2022 Vol. 39, No. 1
2022, 39(1): 1-12.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210593
Abstract:
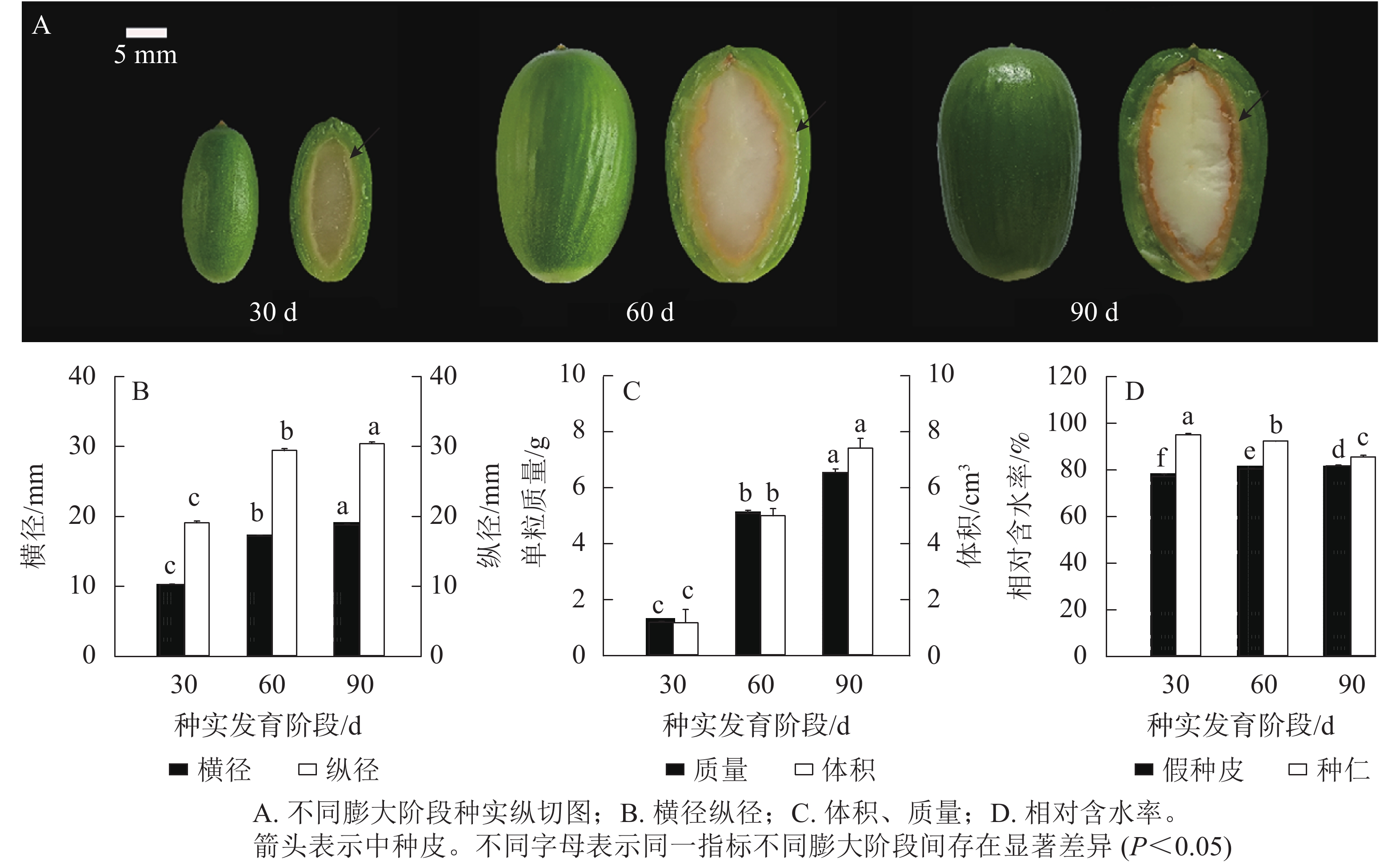
Objective This study is designed to investigate the accumulation and distribution of sucrose and hexose in aril and kernel tissue during seed expansion of Torreya grandis ‘Merrillii’, clarify the effect of sucrose metabolism on the sink vitality of seeds, and explore the effects of key enzyme activity of sucrose metabolism and gene expression patterns on seed expansion. Method The kernel and aril at different stages of T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ seed expansion were used as research materials. The contents of sucrose, glucose, fructose and starch, the activity of enzymes related to sucrose metabolism, the contents of hormones and changes in the expression of genes encoding enzymes related to sucrose metabolism were measured. Result With the expansion of T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ seeds, the contents of sucrose, glucose and fructose in the aril first increased and then decreased, while the starch content decreased continuously to 254.05 mg·g−1 at 90 d after seed protrusion. Sucrose content in seed kernel decreased by 61.24% at 90 d after seed protrusion, and starch content gradually increased from 105.29 mg·g−1 at 30 d after seed protrusion to 149.72 mg·g−1 at 90 d after seed protrusion. The activity of sucrose phosphate synthase increased in seed aril, but decreased in seed kernel by 28.82% at 90 d after seed protrusion. The activity of sucrose invertase also increased significantly (P<0.05) in seed aril. At 90 d after seed protrusion, cytoplasmic invertase and vacuolar invertase increased to 21.52 and 23.49 μmol·mg−1·min−1. Gene expression analysis showed that genes involved in sucrose and hexose transport were significantly up-regulated (P<0.05) during seed expansion, and several transcripts of genes involved in sucrose hydrolysis were also significantly up-regulated (P<0.05). The genes involved in starch synthesis in seed kernel were significantly up-regulated (P<0.05) at the later stage of seed expansion. Correlation analysis showed there was a certain correlation between various hormones in aril and kernel and the contents of glucose, fructose, sucrose, starch and enzyme activity. Conclusion The accumulation of sucrose in the aril tissue mainly occurs during the early stage of seed expansion, while the hydrolysis of sucrose and starch occurs in the later stage of seed expansion. Sucrose in seed kernel is mainly decomposed. There are active carbohydrate transport and metabolism between seed aril and kernel, as well as within kernel. Sucrose invertase is the key enzyme responsible for sucrose hydrolysis, and cytoplasmic invertase and vacuolar invertase play an important role. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 42 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 13-21.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210196
Abstract:
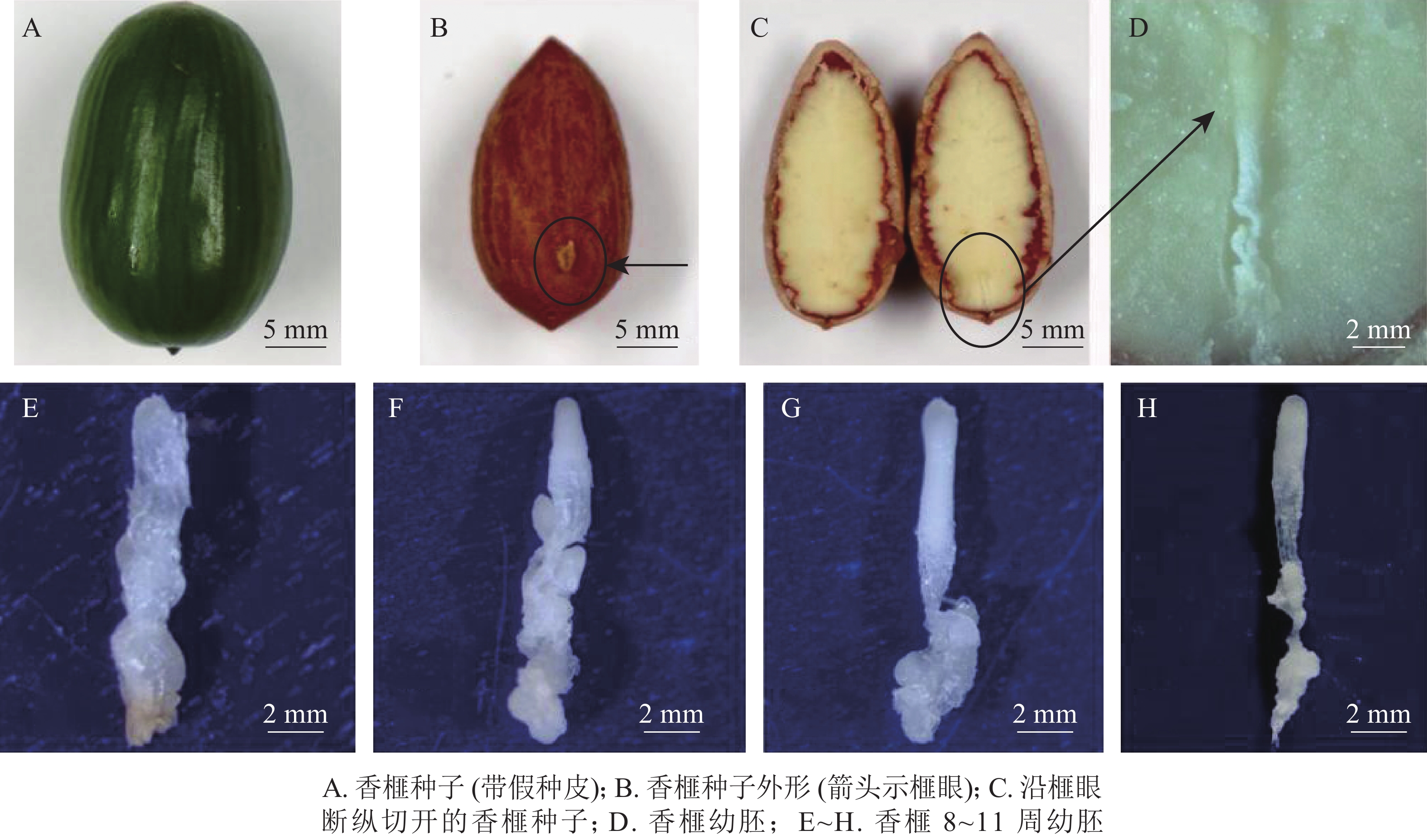
Objective The purpose is to explore genetic transformation mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens using Torreya grandis ‘Merrillii’ immature embryos as receptors, so as to reveal key factors affecting its genetic transformation and establish A. tumefaciens mediated transformation system of T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ embryos. Method The immature embryos of T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ seeds of 8 to 11 weeks after breaking through seed scales were used as transgenic acceptors. The effects of embryo age, A. tumefaciens concentration, infection time and antibiotic concentration on genetic transformation efficiency were compared. Hygromycin, GFP fluorescent expression and GFP gene polymerase chain reaction were used for positive screening and selection of immature embryo culture. Result The stress resistance increased, the contamination rate decreased and the survival rate increased with the increase of embryo age. The survival rates of 10-week and 11-week young embryos were 52.1% and 52.3%, respectively. The contamination rate, survival rate, callus induction rate and somatic embryogenesis rate of young embryos were significantly affected by the concentration of A. tumefaciens and infection time (P<0.05). When the liquid optical density [D(600)] was 0.5, the callus induction rate and somatic embryogenesis rate of young embryos were the highest, which were 17.9% and 17.3% respectively. When the infection time was 10 minutes, the callus induction rate and somatic embryogenesis rate were the highest, reaching 17.5% and 17.1% respectively. Carbenicillin had a significant effect on the removal of A. tumefaciens (P<0.05). When the concentration was 300 mg·L−1, the survival rate, callus induction rate and somatic embryogenesis rate were the highest, which were 60.5%, 15.8% and 17.5% respectively. The concentration of hygromycin in different treatments had a good effect on the positive screening of young embryo culture. The survival rate was 30.5% when the concentration of hygromycin was 100 mg·L−1. Conlusion Immature embryos at the 10th week after the breakthrough of scale, 0.5 [D(600)], 10 minutes duration, 300 mg·L−1 carbenicillin, and 100 mg·L−1 hygromycin were the optimum conditions for genetic transformation of T. grandis ‘Merrillii’. [Ch, 3 fig. 5 tab. 37 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 22-31.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210304
Abstract:
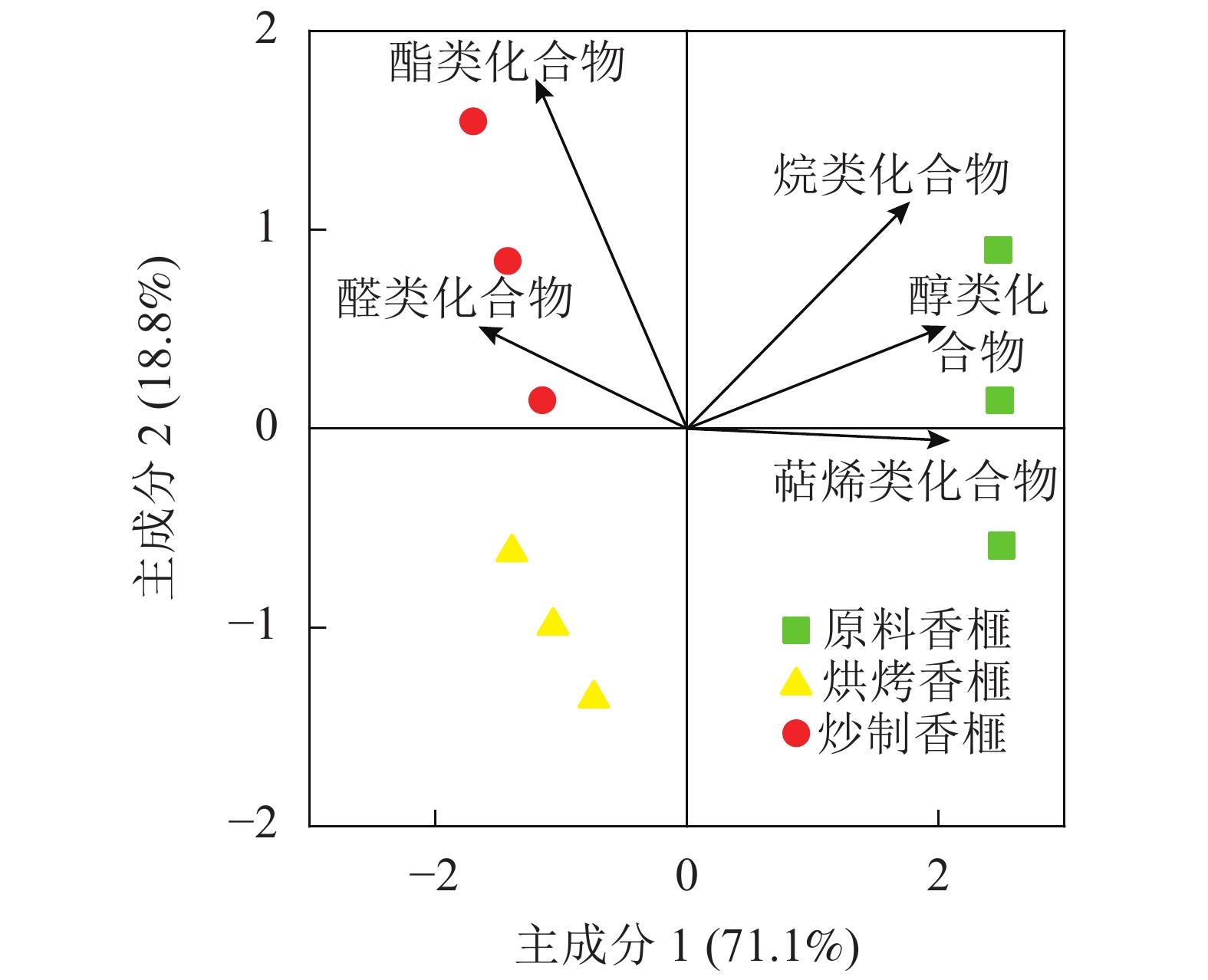
Objective The objective is to investigate the aroma components, oil oxidation and antioxidant capacity of Torreya grandis ‘Merrillii’ nuts with different processing techniques, reveal the influence mechanism of different processing techniques on the formation of aroma substances and oil quality of the nuts, and test the effects of different variables on chromaticity, sensory evaluation and oil quality, so as to explore the optimal baking process. Method The aroma components of the nuts with three processing techniques (fried , roasted, and raw) were compared, and the acid value, peroxide value, total phenol content and DPPH free radical scavenging activity of the three T. grandis ‘ Merrillii’ materials were measured to determine the appropriate processing technique. Furthermore, a single factor experiment with the first baking time, salt soaking time and the second baking time as the variable factors was designed. Combined with sensory evaluation of seeds, and determination of peroxide value, acid value, total phenol and DPPH radical scavenging activity, the best baking processing was optimized by Design-Expert software. Result Terpenes were the main aroma components of the nuts, up to 57.7%–70.5%. The types and total amount of aroma components in roasted nuts were significantly higher than those in fried nuts, and the degree of oil rancidity of roasted kernel was significantly lower than that of fried nuts. According to the effects of different baking factors on sensory evaluation and chromaticity index, it was found that the optimal time for the first baking was 10–14 min(200 ℃), the optimal salting time was 10–15 min, and the optimal time for the second baking was 90–120 min(120 ℃). Conclusion The aroma components and oil quality of T. grandis ‘ Merrillii’ kernels processed by baking are significantly better than those processed by frying. The best baking conditions are as follows: baking at 200 ℃ for 12 min, then soaking in 20% salt solution for 10 min, and finally baking at 120 ℃ for 95 min. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 29 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 32-40.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210394
Abstract:
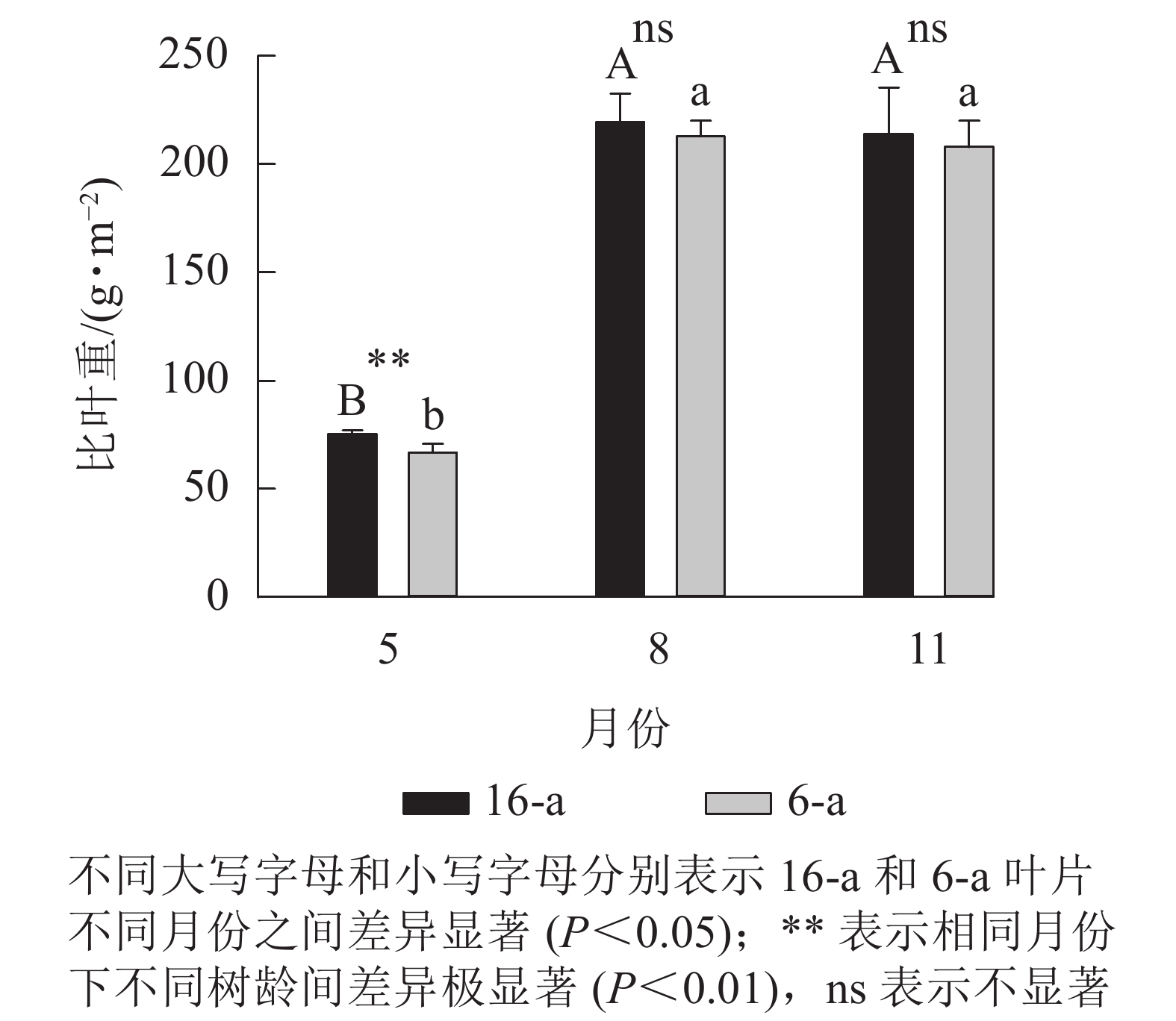
Objective This study aims to investigate the physiological mechanism of seasonal changes of photosynthesis of Torreya grandis ‘Merrillii’ leaves at different tree ages, so as to provide theoretical support for the efficient cultivation and sustainable development of T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ industry. Method The response curves of chlorophyll and CO2, leaf nitrogen content per unit area (NA) and photosynthetic nitrogen use efficiency (PNUE) in leaves of T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ at different tree ages (6 and 16-year-old grafted trees, named as 6-a and 16-a respectively) were measured in May, August and November. The changes of surface photosynthetic characteristics and internal structure of photosynthesis were systematically analyzed and compared. Result In May and August, net photosynthetic rate (Pn), specific leaf weight (SLW), maximum RuBP carboxylation rate (Vcmax), photosynthetic electron transfer rate for RuBP regeneration (Jmax), total chlorophyll content (Chl), nitrogen allocated to Rubisco (Vcmax/NA), nitrogen for RuBP regeneration (Jmax/NA), and nitrogen for light harvesting pigment components (Chl/NA) in leaves increased significantly regardless of tree age, while NA decreased significantly. Regardless of tree age, Chl content, leaf nitrogen content and Jmax/Vcmax ratio in leaves increased significantly in November compared with those in August, while Vcmax, Jmax, Vcmax/NA, Jmax/NA, and Chl/NA decreased significantly. There was no significant change in Amax and SLW. The decrease of Vcmax/NA in 6-a leaves was significantly greater than that in 16-a leaves, while the decrease of Jmax/NA and Chl/NA in 6-a and 16-a leaves was the same. The PNUE of 6-a leaves was significantly higher than that of 16-a leaves in May, August and November. Conclusion From May to August, regardless of tree age, the photosynthetic capacity of leaves gradually enhances, and dry matter accumulates continuously, which significantly dilutes the nitrogen content and makes the leaves mature. From August to November (with the decrease of temperature), leaf senescence never occurs. However, the nitrogen distribution proportion in photosynthetic components changes, that is, the effect of low temperature on RuBP regeneration is mitigated by the relative increase of Jmax. With the decrease of temperature, 6-a leaves allocate less nitrogen to RuBP carboxylation and more nitrogen to RuBP regeneration, which may be the reason for the relatively high PNUE of 6-a leaves. [Ch, 6 fig. 1 tab. 39 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 41-49.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200622
Abstract:
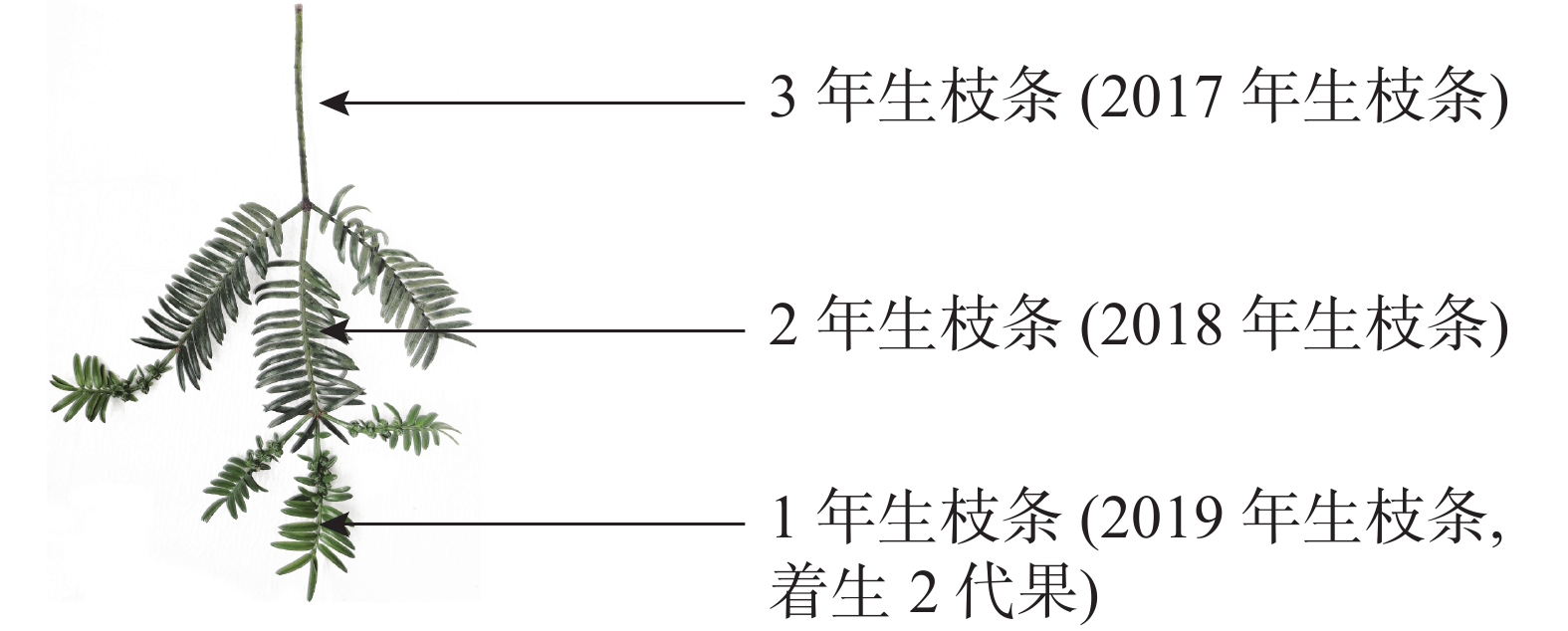
Objective With an exploration of the relationship between the character changing patterns of seed-bearing mother shoots and the seed-bearing capacity of initial seed bearers in Torreya grandis ‘Merrillii’, this study is aimed to provide theoretical and technical rationale for the control of shooting, the culture of seed-bearing mother shoots, and the promotion of seed yield. Method With the T. grandis ‘Merrillii’ trees located in Jinyuan village of Lin’an District, Hangzhou City of Zhejiang Province selected as the subjects, an analysis was conducted of the characteristics of seed-bearing mother shoots either among trees of various levels of vigor or among different layers of a crown, the distribution of seed-bearing mother shoots in terms of shoot length and thickness, and the relationship between the content of mineral elements in shoots and leaves and seed-bearing parameters. Result The seed-bearing mother shoots from moderately vigorous trees were the thickest and significantly longer than those from the trees of weak vigor (P<0.05). Trees of various levels of vigor were significantly different in the percentage of mixed buds and seed-setting rate (P<0.05), with the percentage of mixed buds and seed-setting rate of weak trees being higher than those of vigorous trees. The seed-bearing mother shoots in the upper layer of the crown were the thickest and longest while those in the lower layer of the crown were the thinnest and shortest (P<0.05). The proportion of mixed buds and seed-setting rate were significantly different among layers of the crown (P<0.05) and varied with the vigor of trees, with the seed-setting rate being the highest in the lower layer of the crown of the moderately vigorous and weak trees. The mother shoots with a thickness of 1.91−2.50 mm and a length of 5.51−8.70 cm took up the highest percentage in new seeds and swollen seeds while the seed-setting rate was significantly negatively correlated with the length of the mother shoot (P<0.01). In terms of mineral nutrition, the nitrogen content in the shoots and leaves was significantly different among trees of various levels of vigor (P<0.05), with the percentage of nitrogen in the shoots and leaves sampled in June from the trees of moderate vigor being the highest whereas the Ca content was significantly positively correlated with the length of mother shoots, but significantly negatively correlated with the seed-setting rate (P<0.05). Conclusion In the process of production, the cultivation of moderately growing trees with a proper control over the length of mother shoots and the tree height would be conducive to the increase in seed setting rate and mixed bud proportion. On the other hand, it is of great significance to retain the mother shoots with a thickness of 1.91−3.10 mm and a length of 5.51−11.90 cm to achieve the promotion of seed-setting rate and yield. Also, calcium fertilizer plays an important role in promoting seed growth and improving the seed-setting rate in T. grandis ‘Merrillii’. [Ch, 3 fig. 8 tab. 21 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 50-59.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210188
Abstract:
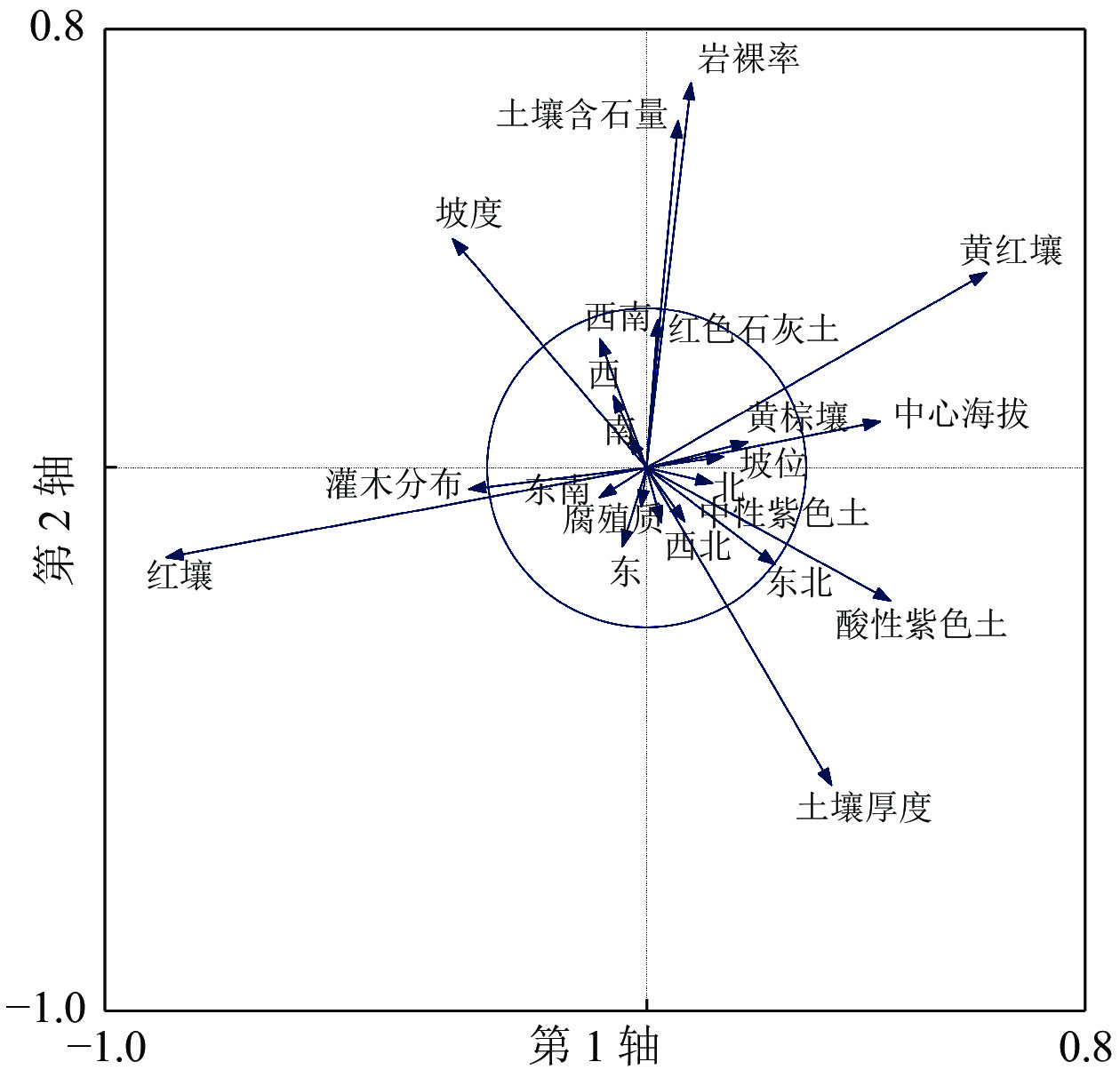
Objective The objective is to study the variation of community plants diversity in the process of ecological rehabilitation of landslide slashed after earthquake and and make environmental interpretation. Method Taking the soil and plant communities in Mt. Fenghuang landslide slash in Beichuan County as the objects, the landslide slashes were divided into landslide area, transition area and non-landslide area. The vegetation changes in the three areas were analyzed by CCA (canonical correspondence analysis) method, and environmental interpretation was made with regard to the distribution of the plant community. Result (1) From 2013 to 2019, the number of plant families, genera and species in landslide area and transition area increased by 4.00%−483.00%, and that in non-landslide area decreased by 2.00%−37.50%. (2) The plant diversity in landslide area and transition area increased by 0.02%−483.33% while in non-landslide area decreased by 2.00%−52.94%, and the evenness also decreased. (3) The sum of the eigenvalues of the first two axes related to CCA ranking in arbor, shrub and grass layer accounted for 60%−80% of the total value, indicating that the first two axes contained most of the ranking imformation. (4) Soil pH and aggregate characteristics had a great impact on the vegetation distribution. Conclusion The diversity of plant communities in landslide slash has been improved to some extent, and the environmental factors have crucial influence on plant communities. [Ch, 2 fig. 5 tab. 33 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 60-67.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210197
Abstract:
Objective With an investigation of the distribution patterns of shrub-grassland communities as well as their relationships with the environment in the same geographical unit in the lower section of Lüzhi basin, this study is aimed to explore the formation mechanism of community distribution and then to find out the important pinch point of ecosystem restoration in dry-hot valley area so as to propose methods of systematical restoration and comprehensive management. Method Two-way indicator species analysis (TWINSPAN) and Principle component analysis (PCA) were employed to classify shrub-grassland communities before a proper analysis was conducted of the relationship between the shrub-grassland communities and the environment on the basis of the forest resources investigation data of the shrub-grassland community in the lower section of Lüzhi River in Eshan County. Result The 854 patches were divided into 19 association groups and 65 associations using the TWINSPAN method. In terms of the PCA ordination, the first axis demonstrated the changes in soil depth, rainfall interception and water holding capacity, while the second axis demonstrated the changes in dry, and heat ranges. Under the vertical climate gradient, the richness of shrub-grassland communities was presented in the following pattern: subtropical plateau zone>dry-hot valley zone>south temperate middle mountain zone. Each vertical climate zone was featured with respective typical indicator types of shrub-grassland community and. In the areas with high disturbance intensity, the main distribution patterns were Osteomeles schwerinae, Symplocos sumuntia, Quercus spp., and Rhododendron simsii. Conclusion Habitat filtering and human disturbance are the main formation mechanisms of shrub-grassland community distribution and with an analysis of the distribution of natural shrub-grassland communities in the same geographical unit, the ecological amplitude and the optimal living areas of species populations can be found, which can provide the selections of native tree species for ecological restoration in the dry-hot valley area. Also, the main ecological stresses on the species in the ecosystem can be confirmed in accordance with the relationship between association groups and the environment, thus providing basis and support for systematical restoration and comprehensive management. [Ch, 3 fig. 5 tab. 34 ref.]
Vertical distribution pattern of vegetation on the east and west slopes of Cangshan Mountain in Dali
2022, 39(1): 68-75.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210136
Abstract:
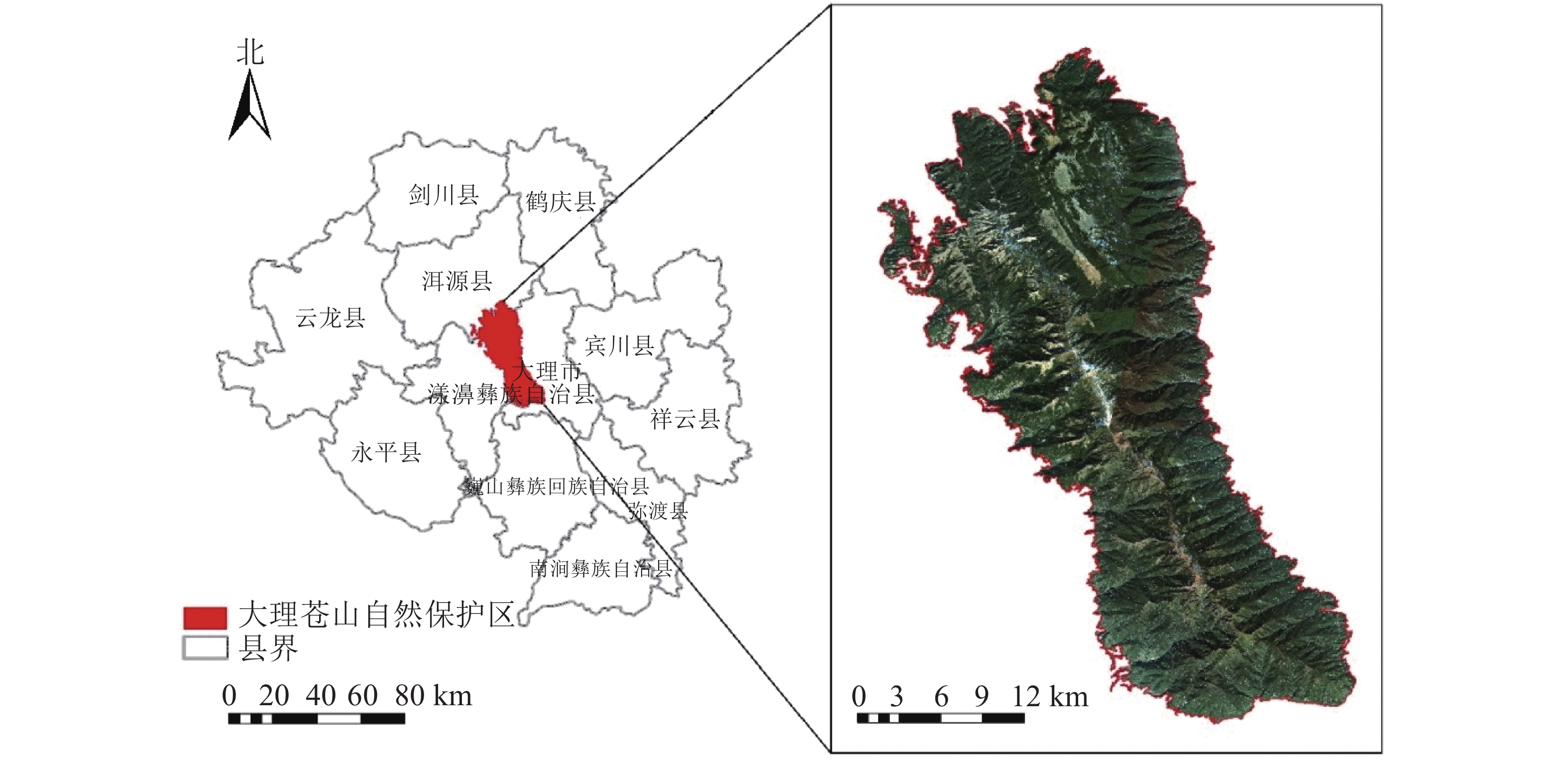
Objective The purpose is to analyze the change characteristics of vertical distribution pattern of vegetation on the east and west slopes of Cangshan Mountain in Dali, Yunnan Province, so as to provide reference for effective protection of ecological environment and species diversity of Cangshan Mountain. Method Taking Cangshan Mountain in Dali as the study area, based on GF-2 high-resolution remote sensing images, combined with the complete vertical zonal distribution law of mountain vegetation in Cangshan Mountain, and supplemented by texture features and digital elevation model (DEM) data, the object-oriented multi-level image segmentation method was adopted by constructing terrain constraint factors to participate in the classification process, accurately select samples, and extract vegetation information in the study area with high precision, and analyze the vertical distribution pattern of vegetation on the east and west slopes of Cangshan Mountain. Result (1) The vegetation types extracted by the object-oriented classification method with auxiliary information were continuous and effective, and the overall classification accuracy was 95.3%, and Kappa coefficient was 0.946 6. (2) The current vegetation vertical distribution pattern on the east and west slopes of Cangshan Mountain is obvious, each of which has six vertical distribution zones. With the increase of altitude, the convergence of vegetation distribution types increases, but there are some differences between the dominant vegetation types in the spectrum of the vertical bands on the east and west slopes. Conclusion Compared with the traditional subjective classification method, the terrain constraint factor with vertical band spectrum information can effectively improve the accuracy of mountain vegetation classification, which fully shows that the object-oriented multi-level segmentation method is suitable for the accurate extraction of vegetation information in Cangshan Mountain. [Ch, 5 fig. 3 tab. 20 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 76-83.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210106
Abstract:
Objective The suitable areas for planting Carya illinoinensis in China at present and in the future are predicted, which can provide reference for the cultivation of C. illinoinensis. Method With the employment of MaxEnt maximum entropy model and ArcGIS, this study is aimed to make predictions of the suitable areas for planting C. illinoinensis in China at present and in the future in different climate scenarios based on distribution data of C. illinoinensis cultivated areas in North America and the global environmental climate variables so as to provide reference for the introduction and cultivation of C. illinoinensis. Result (1) The area under the curve (AUC) of the training data and the testing data were 0.987 and 0.985, indicating high accuracy of the prediction results. (2) The jackknife test results and contribution rate results showed that the annual mean temperature, the mean temperature of the warmest season, the annual precipitation, the precipitation of the driest month, the mean temperature of the driest season, the mean diurnal range and the temperature seasonality were the key climatic variables for the growth of C. illinoinensis. (3) It is predicted that the suitable planting areas of C. illinoinensis in China at present are mainly distributed in Jiangxi, Hunan, Hubei, Anhui, Zhejiang, Jiangsu and Henan whereas under a warmer climate scenario in the future, the highly suitable planting areas of C. illinoinensis in China will increase significantly, and show a tendency of moving northward to cover a some limited areas in eastern Liaoning and Southern Jilin. Conclusion The predictions made of the suitable planting area of C. illinoinensis in China using MaxEnt model were featured with high accuracy: currently, the suitable planting areas of C. illinoinensis are mainly distributed in central and eastern China while in the future, the potential highly suitable planting areas for C. illinoinensis in central and eastern China will expand inward with the increase of temperature and the potential suitable planting areas tend to expand northward. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 36 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 84-94.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210237
Abstract:
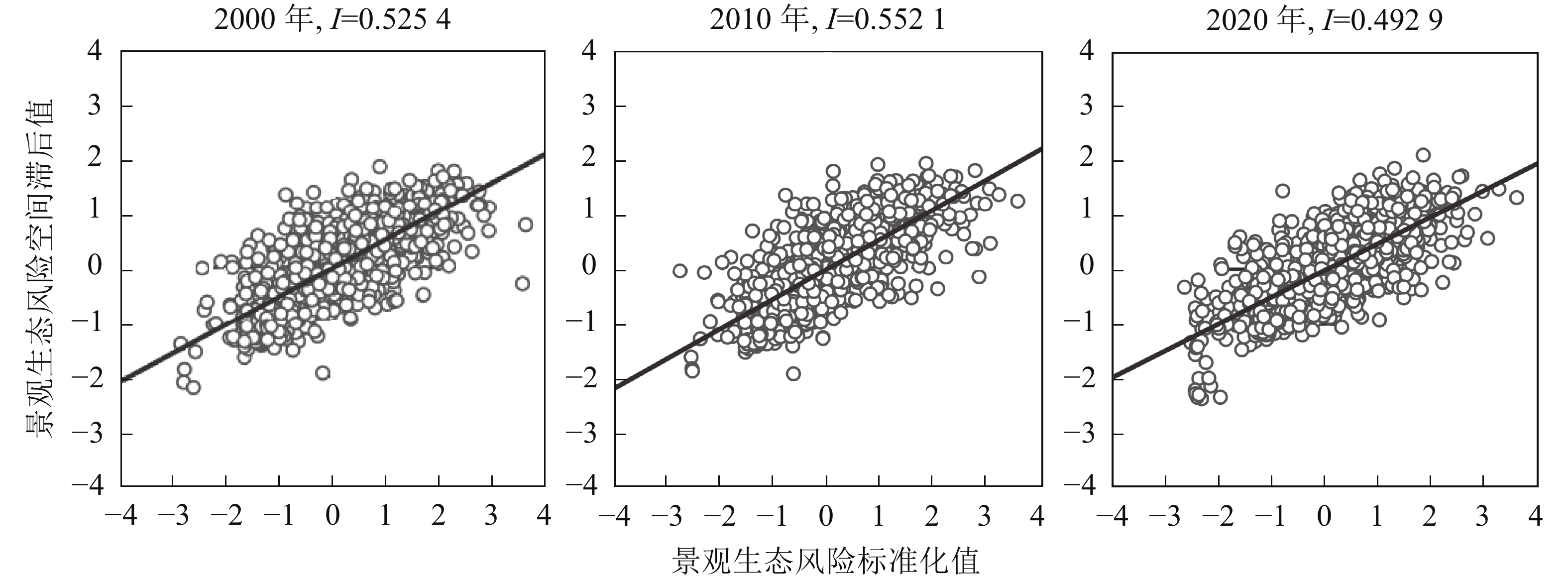
Objective With an exploration of the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of landscape ecological risks in key mountainous development zones as well as the the simulation and prediction of the changing trends of landscape ecological risks, this study is aimed to provide support for the alleviation of the conflicts between ecological protection and construction, so as to promote the sustainable use of land resources, giving full play to the regional central function and furthering the high-quality regional development in small and medium-sized towns. Method Based on the land cover data of 2000, 2010 and 2020, a model of risk assessment on landscape ecology was constructed on the basis of the landscape index to examine the spatiotemporal variations of landscape ecological risk in Anning in Yunnan Province. Then, a prediction was made of the spatial distribution characteristics and trends of landscape ecological risks in different contexts in Anning in 2030 employing the PLUS model which was improved from the FLUS model. Result From 2000 to 2020, the area of artificial surfaces in the study area showed an upward trend, while the area of cultivated land, grassland, shrubland and water bodies showed a downward trend, with the area of forest land staying relatively stable. The spatial agglomeration state of landscape ecological risk values was significant, yet with its degree on the decline and the landscape ecological risk was mainly at medium and high levels in Anning taking up 59.76%−52.95% of the total area. Under the ecological protection scenario in 2030, the area of high ecological risk zone will be the smallest deterioration zone taking up an even smaller share while the area of low ecological risk zone will be the largest. Conclusion The contradiction between ecological risk control and the construction of small and medium-sized towns in mountainous areas was obvious. The spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of landscape ecological risks were closely related to the intensity of human activity intervention, and the higher ecological risk regions were mainly distributed in the fringes of the urban areas. Therefore, focus should be laid on the dynamic changes in the structure of landscape types and their ecological risks as a result of urban land expansion. It was also found that the spatial distribution characteristics and change trends of landscape ecological risk under the ecological protection scenario are closer to the optimization path of ecological security pattern and this scenario is more consistent with the high-quality development of regional economy and society in Anning. [Ch, 5 fig. 5 tab. 30 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 95-104.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210105
Abstract:
Objective Optimize the layout of urban planning to explore the coupling path of urban construction space and green space, optimize the spatial layout of urban land to achieve coordinated and sustainable development. Method Multi-temporal urban LUCC analysis and prediction simulation were carried out based on fractal, artificial neural network cellular automata (ANN-CA) and spatial syntax models. Result (1) The fractal dimension increased from 1.64 in 2003 to 1.70 in 2013 and reached 1.75 in 2018. (2) There is a data mutation point in the aggregation dimension, and the spatial aggregation state is different in different circles. (3)The spatial accessibility of urban greenness decreased significantly from 2003−2018. (4) The ANN-CA-GM(1, 1) urban growth model is constructed to simulate three future scenarios of “free, constrained and ideal”, and the coupling development process of construction space and green space is predicted: the urban construction land will continue to increase to 156.71 km2 in 2025, and the agglomeration range of construction space under the ideal scenario will fall back to 5500 m around the city government, and the area ratio of green space to construction space is 1.00∶1.48. Conclusion (1) The urban form is close to optimal in 2013, followed by an overly dense layout of urban built-up land in 2018 due to high-density urban development, which hinders the coupled exchange with greenness space. (2) In 2018, the construction land was highly concentrated in 14 circles (7 000 m) around the city government. The development of ecological land in this region helps to guide smart growth and build a resilient city. the coupled exchange with greenness space. (3) The area with large green space area and high accessibility are concentrated outside the high aggregation area, while the utilization of riverside green space in the aggregation area is low. (4) The ideal scenario spatial coupling layout provides quantitative data support and spatial layout reference for land spatial planning and “three-line delimitation”, and realizes the effective supply of urban ecological products through green space layout. [Ch, 7 fig. 4 tab. 33 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 105-114.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210178
Abstract:
Objective With an exploration of the temporal and spatial changes of landscape pattern as well as an investigation of its cold and hot spots, this paper is aimed to provide a scientific basis for regional ecological security and high-quality development. Method With landscape type data collected of the Lixiahe Plain, Jiangsu Province over the five periods of 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2018, an analysis was made of the characteristics of temporal and spatial changes of its landscape pattern in the past 40 years using landscape pattern metrics, transfer matrix and comprehensive dynamic index. Then, an investigation was conducted of the cold and hot spot regions of landscape changes on the basis of hot spot analysis. Result Cultivated land, lake wetland and construction land were the dominant landscape types in the study area with the coverage of cultivated land accounting for the largest proportion, but having decreased by 1 000.67 km2 in the past 40 years whereas the areas of lake wetland and construction land increasingly expanded, with the area of construction land increasing by 679.83 km2 and the area of grassland and unused land showed a slightly decreasing trend, while that of forest increased slightly. The landscape types had undergone complex mutual transformations in the past 40 years with those of cultivated land, lake wetland and construction land being the most remarkable with the comprehensive dynamic index of the grid landscape varying between 0 and 5.43% over the study period. The landscape change of the Lixiahe Plain had obvious directionality and agglomeration: the center of change was tilted along the “southeast-northwest” direction, and the hot spots of landscape change were located at Xinghua City, Gaoyou City, Yandu District and Jiangdu District. Conclusion The landscape pattern of the Lixiahe Plain underwent significant changes due to the increase of landscape diversity and the intensification of fragmentation and the impact of human activities on the landscape pattern. The implementation of the natural wetland restoration policy had a positive impact on the landscape ecological security in the Lixiahe Plain. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 32 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 115-126.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210168
Abstract:
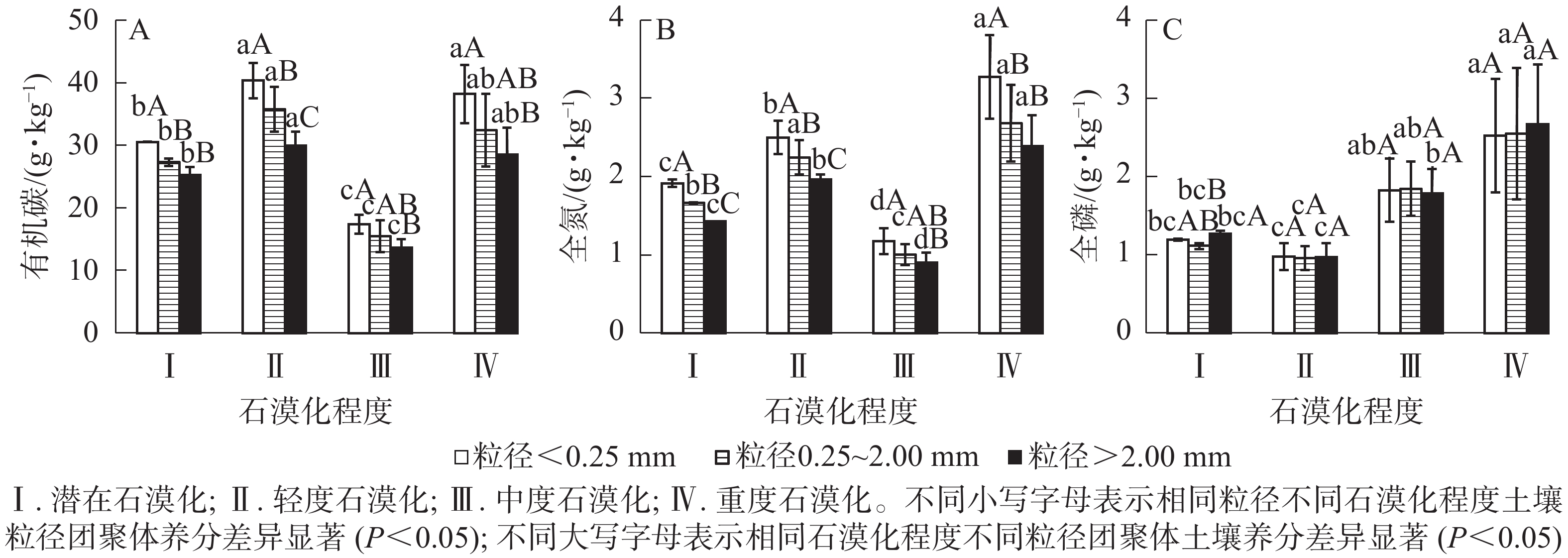
Objective With the features of the nutrient and enzyme activity of the soil aggregates in the rocky desertification area carefully investigated, this study is aimed to provide a theoretical basis for the soil improvement and vegetation recovery. Method With four kinds of soils with different degrees of rocky desertification (potential, mild, moderate and severe rocky desertification) in the Central Yunnan Plateau as the research objects, an analysis was conducted of the distribution characteristics of 3 aggregates (the particle sizes were <0.25, 0.25−2.00, >2.00 mm respectively), the activity of 4 hydrolytic enzymes (amylase, urease, β-glucoside, acid phosphatase) and the content characteristics of 3 nutrients (organic carbon, total nitrogen, total phosphorus) in the aggregates. Result (1) The proportion of aggregates in soil with different degrees of rocky desertification increased with the increase of particle size, from high to low: particle size was >2.00 mm (51.31%), particle size 0.25−2.00 mm (36.53%), particle size <0.25 mm (12.04%). (2) The geometric mean of soil urease, β-glucoside enzyme, acid phosphatase, soil enzyme activity and organic carbon and total nitrogen content of aggregates with different particle sizes all decreased with the increase of aggregate size. The contribution rate of different particle size aggregates to organic carbon, total nitrogen, total phosphorus and enzyme activity is the highest when particle size was >2.00 mm, which was followed by the particle size of 0.25−2.00 mm and the particle size of <0.25 mm in a successive pattern. (3) The mean amylase activity of aggregates with different degrees of stony desertification was 5.70 mg·g−1·h−1, and the change trend for stony desertification soil was potential > mild > severe > moderate whereas the change trend of organic carbon, total nitrogen, urease and β-glucosidase activity for stony desertification soil was severe > mild > potential >moderate. The particle size of aggregates and the degree of rocky desertification had significant effects on soil organic carbon, total nitrogen and enzyme activity (P<0.05), but the interaction of particle size and degree of rocky desertification had no significant effect on soil nutrient and enzyme activity (P>0.05). Conclusion In karst rocky desertification areas, soil aggregates with larger particle sizes are dominant in soil composition and have a relatively higher contribution rate to soil nutrient and enzyme activity, while soil aggregates with smaller particle sizes are more conducive to the accumulation of soil nutrients and enzyme activity, with higher corresponding contents as well. [Ch, 2 fig. 6 tab. 45 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 127-135.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210170
Abstract:
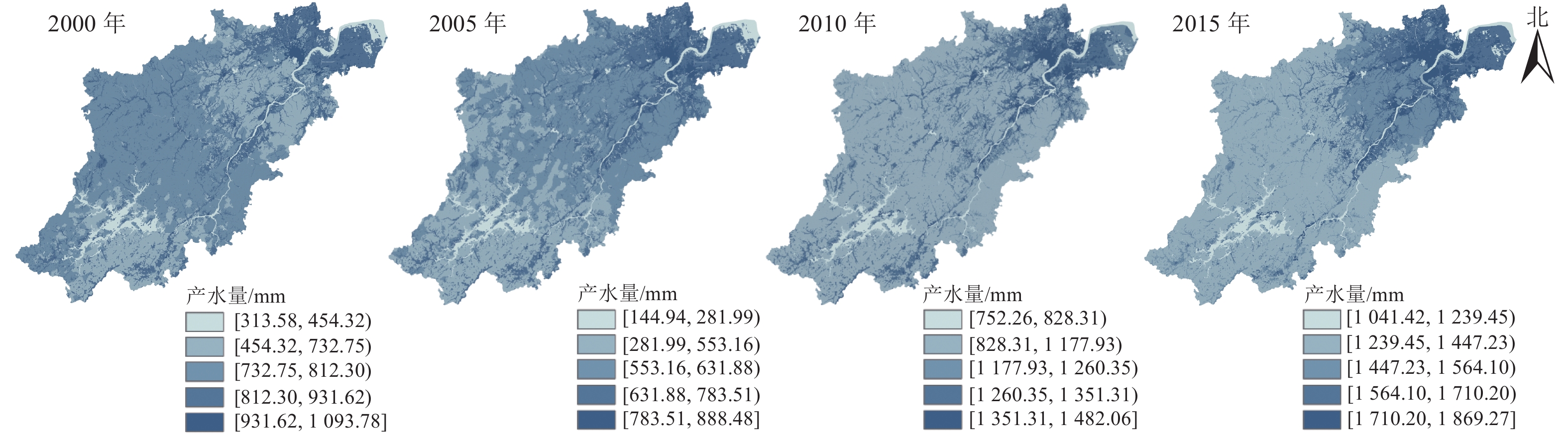
Objective Natural factors and land use changes are important driving factors of ecosystem services change. The analysis of temporal and spatial variation characteristics in annual water yield and its main driving factors have practical significance for maintaining or improving urban soil and water conservation. Method This study took Hangzhou as the research object, adopted methods of landscape pattern analysis, spatial gradient analysis, and correlation analysis with the support of the InVEST model, ArcGIS, Fragstats, SPSS and other tools, identified the characteristics of land use and meteorological factors of Hangzhou, evaluated and analyzed the temporal and spatial variation of annual water yield and its correlation with meteorological factors and landscape pattern indices. Result The annual water yield in Hangzhou showed a first decline and then an upward trend from 2000 to 2015. The water yield is spatially high in the northeast and low in the southwest, and increased first and then decreased with distance from the city center, reaching the maximum at 10 km. Construction land had the largest water yield. The most dramatic change in land use in Hangzhou from 2000 to 2015 was the conversion between cultivated land and construction land. On the whole, the landscape showed a stronger trend of fragmentation and heterogeneity, reaching a peak at 10−20 km from the city center. The annual precipitation in Hangzhou decreased first and then increased. The annual average temperatures fluctuating increased and the annual actual evapotranspiration fluctuated. The annual precipitation does not change significantly within 50 km of the city center. The annual average temperature decreased significantly as it moved away from the urban center, while the annual actual evapotranspiration first decreased and then increased. The correlation between water yield and meteorological factors was greater than that of landscape patterns indices. Water yield had the strongest positive correlation with precipitation in meteorological factors. Conclusion The change of meteorological factors was the main factor causing annual water yield change in Hangzhou, but the impact of landscape pattern was still worthy of attention. The 10 km distance from the city center was the turning point of annual water yield. [Ch, 4 fig. 7 tab. 34 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 136-145.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210260
Abstract:
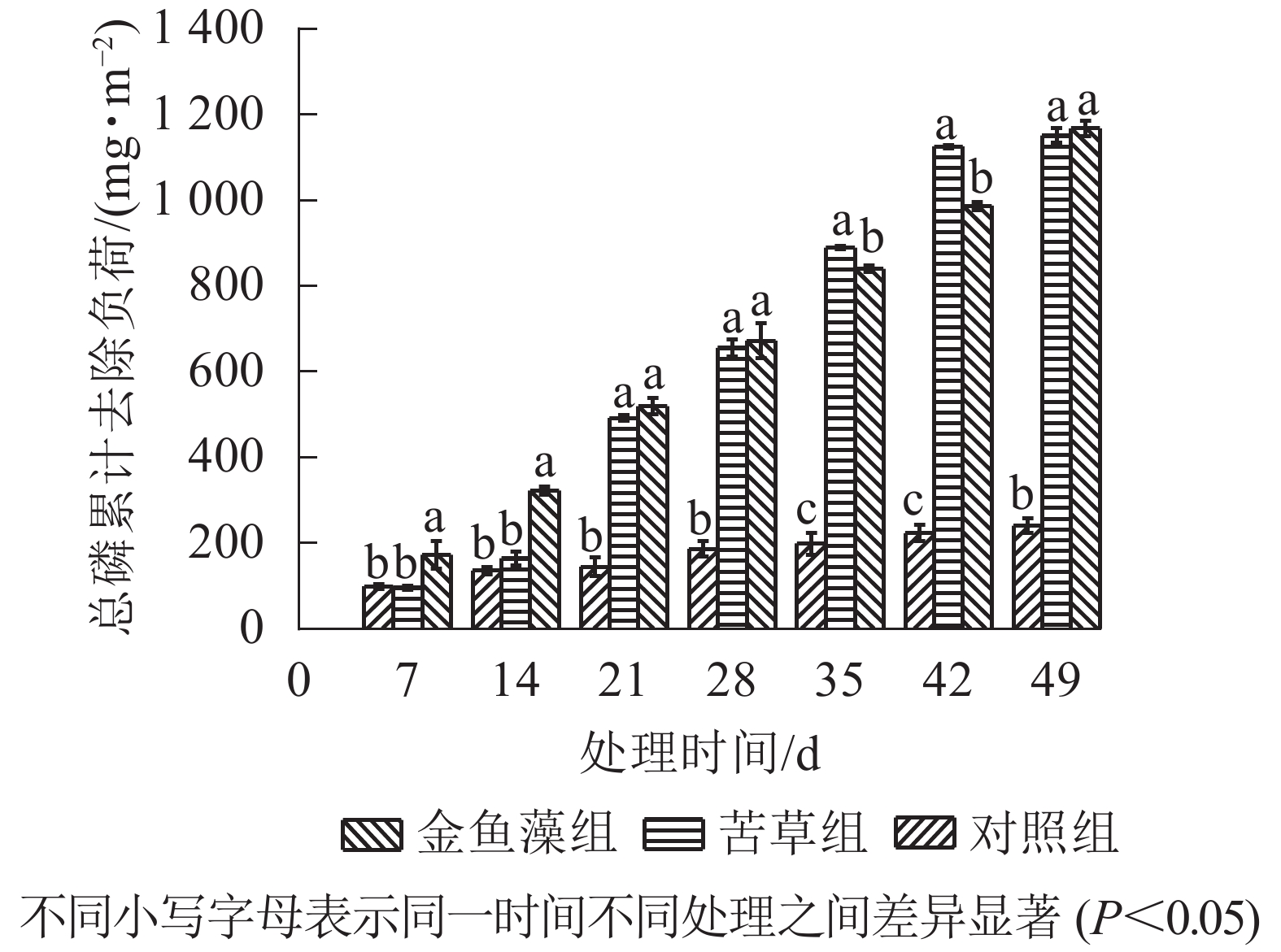
Objective The objective of this study is to investigate the dynamic performance of ecological purification system with submerged macrophytes as pioneer species for treatment of phosphorus pollution in farmland drainage. Method A batch-mode mesocosm experiment was performed to study total phosphorus (TP) purification efficiency and kinetic parameters of two submerged macrophyte systems: Vallisneria natans and Ceratophyllum demersum. Four kinetic models including first-order kinetic, Grau second-order kinetic, Monod kinetic and modified Gompertz model were used to evaluate TP removal efficiency. Result At the end of the experiment (Day 49), there was no significant difference in TP removal efficiency between the two mesocosm systems (P>0.05), and the TP removal rates were 82.8% for V. natans and 84.0% for C. demersum, but the difference in TP removal efficiency was uncertain in time scale. Kinetic simulation analysis showed that except Grau second-order kinetic, first-order kinetic, Monod kinetic and modified Gompertz model were proven capable of predicting TP removal process of the two submerged plant systems under experimental conditions, with R2 (coefficient of determination)>0.930 and RRMSE (relative root mean square error)<0.200. Among them, Monod kinetic and modified Gompertz model showed a higher fitting degree (R2>0.970), and a better agreement between the predicted value and the observed value (RRMSE<0.110). Conclusion The kinetic parameters obtained by the three effective model fitting show significant differences at the plant species level (P<0.05), and V. natans has higher kinetic parameter of TP removal efficiency compared with C. demersum (P<0.05), indicating that TP removal efficiency of V. natans is better than that of C. demersum. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 35 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 146-152.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210165
Abstract:
Objective This objective is to analyze the characteristics of swine breeding wastewater under biochemical treatment mode, and put forward a reasonable and rapid water quality assessment method, so as to provide a theoretical basis for swine farms and related regulatory authorities to understand the wastewater treatment situation. Method A large-scale swine farm in northern Zhejiang was taken as the sampling location, and the treated breeding wastewater was randomly sampled from fall 2018 to fall 2020. Firstly, SPSS software was used to analyze the statistical characteristics of the samples, and then the stepwise multiple regression analysis method was used to determine the key indexes affecting the wastewater quality. Thirdly, combined with the correlation among the water quality indexes, the assessment model of the minimum water quality index for swine wastewater was established. Result (1) The water quality will change in different seasons, it was better in spring and summer than that in fall and winter, and the water quality in summer was the best. (2) Based on the electrical conductivity and chemical oxygen demand, the assessment model of the minimum water quality index was established, its determination coefficient was 0.994. The verification results showed that the consistency of evaluation grades of water quality based on the minimum model and five indexes include ammonia nitrogen, chemical oxygen demand, total nitrogen, total phosphorus and pH can be more than 90%. Conclusion The minimum water quality index model based on key indexes can be used for rapid evaluation of swine breeding wastewater quality under biochemical treatment mode, meanwhile its accuracy and rationality can be ensured. [Ch, 4 fig. 3 tab. 28 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 153-158.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210166
Abstract:
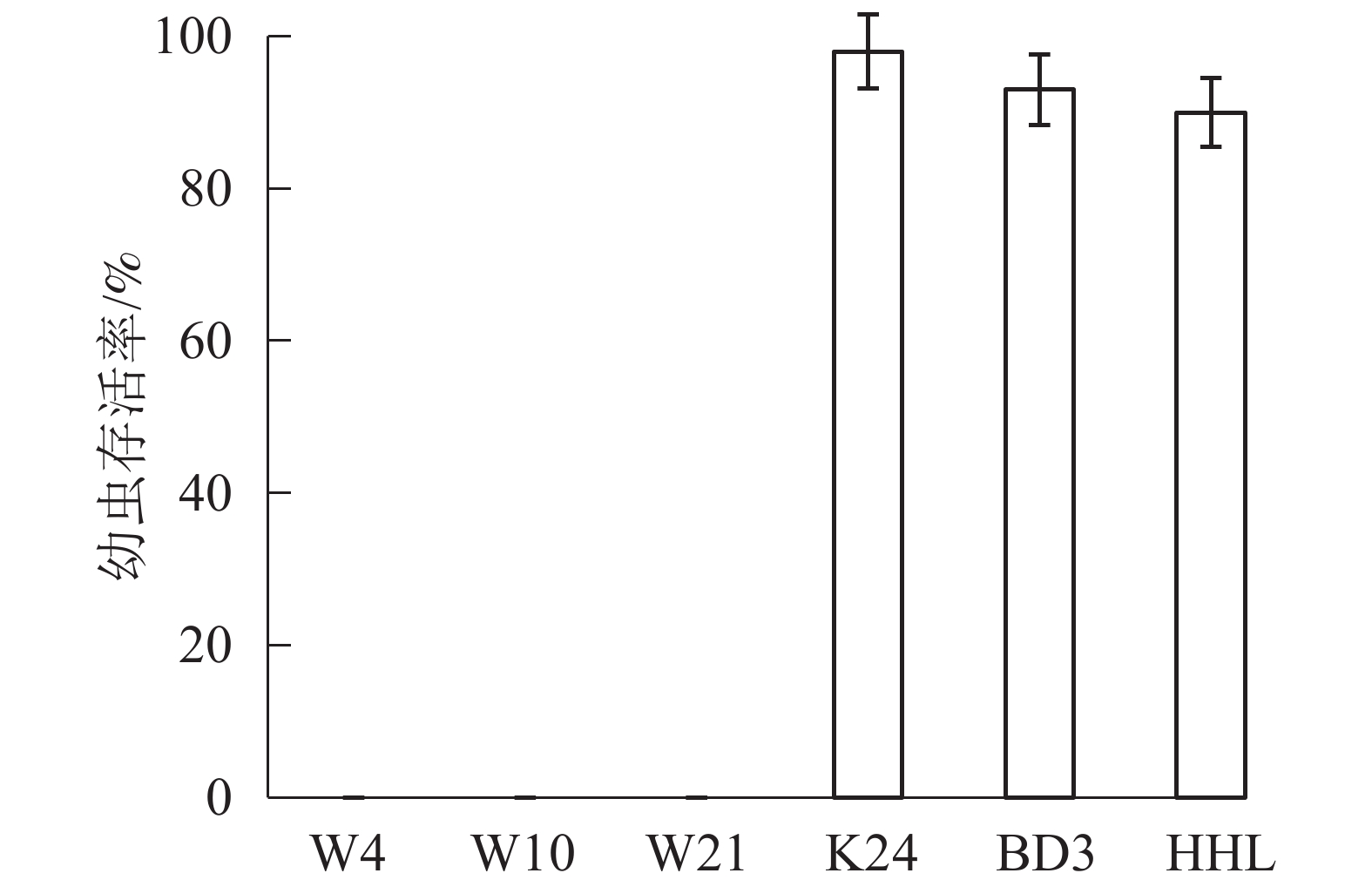
Objective This purpose is to explore the insect resistance of different willows (Salix spp.) to Plagiodera versicolora, and to provide reference for the breeding of willow cultivars with strong insect resistance. Method S. caprea, S. matsudana, S. babylonica and 3 clones of S. triandra were tested in laboratory for insect feeding, and the differential secondary metabolites between insect resistant and non insect resistant groups were determined and screened. Result The survival rate of indoor feeding was 98% for S. matsudana, 93% for S. babylonica, 90% for S. caprea and 0 for S. triandra. There were 23 main different metabolites between the non insect resistant group and the insect resistant group, among which 15 were up-regulated, including fer-agmatine, L-ascorbic acid, gallic acid, (−)-epigallocatechin, (+)-gallocatechin, myricitrin, L-(+)-tartaric acid, D-(−)-arabinose, hydroxy-methoxycinnamate, N-feruloyl agmatine, gluconic acid, 2 ′-Hydroxygenistein, N-Acetyl-DL-tryptophan, eupatilin 3-glucoside, and hexadecylsphingosine, and 8 were down-regulated, including quercetin 3-O-(6″-O-malonyl)-galactoside, hesperidin, rutin, D-galactopyranuronate, 2,5-dihydroxy benzoic acid O-hexside, quercetin O-acetylhexoside, 3-hydroxy-5-methylphenol-1-Oxy-β-D-glucose, and bioquercetin. Conclusion S. triandra has the best insect resistance to P. versicolora. There are significant differences in the main secondary metabolites between the non insect resistant group and the insect resistant group, which indicates that the secondary metabolites of S. triandra may be toxic to the larvae of P. versicolora, or lack of nutrients necessary for larvae growth and development, resulting in the death of the larvae. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 23 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 159-165.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210366
Abstract:
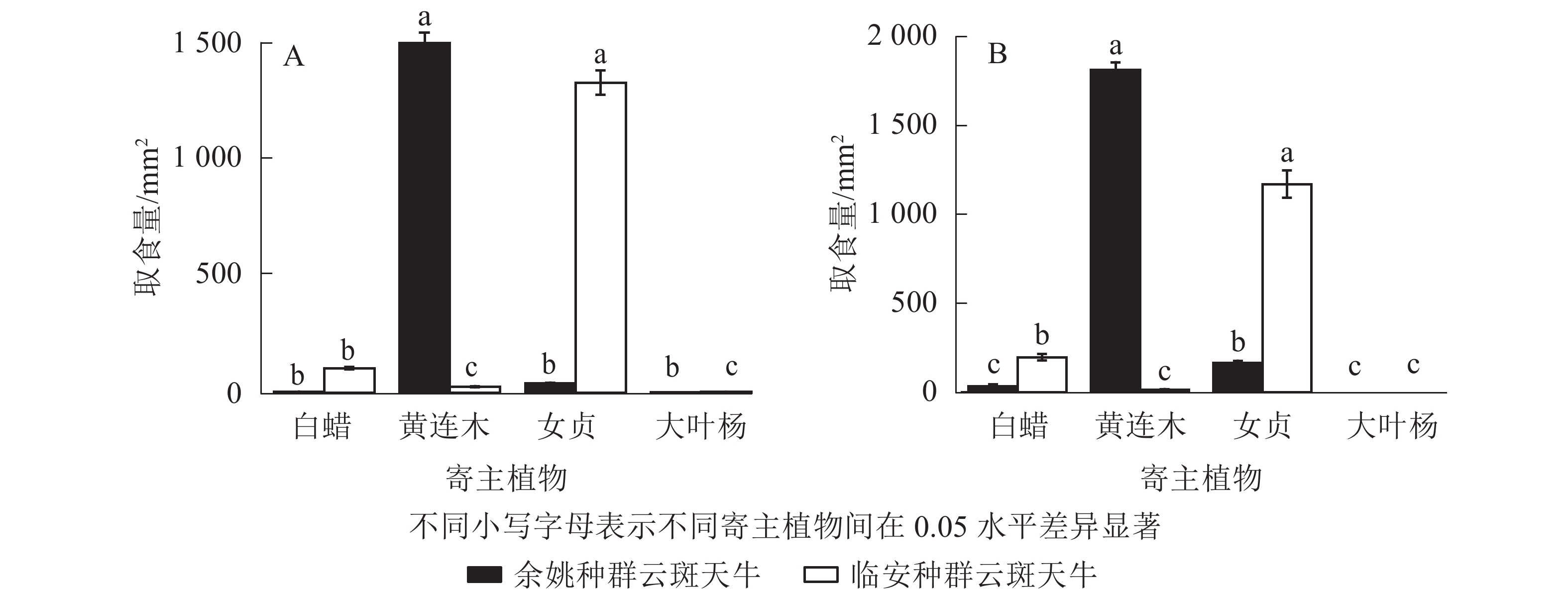
Objective This study aims to explore the adaptability of different populations of Batocera horsfieldi to host plants. Method Through indoor feeding and oviposition experiments, the difference of feeding and oviposition behaviors between B. horsfieldi in Yuyao and that in Lin’an to four host plants were measured. Result The feeding experiment showed that Yuyao population and Lin’an population had different feeding preference for four host plants. The feeding preference of Yuyao population in descending order was Pistacia chinensis, Ligustrum lucidum, Fraxinus chinensis and Populus lasiocarpa. Yuyao population liked P. chinensis best. Under selective and non-selective conditions, the food intake was (1 520.00±34.79) and (1 815.50±42.13) mm2. The feeding preference order of Lin’an population was L. lucidum, P. chinensis, F. chinensis and P. lasiocarpa from high to low. Lin’an population liked L. lucidum best. Under selective and non-selective conditions, the food intake was (1 347.33±51.95) and (1 173.00±75.54) mm2. Yuyao population and Lin’an population showed consistent oviposition preference for four host plants, and they all liked to oviposit on P. lasiocarpa. The oviposition preference order of Yuyao population was P. lasiocarpa, L. lucidum, P. chinensis and F. chinensis from high to low. Under selective and non-selective conditions, the number of grooves on P. lasiocarpa was 72.00±5.87 and 82.00±7.64, and the number of eggs was 60.00±6.19 and 58.00±5.66, respectively. The oviposition preference order of Lin’an population was P. lasiocarpa, L. lucidum, F. chinensis and P. chinensis from high to low. Under selective and non-selective conditions, the number of grooves on P. lasiocarpa was 35.00±5.22 and 30.00±3.85, and the number of eggs was 22.00±4.51 and 25.00±3.08, respectively. Conclusion In order to adapt to different habitat environments, different populations of B. horsfieldi have different feeding preference hosts. Yuyao population prefers to feed on P. chinensis, while Lin’an population prefers to feed on L. lucidum. P. lasiocarpa is the oviposition preference host of both populations. [Ch, 3 fig. 23 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 166-172.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210241
Abstract:
Objective This study is aimed to understand whether there is a conservation gap of epiphyllous liverworts in the in-situ conservation of China. Method A systematic survey of epiphyllous liverworts in Baishanzu National Park and its surrounding habitats was carried out in Qingyuan County, Zhejiang Province. The diversity, distribution, species composition and similarity in and out of the reserve were analyzed and compared. Result (1) A total of 25 species of epiphyllous liverworts belonging to 11 genera and 4 families were recorded, including Lejeuneaceae (21 species), Radulaceae (2 species), Metzgeriaceae (1 species) and Frullaniaceae (1 species). The dominant family in the area was Lejeuneaceae and the dominant genus was Cololejeunea. Cololejeunea longifolia and Leptolejeunea subacuta were common species in this area. (2) Among the 25 species of epiphyllous liverworts in 11 genera and 4 families, 14 species belonging to 9 genera and 4 families were found in the park, and 14 species belonging to 7 genera and 2 families were found out of the park. However, the Jaccard similarity coefficients of families, genera and species in and out of the park were 0.50, 0.45 and 0.12, respectively, indicating that the species composition of the two regions was quite different. (3) Compared with the historical data of Baishanzu National Park, there were 6 species newly recorded in this survey, of which 3 species were only distributed outside the park, including Cheilolejeunea chenii, a species with great protection value. Conclusion There is a conservation gap in the in-situ conservation of epiphyllous liverworts in Qingyuan County, Zhejiang Province. Therefore, research on the conservation gap of epiphyllous liverworts in other regions of China should be carried out as soon as possible. [Ch, 1 tab. 28 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 173-179.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210219
Abstract:
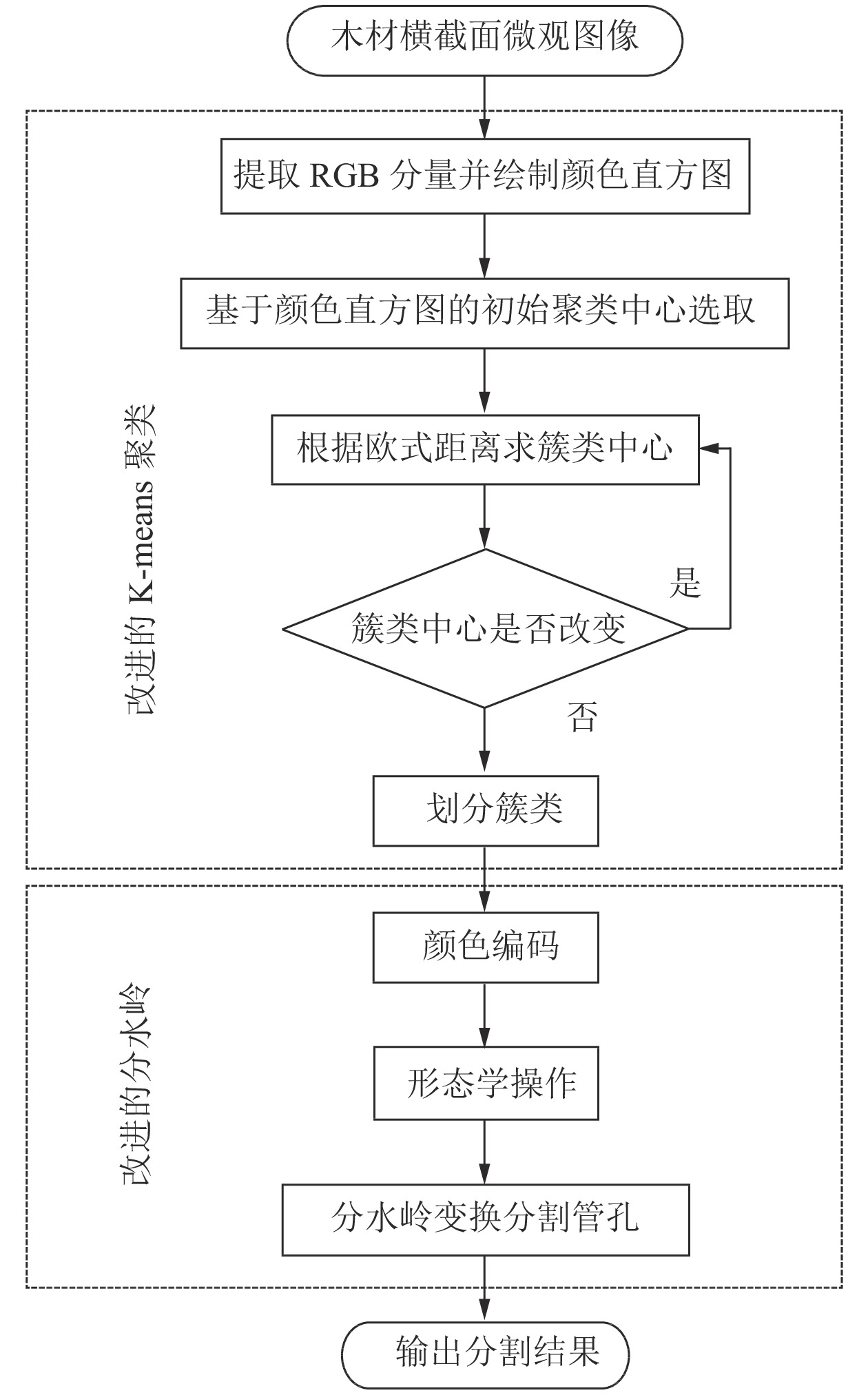
Objective Pore is one of the important characteristics of wood identification. Aiming at the problems of poor robustness of pore segmentation due to random distribution and different sizes of pores and the impact of noise such as wood fiber, wood ray and axial parenchyma on the segmentation effect of pores, this study attempts to propose an improved K-means clustering and watershed algorithm for segmentation of wood cross-section pores. Method The improved K-means clustering was used to segment the pore area, which could distinguish the pore area from noise areas such as wood fiber, wood ray and axial parenchyma. Then, an improved watershed algorithm was used to segment the rough segmentation results, and the segmented pores were basically consistent with the actual pores. Result On average, 97.1% of the pores were segmented in each microscopic image of wood cross section. Compared with other algorithms, the improved algorithm had a significantly improved segmentation effect, high robustness and good segmentation performance in the process of pore segmentation with different sizes and random distribution. Conclusion This algorithm can effectively solve the problems of noise impact and randomness of initial clustering center in traditional K-means clustering algorithm in image segmentation, and lays a solid foundation for the feature extraction and quantitative analysis of hardwood pores. [Ch, 7 fig. 1 tab. 16 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 180-189.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210103
Abstract:
Objective The objective of this study is to scientifically and rationally arrange the forest health care base, realize the effective connection between supply and demand, and promote the orderly development of the forest health care industry. Method A total of 134 forest health care brand resources in Zhejiang Province were selected as the research objects, including China Forest Health Care Base, China Forest Oxygen Bar, Zhejiang Forest Health Care Base, and Zhejiang Forest Oxygen Bar. By using the nearest neighbor index, geographical concentration index, imbalance index, kernel density analysis, buffer analysis and Pearson correlation analysis, this paper explored the spatial distribution characteristics of forest health care brand resources in Zhejiang Province and the natural, social and human factors affecting their spatial distribution. Result The spatial distribution of forest health care brand resources in Zhejiang Province was agglomerated as a whole, and the agglomeration trend was obvious. At the municipal level, Huzhou, Lishui, Taizhou and Wenzhou were homogeneous, while Hangzhou, Quzhou, Jinhua and Shaoxing were agglomerative. The distribution of forest health care brand resources in different cities was not balanced. According to the number of health care bases owned by different cities, they could be divided into four echelons with great differences. Kernel density analysis showed that there were differences in the distribution of forest health care brand resources in different regions, which could be divided into large core area dominated by Anji of Huzhou City, sub-core area dominated by Changxing of Huzhou City, Tonglu of Hangzhou City and Longquan of Lishui City, and small core area dominated by Jiangshan of Quzhou City, Yiwu of Jinhua City and Xinchang of Shaoxing City. The factors affecting the spatial distribution characteristics of forest health care brand resources were topography, forest coverage rate, water system, socio-economic foundation, traffic accessibility, and central city correlation. Conclusion Due to the comprehensive influence of natural and human factors, the brand resources of forest health care in Zhejiang Province are unevenly distributed among cities, and there are great differences in the development process of forest health care industry. Topography, forest coverage rate and water system affect the landscape base and ecological environment in the development and construction of forest health care resources and industry. Socio-economic foundation, traffic accessibility and the degree of correlation with the central city are related to its economic support, market potential and accessibility. In the future development of forest health care industry in this province, it is necessary to further combine policy support, market investigation, reasonable planning and resource integration to achieve the goals of global layout, integration promotion, and standardized management. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 23 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 190-198.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210277
Abstract:
The recreation use of national parks is to allow visitors to enter the specific area of national parks for recreation activities on the premise of protecting ecology, environment and resources. The research on the recreation use of national parks needs to be guided by the practical problems in China’s development nowadays. Based on the domestic research progress and foreign theoretical and technical system, it can be seen that the problems to be faced and dealt with in the recreation use of national parks include ecological environment, recreation products, recreation services and management, economic development and social livelihood. Therefore, an interdisciplinary research perspective should be taken. The research framework can be constructed from the dimensions of epistemology and methodology. In the epistemological dimension, it is a three-dimensional structure from subject to cognition and then to behavior. From the perspective of methodology, it is a linkage development system between recreation use and ecological conservation, economic development and social livelihood. [Ch, 2 fig. 2 tab. 30 ref.]
The recreation use of national parks is to allow visitors to enter the specific area of national parks for recreation activities on the premise of protecting ecology, environment and resources. The research on the recreation use of national parks needs to be guided by the practical problems in China’s development nowadays. Based on the domestic research progress and foreign theoretical and technical system, it can be seen that the problems to be faced and dealt with in the recreation use of national parks include ecological environment, recreation products, recreation services and management, economic development and social livelihood. Therefore, an interdisciplinary research perspective should be taken. The research framework can be constructed from the dimensions of epistemology and methodology. In the epistemological dimension, it is a three-dimensional structure from subject to cognition and then to behavior. From the perspective of methodology, it is a linkage development system between recreation use and ecological conservation, economic development and social livelihood. [Ch, 2 fig. 2 tab. 30 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 199-206.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210148
Abstract:
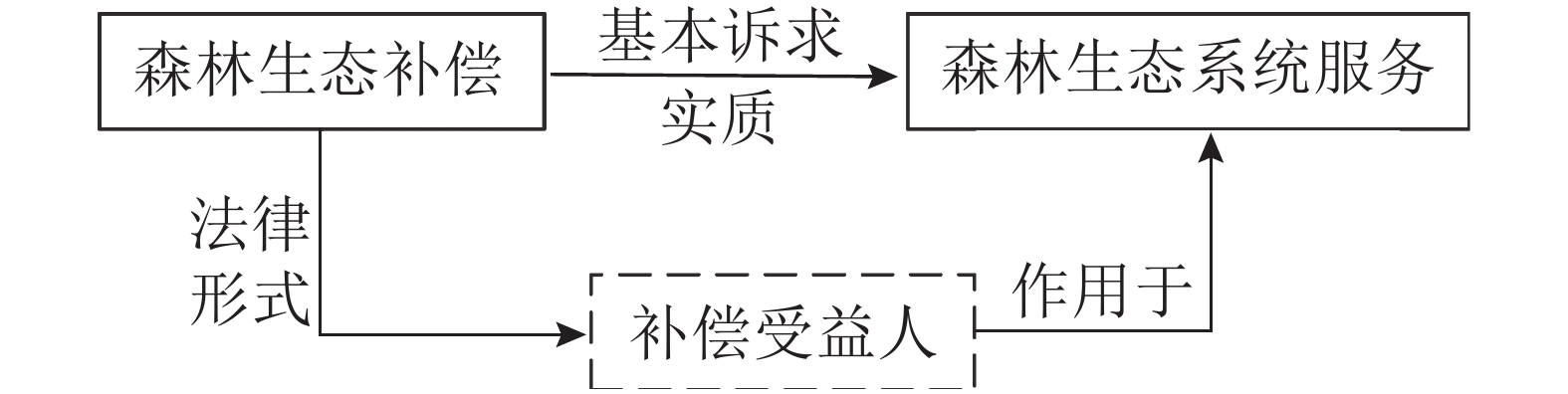
Objective With an exploration of the importance, difficulties and focus of the transformation from “forest area” to “forest stock volume” as the index for the ecological compensation in key public welfare forests, this study is aimed to provide theoretical and technical references for the such transformation in China. Method A three-dimensional comparative analysis of the two ecological compensation bases in key public welfare forests that involve the realization of the compensation target, the incentive of the compensation subjects and the sustainability of the compensation fund. Result Compared with “forest area”, “forest stock volume” is a more accurate index in the actualization of the compensation goal and displays unique advantages in terms of incentives and marketization. Conclusion In the formulation of the ecological compensation for key public welfare forests, the increase in forest stock volume should be the basis of the compensation and regional differences should be fully considered to ensure the execution of differentiated policies. In addition, further explores should be conducted of market-based compensation schemes based on forest stock, with full play given to the market’s efficient regulation and distribution of compensation funds. [Ch, 4 fig. 29 ref.]
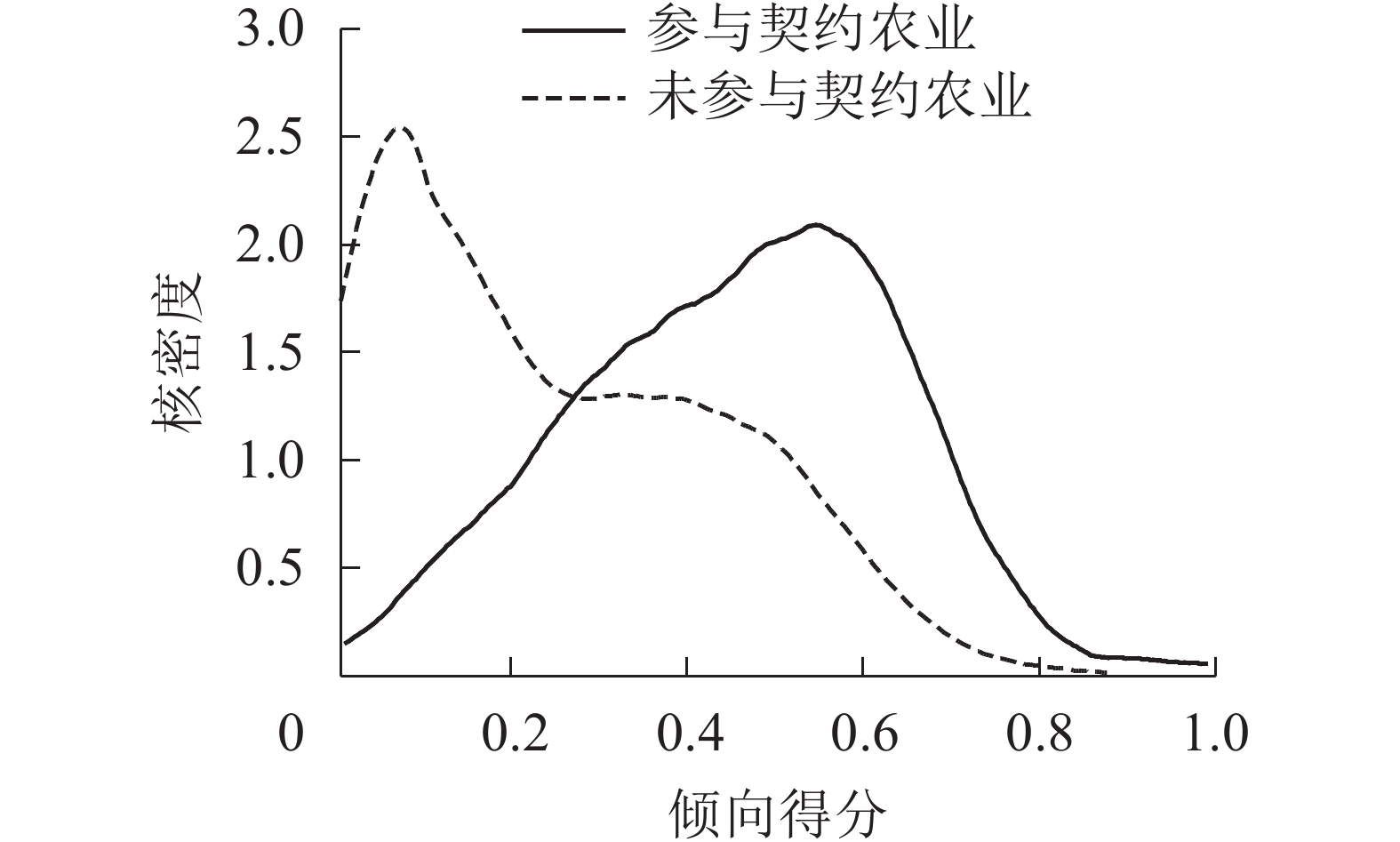
On the impact of contract farming on family farms’ adoption of environmentally friendly technologies
2022, 39(1): 207-213.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20200726
Abstract:
Object It is expected to provide decision-making basis for the promotion of soil testing and formula fertilization technology. Method With 1706 family plantations selected as the subjects, this paper, after an investigation of the influence of contract farming on the adoption of soil testing and formula fertilization technology on family farms by means of Probit and propensity score matching (PSM), is aimed to provide decision-making basis for the promotion of such environmentally friendly technologies. Result The participation of family farms in contract farming has a prominent and effective influence on the adoption of soil testing and formula fertilization technology with an influence coefficient of 0.621. The average treatment effect is about 0.19 and the adoption of such environmentally friendly technologies is also significantly subject to elements like farmers’ participation in soil and fertilizer cultivation technology training, the duration of large-scale agricultural operations, farmers’ experience, farms’ daily records of income and expenditure and farms’ intention for future land expansion. Conclusion Contract farming is a vital factor affecting the adoption of soil testing and formula fertilization technology by family farms, therefore, efforts are called from the government to further accelerate the establishment of a sound participation mechanism of contract farming and support family farms in the promotion of their resource endowment. [Ch, 2 fig. 3 tab. 18 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 214-222.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210201
Abstract:
The riparian vegetation buffer strip in the Yangtze River Basin is an important part of the riparian ecosystem and has an important impact on pollution prevention and ecological environment construction in the Yangtze River Basin. The paper summarized the main ecological functions of the riparian vegetation buffer strips, analyzed the environmental impact factors faced by the riparian vegetation buffer strips in the Yangtze River Basin, expounded the construction technology of the riparian vegetation buffer strips, and proposed prospects for future research. The main ecological functions of the riparian vegetation buffer strips were flood mitigation and revetment, sewage interception and purification, and biological diversity protection. At present, the main influencing factors facing the riparian vegetation buffer strips in the Yangtze River Basin were the invasion of alien species, the construction of a large number of hard engineering projects, and pollutant emission caused by agricultural and industrial development. The construction technology of the riparian vegetation buffer strips in the Yangtze River Basin should be determined according to the characteristics and functions of different riparian strips, and the management of the riparian vegetation buffer strips should be strengthened. Future research should focus on the following aspects: (1) Research on the process and mechanism of the shading effect of riparian vegetation buffer strips. Based on the research results of the shading effect, the advantages and disadvantages of shading and the relationship between shading effect and buffering extreme climate are discussed. (2) Ecological function research under extreme climatic conditions. Models are used to simulate the interception and pollution reduction effects of riparian vegetation buffer strips under extreme climatic conditions (rainstorm, drought, etc.), so as to provide a reference for the construction of vegetation buffer strips. (3) Landscape and watershed scale study. With the help of remote sensing images and data from various meteorological stations, the impact of natural and human activities on the ecological processes and ecological functions of the riparian vegetation buffer strips is studied from landscape and watershed scale in order to explore the comprehensive treatment and management model of riparian vegetation buffer strips. (4) Establishment of a comprehensive evaluation system for the vegetation buffer strips. The structure and ecological function of the riparian vegetation buffer strips are comprehensively evaluated by real-time monitoring of the riparian vegetation buffer strips with the help of digital means, combined with field observation and sample analysis. [Ch, 43 ref.]
The riparian vegetation buffer strip in the Yangtze River Basin is an important part of the riparian ecosystem and has an important impact on pollution prevention and ecological environment construction in the Yangtze River Basin. The paper summarized the main ecological functions of the riparian vegetation buffer strips, analyzed the environmental impact factors faced by the riparian vegetation buffer strips in the Yangtze River Basin, expounded the construction technology of the riparian vegetation buffer strips, and proposed prospects for future research. The main ecological functions of the riparian vegetation buffer strips were flood mitigation and revetment, sewage interception and purification, and biological diversity protection. At present, the main influencing factors facing the riparian vegetation buffer strips in the Yangtze River Basin were the invasion of alien species, the construction of a large number of hard engineering projects, and pollutant emission caused by agricultural and industrial development. The construction technology of the riparian vegetation buffer strips in the Yangtze River Basin should be determined according to the characteristics and functions of different riparian strips, and the management of the riparian vegetation buffer strips should be strengthened. Future research should focus on the following aspects: (1) Research on the process and mechanism of the shading effect of riparian vegetation buffer strips. Based on the research results of the shading effect, the advantages and disadvantages of shading and the relationship between shading effect and buffering extreme climate are discussed. (2) Ecological function research under extreme climatic conditions. Models are used to simulate the interception and pollution reduction effects of riparian vegetation buffer strips under extreme climatic conditions (rainstorm, drought, etc.), so as to provide a reference for the construction of vegetation buffer strips. (3) Landscape and watershed scale study. With the help of remote sensing images and data from various meteorological stations, the impact of natural and human activities on the ecological processes and ecological functions of the riparian vegetation buffer strips is studied from landscape and watershed scale in order to explore the comprehensive treatment and management model of riparian vegetation buffer strips. (4) Establishment of a comprehensive evaluation system for the vegetation buffer strips. The structure and ecological function of the riparian vegetation buffer strips are comprehensively evaluated by real-time monitoring of the riparian vegetation buffer strips with the help of digital means, combined with field observation and sample analysis. [Ch, 43 ref.]
2022, 39(1): 223-232.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210141
Abstract:
Each plant cell harboring all the genetic information of the species has the genetic potential to develop into a whole plant, which is termed plant cell totipotency. Somatic embryogenesis is a form of induced plant cell totipotency, by means of which embryos develop from somatic or vegetative cells in the absence of fertilization. Somatic embryogenesis, an increasingly important tool of plant biotechnology, has been widely applied in germplasm reservation, seedling propagation, molecular breeding and basic research of many plants and it has been implied in previous studies on molecular genetics that somatic embryogenesis is subject to the regulation by a complex network composed of transcription factors, hormone signaling pathways and epigenetic modifications. Therefore, this review, with a summary of the development routes of plant somatic embryogenesis, is aimed to give a comprehensice overview of the research progress achieved in the functions of key genes and epigenetic modification in the process of somatic embryogenesis along with an introduction to the applications of several key genes in genetic engineering. The development of new technologies is conducive to better and more profound insigts into the dynamic changes of of metabolic components, transcriptional regulation, phytohormone signal transduction and epigenetic modification during plant somatic embryogenesis, which will promote the understanding of the underlying molecular mechanism of somatic embryogenesis. Besides, by using those key genes of plant somatic embryogenesis, it is possible to development new methods and technologies to improve the efficiency of somatic embryogenesis induction and genetic transformation. [Ch, 81 ref.]
Each plant cell harboring all the genetic information of the species has the genetic potential to develop into a whole plant, which is termed plant cell totipotency. Somatic embryogenesis is a form of induced plant cell totipotency, by means of which embryos develop from somatic or vegetative cells in the absence of fertilization. Somatic embryogenesis, an increasingly important tool of plant biotechnology, has been widely applied in germplasm reservation, seedling propagation, molecular breeding and basic research of many plants and it has been implied in previous studies on molecular genetics that somatic embryogenesis is subject to the regulation by a complex network composed of transcription factors, hormone signaling pathways and epigenetic modifications. Therefore, this review, with a summary of the development routes of plant somatic embryogenesis, is aimed to give a comprehensice overview of the research progress achieved in the functions of key genes and epigenetic modification in the process of somatic embryogenesis along with an introduction to the applications of several key genes in genetic engineering. The development of new technologies is conducive to better and more profound insigts into the dynamic changes of of metabolic components, transcriptional regulation, phytohormone signal transduction and epigenetic modification during plant somatic embryogenesis, which will promote the understanding of the underlying molecular mechanism of somatic embryogenesis. Besides, by using those key genes of plant somatic embryogenesis, it is possible to development new methods and technologies to improve the efficiency of somatic embryogenesis induction and genetic transformation. [Ch, 81 ref.]