. deltoides was carried out by comprehensive index selection method, and three fast-growing and high-quality hybrid combinations (B106×NL15, S3239×NL15, NL447×SY2) were selected. The genetic gain of volume reached 26.90%. Conclusion The three growth traits and five leaf traits of 1-year-old seedlings of P. deltoides hybrid combinations show rich genetic variations and significant genetic interaction. Seedling height and ground diameter have the greatest direct effect on volume, and the five leaf traits also have a large indirect control effect on volume. The comprehensive index selection method can effectively screen fast-growing and high-quality cross combinations. The genetic gain of volume is higher, and the genetic improvement effect of poplar is better. [Ch, 8 tab. 18 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1153-1160.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200802
Abstract:
Objective The aim of this study is to reveal the mechanism by which overexpression of RAY1 gene (CYC2-like genes) in Senecio vulgaris (Asteraceae) causes ray florets to broaden in varying degrees, and to further explore the underlying causes. Method SvRAY1 gene was cloned and analyzed by bioinformatics, qRT-PCR, construction of overexpression vector, SEM(scanning electron microscopy), and morphological observation and statistics of transgenic plants. Result qRT-PCR reaction showed that SvRAY1 gene was mainly expressed in ray florets and disc florets, with the highest expression level in the third and fourth stages of ray floret. Morphological observation showed that the ray floret of SvRAY1 overexpression plant was significantly shorter and wider than the wild type. The epidermal cells on the ventral side of the ray florets were observed by SEM and it was found that the width of the line was significantly wider than that of the wild type. The cells at the distal end were tightly arranged, small and divided vigorously. Cell division along the central axis was more vigorous than that of the wild type and the shape of cells changed from curved to smooth. Conclusion During the development of S. vulgaris, SvRAY1 gene may promote cell division, and change the morphology and arrangement of ray florets cells in varying degrees, resulting in the widening of the ray floret. [Ch, 6 fig. 2 tab. 28 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1161-1169.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210142
Abstract:
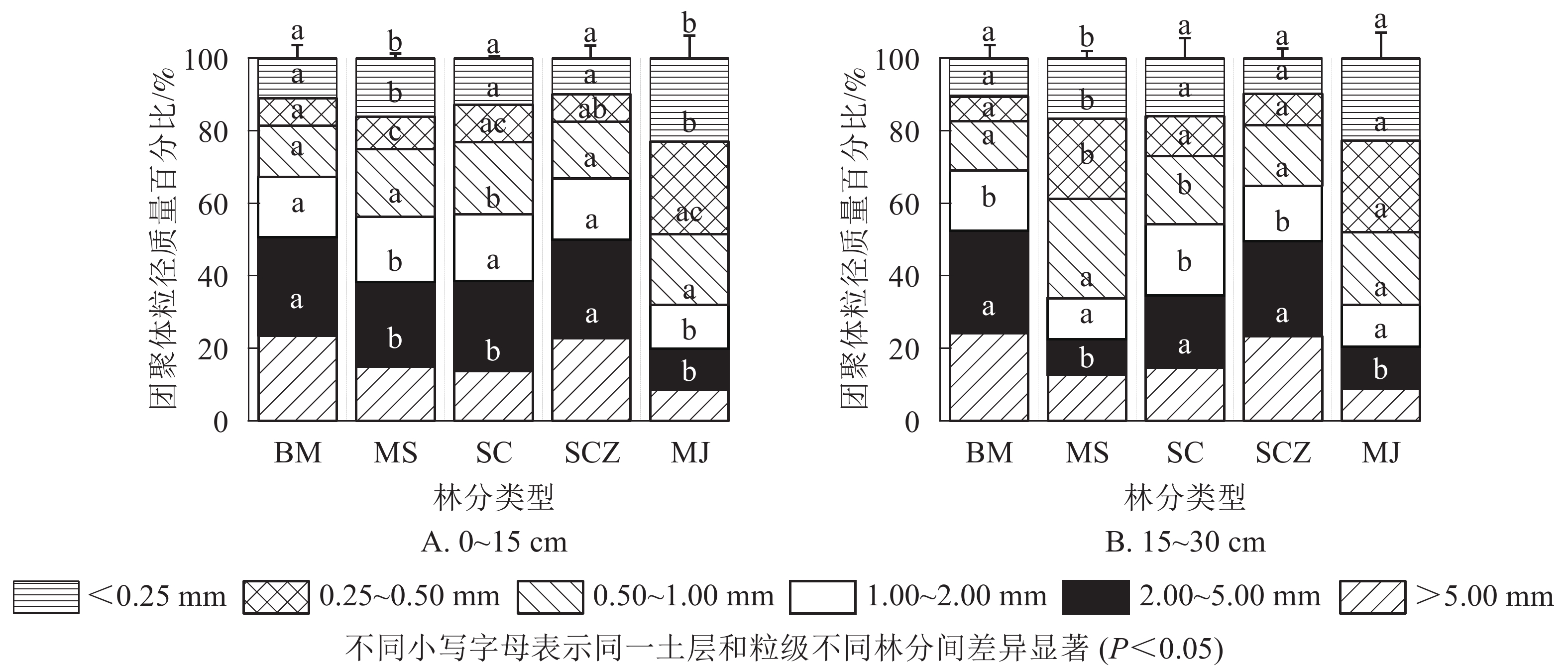
Objective The objective of this study is to explore the characteristics and influencing factors of soil aggregate stability under typical forest stands in Huaying City, Sichuan Province, so as to provide theoretical basis for elucidating the composition and stability mechanism of soil aggregates in this area. Method Five typical stands (Cupressus funebris pure forest, Cunninghamia lanceolata pure forest, Pinus massoniana-Loropetalum chinense mixed forest, P. massoniana-C. lanceolata mixed forest, and near natural C. lanceolata pure forest) were selected as the research objects. The soil physical and chemical properties of the surface layer (0−15 cm) and subsurface layer (15−30 cm) of the stands were measured to analyze the effects on aggregate change characteristics and soil erosion resistance. Result (1) The contents of soil macroaggregates in five typical stands were 77%−93%, with significant differences in mean weight diameter (MWD) and soil erodibility (K) among different stands (P<0.05). The MWD value of C. funebris forest was the largest (2.33 mm, and that of P. massoniana-L. chinense mixed forest was the smallest(1.53 mm). The K values of soil erodibility from large to small followed the order of near natural C. lanceolata pure forest, C. funebris forest, C. lanceolata pure forest, P. massoniana-C. lanceolata mixed forest, and P. massoniana-L. chinense mixed forest. (2) Redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that available potassium, total porosity and organic carbon were significantly positively correlated with MWD and negatively correlated with K value, and soil bulk density was significantly negatively correlated with MWD and positively correlated with K value. Conclusion Among the five typical stands, C. funebris and near natural C. lanceolata pure forest have the highest stability of soil water stable aggregates and strong erosion resistance, while P. massoniana-L. chinense mixed forest displays the lowest stability of soil water stable aggregates. Under the traditional management mode, the soil aggregate of C. funebris is more stable and soil anti-erodibility is stronger. The near natural management mode is conducive to the improvement of soil aggregate stability and soil anti-erodibility. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 32 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1170-1177.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200813
Abstract:
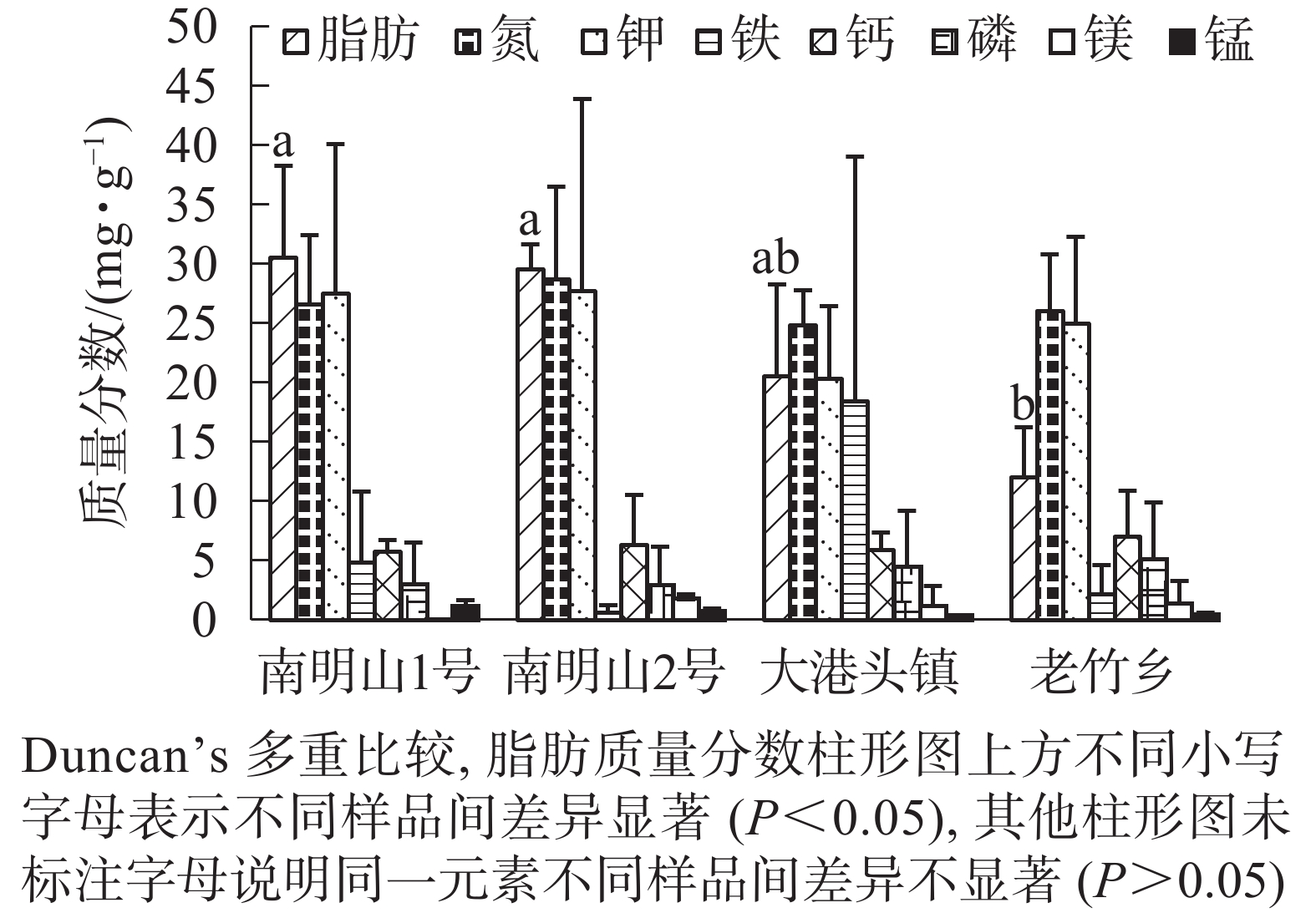
Objective Ranalisma rostratum, a critically endangered plant species, is included in the national level Ⅰ key protection plants. Many breeding bases have been established in China in recent years, and the population of R. rostratum has been effectively increased. This study aims to explore the nutritional composition and acute oral toxicity of R. rostratum for its better protection and utilization. Method The 4 batches of samples from 3 regression plots in Lishui City were selected, and weighed before and after drying. The biomass ratio and dry-to-fresh ratio of each vegetative organ were calculated. The main nutrients and elements (including fat, N, P, K, Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, Zn)in stems, leaves and roots, as well as the acute oral toxicity of stems and leaves in Mus musculus were determined. Result (1) The dry-to-fresh ratio of the plant was 0.17−0.19, indicating that the water content of the whole plant was high. (2) The average contents of 8 nutrient elements from high to low were N, K, Fe, Ca, P, Mg, Mn and Zn. The coefficient of variation of Fe content among samples and tissues was the largest, followed by P and Mg. (3) There was a significant difference in fat content among the 4 samples (P<0.05). There were no significant differences in the other 7 elements except Zn among the 4 samples. There were no significant differences in fat content between stem, leaf and root, but a significant difference in Na, P, K and Ca between the stem, leaf and root (P<0.05). (4) There was a significant (P<0.05) or extremely significant (P<0.01) positive correlation among Na, K and Ca, and the 3 elements had significant or extremely significant negative correlation with P, while P had significant positive correlation with Mg. (5) The stem leaf suspended sample liquid was prepared for the acute oral toxicity test, which showed that the oral LD50 of male and female mice was greater than 7.5 g·kg−1 body weight. Conclusion The mass fraction of Mg, Fe and P in R. rostratum was unstable, while other elements were stable. The distribution of Na, P, K and Ca in the stem, leaf and root of R. rostratum was significantly different. The acute oral toxicity test of stem and leaf in M. musculus showed that it was practically non-toxic. [Ch, 1 fig. 5 tab. 28 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1178-1186.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200755
Abstract:
Objective The purpose of this research is to screen the optimal specific substrate for roof greening by taking perlite as matrix aggregate, aquasorb (A), biosurfactant (B) and slow-release fertilizer as additives, combined with plant growth indexes. Method Based on the analysis of effects of aquasorb [0(A0), 0.5(A0.5), 1.0(A1.0) g·kg−1] and 2% biosurfactant [0(B0), 100(B100), 200(B200) mL·kg−1] on physicochemical properties of perlite under the condition of slow-release fertilizer (30 g·kg−1), two groups of high scoring substrates were chosen by matrix methods for cultivation experiment, and the growth indexes of Caryopteris clandonensis ‘Worcester Gold’ and Iris lactea were analyzed by membership function to determine the optimal substrate. Result The aquasorb and biosurfactant had significant effects on the physicochemical properties of the substrates and plant growth indicators of the cultivated plants (P<0.05). Compared with the control (aquasorb 0 g·kg−1 and 2% biosurfactant 0 mL·kg−1), the bulk density of A1.0B200(aquasorb 1.0 g·kg−1 and 2% biosurfactant 200 mL·kg−1) decreased by 17.11%, capillary porosity and field capacity increased by 10.82% and 55.55%, the mass fraction of total nitrogen, available phosphorus and rapidly available potassium increased by 14.78%, 44.36% and 25.28%, respectively. The plant height, root length, shoot and root fresh weight of A1.0B200 (aquasorb 1.0 g·kg−1, 2% biosurfactant 200 mL·kg−1) were significantly higher than those of the control, and the comprehensive evaluation coefficient of membership function was the highest. Conclusion Aquasorb and biosurfactant can improve the water-gas ratio of perlite substrate and improve the ability of fertilizer supply and conservation. Compared with A1.0B100, A1.0B200 is superior. [Ch, 2 fig. 5 tab. 39 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1187-1194.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200724
Abstract:
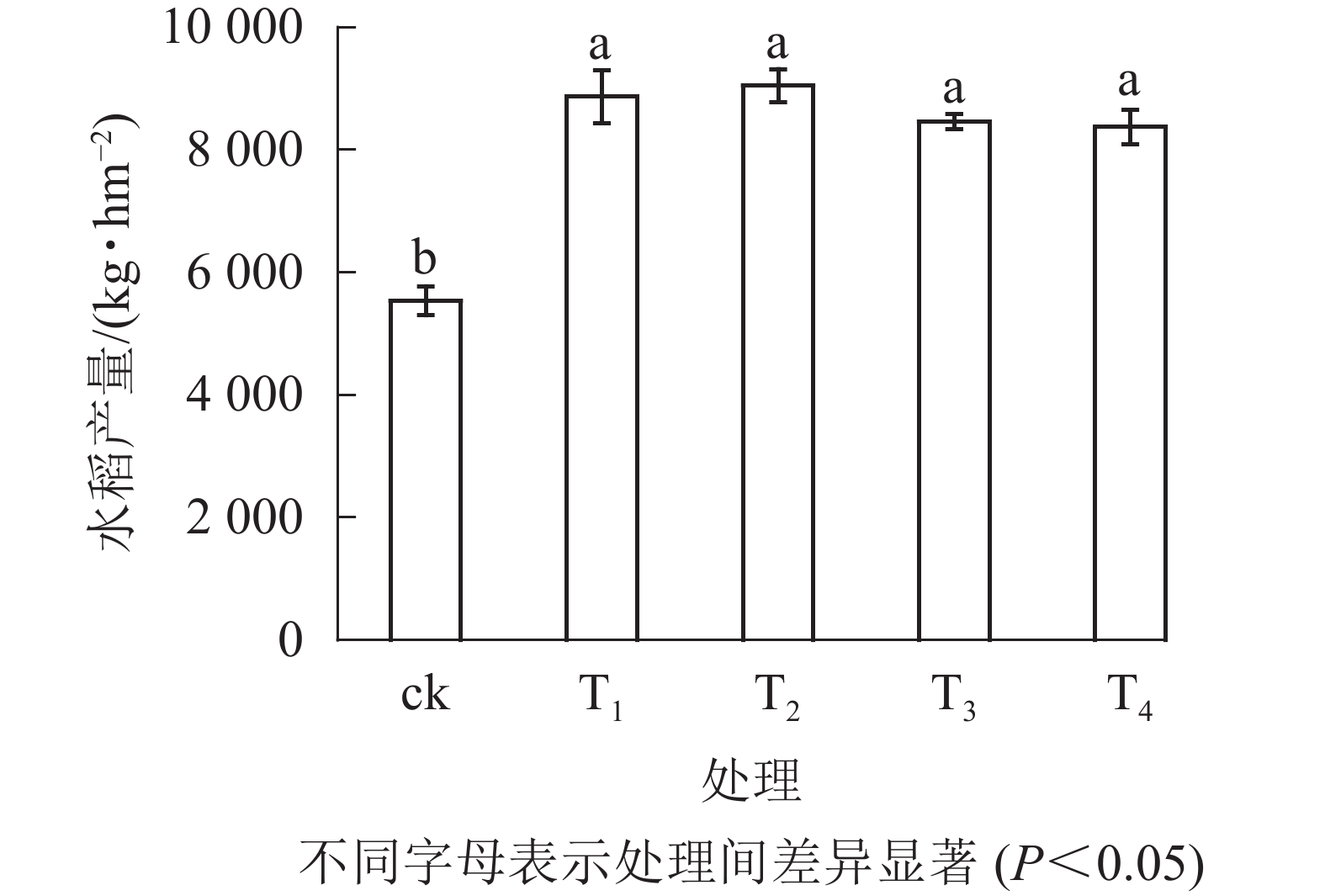
Objective The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of organic fertilizer (rapeseed cake), conditioner (shell sand), and carbon based fertilizer on soil nitrogen and phosphorus loss and rice yield of Oryza sativa. Method The five treatments of this study were no fertilization (ck), conventional fertilization (T1), organic fertilizer substitution (T2), conventional fertilization+conditioner (T3), and carbon based fertilizer (T4). The amount of nitrogen (N), phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) and potassium oxide (K2O) used in different fertilization treatments were 270, 75 and 150 kg·hm−2. The effects of different fertilization treatments on nitrogen and phosphorus loss were studied by comparing the nitrogen and phosphorus contents in soil, rice yield, rice grain and straw before and after fertilization among the five treatments, combined with the monitoring results of nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in runoff from June to September. Result Fertilization significantly increased nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation in rice grain and straw as well as rice grain yield. Compared with ck, the four treatments increased grain yields by 51.22%−63.41% (P<0.05), but there was no significant difference among the four treatments. The loss of nitrogen and phosphorus of the five treatments were 4.91−9.56 kg·hm−2 and 0.70−1.35 kg·hm−2 respectively, and the descending order of loss was T2, T1, T3, T4 and ck. The runoff rates of nitrogen and phosphorus of the four fertilization treatments were 0.82%−1.72% and 0.65%−1.99%, respectively and the descending order was T2, T1, T3 and T4. Conclusion The application of conditioner and carbon based fertilizer can effectively increase rice yield and reduce the loss of nitrogen and phosphorus (P<0.05), but organic fertilizer treatment has the maximum runoff loss. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the time and method of fertilization to effectively reduce nitrogen and phosphorus loss and environmental pollution. [Ch, 5 fig. 4 tab. 32 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1195-1202.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200767
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to explore the effects of partial replacement of chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer in the production of Solanum melongena. Method Taking chemical fertilizer as control (ck), 50% substitution of base nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizer (T1) and 100% substitution of base nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizer (T2) were set up as two treatments. The effects of different treatments on S.melongena yield, quality and soil fertility were studied in open field. Result Compared with ck, soil pH, soil available potassium, organic matter, microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen content increased significantly in both treatments (P<0.05). The fruit weight and fruit number per plant increased significantly (P<0.05), which led to the increase in yield by 13.8%−22.3%, and the yield of T1 was highest, which was 70099.5 kg·hm−2. The anthocyanin mass fraction of S.melongena pericarp increased significantly in both treatments(P<0.05), and thus deepened the fruit color. The mass fraction of magnesium and sulfur in fruits increased significantly (P<0.05), and that of soluble sugars, soluble protein and vitamin C and the molar concentration of amino acid increased in varying degrees, and the comprehensive effect of T1 was better. Conclusion Replacing 50% of the base fertilizer with organic fertilizer can effectively improve S. melongena yield, quality and soil fertility. [Ch, 9 tab. 40 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1203-1212.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20190586
Abstract:
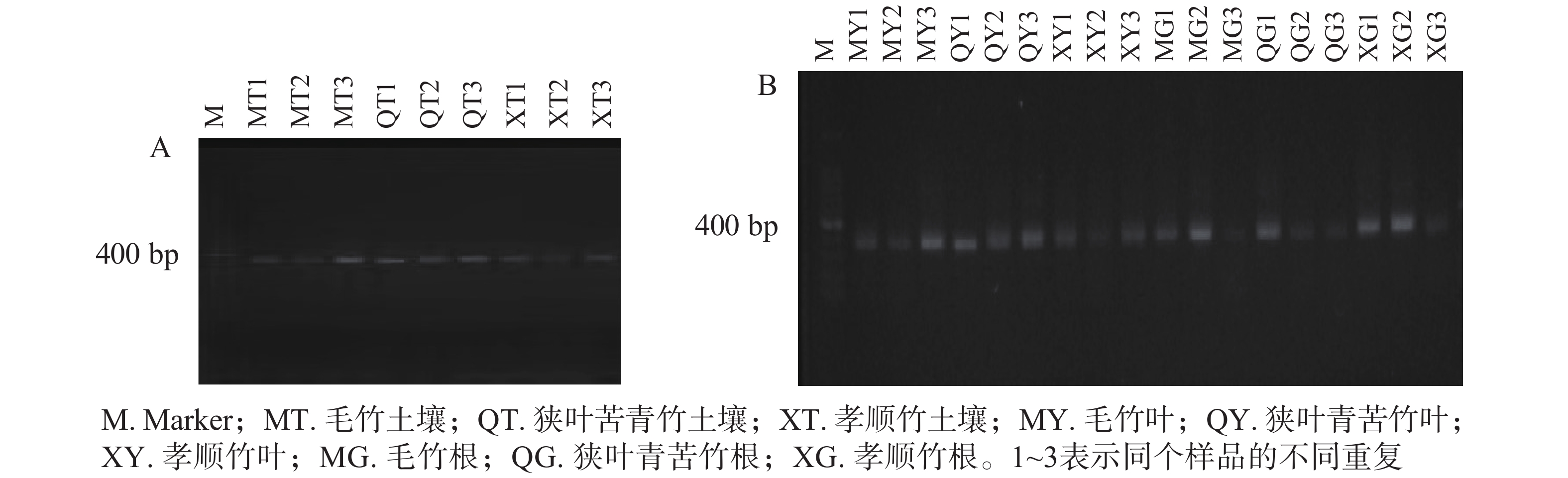
Objective The objective is to investigate the characteristics and biodiversity of endophytic diazotrophs in three bamboo species and in planting soil of root zones. Method Samples of leaves, roots and planting soil from Phyllostachys edulis, Bambusa multiplex and Pleioblastus chino were taken as the objects. The primers of nifH nitrogen fixation gene were designed. PCR-DGGE and random cloning technology were used to construct phylogenetic tree by cluster analysis and Shannon diversity index analysis. Result There were significant differences in community structure of diazotrophs among soils, between roots and leaves of the same bamboo species, between the same organs of different bamboo species, and between the soils of root zones and plants. The similarity of the same bamboo leaf or root was not high. More endophytic diazotrophs were detected in roots than in corresponding leaves. The similarity between diazotrophs in soil and those in roots was higher than that between soil and leaves. Significant differences of diazotrophs among plant species and plant tissues were observed by Shannon diversity index. The Shannon diversity index in leaf (2.73) and soil (2.70) of B. multiplex was higher than that in root (2.53) (P<0.05), and that in roots of P. chino and Ph. edilus was higher than that in leaf and soil (P<0.05). 83 strains of diazotrophs were obtained by random cloning and sequencing of plant samples, and only 12 strains were culturable, belonging to Bradyrhizobium, Dechlorosoma, Azospirillum, Enterobacter, Kosakonia, Gammaproteobacteria, Rubrivivax and Azohydromonas. The sequences of phylogenetic tree indicated that the endophytic diazotrophs in the three bamboo species differed greatly from those in other plants. Conclusion The structural characteristics and diversity of diazotrophs in bamboo are affected by soil properties, species and plant tissues. The diversity of endophytic diazotrophs in roots is significantly higher than that in leaves, and the corresponding taxa are distinct from those of Gramineae reported previously. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 30 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1213-1220.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200819
Abstract:
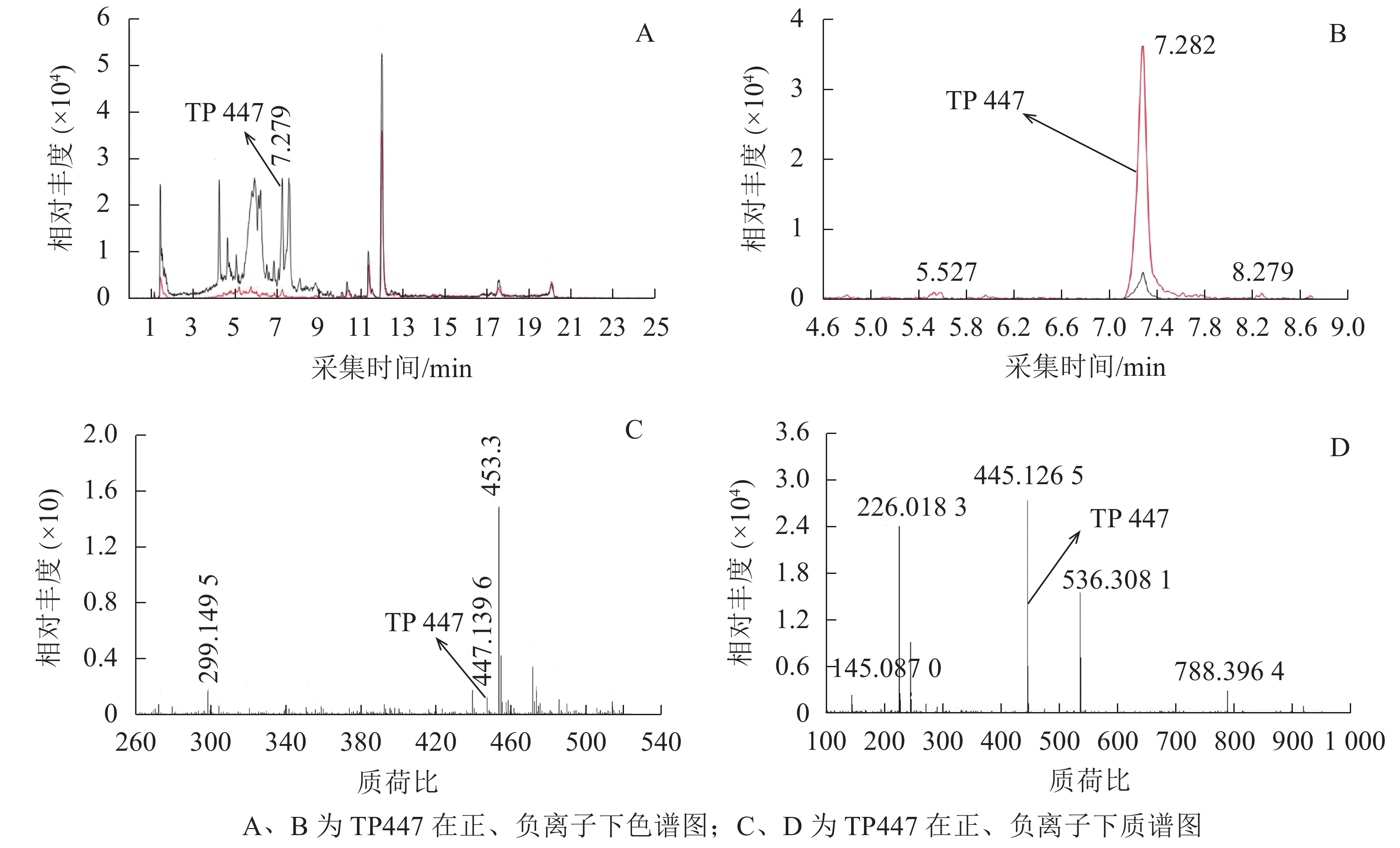
Objective The objective is to determine the effect of a degrading bacterium which can effectively reduce the bio-toxicity of oxytetracycline (OTC) metabolites, so as to provide a preliminary theoretical basis for practical application of the strain. Method Taking Arthrobacter nicotianae ZAF-05, an efficient OTC-degrading bacterium obtained in the previous studies, as the object, the degradation products of OTC were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HPLC-Q-TOF-MS). OTC sensitive Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Scenedesmus obliquus were used as indicators to evaluate the bio-toxicity of degradation products. Result HPLC-Q-TOF-MS analysis showed that the content of highly toxic OTC and its natural hydrolysate epioxytetracycline(EOTC) decreased significantly after treatment with strain ZAF-05, while the content of low toxic isomeric oxytetracyline(ISO-OTC) increased slightly. The growth of tested bacteria and alga in OTC system treated by strain ZAF-05 was significantly better than that in OTC natural hydrolysis treatment and negative control without degrading bacteria, and the difference was significant (P<0.01). The results indicated that the bio-toxicity of OTC metabolites degraded by strain ZAF-05 was greatly reduced compared with the active drug and its natural hydrolysates. Besides, the degradation effect of the strain alleviated the damage of OTC to the ultrastructure of algal cells, as well as the damage to chloroplasts and cell walls. Conclusion Degrading bacterium ZAF-05 can reduce bio-toxicity of OTC residues, which may be related to the conversion of highly toxic substances into non-toxic or low-toxic metabolites in the system. [Ch, 7 fig. 1 tab. 26 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1221-1230.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200778
Abstract:
Objective This study aims to analyze the variation of pollution load in the inlet and outlet sections of the Yangtze River in Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) area and its relationship with the water level of TGR. Method Based on the data of ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) and potassium permanganate index (CODMn) and water flow in TGR area from 2013 to 2018 at the inlet section (Zhutuo, Chongqing) and the outlet section (Nanjinguan, Yichang, Hubei) of the main stream of the Yangtze River, the pollution load and its relationship with the water level of TGR were analyzed through density distribution curve and Mann-kendall trend method. Result (1)The pollution load of NH3-N and CODMn in the inlet section was significantly higher than that of the outlet section, and the pollution load of the inlet and outlet sections was highly correlated (P<0.01). The pollution in TGR area mainly came from the inlet section and tributaries along the way. With the clarification of the reservoir, pollutants decreased along the way. (2) The pollution load at the inlet and outlet sections was negatively correlated with the fluctuation of water level of TGR(P<0.01). (3) Mann-Kendall trend analysis showed that the annual load of NH3-N at the inlet section and that of CODMn at the outlet section increased significantly (P<0.01). Conclusion The pollution load is the largest when TGR is at low water level, and is the smallest when at high water level. When the water level is low, the reservoir has less water storage and the water clarifying effect decreases. When the water level is high, the reservoir has a large water storage capacity and a stable water environment, which helps to dilute pollutants. Water pollution control in TGR area and upstream should not be ignored. [Ch, 6 fig. 4 tab. 33 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1231-1237.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200728
Abstract:
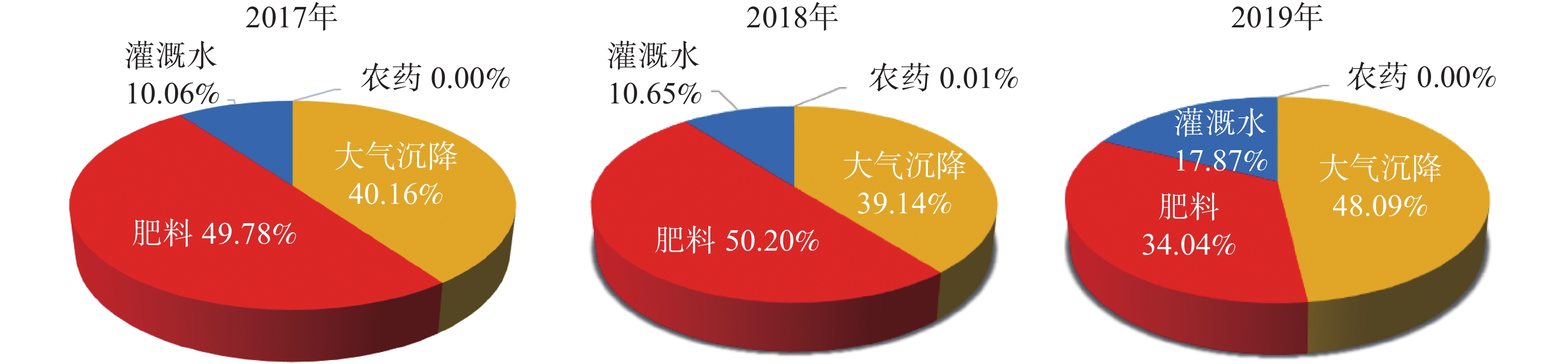
Objective This study is aimed at an accurate interpretation of the source of Cd pollution in farmland soil so as to put forward relevant suggestions for soil heavy metal remediation. Method An investigation was conducted of the input and output of heavy metal Cd in a typical piece of cultivated land in Songyang County of Zhejiang Province for three consecutive years by collecting local inputs and crops. Result During the period time from 2017 to 2019, fertilizer and atmospheric deposition were the main agricultural pollution sources of Cd, accounting for 49.78% and 40.16%, 50.20% and 39.14%, 34.04% and 48.09% respectively whereas the total input of Cd accounted for 0.18%、0.17% and 0.14% of the total soil Cd, respectively. The total output of Cd from rice, rape and tea were 2820.00, 2706.00 and 2629.50 mg·hm−2·a−1, respectively, with an average of 2718.50 mg·hm−2·a−1 and a relatively stable overall annual average output and the annual input and output decreased year by year, but the annual output was greater than the annual input, which may attribute to the enrichment of plant species. Conclusion It is advisable to devote efforts in the continuous implementation of long-term supervision over the atmospheric deposition in the region, the avoidance of direct return of straws to the field, the effective utilization of resources, and the timely restoration of the local contaminated soil and plants. [Ch, 1 fig. 5 tab. 25 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1238-1244.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200725
Abstract:
Objective This study is aimed to examine the effects of alternating current (AC) electric field and soil moisture on the remediation efficiency of cadmium (Cd) contaminated soil via the mixed planting of Salix discolor and Sedum alfredii. Method With a soil pot experiment, an investigation is conducted of the effects of 2 soil water treatments (moist, keeping 60% of the soil field capacity, and high water content, equivalent to paddy field condition, flooding) combined with 2 AC electric field gradients (0, 0.5 V·cm−1) on soil Cd availability and plant growth of S. discolor and S. alfredii. Result The application of 0.5 V·cm−1 AC electric field significantly increased soil available Cd concentration [by 16.13% (P<0.05)], and promoted the absorption and accumulation of Cd in S. discolor and S. afredii, the soil available Cd and Cd accumulation in leaves of S. discolor and the above-ground parts of S. afredii were significantly higher (by 12.61% and 22.50% respectively) than those of the control. The integrated application of high moisture and electric field contributed to the increase of soil pH, alkali-hydrolysable nitrogen concentration and the proportion of residual cadmium by 6.47%, 12.09% and 22.89% (P<0.05) compared with those of the control. This integrated application reduced the accumulation of Cd in S. discolor and S. afredii, the accumulation of Cd in leaves of S. discolor and the above-ground parts of S. afredii were lower than that of the control by 95.60% (P<0.05) and 18.02% respectively. Conclusion Under moist condition, the AC electric field was beneficial to the phytoremediation of Cd contaminated soil via the mixed planting of S. discolor and S. afredii. And the Cd accumulated in the above-ground parts of S. discolor and S. afredii was 1.13−1.93 times of that achieved with other treatments. [Ch, 4 tab. 40 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1245-1252.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200595
Abstract:
Objective This study is aimed to explore the remediation potential of Vetiveria zizanioides on prometryn polluted water. Method The characteristics of absorption and removal of prometryn by V. zizanioides with different initial concentrations (1.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0 mg·L−1)were studied by hydroponic simulation experiment in greenhouse. Result With the same cultivation time, the increase of initial prometryn concentration brought about a significant increase of prometryn concentration (P<0.05) in the shoots and roots of V. zizanioides, which reached the maximum on the 5th day, and then demonstrated a fluctuating decline. The extension of cultivation time led to a significant decrease in prometryn concentration in water (P< 0.05). Compared with the control without V. zizanioides, the degradation half-life of prometryn in the treatment group with V. zizanioides was shortened by 14.80−19.78 days, and the removal rate was increased by 22.52%−55.57%. The concentration of prometryn in water had a significant negative correlation with the transfer coefficient of V. zizanioides (P<0.01), no significant correlation with relative removal rate (P>0.05), but a significant positive correlation with the cultivation time (P<0.01). Conclusion The planting of V. zizanioides can promote the degradation rate and removal rate of prometryn, therefore, V. zizanioides can be used as a pioneer plant in the remediation of prometryn polluted water. [Ch, 2 fig. 4 tab. 31 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1253-1260.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200774
Abstract:
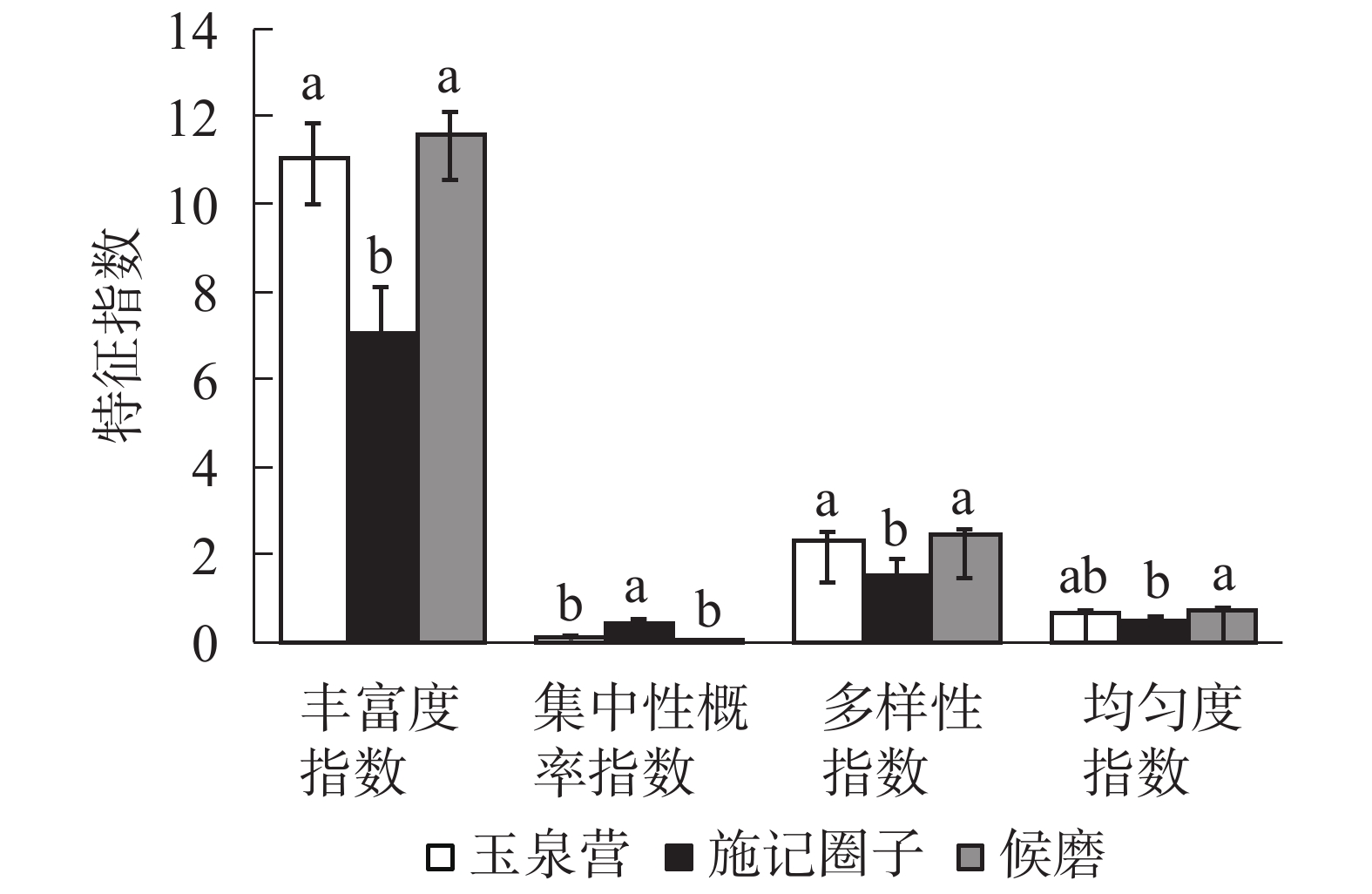
Objective This study aims to clarify the structure and diversity characteristics of insect community of Cerasus humilis orchards in different regions of Ningxia, so as to develop effective pest control strategies. Method The insect community of C. humilis in three different regions of Ningxia was investigated using trap trapping method from May to September in 2019. Result A total of 4743 insect specimens belonging to 10 orders, 46 families and 101 species were obtained. The dominant species were Grapholitha molesta, Serica orientalis, Nysius ericae, Lygus pratensis, Monolepta hieroglyphica, Lagria rufipennis, Hippodamia variegate, Chrysopa formosa, Cataglyphis aenescens and Deraeocoris punctulatus. The descending order of diversity index, evenness index and richness index of insect community of C. humilis orchards was Houmo, Yuquanying, and Shijijuanzi. The concentration probability index from high to low was Shijijuanzi, Yuquanying and Houmo. Similarity analysis showed that the insect community structure in Yuquanying and Shijijuanzi C. humilis orchards was moderately similar in August(0.60). The correlation analysis between pests and natural enemies showed that there was a significant positive correlation between G. molesta and H. variegata (P<0.05). There existed a very significant positive correlation between N. ericae and H. variegata (P<0.01), a positive correlation between L. rufipennis and C. aenescens (P<0.05), and a significant positive correlation between M. hieroglyphica and C. formosa (P<0.01). Conclusion Compared with orchards in Yuquanying and Shijijuanzi, the C. humilis orchard in Houmo has highest stability of insect community. [Ch, 2 fig. 5 tab. 25 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1261-1269.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210363
Abstract:
Objective As an important forestry resource in China, bamboo industry has its unique advantages in the integrated development of agricultural industry. The purpose of this study is to analyze farmers’ participation in the integration of bamboo industry, the impact of farmers’ human capital level on their income and the mechanism relationship between them, so as to provide reference for the integrated development of agricultural industry in bamboo producing areas and mountainous areas. Method Based on the survey data of 260 rural households in Anji County of Huzhou City and Lin’an District of Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, the impact of bamboo industry integration on farmers’ income level and income gap, as well as the direct and regulatory role of human capital were analyzed through statistical analysis and multiple linear regression. Result Participating in the bamboo industry integration and strengthening the human capital accumulation could improve the income level of farmers and narrow the income gap among them. The formal education years of the head of household and the maximum education years of other family members except the head of household had a regulatory effect in the process of participating in bamboo industry integration affecting farmers income. However, the indicators of agricultural skills training for heads of households and family members did not play the expected regulatory role. Conclusion It is necessary to encourage farmers to participate in the bamboo industry integration, increase the formal education years of household heads and family members, and promote horizontal industrial integration, namely the horizontal function expansion of bamboo resources. [Ch, 3 tab. 23 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1270-1278.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210216
Abstract:
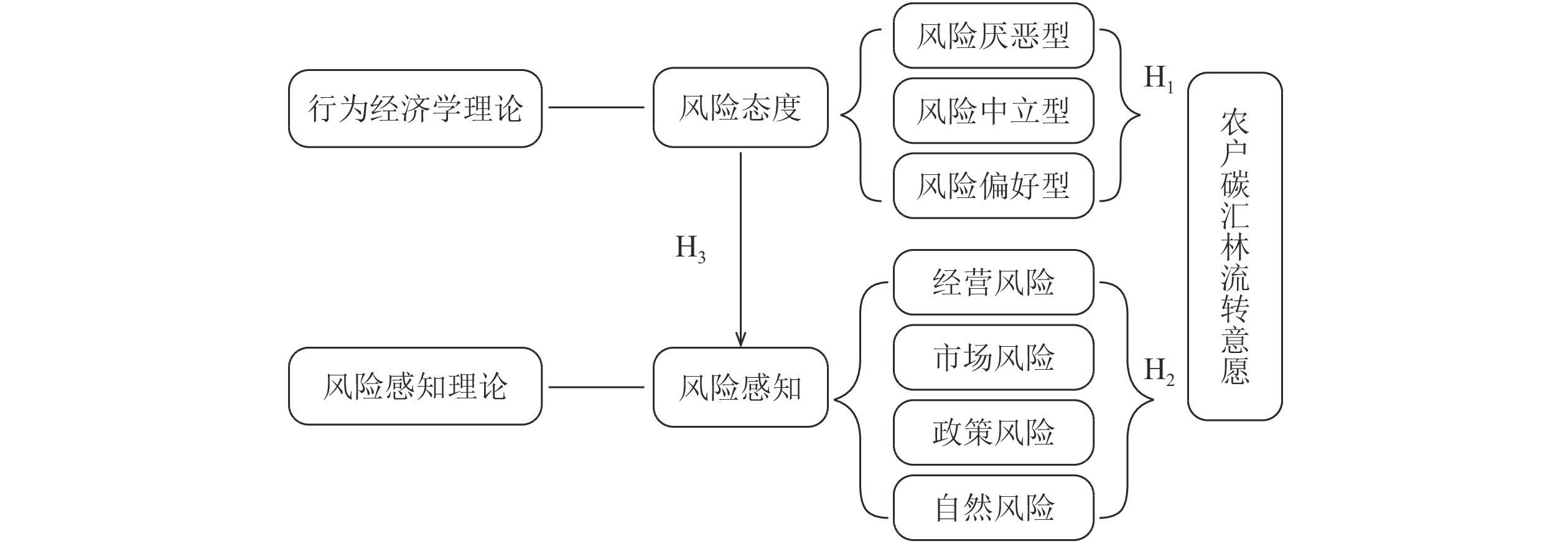
Objective The solution based on forest carbon sequestration is an important means to achieve the goals of “carbon peak by 2030” and “carbon neutral by 2060”. The objective of this study is to investigate the impact of farmers’ risk attitude and risk perception on their willingness to transfer carbon sequestration forests, which is of great significance for sustainable development and promotion of forest carbon sequestration projects. Method Based on the field survey data of farmers involved in CCER (China Certified Emission Reduction) bamboo forest management carbon sequestration projects in Suichang and Jingning, Zhejiang Province, the impact of risk attitude and risk perception on their transfer intention of carbon sink forest was qualitatively analyzed, and the binary Logistics model and mediating effect model were used for empirical test. Result (1)In general, 84.32% of farmers were willing to transfer to more carbon sequestration forests, 10.36% were willing to transfer out of the carbon sequestration forests, and 5.33% were willing to maintain the status quo. In terms of classification, the proportion of risk preference farmers willing to transfer in was as high as 96.67%, and the proportion of risk aversion farmers willing to transfer out was 15.95%. In terms of risk perception, 88.00% of farmers with low perception of management risk, market risk, policy risk and natural risk were willing to transfer in, while 92.00% were not willing to transfer out. (2) According to the empirical results, the risk attitude had a significant positive impact on farmers’ willingness to transfer in carbon sequestration forests at the level of 5%, and had a significant negative effect on farmers’ willingness to transfer out carbon sequestration forests at the level of 5%. Management risk, market risk, and policy risk perception had a significant negative impact on farmers’ willingness to transfer carbon sequestration forests at the levels of 10%, 1%, and 5% respectively, and a significant positive impact on their willingness to transfer carbon sequestration forests at the levels of 10%, 1% and 1% respectively. (3) Market risk perception had a significant mediating effect between risk attitude and transfer intention of carbon sequestration forests. Conclusion Farmers’ enthusiasm to participate in forest carbon sequestration projects is high on the whole. Compared with risk averse farmers, risk preference farmers have higher willingness to transfer in and lower willingness to transfer out. Farmers with higher perception of management risk, market risk and policy risk have weaker transfer in intention and stronger transfer out intention. [Ch, 1 fig. 5 tab. 19 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1279-1288.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200809
Abstract:
Crocus sativus is a perennial herb with medicinal values such as promoting blood circulation and removing stasis, cooling blood and detoxification, anti-cancer and anti-oxidation. Due to vegetative propagation and successive cropping obstacle, the disease of C. sativus is aggravated day by day. And the corm rot disease caused by the fungus is the most common, which causes a sharp decline in C. sativus output, and seriously affects its industrial development. To conquer fungal disease is one of the effective ways to improve its yield and quality. In this study, the research progress on isolation and identification of soil fungal diseases, endophytic fungi and biocontrol bacteria of C. sativus is reviewed, and research prospect is analyzed. The follow-up research can be carried out from three directions. First, based on modern metagenome sequencing technology, the pathogen and antagonistic bacteria of the corm rot of C. sativus should be studied. Second, based on synthetic biology and fermentation engineering methods, heterologous and efficient biosynthesis of effective substances in C. sativus should be realized. The third is to create a new germplasm for detoxification of C. sativus to provide reliable and high quality provenance for production. This study can provide a reference for research on prevention and control of fungal diseases and the development and utilization of biological fertilizer. [Ch, 3 tab. 89 ref.]
Crocus sativus is a perennial herb with medicinal values such as promoting blood circulation and removing stasis, cooling blood and detoxification, anti-cancer and anti-oxidation. Due to vegetative propagation and successive cropping obstacle, the disease of C. sativus is aggravated day by day. And the corm rot disease caused by the fungus is the most common, which causes a sharp decline in C. sativus output, and seriously affects its industrial development. To conquer fungal disease is one of the effective ways to improve its yield and quality. In this study, the research progress on isolation and identification of soil fungal diseases, endophytic fungi and biocontrol bacteria of C. sativus is reviewed, and research prospect is analyzed. The follow-up research can be carried out from three directions. First, based on modern metagenome sequencing technology, the pathogen and antagonistic bacteria of the corm rot of C. sativus should be studied. Second, based on synthetic biology and fermentation engineering methods, heterologous and efficient biosynthesis of effective substances in C. sativus should be realized. The third is to create a new germplasm for detoxification of C. sativus to provide reliable and high quality provenance for production. This study can provide a reference for research on prevention and control of fungal diseases and the development and utilization of biological fertilizer. [Ch, 3 tab. 89 ref.]
2021, 38(6): 1289-1296.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200796
Abstract:
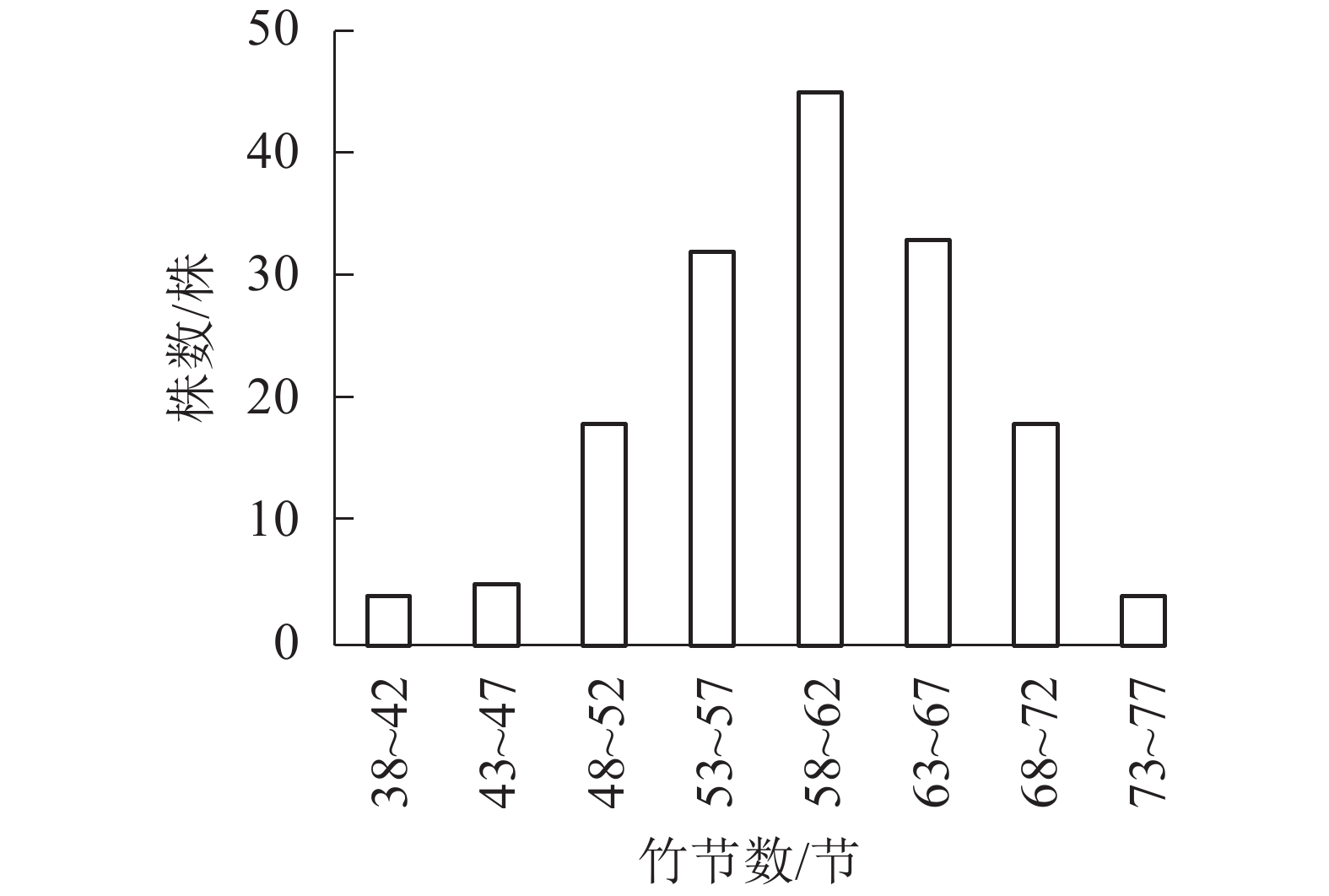
Objective With an analysis of the relationship between stalk structure factors and the dominant factors in stalk structure factors as well as an investigation into the stalk structure factors of culm and their distribution rules dependent on relatively high with the actual high replaced by the ratio of bamboo joint height and bamboo high (i. e. relative high, value range 0−1), this study is aimed to reveal the structure characteristics of culm form so as to better evaluate the growth and development of bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Method With 10 counties and cities (districts) of Zhejiang Province selected to set up sample plots of moso bamboo forest, the sample bamboo trees were cut down to measure the number of bamboo nodes, the length of bamboo nodes and the central diameter of bamboo nodes. Then the distribution patterns of culm form factors depending on relative height were fitted by parabola and line before the relationship between culm form factors was investigated with the correlation analysis whereas the main culm structure factors were studied with the factor analysis. Result The number of bamboo bamboo knots was concentrated in 53−67 sections, consistent with the normal distribution, and the confidence interval of the average bamboo knots at the 95% confidence level is (58.1, 60.4). The length of nodes and the central diameter of nodes depended on the relative height distribution with parabola and straight line distribution respectively while the central diameter of bamboo nodes decreased by 10% with a 10% increase of culm height. With the increase of diameter grades, the length of longest bamboo node tended to increase gradually, but there is no significant variation in the relative height of the longest bamboo node ranging between 0.47 and 0.52, and DBH was positively correlated with the number of bamboo nodes, length of node in half height, the length of longest node and the length of node in chest height (P< 0.01), while negatively correlated with the number of nodes in chest height (P<0.01). Conclusion The culm form of bamboo was featured with both stability and variation but there was no significant variation in the relative height of the longest bamboo nodes with different diameter class, generally at half height. Also, the bigger the bamboo was, the larger the number of nodes was, the longer the bamboo nodes were, and the longer the average length below the chest height was. The wall thickness factor, the length of nodes at half height, the number of bamboo nodes and the culm factor in the height of the chest are the main structural factors reflecting the culm structure. [Ch, 6 fig. 6 tab. 28 ref.]
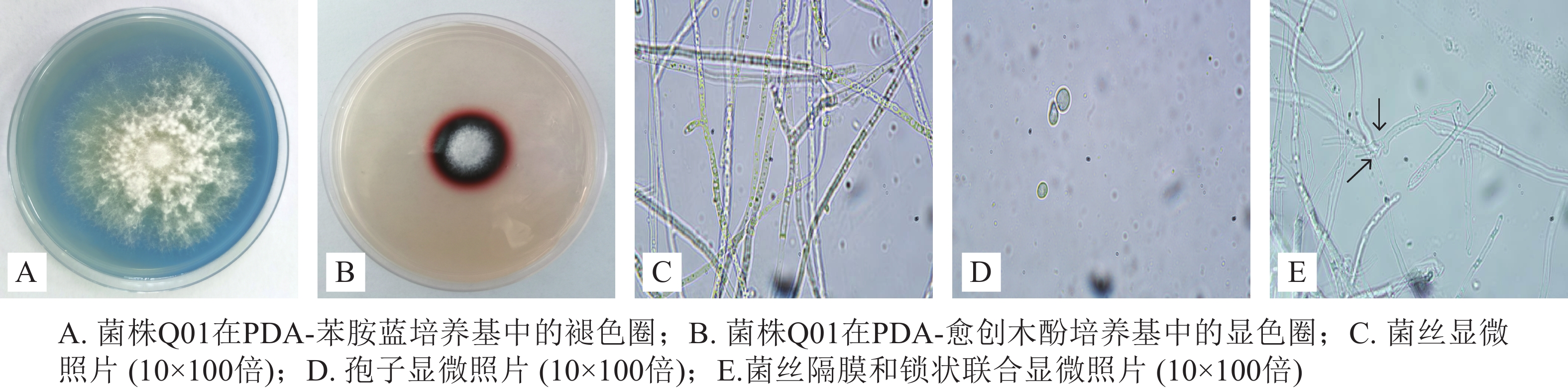
2021, 38(6): 1297-1304.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200814
Abstract:
Objective The purpose is to produce a high efficient liquid inoculum with lignin-degrading bacteria as raw materials for garden waste. Method The target strains were screened from 22 isolated and purified strains by the aniline blue plate fading circle method and the guaiacol plate fading circle method, and were identified by Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) sequencing, and then the single factor test was used to optimize the culture time, inoculum amount and medium formula (carbon and nitrogen source) of the target strains. Finally, according to the results of single factor test, the optimal fermentation conditions of the target strains were found by uniform experiment combined with artificial neural network algorithm. Result According to the results of plate fading and color development, strain Q01 was selected as the target strain and was identified as Trametes. According to the results of single factor test and uniform test, the optimal fermentation conditions for strain Q01 were determined as the culture time of 5 days, inoculation amount 12.5%. The medium formula was composed of sodium lignosulfonate 14.00 g·L−1, peptone 12.30 g·L−1, yeast powder 5.00 g·L−1, soybean cake powder 3.00 g·L−1, copper sulfate pentahydrate 0.12 g·L−1, sodium chloride 0.53 g·L−1, and natural pH. Under the optimized conditions, the biomass, manganese peroxidase activity and lignin peroxidase activity of strain Q01 increased by 1.27 times, 31.71 times and 19.12 times respectively. Laccase activity decreased slightly, but the total enzyme activities of three kinds of lignin enzymes increased by 4.38 times. Conclusion The liquid inoculum prepared by strain Q01 under optimized fermentation conditions has the characteristics of high enzyme activity and high biomass, which has certain application potential in degrading lignin in garden waste. [Ch, 6 fig. 3 tab. 29 ref.]