2023 Vol. 40, No. 2
2023, 40(2): 237-243.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220515
Abstract:
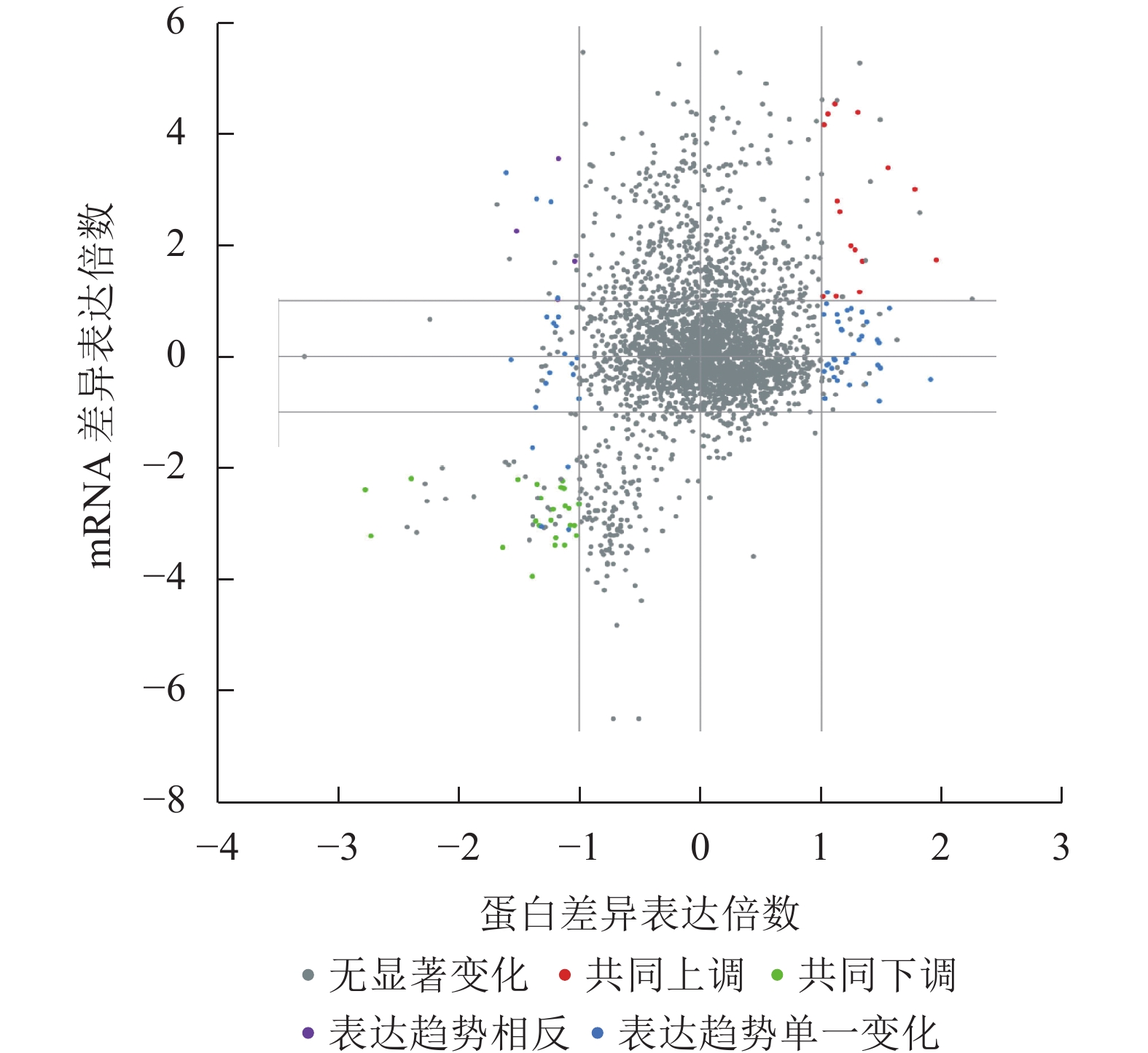
Objective This study aims to explore the regulatory genes and molecular network for shallow photodormant Nicotiana tabacum in the dark. Method Shallow photodormant N. tabacum Y85 seeds were used as experimental materials, and the molecular network of dark germination was studied by integrating transcriptome and proteome data. Result There were five types of differences in the expression of protein or mRNA expression before and after radicle protrusion, among which the jointly up-regulated proteins (genes) were BoGH3B, MAN1, ERD3, MLP31, FAP1, etc., and the jointly down-regulated proteins (genes) were NEC1, MFT, ECP63, SOP1, LE25, SBP65, and so on. The signal pathways enriched by the above proteins (genes) included fructose and mannose metabolism, mannan decomposition, endomannan-1,4-β-mannosidase activity. Functional cellular components included mitochondria, membrane components and chloroplasts. Conclusion By integrating transcriptomic and proteomic data, the dark germination regulatory network for shallow photodormant Y85 seeds was preliminarily constructed. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 24 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 244-253.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220594
Abstract:
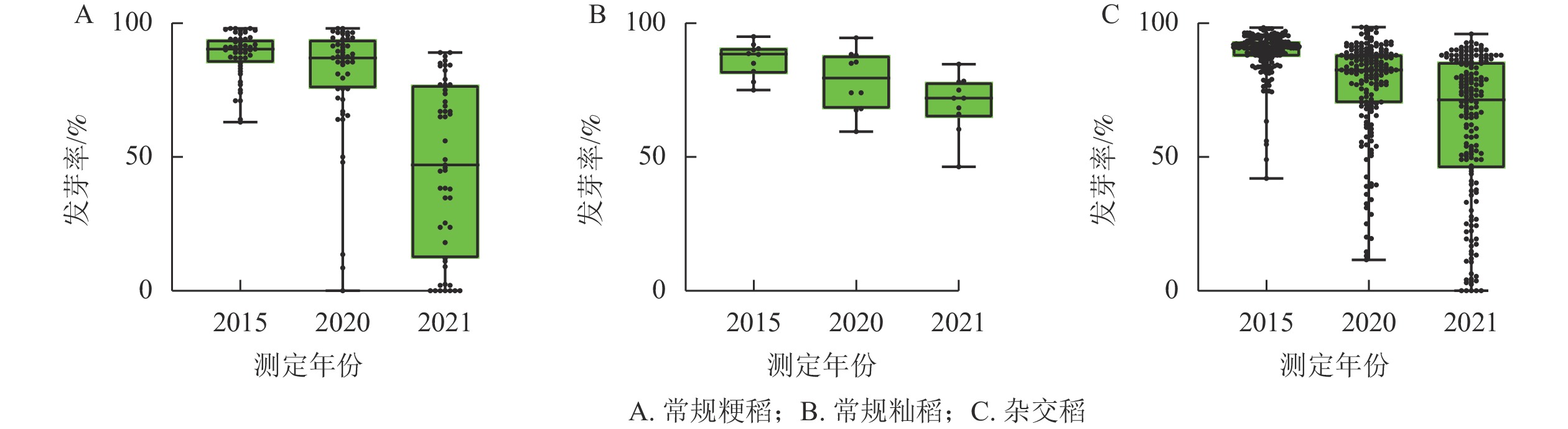
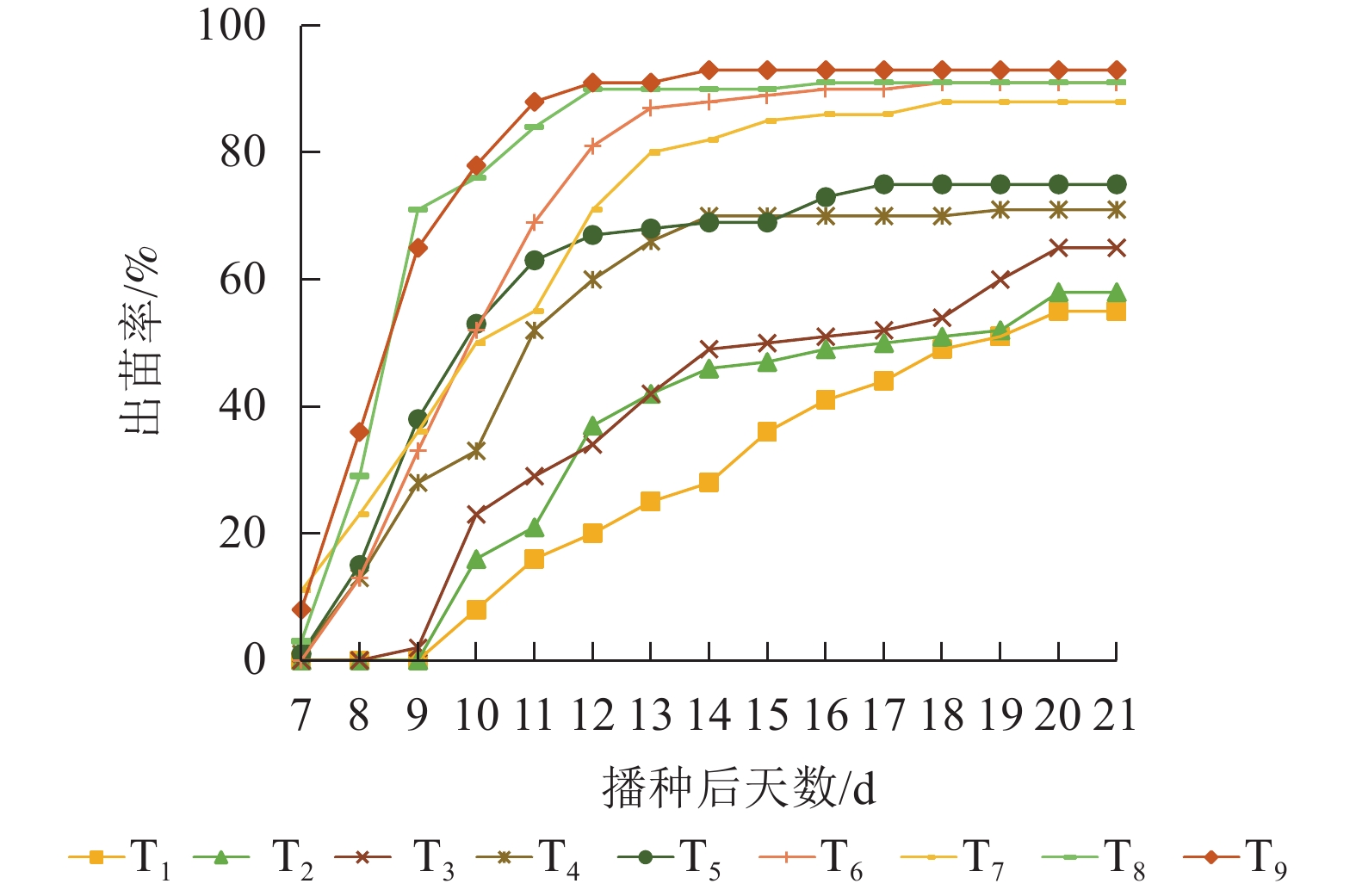
Objective This study, with an investigation of the seed storability, an important trait closely related to seed value, provenance and food security, of rice (Oryza sativa), is aimed to survey the storability characteristics of rice seeds so as to promote the conservation of rice germplasm resources and the protection of national food security. Method Based on 220 rice cultivars, after 5−6 years of natural aging, rice varieties with good storage tolerance were selected employing laboratory standard germination experiment before the physiological characteristics of different cultivars were determined. Result (1) With the prolongation of natural aging time, the germination rate and germination potential of different rice cultivars showed a trend of gradual decrease. (2) Compared with the initial seed quality, the germination rates of conventional japonica rice, conventional indica rice and hybrid rice decreased by 62.2%, 23.4% and 45.3% on average, respectively whereas the germination potential decreased by 55.0%, 38.1% and 50.7% on average. (3) Based on the evaluation criteria (varies with a decrease in germination rate <5% and a decrease in germination potential <15% are regarded as storable cultivars), storable conventional japonica rice represented by ‘Nanjing 44’ ‘Shendao 18’ and ‘Tiandaofeng’ were screened out along with storable conventional indica rice represented by ‘Wanxian 35’ ‘Ganwannuo 7’ and ‘Yongxian 69’; the storable hybrid rice represented by ‘Liangyoupeijiu’ ‘Zhongzheyou 1’ and ‘Jingliangyou Huazhan’. (4) It was further found that ‘Nanjing 44’ ‘Shendao 18’ ‘Tiandaofeng’ ‘Ganwanxian 35’ ‘Ganwanuo 7’ ‘Yongxian 69’ ‘Liangyou Peijiu’ ‘Zhongzhenyou 1’ and ‘Jingliangyou Huazhan’ had the characteristics of high amylase activity, high antioxidant enzyme activity, high proline content and low MDA content. Conclusion In terms of the storability and physiological characteristics, ‘Nanjing 44’ ‘Shendao 18’ ‘Tiandaofeng’ ‘Ganwanxian 35’ ‘Ganwannuo 7’ ‘Yongxian 69’ ‘Liangyoupeijiu’ ‘Zhongzheyou 1’ ‘Jingliangyou Huazhan’ are recommended and storable germplasms, providing new resources for the future selection of rice cultivars with storage tolerance. [Ch, 2 fig. 6 tab. 40 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 254-264.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220681
Abstract:
Seed is the most basic resource for agricultural production. The germination of seeds is essential for plant growth and development, and affects crop yield and quality. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are multifunctional compounds that play a key role in seed germination. In this study, the species, production site and“oxidation window”effect of ROS on seed germination were introduced, the mechanism of ROS regulation on seed germination was summarized. Current studies on ROS regulation of seed germination mainly focus on: (1) When these conditions are permissive for germination, ROS levels are maintained at a level which triggers cellular events associated with germination, such as inducing of GA signaling and inhibition of ABA signaling. (2) However, when seeds are exposed to abiotic stresses, the over accumulation of ROS induces ABA signaling, promotes oxidative damage and thus inhibits seed germination. Moreover, the release of seed dormancy by ROS would be related to oxidation of biomacromolecule, the weakening of seed coat and recession of endosperm. The present review would shed a new light on the signalling roles of ROS in seed physiology. The scope of “oxidation window”which plays a positive role in seed germination should be further explored in future research, and transcriptomics and metabolomics techniques should be combined to screen genes related to the regulation of ROS content in seed germination, so as to better understand the mechanism of ROS promoting seed germination. [Ch, 3 fig. 1 tab. 94 ref.]
Seed is the most basic resource for agricultural production. The germination of seeds is essential for plant growth and development, and affects crop yield and quality. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are multifunctional compounds that play a key role in seed germination. In this study, the species, production site and“oxidation window”effect of ROS on seed germination were introduced, the mechanism of ROS regulation on seed germination was summarized. Current studies on ROS regulation of seed germination mainly focus on: (1) When these conditions are permissive for germination, ROS levels are maintained at a level which triggers cellular events associated with germination, such as inducing of GA signaling and inhibition of ABA signaling. (2) However, when seeds are exposed to abiotic stresses, the over accumulation of ROS induces ABA signaling, promotes oxidative damage and thus inhibits seed germination. Moreover, the release of seed dormancy by ROS would be related to oxidation of biomacromolecule, the weakening of seed coat and recession of endosperm. The present review would shed a new light on the signalling roles of ROS in seed physiology. The scope of “oxidation window”which plays a positive role in seed germination should be further explored in future research, and transcriptomics and metabolomics techniques should be combined to screen genes related to the regulation of ROS content in seed germination, so as to better understand the mechanism of ROS promoting seed germination. [Ch, 3 fig. 1 tab. 94 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 265-273.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220281
Abstract:
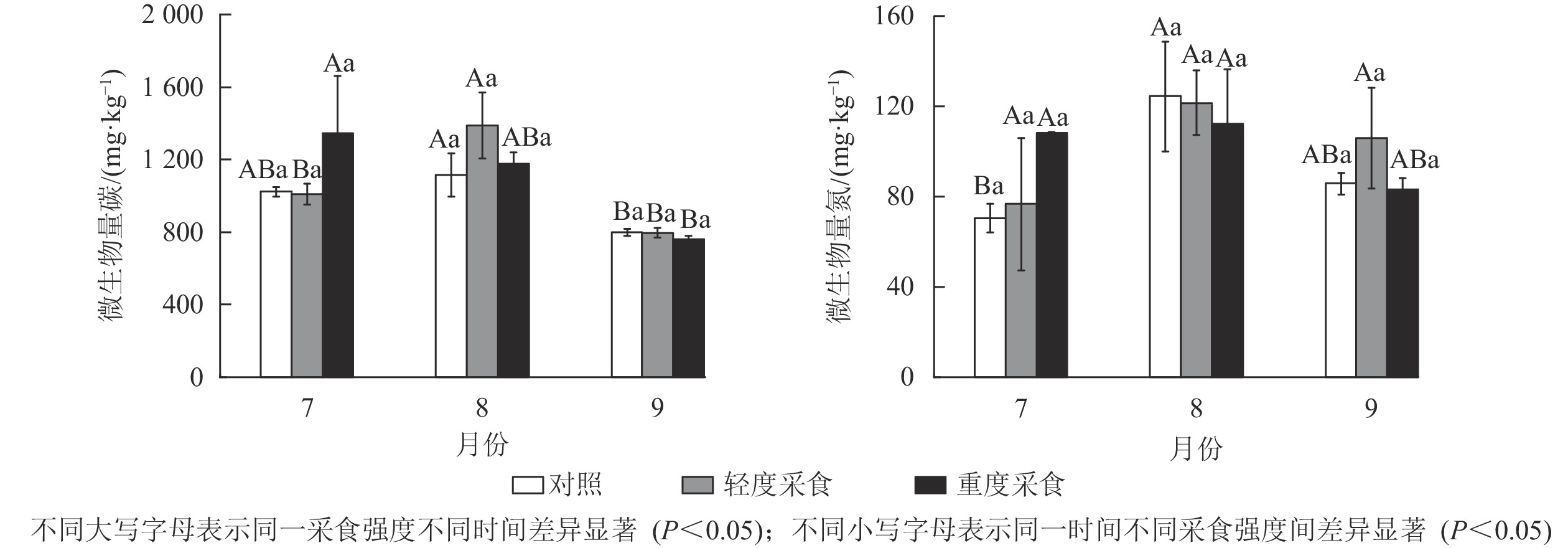
Objective This study aims to investigate the effects of livestock defoliation on soil enzyme activities of alpine meadow, so as to provide evidence for revealing the degradation mechanisms of alpine meadow under human disturbance. Method Livestock defoliation behaviors, including light-intensity defoliation (LD) and heavy-intensity defoliation (HD) were simulated by cutting plants, and the non-grazed meadow was taken as the control (ck). The activity of enzymes obtained by carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, as well as the change characteristics of soil physical and chemical properties were measured. Result Generally, the activities of invertase, β-glucosidase (BG), and urease did not show any significant differences under different defoliation intensities, but there was significant time variation. The activity of cellobiohydrolase (CBH) increased in LD treatment (P<0.05), while it decreased in HD treatment. LD treatment also enhanced the activities of leucine aminopeptidase (LAP), N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) and acid phosphatase (AP). Defoliation behavior of livestock might affect soil enzyme activity by changing soil nutrients. The temporal variation of soil enzyme activity in alpine meadow was controlled by the changes of soil temperature and soil nutrients. Conclusion Mild defoliation behavior may increase soil hydrolase activities, which helps maintain soil quality. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 44 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 274-284.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220377
Abstract:
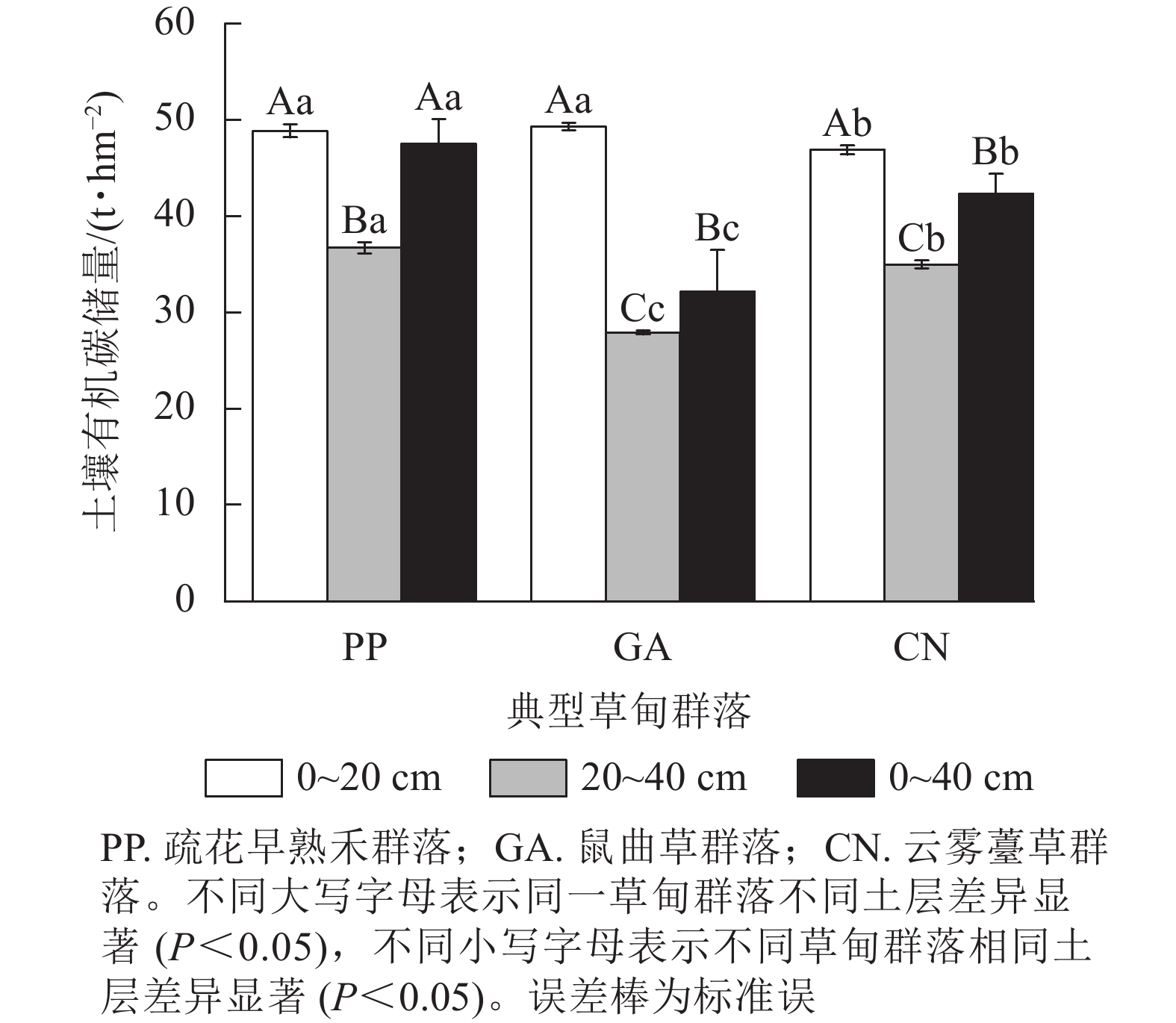
Objective This study aims to explore the change characteristics of soil organic carbon (SOC) components in typical meadow wetlands of Napahai caused by different groundwater levels and their coupling relationship with environmental factors, so as to provide data support for understanding the process of soil carbon cycle in plateau wetlands. Method 3 typical meadow communities of different underground water levels were selected as the research objects in Napahai Wetland in November 2020. The concentration of soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and total organic carbon (TOC), easily oxidized carbon (EOC), and particle organic carbon (POC) as well as the distribution pattern of carbon pool along soil profile were compared. The relationship between carbon components, plant diversity and soil physicochemical factors was analyzed. Result The total soil carbon stocks of different meadow communities (0−40 cm soil layer) ranking from high to low were Poa pratensis community (47.55 t·hm−2), Carex nubigena community (42.28 t·hm−2), and Gnaphalium affine community (32.14 t·hm−2), which decreased along the deepening of soil layers. Soil TOC storage decreased the most in G. affine community. Soil TOC, MBC, EOC and POC decreased with the decrease of groundwater depth, ranging from1.8 to 3.4 times. SOC component decreased by 1.0−3.4 times along the deepening of soil layer in the communities of P. pratensis, C. nubigena and G. affine. Plant biomass, Shannon-Wiener diversity index of plant community, Pielou evenness index, Margalef richness index and Simpson dominance index all decreased by 1.5−2.8 times along the decrease of groundwater depth. Soil water content (SWC), pH and total phosphorus (TP) contents also significantly decreased with decreasing depth of groundwater. RDA redundancy and Pearson correlation analysis showed that aboveground biomass, SWC, soil bulk density (SBD), total nitrogen (TN), and TP had the strongest response to the change in groundwater depth, and were the controlling factors affecting changes of SOC components in typical meadow communities in Napahai. Conclusion The mass fraction and vertical distribution of SOC components in typical meadows of Napahai wetland mainly depend on the change of plant aboveground biomass and soil physicochemical properties caused by different groundwater depths. Therefore, in the process of protecting typical meadow wetlands in Napahai, it is recommended to monitor the groundwater level to prevent the impact of low groundwater level from affecting the stability of wetland carbon pool. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 42 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 285-292.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220370
Abstract:
Objective Soil nutrient heterogeneity widely exists in nature, and affects competition among different plant species. This study aims to explore the effects of soil nutrient heterogeneity on competitiveness of invasive plants, so as to provide reference for the study of invasion hazards. Method The invasive plant Aegilops tauschii and its main endangered crop Triticum aestivum were used as test materials. Under the conditions of homogenous and heterogeneous nutrients, de Wit substitution experiment was carried out to investigate the impact of soil nutrient heterogeneity on the growth and development of A. tauschii and its competition with T. aestivum, based on plant height, leaf area and biomass. Result (1) Soil nutrient heterogeneity promoted the increase of plant height, leaf area and tiller number per plant of A. tauschii and T. aestivum seedlings. In particular, the total biomass of the two plants increased significantly (P<0.05). (2) Under the condition of interspecific competition, the root-shoot ratio of A. tauschii in heterogeneous soil decreased the most, indicating that A. tauschii increased its inhibition on T. aestivum competition by allocating more biomass to the ground surface. (3) Competition balance index showed that the competitiveness of A. tauschii in heterogeneous soil was above 0, and slightly increased compared with that in homogeneous soil, indicating that soil nutrient heterogeneity enhanced the competition of A. tauschii on T. aestivum. Conclusion Soil nutrient heterogeneity promotes the growth of A. tauschii seedling, and enhances its competitive inhibition on T. aestivum. [Ch, 5 fig. 1 tab. 46 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 293-303.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220338
Abstract:
Objective The objective of this study is to explore the effective treatment of catering wastewater, which has become increasingly harmful to the environment with the rapid development of catering industry. Method Sponge pyrolytic carbon (SPCx) with good adsorption performance was prepared from waste sponge by pyrolysis and carbonization. The physical and chemical properties such as the morphology and structure of the materials were characterized by cold field emission scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Through the adsorption of soybean oil in wastewater by SPCx, the effects of pyrolysis temperature, wastewater pH and temperature on the adsorption performance were studied. The adsorption kinetics and adsorption isotherm of SPC600 adsorbent were analyzed, and the Langmuir and Freundlich models were used to analyze the data. Based on this, the oil adsorption-degradation law of SPC600 immobilized microorganisms in simulated wastewater and actual wastewater was explored. Result Sponge pyrolytic carbon (SPC600) had abundant “network” structure and fracture branches, and contained a large number of hydroxyl, carbonyl, ether bonds, and other oxygen-containing functional groups on its surface, which improved its ability to adsorb oil and immobilize microoganism. The optimized SPC600 had an adsorption capacity of 8 093.1 mg·g−1 at pH 7 and adsorption temperature of 30 ℃. The adsorption process of oil conformed to the pseudo-second-order kinetic equation, and was an exothermic process dominated by chemical adsorption. The screened oil-degrading strains and SPC600 were made into immobilized microbial adsorbents, and the degradation rate of actual oil wastewater reached 67.6%, which was 11.0% and 14.4% higher than that of free strain and free strain+SPC600 respectively. Conclusion The sponge pyrolytic carbon immobilized microbial technology can stabilize the degrading strain and improve the oil degradation rate, so as to achieve the effect of “treating waste with waste” and avoid secondary pollution, which has a good application prospect. [Ch, 8 fig. 3 tab. 42 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 304-313.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220292
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to study the effect of decomposed peanut (Arachis hypogaea) shells and humic acid with different proportions on the improvement of green waste compost products, as well as the impact of the improved green waste compost products as nursery substrate on Perilla frutescen seedling emergence, so as to explore the best proportion of the substrate conducive to P. frutescen seedling. Method Using orthogonal design, different mass fractions of the decomposed peanut shells (0, 1.5%, 3.0%) and humic acid (0, 3.0%, 6.0%) were added to the green waste compost products, and the composite effect was observed by measuring physical and chemical properties of the substrate. Based on redundancy analysis (RDA) and membership function method, the effects of improved green waste compost products on seedling emergence were observed through the measurement of germination rate, germination speed and number of seedling leaves per plant, mortality rate, leaf infestation rate and plant infestation rate of P. frutescen. Result Adding decomposed peanut shells and humic acid could significantly (P<0.05) reduce the bulk density, pH and EC values, improve the water content and porosity, and increase the mass fractions of total N, total P, NH4+-N , NO3−-N, available P, available K and organic matter of green waste compost products. And the composite green waste compost products could significantly (P<0.05) increase the germination rate, germination speed and the number of leaves per seedling, reduce the mortality rate, the percentage of insect damaged plants and damaged leaves of P. frutescen. RDA showed that the percentage of seedling emergence, the percentage of damaged leaves and damaged plants of P. frutescen seedlings were positively correlated with the total porosity, mass fractions of total N, total P, total K and available K of the substrate, but negatively correlated with pH, EC and bulk density of the substrate. The number of leaves per plant of P. frutescen seedlings was positively correlated with mass fractions of total N, total P, total K and total porosity of the substrate, but negatively correlated with pH and bulk density of the substrate. The mortality rate of seedlings was positively correlated with pH, EC and bulk density of the substrate, but negatively correlated with mass fractions of total porosity, total N, total P, total K and available K of the substrate. Conclusion The decomposed peanut shells and humic acid can effectively improve the physical and chemical properties of green waste compost products and optimize their quality. The optimized green waste compost products can reduce the death rate of seedlings, and facilitate the rapid emergence and survival of P. frutescen. At the same time, the optimized green waste compost products can significantly reduce the incidence of insect pests, improve insect resistance, and achieve a certain biological control effect. The optimal combination is 3.0% decomposed peanut shells + 3.0% humic acid. [Ch, 2 fig. 5 tab. 27 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 314-320.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220396
Abstract:
Objective The purpose of this study is to explore the expression patterns of Ph-TElncRNA1 and target genes in Phyllostachys edulis, and to preliminarily analyze the function of lncRNA. Method Based on the whole transcriptome sequencing data of Ph. edulis seedlings under high temperature, low temperature, ultraviolet and high salt stress, lncRNAs differentially expressed under stress were screened. The coding characteristics of lncRNA were analyzed by four kinds of software (CNCI, Pfam, CPC2 and PLEK), and the target genes of lncRNA were identified by LncTar software. The expression patterns of lncRNA and target genes under UV stress and leaf coloration were analyzed by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR. Result One differentially expressed lncRNA under UV stress was screened, which was derived from the lncRNA of the Large retrotransposons derivatives and named Ph-TElncRNA1 (Ph. edulis transposable element derived lncRNA1). Ph-TElncRNA1 was a typical non-coding RNA with a total length of 342 bp, 185 bases from exons and 157 bases from introns. The target gene of Ph-TElncRNA1 was psbA, encoding photosystem Ⅱ protein D1. Real time fluorescence quantitative results showed that the relative expression of Ph-TElncRNA1 and psbA was the same, indicating that Ph-TElncRNA1 was positively correlated with psbA under UV stress. Through the analysis of the relative expression of Ph-TElncRNA1 and psbA in Ph. edulis leavesat different coloring stages, it was found that the expression of psbA and Ph-TElncRNA1 reached the peak during chloroplast formation stage. Conclusion Ph-TElncRNA1 and psbA are co-expressed under UV stress, and Ph-TElncRNA1 can participate in the leaf development of Ph. edulis by regulating the target gene psbA. [Ch, 7 fig. 33 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 321-329.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210690
Abstract:
Objective The objective is to analyze the genetic diversity and genetic relationship of 32 Bletilla striata samples from different provenances by ISSR and SRAP markers, so as to provide theoretical basis for identification, classification, conservation and development of B. striata germplasm. Method Primers with high polymorphism, clear amplification bands and good repeatability were selected from 100 ISSR primers and 238 pairs of SRAP primers for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. Genetic diversity parameters and genetic distance of B. striata from 32 different provenances in Zhejiang, Yunnan, Guizhou and Sichuan were calculated by Popgene 32.0, and cluster analysis was performed by NTSYS-PC 2.10e. Result 11 highly polymorphic primers were screened from 100 ISSR primers, and a total of 188 bands were amplified, with an average of 17.09 bands per primer, among which 174 were polymorphic loci, accounting for 92.20% of the total amplified fragments. 11 pairs of highly polymorphic primer pairs were screened from 238 pairs of SRAP primer pairs, and a total of 216 bands were amplified, with an average of 19.64 bands per primer, including 202 polymorphic loci, accounting for 93.52% of the total amplified fragments. Based on ISSR and SRAP markers, the genetic diversity level of B. striata population in Sichuan Province was the highest, while that in Guizhou Province was the lowest. UPGMA and PCoA analysis showed that the clustered B. striata samples were mostly from the same province. The genetic distance of B. striata population between Yunnan Province and Sichuan Province was relatively close, and that between Zhejiang Province and Guizhou Province was relatively close, indicating that there was a certain overlap between genetic distance and geographical distance, but there was no positive correlation. Conclusion B. striata provenances selected in this study have high genetic diversity. Both ISSR and SRAP markers can effectively reveal the genetic diversity and genetic relationship of B. striata. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 25 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 330-337.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220333
Abstract:
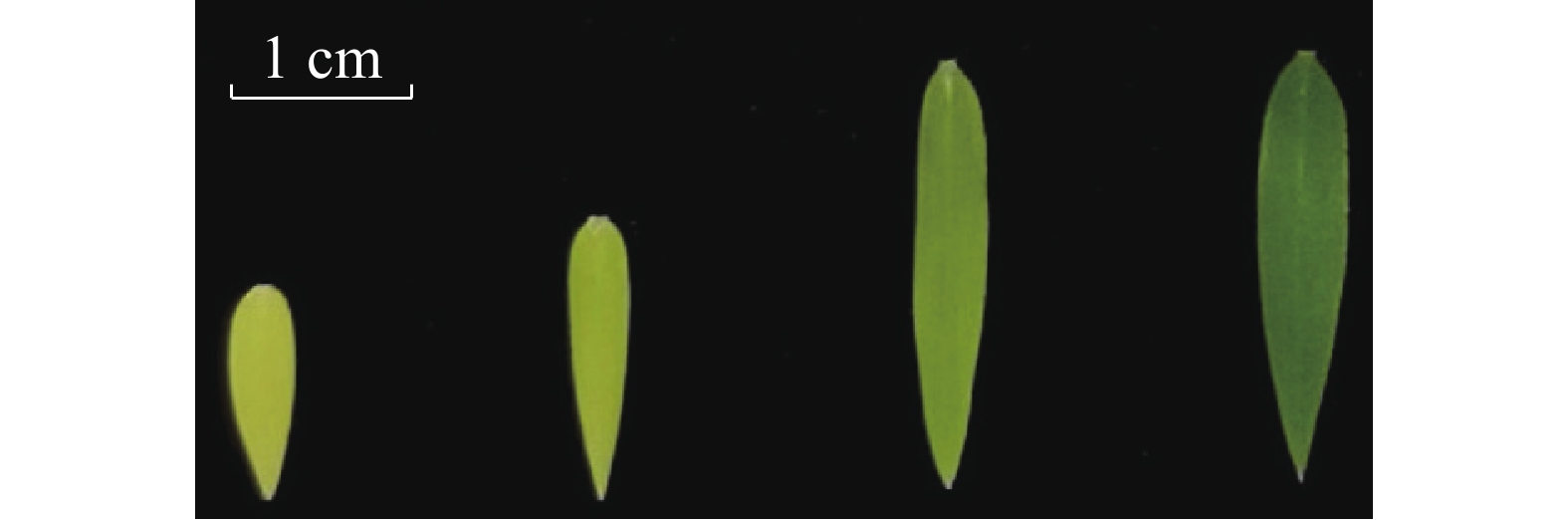
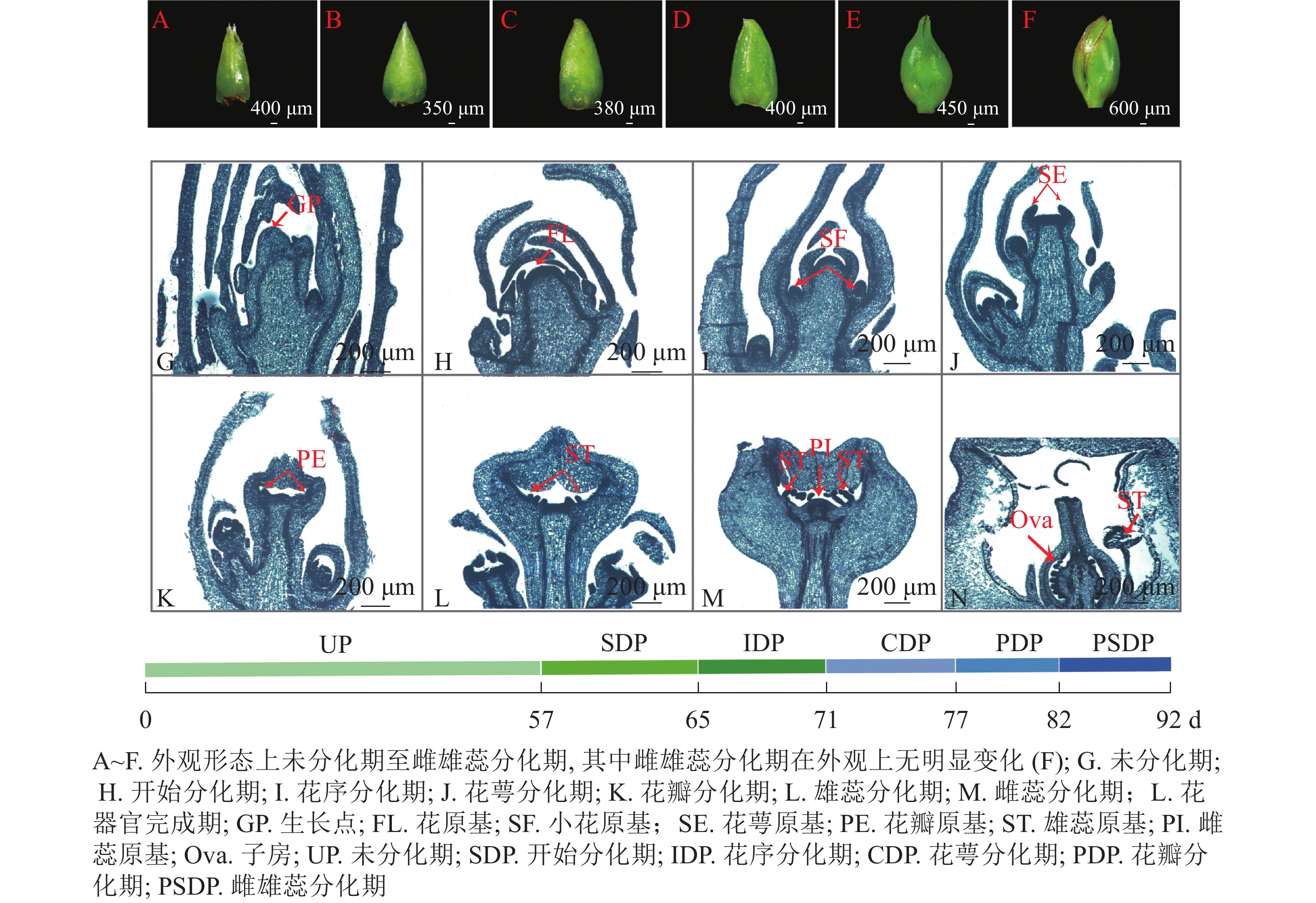
Objective The LiCMB1 gene of Lagerstroemia indica was cloned, and its expressions in different stages of flower bud differentiation and different tissues and organs were analyzed, so as to explore the expression characteristics of LiCMB1 gene. Method The gene sequence of LiCMB1 was cloned from L. indica by simple cloning technology. Physical and chemical properties of the protein were analyzed by online tools including ExPasy, and phylogenetic tree was constructed by MEGA 6.0 software. Combined with the phenotypic observation and paraffin section of L.indica flower bud differentiation, the expressions of LiCMB1 gene in different stages of flower bud differentiation and different tissues and organs were analyzed by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). Result LiCMB1 gene belongs to SEP gene of MADS-box family, except for typical MADS_ MEF2_ like and K-box structure domain, there is also a SEP motif conserved motif near the C-end. The results of RT-qPCR showed that the expression trend of LiCMB1 increased first and then decreased in the process of flower bud differentiation of L. indica. It is expressed in different tissues and organs, and the expression levels of LiCMB1 from high to low were in the order of pistil, sepal, bud, long stamen, short stamen, petal, leaf, stem, root, indicating that LiCMB1 may play an important role in flower bud differentiation and participate in the regulation of flower organ development. Conclusion LiCMB1 gene belongs to the SEP gene of MADS-box family. It plays an important role in the early stage of flower bud differentiation of L. indica, especially in the calyx differentiation period. Tissue specificity analysis indicated that it was likely involved in the regulation of floral organ development. [Ch, 7 fig. 28 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 338-347.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220365
Abstract:
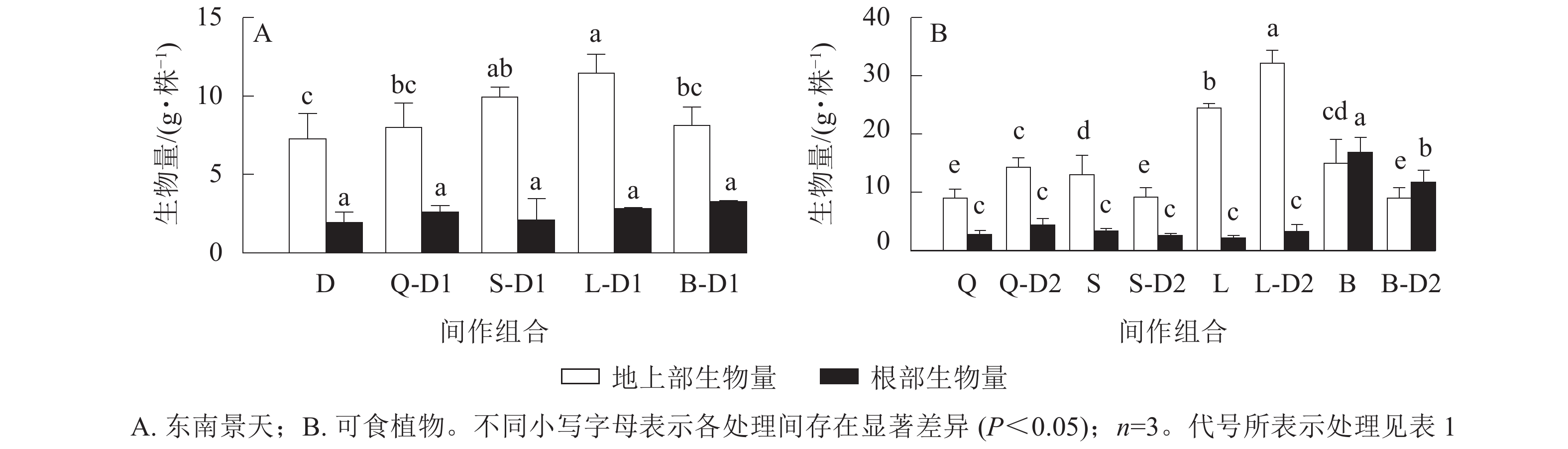
Objective The objective is to study the physiological characteristics of plants in Pb contaminated soil and uptake characteristics of Pb in community gardens intercropped with Sedum alfredi, in order to screen out the best planting mode to reduce the uptake of Pb by edible plants. Method S. alfredii, Apium graveolens, Brassica chinensis, Capsicum annuum and Raphanus sativus were used as research materials. A pot experiment was carried out in Pingshan Nursery of Lin’an District of Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province. The effects of intercropping S. alfredii on physiological and biochemical indexes of edible plants, uptake and transfer characteristics of Pb, the pH of rhizosphere soil and distribution characteristics of Pb were analyzed. Result (1) Intercropping significantly improved the biomass of S. alfredii, A. graveolens and C. annuum, and reduced the biomass of B. chinensis and R. sativus (P<0.05). (2) The content of MDA in leaves of S. alfredii and edible plants showed a consistent pattern, and intercropping was lower than monoculture. In the intercropping system, CAT activities in leaves of A. graveolens, C. annuum and R. sativus significantly increased by 33.92%, 41.94% and 53.80%, compared with the monoculture system (P<0.05). (3) Intercropping S. alfredii significantly reduced Pb accumulation in edible parts of A. graveolens, C. annuum and R. sativus, which decreased by 24.37%, 162.50% and 39.82%, respectively (P< 0.05), compared with monoculture. (4) Intercropping decreased the pH of rhizosphere soil and changed the distribution of Pb in soil. Intercropping S. alfredii decreased the form proportion of weak acid extracted and oxidized Pb in the rhizosphere soil of edible plants, but increased the form proportion of reducible Pb in soil. Conclusion The intercropping mode can promote the enrichment and migration of Pb in S. alfredii and reduce the toxic effect of Pb on edible plants. Intercropping S. alfredii significantly reduces Pb content in edible parts of A. graveolens and C. annuum, reaching the safe edible standard. The Pb content in edible parts of R. sativus tends to decrease, which is an ideal combination mode for intercropping restoration. [Ch, 6 fig. 3 tab. 31 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 348-355.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220202
Abstract:
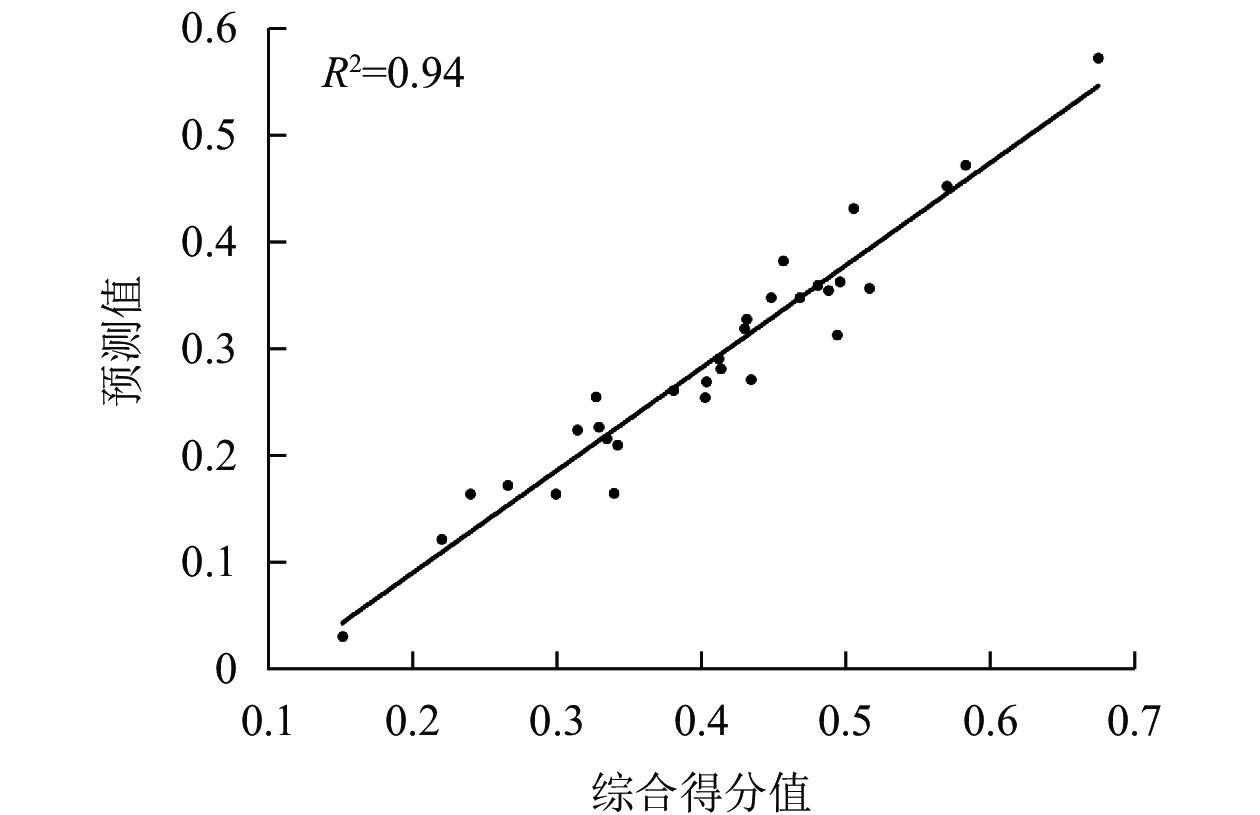
Objective This study aims to evaluate the adaptability of different germplasm resources of Xanthoceras sorbifolium in arid areas, so as to provide a basis for screening drought-resistant germplasm resources for arid and semi-arid areas. Method The leaves of 200 high-yield X. sorbifolium germplasm resources were collected in Tongliao Germplasm Resources Nursery in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. The anatomical structure of leaves was observed by making paraffin section, and 13 indexes related to drought resistance were measured, including leaf thickness, palisade tissue thickness, sponge tissue thickness and wax layer thickness. The drought resistance of different germplasm resources was evaluated by factor analysis, cluster analysis and membership function analysis. Result The anatomical structure indexes of leaves showed significant correlation. Based on factor analysis, 4 common factors were extracted, and the cumulative contribution rate to variation was 89.99%, basically covering most of the information of the 13 indicators. The degree of influence on drought resistance ranging from large to small was as follows: F1 (thickness index factor), F2 (tissue index factor), F3 (epidermal proportion factor), and F4 (wax layer proportion factor). Conclusion The thickness of upper/lower epidermis, thickness of palisade tissue and vessel diameter, which are the most important factors in F1, can be used as the main indicators for drought resistance evaluation of X. sorbifolium. The selected 90 drought-resistant germplasm resources, with advantges of high-yield, water-saving and drought-risistant, could provide materials for the breeding of drought-resistant X. sorbifolium. [Ch, 1 fig. 6 tab. 32 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 356-364.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220263
Abstract:
Objective The present study, with an exploration of the effects of light intensity on growth of Isatis indigotica, and chemical composition, antioxidant activity of isatidis folium, aims to provide reference for the artificial cultivation of I. indigotica. Method With seedlings of I. indigotica planted under 100%, 60% and 20% of full sunlight, their growth indexes were measured at the vigorous growth period, whereas chemical compounds such as indigo, indirubin, total flavonoids, total polysaccharides and total free amino acid, as well as antioxidant activity were determined after harvest. Result The growth of leaves was positively correlated with the light intensity, and the plant height, leaf length, leaf width, number of leaves, and the single leaf area in 100% of full sunlight treatment were the largest. Indigo, total flavonoids and total polysaccharides of isatidis folium were decreased with the decrease of light intensity, and there were significant differences among three groups (P<0.05). Indirubin showed a trend of increasing first and then decreasing, with that of the 60% of full sunlight treatment being the highest (P<0.05), yet no significant differences between the ones of 100% and 20% of full sunlight treatment. The total free amino acid was negatively correlated with light intensity and increased with the decrease of light intensity. The antioxidant activity was positively correlated with the light intensity and the IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration) for DPPH of 20% of full sunlight treatment was significantly higher than that in 60% and 100% of full sunlight treatment (P<0.05). Conclusion The 100% of full sunlight treatment was the optimum light intensity condition to achieve high yield and intrinsic quality of isatidis folium, which is more conducive to the cultivation of isatidis folium than the 60% and 20% full sunlight treatment. [Ch, 8 tab. 39 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 365-373.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220357
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation of the genetic variation of Michelia chapensis and the correlation between the main growth traits of juvenile trees and those of the adult trees, is aimed to determine the suitable age for the early selection of M. chapensis provenances. Method First, two testing forests of M. chapensis provenances with an age range of 3 to 14 planted in Qujiang forest farm and Jiuqushui forest farm, Shaoguan, Guangdong Province were selected for measuring growth traits. Then, an analysis was conducted of the genetic variation of growth traits at different ages with the employment of variance analysis, genetic parameter estimation, correlation analysis and cluster analysis before the suitable age of early selection was determined. Result The preservation rate of testing forest had significantly decreased in 11−14 years with significant differences (P<0.01) in tree height, diameter at breast height (DBH) and individual volume among tested provenances at different ages. The provenance effect had a significant impact on growth traits, which was gradually enhanced or tended to stabilize with the increase of age. The range of the provenance heritability for tree height, DBH and individual volume at different forest ages were 0.69−0.90 displaying significant phenotypic and genetic correlations between the early tree height, early DBH or early individual volume and the individual volume at the age of 14. As was shown in the classification and evaluation of provenances using comprehensive index and single index methods, the consistency of high-yield type Ⅰ provenances obtained by the two evaluation methods was very high, but the single index method was relatively easier to operate. Taking the high-yield type Ⅰ provenances selected in 14 years old as a reference, the early selection risk of single index method was lower than that of comprehensive index method. Using the single index method to carry out early selection at the age of 3 and 6 years, the correct selection rate of the two experimental forests was 83%−100% and the missed selection rates of both was 0. Conclusion The main growth traits of M. chapensis had rich variation among different provenances and the provenance effect had significant and stable influence on growth traits. The provenance heritability of tree height, DBH and individual volume was medium to high. As a result, for the sake of high-yield provenances, it was feasible to carry out early selection of individual volume during the age of 3−6 years. [Ch, 1 fig. 7 tab. 20 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 374-381.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220376
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation of the genetic variation characteristics of economic traits of Camellia semiserrata, is aimed to establish a prediction model based on the core evaluation indexes screened so as to provide a scientific basis for the formulation and utilization of C. semiserrata germplasm resources. Method With 31 excellent trees selected from the core production area of C. semiserrata as research subjects, a determination and analysis was conducted of 20 economic traits such as crown area, fruit yield per plant and oil yield per plant using multivariate statistical methods. Result (1) There were different degrees of variation in the 20 indicators of the participating strains of excellent trees, with a range of 3.25%−69.47% and between these indicators a total of 38 pairs of indicators reached the highly significant level (P<0.01) whereas 15 pairs reached the significant level (P<0.05). (2) With the principal component analysis, the 11 evaluation indicators were simplified into four independent composite indicators, with a cumulative contribution of 80.23%, retaining most of the information of each trait of the test material. (3) Based on the weights of the four integrated indicators and the values of the affiliation functions, the integrated scores of the excellent trees ranged from 0.151−0.674, with HY25, HY4, HY20, HY17 and HY1 displaying better comprehensive evaluation performance. (4) The prediction model was built for the evaluation of Camellia semiserrata excellent trees using a stepwise regression analysis with canopy area, fresh seed yield, dry seed yield, fresh fruit oil content, oil yield per plant and fruit yield efficiency per plant being the six core evaluation indicators. (5) The six core evaluation indicators can be classified into three categories using cluster analysis with categoryⅠ being the high quality type, categoryⅡ displaying better fecundity and quality whereas category Ⅲ being the fecundity type. Conclusion Single plant fruit yield, single plant fruit yield efficiency, canopy area, fruit yield efficiency per plant, oil yield per plant, fresh seed yield, dry seed yield and fresh fruit oil content can be used as important indicators to identify excellent trees of C. semiserrata and in accordance with this model, HY25, HY4, HY20, HY17 and HY1 were selected with favorable comprehensive evaluation. [Ch, 2 fig. 6 tab. 24 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 382-389.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220243
Abstract:
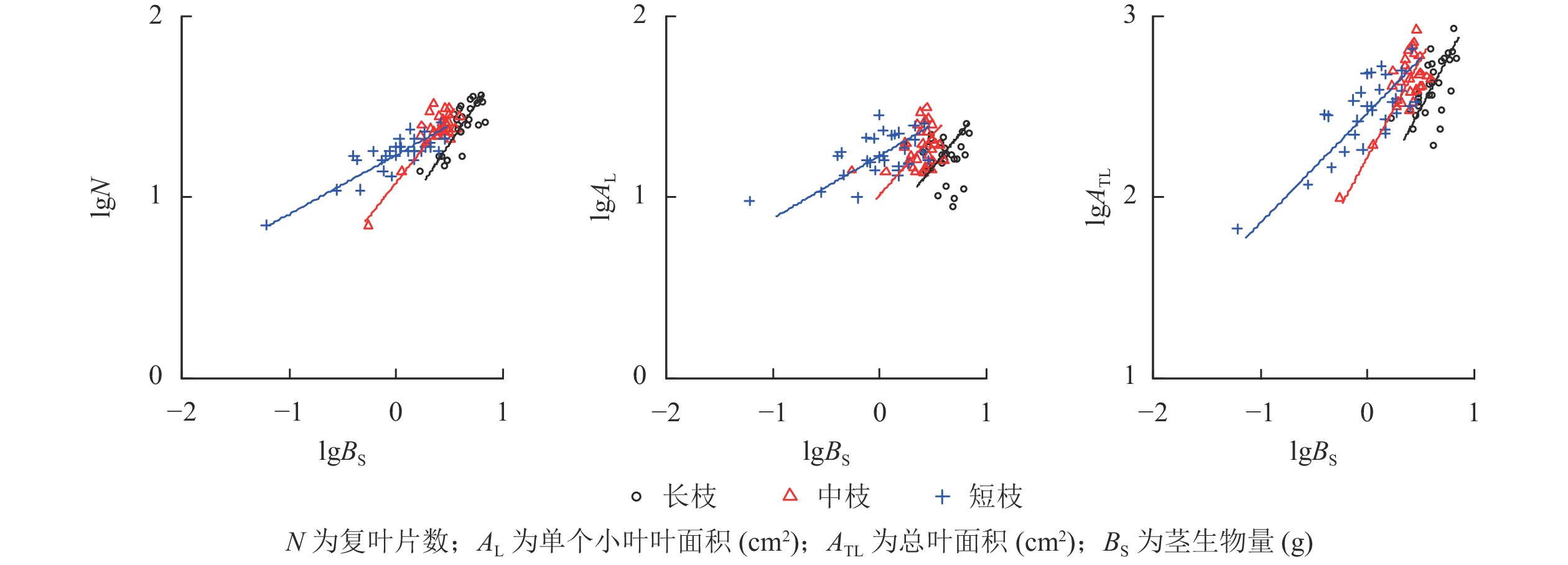
Objective The current-year shoots, as the main parts of woody plants for population spatial expansion, fruiting and photosynthesis, are the most vigorous modulars and reflect the important ecological characteristics of population evolution and adaptive regulation. Therefore, this study, with an investigation into the growth regulation characteristics of current year branches, is aimed to reveal the adaptive mechanism of plant population. Method An analysis was conducted of the allometric growth relationships among the modulars of three types of shoots (long shoot, medium shoot and short shoot) of Fraxinus sogdiana, a plant of second-class protection in China, so as to explore the functional differences of different types of branches and their roles in population adaptation and regulation. Result Leaves and stems of different types of shoots are featured with different growth rules with allometric growth on long shoot and medium shoot (slope was 1.170 and 1.135 respectively), and isokinetic growth on short shoot (slope was 0.657) in terms of total leaf area and stem biomass. Isokinetic, allometric and isokinetic growth rules apply on long shoot, medium shoot and short shoot when it comes to the relationship between leaf biomass and stem biomass with the slope of regression equation being 1.460, 0.908 and 0.840 respectively. The long shoot and the medium shoot had higher leaf growth ability and mainly functioned in the expansion of space and photosynthetic production whereas the short shoot was more involved in the sexual reproduction process. Leaf rachis can also regulate leaf growth, making up for the lack of stem support efficiency for leaf area on medium shoot and short shoots, yet with no obvious effect on long shoots. Conclusion The long and medium shoots of F. sogdiana have higher leaf support efficiency, and their functions are not only reflected in expanding the population growth space, but also in higher photosynthetic production capacity. The current year shoots of F. sogdiana demonstrate more complex functional differentiation, with their roles in population adaptation regulation being more diverse, implying that shoot types should be considered in future studies dealing with the characteristics of plant growth regulation with dimorphic shoots. [Ch, 3 fig. 3 tab. 37 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 390-397.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220267
Abstract:
Objective This study, with an investigation of the spatial distribution pattern and correlation of Malus sieversii population in Emin County, Tacheng Prefecture of Xinjiang, is aimed to explore its biological characteristics so as to provide a scientific basis for the restoration and sustainable management of M. sieversii population in this area. Method First, employing the typical sample plot investigation method, an investigation was conducted of the individuals of M. sieversii in 20 blocks (30 m×30 m) with diameter class structure used instead of age structure and univariate function and bivariate function analysis methods adopted in point pattern analysis. Then, a study was carried out of the spatial distribution pattern and its correlation of M. sieversii individuals with different age classes. Result (1) The age structure of M. sieversii population presented an atypical pyramid like a spindle, with poor regeneration and unstable population structure. (2) The individual parts of M. sieversii with younger age showed aggregation distribution with the tendency to become random with the increase of age. (3) The spatial relevance of individuals with similar age is positively correlated or not significantly correlated whereas with the increase of the gap between individuals’ ages, the spatial relevance was mostly non-correlated. Conclusion The population structure of M. sieversii in Emin County is unstable, and the spatial correlation between individuals of different age classes is not strong. Therefore, efforts should be focused on the enhancement of tending management and the change of their existing random distribution state through artificial planting and other methods, so as to make them aggregate and grow and promote the stable growth of local M. sieversii population and resource recovery. [Ch, 3 fig. 1 tab. 35 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 398-406.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220458
Abstract:
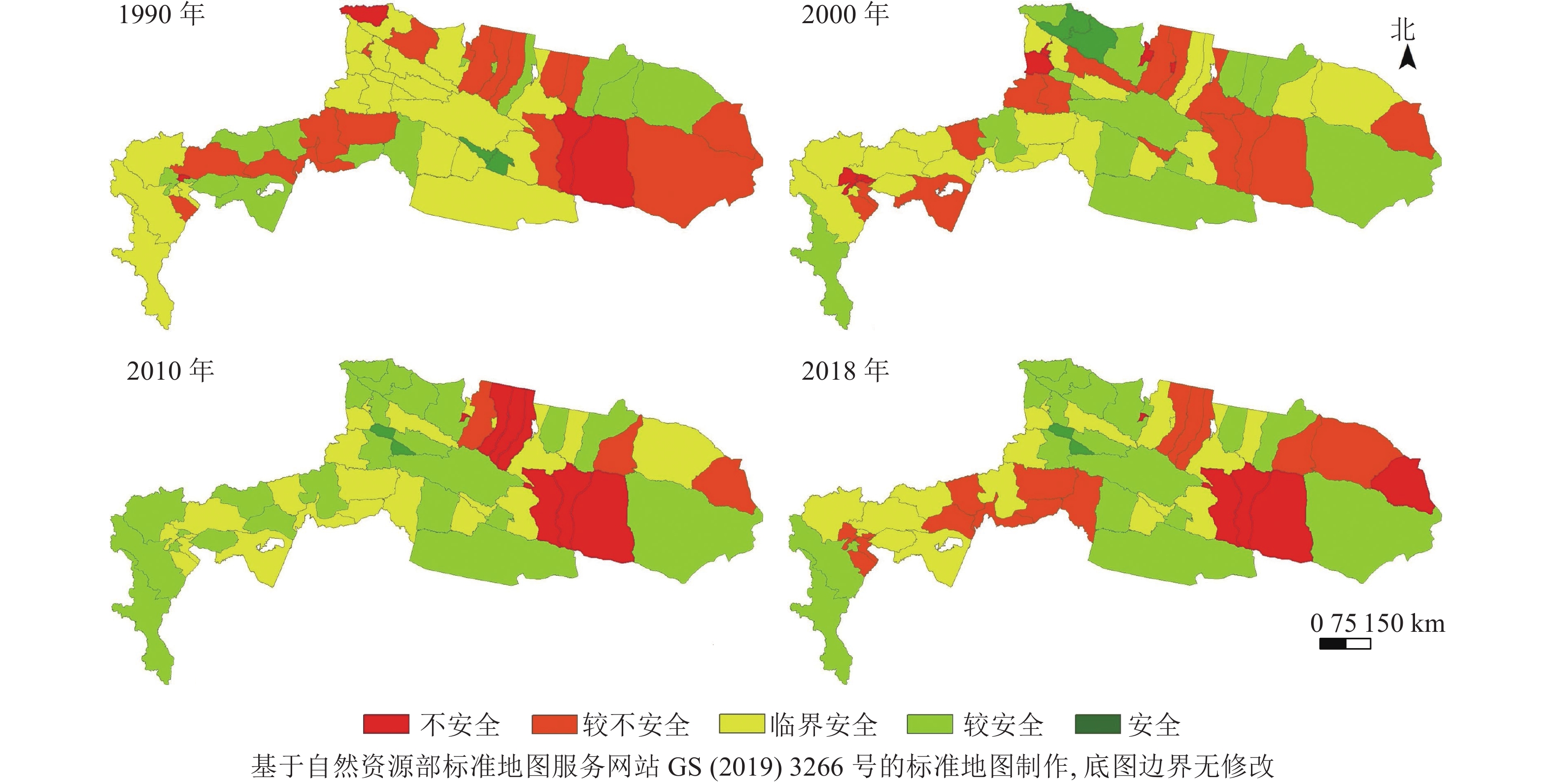
Objective Tianshan-Pamir region, with its unique geographical location and rich and diverse ecosystems, plays an important role as a barrier to China’s ecological security. However, great changes had taken place in the regional economy and ecological environment in the past 30 years, and it is urgent to carry out research on the spatiotemporal evolution of ecological security pattern and its influencing factors in Tianshan-Pamir region under natural and human pressure. Method Taking Tianshan-Pamir region as the study area, 20 key indicators were selected to analyze the ecological security and its influencing factors in the region from 1990 to 2018 by using the pressure-state-response (PSR) model and geographical detector method. Result The distribution pattern of regional ecological security in this region did not change significantly, but the ecological security levels of different cities and counties varied greatly. From 1990 to 2018, the area with ecological security of level Ⅲ or above accounted for 60% or more and reached 80% in 2010, indicating significant improvement of regional ecological environment. 5 factors among them had a relatively stable impact on the ecological security of the region, while other factors had different impacts. The influence of the 3 subsystems from large to small was response, pressure and state, and the change trend of state index and pressure index was similar. Conclusion The ecological security in Tianshan-Pamir region is gradually improving, but there are still some damage phenomena. Among them, Bole City, Jinghe County, Wenquan County, and Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County have significantly improved their ecological security status, and the improvement of response capacity has a great contribution to alleviating ecological pressure. [Ch, 4 fig. 4 tab. 32 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 407-416.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220332
Abstract:
Objective The urban green space is not only an important part of the regional ecological environment, but also an important bearing space for suburban recreation and a structural space that restricts the infinite spread of the city. Therefore, this study, with an investigation of the dynamic landscape changes of green space in Nanjing, a mega city in the Yangtze River Delta and its influencing factors, is aimed to help further optimize the spatial structure of green space and regional sustainable development. In Nanjing so as to promote the sustainable development of the Yangtze River Delta region. Method With the land cover data of Nanjing City in five time nodes in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015 and 2020 selected, an analysis was conducted of the spatio-temporal evolution pattern of the green space in Nanjing City employing dynamic degree calculation and landscape pattern index. Then, the partial least squares regression equation (PLSR) model was adioted to explore the impact of socioeconomic factors and natural factors on the evolution of green space pattern. Result From 2000 to 2020, there was first a decrease and then an increase in the green space in Nanjing. From 2000 to 2005, the green space patches in Nanjing City tended to be integrated, with the fragmentation of green space landscapes easing up. After 2005, the scale of urban green space has increased, with an obvious fragmentation trend and a steady decrease in the overall landscape connectivity, The regression model showed that among the socioeconomic factors, the proportion of the industrial structure, the green area of the built-up area and the changes in the urban green space pattern had a greater correlation, and there were differences in the force of natural factors. Conclusion The overall scale of green space in Nanjing has increased with an obvious trend of pattern fragmentation and the socioeconomic factor being the direct influencing factor in the evolution of urban green space spatial pattern which is subject to the restriction of many natural factors. There is an urgent need to strengthen systematic planning for regional green spaces. [Ch, 5 fig. 6 tab. 29 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 417-426.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20210806
Abstract:
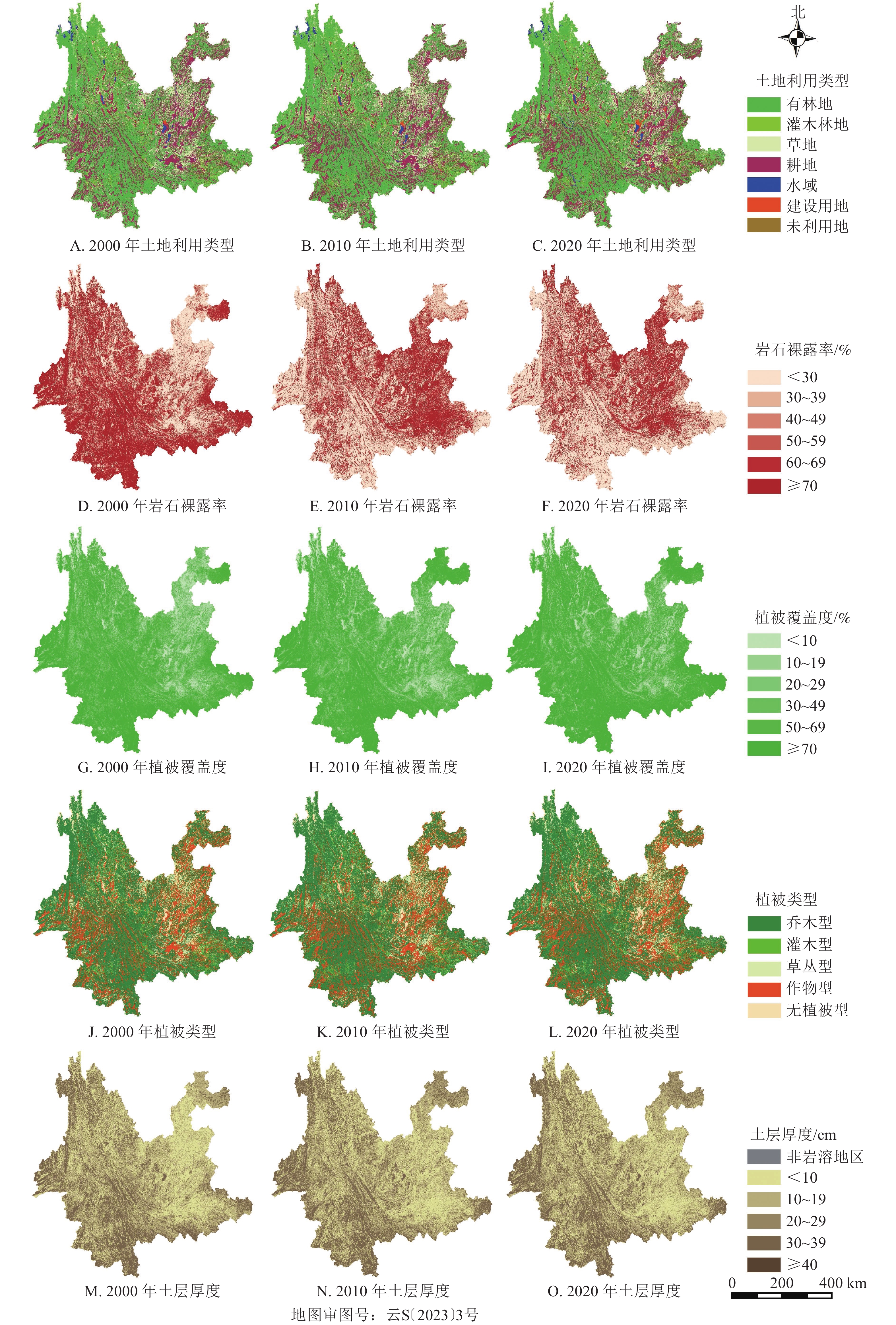
Objective This study aims to identify and extract information of rocky desertification patches at macroscopic scale by remote sensing tools and quantitatively analyze the spatial distribution characteristics and temporal evolution process of rocky desertification, so as to provide technical means and data support for the study of the occurrence process and development of rocky desertification in southwest China. Method Information of rocky desertification patches in Yunnan Province in 2000, 2010 and 2020 was extracted quantitatively by decision tree classification method based on Google Earth Engine platform. The spatio-temporal evolution model was used to analyze the spatial-temporal evolution process and characteristics of rocky desertification. Result (1) The overall rocky desertification situation in Yunnan Province was improved during the study period but still deteriorated in some areas. The ratio of rocky desertification to land area decreased from 9.65% to 6.48%. (2) The spatial distribution of rocky desertification in Yunnan Province was characterized by more in the east and less in the west, and the major distribution areas were Zhaotong, Qujing, Wenshan, Honghe and Kunming, accounting for 65.42%−72.14% of the occurrence area of rocky desertification in the whole province. (3) The evolution of rocky desertification tended to be complex, which shifted to both high grade and low grade of rocky desertification, and the phenomenon of destruction while treatment was not curbed. (4) Most of the extremely severe rocky desertification has shifted to severe rocky desertification in the past 20 years, indicating that it would take a long time for the extremely severe rocky desertification to be restored. (5) The internal evolution process of rocky desertification was intense, and the comprehensive change rate of light rocky desertification and moderate rocky desertification was fast. It was easy to improve but also had a higher risk of deterioration. Conclusion The relevant protocols are used as criteria for determining the grade of rocky desertification, and the macro-scale information of rocky desertification patches can be accurately extracted by decision tree classification method. The area of rocky desertification in Yunnan Province is decreasing, with uneven spatial distribution and mutual transformation among different grades of rocky desertification. [Ch, 3 fig. 4 tab. 25 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 427-435.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220381
Abstract:
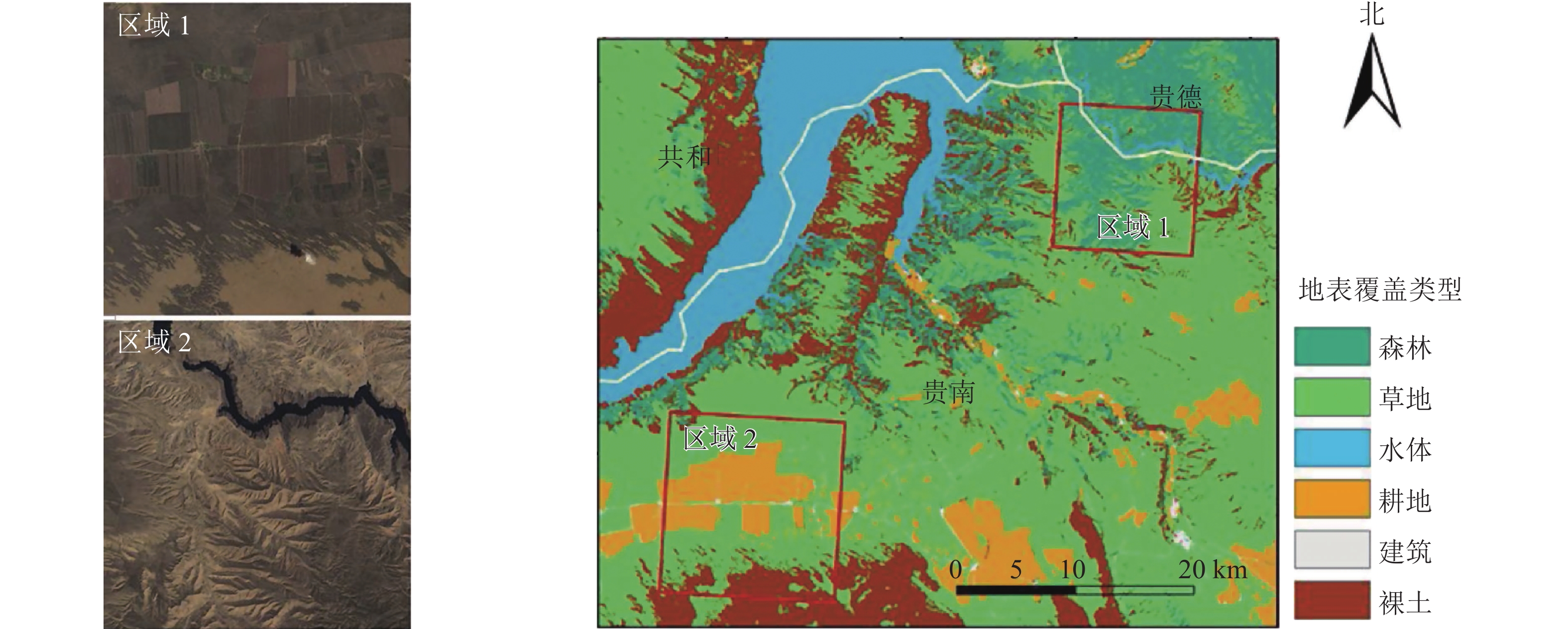
Objective In order to choose adapted fusion methods in vegetation survey and dynamic monitoring, we applied four different spatio-temporal fusion models including spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model (STARFM), enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model (ESTARFM), regression model fitting, spatial filtering and residual compensation (Fit-FC) and the rule-based piecewise regression tree model (RPRTM). Method Based on the four spatio-temporal fusion models (STARFM, ESTARFM, Fit-FC and RPRTM), two sampling regions (region Ⅰ and Ⅱ), with different surfaces characteristics in the Three-River Headwaters Regions were taken to generate the high spatial information of the Landsat NDVI (30 m, 16 d). Based on Landsat NDVI image, the spatial characteristics of the fusion data of different fusion models were evaluated by qualitative visual discrimination and quantitative statistical analysis. Meanwhile, based on the MODIS NDVI time series, the fitting effect of different fusion methods on the dynamic characteristics of surface vegetation was analyzed. Result (1) RPRTM had the optimal spatial fusion performance in region Ⅰ (R2=0.82); and ESTARFM performed the best in region Ⅱ (R2=0.95). (2) RPRTM has achieved the best fusion for capturing temporal dynamics (R2=0.97−0.99), where the NDVI dynamics were highly consistent with the temporal variations of MODIS. (3) Compared with the spatio-temporal comparability of model input data, landscape heterogeneity had a greater impact on the fusion effect of STARFM and ESTARFM. Conclusion Spatio-temporal fusion models can be used effectively to generate NDVI data at high spatial and temporal resolution, with different models having different fusion effects. RPRTM performing well in both complex surface areas and simulated vegetation growth dynamics. [Ch, 4 fig. 1 tab. 38 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 436-445.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220352
Abstract:
Objective With machine vision measurement technology being widely used in the field of forestry as a result of the rapid development of forestry informatization, this study is aimed to propose a contact less tree attribute measuring method combining consumer binocular-grade camera and machine vision technology to replace the traditional one which is featured with high cost, low mobility and complicated operation. Method Firstly, a consumer-grade USB 3.0 binocular camera was used to capture images of tree before a high-quality parallax image was generated by an improved SGM algorithm. Then it was transformed into a depth image in accordance with the triangulation principle so as to obtain a 3D point cloud. Next, the three-dimensional point cloud denoising method based on spatial density clustering and hybrid filtering was employed to remove the aggregated and discrete noise points quickly and accurately after which orientation correction and point cloud segmentation were performed. Finally, the most-valued traversal method and ellipse fitting method were used to achieve contactless measurement of tree height and DBH (diameter at breast height). Result The relative measurement errors of tree height and DBH were less than 2.219% and 5.620%, with the correlation coefficients being 0.918 and 0.995, whereas the root mean square errors being 0.047 m and 0.249 cm respectively. Conclusion The proposed method in this paper, featured as convenient with low cost and high precision, can meet the requirements of contactless measurement. [Ch, 5 fig. 2 tab. 27 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 446-452.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220749
Abstract:
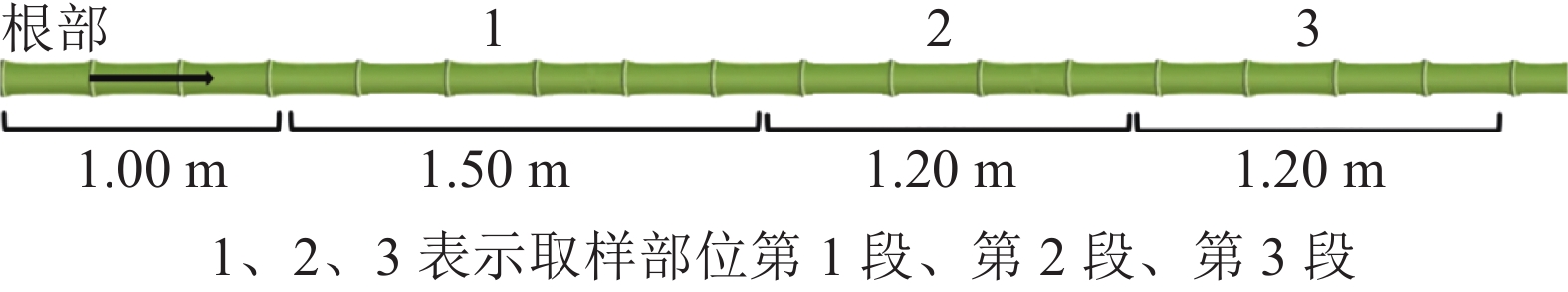
Objective This study, with an investigation of the influence of bamboo age and position on the morphology and crystallinity of Phyllostachys edulis fiber, is aimed to provide basic data for the the reasonable selection and efficient utilization of Ph. edulis in the production of pulp, paper, bamboo textile and other industrial products. Method With fiber segregation method and common optical microscope measurement method employed, the fiber morphology was determined whereas the relative crystallinity was calculated by Segal method. Result Bamboo age was postively correlated with the fiber length of bamboo, 80% of which was between 1 000 and 2 500 µm, belonging with long fiber. The shape of bamboo fiber was less affected by the axial height of bamboo, and the fiber wall cavity ratio and length width ratio had significant differences among the three sampling positions (P<0.05), but there was no obvious change rule, and the fiber length had no significant difference. In radial direction, the fiber length displayed a significant change rule, which was generally reflected as bamboo medium>bamboo green>bamboo yellow. There was no significant relationship between crystallinity and bamboo age, and there was an increasing trend from near yellow to near green in radial direction. Among the factors affecting bamboo fiber morphology, bamboo age had the largest contribution rate and the most obvious influence. Conclusion The fiber morphology of Ph. edulis was most affected by the bamboo age, significantly affected by the radial sampling position, and less affected by the axial height. All samples could be used in industrial production, and it is recommended to take the bamboo age as the priority index for raw material screening. [Ch, 6 fig. 6 tab. 22 ref.]
2023, 40(2): 453-464.
doi: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.20220535
Abstract:
Treatment of orchard waste is an important link in orchard production. The carbonization of orchard waste is a green, environmentally friendly and low-carbon mode of production, which can improve orchard soil, as well as yield and quality of fruits. Therefore, it’s of great scientific significance and application value to carry out research on orchard waste biochar for its rational application and evolution in orchard. The current research on biochar from orchard wastes was reviewed, which mainly focused on the preparation principle and properties of biochar from different types of orchard wastes and the effects on soil improvement, and the impact of its application combined with organic fertilizer on orchard production. The future research directions are proposed: (1) To further classify the orchard wastes to prepare more biochar to meet the differentiated needs. (2) To compare the production benefits of different types of orchard waste biochar application. (3) To prepare biochar-based organic fertilizer for orchard. (4) To explore the effect of orchard waste biochar on orchard environment and ecology. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 94 ref.]
Treatment of orchard waste is an important link in orchard production. The carbonization of orchard waste is a green, environmentally friendly and low-carbon mode of production, which can improve orchard soil, as well as yield and quality of fruits. Therefore, it’s of great scientific significance and application value to carry out research on orchard waste biochar for its rational application and evolution in orchard. The current research on biochar from orchard wastes was reviewed, which mainly focused on the preparation principle and properties of biochar from different types of orchard wastes and the effects on soil improvement, and the impact of its application combined with organic fertilizer on orchard production. The future research directions are proposed: (1) To further classify the orchard wastes to prepare more biochar to meet the differentiated needs. (2) To compare the production benefits of different types of orchard waste biochar application. (3) To prepare biochar-based organic fertilizer for orchard. (4) To explore the effect of orchard waste biochar on orchard environment and ecology. [Ch, 1 fig. 2 tab. 94 ref.]